

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 29-40.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024173
姜安静1( ), 董乙强1,2,3(
), 董乙强1,2,3( ), 周时杰1, 聂婷婷1, 吴悦1, 柳泽宇1, 单兴芸1, 雷雅欣1, 吴凯1, 安沙舟1,2,3
), 周时杰1, 聂婷婷1, 吴悦1, 柳泽宇1, 单兴芸1, 雷雅欣1, 吴凯1, 安沙舟1,2,3
收稿日期:2024-05-14
修回日期:2024-07-01
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-01-02
通讯作者:
董乙强
作者简介:E-mail: xjdyq1210@163.com基金资助:
An-jing JIANG1( ), Yi-qiang DONG1,2,3(
), Yi-qiang DONG1,2,3( ), Shi-jie ZHOU1, Ting-ting NIE1, Yue WU1, Ze-yu LIU1, Xing-yun SHAN1, Ya-xin LEI1, Kai WU1, Sha-zhou AN1,2,3
), Shi-jie ZHOU1, Ting-ting NIE1, Yue WU1, Ze-yu LIU1, Xing-yun SHAN1, Ya-xin LEI1, Kai WU1, Sha-zhou AN1,2,3
Received:2024-05-14
Revised:2024-07-01
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-01-02
Contact:
Yi-qiang DONG
摘要:
探究山地草地生态系统物种多样性沿海拔梯度的分布规律及其驱动因素,对揭示区域植物的环境适应性、区域多样性的保护及修复治理等具有重要意义。以天山北坡东段奇台县山地草地为研究对象,采用野外原生境实地调查取样的方法,对15个海拔梯度,跨度为1250~3150 m的草地植物群落数量特征和物种多样性进行测定分析,并用随机森林模型以及偏最小二乘路径模型解析海拔、气温、降水以及植物数量特征与植物多样性的关系。结果表明:1)随海拔梯度的增加,草地植物群落盖度和密度均呈极显著增加趋势,而植物高度呈极显著降低趋势,生物量则呈先降后升的趋势(P<0.01);2)植物α多样性指数沿海拔梯度均呈先升后降的“单峰”分布规律(P<0.05),相邻海拔间相似度Sorenson 指数整体呈先下降后上升的波动变化,相反物种替代率Cody指数呈先上升后下降的变化趋势;3)植物盖度、生物量以及Patrick指数均与气候呈显著相关关系(P<0.05),植物多样性主要受盖度的直接影响,海拔通过显著影响气温和降水,进而间接影响植物密度,植物密度又显著正向影响植物盖度(P<0.01)。综上,海拔通过影响气候间接影响植物群落特征,使其具有明显的垂直分布特征。
姜安静, 董乙强, 周时杰, 聂婷婷, 吴悦, 柳泽宇, 单兴芸, 雷雅欣, 吴凯, 安沙舟. 草地植物多样性沿海拔梯度分布特征及其驱动因素——以天山北坡东段为例[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 29-40.
An-jing JIANG, Yi-qiang DONG, Shi-jie ZHOU, Ting-ting NIE, Yue WU, Ze-yu LIU, Xing-yun SHAN, Ya-xin LEI, Kai WU, Sha-zhou AN. Distribution characteristics of grassland plant diversity along the altitudinal gradient and its driving factors: A case study of the eastern section of the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(3): 29-40.
| 样地序号Sample plot number | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地理位置 Geographical position | 草地类型 Grassland type | 优势种 Dominant species | 年均温Mean annual temperature (℃) | 年均降水量Mean annual precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1250 | E 89.64°,N 43.76° | 温性荒漠草地Temperate desert grassland | 伊犁绢蒿,小蓬S. transiliense, N. erinaceum | 5.61 | 150.36 |
| 2 | 1270 | E 89.64°,N 43.73° | 温性荒漠草地Temperate desert grassland | 伊犁绢蒿,小蓬S. transiliense, N. erinaceum | 5.34 | 154.71 |
| 3 | 1370 | E 89.61°,N 43.71° | 温性荒漠草地Temperate desert grassland | 伊犁绢蒿S. transiliense | 4.93 | 161.42 |
| 4 | 1590 | E 89.62°,N 43.64° | 温性草原草地Temperate steppe grassland | 羊茅,草原苔草F. ovina, C. liparocarpos | 4.06 | 166.45 |
| 5 | 1750 | E 89.62°,N 43.63° | 温性草原草地Temperate steppe grassland | 羊茅,针茅,草原苔草F. ovina, S. capillata, C. liparocarpos | 3.67 | 172.28 |
| 6 | 1770 | E 89.62°,N 43.60° | 温性草原草地Temperate steppe grassland | 羊茅,草原苔草F. ovina, C. liparocarpos | 3.21 | 177.40 |
| 7 | 2060 | E 89.61°,N 43.55° | 温性草甸草原草地Temperate meadow-steppe grassland | 白尖苔草,草原糙苏,披碱草C. oxyleuca, P. pratensis, Elymus dahuricus | 1.76 | 195.20 |
| 8 | 2170 | E 89.61°,N 43.54° | 温性草甸草原草地Temperate meadow-steppe grassland | 无芒雀麦,白尖苔草B. inermis, C. oxyleuca | 1.28 | 208.60 |
| 9 | 2240 | E 89.60°,N 43.52° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 天山羽衣草A. tianschanica | 0.76 | 212.02 |
| 10 | 2460 | E 89.60°,N 43.51° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 黑花苔草C. melanantha | 0.24 | 222.11 |
| 11 | 2630 | E 89.60°,N 43.50° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 黑花苔草C. melanantha | -0.19 | 229.12 |
| 12 | 2730 | E 89.60°,N 43.50° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 黑花苔草C. melanantha | -1.04 | 246.88 |
| 13 | 2850 | E 89.60°,N 43.49° | 高寒草甸草地Alpine meadow grassland | 细果苔草,天山羽衣草C. stenocarpa, A. tianschanica | -1.49 | 246.09 |
| 14 | 2950 | E 89.59°,N 43.49° | 高寒草甸草地Alpine meadow grassland | 高山早熟禾,天山羽衣草P. alpina, A. tianschanica | -2.40 | 260.66 |
| 15 | 3150 | E 89.58°,N 43.48° | 高寒草甸草地Alpine meadow grassland | 高山早熟禾,细果苔草P. alpina, C. stenocarpa | -3.49 | 271.98 |
表1 研究区地理位置及其基本情况
Table 1 Geographical location and basic information of the study area
| 样地序号Sample plot number | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 地理位置 Geographical position | 草地类型 Grassland type | 优势种 Dominant species | 年均温Mean annual temperature (℃) | 年均降水量Mean annual precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1250 | E 89.64°,N 43.76° | 温性荒漠草地Temperate desert grassland | 伊犁绢蒿,小蓬S. transiliense, N. erinaceum | 5.61 | 150.36 |
| 2 | 1270 | E 89.64°,N 43.73° | 温性荒漠草地Temperate desert grassland | 伊犁绢蒿,小蓬S. transiliense, N. erinaceum | 5.34 | 154.71 |
| 3 | 1370 | E 89.61°,N 43.71° | 温性荒漠草地Temperate desert grassland | 伊犁绢蒿S. transiliense | 4.93 | 161.42 |
| 4 | 1590 | E 89.62°,N 43.64° | 温性草原草地Temperate steppe grassland | 羊茅,草原苔草F. ovina, C. liparocarpos | 4.06 | 166.45 |
| 5 | 1750 | E 89.62°,N 43.63° | 温性草原草地Temperate steppe grassland | 羊茅,针茅,草原苔草F. ovina, S. capillata, C. liparocarpos | 3.67 | 172.28 |
| 6 | 1770 | E 89.62°,N 43.60° | 温性草原草地Temperate steppe grassland | 羊茅,草原苔草F. ovina, C. liparocarpos | 3.21 | 177.40 |
| 7 | 2060 | E 89.61°,N 43.55° | 温性草甸草原草地Temperate meadow-steppe grassland | 白尖苔草,草原糙苏,披碱草C. oxyleuca, P. pratensis, Elymus dahuricus | 1.76 | 195.20 |
| 8 | 2170 | E 89.61°,N 43.54° | 温性草甸草原草地Temperate meadow-steppe grassland | 无芒雀麦,白尖苔草B. inermis, C. oxyleuca | 1.28 | 208.60 |
| 9 | 2240 | E 89.60°,N 43.52° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 天山羽衣草A. tianschanica | 0.76 | 212.02 |
| 10 | 2460 | E 89.60°,N 43.51° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 黑花苔草C. melanantha | 0.24 | 222.11 |
| 11 | 2630 | E 89.60°,N 43.50° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 黑花苔草C. melanantha | -0.19 | 229.12 |
| 12 | 2730 | E 89.60°,N 43.50° | 山地草甸草地Mountain meadow grassland | 黑花苔草C. melanantha | -1.04 | 246.88 |
| 13 | 2850 | E 89.60°,N 43.49° | 高寒草甸草地Alpine meadow grassland | 细果苔草,天山羽衣草C. stenocarpa, A. tianschanica | -1.49 | 246.09 |
| 14 | 2950 | E 89.59°,N 43.49° | 高寒草甸草地Alpine meadow grassland | 高山早熟禾,天山羽衣草P. alpina, A. tianschanica | -2.40 | 260.66 |
| 15 | 3150 | E 89.58°,N 43.48° | 高寒草甸草地Alpine meadow grassland | 高山早熟禾,细果苔草P. alpina, C. stenocarpa | -3.49 | 271.98 |
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 1250 m | 1270 m | 1370 m | 1590 m | 1750 m | 1770 m | 2060 m | 2170 m | 2240 m | 2460 m | 2630 m | 2730 m | 2850 m | 2950 m | 3150 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1250 | 0.94 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1270 | 0.50 | 0.57 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1370 | 3.50 | 3.00 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1590 | 6.00 | 5.50 | 3.50 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1750 | 8.00 | 7.50 | 6.50 | 4.00 | 0.58 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.12 | |
| 1770 | 8.00 | 7.50 | 5.50 | 4.00 | 5.00 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.00 | |
| 2060 | 17.50 | 17.00 | 16.00 | 16.50 | 15.50 | 17.50 | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.17 | |
| 2170 | 15.50 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 13.50 | 12.50 | 14.50 | 13.50 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.33 | |
| 2240 | 11.50 | 11.00 | 10.00 | 11.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 8.00 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 0.59 | |
| 2460 | 19.00 | 18.50 | 17.50 | 19.00 | 19.00 | 19.00 | 19.00 | 15.50 | 9.50 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.61 | |
| 2630 | 14.50 | 14.00 | 13.00 | 13.50 | 14.50 | 14.50 | 14.50 | 12.00 | 7.00 | 7.50 | 0.84 | 0.56 | 0.51 | 0.55 | |
| 2730 | 13.50 | 13.00 | 12.00 | 12.50 | 13.50 | 13.50 | 13.50 | 12.00 | 7.00 | 7.50 | 3.00 | 0.54 | 0.43 | 0.53 | |
| 2850 | 14.00 | 13.50 | 12.50 | 13.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 12.50 | 8.50 | 13.00 | 8.50 | 8.50 | 0.68 | 0.67 | |
| 2950 | 14.00 | 13.50 | 12.50 | 14.00 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 14.50 | 13.50 | 6.50 | 11.00 | 9.50 | 10.50 | 6.00 | 0.77 | |
| 3150 | 14.50 | 14.00 | 13.00 | 14.50 | 14.50 | 15.50 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 7.00 | 9.50 | 9.00 | 9.00 | 6.50 | 4.50 |
表2 不同海拔植物Sorenson相似度指数和Cody指数
Table 2 Sorenson similarity index and Cody index of plants at different altitudes
| 海拔 Altitude (m) | 1250 m | 1270 m | 1370 m | 1590 m | 1750 m | 1770 m | 2060 m | 2170 m | 2240 m | 2460 m | 2630 m | 2730 m | 2850 m | 2950 m | 3150 m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1250 | 0.94 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1270 | 0.50 | 0.57 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1370 | 3.50 | 3.00 | 0.53 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1590 | 6.00 | 5.50 | 3.50 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1750 | 8.00 | 7.50 | 6.50 | 4.00 | 0.58 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.12 | |
| 1770 | 8.00 | 7.50 | 5.50 | 4.00 | 5.00 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.00 | |
| 2060 | 17.50 | 17.00 | 16.00 | 16.50 | 15.50 | 17.50 | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.17 | |
| 2170 | 15.50 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 13.50 | 12.50 | 14.50 | 13.50 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 0.33 | |
| 2240 | 11.50 | 11.00 | 10.00 | 11.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 8.00 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 0.59 | |
| 2460 | 19.00 | 18.50 | 17.50 | 19.00 | 19.00 | 19.00 | 19.00 | 15.50 | 9.50 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.61 | |
| 2630 | 14.50 | 14.00 | 13.00 | 13.50 | 14.50 | 14.50 | 14.50 | 12.00 | 7.00 | 7.50 | 0.84 | 0.56 | 0.51 | 0.55 | |
| 2730 | 13.50 | 13.00 | 12.00 | 12.50 | 13.50 | 13.50 | 13.50 | 12.00 | 7.00 | 7.50 | 3.00 | 0.54 | 0.43 | 0.53 | |
| 2850 | 14.00 | 13.50 | 12.50 | 13.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 12.50 | 8.50 | 13.00 | 8.50 | 8.50 | 0.68 | 0.67 | |
| 2950 | 14.00 | 13.50 | 12.50 | 14.00 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 14.50 | 13.50 | 6.50 | 11.00 | 9.50 | 10.50 | 6.00 | 0.77 | |
| 3150 | 14.50 | 14.00 | 13.00 | 14.50 | 14.50 | 15.50 | 15.00 | 14.00 | 7.00 | 9.50 | 9.00 | 9.00 | 6.50 | 4.50 |

图3 植物盖度、生物量和Patrick指数与气候因子的关系MAP: 年均降水量Mean annual precipitation; MAT: 年均温Mean annual temperature. 下同The same below.
Fig.3 Plant coverage, biomass and Patrick index in relation to climate
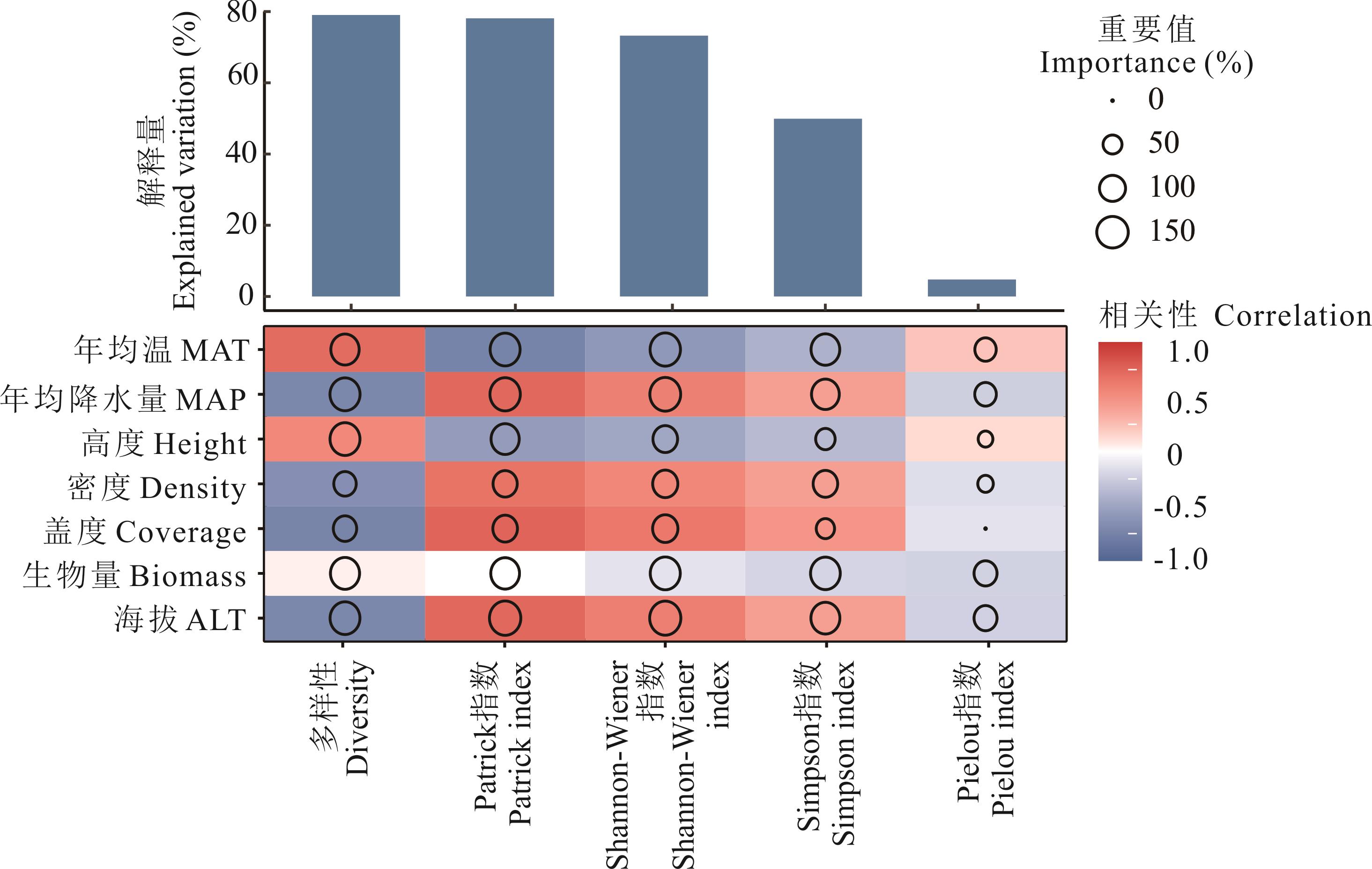
图4 基于相关性和随机森林模型的非生物因子和生物因子对植物α多样性的贡献圆圈大小表示变量的重要性(即通过随机森林模型计算的均方误差增加的百分比)。颜色代表斯皮尔曼的相关性。Circle size represents the variable importance (that is proportion of explained variability calculated via multiple regression modeling and variance decomposition analysis). Colors represent Spearman correlations. ALT: 海拔Altitude.
Fig.4 Contribution of abiotic and biological factors to plant alpha diversity based on correlation and random forest models
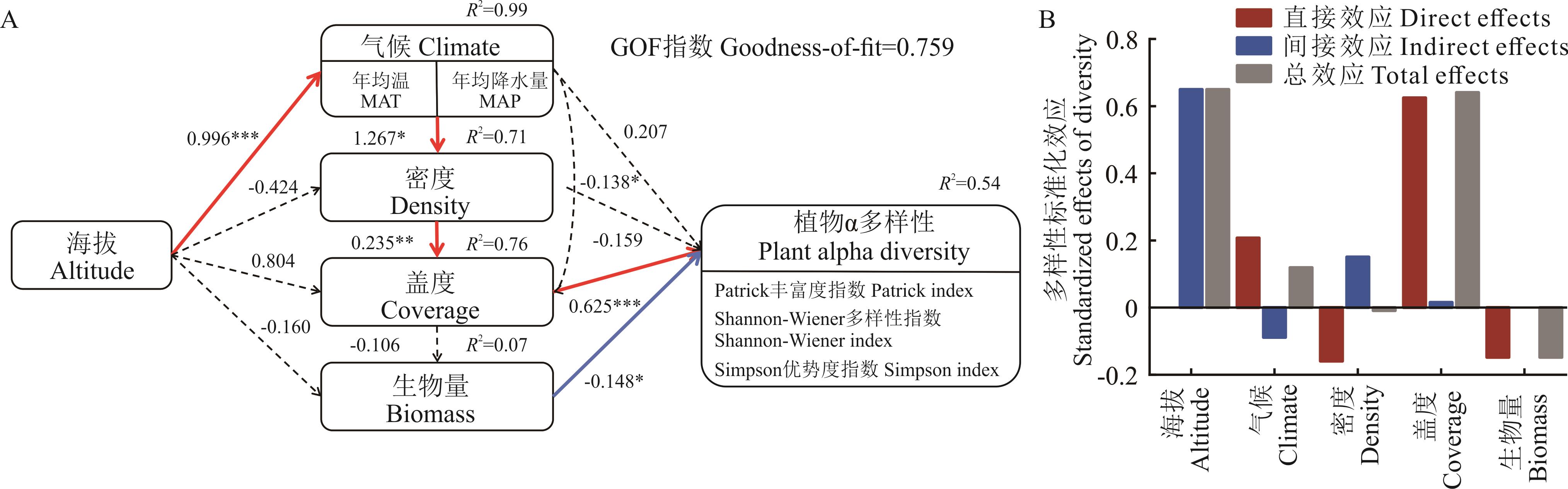
图5 海拔对植物群落多样性的影响及其潜在调控路径A: 红色实线表示显著正相关,蓝色实线表示显著负相关,黑色虚线表示无显著相关性(P>0.05)。The solid red line indicates a significant positive correlation, the solid blue line indicates a significant negative correlation, and the dashed black line indicates no significant correlation (P>0.05). *: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001.
Fig.5 Effect of altitude on plant community diversity and its potential regulatory pathways
| 1 | Han J, Xue T, Yang J, et al. Effects of water retention and fertilization measures on plant community characteristics and species diversity of grassland in Loess Hilly Region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(12): 5399-5411. |
| 韩军, 薛焘, 杨杰, 等. 保水增肥措施对黄土丘陵区草地植物群落特征及物种多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2024, 44(12): 5399-5411. | |
| 2 | Lan L S, You C C, Zhang L, et al. Characteristics of productivity and biodiversity of meadow grassland in western Jilin Province-A case study of grassland in Changling County in 2022. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(5): 1529-1537. |
| 兰理实, 由成成, 张龙, 等. 吉林西部草甸草原生产力和物种多样性特征研究—以2022年长岭县草原为例. 草地学报, 2024, 32(5): 1529-1537. | |
| 3 | Li S J, Wang X M, Liu H F, et al. Diversity of desert plants in Hexi Corridor and its response to environmental factors. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| 4 | Nettesheim F C, Garbin M L, Rajao P H M, et al. Environment is more relevant than spatial structure as a driver of regional variation in tropical tree community richness and composition. Plant Ecology & Diversity, 2018, 11(1): 27-40. |
| 5 | Bagaria G, Rodà F, Pino J. Extinction and colonisation of habitat specialists drive plant species replacement along a Mediterranean grassland-forest succession. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2019, 30(2): 331-340. |
| 6 | Korner C, Spehn E M. Mountain biodiversity: A global assessment. London: Routledge, 2019. |
| 7 | Rahbek C, Borregaard M K, Antonelli A, et al. Building mountain biodiversity: Geological and evolutionary processes. Science, 2019, 365(6458): 1114-1119. |
| 8 | Huang K, Xiang J, Ma Y, et al. Response of soil microbial communities to elevation gradient in central subtropical Pinus taiwanensis and Pinus massoniana forests. Forests, 2023, 14(4): 772. |
| 9 | Zhang X, Wang Y, Wang J, et al. Elevation influences belowground biomass proportion in forests by affecting climatic factors, soil nutrients and key leaf traits. Plants, 2024, 13(5): 674. |
| 10 | Li Y C. Study on vegetation variation and its response to climate factors and human activities in the Qilian Mountain. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2023. |
| 李玉辰. 祁连山植被变化及其对气候因子和人类活动的响应研究. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2023. | |
| 11 | Meng Z X. Ecosystem multifunctional assessment of alpine grassland in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau at different altitude gradients. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2022. |
| 孟泽昕. 不同海拔高度青藏高寒草地生态系统多功能性评估. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2022. | |
| 12 | Zhou S, Dong Y, Julihaiti A, et al. Spatial variation in desert spring vegetation biomass, richness and their environmental controls in the arid region of Central Asia. Sustainability, 2022, 14(19): 12152. |
| 13 | Shi G F, Xu N, Niu Z Q, et al. Altitudinal differences of understory plant biodiversity in eastern Greater Xing’an Mountains, Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(7): 3004-3015. |
| 史恭发, 徐诺, 牛钊倩, 等. 内蒙古大兴安岭东部林下植物生物多样性海拔差异研究. 生态学报, 2024, 44(7): 3004-3015. | |
| 14 | Aqeel M, Khalid N, Noman A, et al. Interplay between edaphic and climatic factors unravels plant and microbial diversity along an altitudinal gradient. Environmental Research, 2024, 242: 117711. |
| 15 | Liang H Z, Liu L L, Gao H, et al. Altitudinal distribution pattern and its driving factors of plant diversity in the middle section of the eastern slope of the Taihang Mountain. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(7): 1091-1100. |
| 梁红柱, 刘丽丽, 高会, 等. 太行山东坡中段植物多样性垂直分布格局及其驱动因素. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(7): 1091-1100. | |
| 16 | Wang X J. Distribution pattern of plant diversity along an elevation gradient in southern Gaoligong Mountain. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2021. |
| 王兴杰. 高黎贡山南段植物多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局研究. 昆明: 云南大学, 2021. | |
| 17 | Dong Y Q. Effects of grazing exclusion on vegetation and soil fractions of active organic carbon of Seriphidium transiliense desert under moderate degeneration. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 董乙强. 禁牧对中度退化伊犁绢蒿荒漠植被和土壤活性有机碳组的影响. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2017. | |
| 18 | Geng Q W, Muhammad A, Yuan Z X, et al. Plant species composition and diversity along successional gradients in arid and semi-arid regions of China. Forest Ecology and Management, 2022, 524: 120542. |
| 19 | Lu W, Yu J, Ren H, et al. Spatial variations in species diversity of mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest community in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 2018, 26(9): 1023-1028. |
| 20 | Zhang H W, Wang M, Li J, et al. Effects of different altitudes on herbaceous plant species diversity and biomass in Jiajin Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2023, 29(5): 1125-1131. |
| 张瀚文, 王敏, 李婧, 等. 不同海拔高度对夹金山草本层植物物种多样性与生物量的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2023, 29(5): 1125-1131. | |
| 21 | Huo X R. Quantitative classification and health evaluation of grassland plant community in Luoshan nature reserve of Ningxia. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2023. |
| 霍新茹. 宁夏罗山自然保护区草地植物群落数量分类及其健康评价. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2023. | |
| 22 | Wu H B, Shui H W, Hu G Z, et al. Species diversity and biomass distribution patterns of alpine grassland along an elevation gradient in the Northern Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(6): 1071-1079. |
| 吴红宝, 水宏伟, 胡国铮, 等. 海拔对藏北高寒草地物种多样性和生物量的影响. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(6): 1071-1079. | |
| 23 | Ma J J, Liu Y H, Sheng J D, et al. Changes of relationships between dominant species and their relative biomass along elevational gradients in Xinjiang grasslands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 25-35. |
| 马婧婧, 刘耘华, 盛建东, 等. 新疆草地优势种植物相对生物量沿海拔梯度变化特征. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 25-35. | |
| 24 | He G, Shi Z, Fang H, et al. Climate and soil stressed elevation patterns of plant species to determine the aboveground biomass distributions in a valley-type Savanna. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1324841. |
| 25 | Li N, Tang S M, Guo J Y, et al. Meta-analysis of effects of grazing on plant community properties in Nei Mongol grassland. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2023, 47(9): 1256-1269. |
| 李娜, 唐士明, 郭建英, 等. 放牧对内蒙古草地植物群落特征影响的Meta分析. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(9): 1256-1269. | |
| 26 | He J S, Chen W L. A review of gradient changes in species diversity of land plant communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1997(1): 93-101. |
| 贺金生, 陈伟烈. 陆地植物群落物种多样性的梯度变化特征. 生态学报, 1997(1): 93-101. | |
| 27 | Duan M J, Gao Q Z, Guo Y Q, et al. Species diversity distribution pattern of alpine grassland communities along an altitudinal gradient in the Northern Tibet. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(10): 1845-1850. |
| 段敏杰, 高清竹, 郭亚奇, 等. 藏北高寒草地植物群落物种多样性沿海拔梯度的分布格局. 草业科学, 2011, 28(10): 1845-1850. | |
| 28 | Bai J, Long C, Quan X, et al. Reverse diversity-biomass patterns in grasslands are constrained by climates and stoichiometry along an elevational gradient. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 917: 170416. |
| 29 | Lv Z L, Liu B, Chang F, et al. Species diversity and phylogenetic diversity in Bayinbrook alpine grasslands: Elevation gradient distribution patterns and drivers. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 等. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. | |
| 30 | Wang C E, Huang M, Wang W Y, et al. Variation characteristics of plant community diversity and above-ground biomass in alpine degraded slopes along altitude gradients in the headwaters region of three-river on Tibetan Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 3640-3655. |
| 王采娥, 黄梅, 王文银, 等. 三江源区高寒坡地退化植物群落多样性和地上生物量沿海拔梯度的变化特征. 生态学报, 2022, 42(9): 3640-3655. | |
| 31 | Li Q. Responses of alpine meadow vegetation, soil and microorganism to altitudes and aspect in eastern Qilian Mountains and its microbial adaptation mechanisms. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2023. |
| 李强. 东祁连山高寒草甸植被、土壤和微生物对海拔和坡向的响应及其微生物适应机制研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2023. | |
| 32 | Yang Y, Qiu K Y, Li J Y, et al. Relationship between altitudinal distribution characteristics of typical plant community diversity and soil factors on the eastern slope of the Helan Mountains. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(12): 4995-5004. |
| 杨壹, 邱开阳, 李静尧, 等. 贺兰山东坡典型植物群落多样性垂直分布特征与土壤因子的关系. 生态学报, 2023, 43(12): 4995-5004. | |
| 33 | Ren S J, Song Z Y, Lin C C, et al. Spatial pattern of plant communities along wetness gradient in alpine grassland of Xizang and their driving factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(5): 1996-2007. |
| 任世杰, 宋朝阳, 林长存, 等. 西藏高寒草原湿润度梯度下植物群落特征空间格局及其驱动因子. 生态学报, 2024, 44(5): 1996-2007. | |
| 34 | Cong M Z, Liu Q J, Sun Z, et al. Interpretation of environmental factors affecting β diversity and its components of plant community in northern slope Changbai Mountain. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2024-02-27. (2024-02-27)[2024-08-07]. https://kns-cnki-net.webvpn.xjau.edu.cn/kcms/detail/32.1161.s.20240226.0919.002.html. |
| 丛明珠, 刘琪璟, 孙震, 等. 长白山北坡植物群落β多样性及其组分的驱动因素. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2024-02-27. (2024-02-27)[2024-08-07]. https://kns-cnki-net.webvpn.xjau.edu.cn/kcms/detail/32.1161.s.20240226.0919.002.html. | |
| 35 | Wang A, Wang X, Tognetti R, et al. Elevation alters carbon and nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in Quercus aquifolioides in southwestern China. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622: 1463-1475. |
| 36 | Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science, 2001, 294(5543): 804-808. |
| 37 | Li T, Xiong Q L, Luo P, et al. Direct and indirect effects of environmental factors, spatial constraints, and functional traits on shaping the plant diversity of montane forests. Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 10: 557-568. |
| 38 | Suttle K B, Thomsen M A, Power M E. Species interactions reverse grassland responses to changing climate. Science, 2007, 315(5812): 640-642. |
| 39 | Tylianakis J M, Didham R K, Bascompte J, et al. Global change and species interactions in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(12): 1351-1363. |
| 40 | Louthan A M, Doak D F, Angert A L. Where and when do species interactions set range limits. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2015, 30(12): 780-792. |
| [1] | 龚昕, 霍新茹, 李雯, 杨彦东, 刘超, 秦伟春, 沈艳, 王国会, 马红彬. 宁夏罗山山地草原植被群落特征及其空间分异[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 1-15. |
| [2] | 王文虎, 王世林, 梁国玲, 李文, 曹文侠. 坡向和坡位对祁连山高寒灌丛植物群落多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 17-28. |
| [3] | 张聪, 王娅, 周立华, 裴孝东, 李军豪, 石贵. 牲畜饲养结构的时空分布特征及驱动因素——以宁夏为例[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 37-49. |
| [4] | 余万洋, 陈怡帆, 方发永, 张金鑫, 李舟, 赵龙山. 1980-2020年贵州省草地空间分布格局演变及驱动力分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 1-18. |
| [5] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [6] | 刘增辉, 卢素锦, 王雨欣, 张春辉, 尹鑫. 三江源地区人工克隆植物群落生物多样性对初级生产力的影响及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 27-38. |
| [7] | 赵敏, 赵坤, 王赟博, 殷国梅, 刘思博, 闫宝龙, 孟卫军, 吕世杰, 韩国栋. 长期放牧干扰降低了短花针茅荒漠草原植物多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 39-49. |
| [8] | 郁国梁, 马紫荆, 吕自立, 刘彬. 海拔和植物群落共同调节天山中段南坡巴伦台地区天然草场土壤化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 68-78. |
| [9] | 雷石龙, 廖李容, 王杰, 张路, 叶振城, 刘国彬, 张超. 高寒草地植物多样性与Godron群落稳定性关系及其环境驱动因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 1-12. |
| [10] | 黄业芸, 邱开阳, 朱亚超, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 杨壹, 王思瑶, 崔璐瑶, 鲍平安. 贺兰山不同海拔植被生物量与土壤分形特征和土壤水分的相关关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 24-35. |
| [11] | 赵朋波, 邱开阳, 谢应忠, 刘王锁, 李小伟, 陈林, 王继飞, 孟文芬, 黄业芸, 李小聪, 杨浩楠. 海拔梯度对贺兰山岩羊主要活动区植物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 79-90. |
| [12] | 王亚晖, 唐文家, 李森, 赵鸿雁, 谢家丽, 马超, 颜长珍. 青海省草地生产力变化及其驱动因素[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 1-13. |
| [13] | 杨克彤, 陈国鹏, 鲜骏仁, 俞筱押, 张金武, 王立. 甘肃省扎尕梁北坡头花杜鹃枝叶性状特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 111-120. |
| [14] | 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 柴继宽. 海拔和品种对燕麦营养品质及表面附着微生物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 147-157. |
| [15] | 马婧婧, 刘耘华, 盛建东, 李宁, 武红旗, 贾宏涛, 孙宗玖, 程军回. 新疆草地优势种植物相对生物量沿海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 25-35. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||