

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 12-22.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022328
吕自立1,2,3( ), 刘彬1,2,3(
), 刘彬1,2,3( ), 常凤4, 马紫荆1,2,3, 曹秋梅1,2,3
), 常凤4, 马紫荆1,2,3, 曹秋梅1,2,3
收稿日期:2022-08-16
修回日期:2022-09-26
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-05-26
通讯作者:
刘彬
作者简介:E-mail: onlinelb@163.com基金资助:
Zi-li LYU1,2,3( ), Bin LIU1,2,3(
), Bin LIU1,2,3( ), Feng CHANG4, Zi-jing MA1,2,3, Qiu-mei CAO1,2,3
), Feng CHANG4, Zi-jing MA1,2,3, Qiu-mei CAO1,2,3
Received:2022-08-16
Revised:2022-09-26
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-05-26
Contact:
Bin LIU
摘要:
沿海拔梯度研究植物群落物种多样性和系统发育多样性可以明晰环境条件对群落构建的影响,可为深入了解群落构建机制提供帮助。选取巴音布鲁克高寒草甸为研究区,针对研究区植物群落物种多样性和系统发育多样性随海拔梯度变化趋势及其环境驱动因子开展研究,探究在群落构建中物种共存及多样性维持过程中环境因子的影响程度。结果表明:1) 随海拔升高,群落Shannon-Wiener多样性指数与Simpson丰富度指数均呈单峰变化趋势,峰值分别在2400和2600 m处;群落Pielou均匀度指数呈逐渐下降趋势;系统发育多样性指数(PD)整体呈下降趋势,系统发育结构逐渐由分散状态转变为聚集状态。2) 系统发育结构指数里净最近种间亲缘关系指数(NTI)和净谱系亲缘关系指数(NRI)与物种多样性指数均呈显著负相关关系(P<0.05),PD指数与物种多样性指数均呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。3) 各土壤因子对不同多样性指数的影响程度不同,其中铵态氮含量是影响物种多样性和系统发育指数的主要因子,全钾含量次之;土壤全氮含量对NTI存在显著影响(P<0.05),全钾含量对NRI存在显著影响(P<0.05), 全磷对PD指数存在显著影响(P<0.05),pH对物种多样性指数存在显著影响(P<0.01)。沿海拔梯度群落物种多样性和系统发育多样性、系统发育结构之间相互关联,受环境因子的影响,两者在海拔梯度上呈现不同的响应策略。
吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22.
Zi-li LYU, Bin LIU, Feng CHANG, Zi-jing MA, Qiu-mei CAO. Species diversity and phylogenetic diversity in Bayinbrook alpine grasslands: elevation gradient distribution patterns and drivers[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 12-22.
指数 Index | 计算公式 Formula | 参数含义 Parameter meaning |
|---|---|---|
净谱系亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index (NRI) | 式中: MPDs表示平均谱系距离观测值, MPDmds表示通过软件随机 999 次模拟出平均谱系距离的平均值,SD 为标准差。In the formula: MPDs represents the observed value of average pedigree distance, MPDmds indicates that the average pedigree distance is randomly simulated 999 times by software, and SD is the standard deviation. | |
净最近种间亲缘关系指数 Net nearest taxa index (NTI) | 式中: MNTDs表示最近相邻谱系距离平均观测值, MNTDmds表示通过软件随机 999 次模拟出最近相邻谱系距离的平均值, SD 为标准差。In the formula: MNTDs represents the average observed distance of the nearest adjacent lineage, MNTDmds indicates that the average distance of the nearest adjacent pedigree is simulated randomly 999 times by the software, and SD is the standard deviation. | |
物种丰富度指数 Species richness index (R) | R=S | 式中: S为样地物种数。In the formula: S is the number of species in the sample plot. |
Simpson丰富度指数 Simpson richness index (D) | 式中: | |
Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | 式中: S代表样地或层次中的物种总数, | |
Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou uniformity index (J) | 式中: S代表样地或层次中的物种总数, |
表1 功能多样性谱系多样性及系统发育结构指数计算公式
Table 1 Formula for calculating the index of functional diversity lineage diversity and phylogenetic structure
指数 Index | 计算公式 Formula | 参数含义 Parameter meaning |
|---|---|---|
净谱系亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index (NRI) | 式中: MPDs表示平均谱系距离观测值, MPDmds表示通过软件随机 999 次模拟出平均谱系距离的平均值,SD 为标准差。In the formula: MPDs represents the observed value of average pedigree distance, MPDmds indicates that the average pedigree distance is randomly simulated 999 times by software, and SD is the standard deviation. | |
净最近种间亲缘关系指数 Net nearest taxa index (NTI) | 式中: MNTDs表示最近相邻谱系距离平均观测值, MNTDmds表示通过软件随机 999 次模拟出最近相邻谱系距离的平均值, SD 为标准差。In the formula: MNTDs represents the average observed distance of the nearest adjacent lineage, MNTDmds indicates that the average distance of the nearest adjacent pedigree is simulated randomly 999 times by the software, and SD is the standard deviation. | |
物种丰富度指数 Species richness index (R) | R=S | 式中: S为样地物种数。In the formula: S is the number of species in the sample plot. |
Simpson丰富度指数 Simpson richness index (D) | 式中: | |
Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | 式中: S代表样地或层次中的物种总数, | |
Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou uniformity index (J) | 式中: S代表样地或层次中的物种总数, |
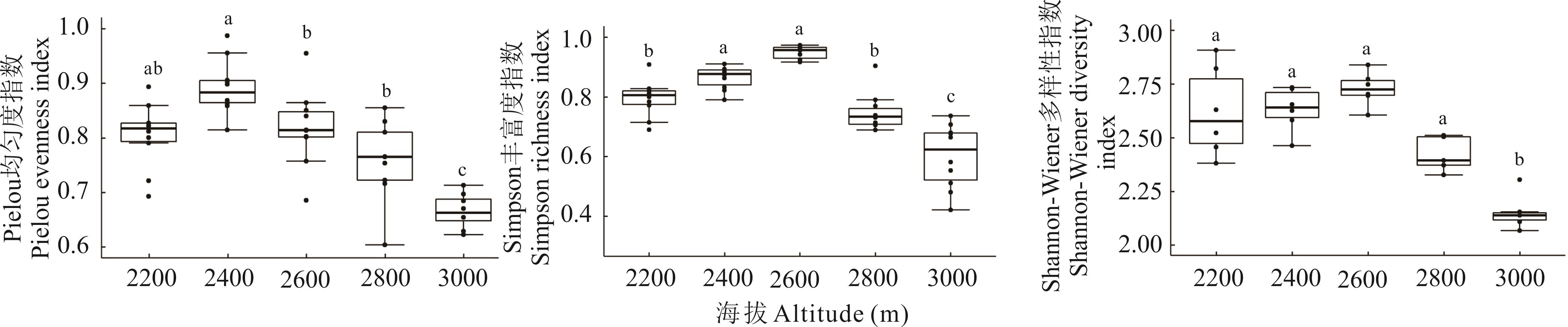
图1 不同海拔梯度物种多样性指数变化不同小写字母表示在不同海拔梯度间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different altitudes (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Changes in species diversity index at different altitudes

图3 群落物种多样性指数与系统发育多样性指数和结构指数的 Pearson 相关性* :P<0.05; **:P<0.01; ***:P<0.001. 蓝色表示正相关,红色表示负相关; 颜色越深,表示相关性越强Blue indicates positive correlation and red indicates negative correlation; The darker the color, the more the relevant. NTI:净最近种间亲缘关系指数Net nearest taxa index;PD:系统发育多样性指数Phylogenetic diversity index;NRI:净谱系亲缘关系指数Net relatedness index;R:丰富度指数Species richness index;J:均匀度指数Pielou uniformity index;H′:Shannon-Wiener多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index;D:Simpson丰富度指数Simpson richness index. 下同The same below.
Fig.3 Pearson correlation among the community species diversity index, the phylogenetic diversity index, the structural index
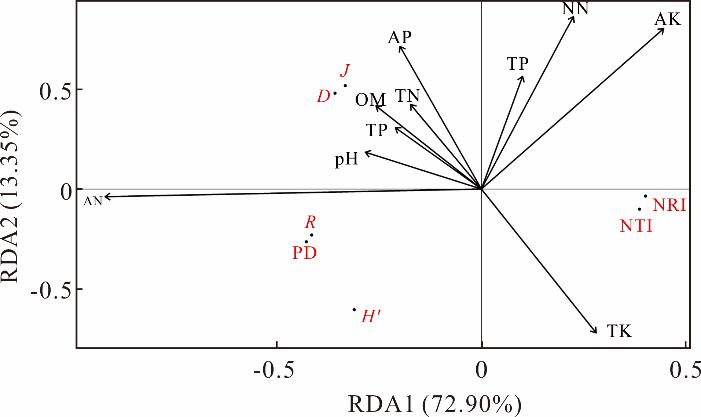
图4 系统发育多样性指数、结构指数及物种多样性指数与土壤环境因子的RDA排序TN:全氮Total nitrogen;TP:全磷Total phosphorus;TK:全钾Total potassium;AN:铵态氮Amino nitrogen;TS:总盐Total salt;NN:硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen;AP:速效磷Available phosphorus; OM:有机质Organic matter.
Fig.4 RDA ranking of phylogenetic diversity index, structural index, species diversity index and soil environmental factors
| 土壤环境影响因子Soil environmental impact factors | R2 | P值P value | 第一主轴得分RDA1 | 第二主轴得分RDA2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | 0.0294 | 0.305 | -0.17304 | 0.42369 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | -0.0550 | 0.586 | -0.21013 | 0.30736 |
| 全钾Total potassium (TK) | 0.1674 | 0.054 | 0.28023 | -0.72105 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN) | 0.5927 | 0.001** | -0.91952 | -0.03867 |
| pH | -0.0235 | 0.590 | -0.28353 | 0.18394 |
| 总盐Total salt (TS) | -0.0454 | 0.658 | 0.10092 | 0.56439 |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen (NN) | 0.0721 | 0.203 | 0.22383 | 0.86144 |
| 速效磷Available phosphorus (AP) | -0.0285 | 0.526 | -0.19898 | 0.71442 |
| 速效钾Available potassium (AK) | 0.1945 | 0.043* | 0.44546 | 0.80393 |
| 有机质Organic matter (OM) | -0.0556 | 0.756 | -0.25739 | 0.41663 |
表2 土壤环境影响因子的显著性检验
Table 2 Significance test of soil environmental impact factors
| 土壤环境影响因子Soil environmental impact factors | R2 | P值P value | 第一主轴得分RDA1 | 第二主轴得分RDA2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | 0.0294 | 0.305 | -0.17304 | 0.42369 |
| 全磷Total phosphorus (TP) | -0.0550 | 0.586 | -0.21013 | 0.30736 |
| 全钾Total potassium (TK) | 0.1674 | 0.054 | 0.28023 | -0.72105 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN) | 0.5927 | 0.001** | -0.91952 | -0.03867 |
| pH | -0.0235 | 0.590 | -0.28353 | 0.18394 |
| 总盐Total salt (TS) | -0.0454 | 0.658 | 0.10092 | 0.56439 |
| 硝态氮Nitrate nitrogen (NN) | 0.0721 | 0.203 | 0.22383 | 0.86144 |
| 速效磷Available phosphorus (AP) | -0.0285 | 0.526 | -0.19898 | 0.71442 |
| 速效钾Available potassium (AK) | 0.1945 | 0.043* | 0.44546 | 0.80393 |
| 有机质Organic matter (OM) | -0.0556 | 0.756 | -0.25739 | 0.41663 |
项目 Item | AIC | R2 | 影响因素 Impact factor | 预估值 Estimate | 标准误差 Std.error | t值 t-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
净最近种间亲缘关系指数 Net nearest taxa index (NTI) | 54.03 | 0.7814 | 全氮Total nitrogen (TN)* | -0.11519 | 0.04248 | -2.712 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | -0.27428 | 0.02990 | -9.173 | |||
净谱系亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index (NRI) | -62.59 | 0.8757 | 全钾Total potassium (TK)* | 0.05729 | 0.03694 | 1.551 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | -0.35362 | 0.02608 | -13.557 | |||
系统发育多样性指数 Phylogenetic diversity index (PD) | 74.52 | 0.6584 | 全磷Total phosphorus (TP)* | -0.7285 | 0.2660 | -2.738 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 2.3243 | 0.3116 | 7.460 | |||
| pH | -22.4648 | 7.2940 | -3.080 | |||
| 总盐Total salt (TS) | 2.6972 | 1.7594 | 1.533 | |||
Pielou 均匀度指数 Pielou uniformity index (J) | -164.72 | 0.6190 | 全氮Total nitrogen (TN)* | -0.017990 | 0.011396 | -1.579 |
| 全钾Total potassium (TK)** | -0.029450 | 0.009118 | -3.230 | |||
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 0.030580 | 0.005471 | 5.590 | |||
| pH** | -0.458820 | 0.150926 | -3.040 | |||
| 总盐Total salt (TS)** | 0.118968 | 0.038658 | 3.077 | |||
Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | -105.03 | 0.5823 | 全钾Total potassium (TK)* | 0.04755 | 0.01937 | 2.455 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 0.08394 | 0.01431 | 5.866 | |||
| pH** | -1.21126 | 0.37073 | -3.267 | |||
Simpson丰富度指数 Simpson richness index (D) | -172.75 | 0.6136 | 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | -0.017600 | 0.009969 | -1.765 |
| 全钾Total potassium (TK)** | -0.025080 | 0.007977 | -3.145 | |||
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 0.026642 | 0.004786 | 5.567 | |||
| pH** | -0.268110 | 0.132031 | -2.031 | |||
| 总盐Total salt (TS)** | 0.100319 | 0.033819 | 2.966 |
表3 影响物种多样性指数、PD指数、NRI和NTI的主要土壤环境因子的逐步回归分析
Table 3 Stepwise regression analysis of major soil environmental factors affecting species diversity index, PD index, NRI and NTI
项目 Item | AIC | R2 | 影响因素 Impact factor | 预估值 Estimate | 标准误差 Std.error | t值 t-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
净最近种间亲缘关系指数 Net nearest taxa index (NTI) | 54.03 | 0.7814 | 全氮Total nitrogen (TN)* | -0.11519 | 0.04248 | -2.712 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | -0.27428 | 0.02990 | -9.173 | |||
净谱系亲缘关系指数 Net relatedness index (NRI) | -62.59 | 0.8757 | 全钾Total potassium (TK)* | 0.05729 | 0.03694 | 1.551 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | -0.35362 | 0.02608 | -13.557 | |||
系统发育多样性指数 Phylogenetic diversity index (PD) | 74.52 | 0.6584 | 全磷Total phosphorus (TP)* | -0.7285 | 0.2660 | -2.738 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 2.3243 | 0.3116 | 7.460 | |||
| pH | -22.4648 | 7.2940 | -3.080 | |||
| 总盐Total salt (TS) | 2.6972 | 1.7594 | 1.533 | |||
Pielou 均匀度指数 Pielou uniformity index (J) | -164.72 | 0.6190 | 全氮Total nitrogen (TN)* | -0.017990 | 0.011396 | -1.579 |
| 全钾Total potassium (TK)** | -0.029450 | 0.009118 | -3.230 | |||
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 0.030580 | 0.005471 | 5.590 | |||
| pH** | -0.458820 | 0.150926 | -3.040 | |||
| 总盐Total salt (TS)** | 0.118968 | 0.038658 | 3.077 | |||
Shannon-Wiener多样性指数 Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H') | -105.03 | 0.5823 | 全钾Total potassium (TK)* | 0.04755 | 0.01937 | 2.455 |
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 0.08394 | 0.01431 | 5.866 | |||
| pH** | -1.21126 | 0.37073 | -3.267 | |||
Simpson丰富度指数 Simpson richness index (D) | -172.75 | 0.6136 | 全氮Total nitrogen (TN) | -0.017600 | 0.009969 | -1.765 |
| 全钾Total potassium (TK)** | -0.025080 | 0.007977 | -3.145 | |||
| 铵态氮Amino nitrogen (AN)*** | 0.026642 | 0.004786 | 5.567 | |||
| pH** | -0.268110 | 0.132031 | -2.031 | |||
| 总盐Total salt (TS)** | 0.100319 | 0.033819 | 2.966 |
| 1 | Wicke K, Fischer M. Comparing the rankings obtained from two biodiversity indices: The fair proportion index and the shapley value. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2017, 430: 207-214. |
| 2 | Schweiger O, Klotz S, Durka W, et al. A comparative test of phylogenetic diversity indices. Oecologia, 2008, 157(3): 485-495. |
| 3 | Petchey O L, Gaston K J. Functional diversity (FD), species richness and community composition. Ecology Letters, 2002, 5(3): 402-411. |
| 4 | Jia P, Du G Z. Measuring functional and phylogenetic diversity in community ecology. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2014, 26(2): 153-157. |
| 贾鹏, 杜国祯. 生态学的多样性指数: 功能与系统发育. 生命科学, 2014, 26(2): 153-157. | |
| 5 | Dong L W, Ren Z W, Zhang R, et al. Functional diversity rather than species diversity can explain community biomass variation following short-term nitrogen addition in an alpine grassland. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(7): 871-881. |
| 董六文, 任正炜, 张蕊, 等. 功能多样性比物种多样性更好解释氮添加对高寒草地生物量的影响. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(7): 871-881. | |
| 6 | Zhang W X, Wang H, Fan X L, et al. Impacts of black locust forest on understory plant species diversity and phylogenetic diversity in Shandong Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(9): 2868-2877. |
| 张文馨, 王蕙, 范小莉, 等. 山东刺槐林对林下植物物种多样性及谱系多样性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(9): 2868-2877. | |
| 7 | Li M J, He Z S, Jiang L, et al. Distribution pattern and driving factors of species diversity and phylogenetic diversity along altitudinal gradient on the south slope of Daiyun Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 1148-1157. |
| 李梦佳, 何中声, 江蓝, 等. 戴云山物种多样性与系统发育多样性海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子. 生态学报, 2021, 41(3):1148-1157. | |
| 8 | Lomolino M V. Elevation gradients of species-density: Historical and prospective views. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2001, 10(1): 3-13. |
| 9 | Willis C G, Halina M, Lehman C, et al. Phylogenetic community structure in Minnesota oak savanna is influenced by spatial extent and environmental variation. Ecography, 2010, 33(3): 565-577. |
| 10 | Moreno R A, Rivadeneira M M, Hernández C E, et al. Do rapoport’s rule,the mid-domain effect or the source-sinkhypotheses predict bathymetric patterns of polychaete richness on the Pacific coast of South America? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 2008, 17(3): 415-423. |
| 11 | Hubbell S P. The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography. Monographs in Population Biology, 2001, 26(7): 340-348. |
| 12 | Jump A S, Matyas C, Penuelas J. The altitude-for-latitude disparity in the range retractions of woody species. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2009, 24(12): 694-701. |
| 13 | Hutchinson G E, Hutchinson G, Hutchinson G, et al. Concluding remarks, coldspring harbor symposium. Quantitative Biology, 1957, 22(1507): 239. |
| 14 | Liu W, Cao W. Phylogenetic structure and influence of environmental factors on phylogenetic structure of plant community in Changbai Mountains. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2013, 27(5): 63-68. |
| 刘巍, 曹伟. 长白山植物群落谱系结构及环境因子对其的影响.干旱区资源与环境, 2013, 27(5): 63-68. | |
| 15 | Kembel S W, Hubbell S P. The phylogenetic structure of a neotropical forest tree community. Ecology, 2006, 87(7): 86-89. |
| 16 | Huang J X, Zheng F Y, Mi X C. Influence of environmental factors on phylogenetic structure at multiple spatial scales in an evergreen broad-leaved forest of China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2010, 34(3): 309-315. |
| 黄建雄, 郑凤英, 米湘成. 不同尺度上环境因子对常绿阔叶林群落的谱系结构的影响. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(3): 309-315. | |
| 17 | Chang F, Liu B, Liu R K, et al. Plant community diversity and environmental interpretation of adaptive region of Gentianella turkestanorum in Kuqa Mountain area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(5): 1084-1090. |
| 常凤, 刘彬, 刘若坤, 等. 库车山区新疆假龙胆适生地植物群落多样性及其环境解释. 草地学报, 2018, 26(5): 1084-1090. | |
| 18 | Wang J Q, Liu B, Chang F, et al. Species diversity of plant communities and their environmental interpretation in Gentianella turkestanorum habitat in Bayinbrook. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(3): 29-36. |
| 王军强, 刘彬, 常凤, 等. 巴音布鲁克新疆假龙胆适生地植物群落物种多样性及其环境解释. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(3): 29-36. | |
| 19 | Wang X, Hu Y K, Rehemudula A, et al. Study on gradient changes of soil factors and underground biomass of alpine grassland slope of Tianshan Mountains. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2008, 30(6): 67-73. |
| 王鑫, 胡玉昆, 热合木都拉·阿迪拉, 等. 天山南坡草地土壤因子与地下生物量的梯度变化研究. 中国草地学报, 2008, 30(6): 67-73. | |
| 20 | Li W L, Wang Y. Vegetation community of the wetland in Bayinbu Lake swan conservation of Xinjiang. Ecological Science, 2007, 26(5): 443-446. |
| 李文利, 王英. 巴音布鲁克天鹅湖保护区湿地植物群落研究. 生态科学, 2007, 26(5): 443-446. | |
| 21 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis (3rd Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2010. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2010. | |
| 22 | Cai Y. Relationship between desert plant diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality along water and salt gradients. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2019. |
| 蔡艳. 水盐梯度下荒漠植物多样性与生态系统多功能性的关系. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2019. | |
| 23 | Ma K P, Liu C R, Liu Y M. Measurement of biome diversity II: A measure of β diversity. Chinese Biodiversity, 1995, 3(1): 38-43. |
| 马克平, 刘灿然, 刘玉明. 生物群落多样性的测度方法II: β多样性的测度方法. 生物多样性, 1995, 3(1): 38-43. | |
| 24 | Newman J A, Varner G, Linguist S. Defending biodiversity: Environmental science and ethics. New York: Biodiversity Science and Ethics, 2017. |
| 25 | Group T. An update of the angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 2009, 161(2): 105-121. |
| 26 | Kraft N J B, Cornwell W K, Webb C O, et al. Trait evolution,community assembly,and the phylogenetic structure of ecological communities. American Naturalist, 2007, 170(2): 271-283. |
| 27 | Lu H, Cong J, Liu X, et al. Plant diversity patterns along altitudinal gradients in alpine meadows in the Three River Headwater Region, China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(7): 197-204. |
| 卢慧, 丛静, 刘晓, 等. 三江源区高寒草甸植物多样性的海拔分布格局. 草业学报, 2015, 24(7): 197-204. | |
| 28 | Li W H, Ganzhu Z B, Cao X J, et al. Effects of altitude on plant productivity and species diversity in alpine meadows of northern Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(9): 200-207. |
| 栗文翰, 干珠扎布, 曹旭娟, 等. 海拔梯度对藏北高寒草地生产力和物种多样性的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 200-207. | |
| 29 | Zhang X H, Zhu J Z, Li H Q. Species diversity and characteristics of Dactylis glomerata community in different altitudes on the eastern and western sections of the northern slope of Tianshan Mountain. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(4): 760-767. |
| 张鲜花, 朱进忠, 李海琪. 天山北坡东段与西段不同海拔鸭茅群落特征及物种多样性研究. 草地学报, 2016, 24(4): 760-767. | |
| 30 | Yan Y J, Yang X, Tang Z Y. Patterns of species diversity and phylogenetic structure of vascular plants on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecology and Evolution, 2013, 3(13): 4584-4595. |
| 31 | Zhang W X, Huang D Z, Wang R Q, et al. Altitudinal patterns of species diversity and phylogenetic diversity across temperate mountain forests of Northern China. PLoS One, 2016, 11(7): e0159995. |
| 32 | Lai J S, Mi X C, Ren H B, et al. Species-habitat associations change in a subtropical forest of China. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2009, 20(3): 415-423. |
| 33 | Yang Y H, Rao S, Hu H F, et al. Plant species richness of alpine grasslands in relation to environmental factors and biomass on the Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 2004, 12(1): 200-205. |
| 杨元合, 饶胜, 胡会峰, 等. 青藏高原高寒草地植物物种丰富度及其与环境因子和生物量的关系. 生物多样性, 2004, 12(1): 200-205. | |
| 34 | Jiang X Y, Gao S J, Jiang Y, et al. Species diversity, functional diversity, and phylogenetic diversity in plant communities at different phases of vegetation restoration in the Mu Us sandy grassland. Biodiversity Science, 2022, 30(5): 18-28. |
| 姜晓燕, 高圣杰, 蒋燕, 等. 毛乌素沙地植被不同恢复阶段植物群落物种多样性、功能多样性和系统发育多样性. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 18-28. | |
| 35 | Long C, Yang X B, Long W X, et al. Soil nutrients influence plant community assembly in two tropical coastal secondary forests. Tropical Conservation Science, 2018, 11: 1-9. |
| 36 | Li R X. Plant diversity patterns and biodiversity-productivity relationships of steppe in Inner Mongolia: In view of species and functional trait. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017. |
| 李瑞新. 内蒙古草原群落多样性格局及其与生产力的关系-基于物种与功能性状维度. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017. | |
| 37 | Wang X, Song N P, Yang X G, et al. The response of grassland plant diversity to soil factors under grazing disturbance. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(5): 27-36. |
| 王兴, 宋乃平, 杨新国, 等. 放牧扰动下草地植物多样性对土壤因子的响应. 草业学报, 2013, 22(5): 27-36. | |
| 38 | Xing Y, Ma X H. Research progress on effect of nitrogen form on plant growth. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(2): 109-117. |
| 邢瑶, 马兴华. 氮素形态对植物生长影响的研究进展. 中国农业科技导报, 2015, 17(2): 109-117. | |
| 39 | Li K H, Hu Y K, Fan Y G, et al. Influence of environmental factors on distribution of plant communities and composition of species in alpine grassland. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2007, 28(4): 378-382. |
| 李凯辉, 胡玉昆, 范永刚, 等. 环境因子对高寒草地植物群落分布和物种组成的影响. 中国农业气象, 2007, 28(4): 378-382. | |
| 40 | Gratlan J S, Newbery D M, Thomas K W, et al. The influence of topography and soil phosphorus on the vegetation of Korup Forest Reserve, Cameroun. Vegetatio, 1986, 65(3): 131-148. |
| 41 | Lu L L. Studies on the effect of N, P, K levels and their combined fertilization on growth and medicinal composition of Pogostemon cablin (Blanco.) Benth. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University,2016. |
| 卢丽兰. 氮磷钾水平及其配合施用对广藿香生长及药效成分影响的研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. | |
| 42 | Tang K, Zhu W W, Zhou W X, et al. Research progress on effects of soil pH on plant growth and development. Crop Research, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. |
| 唐琨, 朱伟文, 周文新, 等. 土壤pH对植物生长发育影响的研究进展. 作物研究, 2013, 27(2): 207-212. |
| [1] | 刘彩凤, 段媛媛, 王玲玲, 王乙茉, 郭正刚. 高原鼠兔干扰对高寒草甸植物物种多样性与土壤生态化学计量比间关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 157-166. |
| [2] | 马婧, 郭方君, 邹枝慧, 孙琳, 陈芳. 腾格里沙漠南缘不同恢复阶段沙质草地植被的季节变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 203-210. |
| [3] | 李美慧, 李玉华, 晏昕辉, 拓行行, 杨梦茹, 王子临, 李伟. 半灌木扩张驱动的草地植物多样性与地上生产力特征及其关系研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 27-39. |
| [4] | 虎雅玲, 哈斯额尔敦, 满良, 杨一, 张萍. 小叶锦鸡儿灌丛地植被对沙源供给的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [5] | 张丽苗, 谭雪, 董智, 郑杰, 袁中勋, 李昌晓. 喜旱莲子草入侵对三峡库区重庆主城河岸带植物多样性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 13-25. |
| [6] | 高瑞, 艾宁, 刘广全, 刘长海, 强方方. 煤矿复垦区不同修复年限林下草本群落特征及其与土壤耦合关系[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 61-68. |
| [7] | 卢俊艳, 红梅, 赵巴音那木拉null, 赵乌英嘎, 王文东, 马尚飞, 杨殿林. 贝加尔针茅草原植物群落结构及生物量对长期养分添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 22-31. |
| [8] | 段媛媛, 张静, 王玲玲, 刘彩凤, 王乙茉, 周俗, 郭正刚. 高原鼠兔对高寒草甸植物物种多样性和功能多样性关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 25-35. |
| [9] | 罗巧玉, 王彦龙, 杜雷, 刘念, 李丽, 马玉寿. 黄河源区发草适生地植物群落特征及其土壤因子解释[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 80-89. |
| [10] | 贺国宝. 祁连山北坡植物群落空间分布格局与多样性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 194-201. |
| [11] | 聂莹莹, 陈金强, 辛晓平, 徐丽君, 杨桂霞, 王旭. 呼伦贝尔草甸草原区主要植物种群生态位特征与物种多样性对封育年限响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 15-25. |
| [12] | 韩福贵, 满多清, 郑庆钟, 赵艳丽, 张裕年, 肖斌, 付贵全, 杜娟. 青土湖典型湿地白刺灌丛沙堆群落物种多样性及土壤养分变化特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 36-45. |
| [13] | 车力木格, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 孙姗姗, 王明明. 半干旱沙地草本植物群落特征对短期降水变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 19-28. |
| [14] | 吴昊, 张辰, 代文魁. 气候变暖和物种多样性交互效应对空心莲子草入侵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 38-48. |
| [15] | 杨鼎, 齐昊昊, 王倩, 徐海鹏, 张静, 张红艳, 郭正刚. 青藏高原高原鼢鼠鼠丘植被恢复过程中植物群落特征的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 114-122. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||