

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 66-78.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024348
卢天一( ), 艾艳梅, 汪洋, 那萌, 徐尚起, 周际海(
), 艾艳梅, 汪洋, 那萌, 徐尚起, 周际海( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-09
修回日期:2024-11-06
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-06-16
通讯作者:
周际海
作者简介:E-mail: zhoujihai2006@163.com基金资助:
Tian-yi LU( ), Yan-mei AI, Yang WANG, Meng NA, Shang-qi XU, Ji-hai ZHOU(
), Yan-mei AI, Yang WANG, Meng NA, Shang-qi XU, Ji-hai ZHOU( )
)
Received:2024-09-09
Revised:2024-11-06
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
Ji-hai ZHOU
摘要:
近年来,土壤镉(Cd)污染问题日趋严重,给人类健康带来了极大的威胁。Cd污染土壤的修复和再利用成为亟待解决的环境问题。本研究以水稻为对象,设置不添加Cd(对照,CK),添加低Cd(0.5 mg·kg-1)、中Cd(2.5 mg·kg-1)和高Cd(10 mg·kg-1)4种处理,解析Cd污染对水稻不同生长时期生理生化特性和Cd富集能力的影响。结果发现,中、高浓度Cd污染显著降低了水稻地上部生物量,成熟期水稻叶绿素含量随着Cd浓度升高显著下降了30.73%~77.64%,低浓度Cd污染使分蘖期水稻脯氨酸含量较对照显著增加45.11%,Cd污染使抽穗期水稻脯氨酸含量显著降低了33.75%~61.10%。各处理成熟期水稻的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)(除低浓度Cd污染的POD)活性较对照显著增强。随Cd污染浓度的增加,水稻各部位Cd含量增加,成熟期水稻根、茎、叶、壳的Cd富集系数逐渐降低,水稻成熟期的土壤酸溶态Cd和可还原态Cd占比增加。水稻Cd含量、土壤不同Cd形态与脯氨酸含量、SOD、POD活性显著正相关,与叶绿素显著负相关。本研究可为Cd在水稻体内的富集和转运及Cd污染土壤的安全利用提供理论依据。
卢天一, 艾艳梅, 汪洋, 那萌, 徐尚起, 周际海. 镉污染土壤中水稻的镉富集特征和生长响应[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 66-78.
Tian-yi LU, Yan-mei AI, Yang WANG, Meng NA, Shang-qi XU, Ji-hai ZHOU. Cadmium enrichment characteristics and growth response of rice under excess cadmium stress in soil[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(8): 66-78.
| pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 镉 Cd (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.51 | 7.15 | 0.18 | 0.53 | 1.63 | 0.19 |
表1 供试土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of test soil
| pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium (g·kg-1) | 镉 Cd (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.51 | 7.15 | 0.18 | 0.53 | 1.63 | 0.19 |
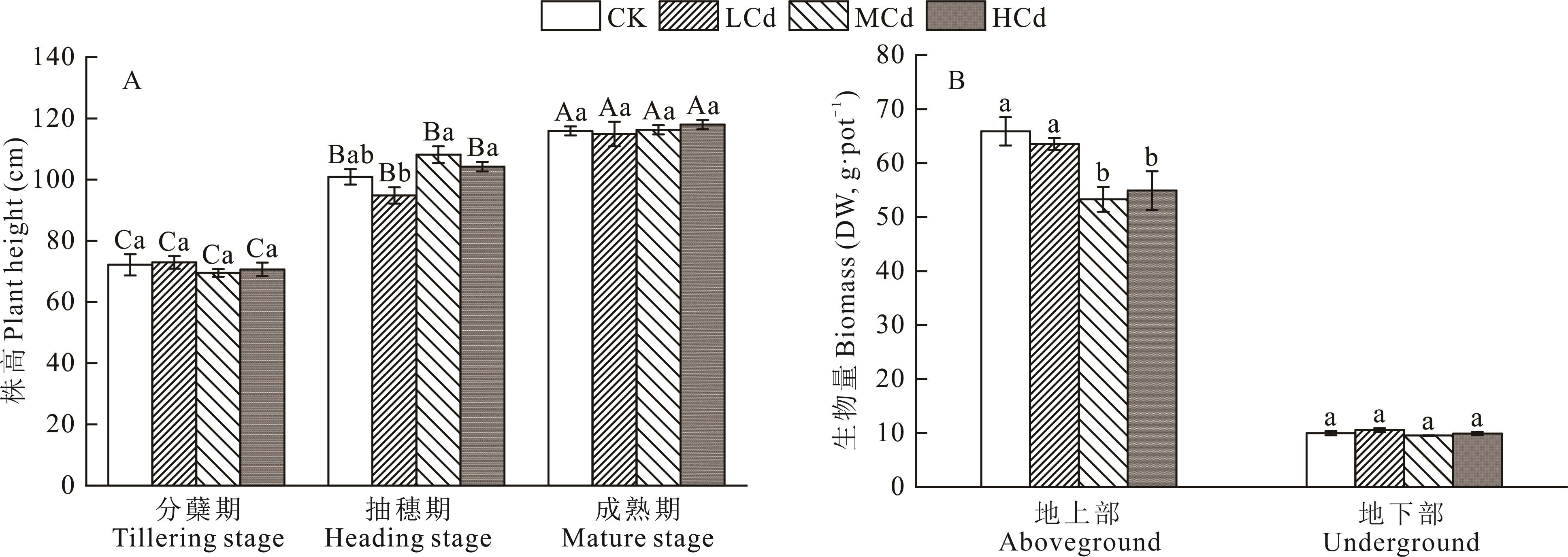
图1 镉对水稻株高和生物量的影响生物量为成熟期水稻生物量;不同小写字母表示相同生长时期不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示不同生长时期相同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Biomass is the biomass of rice at mature stage. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at the same growth stage (P<0.05), and different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different growth stages at the same treatment (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of Cd on plant height and biomass of rice
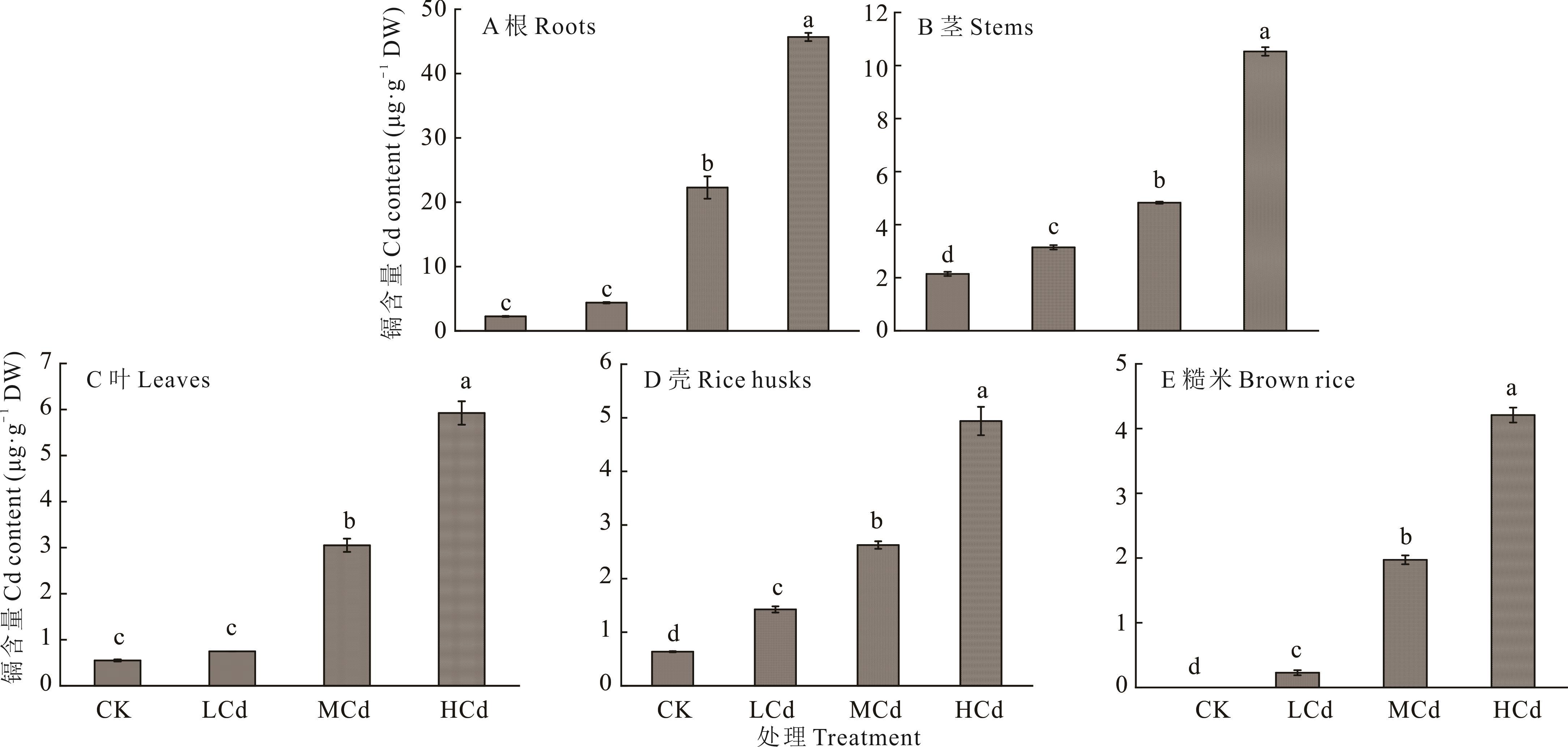
图5 水稻各部位镉含量DW: 干重Dry weight; 不同小写字母表示水稻同一部位不同处理间差异显著Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments in the same part of rice.
Fig.5 Cd content in different parts of rice
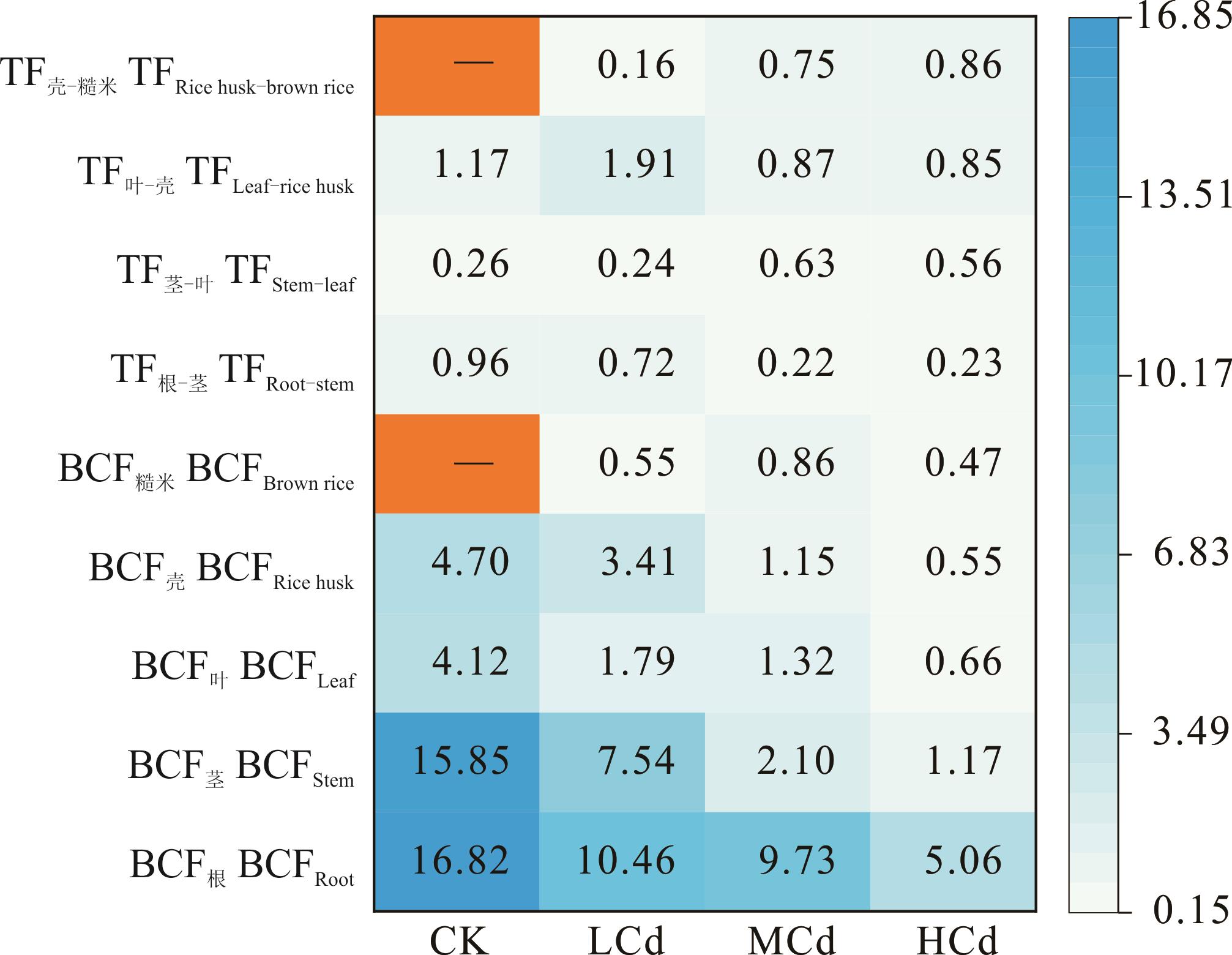
图7 水稻对镉的富集和转运系数图中以橙色为底的“-”表示该数据代表的水稻部位未检出Cd,记为0,相应的计算时作为被除数不成立,故记为缺失值。The “-” at the bottom of orange in the figure indicates that Cd is not detected in the rice part represented by the data, which is recorded as 0. The corresponding calculation is not valid as the dividend number, so it is recorded as missing value.
Fig.7 The bioconcentration factor and translocation factor of Cd in rice
| 1 | Meng Q H, Fan W H, Liu F W, et al. Effect of phosphorus application on eggplant cadmium accumulation and soil cadmium morphology. Sustainability, 2023, 15(23): 16236. |
| 2 | Ashraf S, Ahmad S R, Ali Q, et al. Efficacy of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and novel acidified organic amendment to remediate Cd-contaminated soil by Brassica juncea L. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2024, 46(2): 22. |
| 3 | Neeraj A, Hiranmai R Y, Iqbal K. Comprehensive assessment of pollution indices, sources apportionment and ecological risk mapping of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Raebareli District, Uttar Pradesh, India, employing a GIS approach. Land Degradation & Development, 2023, 34(1): 173-195. |
| 4 | Jo H J, Kim G B, Chang J Y, et al. Chronic exposure to lead and cadmium in residents living near a zinc smelter. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(4): 1731. |
| 5 | Zou M M, Zhou S L, Zhou Y J, et al. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: a review. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 280: 116965. |
| 6 | Mei S N, Lin K N, Williams D V, et al. Cadmium accumulation in cereal crops and tobacco: a review. Agronomy, 2022, 12(8): 1952. |
| 7 | El Rasafi T, Oukarroum A, Haddioui A, et al. Cadmium stress in plants: a critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2022, 52(5): 675-726. |
| 8 | Yan H L, Guo H Y, Li T, et al. High-precision early warning system for rice cadmium accumulation risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 859: 160135. |
| 9 | Wang W, Man Z, Li X L, et al. Multi-phenotype response and cadmium detection of rice stem under toxic cadmium exposure. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 917: 170585. |
| 10 | Liu Q H, Lu W S, Bai C H, et al. Cadmium, arsenic, and mineral nutrients in rice and potential risks for human health in South China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(31): 76842-76852. |
| 11 | Yang Q, Zhao Z Q, Bai Z K,et al. Effects of mycorrhizae and water conditions on perennial ryegrass growth in rare earth tailings.RSC Advances, 2019, 9(19): 10881-10888. |
| 12 | Cvitković D, Lisica P, Zorić Z, et al. Composition and antioxidant properties of pigments of Mediterranean herbs and spices as affected by different extraction methods. Foods, 2021, 10(10): 2477. |
| 13 | Chen H B, Yang X, Gielen G L, et al. Effect of biochars on the bioavailability of cadmium and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate to Brassica chinensis L. in contaminated soils. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 678: 43-52. |
| 14 | Ai Y M, Wang Y, Song L P, et al. Effects of biochar on the physiology and heavy metal enrichment of Vetiveria zizanioides in contaminated soil in mining areas. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 448: 130965. |
| 15 | Ibrahim M, Nawaz S, Iqbal K, et al. Plant-derived smoke solution alleviates cellular oxidative stress caused by arsenic and mercury by modulating the cellular antioxidative defense system in wheat. Plants, 2022, 11(10): 1379. |
| 16 | Bankaji I, Kouki R, Dridi N, et al. Comparison of digestion methods using atomic absorption spectrometry for the determination of metal levels in plants. Separations, 2023, 10(1): 40. |
| 17 | Gao R L, Hu H Q, Fu Q L, et al. Remediation of Pb, Cd, and Cu contaminated soil by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate: speciation transformation, risk evaluation and mechanism inquiry. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 730: 139119. |
| 18 | Hussain B, Ashraf M N, Abbas A, et al. Cadmium stress in paddy fields: effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 754: 142188. |
| 19 | Xu H Z, Yan J P, Qin Y, et al. Effect of different forms of selenium on the physiological response and the cadmium uptake by rice under cadmium stress. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(19): 6991. |
| 20 | Ma Y S, Jie H D, Tang Y Y, et al. The role of hemicellulose in cadmium tolerance in ramie [Boehmeria nivea (L.) gaud.]. Plants, 2022, 11(15): 1941. |
| 21 | El-Okkiah S A F, El-Tahan A M, Ibrahim O M, et al. Under cadmium stress, silicon has a defensive effect on the morphology, physiology, and anatomy of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 997475. |
| 22 | Wang T, Huang Y Y, Chen Y K, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on growth, physiological characteristics and cadmium enrichment and transport of lettuce. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(7): 115-124. |
| 王涛, 黄语燕, 陈永快, 等. Cd胁迫对生菜生长、生理特性及Cd富集转运特征的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(7): 115-124. | |
| 23 | Wang Y P, Chang H, Li C, et al. Effects of exogenous Ca2+ on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and photosystem Ⅱ function of maize seedlings under cadmium stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(5): 40-48. |
| 王玉萍, 常宏, 李成, 等. Ca2+对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生长、光合特征和PSⅡ功能的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 40-48. | |
| 24 | Zhang Y, Huang J F, Wang F M, et al. An extended prospect: advance in the leaf optical properties model separating total chlorophylls into chlorophyll a and b. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 6429. |
| 25 | Kalaji H M, Jajoo A, Oukarroum A, et al. Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a tool to monitor physiological status of plants under abiotic stress conditions. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38: 1-11. |
| 26 | Hu Y, Wang H C, Jia H P, et al. Effects of Cd treatment on morphology, chlorophyll content and antioxidant enzyme activity of Elymus nutans Griseb., a native plant in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2023, 18(1): 2187561. |
| 27 | Wang F, Xiao Y, Cheng X M, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on growth and cadmium enrichment of Chlorophytum comosum and Chlorophytum comosum var. variegatum. Chinese Joural of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(5): 1835-1844. |
| 王菲, 肖雨, 程小毛, 等. 镉胁迫对吊兰及银边吊兰生长及镉富集特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(5): 1835-1844. | |
| 28 | Meena M, Divyanshu K, Kumar S, et al. Regulation of L-proline biosynthesis, signal transduction, transport, accumulation and its vital role in plants during variable environmental conditions. Heliyon, 2019, 5(12): e02952. |
| 29 | Zhou J H, Cheng K, Song L P, et al. Exogenous indoleacetic acid induces cadmium accumulation and growth in Cinnamomum camphora. Scientia Horticulturae, 2024, 323: 112518. |
| 30 | Zhou J H, Cheng K, Gao R R, et al. Photosynthesis and other physiological characteristics of Cinnamomum camphora seedlings under cadmium stress. Forest Science, 2020, 56(6): 193-201. |
| 周际海, 程坤, 郜茹茹, 等. 土壤镉污染对香樟幼苗光合和生理特性的影响. 林业科学, 2020, 56(6): 193-201. | |
| 31 | Shanmugaraj B M, Malla A, Ramalingam S. Cadmium stress and toxicity in plants: an overview//Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Academic Press, 2019: 1-17. |
| 32 | Mouradi M, Bouizgaren A, Farissi M, et al. Seed osmopriming improves plant growth, nodulation, chlorophyll fluorescence and nutrient uptake in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)-rhizobia symbiosis under drought stress. Scientia Horticulturae, 2016, 213: 232-242. |
| 33 | Kaur R, Das S, Bansal S, et al. Heavy metal stress in rice: uptake, transport, signaling, and tolerance mechanisms. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 173(1): 430-448. |
| 34 | Guo J J, Qin S Y, Rengel Z, et al. Cadmium stress increases antioxidant enzyme activities and decreases endogenous hormone concentrations more in Cd-tolerant than Cd-sensitive wheat varieties. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 172(5): 380-387. |
| 35 | Lin X B, Zhou L J, Wu D J, et al. Effect of cadmium stress on growth, physiological characteristics and cadmium enrichment of Pueraria thomsonii Benth.seedlings. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis(Natural Sciences Edition), 2024, 46(4):884-893. |
| 林小兵, 周利军, 吴多基, 等. Cd胁迫对粉葛幼苗生长、生理特性及Cd富集的影响. 江西农业大学学报, 2024, 46(4):884-893. | |
| 36 | Guo Q, Meng L, Zhang Y N, et al. Antioxidative systems, metal ion homeostasis and cadmium distribution in Iris lactea exposed to cadmium stress. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2017, 139(5): 50-55. |
| 37 | Zaari Jabri N, Ait-El-Mokhtar M, Mekkaoui F, et al. Impacts of cadmium toxicity on seed germination and seedling growth of Triticum durum cultivars. Cereal Research Communications, 2023, 52(4): 1399-1409. |
| 38 | Chavez E, He Z L, Stoffella P J, et al. Chemical speciation of cadmium: an approach to evaluate plant-available cadmium in Ecuadorian soils under cacao production. Chemosphere, 2016, 150: 57-62. |
| 39 | Lin H M, Fang C X, Li Y Z, et al. Effect of silicon on grain yield of rice under cadmium-stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(186): 1-13. |
| 40 | Ziaf K, Talha H M, Ghani M A, et al. Differential accumulation pattern of cadmium in plant parts of pea varieties in response to varying cadmium levels. South African Journal of Botany, 2023, 161: 599-606. |
| 41 | He X, Lu Y G, Zhang J, et al. Effects of soil types on potato growth and cadmium accumulation and transport characteristics under cadmium stress. Earth and Environment, 2023, 51(1): 87-101. |
| 何雪, 陆引罡, 张洁, 等. 镉胁迫下不同土壤类型对马铃薯生长及镉富集转运特性的影响. 地球与环境, 2023, 51(1): 87-101. | |
| 42 | National Health Commission of the People’ s Republic of China. National standard for food safety pollutant pollutants in food. Beijing, China: National Health Commission of the People’ s Republic of China, 2022. |
| 43 | Zhou Y M, Long S S, Li B Y, et al. Enrichment of cadmium in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown under different exogenous pollution sources. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(35): 44249-44256. |
| 44 | Bora M S, Gogoi N, Sarma K P. Tolerance mechanism of cadmium in Ceratopteris pteridoides: translocation and subcellular distribution. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 197(7): 110599. |
| 45 | Kaushik S, Ranjan A, Sidhu A, et al. Cadmium toxicity: its’ uptake and retaliation by plant defence system and ja signaling. Biometals, 2024, 37(4): 755-772. |
| 46 | Sun J Y, Guo R, Jiang Q, et al. Brassinosteroid decreases cadmium accumulation via regulating gibberellic acid accumulation and Cd fixation capacity of root cell wall in rice (Oryza sativa). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 469: 133862. |
| 47 | Fu Y Q, Yang X J, Shen H. Root iron plaque alleviates cadmium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 161(10): 534-541. |
| 48 | Tang X Y, Zhu Y G, Cui Y S, et al. The effect of ageing on the bioaccessibility and fractionation of cadmium in some typical soils of China. Environment International, 2006, 32(5): 682-689. |
| 49 | Uraguchi S, Mori S, Kuramata M, et al. Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2009, 60(9): 2677-2688. |
| 50 | Ni Z Y, Zhang M K, Wang J W, et al. Cadmium uptake and accumulation in rice at different growth stages. Journal of Agriculture, 2020, 10(3): 49. |
| [1] | 张晴晴, 马兴羽, 鲁艳, 赵广兴, 曾凡江, 黄彩变. 沙化盐渍土地不同生长时期油莎豆的耐盐性差异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 168-180. |
| [2] | 王小风, 马步东, 黄海霞, 罗永忠, 齐建伟, 邓卓. 干旱胁迫及复水对裸果木幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 93-103. |
| [3] | 王梦琦, 王菲, 赵琬璐, 刘彦奇, 崔灿, 严俊鑫. 不同浓度硅、钙对留兰香幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(3): 154-163. |
| [4] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [5] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [6] | 亓琳, 包云, 杨莹博, 王晓凌, 赵威. 硝态氮诱导细胞分裂素强化燕麦锶富集机制的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 74-82. |
| [7] | 亢燕, 王耀辉, 牛天慧, 滕哲, 祁智, 杨佳. 羊草LcZIP1的铁转运功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 173-180. |
| [8] | 崔婷, 王勇, 马晖玲. 外源IAA作用下草地早熟禾中调控Cd长距离运输的关键基因表达及其代谢通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 146-156. |
| [9] | 李超男, 王磊, 周继强, 赵长兴, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣. 微塑料对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [10] | 杨小涵, 伍国强, 魏明, 王北辰. HKT在植物离子稳态和响应非生物逆境胁迫中的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 190-202. |
| [11] | 孙守江, 唐艺涵, 马馼, 李曼莉, 毛培胜. 紫花苜蓿种子吸胀期胚根线粒体AsA-GSH循环对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 152-162. |
| [12] | 李庭伦, 李一亨, 余慧, 江再莉, 唐立涛, 王长庭, 胡雷. 铅卤钙钛矿泄漏对垂穗披碱草幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 160-170. |
| [13] | 陆姣云, 田宏, 张鹤山, 熊军波, 刘洋, 王振南. H2O2浸种对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 141-152. |
| [14] | 单贵莲, 马祖艳, 李嘉懿, 刘洋, 谢勇, 刘佳, 初晓辉. 大狼毒对紫花苜蓿幼苗生理及内源激素含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 153-161. |
| [15] | 刘牧野, 郭丽珠, 岳跃森, 武菊英, 范希峰, 肖国增, 滕珂. 干旱胁迫下不同性别野牛草生理及抗氧化酶基因表达差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 93-103. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||