

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 107-117.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022104
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-03-02
修回日期:2022-05-18
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
李淑霞
作者简介:E-mail: lishuxia620@163.com基金资助:
Yuan WANG( ), Jing WANG, Shu-xia LI(
), Jing WANG, Shu-xia LI( )
)
Received:2022-03-02
Revised:2022-05-18
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2022-12-30
Contact:
Shu-xia LI
摘要:
盐胁迫是影响植物生长发育的主要非生物胁迫因子之一,BBX家族转录因子在植物色素积累、光形态发生、种子生长发育以及逆境适应等方面具有重要的调节作用。为明确紫花苜蓿BBX基因的功能,本研究使用Primer Premier 5软件根据NCBI数据库MsBBX24基因的序列设计特异性引物,以紫花苜蓿的cDNA为模板克隆MsBBX24基因。利用生物信息学软件对基因序列和结构进行分析,并与其他植物的BBX24进行比对和进化树构建,分析它们之间的进化关系。采用实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)分析MsBBX24基因的表达模式。利用DNA的酶切与连接方法构建MsBBX24过表达载体,采用农杆菌介导法将其转入野生型拟南芥,通过除草剂Basta筛选,以半定量RT-PCR鉴定获得阳性转基因植株。通过对野生型和MsBBX24转基因拟南芥植株的表型观察和生理指标测定分析它们的耐盐性。研究结果表明,MsBBX24基因编码区序列长723 bp,编码240个氨基酸,分子量为30.58 kDa,等电点为7.74,MsBBX24与鹰嘴豆和蒺藜苜蓿的BBX24具有较高的同源性。qRT-PCR检测结果表明,MsBBX24基因的表达量受盐胁迫(150 mmol·L-1 NaCl)诱导。在拟南芥中过表达MsBBX24基因分析表明,在NaCl胁迫下,MsBBX24基因的过表达能够促进幼苗根和侧根的生长,提高子叶绿化率,同时显著降低了转基因植株的相对电导率(IL)、丙二醛(MDA)和过氧化氢(H2O2)含量,提高了叶绿素(Chl)和脯氨酸(Pro)含量、过氧化氢酶(POD)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性。MsBBX24基因响应盐胁迫,主要通过提高抗氧化防御系统清除活性氧以增强转基因植株的耐盐性,MsBBX24基因可为紫花苜蓿耐盐分子育种提供重要的候选基因。
王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117.
Yuan WANG, Jing WANG, Shu-xia LI. Cloning of MsBBX24 from alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and determination of its role in salt tolerance[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 107-117.
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 用途 Application |
|---|---|---|
| MsBBX24-F | ATGAAAATACAGTGTGATGT | 基因克隆 Gene cloning |
| MsBBX24-R | TTAGCCGAAATCTGGCACCA | 基因克隆 Gene cloning |
| cMsBBX24-F | TCGAGCTCAAGCTTCGAATTCATGAAAATACAGTGTGATGTGTG | 载体构建 Vector construction |
| cMsBBX24-R | GTACCGTCGACTGCAGAATTCGCCGAAATCTGGCACC | 载体构建 Vector construction |
| qMsBBX24-F | GCATCCTCTTGGGCTGTTGA | 荧光定量Real-time quatitative PCR (qRT-PCR) |
| qMsBBX24-R | TCTGGCACCATGAAGTGCTC | 荧光定量Real-time quatitative PCR (qRT-PCR) |
| MsActin-F | TTTGAGACTTTCAATGTGCCCGCC | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| MsActin-R | TAGCATGTGGGAGTGCATAACCCT | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| AtActin-F | GCCATCCAAGCTGTTCTCTC | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| AtActin-R | GCTCGTAGTCAACAGCAACAA | 内参基因 Reference gene |
表1 本试验所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in this experiment
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5′-3′) | 用途 Application |
|---|---|---|
| MsBBX24-F | ATGAAAATACAGTGTGATGT | 基因克隆 Gene cloning |
| MsBBX24-R | TTAGCCGAAATCTGGCACCA | 基因克隆 Gene cloning |
| cMsBBX24-F | TCGAGCTCAAGCTTCGAATTCATGAAAATACAGTGTGATGTGTG | 载体构建 Vector construction |
| cMsBBX24-R | GTACCGTCGACTGCAGAATTCGCCGAAATCTGGCACC | 载体构建 Vector construction |
| qMsBBX24-F | GCATCCTCTTGGGCTGTTGA | 荧光定量Real-time quatitative PCR (qRT-PCR) |
| qMsBBX24-R | TCTGGCACCATGAAGTGCTC | 荧光定量Real-time quatitative PCR (qRT-PCR) |
| MsActin-F | TTTGAGACTTTCAATGTGCCCGCC | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| MsActin-R | TAGCATGTGGGAGTGCATAACCCT | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| AtActin-F | GCCATCCAAGCTGTTCTCTC | 内参基因 Reference gene |
| AtActin-R | GCTCGTAGTCAACAGCAACAA | 内参基因 Reference gene |

图1 MsBBX24基因的核苷酸序列及其编码的氨基酸序列ATG:起始密码子;*:终止密码子;横线标记:保守区域。ATG: Initiation codon; *: Temination codon; Horizontal line mark: Conserved domains.
Fig.1 Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences of MsBBX24 gene

图2 MsBBX24蛋白生物信息学分析A:MsBBX24蛋白质亲水性分析;B:MsBBX24蛋白跨膜结构域预测;C:MsBBX24蛋白二级结构预测(图中线条由高到低依次表示:α-螺旋、延伸链、β-转角、不规则卷曲)。A: Hydrophilicity analysis of MsBBX24 protein; B: Transmembrane structure prediction of MsBBX24 protein; C: Secondary structure prediction of MsBBX24 protein (The lines in the figure were alpha helix, extended strand, beta turn and random coil in descending order).
Fig.2 Bioinformatics analysis of MsBBX24 protein
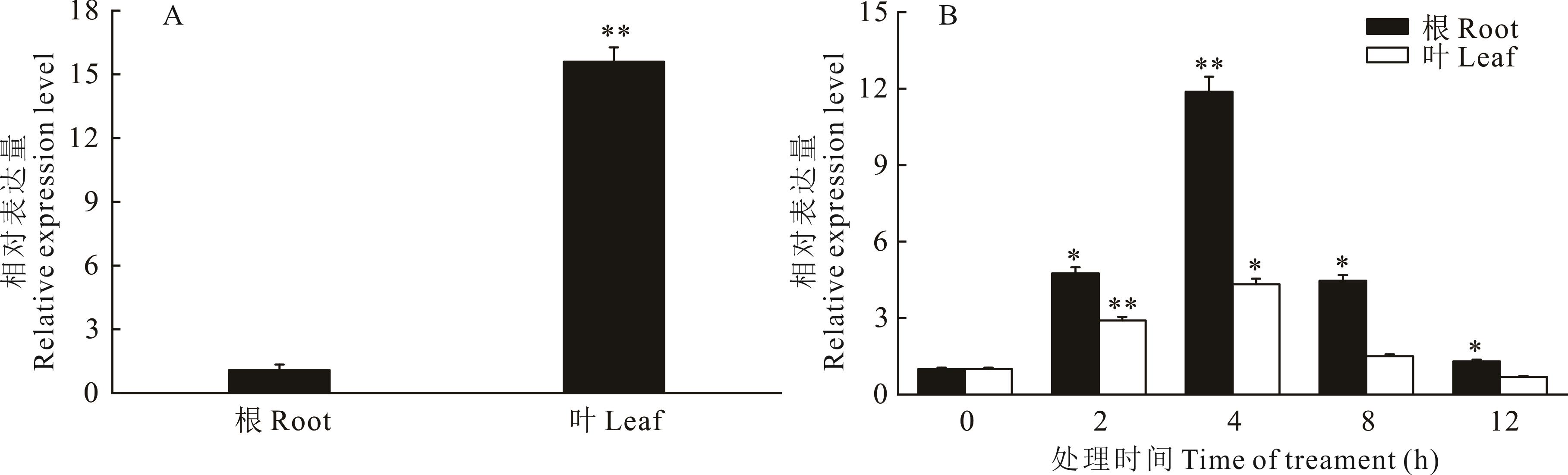
图5 MsBBX24基因的表达量分析A:组织特异性表达,**表示根和叶表达量差异极显著(P<0.01);B:150 mmol·L-1 NaCl处理下根和叶的表达量,*和**分别表示同一组织中不同处理时间的表达量与0 h相比差异显著(P<0.05)和差异极显著(P<0.01)。A: Tissue-specific expression, ** indicated that significant differences in root and leaf expression (P<0.01); B: Relative expression level of roots and leaves under 150 mmol·L-1 NaCl treatment;* and ** respectively indicated the difference between different time in same organization and 0 h is significant (P<0.05) and extremely significant (P<0.01).
Fig.5 Analysis of MsBBX24 gene relative expression level
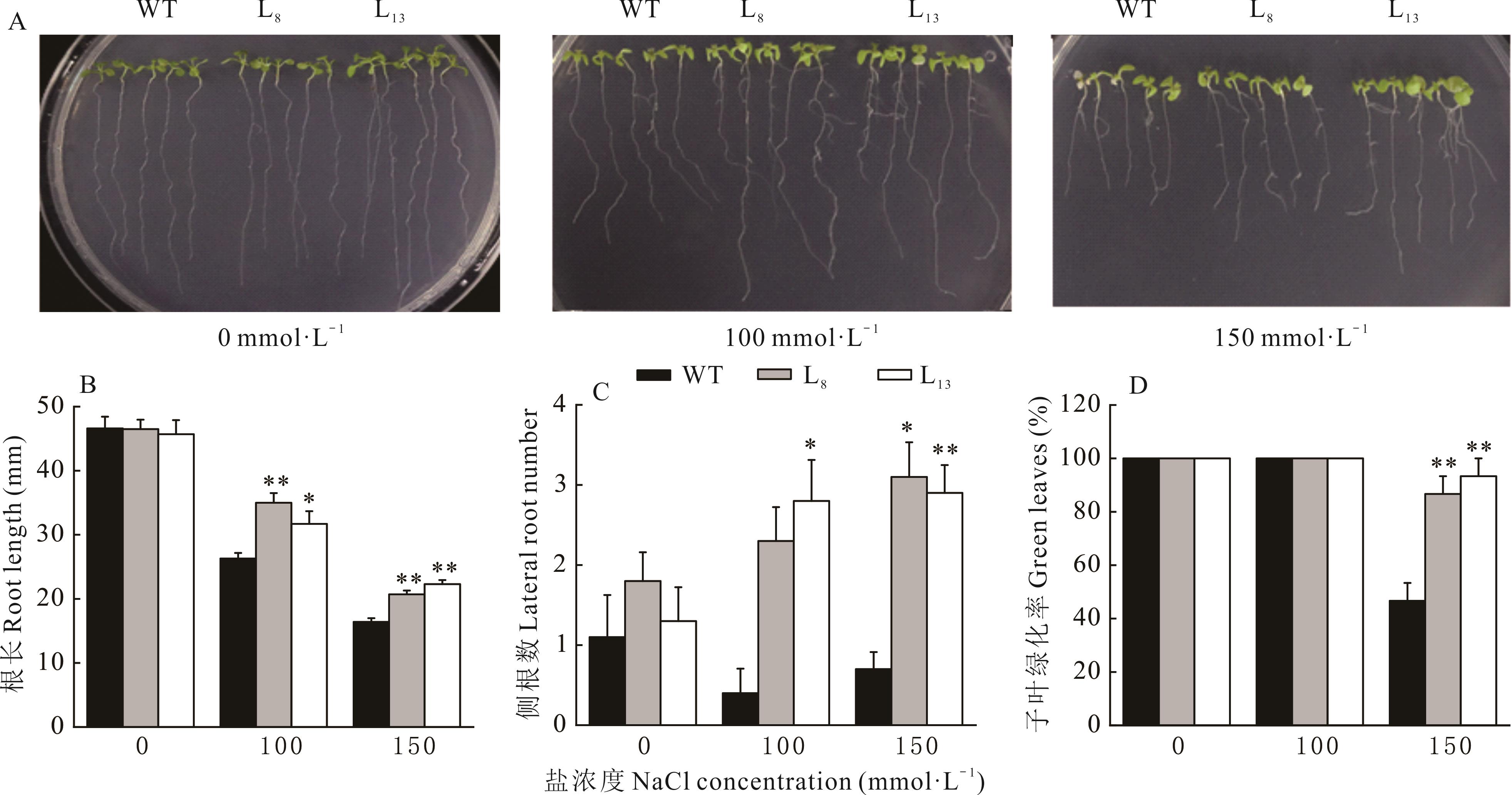
图7 WT和转MsBBX24基因拟南芥的幼苗耐盐性分析*和**分别表示转基因拟南芥植株与野生型相比差异显著(P<0.05)和差异极显著(P<0.01),下同。* and ** respectively indicated the transgenic Arabidopsis plants showed significant difference (P<0.05) and extremely significant difference (P<0.01) compared with wild type, the same below.
Fig.7 Salt tolerance analysis of WT and MsBBX24 transgenic Arabidopsis seedlings
| 1 | Wu X M, Guo P, Chi H W, et al. Diversity analysis of phenotypic traits and quality characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) introducted from abroad germplasm resources. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2018, 19(1): 103-111. |
| 吴欣明, 郭璞, 池惠武, 等. 国外紫花苜蓿种质资源表型性状与品质多样性分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(1): 103-111. | |
| 2 | Cui M M, Ma L, Zhang J J, et al. Gene expression and salt-tolerance analysis of MsDWF4 gene from alfalfa. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(18): 3650-3664. |
| 崔苗苗, 马琳, 张锦锦, 等. 紫花苜蓿MsDWF4的表达特性及耐盐性效应. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(18): 3650-3664. | |
| 3 | Khanna R, Kronmiller B, Maszle D R, et al. The Arabidopsis B-box zinc finger family. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(11): 3416-3420. |
| 4 | Xiong C, Luo D, Lin A, et al. A tomato B-box protein SlBBX20 modulates carotenoid biosynthesis by directly activating PHYTOENE SYNTHASE 1, and is targeted for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation. New Phytologist, 2019, 221(1): 279-294. |
| 5 | Xu D, Jiang Y, Li J, et al. BBX21, an Arabidopsis B-box protein, directly activates HY5 and is targeted by COP1 for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(27): 7655-7660. |
| 6 | Gangappa S N, Botto J F. The BBX family of plant transcription factors. Trends in Plant Science, 2014, 19(7): 460-470. |
| 7 | Song Z, Bian Y, Liu J, et al. B-box proteins: Pivotal players in light-mediated development in plants. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2020, 62(9): 1293-1309. |
| 8 | Feng Z, Li M, Li Y, et al. Comprehensive identification and expression analysis of B-Box genes in cotton. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 1-16. |
| 9 | Yin L L, Xin B L, Chen X L, et al. Genome-wide identification expression patterns of BBX family members in Glycine max. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 6(5): 1-11. |
| 殷丽丽, 邢宝龙, 陈晓亮, 等. 大豆BBX基因家族的鉴定及表达. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 6(5): 1-11. | |
| 10 | Xu Y, Zhao X, Aiwaili P, et al. A zinc finger protein BBX19 interacts with ABF3 to affect drought tolerance negatively in chrysanthemum. The Plant Journal, 2020, 103(5): 1783-1795. |
| 11 | Ye Y J, Li J M, Cao H L, et al. Identification and expression analysis of the CsBBX gene family in tea plants. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2020, 26(6): 1508-1516. |
| 叶一隽, 李佳敏, 曹红利, 等. 茶树CsBBX基因家族的鉴定与表达. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 26(6): 1508-1516. | |
| 12 | Zhang Z H, Tang J M, Zhang C Y, et al. Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of MaBBX gene family in banana. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2020, 11(63): 1-15. |
| 张梓浩, 唐佳美, 张春渝, 等. 香蕉MaBBX基因家族的鉴定、进化及表达. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 11(63): 1-15. | |
| 13 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 14 | Bent A. Arabidopsis thaliana floral dip transformation method. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2006, 343: 87-103. |
| 15 | Dahro B, Wang F, Peng T, et al. PtrA/NINV, an alkaline/neutral invertase gene of Poncirus trifoliata, confers enhanced tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses by modulating ROS levels and maintaining photosynthetic efficiency. BMC Plant Biology, 2016, 16(1): 1-18. |
| 16 | Puckette M C, Weng H, Mahalingam R. Physiological and biochemical responses to acute ozone-induced oxidative stress in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2007, 45(1): 70-79. |
| 17 | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry experiments. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 131-137, 258-260. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 131-137, 258-260. | |
| 18 | Jiang M, Zhang J. Effect of abscisic acid on active oxygen species, antioxidative defence system and oxidative damage in leaves of maize seedlings. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2001, 42(11): 1265-1273. |
| 19 | Zhao L, Liu F, Xu W, et al. Increased expression of OsSPX1 enhances cold/subfreezing tolerance in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2009, 7(6): 550-561. |
| 20 | Polle A, Otter T, Seifert F. Apoplastic peroxidases and lignification in needles of norway spruce (Picea abies L.). Plant Physiology, 1994, 106(1): 53-60. |
| 21 | Giannopolitis C N, Ries S K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiology, 1977, 59(2): 309-314. |
| 22 | Yang X H, Jiang W J, Wei M, et al. Review on plant response and resistance mechanism to salt stress. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2006(2): 302-305, 308. |
| 杨晓慧, 蒋卫杰, 魏珉, 等. 植物对盐胁迫的反应及其抗盐机理研究进展. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2006(2): 302-305, 308. | |
| 23 | Dou J Q, Cheng L J, Xu F H, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of a B-box-type protein gene BlCOL13 in Betula luminifera. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2015, 42(7): 1367-1377. |
| 窦锦青, 程龙军, 徐凤华, 等. 光皮桦BBX类基因BlCOL13的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(7): 1367-1377. | |
| 24 | Liu X. Investigation on B-box protein (BBX) family in apple and MdBBX10 in response to abiotic stress. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 刘欣. 苹果B-box(BBX)家族和MdBBX10响应非生物胁迫的研究. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018. | |
| 25 | Yang N, Cong Q, Wang X R, et al. Identification of EgrBBX gene family and its expression analysis under abiotic stress in Eucalyptus grandis. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2020, 28(4): 658-671. |
| 杨宁, 从青, 王晓荣, 等. 巨桉EgrBBX基因家族鉴定及其在非生物逆境处理下的表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2020, 28(4): 658-671. | |
| 26 | Jia X L, Chen G, Nan G X. Influences of three stress treatments on electric conductivity and malondialdehyde content on Salix linearistipularis seedlings. Heilongjiang Science, 2017, 8(24): 13-14, 19. |
| 贾晓龙, 陈鸽, 南桂仙. 三种非生物胁迫对蒙古柳幼苗电导率和丙二醛含量的影响. 黑龙江科学, 2017, 8(24): 13-14, 19. | |
| 27 | Mishra S, Kumar S, Saha B, et al. Crosstalk between salt, drought, and cold stress in plants: Toward genetic engineering for stress tolerance//Abiotic stress response in plants. New York: Spring-Verlag New York Inc., 2016: 57-88. |
| 28 | Jia H L, Wang X M, Gao T, et al. Characterization of the salt tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana overexpression of MsLEA4-4 from Medicago sativa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 597-605. |
| 贾会丽, 王学敏, 高涛, 等. 转MsLEA4-4基因拟南芥株系的耐盐性分析. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 597-605. | |
| 29 | Ghasemi M, Arzani K, Yadollahi A, et al. Estimate of leaf chlorophyll and nitrogen content in asian pear (Pyrus serotina Rehd.) by CCM-200. Notulae Scientia Biologicae, 2011, 3(1): 91-94. |
| 30 | Mao X H. Genetic engineering improvement of salt tolerance in Medicago sativa L. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2009. |
| 毛秀红. 苜蓿耐盐的基因工程改良研究. 济南: 山东大学, 2009. | |
| 31 | Zhang L Q, Zhang F Y, Hasi A. Reasearch progress on alfalfa salt tolerance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(6): 296-305. |
| 张立全, 张凤英, 哈斯阿古拉. 紫花苜蓿耐盐性研究进展. 草业学报, 2012, 21(6): 296-305. | |
| 32 | Yang Q C, Sun Y, Kang J M. Research on the advancement of salt tolerant gene in alfalfa. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2005, 13(3): 253-256. |
| 杨青川, 孙彦, 康俊梅. 紫花苜蓿耐盐相关基因克隆研究进展. 草地学报, 2005, 13(3): 253-256. | |
| 33 | Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55(1): 373-399. |
| 34 | Yan L P, Xia Y, Liang H M, et al. Transconduct BADH gene into alfalfa and salt tolerance analysis of transgenic generation//Proceedings of the 15th symposium on forage production by the feed production committee of the Chinese Herbal Society. Changzhou: Chinese Grass Society, 2009: 269-276. |
| 燕丽萍, 夏阳, 梁慧敏, 等. 紫花苜蓿转BADH基因及其后代耐盐性分析//中国草学会饲料生产委员会第15次饲草生产学术研讨会论文集. 常州: 中国草学会, 2009: 269-276. | |
| 35 | Liu X, Li R, Dai Y Q, et al. A B-box zinc finger protein, MdBBX10, enhanced salt and drought stresses tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Molecular Biology, 2019, 99(4/5): 437-447. |
| [1] | 王晓龙, 杨曌, 来永才, 李红, 钟鹏, 徐艳霞, 柴华, 李莎莎, 吴玥, 宋敏超, 周景明. 不同秋眠等级苜蓿根系性状对越冬的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 144-153. |
| [2] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| [3] | 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 李生仪, 马春晖, 王旭哲, 张前兵. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| [4] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [5] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [6] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [7] | 王雪萌, 何欣, 张涵, 宋瑞, 毛培胜, 贾善刚. 基于多光谱成像技术快速无损检测紫花苜蓿人工老化种子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 197-208. |
| [8] | 李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75. |
| [9] | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [10] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| [11] | 欧成明, 赵美琦, 孙铭, 毛培胜. 抗坏血酸和水杨酸丸衣对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子发芽特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 93-101. |
| [12] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 赵雅姣, 王静. 内源异黄酮对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮及氮效率的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [13] | 张岳阳, 李芳, 梁维维, 李彦忠. 新疆昌吉32个紫花苜蓿品种的田间抗病性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 133-146. |
| [14] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| [15] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||