

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 63-73.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023356
王峥1( ), 常伟2, 李俊诚2, 苏连泰1, 高鲤1, 周鹏1, 安渊1(
), 常伟2, 李俊诚2, 苏连泰1, 高鲤1, 周鹏1, 安渊1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-21
修回日期:2023-10-30
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-05-13
通讯作者:
安渊
作者简介:E-mail: anyuan@sjtu.edu.cn基金资助:
Zheng WANG1( ), Wei CHANG2, Jun-cheng LI2, Lian-tai SU1, Li GAO1, Peng ZHOU1, Yuan AN1(
), Wei CHANG2, Jun-cheng LI2, Lian-tai SU1, Li GAO1, Peng ZHOU1, Yuan AN1( )
)
Received:2023-09-21
Revised:2023-10-30
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-05-13
Contact:
Yuan AN
摘要:
紫花苜蓿作为绿肥还田,并与玉米周年轮作是改良农田土壤,增加玉米产量的有效途径,但苜蓿绿肥促进玉米增产的生理和分子机制仍不清楚。本试验分别选择秋季种植黑麦草(黑麦草地)和紫花苜蓿(苜蓿地)二个地块,将部分黑麦草还田(即黑麦草绿肥)和紫花苜蓿还田(即苜蓿绿肥)后种植饲料玉米,设置黑麦草还田+玉米(黑麦草绿肥处理)、苜蓿还田+玉米(苜蓿绿肥处理)和黑麦草地施苜蓿绿肥中等量的氮素+玉米(苜蓿等量氮肥处理,即黑麦草地添加与苜蓿绿肥氮素等量的氮肥作为基肥)3个处理。结果显示:与黑麦草绿肥处理相比,苜蓿绿肥和苜蓿等量氮肥处理明显促进了玉米株高和地上生物量的增加,收获期生物量依次提高了48.77%和37.73%,但二者的氮肥偏生产力差异巨大,分别比黑麦草绿肥处理增加48.77%和降低9.61%;苜蓿绿肥处理增加了玉米新叶、老叶和叶鞘的N含量,分别较黑麦草绿肥处理提高9.59%、9.97%和33.90%,增加幅度高于苜蓿等量氮肥处理;而根尖中N含量在苜蓿等量氮肥处理中最高,其次是苜蓿绿肥处理,较黑麦草绿肥处理依次增加78.07%和23.08%;与N转运相关的关键基因ZmNPF6.4和ZmNPF6.6表达量在苜蓿绿肥处理的根中分别上调了96.48%和234.08%,同时ZmNRT2.1、ZmNRT2.2和ZmNPF6.6在白天叶片中显著上调,ZmNPF6.4和ZmNPF6.6在夜间叶片中显著下调。结果表明,紫花苜蓿还田通过影响饲料玉米根系对土壤氮素的吸收和转运,有效促进了玉米生长,提高了玉米产量。
王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73.
Zheng WANG, Wei CHANG, Jun-cheng LI, Lian-tai SU, Li GAO, Peng ZHOU, Yuan AN. Effects of alfalfa green manure on the yield, nitrogen absorption, and nitrogen translocation of feed maize[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(8): 63-73.
处理 Treatment | 土层 Soil layer (cm) | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total K (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黑麦草 Ryegrass | 0~10 | 1.39±0.03 | 0.67±0.05 | 14.37±1.19 | 84.98±10.70 | 7.62±1.06 | 187.90±19.40 | 21.71±2.60 |
| 10~20 | 1.09±0.04 | 0.64±0.07 | 13.07±0.90 | 123.06±17.50 | 8.64±0.97 | 161.59±4.38 | 12.18±1.44 | |
苜蓿 Alfalfa | 0~10 | 1.47±0.08 | 0.87±0.03 | 14.77±1.00 | 101.84±14.16 | 9.16±1.63 | 201.83±15.42 | 26.46±2.28 |
| 10~20 | 1.22±0.02 | 0.81±0.02 | 13.54±0.96 | 130.78±12.87 | 10.21±1.74 | 183.53±13.92 | 17.91±1.34 |
表1 土壤基础养分
Table 1 Basic nutrients in soil
处理 Treatment | 土层 Soil layer (cm) | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P (g·kg-1) | 全钾 Total K (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黑麦草 Ryegrass | 0~10 | 1.39±0.03 | 0.67±0.05 | 14.37±1.19 | 84.98±10.70 | 7.62±1.06 | 187.90±19.40 | 21.71±2.60 |
| 10~20 | 1.09±0.04 | 0.64±0.07 | 13.07±0.90 | 123.06±17.50 | 8.64±0.97 | 161.59±4.38 | 12.18±1.44 | |
苜蓿 Alfalfa | 0~10 | 1.47±0.08 | 0.87±0.03 | 14.77±1.00 | 101.84±14.16 | 9.16±1.63 | 201.83±15.42 | 26.46±2.28 |
| 10~20 | 1.22±0.02 | 0.81±0.02 | 13.54±0.96 | 130.78±12.87 | 10.21±1.74 | 183.53±13.92 | 17.91±1.34 |
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| ZmEIF1-qF | GCCGCCAAGAAGAAATGATGC |
| ZmEIF1-qR | CGCCAAAAGGAGAAATACAAG |
| ZmNRT2.1-qF | GGCTACATCACCGTCAGGTT |
| ZmNRT2.1-qR | GTAGACGAGCGGCATGATGA |
| ZmNRT2.2-qF | TACTACGCCTCCGAGTGGAA |
| ZmNRT2.2-qR | CTGGATGACGTTTCGCTTGC |
| ZmAMT1;1a-qF | GTGGCGGGCTGCTGGTCAAGA |
| ZmAMT1;1a-qR | CGACCGTCAAAGCCGCTAGATTG |
| ZmAMT1;3-qF | CATCGGCAAGCACTTCTTCG |
| ZmAMT1;3-qR | GCGGAGTAGATGAGGTACGC |
| ZmNPF6.4-qF | CCTCGACAACTTCTACTGGC |
| ZmNPF6.4-qR | AATTTAGGGTCGTCCGTCGC |
| ZmNPF6.6-qF | GTCATCAGCGCCATCAACCT |
| ZmNPF6.6-qR | GGGTCACACCGTGTGCCAAA |
表2 实时荧光定量引物
Table 2 Primer information for qRT-PCR analysis
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| ZmEIF1-qF | GCCGCCAAGAAGAAATGATGC |
| ZmEIF1-qR | CGCCAAAAGGAGAAATACAAG |
| ZmNRT2.1-qF | GGCTACATCACCGTCAGGTT |
| ZmNRT2.1-qR | GTAGACGAGCGGCATGATGA |
| ZmNRT2.2-qF | TACTACGCCTCCGAGTGGAA |
| ZmNRT2.2-qR | CTGGATGACGTTTCGCTTGC |
| ZmAMT1;1a-qF | GTGGCGGGCTGCTGGTCAAGA |
| ZmAMT1;1a-qR | CGACCGTCAAAGCCGCTAGATTG |
| ZmAMT1;3-qF | CATCGGCAAGCACTTCTTCG |
| ZmAMT1;3-qR | GCGGAGTAGATGAGGTACGC |
| ZmNPF6.4-qF | CCTCGACAACTTCTACTGGC |
| ZmNPF6.4-qR | AATTTAGGGTCGTCCGTCGC |
| ZmNPF6.6-qF | GTCATCAGCGCCATCAACCT |
| ZmNPF6.6-qR | GGGTCACACCGTGTGCCAAA |
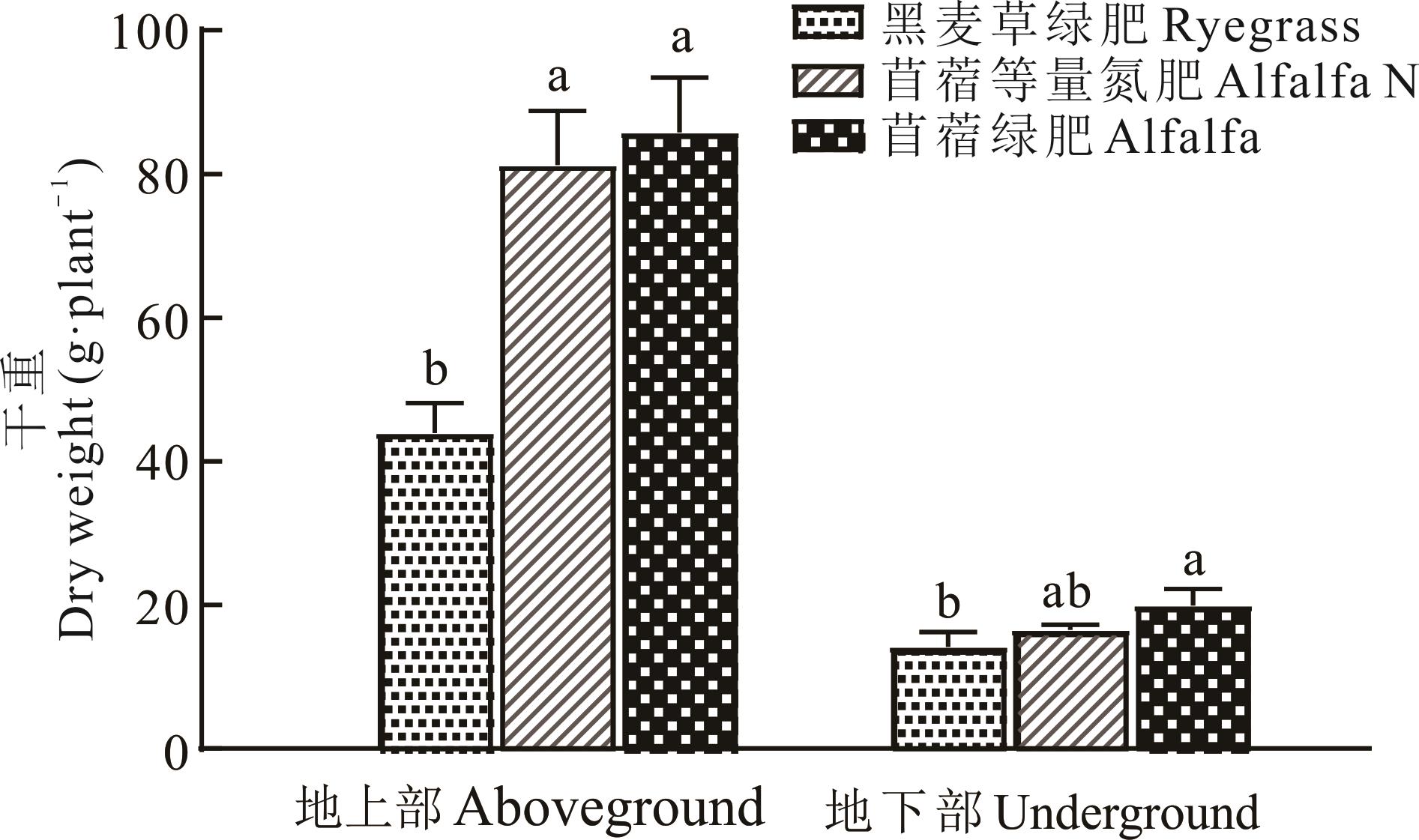
图2 大喇叭口期玉米地上和地下生物量不同字母表示在P<0.05水平上处理间差异显著,下同Different letters indicate significant differences among treatments at P<0.05level, the same below.
Fig.2 Maize biomass of above- and underground at trumpet stage
| 处理Treatment | 新叶New leaf | 老叶Old leaf | 叶鞘Leaf sheath | 根尖Root tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑麦草绿肥Ryegrass | 22.74±0.81b | 26.27±0.81b | 5.87±0.29c | 6.11±0.36b |
| 苜蓿等量氮肥Alfalfa N | 20.09±1.22c | 26.92±1.02b | 6.94±0.16b | 10.88±1.76a |
| 苜蓿绿肥Alfalfa | 24.92±1.05a | 28.89±1.26a | 7.86±0.17a | 7.52±0.48b |
表3 大喇叭口期玉米叶和根尖的N含量
Table 3 Nitrogen contents in leaves and root tips of maize at trumpet stage (g·kg-1)
| 处理Treatment | 新叶New leaf | 老叶Old leaf | 叶鞘Leaf sheath | 根尖Root tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑麦草绿肥Ryegrass | 22.74±0.81b | 26.27±0.81b | 5.87±0.29c | 6.11±0.36b |
| 苜蓿等量氮肥Alfalfa N | 20.09±1.22c | 26.92±1.02b | 6.94±0.16b | 10.88±1.76a |
| 苜蓿绿肥Alfalfa | 24.92±1.05a | 28.89±1.26a | 7.86±0.17a | 7.52±0.48b |

图6 玉米与N转运相关的基因相对表达量L1: 白天叶Leaves at daytime; L2: 晚间叶Leaves at night; R: 根Root.
Fig.6 Relative expression level of genes related to nitrogen translocation in maize
| 1 | Li X Y, Yin X F, Zhou X L, et al. Countermeasures and suggestions for high quality development of forage industry in China. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 889-894. |
| 李新一, 尹晓飞, 周晓丽, 等. 我国饲草产业高质量发展的对策和建议. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 889-894. | |
| 2 | Gao J S, Xu M G, Dong C H, et al. Effects of long-term rice-rice-green manure cropping rotation on rice yield and soil fertility. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(2): 343-349. |
| 高菊生, 徐明岗, 董春华, 等. 长期稻-稻-绿肥轮作对水稻产量及土壤肥力的影响. 作物学报, 2013, 39(2): 343-349. | |
| 3 | Ye X F, Yang C, Li Z, et al. Effects of green manure in corporation on soil enzyme activities and fertility in tobacco-planting soils. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2013, 19(2): 445-454. |
| 叶协锋, 杨超, 李正, 等. 绿肥对植烟土壤酶活性及土壤肥力的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2): 445-454. | |
| 4 | Diao C, Wang W X. The trade pattern of alfalfa importation into China and its influencing factors. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(9): 2424-2434. |
| 刁婵, 王文信. 中国苜蓿草进口贸易格局及其影响因素. 草业科学, 2023, 40(9): 2424-2434. | |
| 5 | General Office of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on promoting the high-quality development of the animal husbandry. Portal of the Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China, 2020. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-09/27/content_5547612.htm. |
| 中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 国务院办公厅关于促进畜牧业高质量发展的意见. 中华人民共和国中央人民政府门户网站, 2020. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-09/27/content_5547612.htm. | |
| 6 | Xu R, Wang Z, Wang Y M, et al. Effect of alfalfa on the yield and sucrose metabolism of rice in an alfalfa-rice rotation system. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(8): 129-140. |
| 徐蕊, 王峥, 王仪明, 等. 紫花苜蓿对轮作水稻产量和蔗糖代谢的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 129-140. | |
| 7 | Qin S H, Cao L, Zhang J L, et al. Effect of rotation of leguminous plants on soil available nutrients and physical and chemical properties in continuous cropping potato field. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1452-1458. |
| 秦舒浩, 曹莉, 张俊莲, 等. 轮作豆科植物对马铃薯连作田土壤速效养分及理化性质的影响. 作物学报, 2014, 40(8): 1452-1458. | |
| 8 | Cai Y, Hao M D. Effects of rotation model and period on wheat yield, nutrient uptake and soil fertility in the Loess Plateau. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2015, 21(4): 864-872. |
| 蔡艳, 郝明德. 轮作模式与周期对黄土高原旱地小麦产量、养分吸收和土壤肥力的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(4): 864-872. | |
| 9 | Ma L, Zhou P, Gao X Y, et al. Growth and nutrient dynamics of non-fall dormancy and semi-fall dormancy alfalfa cultivars in winter fallow land of South-east China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(5): 38-45. |
| 马力, 周鹏, 高小叶, 等. 非秋眠和半秋眠紫花苜蓿品种在华东冬闲田的生长规律和营养动态. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(5): 38-45. | |
| 10 | Li F J, Yu C, Ma L, et al. Effects of fertilizer on alfalfa growth in winter fallow paddy fields and alfalfa green manure on rice yield. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(10): 2008-2018. |
| 李凤杰, 于晨, 马力, 等. 施肥对冬闲稻田紫花苜蓿生长及苜蓿绿肥对轮作水稻产量的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(10): 2008-2018. | |
| 11 | Yu C, Wang Y M, Ma L, et al. An annual rotation model of alfalfa and corn in Yangtze River area. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(5): 996-1005. |
| 于晨, 王仪明, 马力, 等. 长江中下游地区紫花苜蓿与玉米周年轮作栽培模式. 草业科学, 2022, 39(5): 996-1005. | |
| 12 | Hu W Y, Tao T T, Tian K, et al. Status and prospect of farmland soil environmental quality management in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(5): 1094-1109. |
| 胡文友, 陶婷婷, 田康, 等. 中国农田土壤环境质量管理现状与展望. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(5): 1094-1109. | |
| 13 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 14 | Tegeder M, Masclaux-Daubresse C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytologist, 2018, 217(1): 35-53. |
| 15 | Goff B, Feng B C, Gao Q, et al. Benefit analysis of alfalfa and corn rotation in the United States. World Agriculture, 2017(8): 199-201. |
| Goff B, 冯葆昌, 高秋, 等. 美国紫花苜蓿与玉米轮作的效益分析. 世界农业, 2017(8): 199-201. | |
| 16 | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Notice of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs on issuing《Action plan for chemical fertilizer reduction by 2025》 and 《Action plan for chemical pesticide reduction by 2025》. Portal of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2022. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/ ZZYGLS/202212/t20221201_6416398.htm. |
| 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 农业农村部关于印发《到2025年化肥减量化行动方案》和《到2025年化学农药减量化行动方案》的通知. 中华人民共和国农业农村部门户网站, 2022. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/ZZYGLS/202212/t20221201_6416398.htm. | |
| 17 | Qu H K, Gao Y H, Han J R. Research on the nitrogen fertilizer reduction effect of rice with green manure and alfalfa returned to the field. Agricultural Equipment & Technology, 2018, 44(1): 22-24. |
| 瞿怀康, 高月华, 韩九荣. 绿肥紫花苜蓿还田下水稻氮肥减量效应研究. 农业装备技术, 2018, 44(1): 22-24. | |
| 18 | Xiong W Y, Xu K W, Liu M P, et al. Effects of different nitrogen application levels on photosynthetic characteristics, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of spring maize in Sichuan Province. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(9): 1735-1748. |
| 熊伟仡, 徐开未, 刘明鹏, 等. 不同氮用量对四川春玉米光合特性、氮利用效率及产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(9): 1735-1748. | |
| 19 | Overman A R, Scholtz R V. Model for accumulation of dry matter and plant nutrients by corn. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1999, 30(15/16): 2059-2081. |
| 20 | Zhang J T, Liu Y P, Li X H, et al. Dynamic responses of nitrogen accumulation and remobilization in summer maize organs to nitrogen fertilizer. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 506-514. |
| 张经廷, 刘云鹏, 李旭辉, 等. 夏玉米各器官氮素积累与分配动态及其对氮肥的响应. 作物学报, 2013, 39(3): 506-514. | |
| 21 | Zhang L, Wu W M, Chen H, et al. Effect of nitrogen management on dynamic changes of soil inorganic nitrogen, yield, nitrogen uptake and utilization of maize. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(4): 126-134. |
| 张林, 武文明, 陈欢, 等. 氮肥运筹方式对土壤无机氮变化、玉米产量和氮素吸收利用的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(4): 126-134. | |
| 22 | Xie T T, Zhao H, Xiao H J, et al. Responses of dry matter accumulation, nitrogen utilization and yield of table corn to new slow-release fertilizers. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(7): 2024-2032. |
| 谢婷婷, 赵欢, 肖厚军, 等. 鲜食玉米干物质积累、氮素利用及产量对新型缓释肥料的响应. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(7): 2024-2032. | |
| 23 | Bloom A J. The increasing importance of distinguishing among plant nitrogen sources. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2015, 25(1): 10-16. |
| 24 | Fan X R, Naz M, Fan X R, et al. Plant nitrate transporters: from gene function to application. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017, 68(10): 2463-2475. |
| 25 | Tsay Y F, Schroeder J I, Feldmann K A, et al. The herbicide sensitivity gene CHL1 of Arabidopsis encodes a nitrate-inducible nitrate transporter. Cell, 1993, 72(5): 705-713. |
| 26 | Wen Z, Tyerman S D, Dechorgnat J, et al. Maize NPF6 proteins are homologs of Arabidopsis CHL1 that are selective for both nitrate and chloride. The Plant Cell, 2017, 29(10): 2581-2596. |
| 27 | Garnett T, Conn V, Plett D, et al. The response of the maize nitrate transport system to nitrogen demand and supply across the lifecycle. The New Phytologist, 2013, 198(1): 82-94. |
| 28 | Gu R, Duan F, An X, et al. Characterization of AMT-mediated high-affinity ammonium uptake in roots of maize (Zea mays L.). Plant and Cell Physiology, 2013, 54(9): 1515-1524. |
| [1] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [2] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [3] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [4] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [5] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [6] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [7] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [8] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| [9] | 岳海旺, 魏建伟, 王广才, 刘朋程, 陈淑萍, 卜俊周. 基于环境型鉴定技术划分生态区综合评价黄淮海青贮玉米品种[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 120-138. |
| [10] | 李妍, 马富龙, 韩路, 王海珍. 美国‘WL’系列不同秋眠级苜蓿品种在南疆的生产性能与适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 139-149. |
| [11] | 孟超楠, 赵玉洁, 陈佳欣, 张旖璐, 王彦佳, 冯丽荣, 孙玉刚, 郭长虹. 2株青贮玉米根际固氮菌的筛选鉴定及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 174-185. |
| [12] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [13] | 唐璎, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 董霖. 甘肃不同区域青贮紫花苜蓿乳酸菌群落特征及其驱动因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 112-124. |
| [14] | 白旭琴, 贾春云, 李文栓, 李亚敏, 刘长风, 韩秀云, 褚美函, 巩宗强, 李晓军. 叶面喷施硒肥对紫花苜蓿富硒降镉效果的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 50-60. |
| [15] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷耦合下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量及磷素空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 104-115. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||