

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 96-107.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023463
朱城强( ), 温绍福, 江润海, 张梅, 蔡治宏, 何玥琛, 陈鑫, 侯秀丽(
), 温绍福, 江润海, 张梅, 蔡治宏, 何玥琛, 陈鑫, 侯秀丽( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-30
修回日期:2023-12-25
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-07-15
通讯作者:
侯秀丽
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: hxlyn@aliyun.com基金资助:
Cheng-qiang ZHU( ), Shao-fu WEN, Run-hai JIANG, Mei ZHANG, Zhi-hong CAI, Yue-chen HE, Xin CHEN, Xiu-li HOU(
), Shao-fu WEN, Run-hai JIANG, Mei ZHANG, Zhi-hong CAI, Yue-chen HE, Xin CHEN, Xiu-li HOU( )
)
Received:2023-11-30
Revised:2023-12-25
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-15
Contact:
Xiu-li HOU
摘要:
为明确外源生长素对狗牙根在铅(Pb)胁迫下的作用与机制,本研究以Pb耐性植物狗牙根为对象,在盆栽试验条件下,对处于324.4 mg·kg-1土壤Pb胁迫下的狗牙根叶面喷施不同浓度的(0、1、10、100 mg·L-1)吲哚乙酸(IAA)与5、10 mg·L-1的生长素极性运输抑制剂(NPA),探究外源IAA对狗牙根的生长、生理特性及Pb积累的影响。结果表明:外源IAA使狗牙根IAA与细胞分裂素(CTK)含量升高,脱落酸(ABA)含量及吲哚乙酸氧化酶(IAAO)活性降低,促进了狗牙根在Pb胁迫下株高、根长、地上和地下部干重的增加。其中,喷施10 mg·L-1 IAA效果最好。与对照相比,10 mg·L-1 IAA叶面喷施处理使株高、根长及地上与地下部干重分别提高了32.4%、30.1%、32.2%和25.5%,叶绿素a、叶绿素b、胡萝卜素含量分别升高到对照组的1.35、1.36和1.21倍,叶与根中的Ca2+与可溶性蛋白含量显著上升。10 mg·L-1 IAA叶面喷施还改善了狗牙根体内的抗氧化指标,表现为丙二醛(MDA)含量相较于对照组显著下降,过氧化物酶(POD)活性显著升高。此外,10 mg·L-1 IAA叶面喷施促进了根对Pb的吸收和固定,同时抑制Pb的根-冠转移。但喷施NPA加重了Pb对狗牙根的生长抑制且该生长抑制具有对NPA的剂量依赖效应,10 mg·L-1 NPA的抑制效果最强,削弱了狗牙根内源激素对Pb的应激效应、降低了叶绿素荧光参数与光合色素含量、提高了狗牙根地上部分Pb含量、导致MDA含量升高。综合分析表明,本试验条件下狗牙根喷施10 mg·L-1 IAA效果最佳,通过增强狗牙根对Pb的激素应激反应、提高光合作用和抗氧化能力改善了植株生长;同时通过提升胞内Ca2+与可溶性蛋白含量抑制了Pb的根冠迁移,从而降低膜脂质过氧化水平,缓解了Pb胁迫下狗牙根的氧化损伤。本研究结果丰富了狗牙根耐Pb机制,并为应用外源IAA缓解植物Pb毒害提供了科学依据。
朱城强, 温绍福, 江润海, 张梅, 蔡治宏, 何玥琛, 陈鑫, 侯秀丽. 铅胁迫下吲哚乙酸对狗牙根铅累积及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 96-107.
Cheng-qiang ZHU, Shao-fu WEN, Run-hai JIANG, Mei ZHANG, Zhi-hong CAI, Yue-chen HE, Xin CHEN, Xiu-li HOU. Effects of 3-indoleacetic acid on lead accumulation and physiological properties of Cynodon dactylon under lead stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 96-107.
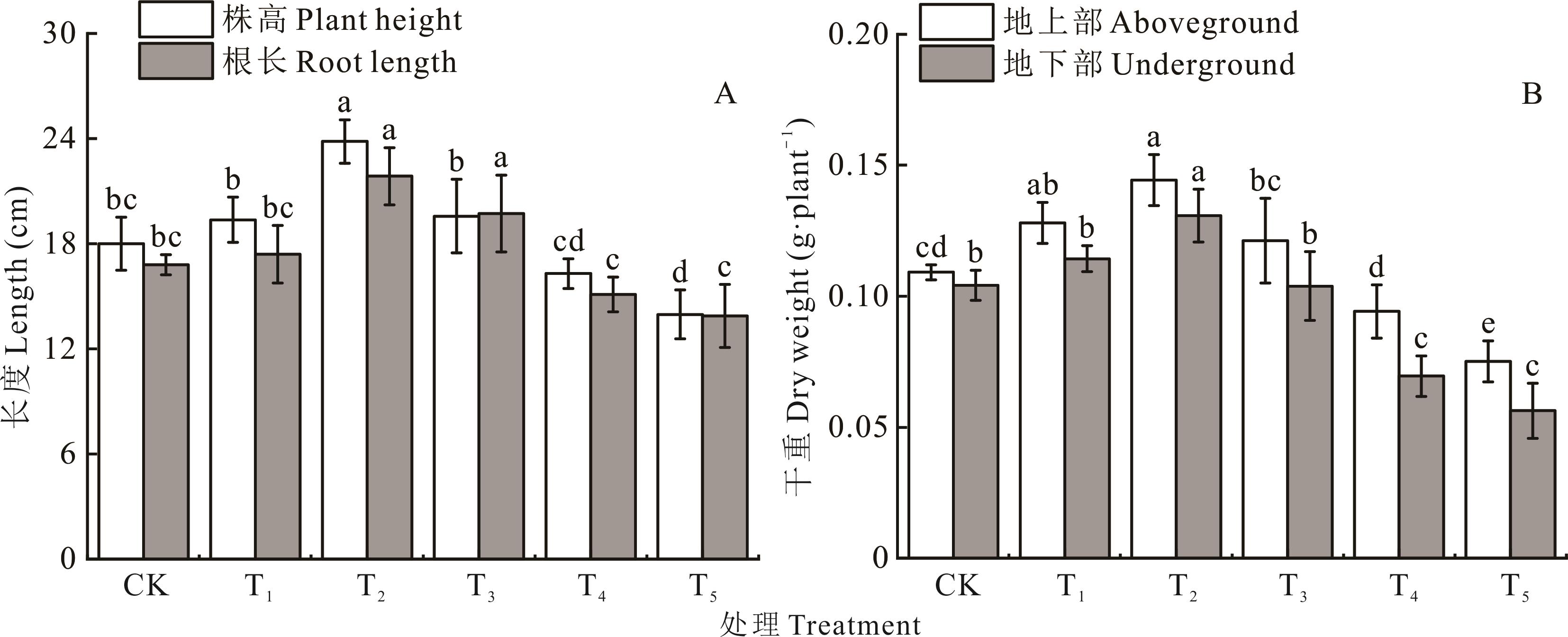
图1 不同浓度IAA与NPA对Pb胁迫下狗牙根株高、根长及生物量的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。DW:干重;FW:鲜重。下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). DW: dry weight; FW: fresh weight. The same below.
Fig. 1 Effects of different concentrations IAA and NPA on plant height, root length and biomass of C. dactylon under Pb stress
处理组 Treatment | 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a (mg·g-1) | 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b (mg·g-1) | 胡萝卜素 Carotene (mg·g-1) | 最大光化学效率 Maximum quantum yield of PSII, Fv/Fm | 实际光化学效率 Practical efficiency, ΦPSⅡ | 相对电子传递速率 Electron transport rate, ETR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.57±0.89bc | 2.10±0.26d | 1.23±0.17bc | 0.78±0.01ab | 0.71±0.01ab | 9.49±0.18b |
| T1 | 6.30±0.35b | 2.45±0.07bc | 1.36±0.14ab | 0.80±0.01ab | 0.70±0.01abc | 9.27±0.94b |
| T2 | 7.53±0.27a | 2.86±0.12a | 1.48±0.07a | 0.81±0.02a | 0.74±0.02a | 9.57±0.79b |
| T3 | 5.90±0.81b | 2.54±0.42b | 1.14±0.21c | 0.78±0.03abc | 0.70±0.01abc | 12.87±0.79a |
| T4 | 5.02±0.24c | 2.09±0.17cd | 1.13±0.03c | 0.77±0.01bc | 0.69±0.03bc | 7.65±0.68c |
| T5 | 3.34±0.17d | 1.22±0.08e | 0.75±0.04d | 0.74±0.02c | 0.70±0.04abc | 6.28±0.85d |
表1 不同浓度IAA、NPA对Pb胁迫下狗牙根光合特性的影响
Table 1 Effects of different concentrations of IAA and NPA on photosynthetic characteristics of C. dactylon under Pb stress
处理组 Treatment | 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a (mg·g-1) | 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b (mg·g-1) | 胡萝卜素 Carotene (mg·g-1) | 最大光化学效率 Maximum quantum yield of PSII, Fv/Fm | 实际光化学效率 Practical efficiency, ΦPSⅡ | 相对电子传递速率 Electron transport rate, ETR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.57±0.89bc | 2.10±0.26d | 1.23±0.17bc | 0.78±0.01ab | 0.71±0.01ab | 9.49±0.18b |
| T1 | 6.30±0.35b | 2.45±0.07bc | 1.36±0.14ab | 0.80±0.01ab | 0.70±0.01abc | 9.27±0.94b |
| T2 | 7.53±0.27a | 2.86±0.12a | 1.48±0.07a | 0.81±0.02a | 0.74±0.02a | 9.57±0.79b |
| T3 | 5.90±0.81b | 2.54±0.42b | 1.14±0.21c | 0.78±0.03abc | 0.70±0.01abc | 12.87±0.79a |
| T4 | 5.02±0.24c | 2.09±0.17cd | 1.13±0.03c | 0.77±0.01bc | 0.69±0.03bc | 7.65±0.68c |
| T5 | 3.34±0.17d | 1.22±0.08e | 0.75±0.04d | 0.74±0.02c | 0.70±0.04abc | 6.28±0.85d |
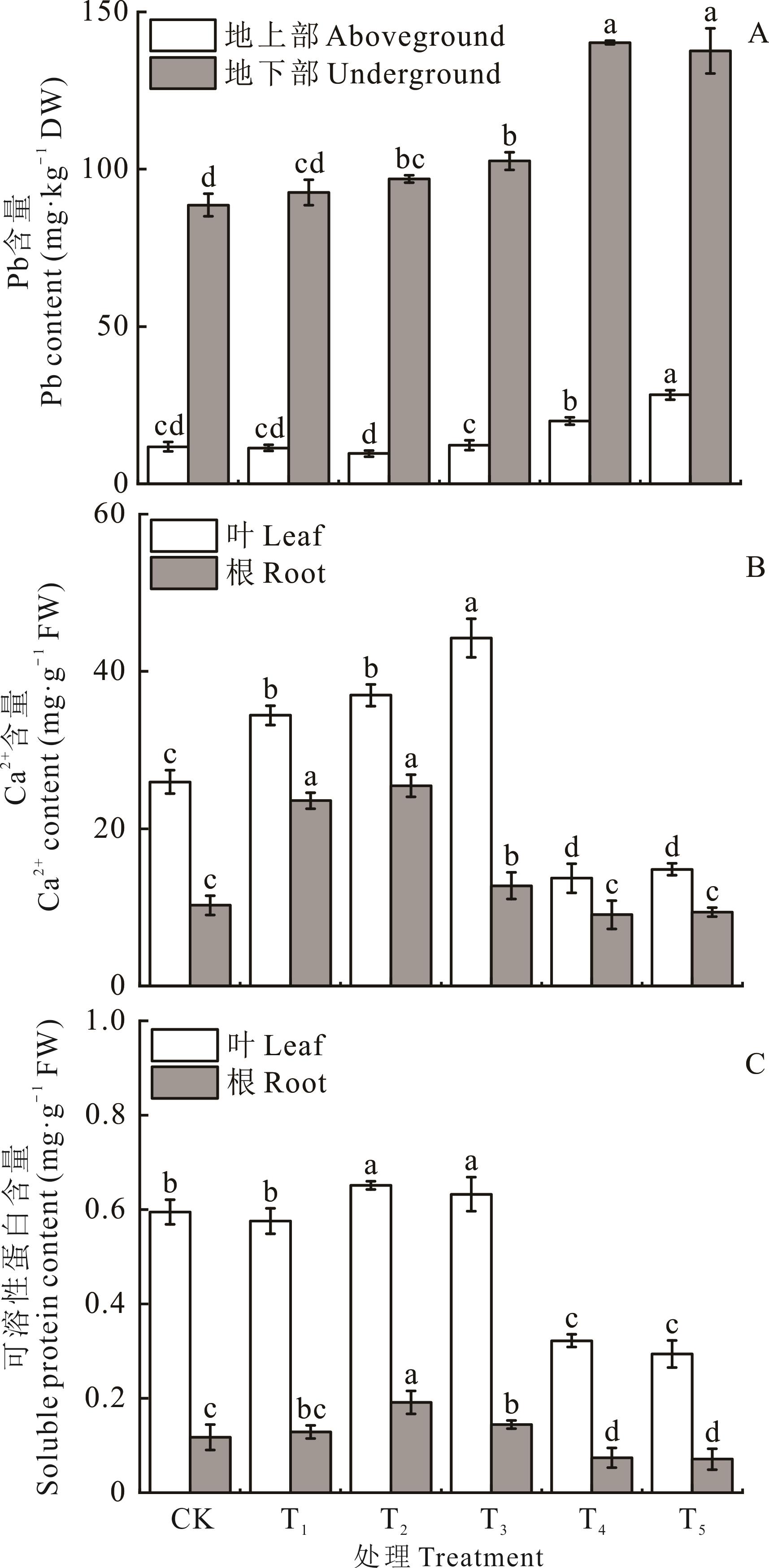
图2 不同浓度IAA与NPA对Pb胁迫下狗牙根Pb、Ca2+与可溶性蛋白含量的影响
Fig.2 Effects of different concentrations IAA and NPA on Pb, Ca2+ and soluble protein content of C. dactylon under Pb stress
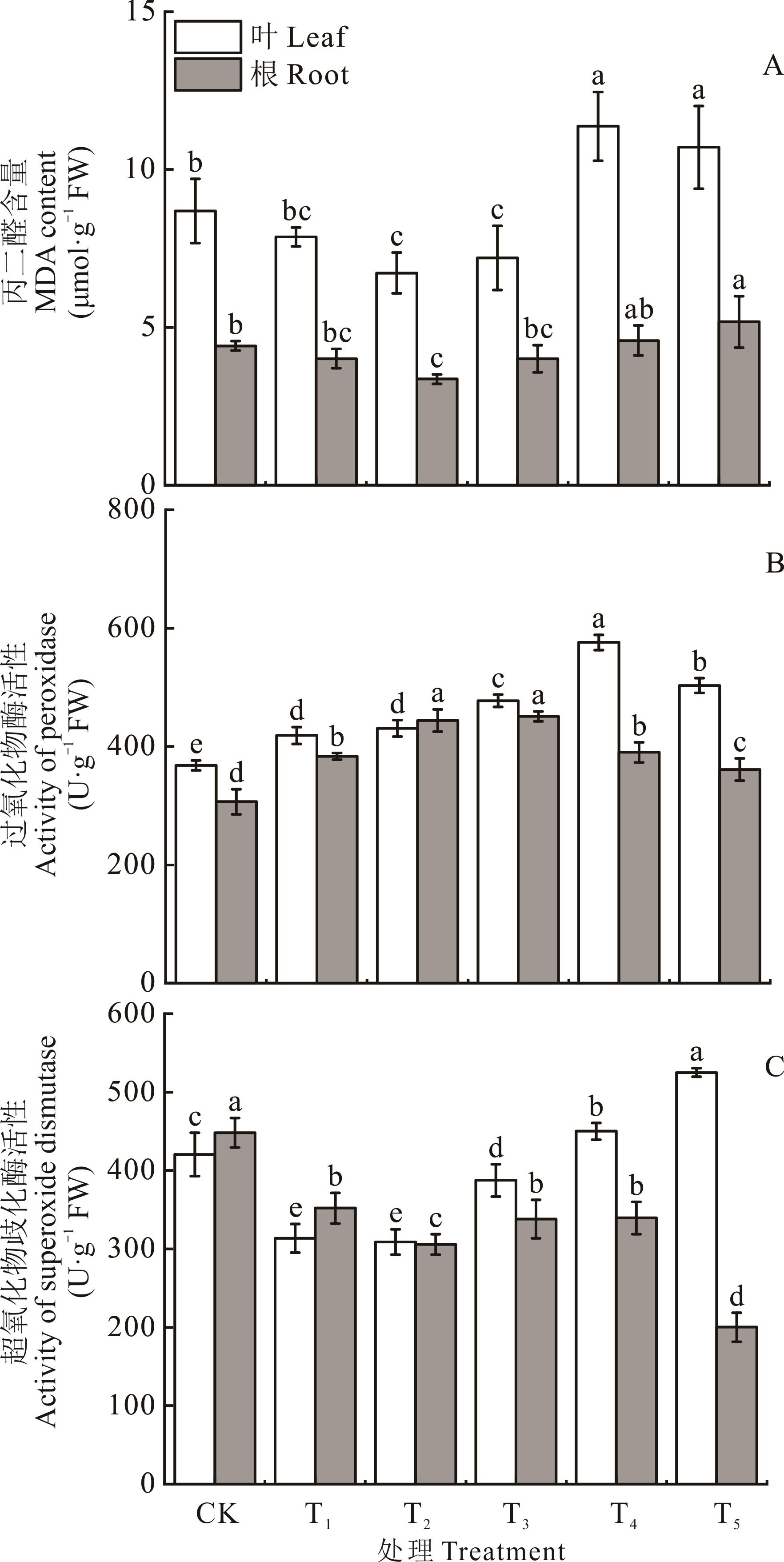
图3 不同浓度IAA与NPA对Pb胁迫下狗牙根MDA含量、SOD、POD活性的影响
Fig.3 Effects of different concentrations of IAA and NPA on MDA content, SOD and POD activity in C. dactylon under Pb stress
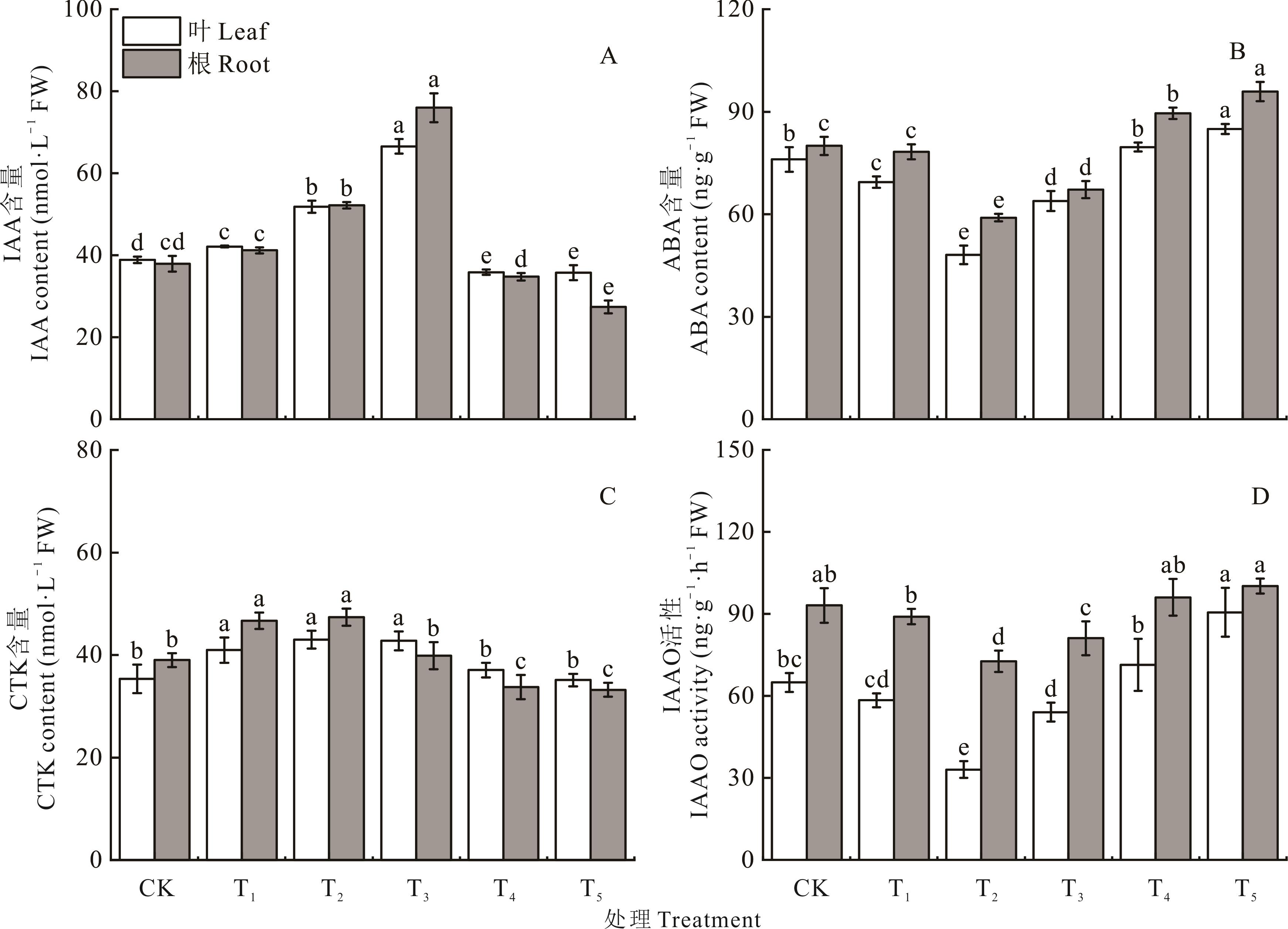
图4 不同浓度IAA与NPA对Pb胁迫下狗牙根内源激素含量及IAAO活性的影响
Fig.4 Effects of different concentrations of IAA and NPA on the contents of endogenous hormones and IAAO activity in C. dactylon under Pb stress
| 1 | Zhang J D, Xi F R. Study on ecological restoration of abandoned mines in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(21): 7921-7930. |
| 张进德, 郗富瑞. 我国废弃矿山生态修复研究. 生态学报, 2020, 40(21): 7921-7930. | |
| 2 | Bandara T, Franks A, Xu J, et al. Chemical and biological immobilization mechanisms of potentially toxic elements in biochar-amended soils. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 50(9): 903-978. |
| 3 | Shahid M, Niazi N K, Rinklebe J, et al. Trace elements-induced phytohormesis: A critical review and mechanistic interpretation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 50(19): 1984-2015. |
| 4 | Saini S, Kaur N, Pati P K. Phytohormones: Key players in the modulation of heavy metal stress tolerance in plants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 223(1): 112578. |
| 5 | Kong Y S, Xu H Y, Huang X H, et al. Relationship between leaf traits and photosynthetic efficiency of Ligustrum lucidum under Pb stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2022, 41(10): 1881-1886. |
| 孔佑莎, 许洪扬, 黄鑫浩, 等. Pb胁迫下大叶女贞叶片性状与光合效率的关系. 生态学杂志, 2022, 41(10): 1881-1886. | |
| 6 | Chen Y T, Xu Z Z. Review on research of leaf economics spectrum. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(10): 1135-1153. |
| 陈莹婷, 许振柱. 植物叶经济谱的研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(10): 1135-1153. | |
| 7 | Ashraf U, Kanu A S, Mo Z, et al. Lead toxicity in rice: effects, mechanisms, and mitigation strategies—A mini review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(23): 18318-18332. |
| 8 | Zhang Q M, Gong M, Liu K, et al. Rhizoglomus intraradices improves plant growth, root morphology and phytohormone balance of Robinia pseudoacacia in arsenic-contaminated soils. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 1428. |
| 9 | Li N, Euring D, Cha J Y, et al. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of heat tolerance in response to global climate change. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 11: 627969. |
| 10 | Sun P, Tian Q Y, Chen J, et al. Aluminium-induced inhibition of root elongation in Arabidopsis is mediated by ethylene and auxin. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(2): 347-356. |
| 11 | Luo J, Zhou J J, Zhang J Z. Aux/IAA gene family in plants: molecular structure, regulation, and function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(1): 259. |
| 12 | Anfang M, Shani E. Transport mechanisms of plant hormones. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2021, 63: 102055. |
| 13 | Khare S, Singh N B, Niharika, et al. Phytochemicals mitigation of Brassica napus by IAA grown under Cd and Pb toxicity and its impact on growth responses of Anagallis arvensis. Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 343: 83-95. |
| 14 | Piotrowska N A, Andrzej B, Elżbieta Z S, et al. Exogenously applied auxins and cytokinins ameliorate lead toxicity by inducing antioxidant defence system in green alga Acutodesmus obliquus. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 132: 535-546. |
| 15 | Zhu X F, Wang Z W, Dong F, et al. Exogenous auxin alleviates cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana by stimulating synthesis of hemicellulose 1 and increasing the cadmium fixation capacity of root cell walls. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 263(2): 398-403. |
| 16 | Vanneste S, Friml J. Auxin: a trigger for change in plant development. Cell, 2009, 136(6): 1005-1016. |
| 17 | Lu G W, Coneva V, Casaretto J A, et al. OsPIN5 bmodulates rice (Oryza sativa)plant architecture and yield by changing auxin homeostasis, transport and distribution. The Plant Journal, 2015, 83(5): 913-925. |
| 18 | Fattorini L, Ronzan M, Piacentini D, et al. Cadmium and arsenic affect quiescent centre formation and maintenance in Arabidopsis thaliana post-embryonic roots disrupting auxin biosynthesis and transport. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 144: 37-48. |
| 19 | Ronzan M, Piacentini D, Fattorini L, et al. Cadmium and arsenic affect root development in Oryza sativa L. negatively interacting with auxin. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2018, 151: 64-75. |
| 20 | Yang Z, Xia J, Hong J, et al. Structural insights into auxin recognition and efflux by Arabidopsis PIN1. Nature, 2022, 609(7927): 611-615. |
| 21 | Matanzas N, Afif E, DÍaz T E, et al. Phytoremediation potential of native herbaceous plant species growing on a paradigmatic brown field site. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2021, 232(7): 290. |
| 22 | Wang Z, Wu Y Q, Mao K. Research progress of Cynodon dactylon. Pratacultural Science, 2001, 18(5): 37-41. |
| 王赞, 吴彦奇, 毛凯. 狗牙根研究进展. 草业科学, 2001, 18(5): 37-41. | |
| 23 | Wang J, Cheng Q, Xue S, et al. Pollution characteristics of surface runoff under different restoration types in manganese tailing wasteland. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(10): 9998-10005. |
| 24 | Yu F, Ma H T C, Zhong W X, et al. Effect of lead stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of Pogonatherum paniceum and Cynodon dactylon. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(11): 2602-2613. |
| 于飞, 马海天才, 钟沃秀, 等. 铅胁迫下金发草和狗牙根耐受性的对比. 草业科学, 2018, 35(11): 2602-2613. | |
| 25 | Li X, Wu Y J, Sun L X. Growth and physiological responses of three warm-season turf grasses to lead stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 171-180. |
| 李西, 吴亚娇, 孙凌霞. 铅胁迫对三种暖季型草坪草生长和生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 171-180. | |
| 26 | Zhang T T, Zhu Y X Y, Wu Y H, et al. Effects of exogenous IAA on physiological changes and cadmium tolerance of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. under cadmium stress. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(4): 335-341. |
| 张婷婷, 朱叶心怡, 吴玉环, 等. 镉胁迫下外源IAA对栝楼生理变化和耐镉性的影响. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(4): 335-341. | |
| 27 | Jin M, Liu Y, Shi B, et al. Exogenous IAA improves the seedling growth of Syringa villosa via regulating the endogenous hormones and enhancing the photosynthesis. Scientia Horticulturae, 2023, 308(27): 111585. |
| 28 | Zhan Y H, Zhang C H, Zheng Q X, et al. Cadmium stress inhibits the growth of primary roots by interfering auxin homeostasis in Sorghum bicolor seedlings. Journal of Plant Biology, 2017, 60(6): 593-603. |
| 29 | Li B Z. The measurement of IAA oxidase in “Ping Guo Li” leaves. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2001, 21(6): 837-839. |
| 李秉真. 苹果梨叶片中IAA氧化酶的测定. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2001, 21(6): 837-839. | |
| 30 | Jiang D C, Gao S, Gao H L, et al. The details of protein content determination by Coomassie brilliant blue staining. Experiment Science and Technology, 2018, 16(4): 119-123. |
| 蒋大程, 高珊, 高海伦, 等. 考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白质含量中的细节问题. 实验科学与技术, 2018, 16(4): 119-123. | |
| 31 | He W Y, Yang X E, Yang J Y, et al. Effect of lead on plant availability of phosphorus and potassium in a vegetable-soil system. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(34): 34793-34797. |
| 32 | Fatemi H, Esmaiel P B, Rizwan M. Foliar application of silicon nanoparticles affected the growth, vitamin C, flavonoid, and antioxidant enzyme activities of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) plants grown in lead (Pb)-spiked soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(2): 1417-1425. |
| 33 | Zeng F, Mallhi Z I, Khan N, et al. Combined citric acid and glutathione augments lead (Pb) stress tolerance and phytoremediation of Castorbean through antioxidant machinery and Pb uptake. Sustainability, 2021, 13(7): 4073. |
| 34 | Ma X L, Zhou H K, Zhang Z F. et al. The effects of exogenous IAA on seed germination and seedling growth of Onobrychis viciifolia Scop. under the drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(3): 796-803. |
| 马小兰, 周华坤, 张正芳, 等. 外源IAA对干旱胁迫下红豆草种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 草地学报, 2023, 31(3): 796-803. | |
| 35 | Ma L, Zhao Y, Chen M, et al. The microRNA ppe-miR393 mediates auxin-induced peach fruit softening by promoting ethylene production. Plant Physiology, 2023, 192(2): 1638-1655. |
| 36 | Talukdar M, Swain D K, Bhadoria P B S. Effect of IAA and BAP application in varying concentration on seed yield and oil quality of Guizotia abyssinica (L.f.) cass. Annals of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 67(1): 15-23. |
| 37 | Moon J Y, Belloeil C, Ianna M L, et al. Arabidopsis CNGC family members contribute to heavy metal ion uptake in plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(2): 413. |
| 38 | Gong Q, Li Z, Wang L, et al. Exogenous of indole-3-acetic acid application alleviates copper toxicity in spinach seedlings by enhancing antioxidant systems and nitrogen metabolism. Toxics, 2020, 8(1): 1. |
| 39 | Shi W G, Liu W, Yu W, et al. Abscisic acid enhances lead translocation from the roots to the leaves and alleviates its toxicity in Populus × canescens. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 362: 275-285. |
| 40 | Ojuederie O B. Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: a review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(12): 1504. |
| 41 | Li J, Pan L, Pan W, et al. Recent progress of oxidative stress associated biomarker detection. Chemical Communications, 2023, 59(48): 7361-7374. |
| 42 | Simkin A J, Kapoor L, Doss C G P, et al. The role of photosynthesis related pigments in light harvesting, photoprotection and enhancement of photosynthetic yield in planta. Photosynthesis Research, 2022, 152(3): 23-42. |
| 43 | Li D, Zhang L, Chen M, et al. Defense mechanisms of two pioneer submerged plants during their optimal performance period in the bioaccumulation of lead: A comparative study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(12): 2844. |
| 44 | Ai J X, Song J Y, Yan Z N, et al. Effects of melatonin on physiological response and DNA damage of Ardisia mamillata and A. crenata under lead stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 171-181. |
| 艾金祥, 宋嘉怡, 严浙楠, 等. 褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 171-181. | |
| 45 | Tan Z, Wu C, Xuan Z, et al. Lead exposure dose-dependently affects oxidative stress, AsA-GSH, photosynthesis, and mineral content in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1007276. |
| 46 | Tan Z, Xuan Z, Wu C, et al. Effects of selenium on the AsA-GSH system and photosynthesis of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) under lead stress. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2022, 22(4): 5111-5122. |
| 47 | Lu T, Yu H, Li Q, et al. Improving plant growth and alleviating photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress from low-light stress with exogenous GR24 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seedlings. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 490. |
| 48 | Su L, Xie J, Wen W, et al. Interaction of zinc and IAA alleviate aluminum-induced damage on photosystems via promoting proton motive force and reducing proton gradient in alfalfa. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 433. |
| 49 | Ayangbenro A S, Babalola O O. A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: a review of microbial biosorbents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14(1): 94. |
| 50 | Gharib F A E L, Ahmed E Z. Spirulina platensis improves growth, oil content, and antioxidant activity of rosemary plant under cadmium and lead stress. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 8008. |
| 51 | Mohamed H I, Latif H H, Hanafy R S. Influence of nitric oxide application on some biochemical aspects, endogenous hormones, minerals and phenolic compounds of Vicia faba plant grown under arsenic stress. Gesunde Pflanzen, 2016, 68(2): 99-107. |
| 52 | Liu W C, Song R F, Zheng S Q, et al. Coordination of plant growth and abiotic stress responses by tryptophan synthase βSubunit 1 through modulating tryptophan and ABA homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15(6): 973-990. |
| 53 | Park J, Lee S, Park G, et al. Cytokinin-responsive growth regulator regulates cell expansion and cytokinin-mediated cell cycle progression. Plant Physiology, 2021, 186(3): 1734-1746. |
| 54 | Hou M, Huo Y, Zhang Z Z, et al. Effects of exogenous vanadium stress on vanadium accumulation and subcellular distribution, and non-pro-teinthiol content in maize (Zea mays L.) crops. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(5): 964-972. |
| 侯明, 霍岩, 张志专, 等. 土壤外源钒施加对玉米中钒积累, 亚细胞分布和非蛋白巯基含量的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(5): 964-972. | |
| 55 | Guo B, Liu C, Liang Y, et al. Salicylic acid signals plant defence against cadmium toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(12): 2960. |
| 56 | Sudhakar S, Kumar S A, Penna S, et al. Identification and profiling of arsenic stress-induced microRNAs in Brassica juncea. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2013, 64(1): 303-315. |
| 57 | Piotrowska-niczyporuk A, Bajguz A, Kotowska U, et al. Auxins and cytokinins regulate phytohormone homeostasis and thiol-mediated detoxification in the green alga Acutodesmus obliquus exposed to lead stress. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 10193. |
| 58 | Gong W, Long J, Wu Y, et al. Application of NPA restrained leaf expansion by reduced cell division in soybean under shade stress. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 41(8): 3345-3358. |
| [1] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [2] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [3] | 张一龙, 喻启坤, 李雯, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根地上地下表型特征及内源激素对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [4] | 李庭伦, 李一亨, 余慧, 江再莉, 唐立涛, 王长庭, 胡雷. 铅卤钙钛矿泄漏对垂穗披碱草幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 160-170. |
| [5] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 孙晓梵. 两类新疆狗牙根抗旱基因型抗氧化酶保护系统及其基因表达差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| [6] | 孙晓梵, 张一龙, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同施氮量对干旱下狗牙根抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. |
| [7] | 卫宏健, 丁杰, 张巨明, 杨文, 王咏琪, 刘天增. 践踏胁迫下狗牙根草坪土壤真菌群落结构的变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 102-112. |
| [8] | 任雪锋, 邓亚博, 臧国长, 郑轶琦. 基于SSR标记的河南省狗牙根遗传多样性及群体遗传结构分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 60-70. |
| [9] | 穆海婷, 王英哲, 苗一凡, 郁伟杰, 徐博. 重金属铜和铅胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 139-146. |
| [10] | 赵欣桐, 陈晓东, 李子吉, 张巨明, 刘天增. 植物内生肠杆菌对狗牙根耐盐性的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 127-136. |
| [11] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙晓梵, 孙宗玖. 新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 155-169. |
| [12] | 李柯, 施宠, 何飞焱, 李昊宇. Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. |
| [13] | 李晓雪, 李昌晓, 宋虹, 袁中勋. 水淹和密度配置对牛鞭草与狗牙根扦插苗光合作用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 197-206. |
| [14] | 高亚敏, 姚拓, 李海云, 罗慧琴, 张建贵, 杨琰珊, 刘婷. 高寒草甸嵩草、珠芽蓼根际优良植物根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 114-123. |
| [15] | 韩航,陈顺钰,薛凌云,侯晓龙,蔡丽平,刘爱琴,周垂帆. 铅胁迫对金丝草生长及生理生化的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 131-138. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||