

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 61-75.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021109
李满有1( ), 李东宁2, 王斌1, 李小云1, 沈笑天1, 曹立娟1, 倪旺1, 王腾飞1, 兰剑1,3(
), 李东宁2, 王斌1, 李小云1, 沈笑天1, 曹立娟1, 倪旺1, 王腾飞1, 兰剑1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-23
修回日期:2021-04-26
出版日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-03-30
通讯作者:
兰剑
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: ndlanjian@163.com基金资助:
Man-you LI1( ), Dong-ning LI2, Bin WANG1, Xiao-yun LI1, Xiao-tian SHEN1, Li-juan CAO1, Wang NI1, Teng-fei WANG1, Jian LAN1,3(
), Dong-ning LI2, Bin WANG1, Xiao-yun LI1, Xiao-tian SHEN1, Li-juan CAO1, Wang NI1, Teng-fei WANG1, Jian LAN1,3( )
)
Received:2021-03-23
Revised:2021-04-26
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-03-30
Contact:
Jian LAN
摘要:
以紫花苜蓿品种‘巨能7’、‘三得利’为供试材料,采用混播方式(‘巨能7’单播,‘巨能7’与‘三得利’同行混播,‘巨能7’与‘三得利’间行混播)和播种量(13.5、18.0、22.5 kg·hm-2)二因素随机区组设计,探究了干旱地区滴灌条件下混播方式和播种量对2017-2019年紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响,并利用主成分分析方法(principal component analysis, PCA)进行综合评价,以期得到紫花苜蓿适宜混播方式和播种量。结果表明,混播方式和播种量对2017-2019年苜蓿平均株高、一级分枝数、干草产量、粗灰分、中性洗涤纤维含量和相对饲喂价值影响显著(P<0.05),而对鲜干比、叶茎比、酸性洗涤纤维和粗蛋白含量影响不显著。其中,‘巨能7’与‘三得利’同行混播、播种量为18.0 kg·hm-2时苜蓿干草产量显著高于间行混播、播种量为22.5 kg·hm-2组合,高达16.79 t·hm-2;‘巨能7’与‘三得利’同行混播、播种量为18.0 kg·hm-2时苜蓿相对饲喂价值为156.87,仅次于同行混播、播种量为13.5 kg·hm-2组合。经PCA综合分析,‘巨能7’与‘三得利’同行混播、播种量为18.0 kg·hm-2时苜蓿综合表现最好,可在宁夏引黄灌区推广应用。
李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75.
Man-you LI, Dong-ning LI, Bin WANG, Xiao-yun LI, Xiao-tian SHEN, Li-juan CAO, Wang NI, Teng-fei WANG, Jian LAN. The effect of mixed sowing and sowing rate of different alfalfa varieties on the yield and quality of forage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 61-75.
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 13.5 (B1) | 18.0 (B2) | 22.5 (B3) | |
| A1 (‘巨能7’单播‘Magnum Ⅶ’ unicast) | A1B1 | A1B2 | A1B3 |
| A2 (‘巨能7’与‘三得利’同行混播‘Magnum Ⅶ’ and ‘Sanditi’ peer mixed) | A2B1 | A2B2 | A2B3 |
| A3 (‘巨能7’与‘三得利’间行混播‘Magnum Ⅶ’ and ‘Sanditi’ interline mixed) | A3B1 | A3B2 | A3B3 |
表1 试验设计
Table 1 Experiment design
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 13.5 (B1) | 18.0 (B2) | 22.5 (B3) | |
| A1 (‘巨能7’单播‘Magnum Ⅶ’ unicast) | A1B1 | A1B2 | A1B3 |
| A2 (‘巨能7’与‘三得利’同行混播‘Magnum Ⅶ’ and ‘Sanditi’ peer mixed) | A2B1 | A2B2 | A2B3 |
| A3 (‘巨能7’与‘三得利’间行混播‘Magnum Ⅶ’ and ‘Sanditi’ interline mixed) | A3B1 | A3B2 | A3B3 |
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 一级分枝数 Number of first-level branches (pieces·m-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 73.31±2.33a | 73.58±3.14a | 71.21±0.27b | 85±1.52b | 109±1.45b | 143±6.10a |
| B2 | 72.70±1.23a | 77.10±3.80a | 77.19±1.34a | 112±2.44a | 132±6.35a | 144±3.45a | |
| B3 | 73.76±0.89a | 77.93±4.60a | 73.77±2.28ab | 102±1.23ab | 102±1.23b | 105±6.57b | |
| A2 | B1 | 82.04±1.58a | 78.25±3.74a | 76.37±0.49a | 100±3.95a | 104±3.25b | 164±8.14ab |
| B2 | 81.31±1.25a | 78.88±3.83a | 78.42±0.45a | 99±2.17a | 129±1.56a | 175±2.47a | |
| B3 | 80.34±1.20a | 78.25±3.02a | 81.33±7.57a | 103±1.47a | 117±4.25ab | 158±7.12b | |
| A3 | B1 | 77.36±0.33a | 77.25±2.74a | 79.05±0.50a | 87±1.64b | 96±4.98b | 139±4.36a |
| B2 | 80.74±0.88a | 76.68±4.53a | 79.60±0.60a | 102±1.45a | 109±2.39a | 131±2.28a | |
| B3 | 76.06±1.00a | 78.55±3.79a | 76.28±1.38a | 104±1.42a | 105±3.33a | 112±3.18b | |
表2 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿株高、一级分枝数的影响
Table 2 The influence of mixed mode and sowing amount on alfalfa plant height and the number of first-level branches
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 一级分枝数 Number of first-level branches (pieces·m-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 73.31±2.33a | 73.58±3.14a | 71.21±0.27b | 85±1.52b | 109±1.45b | 143±6.10a |
| B2 | 72.70±1.23a | 77.10±3.80a | 77.19±1.34a | 112±2.44a | 132±6.35a | 144±3.45a | |
| B3 | 73.76±0.89a | 77.93±4.60a | 73.77±2.28ab | 102±1.23ab | 102±1.23b | 105±6.57b | |
| A2 | B1 | 82.04±1.58a | 78.25±3.74a | 76.37±0.49a | 100±3.95a | 104±3.25b | 164±8.14ab |
| B2 | 81.31±1.25a | 78.88±3.83a | 78.42±0.45a | 99±2.17a | 129±1.56a | 175±2.47a | |
| B3 | 80.34±1.20a | 78.25±3.02a | 81.33±7.57a | 103±1.47a | 117±4.25ab | 158±7.12b | |
| A3 | B1 | 77.36±0.33a | 77.25±2.74a | 79.05±0.50a | 87±1.64b | 96±4.98b | 139±4.36a |
| B2 | 80.74±0.88a | 76.68±4.53a | 79.60±0.60a | 102±1.45a | 109±2.39a | 131±2.28a | |
| B3 | 76.06±1.00a | 78.55±3.79a | 76.28±1.38a | 104±1.42a | 105±3.33a | 112±3.18b | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 一级分枝数Number of primary branches (pieces·m-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 73.26b | 76.14a | 74.52a | 97.07a | 106.40a | 115.18b |
| A2 | 81.23a | 78.46a | 78.71a | 100.67a | 116.67a | 165.67a | |
| A3 | 78.05ab | 77.49a | 78.31a | 97.67a | 103.33a | 127.33b | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 77.57a | 76.30a | 76.01a | 88.07b | 95.07b | 133.18a |
| B2 | 78.25a | 77.55a | 78.40a | 104.33a | 123.33a | 150.00a | |
| B3 | 76.72a | 78.24a | 77.13a | 103.00a | 108.00ab | 125.00a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.012* | 0.244 | 0.392 | 0.820 | 0.330 | 0.024* |
| B | 0.554 | 0.337 | 0.774 | 0.034* | 0.022* | 0.351 | |
| A×B | 0.962 | 0.971 | 0.857 | 0.241 | 0.629 | 0.748 | |
表3 混播方式和播种量互作对苜蓿株高、一级分枝数的影响
Table 3 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on alfalfa plant height and primary branch number
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 株高Plant height (cm) | 一级分枝数Number of primary branches (pieces·m-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 73.26b | 76.14a | 74.52a | 97.07a | 106.40a | 115.18b |
| A2 | 81.23a | 78.46a | 78.71a | 100.67a | 116.67a | 165.67a | |
| A3 | 78.05ab | 77.49a | 78.31a | 97.67a | 103.33a | 127.33b | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 77.57a | 76.30a | 76.01a | 88.07b | 95.07b | 133.18a |
| B2 | 78.25a | 77.55a | 78.40a | 104.33a | 123.33a | 150.00a | |
| B3 | 76.72a | 78.24a | 77.13a | 103.00a | 108.00ab | 125.00a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.012* | 0.244 | 0.392 | 0.820 | 0.330 | 0.024* |
| B | 0.554 | 0.337 | 0.774 | 0.034* | 0.022* | 0.351 | |
| A×B | 0.962 | 0.971 | 0.857 | 0.241 | 0.629 | 0.748 | |
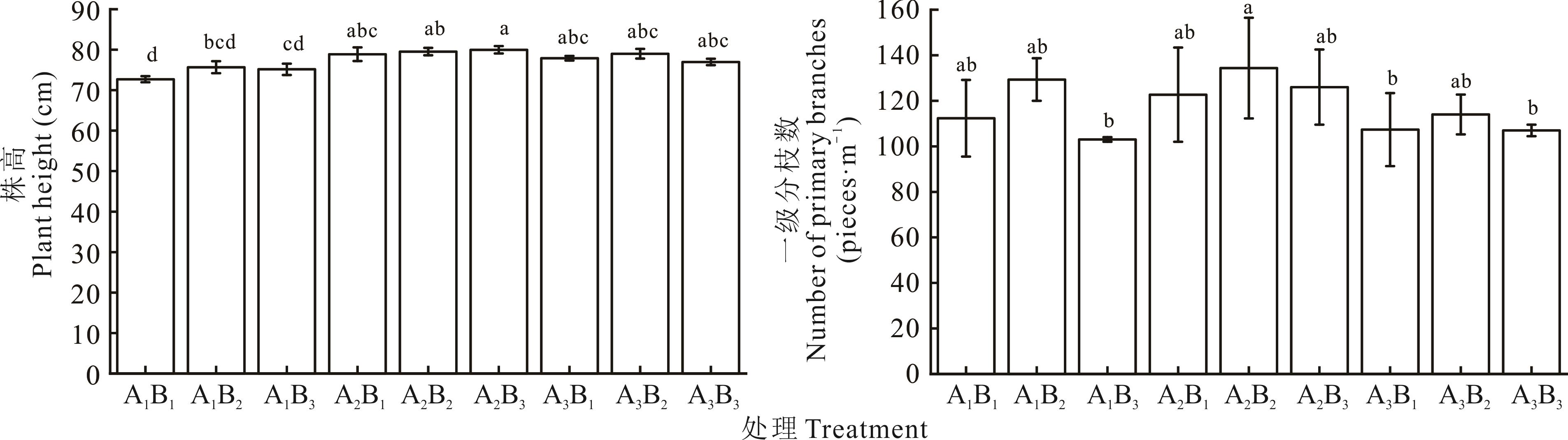
图1 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿3年株高、一级分枝数均值的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著,下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments, the same below.
Fig.1 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the average value of three-year alfalfa plant height and the number of primary branches
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 叶茎比Leaf-stem ratio | 鲜干比Fresh-dry ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 0.83±0.12a | 0.63±0.54ab | 0.79±0.09a | 2.94±0.50a | 4.36±0.41a | 4.31±0.28a |
| B2 | 0.87±0.29a | 0.56±0.62b | 0.83±0.24a | 3.21±0.88a | 4.30±0.69a | 4.17±0.56a | |
| B3 | 0.72±0.34b | 0.66±0.47a | 0.86±0.15a | 3.23±0.86a | 4.22±0.21a | 4.16±0.66a | |
| A2 | B1 | 0.78±0.32a | 0.71±0.41a | 0.81±0.39a | 2.63±0.24a | 4.28±0.65ab | 4.44±0.50a |
| B2 | 0.72±0.13a | 0.70±0.28a | 0.81±0.11a | 2.80±0.14a | 4.72±0.44a | 4.23±0.49a | |
| B3 | 0.72±0.30a | 0.70±0.42a | 0.86±0.35a | 2.88±0.19a | 4.12±0.76b | 4.07±0.65a | |
| A3 | B1 | 0.83±0.18a | 0.65±0.75a | 0.82±0.13a | 2.97±0.59a | 4.55±0.51a | 4.17±0.44a |
| B2 | 0.81±0.09a | 0.70±0.37a | 0.83±0.20a | 3.10±0.62a | 4.34±0.24a | 4.34±0.83a | |
| B3 | 0.80±0.13a | 0.69±0.39a | 0.90±0.06a | 2.89±0.26a | 4.32±0.30a | 4.21±0.71a | |
表4 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿叶茎比、鲜干比的影响
Table 4 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on alfalfa leaf-stem ratio and fresh-dry ratio
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 叶茎比Leaf-stem ratio | 鲜干比Fresh-dry ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 0.83±0.12a | 0.63±0.54ab | 0.79±0.09a | 2.94±0.50a | 4.36±0.41a | 4.31±0.28a |
| B2 | 0.87±0.29a | 0.56±0.62b | 0.83±0.24a | 3.21±0.88a | 4.30±0.69a | 4.17±0.56a | |
| B3 | 0.72±0.34b | 0.66±0.47a | 0.86±0.15a | 3.23±0.86a | 4.22±0.21a | 4.16±0.66a | |
| A2 | B1 | 0.78±0.32a | 0.71±0.41a | 0.81±0.39a | 2.63±0.24a | 4.28±0.65ab | 4.44±0.50a |
| B2 | 0.72±0.13a | 0.70±0.28a | 0.81±0.11a | 2.80±0.14a | 4.72±0.44a | 4.23±0.49a | |
| B3 | 0.72±0.30a | 0.70±0.42a | 0.86±0.35a | 2.88±0.19a | 4.12±0.76b | 4.07±0.65a | |
| A3 | B1 | 0.83±0.18a | 0.65±0.75a | 0.82±0.13a | 2.97±0.59a | 4.55±0.51a | 4.17±0.44a |
| B2 | 0.81±0.09a | 0.70±0.37a | 0.83±0.20a | 3.10±0.62a | 4.34±0.24a | 4.34±0.83a | |
| B3 | 0.80±0.13a | 0.69±0.39a | 0.90±0.06a | 2.89±0.26a | 4.32±0.30a | 4.21±0.71a | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 叶茎比 Leaf-stem ratio | 鲜干比 Fresh-dry ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 0.81a | 0.62a | 0.83a | 3.13ab | 4.29a | 4.21a |
| A2 | 0.74a | 0.70a | 0.83a | 2.77b | 4.37a | 4.25a | |
| A3 | 0.81a | 0.77a | 0.93a | 3.34a | 4.40a | 4.24a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 0.81a | 0.66a | 0.81a | 2.85a | 4.40a | 4.31a |
| B2 | 0.80a | 0.65a | 0.81a | 3.04a | 4.45a | 4.25a | |
| B3 | 0.75a | 0.78a | 0.97a | 3.36a | 4.22a | 4.15a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.100 | 0.182 | 0.476 | 0.023* | 0.893 | 0.982 |
| B | 0.166 | 0.267 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.604 | 0.689 | |
| A×B | 0.433 | 0.473 | 0.448 | 0.603 | 0.785 | 0.880 | |
表5 混播方式和播种量互作对苜蓿叶茎比、鲜干比的影响
Table 5 The effect of the interaction of mixed mode and sowing amount on alfalfa leaf stem-ratio and fresh-dry ratio
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 叶茎比 Leaf-stem ratio | 鲜干比 Fresh-dry ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 0.81a | 0.62a | 0.83a | 3.13ab | 4.29a | 4.21a |
| A2 | 0.74a | 0.70a | 0.83a | 2.77b | 4.37a | 4.25a | |
| A3 | 0.81a | 0.77a | 0.93a | 3.34a | 4.40a | 4.24a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 0.81a | 0.66a | 0.81a | 2.85a | 4.40a | 4.31a |
| B2 | 0.80a | 0.65a | 0.81a | 3.04a | 4.45a | 4.25a | |
| B3 | 0.75a | 0.78a | 0.97a | 3.36a | 4.22a | 4.15a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.100 | 0.182 | 0.476 | 0.023* | 0.893 | 0.982 |
| B | 0.166 | 0.267 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.604 | 0.689 | |
| A×B | 0.433 | 0.473 | 0.448 | 0.603 | 0.785 | 0.880 | |
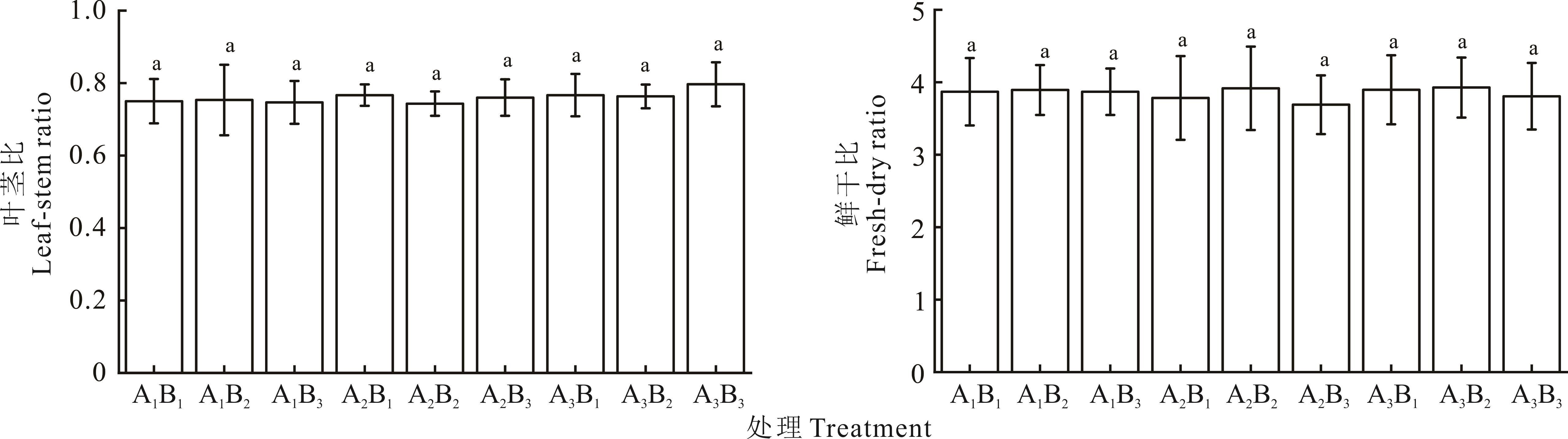
图2 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿3年叶茎比、鲜干比均值的影响
Fig.2 Effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the average value of leaf-stem ratio and fresh-dry ratio of alfalfa in 3 years
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 干草产量Hay yield (t·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 15.60±0.50a | 16.58±0.56a | 14.44±0.31a |
| B2 | 15.40±0.66a | 16.85±1.00a | 14.85±0.52a | |
| B3 | 16.40±0.53a | 16.39±0.64a | 14.23±0.47a | |
| A2 | B1 | 16.40±0.52a | 15.89±0.93a | 15.82±0.28a |
| B2 | 16.50±0.95a | 16.67±0.32a | 16.20±0.22a | |
| B3 | 16.50±1.17a | 16.28±1.20a | 15.24±0.18a | |
| A3 | B1 | 13.80±0.58b | 15.22±1.25b | 15.45±0.23a |
| B2 | 16.30±1.13a | 17.38±1.02a | 15.56±0.56a | |
| B3 | 13.30±1.10b | 15.12±0.58b | 12.98±0.61b | |
表6 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿干草产量的影响
Table 6 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on alfalfa hay yield
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 干草产量Hay yield (t·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 15.60±0.50a | 16.58±0.56a | 14.44±0.31a |
| B2 | 15.40±0.66a | 16.85±1.00a | 14.85±0.52a | |
| B3 | 16.40±0.53a | 16.39±0.64a | 14.23±0.47a | |
| A2 | B1 | 16.40±0.52a | 15.89±0.93a | 15.82±0.28a |
| B2 | 16.50±0.95a | 16.67±0.32a | 16.20±0.22a | |
| B3 | 16.50±1.17a | 16.28±1.20a | 15.24±0.18a | |
| A3 | B1 | 13.80±0.58b | 15.22±1.25b | 15.45±0.23a |
| B2 | 16.30±1.13a | 17.38±1.02a | 15.56±0.56a | |
| B3 | 13.30±1.10b | 15.12±0.58b | 12.98±0.61b | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 干草产量Hay yield (t·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 15.80a | 16.61a | 14.51a |
| A2 | 16.13a | 16.28a | 15.42a | |
| A3 | 14.47b | 15.91a | 14.60a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 15.27a | 15.90a | 15.24a |
| B2 | 15.73a | 16.97a | 15.14a | |
| B3 | 15.40a | 15.93a | 14.15a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.001** | 0.409 | 0.235 |
| B | 0.442 | 0.087 | 0.135 | |
| A×B | 0.001** | 0.471 | 0.366 | |
表7 混播方式和播种量互作对苜蓿干草产量的影响
Table 7 Interaction of mixed mode and sowing amount on the yield of alfalfa hay yield
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 干草产量Hay yield (t·hm-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 15.80a | 16.61a | 14.51a |
| A2 | 16.13a | 16.28a | 15.42a | |
| A3 | 14.47b | 15.91a | 14.60a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 15.27a | 15.90a | 15.24a |
| B2 | 15.73a | 16.97a | 15.14a | |
| B3 | 15.40a | 15.93a | 14.15a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.001** | 0.409 | 0.235 |
| B | 0.442 | 0.087 | 0.135 | |
| A×B | 0.001** | 0.471 | 0.366 | |
| 混播方式Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 粗灰分含量Crude ash content (%) | 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 9.84±0.45a | 11.76±0.46a | 9.94±0.16a | 21.21±0.52a | 17.03±0.27a | 16.19±0.60a |
| B2 | 9.50±0.12ab | 10.80±0.46ab | 9.51±0.39a | 21.32±0.26a | 17.34±0.32a | 16.59±1.01a | |
| B3 | 8.47±0.06b | 10.11±0.39b | 9.84±0.21a | 20.77±0.15a | 16.83±0.68a | 16.31±0.39a | |
| A2 | B1 | 9.52±0.23a | 11.34±0.37a | 9.96±0.85a | 21.02±0.17a | 16.78±0.38a | 16.53±0.83a |
| B2 | 8.42±0.47b | 9.75±0.16b | 9.27±0.78a | 18.79±0.65a | 16.46±0.39a | 16.53±0.11a | |
| B3 | 8.94±0.27ab | 10.09±0.41b | 9.88±0.62a | 20.20±0.31a | 16.89±0.37a | 17.92±1.11a | |
| A3 | B1 | 9.81±0.35a | 11.18±0.28a | 11.97±2.75a | 21.24±0.22a | 16.79±0.11a | 17.20±0.25a |
| B2 | 9.70±0.36a | 10.23±0.54a | 8.56±0.32c | 20.82±0.44a | 16.46±0.73a | 16.75±0.69a | |
| B3 | 9.72±0.15a | 10.78±0.32a | 10.33±0.34b | 20.61±0.12a | 17.12±0.37a | 17.68±0.23a | |
表8 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿粗灰分、粗蛋白含量的影响
Table 8 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the crude ash and crude protein content of alfalfa
| 混播方式Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 粗灰分含量Crude ash content (%) | 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 9.84±0.45a | 11.76±0.46a | 9.94±0.16a | 21.21±0.52a | 17.03±0.27a | 16.19±0.60a |
| B2 | 9.50±0.12ab | 10.80±0.46ab | 9.51±0.39a | 21.32±0.26a | 17.34±0.32a | 16.59±1.01a | |
| B3 | 8.47±0.06b | 10.11±0.39b | 9.84±0.21a | 20.77±0.15a | 16.83±0.68a | 16.31±0.39a | |
| A2 | B1 | 9.52±0.23a | 11.34±0.37a | 9.96±0.85a | 21.02±0.17a | 16.78±0.38a | 16.53±0.83a |
| B2 | 8.42±0.47b | 9.75±0.16b | 9.27±0.78a | 18.79±0.65a | 16.46±0.39a | 16.53±0.11a | |
| B3 | 8.94±0.27ab | 10.09±0.41b | 9.88±0.62a | 20.20±0.31a | 16.89±0.37a | 17.92±1.11a | |
| A3 | B1 | 9.81±0.35a | 11.18±0.28a | 11.97±2.75a | 21.24±0.22a | 16.79±0.11a | 17.20±0.25a |
| B2 | 9.70±0.36a | 10.23±0.54a | 8.56±0.32c | 20.82±0.44a | 16.46±0.73a | 16.75±0.69a | |
| B3 | 9.72±0.15a | 10.78±0.32a | 10.33±0.34b | 20.61±0.12a | 17.12±0.37a | 17.68±0.23a | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 粗灰分含量Crude ash content (%) | 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 9.27ab | 10.89a | 9.76a | 21.10a | 17.07a | 16.36a |
| A2 | 8.96b | 10.39a | 9.70a | 20.00b | 16.71a | 16.99a | |
| A3 | 9.74a | 10.73a | 10.29a | 20.89a | 16.79a | 17.21a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 9.72a | 11.43a | 10.39a | 21.16a | 16.87a | 16.64a |
| B2 | 9.21ab | 10.26b | 9.34a | 20.51b | 16.75a | 16.62a | |
| B3 | 9.04b | 10.33b | 10.02a | 20.31b | 16.95a | 17.30a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.022* | 0.197 | 0.433 | 0.001** | 0.852 | 0.517 |
| B | 0.041* | 0.001** | 0.120 | 0.012* | 0.957 | 0.596 | |
| A×B | 0.106 | 0.241 | 0.040* | 0.011* | 0.959 | 0.895 | |
表9 混播方式和播种量互作对苜蓿粗灰分、粗蛋白含量的影响
Table 9 The interaction of mixed mode and sowing amount on the crude ash and crude protein content of alfalfa
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 粗灰分含量Crude ash content (%) | 粗蛋白含量Crude protein content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 9.27ab | 10.89a | 9.76a | 21.10a | 17.07a | 16.36a |
| A2 | 8.96b | 10.39a | 9.70a | 20.00b | 16.71a | 16.99a | |
| A3 | 9.74a | 10.73a | 10.29a | 20.89a | 16.79a | 17.21a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 9.72a | 11.43a | 10.39a | 21.16a | 16.87a | 16.64a |
| B2 | 9.21ab | 10.26b | 9.34a | 20.51b | 16.75a | 16.62a | |
| B3 | 9.04b | 10.33b | 10.02a | 20.31b | 16.95a | 17.30a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.022* | 0.197 | 0.433 | 0.001** | 0.852 | 0.517 |
| B | 0.041* | 0.001** | 0.120 | 0.012* | 0.957 | 0.596 | |
| A×B | 0.106 | 0.241 | 0.040* | 0.011* | 0.959 | 0.895 | |

图4 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿3年粗灰分、粗蛋白含量均值的影响
Fig.4 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the average value of crude ash and crude protein content of alfalfa in 3 years
| 混播方式Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 中性洗涤纤维含量 Neutral detergent fiber content (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维含量 Acid detergent fiber content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 45.72±3.26a | 42.69±1.09a | 40.79±0.63a | 32.62±2.58a | 23.97±1.55a | 22.84±1.47a |
| B2 | 44.13±6.56a | 39.63±6.68a | 39.68±2.12a | 32.68±8.39a | 21.33±1.57a | 21.53±0.31a | |
| B3 | 45.14±0.79a | 41.35±2.37a | 39.46±4.48a | 32.83±1.21a | 22.12±1.05a | 20.75±2.12a | |
| A2 | B1 | 44.74±1.38a | 40.79±3.62a | 37.98±2.70a | 34.47±5.32a | 20.50±2.23a | 19.79±5.57a |
| B2 | 46.47±4.48a | 40.06±2.09a | 38.16±1.88a | 36.18±5.65a | 21.70±2.12a | 20.07±4.79a | |
| B3 | 46.27±0.46a | 40.94±1.01a | 39.09±2.73a | 36.60±5.32a | 21.48±3.14a | 21.31±3.21a | |
| A3 | B1 | 46.50±2.58a | 41.65±1.35a | 37.75±1.17a | 33.03±3.24a | 22.19±2.27a | 20.72±2.92a |
| B2 | 44.92±2.32a | 42.01±0.55a | 38.43±3.85a | 34.14±4.42a | 22.15±4.13a | 19.75±1.65a | |
| B3 | 46.34±5.26a | 40.68±1.41a | 38.52±1.67a | 34.93±3.25a | 21.26±2.25a | 20.95±2.68a | |
表10 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响
Table 10 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the content of neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber of alfalfa
| 混播方式Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 中性洗涤纤维含量 Neutral detergent fiber content (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维含量 Acid detergent fiber content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 45.72±3.26a | 42.69±1.09a | 40.79±0.63a | 32.62±2.58a | 23.97±1.55a | 22.84±1.47a |
| B2 | 44.13±6.56a | 39.63±6.68a | 39.68±2.12a | 32.68±8.39a | 21.33±1.57a | 21.53±0.31a | |
| B3 | 45.14±0.79a | 41.35±2.37a | 39.46±4.48a | 32.83±1.21a | 22.12±1.05a | 20.75±2.12a | |
| A2 | B1 | 44.74±1.38a | 40.79±3.62a | 37.98±2.70a | 34.47±5.32a | 20.50±2.23a | 19.79±5.57a |
| B2 | 46.47±4.48a | 40.06±2.09a | 38.16±1.88a | 36.18±5.65a | 21.70±2.12a | 20.07±4.79a | |
| B3 | 46.27±0.46a | 40.94±1.01a | 39.09±2.73a | 36.60±5.32a | 21.48±3.14a | 21.31±3.21a | |
| A3 | B1 | 46.50±2.58a | 41.65±1.35a | 37.75±1.17a | 33.03±3.24a | 22.19±2.27a | 20.72±2.92a |
| B2 | 44.92±2.32a | 42.01±0.55a | 38.43±3.85a | 34.14±4.42a | 22.15±4.13a | 19.75±1.65a | |
| B3 | 46.34±5.26a | 40.68±1.41a | 38.52±1.67a | 34.93±3.25a | 21.26±2.25a | 20.95±2.68a | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 中性洗涤纤维含量Neutral detergent fiber content (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维含量Acid detergent fiber content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 44.97a | 41.22a | 39.98a | 32.67b | 22.47a | 21.71a |
| A2 | 45.77a | 40.62a | 38.41a | 35.70a | 21.23a | 20.39a | |
| A3 | 45.73a | 41.45a | 38.23a | 34.00ab | 21.87a | 20.47a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 45.47a | 41.71a | 38.84a | 33.33a | 22.22a | 21.12a |
| B2 | 45.13a | 40.57a | 38.76a | 34.27a | 21.73a | 20.45a | |
| B3 | 45.87a | 40.99a | 39.02a | 34.77a | 21.62a | 21.00a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.676 | 0.746 | 0.419 | 0.026* | 0.233 | 0.133 |
| B | 0.771 | 0.607 | 0.982 | 0.369 | 0.664 | 0.595 | |
| A×B | 0.708 | 0.719 | 0.954 | 0.922 | 0.245 | 0.326 | |
表11 混播方式和播种量互作对苜蓿中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维含量的影响
Table 11 The interaction of mixed mode and sowing amount on the content of neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber of alfalfa
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 中性洗涤纤维含量Neutral detergent fiber content (%) | 酸性洗涤纤维含量Acid detergent fiber content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 44.97a | 41.22a | 39.98a | 32.67b | 22.47a | 21.71a |
| A2 | 45.77a | 40.62a | 38.41a | 35.70a | 21.23a | 20.39a | |
| A3 | 45.73a | 41.45a | 38.23a | 34.00ab | 21.87a | 20.47a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 45.47a | 41.71a | 38.84a | 33.33a | 22.22a | 21.12a |
| B2 | 45.13a | 40.57a | 38.76a | 34.27a | 21.73a | 20.45a | |
| B3 | 45.87a | 40.99a | 39.02a | 34.77a | 21.62a | 21.00a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.676 | 0.746 | 0.419 | 0.026* | 0.233 | 0.133 |
| B | 0.771 | 0.607 | 0.982 | 0.369 | 0.664 | 0.595 | |
| A×B | 0.708 | 0.719 | 0.954 | 0.922 | 0.245 | 0.326 | |

图5 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿3年中性洗涤纤维、酸性洗涤纤维含量均值的影响
Fig.5 Effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the average content of neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber of alfalfa in 3 years
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 相对饲喂价值Relative feeding value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 129.26±12.12a | 153.03±15.34b | 162.16±14.55b |
| B2 | 133.95±5.25a | 169.67±14.22a | 169.09±10.84ab | |
| B3 | 130.66±7.98a | 161.23±11.47ab | 171.47±17.88a | |
| A2 | B1 | 129.24±13.45a | 166.32±15.98a | 179.98±19.65a |
| B2 | 121.85±10.27b | 167.18±10.65a | 178.60±11.25a | |
| B3 | 121.59±12.45b | 163.98±12.32a | 172.05±13.65a | |
| A3 | B1 | 127.79±11.75a | 159.95±14.34a | 179.29±17.85a |
| B2 | 129.15±9.21a | 158.64±18.95a | 177.95±14.51a | |
| B3 | 123.99±9.36a | 165.42±11.08a | 175.28±15.40a | |
表12 混播方式和播种量对苜蓿相对饲喂价值的影响
Table 12 The effect of mixed mode and sowing amount on the relative feeding value of alfalfa
混播方式 Mixed mode | 播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) | 相对饲喂价值Relative feeding value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
| A1 | B1 | 129.26±12.12a | 153.03±15.34b | 162.16±14.55b |
| B2 | 133.95±5.25a | 169.67±14.22a | 169.09±10.84ab | |
| B3 | 130.66±7.98a | 161.23±11.47ab | 171.47±17.88a | |
| A2 | B1 | 129.24±13.45a | 166.32±15.98a | 179.98±19.65a |
| B2 | 121.85±10.27b | 167.18±10.65a | 178.60±11.25a | |
| B3 | 121.59±12.45b | 163.98±12.32a | 172.05±13.65a | |
| A3 | B1 | 127.79±11.75a | 159.95±14.34a | 179.29±17.85a |
| B2 | 129.15±9.21a | 158.64±18.95a | 177.95±14.51a | |
| B3 | 123.99±9.36a | 165.42±11.08a | 175.28±15.40a | |
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 相对饲喂价值Relative feeding value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 131.29a | 161.31a | 167.57b |
| A2 | 124.23b | 165.83a | 176.88a | |
| A3 | 126.98b | 161.34a | 177.51a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 128.76a | 159.77a | 173.81a |
| B2 | 128.32a | 165.16a | 175.21a | |
| B3 | 125.41a | 163.54a | 172.93a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.002** | 0.365 | 0.025* |
| B | 0.106 | 0.322 | 0.821 | |
| A×B | 0.058 | 0.214 | 0.414 | |
表13 混播方式和播种量互作对苜蓿相对饲喂价值的影响
Table 13 The effect of the interaction of mixed mode and sowing amount on the relative feeding value of alfalfa
项目 Item | 处理 Treatment | 相对饲喂价值Relative feeding value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | ||
混播方式 Mixed mode (A) | A1 | 131.29a | 161.31a | 167.57b |
| A2 | 124.23b | 165.83a | 176.88a | |
| A3 | 126.98b | 161.34a | 177.51a | |
播种量 Sowing amount (kg·hm-2) (B) | B1 | 128.76a | 159.77a | 173.81a |
| B2 | 128.32a | 165.16a | 175.21a | |
| B3 | 125.41a | 163.54a | 172.93a | |
P值 P value | A | 0.002** | 0.365 | 0.025* |
| B | 0.106 | 0.322 | 0.821 | |
| A×B | 0.058 | 0.214 | 0.414 | |
| 性状Traits | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| X2 | 0.306 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X3 | 0.244 | -0.489 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X4 | -0.242 | -0.112 | -0.409 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X5 | 0.099 | 0.540 | -0.671* | 0.046 | 1.000 | |||||
| X6 | 0.329 | 0.469 | -0.576 | 0.408 | 0.420 | 1.000 | ||||
| X7 | -0.322 | -0.462 | 0.579 | -0.408 | -0.432 | -0.130 | 1.000 | |||
| X8 | 0.374 | 0.461 | 0.167 | 0.055 | 0.100 | 0.077 | -0.071 | 1.000 | ||
| X9 | -0.052 | -0.125 | 0.243 | 0.306 | 0.031 | -0.113 | 0.107 | 0.736* | 1.000 | |
| X10 | 0.371 | 0.309 | 0.241 | 0.120 | 0.035 | 0.067 | -0.062 | 0.982** | 0.822** | 1.000 |
表14 苜蓿主要性状的相关系数矩阵
Table 14 Correlation coefficient matrix of main characters of alfalfa
| 性状Traits | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| X2 | 0.306 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X3 | 0.244 | -0.489 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X4 | -0.242 | -0.112 | -0.409 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X5 | 0.099 | 0.540 | -0.671* | 0.046 | 1.000 | |||||
| X6 | 0.329 | 0.469 | -0.576 | 0.408 | 0.420 | 1.000 | ||||
| X7 | -0.322 | -0.462 | 0.579 | -0.408 | -0.432 | -0.130 | 1.000 | |||
| X8 | 0.374 | 0.461 | 0.167 | 0.055 | 0.100 | 0.077 | -0.071 | 1.000 | ||
| X9 | -0.052 | -0.125 | 0.243 | 0.306 | 0.031 | -0.113 | 0.107 | 0.736* | 1.000 | |
| X10 | 0.371 | 0.309 | 0.241 | 0.120 | 0.035 | 0.067 | -0.062 | 0.982** | 0.822** | 1.000 |
性状 Traits | 因子1 Factor 1 | 因子2 Factor 2 | 因子3 Factor 3 | 因子4 Factor 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.339 | 0.340 | 0.661 | -0.452 |
| X2 | 0.732 | 0.086 | 0.412 | 0.361 |
| X3 | -0.691 | 0.525 | 0.252 | -0.346 |
| X4 | 0.377 | -0.043 | -0.818 | -0.276 |
| X5 | 0.678 | -0.164 | 0.074 | 0.528 |
| X6 | 0.878 | -0.220 | -0.024 | -0.381 |
| X7 | -0.878 | 0.224 | 0.031 | 0.374 |
| X8 | 0.372 | 0.907 | 0.034 | 0.122 |
| X9 | 0.080 | 0.822 | -0.490 | 0.104 |
| X10 | 0.317 | 0.943 | -0.059 | 0.017 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.518 | 2.913 | 1.592 | 1.120 |
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate (%) | 35.183 | 29.133 | 15.915 | 11.203 |
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 35.183 | 64.316 | 80.231 | 91.434 |
表15 苜蓿主要性状的特征值和累计贡献率
Table 15 Characteristic values and cumulative contribution rates of main characters of alfalfa
性状 Traits | 因子1 Factor 1 | 因子2 Factor 2 | 因子3 Factor 3 | 因子4 Factor 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.339 | 0.340 | 0.661 | -0.452 |
| X2 | 0.732 | 0.086 | 0.412 | 0.361 |
| X3 | -0.691 | 0.525 | 0.252 | -0.346 |
| X4 | 0.377 | -0.043 | -0.818 | -0.276 |
| X5 | 0.678 | -0.164 | 0.074 | 0.528 |
| X6 | 0.878 | -0.220 | -0.024 | -0.381 |
| X7 | -0.878 | 0.224 | 0.031 | 0.374 |
| X8 | 0.372 | 0.907 | 0.034 | 0.122 |
| X9 | 0.080 | 0.822 | -0.490 | 0.104 |
| X10 | 0.317 | 0.943 | -0.059 | 0.017 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 3.518 | 2.913 | 1.592 | 1.120 |
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate (%) | 35.183 | 29.133 | 15.915 | 11.203 |
| 累积贡献率Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 35.183 | 64.316 | 80.231 | 91.434 |
| 性状Traits | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | 性状Traits | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.181 | 0.199 | 0.524 | -0.427 | X6 | 0.468 | -0.129 | -0.019 | -0.360 |
| X2 | 0.390 | 0.050 | 0.327 | 0.341 | X7 | -0.468 | 0.131 | 0.025 | 0.353 |
| X3 | -0.368 | 0.308 | 0.200 | -0.327 | X8 | 0.198 | 0.531 | 0.027 | 0.115 |
| X4 | 0.201 | -0.025 | -0.648 | -0.261 | X9 | 0.043 | 0.482 | -0.388 | 0.098 |
| X5 | 0.361 | -0.096 | 0.059 | 0.499 | X10 | 0.169 | 0.553 | -0.047 | 0.016 |
表16 苜蓿主要性状的特征向量(Ai)
Table 16 Feature vectors (Ai) of main characters of alfalfa
| 性状Traits | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | 性状Traits | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.181 | 0.199 | 0.524 | -0.427 | X6 | 0.468 | -0.129 | -0.019 | -0.360 |
| X2 | 0.390 | 0.050 | 0.327 | 0.341 | X7 | -0.468 | 0.131 | 0.025 | 0.353 |
| X3 | -0.368 | 0.308 | 0.200 | -0.327 | X8 | 0.198 | 0.531 | 0.027 | 0.115 |
| X4 | 0.201 | -0.025 | -0.648 | -0.261 | X9 | 0.043 | 0.482 | -0.388 | 0.098 |
| X5 | 0.361 | -0.096 | 0.059 | 0.499 | X10 | 0.169 | 0.553 | -0.047 | 0.016 |
| 处理Treatment | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1B1 | -1.673 | -0.552 | -0.659 | 0.243 | 0.035 | -0.081 | 0.064 | -2.150 | -1.484 | -2.191 |
| A1B2 | -1.128 | 1.103 | -0.659 | 0.501 | 0.244 | -0.754 | 0.770 | 1.209 | 0.804 | 0.927 |
| A1B3 | -0.850 | -0.876 | -0.659 | 0.243 | 0.205 | 0.405 | -0.433 | -0.281 | 0.677 | -0.106 |
| A2B1 | 0.350 | 0.455 | 0.958 | -0.915 | 0.558 | 0.021 | -0.041 | 1.172 | 1.265 | 1.238 |
| A2B2 | 1.133 | 1.589 | -1.197 | 0.887 | 0.362 | 2.345 | -2.316 | 0.483 | -0.628 | 0.367 |
| A2B3 | 0.988 | 0.779 | -0.120 | -2.074 | 0.649 | -0.582 | 0.587 | -0.474 | -1.468 | -0.738 |
| A3B1 | -0.032 | -1.038 | 0.419 | 0.629 | -0.906 | -0.730 | 0.744 | 0.019 | 0.532 | 0.301 |
| A3B2 | 0.820 | -0.389 | -0.120 | 1.015 | 1.094 | 0.277 | -0.302 | 0.055 | 0.478 | 0.159 |
| A3B3 | 0.391 | -1.070 | 2.036 | -0.529 | -2.240 | -0.901 | 0.927 | -0.034 | -0.178 | 0.043 |
表17 播种量和混播方式下的苜蓿主要性状的标准化数据
Table 17 Standardized data of main traits of alfalfa under sowing amount and mixed mode
| 处理Treatment | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1B1 | -1.673 | -0.552 | -0.659 | 0.243 | 0.035 | -0.081 | 0.064 | -2.150 | -1.484 | -2.191 |
| A1B2 | -1.128 | 1.103 | -0.659 | 0.501 | 0.244 | -0.754 | 0.770 | 1.209 | 0.804 | 0.927 |
| A1B3 | -0.850 | -0.876 | -0.659 | 0.243 | 0.205 | 0.405 | -0.433 | -0.281 | 0.677 | -0.106 |
| A2B1 | 0.350 | 0.455 | 0.958 | -0.915 | 0.558 | 0.021 | -0.041 | 1.172 | 1.265 | 1.238 |
| A2B2 | 1.133 | 1.589 | -1.197 | 0.887 | 0.362 | 2.345 | -2.316 | 0.483 | -0.628 | 0.367 |
| A2B3 | 0.988 | 0.779 | -0.120 | -2.074 | 0.649 | -0.582 | 0.587 | -0.474 | -1.468 | -0.738 |
| A3B1 | -0.032 | -1.038 | 0.419 | 0.629 | -0.906 | -0.730 | 0.744 | 0.019 | 0.532 | 0.301 |
| A3B2 | 0.820 | -0.389 | -0.120 | 1.015 | 1.094 | 0.277 | -0.302 | 0.055 | 0.478 | 0.159 |
| A3B3 | 0.391 | -1.070 | 2.036 | -0.529 | -2.240 | -0.901 | 0.927 | -0.034 | -0.178 | 0.043 |
| 处理Treatment | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | Y | 排名Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1B1 | -1.142 | -3.623 | -0.720 | 0.319 | -1.680 | 9 |
| A1B2 | 0.969 | 0.249 | -0.519 | -0.313 | 0.323 | 4 |
| A1B3 | 0.218 | -0.432 | -1.292 | 0.052 | -0.272 | 6 |
| A2B1 | 0.430 | 2.266 | 0.631 | 0.466 | 1.054 | 2 |
| A2B2 | 3.887 | -0.569 | 0.457 | -1.263 | 1.239 | 1 |
| A2B3 | -0.485 | -1.027 | 2.748 | 0.954 | 0.082 | 5 |
| A3B1 | -1.378 | 0.767 | -0.921 | -0.509 | -0.509 | 7 |
| A3B2 | 0.374 | 1.332 | -0.961 | 1.840 | 0.626 | 3 |
| A3B3 | -2.873 | 1.037 | 0.579 | -1.546 | -0.864 | 8 |
表18 混播方式和播种量下的苜蓿主要性状的综合排名
Table 18 Comprehensive ranking of main traits of alfalfa under mixed mode and sowing amount
| 处理Treatment | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | Y | 排名Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1B1 | -1.142 | -3.623 | -0.720 | 0.319 | -1.680 | 9 |
| A1B2 | 0.969 | 0.249 | -0.519 | -0.313 | 0.323 | 4 |
| A1B3 | 0.218 | -0.432 | -1.292 | 0.052 | -0.272 | 6 |
| A2B1 | 0.430 | 2.266 | 0.631 | 0.466 | 1.054 | 2 |
| A2B2 | 3.887 | -0.569 | 0.457 | -1.263 | 1.239 | 1 |
| A2B3 | -0.485 | -1.027 | 2.748 | 0.954 | 0.082 | 5 |
| A3B1 | -1.378 | 0.767 | -0.921 | -0.509 | -0.509 | 7 |
| A3B2 | 0.374 | 1.332 | -0.961 | 1.840 | 0.626 | 3 |
| A3B3 | -2.873 | 1.037 | 0.579 | -1.546 | -0.864 | 8 |
| 1 | Zhang Y L, Pan D, Wu M H. Effect of mixed alfalfa and grass cultivation on the forage yield of grasslands after two-year mixed sowing. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(9): 2210-2219. |
| 张永亮, 潘东, 吴明浩. 苜蓿+禾草混播方式对二龄混播草地牧草产量的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(9): 2210-2219. | |
| 2 | Zhu H F, Wang L H, Lin Y F, et al. The study on production performance and feeding value of the different species of forage sorghum in Ningxia Yellow River irrigation area. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(5): 40-46. |
| 朱鸿福, 王丽慧, 林语梵, 等. 宁夏黄灌区国外饲用高粱品种生产性能及饲用价值研究. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(5): 40-46. | |
| 3 | Ding C L, Xu N X, Cheng Y H, et al. Production performance and fodder value of different silage maize varieties. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(6): 270-272. |
| 丁成龙, 许能祥, 程云辉, 等. 不同饲用玉米品种的生产性能及饲用价值比较. 江苏农业科学, 2009, 37(6): 270-272. | |
| 4 | Liu Q, Wang H M, Fu P, et al. Effects of different mixture models of Italian ryegrass and smooth vetch on above ground biomass and quality. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(10): 1584-1588. |
| 柳茜, 王红梅, 傅平, 等. 多花黑麦草+光叶紫花苕混播草地生产力特征. 草业科学, 2013, 30(10): 1584-1588. | |
| 5 | Tessema Z K, Feleke B S. Yield, yield dynamics and nutritional quality of grass-legume mixed pasture. Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences, 2018, 28(1): 155-164. |
| 6 | Xie K Y, Wang Y X, Wan J C, et al. Mechanisms and factors affecting nitrogen transfer in mixed legume/grass swards: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. |
| 谢开云, 王玉祥, 万江春, 等. 混播草地中豆科/禾本科牧草氮转移机理及其影响因素. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. | |
| 7 | Xie K Y, Zhao Y, Li X L, et al. Relationships between grasses and legumes in mixed grassland: A review. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(3): 284-296. |
| 谢开云, 赵云, 李向林, 等. 豆-禾混播草地种间关系研究进展. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 284-296. | |
| 8 | Wang Y G. Effects of multi-dosage soil amendment on turfgrass analyzed by grey relevancy. Pratacultural Science, 2007, 24(2): 92-95. |
| 王有国. 不同剂量改良剂施用效果的灰色关联性分析. 草业科学, 2007, 24(2): 92-95. | |
| 9 | Eaglesham A, Ayanaba A, Rao V R, et al. Improving the nitrogen nutrition of maize by intercropping with cowpea. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1981, 13(2): 169-171. |
| 10 | Droushiotis D N. Effect of variety and harvesting stage on forage production of vetch in a low rainfall environment. Field Crops Research, 1985, 10(3): 49-55. |
| 11 | Lv H G, Kang J M, Long R C, et al. Effects of seeding rate and row spacing on the hay yield and quality of alfalfa in saline-alkali land. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(3): 164-174. |
| 吕会刚, 康俊梅, 龙瑞才, 等. 播种量和行距配置对盐碱地紫花苜蓿草产量及品质的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 164-174. | |
| 12 | Min D D, Fan Y, Guo Z G, et al. Optimization of seed hydropriming conditions for Medicago sativa. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(4): 669-673. |
| 闵丹丹, 范燕, 郭正刚, 等. 紫花苜蓿种子水引发条件的优化. 草业科学, 2016, 33(4): 669-673. | |
| 13 | Zhang F, Kang J M, Zhao Z X, et al. Effect of between-row spacing and seeding rate on alfalfa hay yield and quality of Huang Huai Hai Plain. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(12): 2960-2967. |
| 张帆, 康俊梅, 赵忠祥, 等. 行距和播种量对黄淮海平原紫花苜蓿产草量及品质的影响. 草业科学, 2018, 35(12): 2960-2967. | |
| 14 | Gu C, Liu J Y, Du Y F, et al. Effects of seeding rates on forage yields and seed productions of Medicago falcata. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(2): 86-91. |
| 古琛, 刘佳月, 杜宇凡, 等. 播量对黄花苜蓿草产量与种子生产的影响. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(2): 86-91. | |
| 15 | Zhang H H, Zhang X Z, Lan J Y, et al. Effect of sowing rate on biological characteristics and yield of Medicago Sativa. Grass-Feeding Livestock, 2016, 3(3): 49-52. |
| 张荟荟, 张学洲, 兰吉勇, 等. 播种量对紫花苜蓿生物学特性及产草量的影响. 草食家畜, 2016, 3(3): 49-52. | |
| 16 | Yu Y C, Zhao Y H, Guo H J, et al. Effect of alfalfa sowing quantity in autumn on fresh yield in the second year. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2007, 28(5): 86-88. |
| 余有成, 赵永宏, 郭海俊, 等. 播种量对秋播苜蓿越年草产量的影响. 家畜生态学报, 2007, 28(5): 86-88. | |
| 17 | Wan Z Q. Studies on response of productivity and nitrogen allocation of artificial grassland to precipitation typical steppe in Inner Mongolia. Huhhot: Inner Mongolian University, 2018. |
| 万志强. 内蒙古典型草原区人工草地生产力和氮素分配对水分响应研究. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2018. | |
| 18 | Xie K Y, Li X L, He F, et al. Response of alfalfa and smooth brome to nitrogen fertilizer in monoculture and mixed grasslands. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(6): 148-156. |
| 谢开云, 李向林, 何峰, 等. 单播与混播下紫花苜蓿与无芒雀麦生物量对氮肥的响应. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 148-156. | |
| 19 | Zhang R P, Yu L, Lu W H. The effect of seeding rates and cutting time on yield and quality of mixture pasture. Pratacultural Science, 2009, 26(5): 139-143. |
| 张仁平, 于磊, 鲁为华. 混播比例和刈割期对混播草地产量及品质影响的研究. 草业科学, 2009, 26(5): 139-143. | |
| 20 | Wang H Q, Tian Y H, Huang W L, et al. Analyzing the impact of irrigation quantity on biomass and water use efficiency of main grasses in artificial grassland in Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 3225-3232. |
| 王海青, 田育红, 黄薇霖, 等. 不同灌溉量对内蒙古人工草地主要牧草产量和水分利用效率的影响. 生态学报, 2015, 35(10): 3225-3232. | |
| 21 | Xi W L, Zhang R P. Effect of mixed sowing ratio and cutting time on forage yield and interspecific competition. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2009, 31(4): 36-40. |
| 锡文林, 张仁平. 混播比例和刈割期对混播草地产草量及种间竞争的影响. 中国草地学报, 2009, 31(4): 36-40. | |
| 22 | Zhang X H, Zhu J Z, Ding H L. Effects of different mixed sowing patterns on productivity of legume/grass mixture. Grassland and Turf, 2014, 34(1): 44-48, 54. |
| 张鲜花, 朱进忠, 丁红领. 豆禾混播草地不同建植方式对草地生产性能的影响. 草原与草坪, 2014, 34(1): 44-48, 54. | |
| 23 | Zhu Y Q, Zheng W, Wang X, et al. Effect of mixed pattern on growth efficiency and mixed advantage of Bromus innermis+Onobrychis viciaefolia mixture pasture. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(11): 2335-2346. |
| 朱亚琼, 郑伟, 王祥, 等. 混播方式对无芒雀麦+红豆草混播草地植物生长效率及混播效应的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(11): 2335-2346. | |
| 24 | Liu P Q. Quality testing methods and quality management of feed and feed additives. Chinese Abstracts of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 33(8): 228. |
| 刘沛钦. 饲料及饲料添加剂质量检测方法与品质管理. 中国畜牧兽医文摘, 2017, 33(8): 228. | |
| 25 | Shu C C, Liu T, Wang Q, et al. Effects of seeding rate on botanical characteristics of Medicago sativa under different salt concentration. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(9): 1889-1897. |
| 舒朝成, 刘彤, 王倩, 等. 不同盐浓度下播种量对紫花苜蓿植物学特性的影响. 草业科学, 2017, 34(9): 1889-1897. | |
| 26 | Miao J S, Jia C L, Yang Q L, et al. Effects of quantities of seeds sowed in salina on the growth and yields of alfalfa. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2009, 24(S1): 309-311. |
| 苗锦山, 贾春林, 杨秋玲, 等. 不同播种量对盐碱地紫花苜蓿生育和产量的影响. 华北农学报, 2009, 24(S1): 309-311. | |
| 27 | Sun S X, Mao H M, Bi Y F. Study of the experiment of cultivation for alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2009(11): 210-211. |
| 孙仕仙, 毛华明, 毕玉芬. 苜蓿栽培试验研究. 现代农业科技, 2009(11): 210-211. | |
| 28 | Wang W, Xu C T. Evaluation on production performance of different mixture ratio of oat and common vetch in Henan County. Chinese Qinghai Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 2016, 46(1): 10-12. |
| 王伟, 徐成体. 河南县燕麦和箭筈豌豆不同混播比例草地生产性能的综合评价. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2016, 46(1): 10-12. | |
| 29 | Yao Z Y, Li J, Song L Z, et al. Study on the leguminous-gramineous grass mixed sowing in Bashang area of Zhangjiakou. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 1076-1082. |
| 姚泽英, 李军, 宋连昭, 等. 张家口坝上地区豆-禾牧草混播效果研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 1076-1082. | |
| 30 | Wang Y H, Wang C Z, Li D F, et al. Effects of seeding rate on plant number, production performance, and quality of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(2): 123-135. |
| 王彦华, 王成章, 李德锋, 等. 播种量和品种对紫花苜蓿植株动态变化、产量及品质的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 123-135. | |
| 31 | Li Y Z, Wu F, Shi S L, et al. Evaluation on production and nutritional value of 13 introduced alfalfa cultivars in Hexi corridor of Gansu Province. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2019, 37(5): 119-129. |
| 李玉珠, 吴芳, 师尚礼, 等. 河西走廊13个引进紫花苜蓿品种生产性能和营养价值评价. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(5): 119-129. | |
| 32 | Lloveras J, Chocarro C, Freixes O, et al. Yield, yield components, and forage nutritive value of alfalfa as affected by seeding rate under irrigated conditions. Agronomy Journal, 2008, 100(1): 191-197. |
| 33 | Li Y, You Y L, Wu R X, et al. Effect of different planting patterns on the production characters and forage quality of alfalfa in Haihe Plain. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(1): 257-262. |
| 李源, 游永亮, 武瑞鑫, 等. 不同种植方式对紫花苜蓿生产性状及饲用品质的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(1): 257-262. | |
| 34 | Chen Y, Wang Z S, Zhang X M, et al. Analysis of the nutritional components and feeding values of commonly used roughages. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(5): 117-125. |
| 陈艳, 王之盛, 张晓明, 等. 常用粗饲料营养成分和饲用价值分析. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 117-125. |
| [1] | 金有顺, 侯扶江. 放牧家畜养分消化率的测定[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 200-212. |
| [2] | 张欢, 牟怡晓, 张桂杰. 添加枸杞副产物对紫花苜蓿青贮发酵品质及微生物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 136-144. |
| [3] | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [4] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| [5] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 陈敏豪, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 白洁, 苏明. 化肥减量配施微生物肥料对垂穗披碱草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 53-61. |
| [6] | 李满有, 杨彦军, 王斌, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 李小云, 倪旺, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下燕麦与光叶紫花苕不同混播模式的生产性能、品质及综合评价研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 62-71. |
| [7] | 吴海艳, 曲尼, 曲珍, 同桑措姆, 达娃卓嘎, 德央, 尼玛卓嘎, 刘昭明, 马玉寿. 6个燕麦品种在昂仁县的生产性能及饲草品质比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 72-80. |
| [8] | 欧成明, 赵美琦, 孙铭, 毛培胜. 抗坏血酸和水杨酸丸衣对NaCl胁迫下紫花苜蓿种子发芽特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 93-101. |
| [9] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 赵雅姣, 王静. 内源异黄酮对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮及氮效率的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [10] | 撖冬荣, 姚拓, 李海云, 黄书超, 杨琰珊, 高亚敏, 李昌宁, 张银翠. 微生物肥料与化肥减量配施对多年生黑麦草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [11] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [12] | 刘启宇, 云岚, 陈逸凡, 郭宏宇, 李珍, 高志琦, 王俊, 石凤翎. 苜蓿—禾草混播草地牧草产量及种间竞争关系的动态研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 181-191. |
| [13] | 刘丽英, 贾玉山, 范文强, 尹强, 成启明, 王志军. 影响苜蓿自然干燥的主要环境因子研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 121-132. |
| [14] | 张岳阳, 李芳, 梁维维, 李彦忠. 新疆昌吉32个紫花苜蓿品种的田间抗病性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 133-146. |
| [15] | 王斌, 杨雨琦, 李满有, 倪旺, 海艺蕊, 张顺香, 董秀, 兰剑. 不同播种量下行距配置对紫花苜蓿产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 147-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||