

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 15-27.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021231
杨志新1,3( ), 郑旭1,3, 陈来宝1,3, 于泳鑫1,3, 张凤华1,2, 李鲁华1,2, 王家平1,2,3(
), 郑旭1,3, 陈来宝1,3, 于泳鑫1,3, 张凤华1,2, 李鲁华1,2, 王家平1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2021-06-09
修回日期:2021-10-11
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
王家平
作者简介:E-mail: 2006wjp@163.com基金资助:
Zhi-xin YANG1,3( ), Xu ZHENG1,3, Lai-bao CHEN1,3, Yong-xin YU1,3, Feng-hua ZHANG1,2, Lu-hua LI1,2, Jia-ping WANG1,2,3(
), Xu ZHENG1,3, Lai-bao CHEN1,3, Yong-xin YU1,3, Feng-hua ZHANG1,2, Lu-hua LI1,2, Jia-ping WANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2021-06-09
Revised:2021-10-11
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
Jia-ping WANG
摘要:
为明确食叶草根系应对盐碱胁迫表现的形态适应策略,采用剖面法对新疆石河子垦区盐碱地食叶草进行根系剖面采集,分析不同时期食叶草根系形态特征及空间分布规律,探究食叶草根系形态分布及对盐碱环境的适应策略。结果表明:食叶草根系显著降低了根系周围土壤电导率,与根长、根生物量增加显著正相关。随着土壤深度增加,根长、根生物量、根体积等指标呈现下降趋势,7-10月,0~20 cm土层根系生长最快,根体积增加了71.26%。水平距离上,25~35 cm内根系较5~25 cm生长缓慢,密集程度低,从而规避高盐区域并提高营养吸收能力。细根(d≤2 mm)是食叶草根长增加的主要体现,占总根长90%以上。食叶草根系在盐碱地中形成了抵抗胁迫并增强自身抗逆性的形态适应策略,主要表现为根系快速向深层拓展,距植株水平距离0~15 cm内侧根密集且快速增加。研究结果为干旱区盐碱地治理过程耐盐植物管理与配置提供依据。
杨志新, 郑旭, 陈来宝, 于泳鑫, 张凤华, 李鲁华, 王家平. 干旱区盐碱地食叶草根系形态分布适应策略研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 15-27.
Zhi-xin YANG, Xu ZHENG, Lai-bao CHEN, Yong-xin YU, Feng-hua ZHANG, Lu-hua LI, Jia-ping WANG. Morphological adaptation strategies of Rumex hanus planted in saline-alkali land of arid areas[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 15-27.
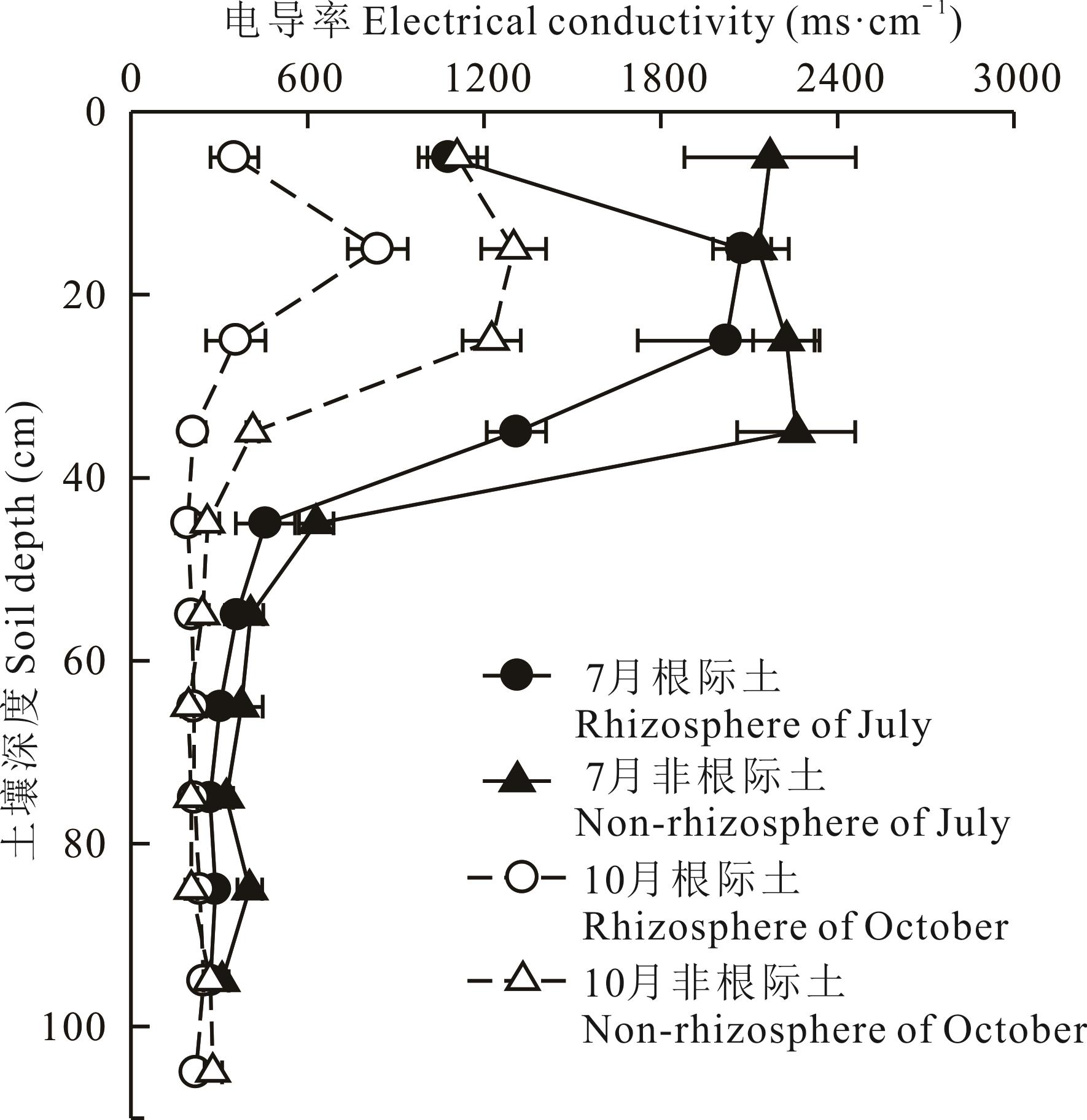
图2 不同时期食叶草根系土壤电导率剖面分布特征7,10月根系最深分别生长至地下80、110 cm处。The root grows deepest to 80 and 110 cm from the ground in July and October, respectively.
Fig.2 Profile distribution of soil electrical conductivity in the root system of R. hanus in different months
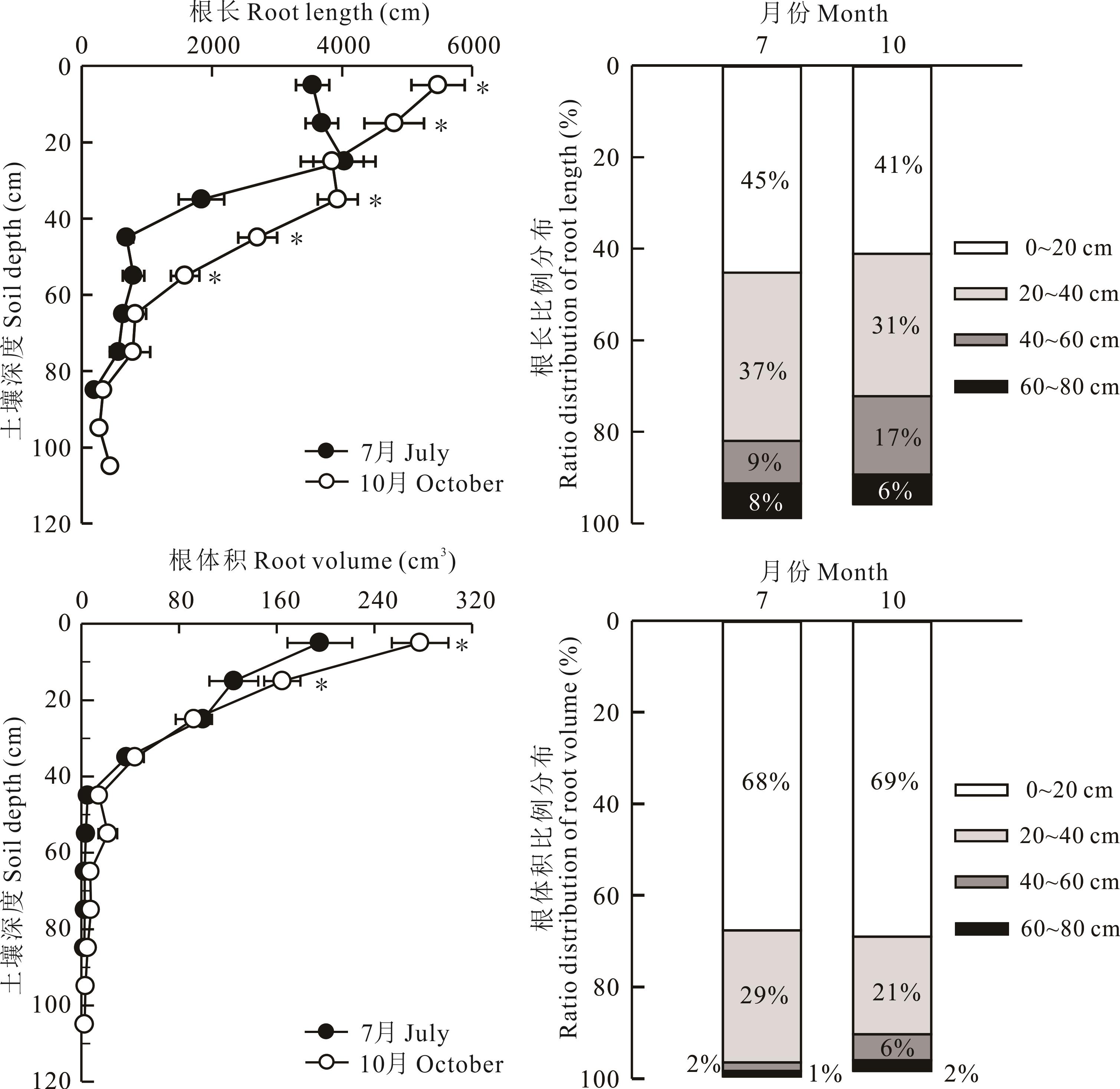
图3 不同深度土壤食叶草根长和根体积变化特征* 表示在0.05水平显著相关。下同。* means the correlation was significant at 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.3 Root length and volume characteristics of R. hanus in different soil depths

图4 食叶草不同深度细根长度变化特征* 表示在0.05水平显著相关。下同。* means the correlation was significant at 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig. 4 Variations of fine root length for R. hanus at different soil depths
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 7月July | 10月October | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
细根长度比例 Fine root length ratio | 细根生物量比例 Fine root biomass ratio | 细根长度比例 Fine root length ratio | 细根生物量比例 Fine root biomass ratio | |
| 0~10 | 94.90±3.01a | 1.30±0.12f | 97.36±2.81a | 1.35±0.18g |
| 10~20 | 95.09±2.38a | 3.96±0.79e | 97.91±1.38a | 2.01±0.95f |
| 20~30 | 95.24±4.21a | 6.64±1.24d | 88.78±8.73b | 4.16±0.49e |
| 30~40 | 95.48±1.13a | 15.70±3.56c | 88.64±0.92b | 5.22±1.09e |
| 40~50 | 91.54±5.30a | 54.84±19.11ab | 87.52±8.03b | 53.47±13.86c |
| 50~60 | 93.46±1.78a | 70.58±15.54a | 88.08±5.41b | 33.63±10.12d |
| 60~70 | 95.27±2.76a | 84.31±17.17a | 84.51±7.23b | 29.26±5.45d |
| 70~80 | 98.95±0.21a | 81.06±12.81a | 83.62±7.17b | 40.74±13.09cd |
| 80~90 | 97.25±1.14a | 77.78±18.49a | 85.82±8.23b | 45.41±6.49c |
| 90~100 | - | 100.00±0.00a | 94.21±5.02a | 63.30±4.90b |
| 100~110 | - | - | 97.24±2.59a | 86.61±9.21a |
表1 不同深度土壤内食叶草细根长度和生物量比例
Table 1 The length and biomass ratio of fine roots of R. hanus in different soil depths (%)
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 7月July | 10月October | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
细根长度比例 Fine root length ratio | 细根生物量比例 Fine root biomass ratio | 细根长度比例 Fine root length ratio | 细根生物量比例 Fine root biomass ratio | |
| 0~10 | 94.90±3.01a | 1.30±0.12f | 97.36±2.81a | 1.35±0.18g |
| 10~20 | 95.09±2.38a | 3.96±0.79e | 97.91±1.38a | 2.01±0.95f |
| 20~30 | 95.24±4.21a | 6.64±1.24d | 88.78±8.73b | 4.16±0.49e |
| 30~40 | 95.48±1.13a | 15.70±3.56c | 88.64±0.92b | 5.22±1.09e |
| 40~50 | 91.54±5.30a | 54.84±19.11ab | 87.52±8.03b | 53.47±13.86c |
| 50~60 | 93.46±1.78a | 70.58±15.54a | 88.08±5.41b | 33.63±10.12d |
| 60~70 | 95.27±2.76a | 84.31±17.17a | 84.51±7.23b | 29.26±5.45d |
| 70~80 | 98.95±0.21a | 81.06±12.81a | 83.62±7.17b | 40.74±13.09cd |
| 80~90 | 97.25±1.14a | 77.78±18.49a | 85.82±8.23b | 45.41±6.49c |
| 90~100 | - | 100.00±0.00a | 94.21±5.02a | 63.30±4.90b |
| 100~110 | - | - | 97.24±2.59a | 86.61±9.21a |
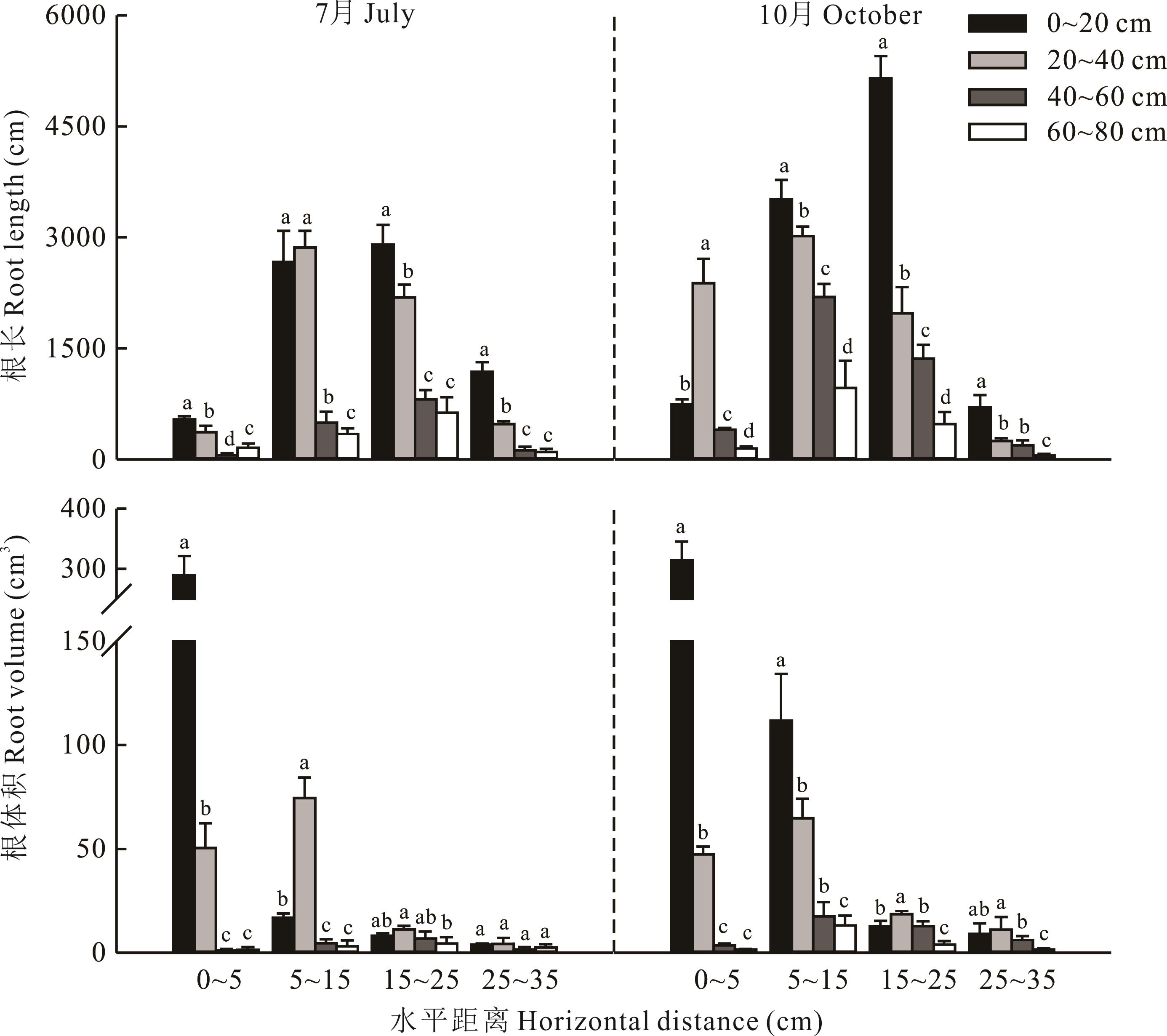
图5 不同水平距离食叶草根长和根体积变化特征不同小写字母表示水平距离内不同深度根长、根体积差异显著(P<0.05 )。Different lowercase letters mean significant differences of root length and volume among soil depths within the same horizontal distance (P<0.05 ).
Fig. 5 Root length and volume characteristics of R. hanus at different horizontal distances from plants
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 月份 Month | 细根长度比例 Fine root length ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 cm | 5~15 cm | 15~25 cm | 25~35 cm | ||
| 0~20 | 7 | 4.31±0.41b | 37.27±2.72a | 42.15±2.14b | 17.79±1.15a |
| 10 | 6.57±0.86a | 35.17±6.93a | 53.81±3.22a | 7.41±0.83b | |
| 20~40 | 7 | 6.47±2.05b | 45.81±5.04a | 39.51±4.91a | 10.63±1.74a |
| 10 | 31.33±7.17a | 36.62±10.66a | 29.21±4.36b | 4.69±0.61b | |
| 40~60 | 7 | 4.09±0.23a | 33.71±4.14b | 55.63±4.06a | 9.02±1.22a |
| 10 | 4.27±0.71a | 52.27±8.52a | 38.27±1.61b | 5.18±1.14b | |
| 60~80 | 7 | 13.69±2.36a | 28.09±5.09b | 51.94±4.97a | 8.08±0.73a |
| 10 | 10.15±2.12a | 58.84±7.24a | 29.17±2.19b | 3.94±0.55b | |
表2 距植株水平距离0~35 cm内食叶草细根长度比例
Table 2 Ratio of the fine roots length of R. hanus within 0-35 cm from the horizontal distance of the plant
土壤深度 Soil depth (cm) | 月份 Month | 细根长度比例 Fine root length ratio (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 cm | 5~15 cm | 15~25 cm | 25~35 cm | ||
| 0~20 | 7 | 4.31±0.41b | 37.27±2.72a | 42.15±2.14b | 17.79±1.15a |
| 10 | 6.57±0.86a | 35.17±6.93a | 53.81±3.22a | 7.41±0.83b | |
| 20~40 | 7 | 6.47±2.05b | 45.81±5.04a | 39.51±4.91a | 10.63±1.74a |
| 10 | 31.33±7.17a | 36.62±10.66a | 29.21±4.36b | 4.69±0.61b | |
| 40~60 | 7 | 4.09±0.23a | 33.71±4.14b | 55.63±4.06a | 9.02±1.22a |
| 10 | 4.27±0.71a | 52.27±8.52a | 38.27±1.61b | 5.18±1.14b | |
| 60~80 | 7 | 13.69±2.36a | 28.09±5.09b | 51.94±4.97a | 8.08±0.73a |
| 10 | 10.15±2.12a | 58.84±7.24a | 29.17±2.19b | 3.94±0.55b | |
指标 Index | 根长增加量 Root length increment | 根体积增加量 Root volume increment | 根生物量增加量 Root biomass increment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 电导率减少量Electrical conductivity decrement | 0.76** | 0.33 | 0.67* |
| 根长增加量Root length increment | 0.40 | 0.62 | |
| 根体积增加量Root volume increment | 0.82** |
表3 土壤电导率与食叶草根系指标相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of root indicators of R. hanus and soil electrical conductivity
指标 Index | 根长增加量 Root length increment | 根体积增加量 Root volume increment | 根生物量增加量 Root biomass increment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 电导率减少量Electrical conductivity decrement | 0.76** | 0.33 | 0.67* |
| 根长增加量Root length increment | 0.40 | 0.62 | |
| 根体积增加量Root volume increment | 0.82** |
| 1 | Li W H, Wang Z H, Zheng X R, et al. Effects of local dynamic change of groundwater on soil salinity in wasteland under drip irrigation in saline or alkaline land of oasis in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Research, 2016, 33(5): 1110-1118. |
| 李文昊, 王振华, 郑旭荣, 等. 新疆绿洲盐碱地滴灌条件下地下水局部动态对荒地盐分的影响. 干旱区研究, 2016, 33(5): 1110-1118. | |
| 2 | Liu X J. Reclamation and utilization of saline soils in water-scarce regions of Bohai Sea. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(10): 1521-1527. |
| 刘小京. 环渤海缺水区盐碱地改良利用技术研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(10): 1521-1527. | |
| 3 | Pang H C, Li Y Y. Saline-alkali soils amelioration and utilization in northwest yellow river irrigation districts. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. |
| 逄煥成, 李玉义. 西北沿黄灌区盐碱地改良与利用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. | |
| 4 | Guo Y, Chen B L, Sheng J D, et al. Salt absorption capacities of several annul halophytes. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(1): 269-276. |
| 郭洋, 陈波浪, 盛建东, 等. 几种一年生盐生植物的吸盐能力. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(1): 269-276. | |
| 5 | Tian C Y, Mai W X, Zhao Z Y. Study on key technologies of ecological management of saline alkali land in arid area of Xinjiang. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(22): 7064-7068. |
| 田长彦, 买文选, 赵振勇. 新疆干旱区盐碱地生态治理关键技术研究. 生态学报, 2016, 36(22): 7064-7068. | |
| 6 | Cui Z Z. Study on improveing technology of saline-alkali land with greening in Luyang Lake, Weinan. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2015. |
| 崔志忠. 渭南市卤阳湖盐碱地绿化改良技术研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. | |
| 7 | Jian S Q, Zhao C Y, Peng H H, et al. Root influence on soil macropores by dye tracing and image processing technology. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2011, 47(5): 62-66. |
| 荐圣淇, 赵传燕, 彭焕华, 等. 利用染色示踪与图像处理术研究根系对土壤大孔隙的影响. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 47(5): 62-66. | |
| 8 | Zhang J M, Xu Z M. Dye tracer infiltration technique to investigate macropore flow paths in Maka Mountain, Yunnan Province, China. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(8): 2101-2109. |
| 9 | Yang F, Cheng J H, Zhang H J, et al. Effect of herb plants on soil detachment and erosion dynamics. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(5): 129-137. |
| 杨帆, 程金花, 张洪江, 等. 坡面草本植物对土壤分离及侵蚀动力的影响研究. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(5): 129-137. | |
| 10 | Xiao L, Yao K, Li P, et al. Increased soil aggregate stability is strongly correlated with root and soil properties along a gradient of secondary succession on the Loess Plateau. Ecological Engineering, 2020(1), DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105671. |
| 11 | Wang H, Liu N, Liu J L, et al. Relationship between morphological characteristics of Tamarix chinensis and soil nutrient content in saline-alkali soil of north Shanxi Province. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2020, 40(1): 37-48. |
| 王慧, 刘宁, 刘金龙, 等. 晋北干旱区盐碱地柽柳形态特征及其与土壤养分的关系. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2020, 40(1): 37-48. | |
| 12 | Piechulla B, Lemfack M C, Kai M. Effects of discrete bioactive microbial volatiles on plants and fungi. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2017, 40(10): 2042-2067. |
| 13 | Yan Q Q, Zhang J S, Li X X, et al. Effects of salinity stress on seed germination and root growth of seedlings in island cotton. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 100-110. |
| 严青青, 张巨松, 李星星, 等. 盐碱胁迫对海岛棉种子萌发及幼苗根系生长的影响. 作物学报, 2019, 45(1): 100-110. | |
| 14 | Guo Y D, Cheng M, Zhao X F, et al. Effects of green manure rotation on soil properties and yield and quality of silage maize in saline-alkali soils. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(6): 856-864. |
| 郭耀东, 程曼, 赵秀峰, 等. 轮作绿肥对盐碱地土壤性质、后作青贮玉米产量及品质的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(6): 856-864. | |
| 15 | Yu P J, Liu S W, Yang H T, et al. Short-term land use conversions influence the profile distribution of soil salinity and sodicity in northeastern China. Ecological Indicators, 2018, 88: 79-87. |
| 16 | Sun J, Xia J B, Su L, et al. Soil amelioration of different vegetation types in saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(4): 1323-1332. |
| 孙佳, 夏江宝, 苏丽, 等. 黄河三角洲盐碱地不同植被模式的土壤改良效应. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4): 1323-1332. | |
| 17 | Zheng X, Li B, Zhang W Y, et al. Effects of cultivation patterns on the root growth and foliage yield of Rumex hanus by. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(2): 470-478. |
| 郑旭, 李斌, 张万银, 等. 垄上栽培对盐碱地食叶草根系生长和产量的影响. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(2): 470-478. | |
| 18 | Farooq M, Hussain M, Wakeel A, et al. Salt stress in maize: effects, resistance mechanisms, and management. A review. Agmnomy for Sustainable Development, 2015, 35(2): 461-481. |
| 19 | Zhang K, Tian C Y, Li C J, et al. Review of progress of study on salt-tolerance mechanisms of annual halophytes. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2009, 33(6): 1220-1231. |
| 张科, 田长彦, 李春俭. 一年生盐生植物耐盐机制研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2009, 33(6): 1220-1231. | |
| 20 | Blonder B, Violle C, Enquist B J. Assessing the causes and scales of the leaf economics spectrum using venation networks in Populus tremuloides. Journal of Ecology, 2013, 101(4): 981-989. |
| 21 | Wang J W, Zhao C Z, Zhao L C, et al. Response of root morphology and biomass of Phragmites australis to soil salinity in inland salt marsh. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4843-4851. |
| 王继伟, 赵成章, 赵连春, 等. 内陆盐沼芦苇根系形态及生物量分配对土壤盐分因子的响应. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4843-4851. | |
| 22 | Keller C, Hammer D, Kayser A, et al. Root development and heavy metal phytoextraction efficiency: Comparison of different plant species in the field. Plant and Soil, 2003, 249(1): 67-81. |
| 23 | Day S D, Eric Wiseman P, Dickinson S B, et al. Tree root ecology in the urban environment and implications for a sustainable rhizosphere. Journal of Arboriculture, 2010, 36(5): 193. |
| 24 | Jing Y P, Lian H F, Li Y J, et al. Analysis on the difference of soil salinization characteristics in hetao saline-alkali soil with different land use. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(4): 354-363. |
| 景宇鹏, 连海飞, 李跃进, 等. 河套盐碱地不同利用方式土壤盐碱化特征差异分析. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(4): 354-363. | |
| 25 | Xi J B, Zhang F S, Chen Y, et al. A preliminary study on salt contents of soil in root-canopy area of halophytes. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004(1): 53-58. |
| 郗金标, 张福锁, 陈阳, 等. 盐生植物根冠区土壤盐分变化的初步研究. 应用生态学报, 2004(1): 53-58. | |
| 26 | Yin C H, Dong J Z, Shi Q M, et al. Salt island effect of halophytic shrubs in different habitats and its ecological implication. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2012, 49(2): 289-295. |
| 尹传华, 董积忠, 石秋梅, 等. 不同生境下盐生灌木盐岛效应的变化及生态学意义. 土壤学报, 2012, 49(2): 289-295. | |
| 27 | Li C J, Lei J Q, Xu X W, et al. The effects of stemflow on the formation of “Fertile Island” and “Salt Island” for Haloxylon ammodendron Bge. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(15): 4819-4826. |
| 李从娟, 雷加强, 徐新文, 等. 树干径流对梭梭“肥岛”和“盐岛”效应的作用机制. 生态学报, 2012, 32(15): 4819-4826. | |
| 28 | Wang Y, Meng Y L, Chen B L, et al. Studies on the soil microorganism quality and soil nutrient content at the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere region of cotton in wheat-cotton intercropping system. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006(10): 3485-3490. |
| 王瑛, 孟亚利, 陈兵林, 等. 麦棉套作棉花根际非根际土壤微生物和土壤养分. 生态学报, 2006(10): 3485-3490. | |
| 29 | Breckle S W. How do halophytes overcome salinity. Biology of Salt Tolerant Plants, 1995, 23: 199-203. |
| 30 | Wu X X, Bai T H, Zhang L, et al. Research progress on mechanisms underlying salt secretion in recretohalophytes. Plant Physiology Journal, 2020, 56(12): 2526-2532. |
| 吴欣欣, 白天惠, 张乐, 等. 泌盐盐生植物的泌盐机理研究进展. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12): 2526-2532. | |
| 31 | Morel J L, Habib L, Plantureux S, et al. Influence of maize root mucilage on soil aggregate stability. Plant and Soil, 1991, 136(1): 111-119. |
| 32 | Li F, Xie Y H, Qin Y Y. Adaptive strategies of wetland plants in salt stress environment. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2009, 28(2): 314-321. |
| 李峰, 谢永宏, 覃盈盈. 盐胁迫条件下湿地植物的适应策略. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 314-321. | |
| 33 | Yi L P, Wang Z W. Root system characters in growth and distribution among three littoral halophytes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(5): 1195-1202. |
| 弋良朋, 王祖伟. 盐胁迫下3种滨海盐生植物的根系生长和分布. 生态学报, 2011, 31(5): 1195-1202. | |
| 34 | Zhang W Y. Study on the root distribution characteristics of Rumex dapibus herba by.in saline-alkali soil in Shihezi reclamation area. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2020. |
| 张万银. 石河子垦区盐碱地食叶草根系分布特征研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2020. | |
| 35 | Wang S F, Hu Y X, Sun H J, et al. Effects of salt stress on growth and root development of two oak seedlings. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(4): 1021-1029. |
| 王树凤, 胡韵雪, 孙海菁, 等. 盐胁迫对2种栎树苗期生长和根系生长发育的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(4): 1021-1029. | |
| 36 | Zhang X D, Wang Z W, Han Q F, et al. Effects of water stress on the root structure and physiological characteristics of early-stage maize. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(10): 2969-2977. |
| 张旭东, 王智威, 韩清芳, 等. 玉米早期根系构型及其生理特性对土壤水分的响应. 生态学报, 2016, 36(10): 2969-2977. | |
| 37 | Yao J, Shi W M. Effect of salt stress on structure and growth of tomato seedling roots. Soils, 2008(2): 279-282. |
| 姚静, 施卫明. 盐胁迫对番茄根形态和幼苗生长的影响. 土壤, 2008(2): 279-282. | |
| 38 | Bolu W H, Polle A. Growth and stress reactions in roots and shoots of a salt-sensitive poplar species (Populus×canescens). Tropical Ecology, 2004, 45(1): 161-172. |
| 39 | Du Z Y, Liu F C, Ma B Y, et al. Root distribution and fine root growth in mixed plantation of Robinia pseudoacacia and Fraxinus velutina in coastal saline-alkali area. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2014, 50(3): 10-15. |
| 杜振宇, 刘方春, 马丙尧, 等. 滨海盐碱地人工刺槐绒毛白蜡混交林的根系分布与细根生长. 林业科学, 2014, 50(3): 10-15. | |
| 40 | Liu M X, Yang J S, Li X M, et al. Effects of drip irrigation strategy on cotton root distribution and water use efficiency. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(S1): 98-105. |
| 刘梅先, 杨劲松, 李晓明, 等. 滴灌模式对棉花根系分布和水分利用效率的影响. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(S1): 98-105. | |
| 41 | Bu H Y, Song W Z, Cao C G, et al. Root growth responses to soil water deficit for a water-saving and drought-resistant rice genotype Hanyou113. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(22): 4277-4289. |
| 补红英, 宋维周, 曹凑贵, 等. 节水抗旱稻旱优113号的根系生长对土壤水分亏缺的响应. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(22): 4277-4289. | |
| 42 | Guo C, Niu W Q. Effects of rhizosphere ventilation on growth and root activity of potted maize. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(6): 1194-1198. |
| 郭超, 牛文全. 根际通气对盆栽玉米生长与根系活力的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(6): 1194-1198. | |
| 43 | Qi L, Bai X F, Niu W H, et al. Effect of rhizosphere ventilation on growth of cotton seedlings under salt stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 16-23. |
| 祁琳, 柏新富, 牛玮浩, 等. 根际通气状况对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗生长的影响. 植物学报, 2016, 51(1): 16-23. | |
| 44 | Jackson R B, Mooney H A, Schulze E D. A global budget for fine root biomass, surface area, and nutrient contents. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1997, 94(14): 7362-7366. |
| 45 | Deng Q, Li T, Yuan Z Y, et al. Fine root biomass and production of four vegetation types in Loess Plateau, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(11): 3091-3098. |
| 邓强, 李婷, 袁志友, 等. 黄土高原4种植被类型的细根生物量和年生产量. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(11): 3091-3098. | |
| 46 | Schleiff U. Conceptual approach to lateral salinity gradients around roots of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant crops under irrigation conditions. Ecological Questions, 2011, 14: 35-38. |
| 47 | Song X J, Li S N, Guo J, et al. Effects of different salinity levels on the growth and physiological characteristics of roots of Tamarix chinensis cuttings. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(2): 606-614. |
| 宋香静, 李胜男, 郭嘉, 等. 不同盐分水平对柽柳扦插苗根系生长及生理特性的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(2): 606-614. | |
| 48 | Wang Q H, Han W, Hou Y Y, et al. Responses of main characters of root system to salt stress among cotton varieties with different salt tolerance. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2018, 29(3): 865-873. |
| 王庆惠, 韩伟, 侯银莹, 等. 不同耐盐品种棉花根系主要指标对盐分胁迫的响应. 应用生态学报, 2018, 29(3): 865-873. |
| [1] | 李宏伟, 郑琪, 李滨, 赵茂林, 李振声. 一种耐盐碱牧草——长穗偃麦草研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 190-199. |
| [2] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 贾瑜琀. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. |
| [3] | 孙小富, 黄莉娟, 王普昶, 赵丽丽, 刘芳. 不同供磷水平对宽叶雀稗形态及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 58-69. |
| [4] | 卿悦, 李廷轩, 叶代桦. 无机氮处理对矿山生态型水蓼氮积累及根系形态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 203-210. |
| [5] | 郭雄飞. 生物炭和AM真菌对重金属污染下土壤养分及望江南生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(11): 150-161. |
| [6] | 朱亚琼, 郑伟, 王祥, 关正翾. 混播方式对豆禾混播草地植物根系构型特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 73-85. |
| [7] | 罗永清, 赵学勇, 王涛, 李玉强. 沙地植物根系特征及其与土壤有机碳和总氮的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 200-206. |
| [8] | 高嵩涓, 曹卫东. 利用根管法对油菜和冬小麦苗期根系形态的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 134-142. |
| [9] | 李帅, 赵国靖, 徐伟洲, 高志娟, 吴爱姣, 徐炳成. 白羊草根系形态特征对土壤水分阶段变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 169-177. |
| [10] | 李希铭, 宋桂龙. 镉胁迫对紫花苜蓿镉吸收特征及根系形态影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. |
| [11] | 段桂芳, 单立山, 李毅, 张正中, 张荣, 种培芳. 红砂幼苗根系形态特征对降水格局变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 95-103. |
| [12] | 刘晚苟,李良贤,谢海容,何泳怡,刘金祥. 土壤容重对野生香根草幼苗根系形态及其生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(4): 214-220. |
| [13] | 陈伟,张苗苗,宋阳阳,陈建纲,张德罡. 重金属离子对2种草坪草荧光特性及根系形态的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 333-342. |
| [14] | 王升,王全九,周蓓蓓,吴军虎,史文娟,罗小东. 膜下滴灌棉田间作盐生植物改良盐碱地效果[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3): 362-367. |
| [15] | 李美,高兴祥,刘士国,白兴勇,高宗军,房锋,孙作文,张柏松. 山东盐碱地棉田不同杂草群落对棉花产量影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 328-334. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||