

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 146-156.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022276
收稿日期:2022-06-28
修回日期:2022-09-28
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-04-21
通讯作者:
马晖玲
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: mahl@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Ting CUI( ), Yong WANG, Hui-ling MA(
), Yong WANG, Hui-ling MA( )
)
Received:2022-06-28
Revised:2022-09-28
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-04-21
Contact:
Hui-ling MA
摘要:
为探究吲哚乙酸(indole-3-acetic acid, IAA)对草地早熟禾中镉(cadmium,Cd)从根系到叶片长距离运输的影响及相关机制,分析IAA作用下草地早熟禾响应Cd胁迫的差异基因及代谢通路。以草地早熟禾为试验材料,在水培条件下,叶面喷施400 nmol·L-1外源IAA并施加600 μmol·L-1 Cd胁迫。进行株高、根长、根系和叶片Cd含量测定及转录组测序。利用实时荧光定量验证转录组数据准确性。结果表明,外源施加IAA可促进Cd胁迫下草地早熟禾株高和根长,抑制Cd从根系向叶片的长距离运输。转录组分析发现,Cd胁迫下共有1294条基因被IAA显著调控。实时荧光定量结果与RNA-Seq表达模式一致。GO富集分析表明,IAA可调控响应高温、低温、Cd离子及病毒的相关基因抵御Cd胁迫,其中分子伴侣蛋白HSP70、激酶MAPK和转录因子MYB46被明显上调。另外,外源IAA可上调谷胱甘肽代谢及木质素合成通路上的基因,可能增加谷胱甘肽合成及细胞壁木质化,进一步增加液泡区隔化和降低Cd进入细胞,从而减少叶片Cd含量。本研究可为IAA信号作用下Cd转运与分配机制研究提供参考。
崔婷, 王勇, 马晖玲. 外源IAA作用下草地早熟禾中调控Cd长距离运输的关键基因表达及其代谢通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 146-156.
Ting CUI, Yong WANG, Hui-ling MA. Analysis of the key exogenous IAA-induced gene expression levels and metabolic pathways involved in long-distance translocation of Cd in Poa pratensis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 146-156.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 上游引物Forward primers | 下游引物Reverse primers |
|---|---|---|
| TRINITY_DN115423_c2_g1 | GCACATGTTCGTCGTCAAGG | AATCTCCTTCTTGTCCGGCG |
| TRINITY_DN145731_c0_g2 | AAGAGCCATTGCCGTACTCC | TGGTCGTGCTTGGTCTCAAA |
| TRINITY_DN163800_c1_g2 | TCTCGAGATCTGACCTGGCA | GTTCGTCGCCACTTGGAGTA |
| TRINITY_DN145701_c0_g1 | CATCACGTCTGTGAACCCCA | GTCCGTGTTTGGGCTGTTTC |
| TRINITY_DN141021_c0_g2 | CAACACATTCCCACCCTCCA | CAGCTGGATGTTCACCGGAT |
| TRINITY_DN142220_c1_g2 | GACTGGCCAACTCAGACCTC | CGACCGTGACCTTCATAGGG |
| TRINITY_DN135644_c0_g2 | TTCTACCGTTGCAGCTTCGT | TGGTGCCGTAGATGTCACAC |
| TRINITY_DN155113_c1_g1 | CTTCACTCACTGCCAAACGC | GAGGCAAAAGACTGCTGCAC |
| TRINITY_DN72438_c0_g1 | GACCATTGTCACCGGTCGTA | ATCTCCCTGGTTGCGGAATG |
| TRINITY_DN168047_c0_g1 | ATCCTAGCGCCTTCATGCTC | GTACTTGCCGACACCAGTGA |
| TRINITY_DN139972_c1_g1 | TGGCAGGCCCTACCTAGATT | TCCCAAAGCTCCTGCTTGTC |
| TRINITY_DN167060_c4_g1 | AGGGCCGCTACTAAATACGC | CAGCACCTGAGCTTTCCTGA |
| TRINITY_DN163988_c1_g1 | TGCAATATCCCAAGCAGCCA | CAGTCTTTAGCCCCTCACCG |
| TRINITY_DN165172_c2_g1 | CAGCAGGCCCTGTCATTGTA | CGGTACCGGAACACGAAGAA |
| TRINITY_DN165077_c2_g1 | CGGCGATTCTCTACCTCGTC | GCGTGGAATCGTTCTTGAGC |
表1 15条随机选取的基因上下游引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of forward and reverse primer of 15 randomly selected genes
| 基因ID Gene ID | 上游引物Forward primers | 下游引物Reverse primers |
|---|---|---|
| TRINITY_DN115423_c2_g1 | GCACATGTTCGTCGTCAAGG | AATCTCCTTCTTGTCCGGCG |
| TRINITY_DN145731_c0_g2 | AAGAGCCATTGCCGTACTCC | TGGTCGTGCTTGGTCTCAAA |
| TRINITY_DN163800_c1_g2 | TCTCGAGATCTGACCTGGCA | GTTCGTCGCCACTTGGAGTA |
| TRINITY_DN145701_c0_g1 | CATCACGTCTGTGAACCCCA | GTCCGTGTTTGGGCTGTTTC |
| TRINITY_DN141021_c0_g2 | CAACACATTCCCACCCTCCA | CAGCTGGATGTTCACCGGAT |
| TRINITY_DN142220_c1_g2 | GACTGGCCAACTCAGACCTC | CGACCGTGACCTTCATAGGG |
| TRINITY_DN135644_c0_g2 | TTCTACCGTTGCAGCTTCGT | TGGTGCCGTAGATGTCACAC |
| TRINITY_DN155113_c1_g1 | CTTCACTCACTGCCAAACGC | GAGGCAAAAGACTGCTGCAC |
| TRINITY_DN72438_c0_g1 | GACCATTGTCACCGGTCGTA | ATCTCCCTGGTTGCGGAATG |
| TRINITY_DN168047_c0_g1 | ATCCTAGCGCCTTCATGCTC | GTACTTGCCGACACCAGTGA |
| TRINITY_DN139972_c1_g1 | TGGCAGGCCCTACCTAGATT | TCCCAAAGCTCCTGCTTGTC |
| TRINITY_DN167060_c4_g1 | AGGGCCGCTACTAAATACGC | CAGCACCTGAGCTTTCCTGA |
| TRINITY_DN163988_c1_g1 | TGCAATATCCCAAGCAGCCA | CAGTCTTTAGCCCCTCACCG |
| TRINITY_DN165172_c2_g1 | CAGCAGGCCCTGTCATTGTA | CGGTACCGGAACACGAAGAA |
| TRINITY_DN165077_c2_g1 | CGGCGATTCTCTACCTCGTC | GCGTGGAATCGTTCTTGAGC |

图1 外源IAA对Cd胁迫下草地早熟禾株高(A)、根长(B)和Cd含量(C)的影响不同小写字母和*代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different lowercase letters and * indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.1 Effects of exogenous IAA on plant height (A), root length (B) and Cd concentration (C) in Kentucky bluegrass under Cd stress
| 样本Simples | 原始序列数量Raw reads | 清洁序列数量Valid reads | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd_1 | 47397864 | 46440412 | 98.46 | 94.79 | 52.51 |
| Cd_2 | 50450066 | 49185876 | 98.54 | 95.08 | 52.75 |
| Cd_3 | 51288708 | 50076930 | 98.49 | 94.94 | 52.78 |
| Cd+IAA_1 | 47775358 | 46702260 | 98.51 | 94.97 | 52.66 |
| Cd+IAA_2 | 52741792 | 51346028 | 98.46 | 94.89 | 52.86 |
| Cd+IAA_3 | 54986698 | 53830218 | 98.53 | 95.05 | 52.72 |
| CK_1 | 52312058 | 51101542 | 98.48 | 94.87 | 52.20 |
| CK_2 | 44140396 | 43228210 | 98.52 | 94.97 | 52.03 |
| CK_3 | 39566018 | 38686352 | 98.43 | 94.68 | 51.55 |
| IAA_1 | 42275074 | 41366510 | 98.51 | 95.00 | 52.46 |
| IAA_2 | 47238292 | 46138970 | 98.51 | 94.96 | 52.58 |
| IAA_3 | 54196830 | 52731944 | 98.51 | 94.96 | 52.27 |
表2 转录组测序数据结果统计
Table 2 Statistics of RNA-seq results
| 样本Simples | 原始序列数量Raw reads | 清洁序列数量Valid reads | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd_1 | 47397864 | 46440412 | 98.46 | 94.79 | 52.51 |
| Cd_2 | 50450066 | 49185876 | 98.54 | 95.08 | 52.75 |
| Cd_3 | 51288708 | 50076930 | 98.49 | 94.94 | 52.78 |
| Cd+IAA_1 | 47775358 | 46702260 | 98.51 | 94.97 | 52.66 |
| Cd+IAA_2 | 52741792 | 51346028 | 98.46 | 94.89 | 52.86 |
| Cd+IAA_3 | 54986698 | 53830218 | 98.53 | 95.05 | 52.72 |
| CK_1 | 52312058 | 51101542 | 98.48 | 94.87 | 52.20 |
| CK_2 | 44140396 | 43228210 | 98.52 | 94.97 | 52.03 |
| CK_3 | 39566018 | 38686352 | 98.43 | 94.68 | 51.55 |
| IAA_1 | 42275074 | 41366510 | 98.51 | 95.00 | 52.46 |
| IAA_2 | 47238292 | 46138970 | 98.51 | 94.96 | 52.58 |
| IAA_3 | 54196830 | 52731944 | 98.51 | 94.96 | 52.27 |
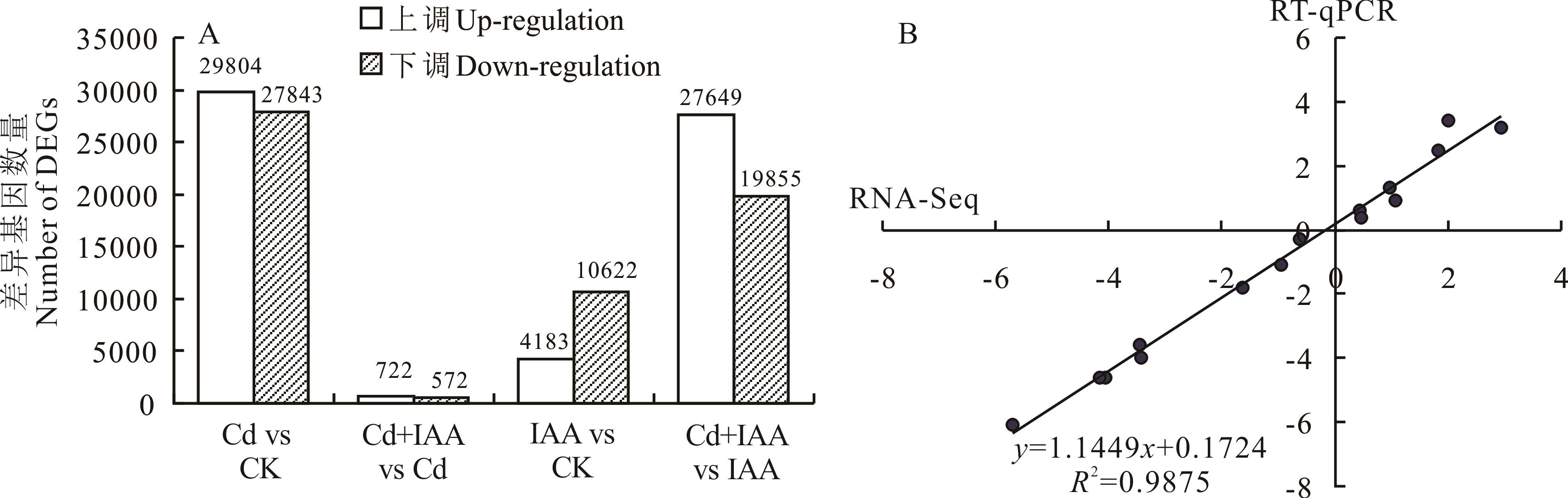
图2 不同处理间的差异基因数量(A)及RT-qPCR验证基因表达量(B)DEGs:差异表达基因 Differentially expressed genes.下同 The same below.
Fig.2 Number of DEGs between different treatments (A) and verification of gene expressional levels by using RT-qPCR (B)
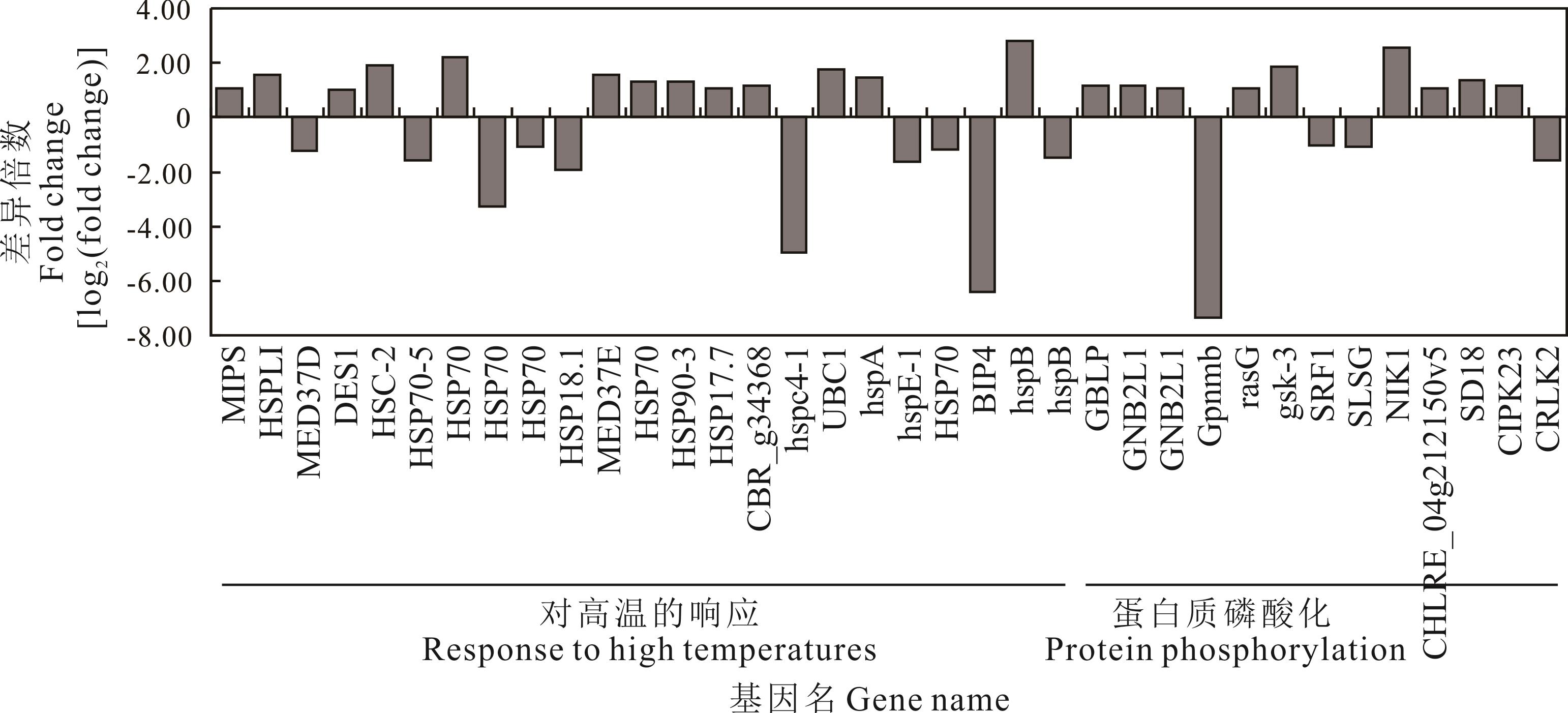
图4 Cd胁迫下外源IAA诱导的草地早熟禾对高温的响应及蛋白质磷酸化相关差异基因MIPS:磷酸肌醇合成酶Myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase;MED37D:介导RNA聚合酶II转录Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 37c isoform X1;DES1:鞘脂类去饱和酶4Sphingolipid delta(4)-desaturase;HSC-2:热休克蛋白同源蛋白Heat shock cognate 70 kDa protein;HSP:热休克蛋白同源蛋白Heat shock protein;UBC1:泛素缀合酶E2-16 kDa Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-16 kDa;GBLP:鸟嘌呤核苷酸结合蛋白Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein;GNB2L1:鸟嘌呤核苷酸结合蛋白Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein;Gpnmb:糖蛋白非转移性黑色素瘤蛋白B Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B;rasG:ras相关蛋白ras-like protein;gsk:糖原合成激酶Glycogen synthase kinase;SRF1:蛋白strubbelig受体家族3-like isoform X2 Protein strubbelig-receptor family 3-like isoform X2;SLSG:G型凝集素s受体样丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase B120;NIK1:NSP蛋白相互作用激酶Protein NSP-interacting kinase 1-like;SD18:G型凝集素s受体样丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11300 At1g11301;CRLK2:富含亮氨酸重复受体样丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶Putative leucine-rich repeat receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase.
Fig.4 Exogenous IAA-induced DEGs related to high temperature responding and protein phosphorylation under Cd stress

图5 Cd胁迫下外源IAA诱导的草地早熟禾对低温的响应、对Cd2+的响应、脂质代谢、信号转导、木质素生物合成及响应病毒相关差异基因ADH:乙醇脱氢酶Alcohol dehydrogenase; AHL20:核定位蛋白20-likeAT-hook motif Nuclear-localized protein 20-like AT-hook motif;CCR:肉桂酰辅酶A还原酶Cinnamoyl-CoA reductase; CIPK:钙调磷酸酶互作蛋白激酶B-LikeCalcineurin B-like-interacting protein kinase;PAG1:糖鞘脂富集微域相关磷蛋白Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains;cspLA:包含冷休克域蛋白Cold shock domain containing protein;PRX1:过氧化物酶Peroxiredoxin;TUBA:β-微管蛋白Beta-tubulin;Elovl3:长链脂肪酸延长酶Long-chain fatty acid elongase;Fabp5:脂肪酸结合蛋白Fatty acid-binding protein;Apoe:E载脂蛋白E基因Apolipoprotein;ACACA:乙酰辅酶a羧化酶1Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1-like;ARF:ADP核基化因子ADP-ribosylation factor;Rac1:ras相关C3肉毒毒素底物Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1-like isoform X2;ARHGDIA:鸟苷二磷酸解离抑制剂α Rho GDP (guanosine diphosphate) dissociation inhibitor α;MAPK:丝裂原激活的蛋白激酶Mitogen-activated protein kinase;fkr-3:肽基脯氨酸顺反异构酶Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase-like;cap:环化酶Cyclase-associated 1;CYP98A1:细胞色素P450 98A1 CytochromeP450 98A1;CCR:肉桂酰辅酶A还原酶Cinnamoyl-CoA reductase;LAC4:漆酶4 Laccase4;PER52:过氧化物酶52 Peroxidase52.
Fig.5 Exogenous IAA-induced DEGs related to low temperature responding, response to Cd2+, lipid metabolism, signal transduction, lignin biosynthesis, and response to virus under Cd stress
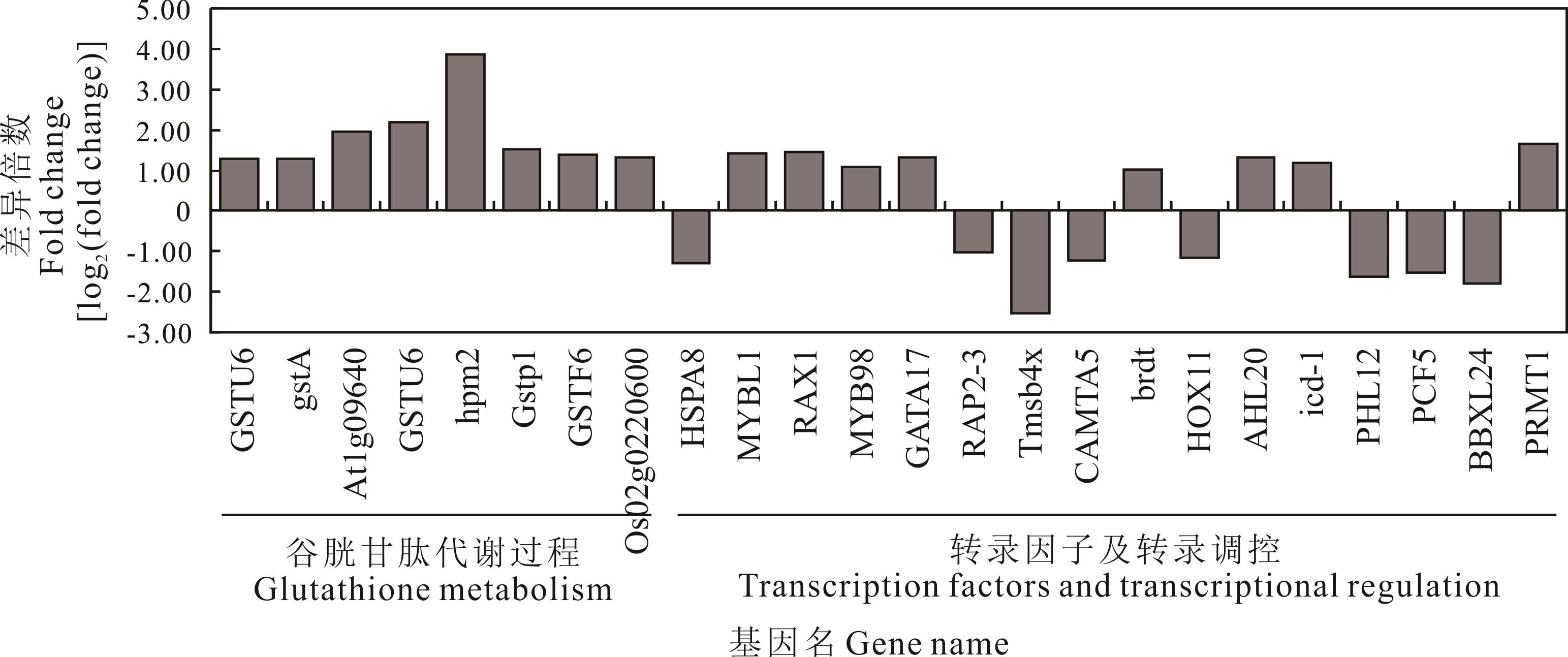
图6 Cd胁迫下外源IAA诱导的草地早熟禾谷胱甘肽代谢过程和转录因子及转录调控相关差异基因GST:谷胱甘肽巯基转移酶Glutathione S-transferase;hpm2:谷胱甘肽巯基转移酶hmp2-like Glutathione S-transferase hmp2-like;HSP:热休克蛋白同源蛋白Heat shock protein;RAX1:类MYB98转录因子Transcription factor MYB98-like;RAP2-3:乙烯响应因子071-like isoform X2 Ethylene-responsive transcription factor ERF071-like isoform X2;CAMTA5:钙调素结合转录激活因子5 Calmodulin-binding transcription activator 5;HOX11:同源域亮氨酸拉链蛋白Homeobox-leucine zipper protein HOX11;AHL20:核定位蛋白20-like AT-hook motif Nuclear-localized protein 20-like AT-hook motif;AHL20:核定位蛋白20-like AT-hook Motif nuclear-localized protein 20;icd-1:异柠檬酸脱氢酶Isocitrate dehydrogenases;BBXL24:B-box锌指蛋白24 B-box zinc finger protein 24.
Fig.6 Exogenous IAA-induced DEGs related to glutathione metabolism, transcription factors and transcriptional regulation under Cd stress

图7 Cd胁迫下外源IAA诱导的草地早熟禾谷胱甘肽代谢及细胞壁修饰相关DEGsA:Cd胁迫下外源IAA诱导的草地早熟禾谷胱甘肽代谢相关差异基因热图;B:Cd胁迫下外源IAA诱导的草地早熟禾细胞壁修饰相关差异基因热图。A: Heatmap of exogenous IAA-induced DEGs related to glutathione metabolism in Kentucky bluegrass under Cd stress; B: Heatmap of exogenous IAA-induced DEGs related to cell wall modification in Kentucky bluegrass under Cd stress. 热图数据为经Z-score算法标准化后的基因表达量,红色代表上调,蓝色代表下调。The heatmap data was the gene expression level that normalized by Z-score method, the red color represents the up-regulated genes, while the blue color represents the down-regulated genes.
Fig.7 Exogenous IAA-induced DEGs in Kentucky bluegrass that involves in glutathione metabolism and cell wall modification under Cd stress
| 1 | Zhou L, Xiao F, Xiao H, et al. Effects of lime on cadmium accumulation of double-season rice in paddy fields with different cadmium pollution degrees. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2021, 54(4): 780-791. |
| 周亮, 肖峰, 肖欢, 等. 施用石灰降低污染稻田上双季稻镉积累的效果. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(4): 780-791. | |
| 2 | Wu X, Tian H, Li L, et al. Higher Cd-accumulating oilseed rape has stronger Cd tolerance due to stronger Cd fixation in pectin and hemicellulose and higher Cd chelation. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 285: 117218. |
| 3 | Zhang Z H, Zhou T, Tang T J, et al. A multiomics approach reveals the pivotal role of subcellular reallocation in determining rapeseed resistance to cadmium toxicity. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(19): 5437-5455. |
| 4 | Li Z, Ma Z, van der Kuijp T J, et al. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468/469: 843-853. |
| 5 | Guo Z C, Zhou B H, Zhao K, et al. Morphological characteristics of Cd and its pollution assessment in farmland soils along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Journal of Anqing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 27(1): 96-101. |
| 郭展翅, 周葆华, 赵宽, 等. 长江中下游某地区农田Cd形态特征及污染评价. 安庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 27(1): 96-101. | |
| 6 | Chen J. Effects of exogenous auxins on growth and physiological characteristics of maize seedlings under cadmium stress. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2016. |
| 陈晶. 生长素类物质对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 重庆: 西南大学, 2016. | |
| 7 | Demecsová L, Tamás L. Reactive oxygen species, auxin and nitric oxide in metal-stressed roots: toxicity or defence. BioMetals, 2019, 32(5): 717-744. |
| 8 | Pasternak T, Potters G, Caubergs R, et al. Complementary interactions between oxidative stress and auxins control plant growth responses at plant, organ, and cellular level. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2005, 56(418): 1991-2001. |
| 9 | Chaoui A, El Ferjani E. Effects of cadmium and copper on antioxidant capacities, lignification and auxin degradation in leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 2005, 328(1): 23-31. |
| 10 | Wang K, Yu H, Zhang X, et al. A transcriptomic view of cadmium retention in roots of cadmium-safe rice line (Oryza sativa L.). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 418: 126379. |
| 11 | Bočová B, Huttová J, Mistrík I, et al. Auxin signalling is involved in cadmium-induced glutathione-S-transferase activity in barley root. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2013, 35(9): 2685-2690. |
| 12 | Ning R Y, Liu N, Cheng H Y, et al. Effects of microplastics,cadmium and their combination on the growth and cadmium accumulation of hyperaccumulators. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(6): 415-425. |
| 宁瑞艳, 刘娜, 程红艳, 等. 微塑料和镉及其复合对超富集植物生长和富集镉的影响. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(6):415-425. | |
| 13 | Wu P, Zhang X F, Gao B, et al. Effects of polyethylene on Cd accumulation of hyperaccumulator Solanum photeinocarpum. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 45(1): 174-181. |
| 吴萍, 张杏锋, 高波, 等. 微塑料对超富集植物少花龙葵Cd累积的影响. 环境科学与技术, 2022, 45(1): 174-181. | |
| 14 | Yang Y, Wang C J, Guo J H, et al. The effects of cadmium stress on seed germination and seedling growth of Bidens pilosa (L.) and Pennisetum alopecuroides(L.). Journal of Yunnan Normal University(Natural Sciences Edition), 2022, 42(1): 58-63. |
| 杨云, 王晨骄, 郭嘉航, 等. 镉胁迫对鬼针草和狼尾草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(1): 58-63. | |
| 15 | Xu P X. Studies on cadmium tolerance and detoxification in tall fescue and Kentucky bluegrass. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2014. |
| 徐佩贤. 高羊茅和草地早熟禾对镉的耐受能力和解毒机制研究. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014. | |
| 16 | Xian J, Wang Y, Niu K, et al. Transcriptional regulation and expression network responding to cadmium stress in a Cd-tolerant perennial grass Poa pratensis. Chemosphere, 2020, 250: 126158. |
| 17 | Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. Journal, 2011, 17(1): 10-12. |
| 18 | Grabherr M G, Haas B J, Yassour M, et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29(7): 644-652. |
| 19 | Kallberg Y, Persson B. KIND-a non-redundant protein database. Bioinformatics, 1999, 15(3): 260-261. |
| 20 | Ashburner M, Ball C A, Blake J A, et al. Gene Ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genetics, 2000, 25(1): 25-29. |
| 21 | Bairoch A, Boeckmann B. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank. Nucleic Acids Research, 1991, 19(Suppl): 2247-2249. |
| 22 | Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, et al. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, 27(1): 29-34. |
| 23 | Huerta-Cepas J, Szklarczyk D, Heller D, et al. eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): 309-314. |
| 24 | Niu K, Zhang R, Zhu R, et al. Cadmium stress suppresses the tillering of perennial ryegrass and is associated with the transcriptional regulation of genes controlling axillary bud outgrowth. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 212: 112002. |
| 25 | Zhao F Y, Hu F, Zhang S Y, et al. MAPKs regulate root growth by influencing auxin signaling and cell cycle-related gene expression in cadmium-stressed rice. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20(8): 5449-5460. |
| 26 | Ray D, Ghosh A, Mustafi S B, et al. Plant stress response: Hsp70 in the spotlight//Asea A, Kaur P, Calderwood S K. Heat shock proteins and plants. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 123-147. |
| 27 | Chen P, Song Y, Liu X, et al. LncRNA PMAT-PtoMYB46 module represses PtoMATE and PtoARF2 promoting Pb2+ uptake and plant growth in poplar. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 433: 128769. |
| 28 | Yang L P, Zhu J, Wang P, et al. Effect of Cd on growth, physiological response, Cd subcellular distribution and chemical forms of Koelreuteria paniculata. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 160: 10-18. |
| 29 | Zhu X F, Lei G J, Jiang T, et al. Cell wall polysaccharides are involved in P-deficiency-induced Cd exclusion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta, 2012, 236(4): 989-997. |
| 30 | Finger-Teixeira A, Lucio Ferrarese M de L, Ricardo Soares A, et al. Cadmium-induced lignification restricts soybean root growth. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2010, 73(8): 1959-1964. |
| 31 | Elobeid M, Göbel C, Feussner I, et al. Cadmium interferes with auxin physiology and lignification in poplar. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(3): 1413-1421. |
| 32 | Loix C, Huybrechts M, Vangronsveld J, et al. Reciprocal interactions between cadmium-induced cell wall responses and oxidative stress in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1867. |
| 33 | Lv Z Q, Ren D D, Zhou H, et al. Cloning and expression of HHT gene in ‘Huanghua’ pear and its bud mutant ‘Lvhuanghua’ pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2016, 36(6): 1105-1109. |
| 吕照清, 任丹丹, 周贺, 等. ‘黄花’梨及其芽变‘绿黄花’梨HHT基因克隆与表达分析. 西北植物学报, 2016, 36(6): 1105-1109. | |
| 34 | Wang Y, Cui T, Niu K, et al. Comparison and characterization of oxidation resistance and carbohydrate content in Cd-tolerant and -sensitive kentucky bluegrass under Cd stress. Agronomy, 2021, 11(11): 2358. |
| 35 | Zhang S, Wang S, Han S F, et al. The research progress of glutaredoxin in plants. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(S1): 202-209. |
| 张硕, 王硕, 韩胜芳, 等. 植物中谷氧还蛋白研究进展. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(S1): 202-209. | |
| 36 | Qiao X R, Zhang J Y. Research progress on GPX in plants. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(9): 7-13. |
| 乔新荣, 张继英. 植物谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPX)研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(9): 7-13. |
| [1] | 杨瑞鑫, 李勇, 蔡小芳, 韩铖星, 郭艳丽. 不同物理形态的开食料对羔羊瘤胃转录组的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 159-170. |
| [2] | 尚盼盼, 曾兵, 屈明好, 李明阳, 杨兴云, 郑玉倩, 沈秉娜, 毕磊, 杨成, 曾兵. 红三叶响应淹水胁迫的相关通路及差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 112-128. |
| [3] | 哈雪, 张金青, 白方旭, 马祥荣, 王安琦, 马晖玲. 甘肃野生草地早熟禾种质种子产量相关性状分析及其对矿质元素利用效应评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 54-67. |
| [4] | 钱文武, 郭鹏, 朱慧森, 张士敏, 李德颖. 草地早熟禾叶片表皮特征、解剖结构及光合特性对不同施氮量的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 131-143. |
| [5] | 孙禄娟, 何建军, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 杨轲, 李葆春, 马小乐, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄, 王化俊. 基于全长转录组测序的盐生草SSR标记开发及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 199-210. |
| [6] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [7] | 赵利清, 郝志刚, 崔笑岩, 彭向永. 赤霉素及其抑制剂调控草地早熟禾生长及赤霉素相关基因表达的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 85-91. |
| [8] | 杨志民, 邢瑞, 丁鋆嘉, 庄黎丽. 基于转录组测序的高羊茅分蘖与株高相关差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 145-163. |
| [9] | 张金青, 牛奎举, 李玉珠, 马晖玲. 植物无融合生殖发生因素解析及其在草地早熟禾育种中的应用前景展望[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 205-217. |
| [10] | 张宁, 曹允馨, 徐伟, 常智慧. 干旱胁迫下污泥对草地早熟禾生长及激素代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 167-176. |
| [11] | 周晶, 陈思齐, 史文娇, 阳伏林, 林辉, 林占熺. 巨菌草幼叶及根转录组功能基因测序及分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 143-155. |
| [12] | 舒新月, 江波, 马丽, 郑爱萍. 不同侵染时间点稻粒黑粉病菌的转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 190-202. |
| [13] | 刘燕, 于美玲, 张然, 牛奎举, 李玉珠, 张金青, 马晖玲. 甘肃野生草地早熟禾内源激素含量的变化与无融合生殖率的关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 99-111. |
| [14] | 王贞升, 李彦雪, 于成龙, 狄小琳, 陈鹏, 田静瑶, 王竞红. 不同模拟降水量下草地早熟禾根系形态与解剖结构的动态变化[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 70-80. |
| [15] | 宫文龙, 王赞, 赵桂琴, 马琳, 韦宝, 龚攀, 刘希强. 沙打旺EST-SSR分子标记开发及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 147-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||