

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 35-46.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023182
黄琳曦( ), 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧(
), 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧( ), 汪琼(
), 汪琼( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-30
修回日期:2023-07-28
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-01-15
通讯作者:
辛培尧,汪琼
作者简介:E-mail: 1006078164@qq.com基金资助:
Lin-xi HUANG( ), Qian CHEN, Xian-yan ZHANG, Shun YAN, Yun YANG, Pei-yao XIN(
), Qian CHEN, Xian-yan ZHANG, Shun YAN, Yun YANG, Pei-yao XIN( ), Qiong WANG(
), Qiong WANG( )
)
Received:2023-05-30
Revised:2023-07-28
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-01-15
Contact:
Pei-yao XIN,Qiong WANG
摘要:
乔木搭配人工草坪是园林绿化中常见的植物配置方案,但乔木凋落物可能会影响林下草坪草的生长。为探究两种乔木栾树、樱树凋落物对地毯草草坪的影响,本研究将栾树、樱树凋落叶分别制成10、20、40 g·L-1质量浓度的水浸提液,通过盆栽试验分析两种凋落叶浸提液处理下地毯草根际土壤水解酶活性及其化学计量比的变化,初步探讨林下植被管理对地毯草土壤质量的影响。结果表明:1)在不同质量浓度的栾树凋落叶浸提液处理下,地毯草根际土壤β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶(BG)、β-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶(NAG)、酸性磷酸酶(PHOS)活性均呈先增后减的变化趋势,木糖聚酶(XYL)则呈先减少后增加,最后减少的变化趋势,而在不同质量浓度的樱树凋落叶浸提液处理下,地毯草根际土壤β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶、β-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶、木糖聚酶活性则表现为先减后增的变化规律,酸性磷酸酶随质量浓度的增加呈递减的变化规律;2)相关性分析表明,N、P获取酶活性与土壤有机碳(SOC)含量呈显著正相关,酶C/N、酶C/P与总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)含量呈显著负相关,酶N/P与SOC含量呈显著负相关。矢量模型分析发现凋落物浸提液处理下地毯草根际土壤微生物呈P养分限制特征,樱树凋落叶浸提液处理能缓解微生物C、P限制;3)冗余分析进一步揭示了栾树和樱树凋落叶浸提液处理下地毯草根际土壤SOC、TP含量和土壤C/P、土壤含水量(SWC)、pH是影响土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的主要因子。因此,在人工草坪日常管理中应适时添加栾树、樱树凋落叶,在提高土壤微生物酶活性的同时缓解了地毯草生长中的碳和磷限制。
黄琳曦, 陈倩, 张先言, 闫顺, 杨云, 辛培尧, 汪琼. 两种乔木凋落叶浸提液处理对地毯草土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 35-46.
Lin-xi HUANG, Qian CHEN, Xian-yan ZHANG, Shun YAN, Yun YANG, Pei-yao XIN, Qiong WANG. Effect of two kinds of tree litter leaf extracts on soil enzyme activities and eco-enzymatic stoichiometry of Axonopus compressus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 35-46.

图1 两种树种凋落叶浸提液处理下地毯草的生物量大写字母表示同一树种不同质量浓度间差异显著,小写字母表示同一质量浓度不同树种间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different mass concentrations of the same species, and lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different species of the same mass concentration (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 The biomass of A. compressus under the treatment of two kinds of litter leaf extract
| 处理Treatment | MC (g·L-1) | pH | SWC (%) | SOC (g·kg-1) | TN (g·kg-1) | TP (g·kg-1) | C/N | C/P | N/P | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
栾树 K.paniculata | 0 | 6.16±0.04Aa | 50.50±3.19Ba | 132.96±12.85Aa | 3.56±0.29Ba | 0.08±0.01 Ca | 37.40±2.35Aa | 1775.07±242.84Aa | 47.33±3.75Aa | ||||||||
| 10 | 6.23±0.06Aa | 54.35±2.66Ba | 129.57±6.05Aa | 7.98±0.85Aa | 0.49±0.02Aa | 16.36±1.85Ba | 265.47±15.21Ba | 16.41±2.60BCa | |||||||||
| 20 | 6.26±0.07Aa | 71.12±4.50Aa | 139.47±1.38Aa | 7.57±0.56Aa | 0.53±0.08Aa | 18.49±1.53Ba | 267.20±44.33Ba | 14.39±1.21Ca | |||||||||
| 40 | 6.22±0.06Ab | 57.03±9.63Ba | 112.44±6.42Ba | 6.91±0.85Aa | 0.36±0.08Ba | 16.49±2.77Ba | 323.63±78.45Ba | 19.45±1.64Ba | |||||||||
樱树 P.serrulata | 0 | 6.16±0.04Ba | 50.50±3.19Ba | 132.96±12.85Aa | 3.56±0.29Ca | 0.08±0.01Ba | 37.40±2.35Aa | 1775.07±242.84Aa | 47.33±3.75Aa | ||||||||
| 10 | 6.27±0.06ABa | 57.41±1.51Aa | 118.37±2.75ABa | 6.50±0.62Aa | 0.47±0.07Aa | 18.35±2.14Ba | 254.76±42.12Ba | 13.83±0.74Ba | |||||||||
| 20 | 6.26±0.09ABa | 56.76±1.97Ab | 108.94±4.68Bb | 4.98±0.51Bb | 0.36±0.05Ab | 22.07±3.08Ba | 305.97±52.51Ba | 13.84±0.96Ba | |||||||||
| 40 | 6.36±0.07Aa | 59.80±3.62Aa | 90.30±7.76Cb | 4.38±0.99BCb | 0.37±0.09Aa | 21.69±7.21Ba | 259.19±88.83Ba | 11.93±0.27Bb | |||||||||
| 自由度df | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| T | 3.28 | 0.09 | 1.37 | 0.26 | 24.51 | *** | 36.61 | *** | 3.35 | 0.09 | 3.84 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.87 | 8.40 | ** | |
| MC | 4.9 | * | 9.4 | ** | 17.5 | *** | 32.6 | *** | 57.7 | *** | 46.1 | *** | 193.6 | *** | 310.4 | *** | |
| T×MC | 1.79 | 0.19 | 5.14 | * | 4.23 | * | 4.95 | * | 2.97 | 0.06 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.92 | 3.47 | * | |
表1 两种树种凋落叶浸提液处理下地毯草的土壤理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of rhizosphere soil in A. compressus under the treatment of two kinds of litter leaf extract
| 处理Treatment | MC (g·L-1) | pH | SWC (%) | SOC (g·kg-1) | TN (g·kg-1) | TP (g·kg-1) | C/N | C/P | N/P | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
栾树 K.paniculata | 0 | 6.16±0.04Aa | 50.50±3.19Ba | 132.96±12.85Aa | 3.56±0.29Ba | 0.08±0.01 Ca | 37.40±2.35Aa | 1775.07±242.84Aa | 47.33±3.75Aa | ||||||||
| 10 | 6.23±0.06Aa | 54.35±2.66Ba | 129.57±6.05Aa | 7.98±0.85Aa | 0.49±0.02Aa | 16.36±1.85Ba | 265.47±15.21Ba | 16.41±2.60BCa | |||||||||
| 20 | 6.26±0.07Aa | 71.12±4.50Aa | 139.47±1.38Aa | 7.57±0.56Aa | 0.53±0.08Aa | 18.49±1.53Ba | 267.20±44.33Ba | 14.39±1.21Ca | |||||||||
| 40 | 6.22±0.06Ab | 57.03±9.63Ba | 112.44±6.42Ba | 6.91±0.85Aa | 0.36±0.08Ba | 16.49±2.77Ba | 323.63±78.45Ba | 19.45±1.64Ba | |||||||||
樱树 P.serrulata | 0 | 6.16±0.04Ba | 50.50±3.19Ba | 132.96±12.85Aa | 3.56±0.29Ca | 0.08±0.01Ba | 37.40±2.35Aa | 1775.07±242.84Aa | 47.33±3.75Aa | ||||||||
| 10 | 6.27±0.06ABa | 57.41±1.51Aa | 118.37±2.75ABa | 6.50±0.62Aa | 0.47±0.07Aa | 18.35±2.14Ba | 254.76±42.12Ba | 13.83±0.74Ba | |||||||||
| 20 | 6.26±0.09ABa | 56.76±1.97Ab | 108.94±4.68Bb | 4.98±0.51Bb | 0.36±0.05Ab | 22.07±3.08Ba | 305.97±52.51Ba | 13.84±0.96Ba | |||||||||
| 40 | 6.36±0.07Aa | 59.80±3.62Aa | 90.30±7.76Cb | 4.38±0.99BCb | 0.37±0.09Aa | 21.69±7.21Ba | 259.19±88.83Ba | 11.93±0.27Bb | |||||||||
| 自由度df | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| T | 3.28 | 0.09 | 1.37 | 0.26 | 24.51 | *** | 36.61 | *** | 3.35 | 0.09 | 3.84 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.87 | 8.40 | ** | |
| MC | 4.9 | * | 9.4 | ** | 17.5 | *** | 32.6 | *** | 57.7 | *** | 46.1 | *** | 193.6 | *** | 310.4 | *** | |
| T×MC | 1.79 | 0.19 | 5.14 | * | 4.23 | * | 4.95 | * | 2.97 | 0.06 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.92 | 3.47 | * | |
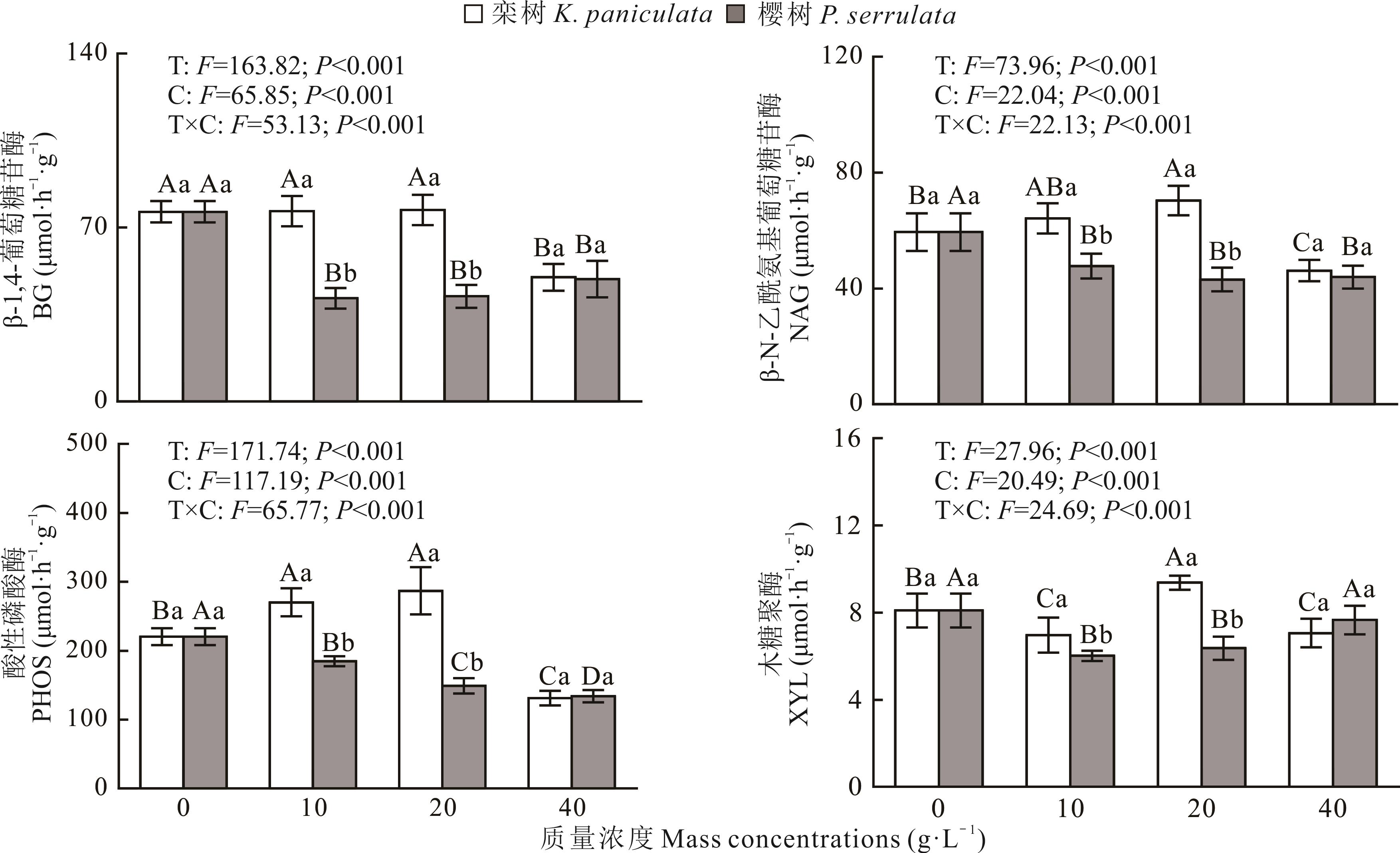
图2 两种不同凋落叶浸提液处理下土壤酶活性T, C和T×C分别表示处理,质量浓度以及处理与质量浓度的交互作用,下同。T, C and T×C represent treatments, mass concentrations and the interaction between treatments and mass concentrations, respectively, the same below.
Fig.2 Soil enzymes activities under the treatment of two kinds of litter leaf extract

图5 土壤理化性质与土壤酶活性及其化学计量比的相关性A: 栾树凋落叶浸提液处理K. paniculata litter extract treatment; B: 樱树凋落叶浸提液处理P. serrulata litter extract treatment; SWC: 土壤含水量Soil water content; SOC: 土壤有机质Soil organic carbon; TN: 总氮Total nitrogen; TP: 总磷Total phosphorus; soil C/N: 土壤碳氮比Soil carbon and nitrogen ratio; soil C/P: 土壤碳磷比Soil carbon and phosphorus ratio; soil N/P: 土壤氮磷比Soil nitrogen and phosphorus ratio; BG+XYL: 土壤碳循环相关酶活性Soil carbon cycle-related enzyme activity; NAG: 土壤氮循环相关酶活性Soil nitrogen cycle-related enzyme activity; PHOS: 土壤磷循环相关酶活性Soil phosphorus cycle-related enzyme activity; C/N-enzymes: 酶活性碳氮比Enzyme active carbon-nitrogen ratio; C/P-enzymes: 酶活性碳磷比Enzyme active carbon-phosphorus ratio; N/P-enzymes: 酶活性氮磷比Enzyme active nitrogen-phosphorus ratio; Length: 矢量长度Vector length; Angle: 矢量角度Vector angle. 下同The same below.
Fig.5 Correlation between soil enzyme activities, soil enzyme stoichiometry and soil properties

图6 土壤理化性质与土壤酶活性及其化学计量的冗余分析A: 栾树凋落叶浸提液处理K. paniculata litter extract treatment; B: 樱树凋落叶浸提液处理P. serrulata litter extract treatment; *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01。
Fig. 6 The redundancy analysis (RDA) of soil properties, enzyme activities and stoichiometry
| 1 | Wang J, Zhao M L, Han G D, et al. The effect of litter on grassland ecosystem// Proceedings of the 2013 Annual Conference of the Chinese Grass Society. Tianjin: Conference of the Chinese Grass Society, 2013: 117-120. |
| 王静, 赵萌莉, 韩国栋, 等. 凋落物对草地生态系统的影响// 中国草学会2013学术年会论文集. 天津: 中国草学会, 2013: 117-120. | |
| 2 | Hu Y L, Wang S L, Huang Y, et al. Effects of litter chemistry on soil biological property and enzymatic activity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005(10): 2662-2668. |
| 胡亚林, 汪思龙, 黄宇, 等. 凋落物化学组成对土壤微生物学性状及土壤酶活性的影响. 生态学报, 2005(10): 2662-2668. | |
| 3 | Lu Y H, Cao Y, Xu L M, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of plants, litter and soils in desertification area of Poyang Lake. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(2): 329-335. |
| 陆远鸿, 曹昀, 许令明, 等. 鄱阳湖沙化土地植物-凋落物-土壤化学计量特征. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(2): 329-335. | |
| 4 | Fanin N, Moorhead D, Bertrand I, et al. Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry and enzymatic vectors reveal differential C,N,P dynamics in decaying litter along a land-use gradient. Biogeochemistry, 2016, 129: 21-36. |
| 5 | Zeng Q, Chen Z, Tan W, et al. Litter quality regulates soil eco-enzymatic stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation in a citrus orchard. Plant and Soil, 2021, 466: 179-191. |
| 6 | Qi Z C. Effects of litter decomposition on soil organic carbon and its stability in grassland of Loss Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. |
| 祁正超. 凋落物分解对黄土高原草地土壤有机碳及其稳定性的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. | |
| 7 | Xu Y X, Kang Y M, Han C, et al. Effects of precipitation on ecological stoichiometric characteristics of litter and soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 21-31. |
| 许艺馨, 康扬眉, 韩翠, 等. 降水量对荒漠草原凋落物-土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 21-31. | |
| 8 | Li Q, Qi H, He G X, et al. Response of soil enzymes activities and their stoichiometric characteristics to altitude and aspect of alpine meadow in eastern Qilian Mountains. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(4): 357-364. |
| 李强, 漆昊, 何国兴, 等. 东祁连山高寒草甸土壤酶活性及其化学计量特征对海拔和坡向的响应. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(4): 357-364. | |
| 9 | Cui Y B, Zhang X, Liu Y Z, et al. Allelopathy of Koelreuteria bipinnata Franch.var.integrifoliola(Merr.)T.Chen aqueous extracts on seed germination of Trifolium repens. Journal of Liaocheng University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 29(4): 24-27, 63. |
| 崔迎宾, 张霞, 刘玉真, 等. 栾树水浸液对白三叶种子萌发的化感效应. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 29(4): 24-27, 63. | |
| 10 | Ma Y, Fan X H, Liu Z W. Allelopathy response of four crops to falling flowers in common urban greening trees. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2021, 39(5): 90-98. |
| 马勇, 范晓慧, 刘增文. 4种农作物对常见城市绿化树木落花的化感响应. 干旱地区农业研究, 2021, 39(5): 90-98. | |
| 11 | Zhu T, Liu Z W, Fan X H, et al. Allelopathic effects of greening leaves extract on 5 herbaceous plants. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 976-982. |
| 朱彤, 刘增文, 范晓慧, 等. 绿化树落叶浸提液对5种草本植物的化感效应. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 976-982. | |
| 12 | Guan W T, Zheng Z R, Diao Z Y, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics and their storage of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the temperate meadow steppe under different disturbances. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(11): 2959-2966. |
| 关伟涛, 郑志荣, 刁兆岩, 等. 不同干扰方式下温性草甸草原土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征及其储量研究. 草地学报, 2022, 30(11): 2959-2966. | |
| 13 | Saiya-Cork K R, Sinsabaugh R L, Zak D R. The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34(9): 1309-1315. |
| 14 | Cui Y, Fang L, Guo X, et al. Natural grassland as the optimal pattern of vegetation restoration in arid and semi-arid regions: Evidence from nutrient limitation of soil microbes. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 648: 388-397. |
| 15 | Suseela V, Tharayil N, Xing B, et al. Warming alters potential enzyme activity but precipitation regulates chemical transformations in grass litter exposed to simulated climatic changes. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 75: 102-112. |
| 16 | Fu Q, Xing Y J, Yan G Y, et al. Response of litter dynamics of boreal forest to long-term nitrogen deposition. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(7): 1341-1350. |
| 付琦, 邢亚娟, 闫国永, 等. 北方森林凋落物动态对长期氮沉降的响应. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(7): 1341-1350. | |
| 17 | Liao M Y, Hu T X, Deng C M, et al. Effect of leaf litter water extract of three species on growth and resistance physiology of Bidens pilosa. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2014, 30(6): 724-730. |
| 廖梦雨, 胡庭兴, 邓承敏, 等. 3个树种凋落叶水浸提液对三叶鬼针草生长及抗性生理的影响. 生态与农村环境学报, 2014, 30(6): 724-730. | |
| 18 | Xiao C, Janssens I A, Zhou Y, et al. Strong stoichiometric resilience after litter manipulation experiments: A case study in a Chinese grassland. Biogeosciences, 2015,12: 757-767. |
| 19 | Wen M Z, Yu D, Guo J X. Influence of litter layer on microenvironment in northeast Leymus chinensis grassland. Plant Science Journal, 2003, 21(5): 395-400. |
| 温明章, 于丹, 郭继勋. 凋落物层对东北羊草草原微环境的影响. 植物科学学报, 2003, 21(5): 395-400. | |
| 20 | Liu R, Chen F S, Fang X M, et al. Effects of litter addition and removal on soil hydrolytic enzyme activities and ecoenzymatic stoichiometry in Chinese fir plantation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(16): 5739-5750. |
| 刘仁, 陈伏生, 方向民, 等. 凋落物添加和移除对杉木人工林土壤水解酶活性及其化学计量比的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(16): 5739-5750. | |
| 21 | Wei C C, Liu X F, Lin C F, et al. Response of soil enzyme activities to litter input changes in two secondary Castanopsis carlessii forests in subtropical China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2018, 42(6): 692-702. |
| 魏翠翠, 刘小飞, 林成芳, 等. 凋落物输入改变对亚热带两种米槠次生林土壤酶活性的影响. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(6): 692-702. | |
| 22 | Sayer E J, Heard M S, Grant H K, et al. Soil carbon release enhanced by increased tropical forest litterfall.Nature Climate Change, 2011,1(6): 304-307. |
| 23 | Craig M E, Geyer K M, Beidler K V, et al. Fast-decaying plant litter enhances soil carbon in temperate forests but not through microbial physiological traits. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 1229. |
| 24 | Xiao X Q, Zhang H K, Feng Y S, et al. Effects of plant residues on C∶N∶P of soil, microbial biomass, and extracellular enzyme in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(1): 58-66. |
| 肖向前, 张海阔, 冯娅斯, 等. 植物残体对青藏高原高寒草甸土壤、微生物和胞外酶C∶N∶P化学计量特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(1): 58-66. | |
| 25 | Zhang J, Zhou J, Lambers H, et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus addition exerted different influences on litter and soil carbon release in a tropical forest. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 832: 155049. |
| 26 | Wang S Q, Yu G R. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| 王绍强, 于贵瑞. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征. 生态学报, 2008, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| 27 | An H, Li G Q. Effects of grazing on carbon and nitrogen in plants and soils in a semiarid desert grassland, China. Journal of Arid Land, 2015, 7(3): 341-349. |
| 28 | Tian H Q, Chen G S, Zhang C, et al. Pattern and variation of C∶N∶P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 98: 139-151. |
| 29 | Waring B G, Weintraub S R, Sinsabaugh R L, et al. Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry of microbial nutrient acquisition in tropical soils. Biogeochemistry, 2014, 117(1): 101-113. |
| 30 | Qiao H, Mo X Q, Luo Y H, et al. Patterns of soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and its influencing factors during stand development in Camellia oleifera plantations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 1887-1896. |
| 乔航, 莫小勤, 罗艳华, 等. 不同林龄油茶人工林土壤酶化学计量及其影响因素. 生态学报, 2019, 39(6): 1887-1896. | |
| 31 | Wang L Y, Zhou G N, Zhu X Y, et al. Effects of litter on soil organic carbon and microbial functional diversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(7): 2709-2718. |
| 王利彦, 周国娜, 朱新玉, 等. 凋落物对土壤有机碳与微生物功能多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(7): 2709-2718. | |
| 32 | Shi L J, Wang H M, Fu X L, et al. Soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometry of typical plantations in midsubtropical China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(6): 1980-1988. |
| 史丽娟, 王辉民, 付晓莉, 等. 中亚热带典型人工林土壤酶活性及其化学计量特征. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(6): 1980-1988. | |
| 33 | Zhou S X, Huang C D, Xiang Y B, et al. Effects of reduced precipitation on litter decomposition in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in western China. Forest Ecology and Management, 2018, 430: 219-227. |
| 34 | Grosso F, Bååth E, De Nicola F. Bacterial and fungal growth on different plant litter in Mediterranean soils: effects of C/N ratio and soil pH. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 108: 1-7. |
| 35 | Tian M Y, Yu C J, Wang J K, et al. Effect of nitrogen additions on soil pH, phosphorus contents and phosphatase activities in grassland. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(9): 2985-2992. |
| 田沐雨, 于春甲, 汪景宽, 等. 氮添加对草地生态系统土壤pH, 磷含量和磷酸酶活性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(9): 2985-2992. | |
| 36 | Rutigliano F A, Castald S, D’Ascoli R, et al. Soil activities related to nitrogen cycle under three plant cover types in Mediterranean environment. Applied Soil Ecology, 2009, 43(1): 40-46. |
| 37 | Sinsabaugh R L,Hill B H,Shah J J F, et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature, 2009, 462: 795-798. |
| 38 | Cleveland C C, Liptzin D. C∶N∶P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield Ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(3): 235-252. |
| 39 | Yu Y F, Peng W X, Song T Q, et al. Stoichiometric characteristics of plant and soil C, N and P in different forest types in depressions between karst hills, southwest China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(4): 947-954. |
| 俞月凤, 彭晚霞, 宋同清, 等. 喀斯特峰丛洼地不同森林类型植物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(4): 947-954. | |
| 40 | Zhang X X, Yang L M, Chen Z, et al. Patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry on types of forest soils form different parent materials in subtropical areas. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(16): 5828-5836. |
| 张星星, 杨柳明, 陈忠, 等. 中亚热带不同母质和森林类型土壤生态酶化学计量特征. 生态学报, 2018, 38(16): 5828-5836. | |
| 41 | Xu Z, Yu G, Zhang X, et al. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the North-South Transect in Eastern China (NSTEC). Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2017, 104: 152-163. |
| [1] | 张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92. |
| [2] | 马嵩科, 霍克, 张冬霞, 张静, 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 王贺正. 玉米秸秆还田配施氮肥对豫西旱地小麦土壤酶活性和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 120-133. |
| [3] | 刘彩凤, 段媛媛, 王玲玲, 王乙茉, 郭正刚. 高原鼠兔干扰对高寒草甸植物物种多样性与土壤生态化学计量比间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 157-166. |
| [4] | 王志婷, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 李东方, 刘小勇. 半干旱草甸草地不同处理下植被特征与土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 41-55. |
| [5] | 苏乐乐, 秦燕, 王瞾敏, 张永超, 刘文辉. 氮磷添加对燕麦与箭筈豌豆不同种植方式草地土壤微生物-胞外酶化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 56-66. |
| [6] | 马文明, 刘超文, 周青平, 邓增卓玛, 唐思洪, 迪力亚尔·莫合塔尔null, 侯晨. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体生态化学计量学及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| [7] | 马英, 许志豪, 曾巧红, 孟建龙, 胡亚虎, 苏洁琼. 氮素添加对荒漠化草原草本植物养分化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 64-72. |
| [8] | 程分生, 尤龙辉, 余锦林, 徐惠昌, 游惠明, 聂森, 李建民, 叶功富. 冷季型绿肥对锥栗园土壤生化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 62-75. |
| [9] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [10] | 宗文贞, 郭家昊, 贾云龙, 郑永兴, 杨旭, 胡芳弟, 王静. 单宁在植物-土壤氮循环中作用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 174-183. |
| [11] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [12] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [13] | 李争艳, 徐智明, 师尚礼, 贺春贵. 江淮地区不同轮茬作物对苜蓿产量及根际土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 28-39. |
| [14] | 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 靳长青. 围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| [15] | 秦燕, 刘文辉, 何峰, 仝宗永, 李向林. 施肥与切根对退化羊草草原土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 5-14. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||