

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 17-26.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022419
凤紫棋1,2( ), 孙文义1,3(
), 孙文义1,3( ), 穆兴民1,3, 高鹏1,3, 赵广举1,3, 陈帅4
), 穆兴民1,3, 高鹏1,3, 赵广举1,3, 陈帅4
收稿日期:2022-10-27
修回日期:2022-11-28
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-07-12
通讯作者:
孙文义
作者简介:E-mail: sunwy@ms.iswc.ac.cn基金资助:
Zi-qi FENG1,2( ), Wen-yi SUN1,3(
), Wen-yi SUN1,3( ), Xing-min MU1,3, Peng GAO1,3, Guang-ju ZHAO1,3, Shuai CHEN4
), Xing-min MU1,3, Peng GAO1,3, Guang-ju ZHAO1,3, Shuai CHEN4
Received:2022-10-27
Revised:2022-11-28
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-07-12
Contact:
Wen-yi SUN
摘要:
解析杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素,可为南方山区森林的可持续经营提供理论依据。通过收集115份杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性研究文献,采用相关性分析、方差分解分析和结构方程模型探究了环境因子和林分结构与杉木林下草本植物多样性的关系,通过最大熵模型模拟杉木人工林林下植物多样性较为丰富区域的潜在地理分布。结果表明:1)气候因子单独效应、气候和地形因子共同效应解释率较大,分别为19.31%、12.34%。2)年均降水量和郁闭度对林下草本植物多样性具有极显著影响(P<0.01),总影响系数分别为0.72和-0.49;海拔、年均气温、土壤有机质、全氮含量对林下植物多样性具有显著影响(P<0.05),总影响系数为-0.33、0.17、0.23和0.34。3)影响杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的主导环境因子及贡献率分别为:年均降水量(37.1%)>海拔(19.5%)>年均气温(15.2%)>土壤有机质(8.9%)>土壤全氮(7.5%),累积贡献率为88.2%。4)年均降水量≥1650 mm、年均气温18~22 ℃、海拔510~680 m、土壤有机质含量≥20 g·kg-1的区域林下草本植物多样性较为丰富。
凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26.
Zi-qi FENG, Wen-yi SUN, Xing-min MU, Peng GAO, Guang-ju ZHAO, Shuai CHEN. Factors influencing undergrowth herbaceous diversity of Cunninghamialanceolata plantations in southern mountainous areas[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 17-26.
| 环境变量类型Envionment variable type | 变量因子Variable factors | 数据来源Data source |
|---|---|---|
| 气候因子Climate factor | 年均降水量MAP,年均气温MAT | 中国气象数据网 |
| 地形因子Terrain factor | 海拔Altitude,坡度Slope degree,坡向Aspect | 地理空间数据云STRM 90 m高程数据提取 |
| 土壤养分因子Soil nutrient factor | 土壤有机质SOM | 中国科学院寒旱所遥感与地理信息科学研究室Laboratory of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Science, Institute of Cold and Arid, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 全氮TN | ||
| 全磷TP | ||
| 全钾TK | ||
| 速效氮AN | ||
| 速效磷AP | ||
| 速效钾AK |
表1 环境变量数据及来源
Table 1 Environment variable data and sources
| 环境变量类型Envionment variable type | 变量因子Variable factors | 数据来源Data source |
|---|---|---|
| 气候因子Climate factor | 年均降水量MAP,年均气温MAT | 中国气象数据网 |
| 地形因子Terrain factor | 海拔Altitude,坡度Slope degree,坡向Aspect | 地理空间数据云STRM 90 m高程数据提取 |
| 土壤养分因子Soil nutrient factor | 土壤有机质SOM | 中国科学院寒旱所遥感与地理信息科学研究室Laboratory of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Science, Institute of Cold and Arid, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| 全氮TN | ||
| 全磷TP | ||
| 全钾TK | ||
| 速效氮AN | ||
| 速效磷AP | ||
| 速效钾AK |

图1 林下草本植物多样性与影响因子的相关性MAT: 年均气温Mean annual temperature; MAP: 年均降水量Mean annual precipitation; SOM: 土壤有机质Soil organic matter; TN: 全氮Total nitrogen; TP:全磷Total phosphorus; TK: 全钾Total potassium; SW index: 香农-威纳指数Shannon-Wiener index. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Correlation analysis between influencing factors and understory herbaceous diversity
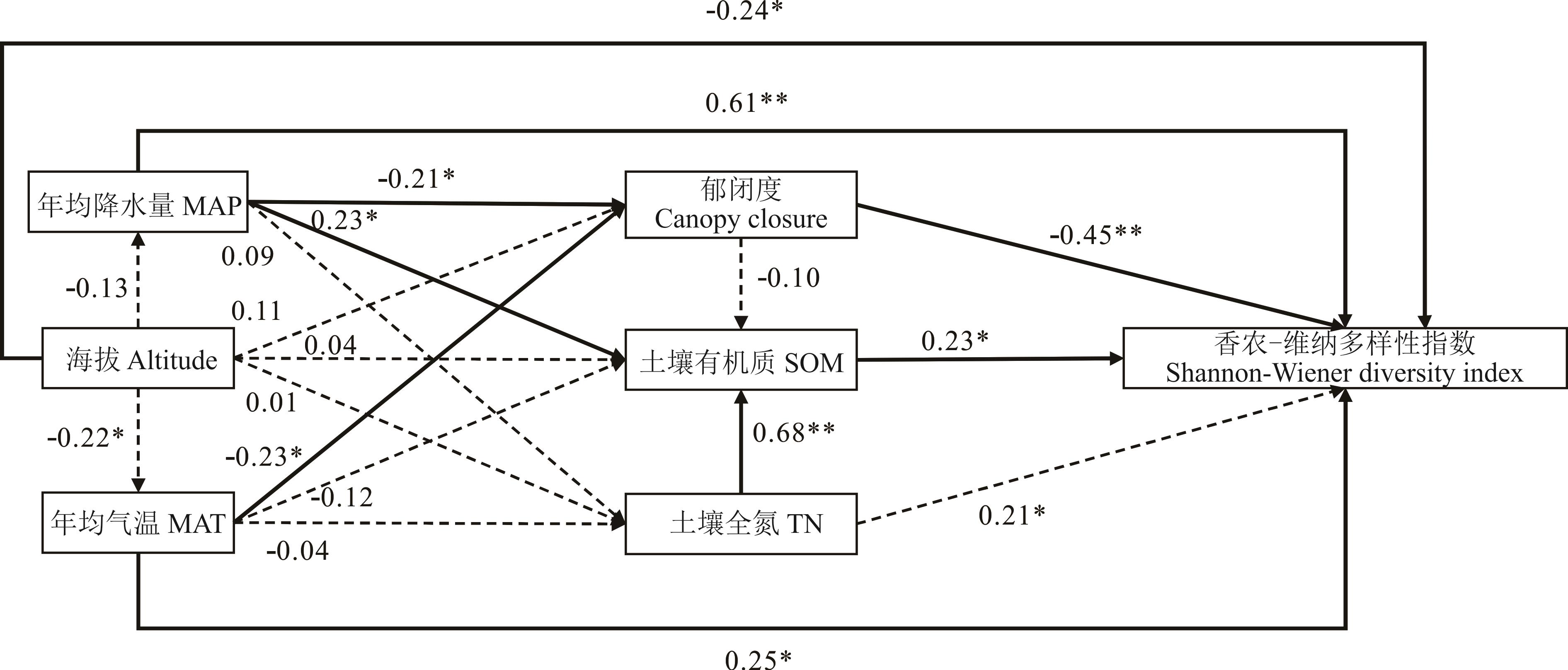
图3 环境因子与林分结构对林下草本物种多样性效应的结构方程模型实线表明两个变量间的因果关系具有显著性,虚线表明不具备显著性。The solid line indicates that the causal relationship between the two variables is significant, while the dashed line indicates that it is not significant. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01.
Fig.3 Structural equation model of the effects of environmental factors and stand structure on understory herbaceous species diversity
| 影响因子Factor | 直接效应Direct effects | 间接效应Indirect effects | 总效应Total effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年均降水量MAP | 0.61 | 0.11 | 0.72 |
| 年均气温MAT | 0.25 | -0.08 | 0.17 |
| 郁闭度Canopy closure | -0.45 | -0.04 | -0.49 |
| 海拔Altitude | -0.24 | -0.09 | -0.33 |
| 土壤有机质SOM | 0.23 | - | 0.23 |
| 土壤全氮TN | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.34 |
表2 林下草本物种多样性与因子间的标准化影响效应
Table 2 Standardization effect of understory herbaceous species diversity and factors
| 影响因子Factor | 直接效应Direct effects | 间接效应Indirect effects | 总效应Total effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年均降水量MAP | 0.61 | 0.11 | 0.72 |
| 年均气温MAT | 0.25 | -0.08 | 0.17 |
| 郁闭度Canopy closure | -0.45 | -0.04 | -0.49 |
| 海拔Altitude | -0.24 | -0.09 | -0.33 |
| 土壤有机质SOM | 0.23 | - | 0.23 |
| 土壤全氮TN | 0.21 | 0.13 | 0.34 |
变量因子 Variable factors | 贡献率 Contribution rate | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate |
|---|---|---|
| 年均降水量MAP | 37.10 | 44.14 |
| 海拔Altitude | 19.53 | 63.21 |
| 年均气温MAT | 15.21 | 74.23 |
| 土壤有机质SOM | 8.93 | 81.34 |
| 土壤全氮TN | 7.52 | 88.21 |
| 坡度Slope degree | 3.31 | 91.53 |
| 速效氮AN | 1.74 | 93.20 |
表3 环境因子对林下草本植物多样性的贡献率及累计贡献率
Table 3 Contribution rate and cumulative contribution rate of environmental factors to understory herbaceous diversity (%)
变量因子 Variable factors | 贡献率 Contribution rate | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate |
|---|---|---|
| 年均降水量MAP | 37.10 | 44.14 |
| 海拔Altitude | 19.53 | 63.21 |
| 年均气温MAT | 15.21 | 74.23 |
| 土壤有机质SOM | 8.93 | 81.34 |
| 土壤全氮TN | 7.52 | 88.21 |
| 坡度Slope degree | 3.31 | 91.53 |
| 速效氮AN | 1.74 | 93.20 |

图5 植物多样性较为丰富区域的存在概率对环境因子的响应曲线
Fig.5 Response curves of the probability of plant existence in regions with rich plant diversity to environmental factors
| 变量因子Variable factors | 适宜范围Suitable ranges | 最佳适宜范围Optimum suitable ranges |
|---|---|---|
| 年均降水量MAP (mm) | ≥1400 | ≥1650 |
| 年均气温MAT (℃) | 12~28 | 18~22 |
| 海拔Altitude (m) | 305~725 | 510~680 |
| 土壤有机质SOM (g·kg-1) | ≥12.50 | ≥20.00 |
表4 各环境因子对林下草本植物多样性的适宜范围和最佳适宜范围
Table 4 The suitable range and optimum suitable range of understory herbaceous diversity for each environmental factor
| 变量因子Variable factors | 适宜范围Suitable ranges | 最佳适宜范围Optimum suitable ranges |
|---|---|---|
| 年均降水量MAP (mm) | ≥1400 | ≥1650 |
| 年均气温MAT (℃) | 12~28 | 18~22 |
| 海拔Altitude (m) | 305~725 | 510~680 |
| 土壤有机质SOM (g·kg-1) | ≥12.50 | ≥20.00 |
| 1 | Moradi M, Jorfi M R, Basiri R, et al. Beneficial effects of livestock exclusion on tree regeneration, understory plant diversity, and soil properties in semiarid forests in Iran. Land Degradation & Development, 2021, 33(2): 324-332. |
| 2 | Wu B C, Zhou L J, Qi S, et al. Effect of habitat factors on the understory plant diversity of Platycladus orientalis plantations in Beijing mountainous areas based on MaxEnt model. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 129(6): 1245-1252. |
| 3 | Gong C, Tan Q Y, Liu G B, et al. Impacts of tree mixtures on understory plant diversity in China. Forest Ecology and Management, 2021, 498: 119545. |
| 4 | Zhao H L, Okuro T, Li Y L, et al. Effects of human activities and climate changes on plant diversity in Horqin sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2008, 17(5): 1-8. |
| 赵哈林, 大黑俊哉, 李玉霖, 等. 人类放牧活动与气候变化对科尔沁沙质草地植物多样性的影响. 草业学报, 2008, 17(5): 1-8. | |
| 5 | Cao M, Pan P, Ouyang X Z, et al. Relationships between the composition and diversity of understory vegetation and environmental factors in aerially seeded Pinus massoniana plantations. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(1): 1-8. |
| 曹梦, 潘萍, 欧阳勋志, 等. 飞播马尾松林林下植被组成、多样性及其与环境因子的关系. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(1): 1-8. | |
| 6 | Dou P T, He S T, Gao C J, et al. Effects of different restoration communities on understory species diversity and soil physical and chemical properties in dry-hot valley. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2022, 39(3): 616-624. |
| 窦沛彤, 贺思腾, 高成杰, 等. 干热河谷不同恢复群落对林下物种多样性和土壤理化性质的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 2022, 39(3): 616-624. | |
| 7 | Wang Z T, Yang L, Li G, et al. Effects of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) degradation on herbage distribution and diversity in the semi-arid Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(10): 3720-3729. |
| 王子婷, 杨磊, 李广, 等. 半干旱黄土区苜蓿退化对坡面草本植物分布及多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(10): 3720-3729. | |
| 8 | Shu W W, Lu L H, Li H, et al. Effects of stand density on understory vegetation and soil properties of Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 4521-4530. |
| 舒韦维, 卢立华, 李华, 等. 林分密度对杉木人工林林下植被和土壤性质的影响. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11): 4521-4530. | |
| 9 | Zhao Y B, Zhang D J, Zhang J, et al. Understory vegetation diversity of Pinus massoniana plantations with various canopy density. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2016, 22(6): 1048-1054. |
| 赵燕波, 张丹桔, 张健, 等. 不同郁闭度马尾松人工林林下植物多样性. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(6): 1048-1054. | |
| 10 | Kooijman A M, Weiler H A, Cusell C, et al. Litter quality and microtopography as key drivers to topsoil properties and understorey plant diversity in ancient broadleaved forests on decalcified marl. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 684(9): 113-125. |
| 11 | Ahmad B, Wang Y H, Hao J, et al. Optimizing stand structure for trade-offs between overstory timber production and understory plant diversity: A case-study of a larch plantation in Northwest China. Land Degradation & Development, 2018, 29(9): 2998-3008. |
| 12 | Luciana M, Mónica T M, Rosina S, et al. The influence of canopy-layer composition on understory plant diversity in southern temperate forests. Forest Ecosystems, 2017, 4(2): 154-166. |
| 13 | Li M, Chen Y K, Xu H C, et al. Effects of different thinning intensities undergrowth plant functional groups in subtropical Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(14): 4985-4993. |
| 李萌, 陈永康, 徐浩成, 等. 不同间伐强度对南亚热带杉木人工林林下植物功能群的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(14): 4985-4993. | |
| 14 | Zhang H D, Kang X R, Shao W H, et al. Characteristics of herbaceous plant biodiversity in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations with different community structures. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(6): 2118-2128. |
| 张涵丹, 康希睿, 邵文豪, 等. 不同类型杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性特征. 生态学报, 2021, 41(6): 2118-2128. | |
| 15 | Cao X Y, Li J P, Zhao W F, et al. Effects of stand structure on herbaceous species diversity based on structural equation modeling. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(24): 9164-9173. |
| 曹小玉, 李际平, 赵文菲, 等. 基于结构方程模型分析林分空间结构对草本物种多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(24): 9164-9173. | |
| 16 | Zhang Y H, Dian Y Y, Huang G T, et al. Effects of spatial structure on species diversity of Pinus massoniana of different succession stages. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(8): 2357-2365. |
| 张亚昊, 佃袁勇, 黄光体, 等. 不同演替阶段马尾松林林分空间结构对物种多样性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(8): 2357-2365. | |
| 17 | Oktari R S, Latuamury B, Idroes R, et al. Validating knowledge creation factors for community resilience to disaster using structural equation modelling. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2022, 81: 103290. |
| 18 | Nora  D, Knorst J K, Comim L D, et al. Factors associated with a cariogenic diet among adolescents: A structural equation modeling approach. Clinical Oral Investigations, 2023, 27: 213-220. |
| 19 | Mooney S, Boudou M, O’Dwyer J, et al. Behavioral pathways to private well risk mitigation: A structural equation modeling approach. Risk Analysis: An Official Publication of the Society for Risk Analysis, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.14021. |
| 20 | Wang M, Wang Y, Liu G L, et al. Potential distribution of seagrass meadows based on the MaxEnt model in Chinese coastal waters. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2022, 21(5): 1351-1361. |
| 21 | Zhao X F, Lei M, Wei C H, et al. Assessing the suitable regions and the key factors for three Cd-accumulating plants (Sedum alfredii, Phytolacca americana, and Hylotelephium spectabile) in China using MaxEnt model. The Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 852: 158202. |
| 22 | Choi J, Lee S. Principal bioclimatic variables of ten dominant plant species in Korea wetland using the Maxent model. Ecological Engineering, 2022, 183: 106729. |
| 23 | Rai R, Zhang Y L, Wang Z F, et al. Use of the MaxEnt model to predict changes in sloth bear (Melursus ursinus) habitats in the Gandaki River Basin, Nepal. Journal of Mountain Science, 2022, 19(7): 1988-1997. |
| 24 | Andrew J, Lindsey M, Linda M. Efficacy of treatments against garlic mustard (Alliaria petiolata) and effects on forest understory plant diversity. Forests, 2012, 3(3): 605-613. |
| 25 | Guo H T, Ji X F, Wang C, et al. Spatial variation and influencing factors of plant diversity in understory shrub layer of Chinese plantation. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 46(4): 144-152. |
| 郭弘婷, 纪小芳, 汪成, 等. 我国人工林林下灌木层植物多样性空间变异及影响要素. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(4): 144-152. | |
| 26 | Wagner S, Fischer H, Huth F. Canopy effects on vegetation caused by harvesting and regeneration treatments European. Journal of Forest Research, 2011, 130(1): 17-40. |
| 27 | Zhang Y Q, Li Z C, Hou L Y, et al. Effects of stand density on understory species diversity and soil nutrients in Chinese fir plantation. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(1): 239-250. |
| 张勇强, 李智超, 厚凌宇, 等. 林分密度对杉木人工林下物种多样性和土壤养分的影响. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1): 239-250. | |
| 28 | Chen X, Li Y H, Zuo Y F, et al. Effects of stand characteristics and soil nutrients on understory herbaceous diversity. Acta Botanica Boreali-occidentalia Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 1396-1407. |
| 陈笑, 李远航, 左亚凡, 等. 林分特征和土壤养分对林下草本物种多样性的影响. 西北植物学报, 2022, 42(8): 1396-1407. | |
| 29 | Hou Y L, Han G X, Zhu L Q, et al. Effects of simulated precipitation changes on plant community characteristics of wetland in the yellow river delta, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(5): 1260-1266. |
| 侯雅琳, 韩广轩, 朱连奇, 等. 模拟降雨量变化对黄河三角洲湿地植物群落特征的影响. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(5): 1260-1266. | |
| 30 | Gao J P, Zhao R F, Zhang L H, et al. Effects of precipitation changes on plant community diversity and soil C∶N∶P ecological stoichiometric characteristics in a desert steppe of china. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2): 977-987. |
| 高江平, 赵锐锋, 张丽华, 等. 降雨变化对荒漠草原植物群落多样性与土壤C∶N∶P生态化学计量特征的影响. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2): 977-987. | |
| 31 | Fu F, Wei H Y, Chang Y T, et al. Elevational patterns of life history and ecological trait diversity of aquatic insects in the middle of the Lancang River: The effects of climate and land use variables. Biodiversity Science, 2022, 30(5): 66-77. |
| 付飞, 魏慧玉, 常育腾, 等. 澜沧江中游水生昆虫生活史和生态学性状多样性的海拔格局:气候和土地利用的影响. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 66-77. | |
| 32 | Wang C E, Huang M, Wang W Y, et al. Variation characteristics of plant community diversity and above-ground biomass in alpine degraded slopes along altitude gradients in the headwaters region of three-river on Tibetan plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(9): 3640-3655. |
| 王采娥, 黄梅, 王文银, 等. 三江源区高寒坡地退化植物群落多样性和地上生物量沿海拔梯度的变化特征. 生态学报, 2022, 42(9): 3640-3655. | |
| 33 | Hu L D, Zhou H J, Huang Y Z, et al. A study on plant species diversity and soil carbon and nitrogen in different Cunninghamia lanceolata stand types. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. |
| 胡靓达, 周海菊, 黄永珍, 等. 不同杉木林分类型植物多样性及其土壤碳氮关系的研究. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 451-459. | |
| 34 | Tan X M, Zhang W, Xiao N, et al. Effects of understory plant species composition and diversity under transforming Chinese fir into precious indigenous broadleaf plantations. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(7): 2931-2942. |
| 谭许脉, 张文, 肖纳, 等. 杉木林改造成乡土阔叶林对林下植物物种组成和多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(7): 2931-2942. | |
| 35 | Zhang L, Qi S, Zhou P, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of understory herbaceous plant diversity Platycladus orientalis orientalis in Beijing mountainous areas. Journal of Grassland, 2022, 30(8): 2199-2206. |
| 张林, 齐实, 周飘, 等. 北京山区侧柏林下草本植物多样性的影响因素分析. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8): 2199-2206. | |
| 36 | Su T C, Wang Y Y, Xiang L, et al. Effects of forest management on community structure and species diversity in poplar plantations of Chengdu ring expressway area. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(5): 1144-1150. |
| 苏天成, 王姚瑶, 向琳, 等. 营林措施对成都绕城高速路域杨树人工林群落结构和物种多样性的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(5): 1144-1150. | |
| 37 | Huang Q Y, Cao H J, Xie L H, et al. Species diversity and environmental interpretation of in lava platform of Wudalianchi, China. Biodiversity Science, 2020, 28(6): 658-667. |
| 黄庆阳, 曹宏杰, 谢立红, 等. 五大连池火山熔岩台地草本层物种多样性及环境解释. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 658-667. |
| [1] | 宋达成, 吴昊, 王理德, 王飞, 张裕凯, 赵学成. 双龙沟废弃矿区不同造林年限人工沙棘林土壤重金属分布特征及其对酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 61-70. |
| [2] | 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| [3] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| [4] | 杨鑫, 曹文侠, 鱼小军, 汪海斌, 郝媛媛. 基于近20年MODIS NDVI日数据的青海省草地资源动态监测及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 1-14. |
| [5] | 张敏, NIPAPAN Kanjana, 李铷, 傅杨, 汤东生. 环境因子对云南扁穗雀麦种子萌发和出苗的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 143-151. |
| [6] | 孙思思, 吴战平, 肖启涛, 于飞, 古书鸿, 方荻, 李浪, 赵兴炳. 云贵高原草地生态系统CO2通量变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 184-191. |
| [7] | 马倩倩, 刘彤, 董合干, 王寒月, 赵文轩, 王瑞丽, 刘延, 陈乐. 气候变化下三裂叶豚草在新疆的潜在地理分布[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 73-85. |
| [8] | 王百竹, 朱媛君, 刘艳书, 马风云, 张晓, 时忠杰, 杨晓晖. 典型草原建群种长芒草(Stipa bungeana)在中国的潜在分布范围预测及主要影响因子分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 3-13. |
| [9] | 王丽佳, 刘兴元. 甘肃牧区牧民对草原生态补奖政策满意度研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 1-11. |
| [10] | 孙丽坤, 刘光琇, 张宝贵, 章高森. 环境因子对中国柽柳遗传变异的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 178-186. |
| [11] | 陆姣云,段兵红,杨梅,杨晗,杨惠敏. 植物叶片氮磷养分重吸收规律及其调控机制研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 178-188. |
| [12] | 范顺祥, 郑建伟, 魏士凯, 黄选瑞, 张志东. 河北省森林草原区主要草本植物功能群适宜分布预测[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 24-32. |
| [13] | 葛兆轩, 孙国龙, 袁业, 黄选瑞, 张志东. 河北省森林草原区草本植物物种多样性和功能多样性[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 35-44. |
| [14] | 吴仁吉, 康萨如拉, 张庆, 任海娟, 任婧, 周俊梅, 王珍, 李丹, 牛建明. 锡林河流域羊草草原植被分异的驱动力[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 15-23. |
| [15] | 陶冶, 刘耀斌, 吴甘霖, 张元明. 准噶尔荒漠区域尺度浅层土壤化学计量特征及其空间分布格[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 13-23. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||