

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 32-42.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021077
收稿日期:2021-03-01
修回日期:2021-04-06
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-01-25
通讯作者:
孙洪仁
作者简介:Corresponding author.基金资助:
Hong-ren SUN1( ), Xian-guo WANG1, Yao-jun BU2, Nan QIAO2, Bo REN3
), Xian-guo WANG1, Yao-jun BU2, Nan QIAO2, Bo REN3
Received:2021-03-01
Revised:2021-04-06
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-01-25
Contact:
Hong-ren SUN
摘要:
为了给黄土高原紫花苜蓿测土施肥奠定科学基础,搜集黄土高原紫花苜蓿施肥试验文献,提取土壤氮素含量、施氮处理和缺氮处理的产草量数据,采用零散试验数据整合法和养分平衡-地力差减法新应用公式,开展了该自然区域紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量研究。结果表明,黄土高原生长第1年紫花苜蓿土壤碱解氮第1~6级丰缺指标为≥73、55~73、39~55、26~39、13~26和<13 mg·kg-1,土壤全氮第1~5级丰缺指标为≥1.5、1.1~1.5、0.7~1.1、0.4~0.7和<0.4 g·kg-1,土壤有机质第1~6级丰缺指标为≥19、13~19、9~13、5~9、2~5和<2 g·kg-1;生长第2年及以上紫花苜蓿土壤碱解氮第1~5级丰缺指标为≥79、51~79、30~51、13~30和<13 mg·kg-1;未区分生长年限紫花苜蓿土壤全氮第1~4级丰缺指标为≥1.9、1.2~1.9、0.5~1.2和<0.5 g·kg-1,土壤有机质第1~5级丰缺指标为≥24、13~24、6~13、2~6和<2 g·kg-1。当目标产量为9.0~22.5 t·hm-2、氮肥利用率为40%时,第1~6级土壤的推荐施氮量分别为0~0、68~169、135~338、203~506、270~675和338~844 kg·hm-2。本研究初步建立了黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标推荐施肥系统,为该区域紫花苜蓿测土施氮提供了科学依据。
孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42.
Hong-ren SUN, Xian-guo WANG, Yao-jun BU, Nan QIAO, Bo REN. Preliminary study of a sufficiency index of soil N and recommended N fertilizer application rates for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(4): 32-42.
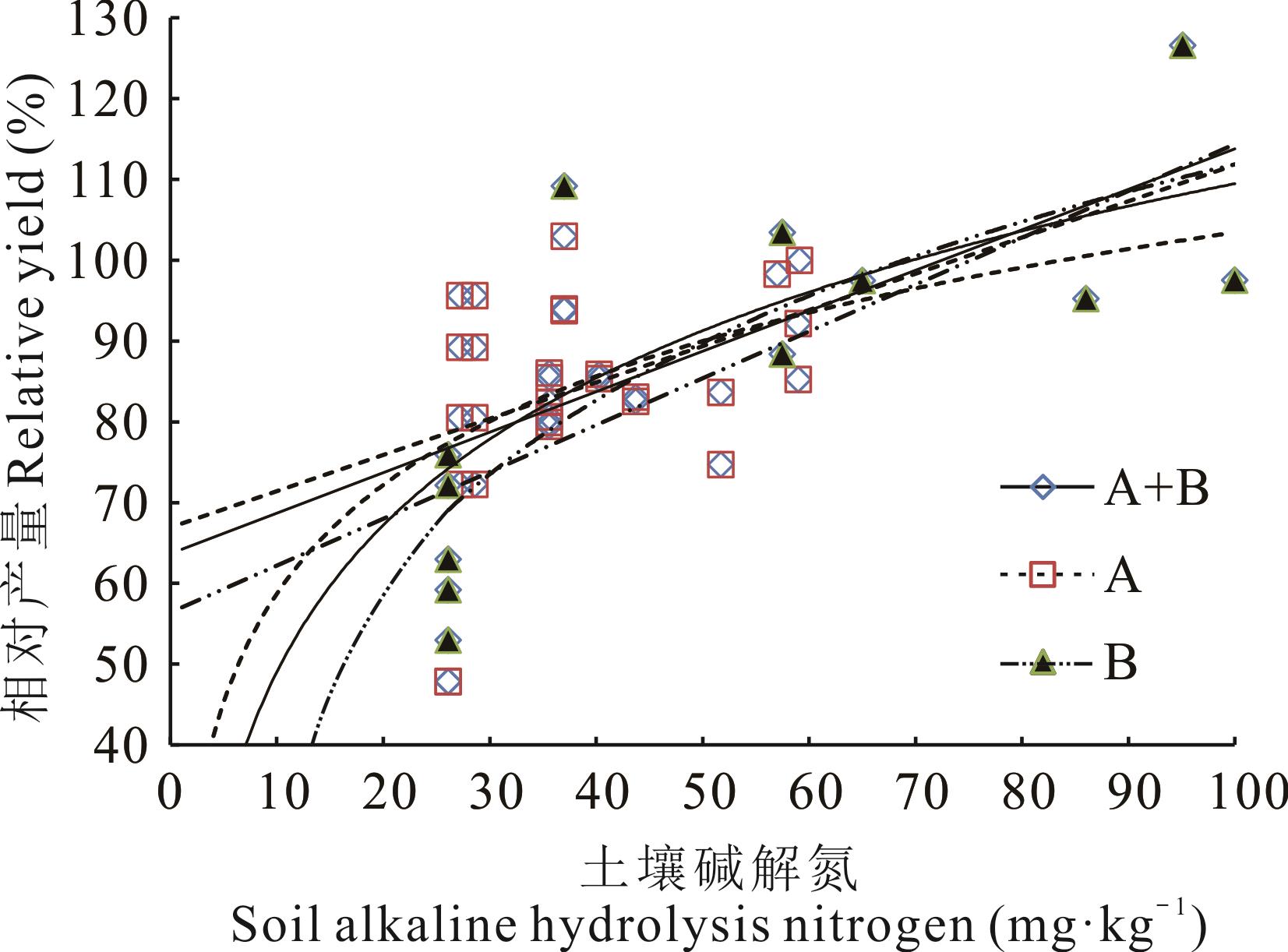
图1 黄土高原紫花苜蓿缺氮处理相对产量与土壤碱解氮含量的回归关系A+B: 全体 Total; A: 生长第2年及以上Second and more growing year; B: 生长第1年First growing year. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 The regression relation between relative yields without N treatment and the concentration of soil alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau
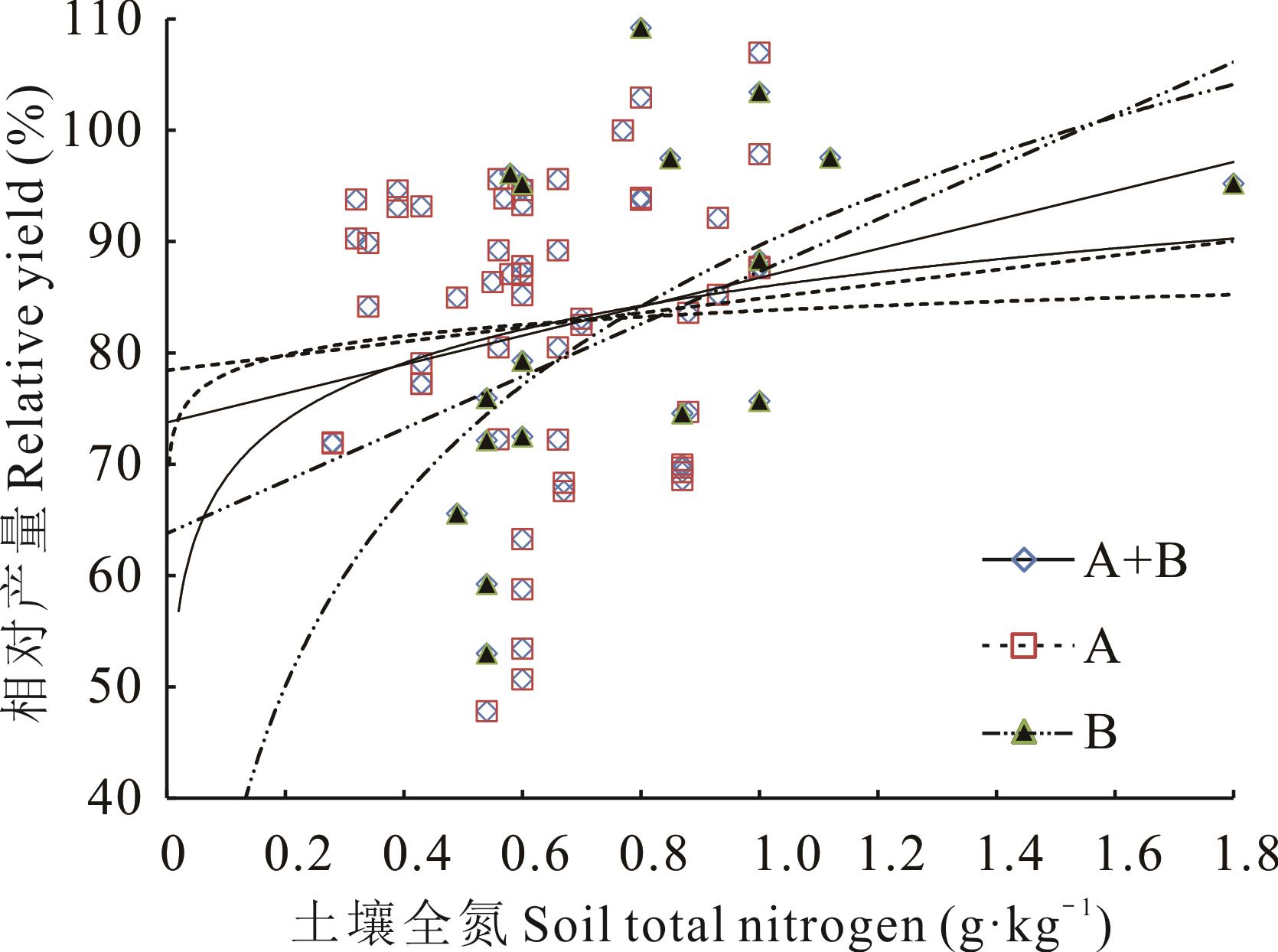
图2 黄土高原紫花苜蓿缺氮处理相对产量与土壤全氮含量的回归关系
Fig.2 The regression relation between relative yields without N treatment and the concentration of soil total nitrogen for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau
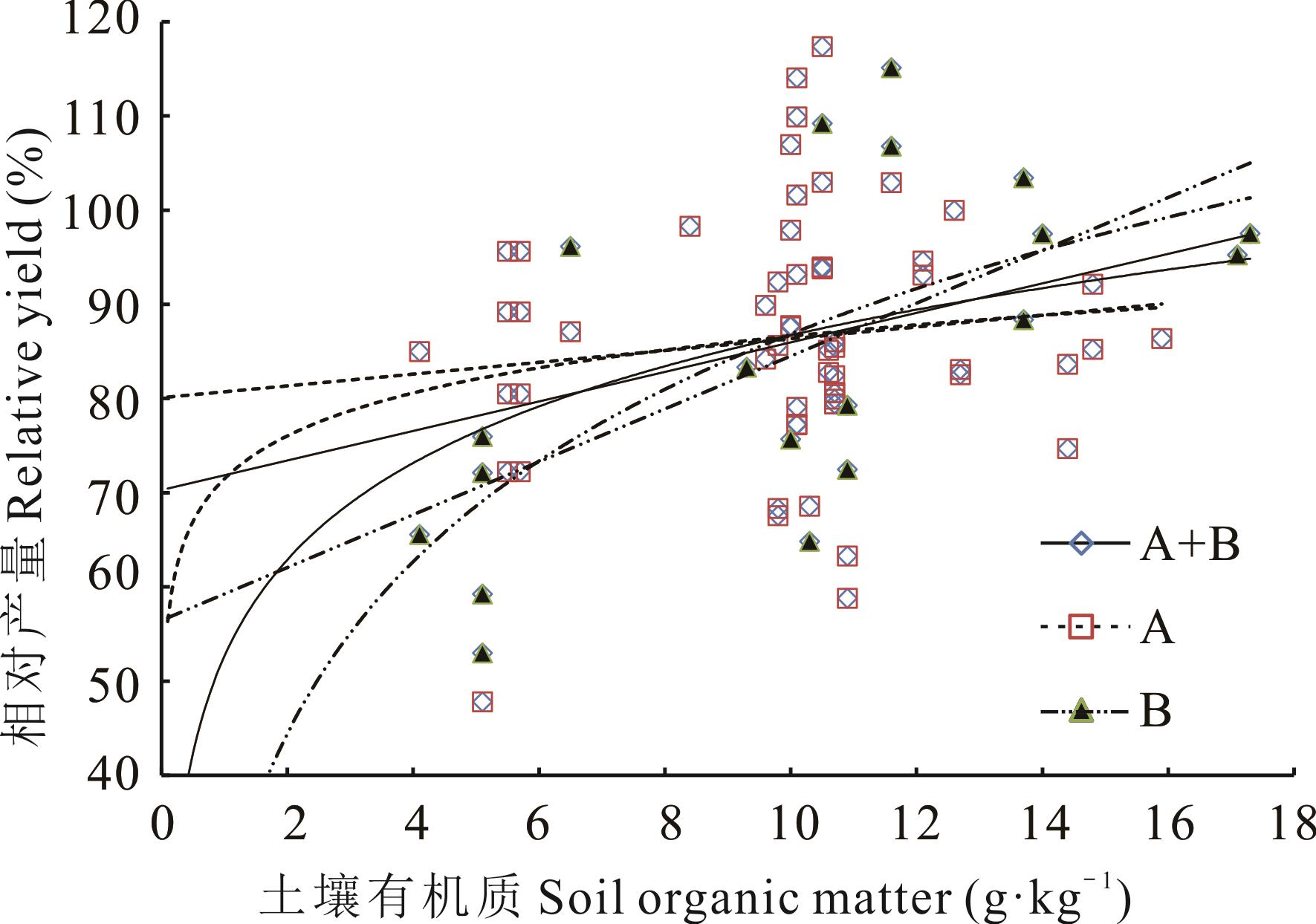
图3 黄土高原紫花苜蓿缺氮处理相对产量与土壤有机质含量的回归关系
Fig.3 The regression relation between relative yields without N treatment and the concentration of soil organic matter for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau
养分 Nutrients | 生长年限 Growing years | 模型 Models | 回归方程 Regression equations | 样本数Sample number (n) | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (r) | 缺氮处理相对产量 Relative yields without N treatment (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 95 | 100 | ||||||
碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | A+B | L | y=0.5012x+63.66 | 42 | 0.5935** | 32.6 | 52.6 | 62.5 | 72.5 | |||
| N | y=26.247ln x-11.415 | 42 | 0.6297** | 32.6 | 47.7 | 57.7 | 69.8 | |||||
| A | L | y=0.4486x+66.921 | 30 | 0.3801* | 29.2 | 51.5 | 62.6 | |||||
| N | y=19.413ln x+14.026 | 30 | 0.4093* | 29.9 | 50.1 | 64.8 | ||||||
| B | L | y=0.5793x+56.43 | 12 | 0.7115** | 40.7 | 58.0 | 66.6 | 75.2 | ||||
| N | y=31.855ln x-34.84 | 12 | 0.7938** | 26.9 | 36.8 | 50.4 | 58.9 | 68.9 | ||||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | y=14.229x+73.366 | 73 | 0.2552* | 0.47 | 1.17 | 1.52 | ||||
| N | y=8.433ln x+86.794 | 73 | 0.2180ns | 0.45 | 1.46 | |||||||
| A | L | y=7.6476x+77.954 | 55 | 0.1175ns | ||||||||
| N | y=3.1583ln x+84.415 | 55 | 0.0819ns | |||||||||
| B | L | y=24.232x+64.174 | 18 | 0.5008* | 0.65 | 1.07 | 1.27 | 1.48 | ||||
| N | y=25.841ln x+90.97 | 18 | 0.5773* | 0.65 | 0.96 | 1.17 | 1.42 | |||||
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | y=1.2736x+73.534 | 79 | 0.3089** | 5.1 | 12.9 | 16.9 | ||||
| N | y=13.53ln x+55.867 | 79 | 0.3581** | 6.0 | 12.5 | |||||||
| A | L | y=0.5911x+81.239 | 58 | 0.1378ns | 14.7 | |||||||
| N | y=7.0091ln x+71.395 | 58 | 0.1836ns | 14.2 | ||||||||
| B | L | y=2.1529x+61.524 | 21 | 0.5470* | 8.6 | 13.2 | 15.6 | |||||
| N | y=21.999ln x+34.462 | 21 | 0.5948** | 5.0 | 7.9 | 12.5 | 15.7 | |||||
表1 黄土高原紫花苜蓿缺素处理相对产量与土壤氮素含量回归方程及若干节点土壤氮素含量临界值
Table 1 The regression equations between relative yields without N treatment and soil N concentration and several critical values of soil N concentration for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau
养分 Nutrients | 生长年限 Growing years | 模型 Models | 回归方程 Regression equations | 样本数Sample number (n) | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (r) | 缺氮处理相对产量 Relative yields without N treatment (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 95 | 100 | ||||||
碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | A+B | L | y=0.5012x+63.66 | 42 | 0.5935** | 32.6 | 52.6 | 62.5 | 72.5 | |||
| N | y=26.247ln x-11.415 | 42 | 0.6297** | 32.6 | 47.7 | 57.7 | 69.8 | |||||
| A | L | y=0.4486x+66.921 | 30 | 0.3801* | 29.2 | 51.5 | 62.6 | |||||
| N | y=19.413ln x+14.026 | 30 | 0.4093* | 29.9 | 50.1 | 64.8 | ||||||
| B | L | y=0.5793x+56.43 | 12 | 0.7115** | 40.7 | 58.0 | 66.6 | 75.2 | ||||
| N | y=31.855ln x-34.84 | 12 | 0.7938** | 26.9 | 36.8 | 50.4 | 58.9 | 68.9 | ||||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | y=14.229x+73.366 | 73 | 0.2552* | 0.47 | 1.17 | 1.52 | ||||
| N | y=8.433ln x+86.794 | 73 | 0.2180ns | 0.45 | 1.46 | |||||||
| A | L | y=7.6476x+77.954 | 55 | 0.1175ns | ||||||||
| N | y=3.1583ln x+84.415 | 55 | 0.0819ns | |||||||||
| B | L | y=24.232x+64.174 | 18 | 0.5008* | 0.65 | 1.07 | 1.27 | 1.48 | ||||
| N | y=25.841ln x+90.97 | 18 | 0.5773* | 0.65 | 0.96 | 1.17 | 1.42 | |||||
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | y=1.2736x+73.534 | 79 | 0.3089** | 5.1 | 12.9 | 16.9 | ||||
| N | y=13.53ln x+55.867 | 79 | 0.3581** | 6.0 | 12.5 | |||||||
| A | L | y=0.5911x+81.239 | 58 | 0.1378ns | 14.7 | |||||||
| N | y=7.0091ln x+71.395 | 58 | 0.1836ns | 14.2 | ||||||||
| B | L | y=2.1529x+61.524 | 21 | 0.5470* | 8.6 | 13.2 | 15.6 | |||||
| N | y=21.999ln x+34.462 | 21 | 0.5948** | 5.0 | 7.9 | 12.5 | 15.7 | |||||
养分 Nutrients | 生长年限 Growing years | 模型 Models | 丰缺级别Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | A+B | L | < | 33~53 | 53~73 | ≥73 | ||
| N | < | 33~53 | 48~70 | ≥70 | ||||
| A | L | < | 30~52 | 52~ | ≥ | |||
| N | < | 30~51 | 51~ | ≥ | ||||
| B | L | < | 41~58 | 58~76 | ≥76 | |||
| N | < | 27~37 | 37~51 | 51~69 | ≥69 | |||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | <0.5 | 0.5~1.2 | 1.2~ | ≥ | ||
| B | L | < | 0.7~1.1 | 1.1~1.5 | ≥1.5 | |||
| N | < | 0.7~1.0 | 1.0~1.5 | ≥1.5 | ||||
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | <6 | 6~13 | 13~ | ≥ | ||
| N | < | 6~13 | 13~ | ≥ | ||||
| B | L | < | 9~14 | 14~ | ≥ | |||
| N | < | 5~8 | 8~13 | 13~ | ≥ | |||
| 缺氮处理相对产量Relative yield without N treatment (%) | <60 | 60~70 | 70~80 | 80~90 | 90~100 | ≥100 | ||
表2 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标
Table 2 The rich-lack index of soil N for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau
养分 Nutrients | 生长年限 Growing years | 模型 Models | 丰缺级别Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||
碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | A+B | L | < | 33~53 | 53~73 | ≥73 | ||
| N | < | 33~53 | 48~70 | ≥70 | ||||
| A | L | < | 30~52 | 52~ | ≥ | |||
| N | < | 30~51 | 51~ | ≥ | ||||
| B | L | < | 41~58 | 58~76 | ≥76 | |||
| N | < | 27~37 | 37~51 | 51~69 | ≥69 | |||
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | <0.5 | 0.5~1.2 | 1.2~ | ≥ | ||
| B | L | < | 0.7~1.1 | 1.1~1.5 | ≥1.5 | |||
| N | < | 0.7~1.0 | 1.0~1.5 | ≥1.5 | ||||
有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | A+B | L | <6 | 6~13 | 13~ | ≥ | ||
| N | < | 6~13 | 13~ | ≥ | ||||
| B | L | < | 9~14 | 14~ | ≥ | |||
| N | < | 5~8 | 8~13 | 13~ | ≥ | |||
| 缺氮处理相对产量Relative yield without N treatment (%) | <60 | 60~70 | 70~80 | 80~90 | 90~100 | ≥100 | ||
目标产量 Target yield (t·hm-2) | 氮肥利用率 N fertilizer use efficiency (%) | 丰缺级别Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 9.0 | 50 | 270 | 216 | 162 | 108 | 54 | 0 |
| 40 | 338 | 270 | 203 | 135 | 68 | 0 | |
| 30 | 451 | 359 | 270 | 181 | 89 | 0 | |
| 10.5 | 50 | 315 | 252 | 189 | 126 | 63 | 0 |
| 40 | 394 | 315 | 236 | 158 | 79 | 0 | |
| 30 | 526 | 419 | 315 | 211 | 104 | 0 | |
| 12.0 | 50 | 360 | 288 | 216 | 144 | 72 | 0 |
| 40 | 450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 | |
| 30 | 601 | 479 | 360 | 241 | 119 | 0 | |
| 13.5 | 50 | 405 | 324 | 243 | 162 | 81 | 0 |
| 40 | 506 | 405 | 304 | 203 | 101 | 0 | |
| 30 | 676 | 539 | 405 | 271 | 134 | 0 | |
| 15.0 | 50 | 450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 |
| 40 | 563 | 450 | 338 | 225 | 113 | 0 | |
| 30 | 752 | 599 | 450 | 302 | 149 | 0 | |
| 16.5 | 50 | 495 | 396 | 297 | 198 | 99 | 0 |
| 40 | 619 | 495 | 371 | 248 | 124 | 0 | |
| 30 | 827 | 658 | 495 | 332 | 163 | 0 | |
| 18.0 | 50 | 540 | 432 | 324 | 216 | 108 | 0 |
| 40 | 675 | 540 | 405 | 270 | 135 | 0 | |
| 30 | 902 | 718 | 540 | 362 | 178 | 0 | |
| 19.5 | 50 | 585 | 468 | 351 | 234 | 117 | 0 |
| 40 | 731 | 585 | 439 | 293 | 146 | 0 | |
| 30 | 977 | 778 | 585 | 392 | 193 | 0 | |
| 21.0 | 50 | 630 | 504 | 378 | 252 | 126 | 0 |
| 40 | 788 | 630 | 473 | 315 | 158 | 0 | |
| 30 | 1052 | 838 | 630 | 422 | 208 | 0 | |
| 22.5 | 50 | 675 | 540 | 405 | 270 | 135 | 0 |
| 40 | 844 | 675 | 506 | 338 | 169 | 0 | |
| 30 | 1127 | 898 | 675 | 452 | 223 | 0 | |
表3 黄土高原紫花苜蓿推荐施氮量
Table 3 Recommended N application rates for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau (kg·hm-2)
目标产量 Target yield (t·hm-2) | 氮肥利用率 N fertilizer use efficiency (%) | 丰缺级别Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 9.0 | 50 | 270 | 216 | 162 | 108 | 54 | 0 |
| 40 | 338 | 270 | 203 | 135 | 68 | 0 | |
| 30 | 451 | 359 | 270 | 181 | 89 | 0 | |
| 10.5 | 50 | 315 | 252 | 189 | 126 | 63 | 0 |
| 40 | 394 | 315 | 236 | 158 | 79 | 0 | |
| 30 | 526 | 419 | 315 | 211 | 104 | 0 | |
| 12.0 | 50 | 360 | 288 | 216 | 144 | 72 | 0 |
| 40 | 450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 | |
| 30 | 601 | 479 | 360 | 241 | 119 | 0 | |
| 13.5 | 50 | 405 | 324 | 243 | 162 | 81 | 0 |
| 40 | 506 | 405 | 304 | 203 | 101 | 0 | |
| 30 | 676 | 539 | 405 | 271 | 134 | 0 | |
| 15.0 | 50 | 450 | 360 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 0 |
| 40 | 563 | 450 | 338 | 225 | 113 | 0 | |
| 30 | 752 | 599 | 450 | 302 | 149 | 0 | |
| 16.5 | 50 | 495 | 396 | 297 | 198 | 99 | 0 |
| 40 | 619 | 495 | 371 | 248 | 124 | 0 | |
| 30 | 827 | 658 | 495 | 332 | 163 | 0 | |
| 18.0 | 50 | 540 | 432 | 324 | 216 | 108 | 0 |
| 40 | 675 | 540 | 405 | 270 | 135 | 0 | |
| 30 | 902 | 718 | 540 | 362 | 178 | 0 | |
| 19.5 | 50 | 585 | 468 | 351 | 234 | 117 | 0 |
| 40 | 731 | 585 | 439 | 293 | 146 | 0 | |
| 30 | 977 | 778 | 585 | 392 | 193 | 0 | |
| 21.0 | 50 | 630 | 504 | 378 | 252 | 126 | 0 |
| 40 | 788 | 630 | 473 | 315 | 158 | 0 | |
| 30 | 1052 | 838 | 630 | 422 | 208 | 0 | |
| 22.5 | 50 | 675 | 540 | 405 | 270 | 135 | 0 |
| 40 | 844 | 675 | 506 | 338 | 169 | 0 | |
| 30 | 1127 | 898 | 675 | 452 | 223 | 0 | |
| 1 | Wang D, Xie K Y, He F, et al. Progress in study on nitrogen fertilizer application to alfalfa. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2013, 35(6): 98-103. |
| 王丹, 谢开云, 何峰, 等. 紫花苜蓿施氮研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2013, 35(6): 98-103. | |
| 2 | Bray R H. Soil-plant relations: I. The quantitative relation of exchangeable potassium to crop yields and to crop response to potash additions. Soil Science, 1944, 58: 305-324. |
| 3 | Lin R, Jiang P A, Zhou Y Q, et al. Preliminary study on abundance and deficiency index of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium for the alfalfa soil. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2004, 27(1): 23-28. |
| 蔺蕊, 蒋平安, 周抑强, 等. 苜蓿土壤氮磷钾丰缺指标初步研究. 新疆农业大学学报, 2004, 27(1): 23-28. | |
| 4 | Xie Y, Sun H R, Zhang X Q, et al. Preliminary study on abundance and deficiency index of iron, manganese and zinc for alfalfa soil in Bashang area. Prataculture & Animal Husbandry, 2010(10): 6-11. |
| 谢勇, 孙洪仁, 张新全, 等. 坝上地区紫花苜蓿土壤铁、锰和锌丰缺指标初步研究. 草业与畜牧, 2010(10): 6-11. | |
| 5 | Xie Y, Sun H R, Zhang X Q, et al. Preliminary study on abundance and deficiency index of available phosphorus and potassium for alfalfa in Bashang soil. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(2): 231-235. |
| 谢勇, 孙洪仁, 张新全, 等. 坝上地区紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷、钾丰缺指标初探. 草业科学, 2011, 28(2): 231-235. | |
| 6 | Shao G W, Liu Z B, Sun H R, et al. A preliminary study on rich-lack index of available P for alfalfa in Huanghua City. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(12): 1805-1809. |
| 邵光武, 刘治波, 孙洪仁, 等.黄骅市紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标初步研究.草业科学, 2012, 29(12): 1805-1809. | |
| 7 | Sun H R, Cao Y, Liu L, et al. Preliminary study on abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and appropriate phosphorus application rates for alfalfa in the North of China. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2016(3): 30-36. |
| 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 中国北方紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量初步研究. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(3): 30-36. | |
| 8 | Sun H R, Cao Y, Liu L, et al. Preliminary study on the abundance and deficiency index of soil available potassium and appropriate amount of potassium application for alfalfa in the North of China. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2017(1): 1-4. |
| 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 中国北方紫花苜蓿土壤速效钾丰缺指标与适宜施钾量初步研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2017(1): 1-4. | |
| 9 | Sun H R, Cao Y, Liu L, et al. Study on abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and K and appropriate fertilizer application rates for alfalfa in the Inner Mongolia Plateau and Loess Plateau of China. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2018(19): 30-35. |
| 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 内蒙古高原和黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷和速效钾丰缺指标与适宜施肥量研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018(19): 30-35. | |
| 10 | Zhong P G, Sun H R, Yan X D, et al. Study on the abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and appropriate P fertilizer application rates for alfalfa soil in the Huanghuaihai plain. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2019(23): 88-91. |
| 钟培阁, 孙洪仁, 阎旭东, 等. 黄淮海平原紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(23): 88-91. | |
| 11 | Wang Y, Zhu K D, Sun H R, et al. Study on rich-lack index of soil available P and recommended phosphate fertilizer application rates for alfalfa in the Inner Mongolia plateau of China. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(2): 577-582. |
| 王彦, 朱凯迪, 孙洪仁, 等. 内蒙古高原紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标与推荐施磷量研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(2): 577-582. | |
| 12 | Sun H R, Bu Y J, Yang C L, et al. Study on abundance-deficiency index of soil available P and appropriate P fertilizer application rates for alfalfa in the Loess Plateau of China.Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 42(2): 41-46. |
| 孙洪仁, 卜耀军, 杨彩林, 等. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量研究. 中国草地学报, 2020, 42(2): 41-46. | |
| 13 | Sun H R, Maimaiti M, Shabihan S, et al. Study on rich-lack index of soil available P and recommended phosphate fertilizer application rates for alfalfa in the northwest desert oasis of China.Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(1): 76-82. |
| 孙洪仁, 穆尼热·买买提, 沙吾列·沙比汗, 等. 西北荒漠绿洲区紫花苜蓿土壤有效磷丰缺指标与推荐施磷量. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(1): 76-82. | |
| 14 | Sun H R, Cao Y, Liu L, et al. An improved scheme for the grading of abundance and deficiency of soil available nutrients in soil testing and fertilizer recommendation. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2014(19): 1-5. |
| 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 测土施肥土壤有效养分丰缺分级改良方案. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(19): 1-5. | |
| 15 | Sun H R, Cao Y, Liu L, et al. A new application formula for determining the appropriate amount of fertilizer application with the methods of nutrient balance and dissimilar subtraction of soil fertility. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2014(7): 1-4. |
| 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. “养分平衡-地力差减法”确定适宜施肥量的新应用公式. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(7): 1-4. | |
| 16 | Sun H R, Cao Y, Liu L, et al. The appropriate amount of fertilizer application for the soils with different levels of nutrient abundance and deficiency using soil testing and fertilizer recommendation. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2014(23): 7-11. |
| 孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 测土施肥不同丰缺级别土壤的适宜施肥量. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(23): 7-11. | |
| 17 | Hou X Y. On planting Medicago sativa L. in Northwest of Shanxi and application of fertilizer. Journal of Shanxi University (Nature Science Edition), 1990(Supplement):84-89. |
| 侯向阳. 晋西北种植紫花苜蓿及其施肥问题. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 1990(增刊): 84-89. | |
| 18 | Zhang J X, Chen S.A study on N and P applied of alfalfa. Pratacultural Science, 1990, 7(4): 70-72. |
| 张积祥, 陈松. 紫花苜蓿NP肥配施研究. 草业科学, 1990, 7(4): 70-72. | |
| 19 | Jia H Y, Peng X L, Yong S P, et al. Effect of Astragalus adsurgens and Medicago sativa on N, P, K. Pratacultural Science, 1994, 11(5): 42-45. |
| 贾恒义, 彭祥林, 雍绍萍, 等. 沙打旺、苜蓿对氮磷钾的效应. 草业科学, 1994, 11(5): 42-45. | |
| 20 | Hao M D, Zhang C X, Wei X R, et al. Effect of rotation and fertilization to alfalfa productivity on the Loess Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2004, 12(3): 195-198. |
| 郝明德, 张春霞, 魏孝荣, 等. 黄土高原地区施肥对苜蓿生产力的影响. 草地学报, 2004, 12(3): 195-198. | |
| 21 | Wan S M. Study on the production characters of alfalfa under different fertilizer level. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2005. |
| 万素梅. 不同施肥水平苜蓿生产性能研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2005. | |
| 22 | Sun Z M. Study on the technical system and the mode of the grassland farming in south dryland farming region of Ningxia China. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2005. |
| 孙兆敏. 宁南旱作农区草地农业发展模式与技术体系研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2005 | |
| 23 | Zeng Q F. Fertilization effects on alfalfa production characteristics and soil fertility. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2005. |
| 曾庆飞. 施肥对紫花苜蓿生产性能和土壤肥力的影响研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2005. | |
| 24 | Chen L, Hao M D, Zhang S M, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on the soil water and nutrient contents of rainfed wheat and alfalfa lands in Loess plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2007, 15(4): 371-375. |
| 陈磊, 郝明德, 张少民, 等. 黄土高原旱地施肥对小麦与苜蓿土壤水分养分含量的影响. 草地学报, 2007, 15(4): 371-375. | |
| 25 | Fan P, Tian F, Gang C W. The influence of fertilizer to the yield of Medicago sativa L. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2007, 25(5): 31-34. |
| 樊萍, 田丰, 刚存武. 施肥对紫花苜蓿产量的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 2007, 25(5): 31-34. | |
| 26 | Sun L N. Interaction between phosphate solubilizing bacteria and Rhizobium of alfalfa and the effects of their inoculum on alfalfa growth and quality. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2008. |
| 孙丽娜. 苜蓿根瘤菌与溶磷菌互作及其菌肥对苜蓿生长和品质影响研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2008. | |
| 27 | Jia J, Han Q F, Zhou F, et al. Effects of different N/P ratio on forage yield components and nutritional composites in non-irrigated land. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2009, 31(3): 77-82. |
| 贾珺, 韩清芳, 周芳, 等. 氮磷配比对旱地紫花苜蓿产量构成因子及营养成分的影响. 中国草地学报, 2009, 31(3): 77-82. | |
| 28 | Tao W H, Shi Y Y, Li S Q. Effects of fertilization on the biomass of plant canopy and roots. Shaanxi Agricultural Science, 2012(2): 81-85. |
| 陶武辉, 史亚亚, 李世清. 施肥对黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错区植物冠层及根系生物量的影响. 陕西农业科学,2012(2): 81-85. | |
| 29 | He S B. Study on the mechanisms of carbon assimilation and C/N ratio in alfalfa responding to nitrogen and water availabilities. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2012. |
| 何树斌. 不同氮素和水分供应下紫花苜蓿碳同化和C、N响应机制研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2012. | |
| 30 | Liu X J, Liu Y N, Kuai J L, et al. Effect of different N levels on productivity and quality of alfalfa varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(4): 702-707. |
| 刘晓静, 刘艳楠, 蒯佳林, 等. 供氮水平对不同紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响. 草地学报, 2013, 21(4): 702-707. | |
| 31 | Liu Y N, Liu X J, Zhang X L, et al. Effect of clipping and fertilization on production performance of different alfalfa varieties. Grassland and Turf, 2013, 33(3): 69-73,77. |
| 刘艳楠, 刘晓静, 张晓磊, 等. 施肥与刈割对不同紫花苜蓿品种生产性能的影响. 草原与草坪, 2013, 33(3): 69-73, 77. | |
| 32 | Wang B L, Luo S W, Xu L F. Influence of NPK fertilizer on yield of alfalfa seed. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(2): 7-9. |
| 王秉龙, 罗世武, 徐丽芳. 氮磷钾配施对紫花苜蓿种子产量的影响. 甘肃农业科技, 2013(2): 7-9. | |
| 33 | Kang G L. Effect of different potassium fertilizer on the yield and quality of alfalfa. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 20(7): 81-82. |
| 康桂兰. 不同钾肥对紫花苜蓿产量和品质的影响. 天津农业科学, 2014, 20(7): 81-82. | |
| 34 | Liu X J, Zhang J X, Li W Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition and cuttings on yield and quality of alfalfa in dry region of Gansu, China. Journal of Desert Research, 2014, 34(6): 1516-1526. |
| 刘晓静, 张进霞, 李文卿, 等. 施肥及刈割对干旱地区紫花苜蓿产量和品质的影响. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(6): 1516-1526. | |
| 35 | Zhang J X, Li W Q, Liu X J, et al. Effects of different nitrogen levels on alfalfa productivity in different growing years. Grassland and Turf, 2014, 34(3): 46-50. |
| 张进霞, 李文卿, 刘晓静, 等. 施氮对紫花苜蓿生长特性的影响. 草原与草坪, 2014, 34(3): 46-50. | |
| 36 | Liu X J, Zhang J X, Ye F, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on nitrogen metabolism and nitrogen accumulation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 29(7): 1399-1405. |
| 刘晓静, 张进霞, 叶芳, 等. 施氮对紫花苜蓿氮代谢及氮积累的影响. 核农学报, 2015, 29(7): 1399-1405. | |
| 37 | Qi P, Liu X J, Liu Y N, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen accumulation in alfalfa and the content of nitrogen in soil. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(5): 1026-1032. |
| 齐鹏, 刘晓静, 刘艳楠, 等. 施氮对不同紫花苜蓿品种氮积累及土壤氮动态变化的影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(5): 1026-1032. | |
| 38 | Fan J W. Effects of limited water and fertilizer in soil and defoliation on forage growth and mycorrhiza formation. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015. |
| 樊经纬. 水肥亏缺和刈割对牧草生长和丛枝菌根真菌的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. | |
| 39 | Wang B R. The respond of alfalfa yield and soil quality to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer applied in the Loess Plateau semi-arid areas. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015. |
| 王冰如. 黄土高原半干旱区苜蓿草地产量及土壤质量对氮磷肥施加的响应. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. | |
| 40 | Li Y. Response of N2O emissions and productivity of lucerne stand to nitrogen addition. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016. |
| 李渊. 黄土高原苜蓿草地N2O排放及生产性能对氮添加的响应. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016. | |
| 41 | Meng X C. Analysis of planting structure and the study on film mulch and fertilization effect of alfalfa in dryland of Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016. |
| 孟宣辰. 黄土高原旱作区种植结构分析和紫花苜蓿覆膜施肥效应研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016. | |
| 42 | Hao F. Study on nitrogen efficiency mechanism and division growth period by nitrogen nutrition stage of alfalfa. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 郝凤. 紫花苜蓿氮效率差异机制与氮营养阶段生育期划分的研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2017. | |
| 43 | Pan J. Cultivation techniques of alfalfa on the Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 潘佳. 黄土高原区紫花苜蓿高效种植技术研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 44 | Cheng T T. Study on the relationship between leaf characteristics and production characteristics and quality of alfalfa with different nitrogen efficiency. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 程甜甜. 不同氮效率类型紫花苜蓿叶特征及其与生产性能和品质相互关系的研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. | |
| 45 | Shi X P. The effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer on different growing year alfalfa aboveground biomass, soil nutrients and soil water in the semi-arid area. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 史晓鹏. 施氮磷肥对半干旱区不同生长年限紫花苜蓿地上生物量及土壤养分和水分的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. | |
| 46 | Chen X L, Pan J, Chen L J, et al. Effects of fertilization on hay yield and quality of alfalfa on the Loess Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(12): 3145-3154. |
| 陈香来, 潘佳, 陈利军, 等. 施肥对黄土高原紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响. 草业科学, 2019, 36(12): 3145-3154. | |
| 47 | Lu J Y. Effects of N and P fertilizations on leaf nutrient resorption of alfalfa at different growth stage in the Loess Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 陆姣云. 施氮磷肥对黄土高原不同生长阶段紫花苜蓿叶片养分重吸收的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 48 | Bai X K. Effects of nitrogen addition, warming and rainfall increase on stoichiometry of alfalfa leaves in the Loess Plateau of China. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019. |
| 白晓珂. 氮添加、增温和降雨增加对黄土高原紫花苜蓿叶片化学计量学特征的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019. | |
| 49 | Ni H, Yang X L, Wang G, et al. Effects of nitrogen application and nitrification inhibitor addition on N2O emissions in Medicago sativa L. grassland. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2020, 28(3): 317-327. |
| 倪红, 杨宪龙, 王刚, 等. 施氮及添加硝化抑制剂对苜蓿草地N2O排放的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2020, 28(3): 317-327. | |
| 50 | Xu R R, Chang S H, Jia Q M, et al. Effects of nitrogen application and utilization methods on yield, quality and water use of grass-legume mixed grassland in Loess Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1744-1755. |
| 徐然然, 常生华, 贾倩民, 等. 施氮和利用方式对黄土高原禾豆混播草地产量、品质和水分利用的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1744-1755. | |
| 51 | Li X Y, Sun H R, Ma J X, et al. High-yield cultivation technical handbook for main fine forage. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010: 15-20. |
| 李新一, 孙洪仁, 马金星, 等. 主要优良饲草高产栽培技术手册. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010: 15-20. | |
| 52 | Undersander D, Cosgrove D, Cullen E, et al. Alfalfa management guide. Madison, Wisconsin, USA: American Society of Agronomy, Incorporated Publisher, 2011: 18. |
| 53 | Sun J L, Wei D, Ma X Z, et al. Establishing fertilization recommendation index of soybean in black soil region of Heilongjiang Province. Soybean Science, 2013, 32(4): 512-516. |
| 孙景玲, 魏丹, 马星竹, 等. 黑龙江省黑土区大豆测土配方施肥指标体系的建立. 大豆科学, 2013, 32(4): 512-516. | |
| 54 | Wang Z G, Gao Q, Feng G Z. Preliminary raising fertilization index system for soybean in Jilin Province. Soybean Science, 2010, 29(4): 669-672. |
| 王志刚, 高强, 冯国忠. 吉林省大豆施肥指标体系初步建立.大豆科学, 2010, 29(4): 669-672. | |
| 55 | Dong H, Lou C R, Niu S W, et al. The research of the rich-lack index on the soil nutrient of soybean in the Liaoning Province. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2011, 42(1): 145-147. |
| 董环, 娄春荣, 牛世伟, 等. 辽宁省大豆土壤养分丰缺指标研究. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(1): 145-147. | |
| 56 | Sun H R, Gang L H, Zhang J P, et al. Study on the abundance-deficiency indices of soil N and appropriate nitrogen application rates for wheat in China. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2018, 46(2): 41-46. |
| 孙洪仁, 冮丽华, 张吉萍, 等. 中国小麦土壤氮素丰缺指标与适宜施氮量研究. 北方农业学报, 2018, 46(2): 41-46. | |
| 57 | Sun H R, Zhang J P, Gang L H, et al. Corn fertilizer recommendation system based on abundance-deficiency index of soil N in four great natural regions and whole China. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(14): 80-87. |
| 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 冮丽华, 等. 四大自然区域和全国玉米土壤氮素丰缺指标推荐施肥系统. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(14): 80-87. | |
| 58 | Sun H R, Gang L H, Zhang J P, et al. Abundance-deficiency indices of soil N and appropriate nitrogen application rates for rice in China. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(11): 82-87. |
| 孙洪仁, 冮丽华, 张吉萍, 等. 中国水稻土壤氮素丰缺指标与适宜施氮量. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(11): 82-87. | |
| 59 | Sun H R, Zeng H, Liu J Y, et al. Preliminary study on abundance-deficiency index of soil N and appropriate nitrogen application rates for oats in the farming-grazing transitional zone of China. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2017, 45(5): 22-27. |
| 孙洪仁, 曾红, 刘江扬, 等. 中国农牧交错带燕麦土壤氮素丰缺指标与适宜施氮量初步研究. 北方农业学报, 2017, 45(5): 22-27. | |
| 60 | Sun H R, Gang L H, Zhang J P, et al. The abundance-deficiency indexes of soil NPK and appropriate fertilization rates for potato in China. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(5): 78-85. |
| 孙洪仁, 冮丽华, 张吉萍, 等. 中国马铃薯土壤氮磷钾丰缺指标与适宜施肥量. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(5): 78-85. | |
| 61 | Sun H R, Zhang J P, Lv Y C, et al. Abundance -deficiency index of soil alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen and appropriate nitrogen application rates for sugar beet in the north of China. Sugar Crops of China, 2019, 41(2): 14-17. |
| 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 等. 中国北方甜菜土壤碱解氮丰缺指标与适宜施氮量研究. 中国糖料, 2019, 41(2): 14-17. | |
| 62 | Zhong P G, Sun H R, Zhang J P, et al. Preliminary study on abundance-deficiency index of soil total nitrogen and appropriate N fertilizer application rates for sugarcane in the south of China. Sugar Crops of China, 2020, 42(3): 43-48. |
| 钟培阁, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 中国南方甘蔗土壤全氮丰缺指标与适宜施氮量初步研究. 中国糖料, 2020, 42(3): 43-48. | |
| 63 | Zhang F S, Chen X P, Chen Q. Fertilization guide for main crops in China. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2009: 6-158. |
| 张福锁, 陈新平, 陈清. 中国主要作物施肥指南. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2009: 6-158. |
| [1] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 赵雅姣, 王静. 内源异黄酮对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮及氮效率的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [2] | 张岳阳, 李芳, 梁维维, 李彦忠. 新疆昌吉32个紫花苜蓿品种的田间抗病性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 133-146. |
| [3] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| [4] | 张辉辉, 师尚礼, 武蓓, 李自立, 李小龙. 苜蓿与3种多年生禾草混播效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 159-170. |
| [5] | 白婕, 臧真凤, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 王可珍, 屈洋, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿叶片和根系膜脂过氧化及C、N特征对水分和N添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 213-220. |
| [6] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [7] | 韩小雨, 郭宁, 李冬冬, 谢明阳, 焦峰. 氮添加对内蒙古不同草原生物量及土壤碳氮变化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 13-25. |
| [8] | 徐睿智, 吴晓娟, 杨惠敏. 刈割后追肥对建植当年紫花苜蓿生长和生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 195-204. |
| [9] | 王星, 于双, 许冬梅, 宋珂辰. 不同恢复措施对退化荒漠草原土壤碳氮及其组分特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 26-35. |
| [10] | 汪梦寒, 董利利, 李富翠, 韩烈保, 王祥. 不同有机/无机氮添加对草原土壤氮素分配和转化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 36-46. |
| [11] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [12] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| [13] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| [14] | 周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52. |
| [15] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||