

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 123-134.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023498
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王雨欣1( ), 陶佳丽2, 朱慧森1(
), 陶佳丽2, 朱慧森1( ), 许涛1(
), 许涛1( ), 张逸飞1, 岑慧芳1
), 张逸飞1, 岑慧芳1
收稿日期:2023-12-26
修回日期:2024-03-18
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
朱慧森,许涛
作者简介:xutao@sxau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yu-xin WANG1( ), Jia-li TAO2, Hui-sen ZHU1(
), Jia-li TAO2, Hui-sen ZHU1( ), Tao XU1(
), Tao XU1( ), Yi-fei ZHANG1, Hui-fang CEN1
), Yi-fei ZHANG1, Hui-fang CEN1
Received:2023-12-26
Revised:2024-03-18
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Hui-sen ZHU,Tao XU
摘要:
偏关苜蓿是山西地方优良种质,具有抗逆性强、适应性强、耐瘠薄的特点,挖掘偏关苜蓿抗旱相关基因,并将其应用于紫花苜蓿遗传改良,对于优异新种质创制具有重要意义。利用miRNA测序从偏关苜蓿中筛选出miR397-5p为潜在的干旱胁迫响应基因,通过转基因烟草验证了偏关苜蓿miR397-5p对干旱胁迫的响应,并找到其潜在的下游调控因子。结果表明:干旱胁迫处理后,过表达miR397-5p烟草的可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白、脯氨酸等渗透调节物质含量增加,过氧化氢酶(CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)的活性提高,丙二醛(MDA)含量降低。干旱胁迫下,miR397-5p下调其靶基因LAC4的表达;在过表达miR397-5p烟草中,PAL、4CL、CCR、CAD、HCT、F5H、PAO等大部分木质素生物合成途径关键酶基因相对表达量下调,仅C4H、CCoAOMT、COMT等基因相对表达量上调,同时,过表达miR397-5p烟草木质素含量降低,大部分基因相对表达量和木质素含量具有一致的变化趋势。由此推断偏关苜蓿可能通过miR397-5p-LAC4调控木质素积累响应干旱胁迫,但具体内在机制有待进一步研究。研究结果可为紫花苜蓿遗传改良提供基因资源,对于优异新种质的创制具有潜在价值。
王雨欣, 陶佳丽, 朱慧森, 许涛, 张逸飞, 岑慧芳. 异源表达偏关苜蓿miR397-5p增强烟草干旱胁迫耐受能力[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 123-134.
Yu-xin WANG, Jia-li TAO, Hui-sen ZHU, Tao XU, Yi-fei ZHANG, Hui-fang CEN. Heterologous expression of miR397-5p from Medicago sativa cv. ‘Pianguan’ improves the drought tolerance of tobacco[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 123-134.
| 基因Gene | 正向引物Forward primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| conservative_7_25433 | TTTCCAATTCCACCCATTCCTA |
| conservative_8_17329 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC |
| conservative_8_17330 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC |
| miR397-5p | TCATTGAGTGCAGCGTTGATG |
| miR5205a | CATACAATTTGGGACGGAGGGAG |
| miR530 | TGCATTTGCACCTGCACTTTC |
| unconservative_6_4438 | GCGTTAGCTCAGTTAGTAAGGACAATG |
| U6 | CCTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAT |
表1 7个miRNAs的引物
Table 1 Primers for 7 miRNAs
| 基因Gene | 正向引物Forward primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| conservative_7_25433 | TTTCCAATTCCACCCATTCCTA |
| conservative_8_17329 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC |
| conservative_8_17330 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC |
| miR397-5p | TCATTGAGTGCAGCGTTGATG |
| miR5205a | CATACAATTTGGGACGGAGGGAG |
| miR530 | TGCATTTGCACCTGCACTTTC |
| unconservative_6_4438 | GCGTTAGCTCAGTTAGTAAGGACAATG |
| U6 | CCTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAT |
| 基因Gene | 正向引物Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| MTR_4g015120 | AACTACCTGTGGAGAGTGGC ACTAGGCCATGGATCCGATG | CATCGGATCCATGGCCTAGT GCCACTCTCCACAGGTAGTT |
| MsActin | TCGAGACCTTCAATGTGCCT | ACTCACACCGTCACCAGAAT |
| PAL | NATWGACTTGAGGCAYTTGG | TTYTGCATYARTGGGTAGTT |
| C4H | GGCAATCCCTCTTTTAGTCCC | CTCCTACCAACACCAAATGGA |
| F5H | CCAGCGACCGTAGCCATAAGTTAC | TGCCGCCAGAAGAGTCCATAGTC |
| 4CL | CTCTGGKACTACRGGKCTGC | AYTCCARGAACGGAGCAATG |
| CCR | TGGCAAACAGAGCAGGTGAAGTAG | CGGTGGCGTGAACAGTGTAGC |
| HCT | CTCAACCCACTCCCAACCAT | GCCTCCTTTAGCACTTTTCCG |
| CCoAOMT | AATGGTTCTGTGGTGGCTCC | CGGCGGCACAAGGTAATG |
| COMT | GATGTTGGAGGTGGTCTTGGA | CTGGTTTCACTGGTAAAATGGC |
| CAD | GAGGGTATGGCACCAGAACAA | GATGTCCCATTGCCTTTGCTAT |
| PAO | GTCGCTGCTCTGTCGTCATAGTC | CGCCGAATTCCTCCTTCCTTATCC |
| NtL25 | GCTTTCTTCGTCCCATCA | CCCCAAGTACCCTCGTAT |
表2 qRT-PCR引物
Table 2 Primers for qRT-PCR
| 基因Gene | 正向引物Forward primer (5'-3') | 反向引物Reverse primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| MTR_4g015120 | AACTACCTGTGGAGAGTGGC ACTAGGCCATGGATCCGATG | CATCGGATCCATGGCCTAGT GCCACTCTCCACAGGTAGTT |
| MsActin | TCGAGACCTTCAATGTGCCT | ACTCACACCGTCACCAGAAT |
| PAL | NATWGACTTGAGGCAYTTGG | TTYTGCATYARTGGGTAGTT |
| C4H | GGCAATCCCTCTTTTAGTCCC | CTCCTACCAACACCAAATGGA |
| F5H | CCAGCGACCGTAGCCATAAGTTAC | TGCCGCCAGAAGAGTCCATAGTC |
| 4CL | CTCTGGKACTACRGGKCTGC | AYTCCARGAACGGAGCAATG |
| CCR | TGGCAAACAGAGCAGGTGAAGTAG | CGGTGGCGTGAACAGTGTAGC |
| HCT | CTCAACCCACTCCCAACCAT | GCCTCCTTTAGCACTTTTCCG |
| CCoAOMT | AATGGTTCTGTGGTGGCTCC | CGGCGGCACAAGGTAATG |
| COMT | GATGTTGGAGGTGGTCTTGGA | CTGGTTTCACTGGTAAAATGGC |
| CAD | GAGGGTATGGCACCAGAACAA | GATGTCCCATTGCCTTTGCTAT |
| PAO | GTCGCTGCTCTGTCGTCATAGTC | CGCCGAATTCCTCCTTCCTTATCC |
| NtL25 | GCTTTCTTCGTCCCATCA | CCCCAAGTACCCTCGTAT |
| miRNA | 序列Sequence | log2(FC) (72 h VS 0 h) | 靶基因Target gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| conservative_7_25433 | TTTCCAATTCCACCCATTCCTA | -1.69 | MTR_0038s0060 |
| conservative_8_17329 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC | 2.19 | MTR_3g011610 |
| conservative_8_17330 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC | 2.19 | MTR_8g042410 |
| miR397-5p | TCATTGAGTGCAGCGTTGATG | 2.02 | MTR_4g015120 |
| miR5205a | CATACAATTTGGGACGGAGGGAG | -1.25 | MTR_7g100190 |
| miR530 | TGCATTTGCACCTGCACTTTC | 0.32 | MTR_1g107575 |
| unconservative_6_4438 | TTAGCTCAGTTAGTAAGGACAATG | -1.54 | MTR_2g020900 |
表3 差异miRNA基本信息
Table 3 Information of differential miRNA
| miRNA | 序列Sequence | log2(FC) (72 h VS 0 h) | 靶基因Target gene |
|---|---|---|---|
| conservative_7_25433 | TTTCCAATTCCACCCATTCCTA | -1.69 | MTR_0038s0060 |
| conservative_8_17329 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC | 2.19 | MTR_3g011610 |
| conservative_8_17330 | ATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCC | 2.19 | MTR_8g042410 |
| miR397-5p | TCATTGAGTGCAGCGTTGATG | 2.02 | MTR_4g015120 |
| miR5205a | CATACAATTTGGGACGGAGGGAG | -1.25 | MTR_7g100190 |
| miR530 | TGCATTTGCACCTGCACTTTC | 0.32 | MTR_1g107575 |
| unconservative_6_4438 | TTAGCTCAGTTAGTAAGGACAATG | -1.54 | MTR_2g020900 |
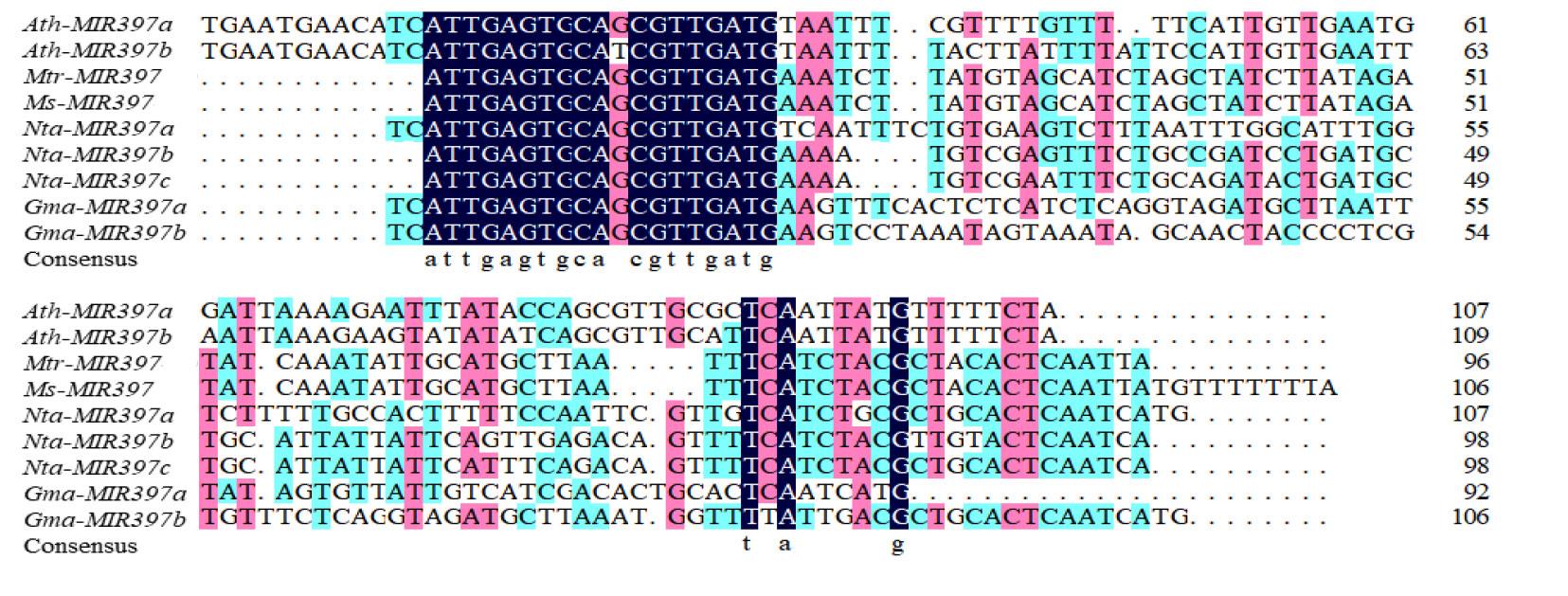
图2 miR397前体序列比对Mtr: 蒺藜苜蓿M. truncatula; Ms: 偏关苜蓿M. sativa ‘Pianguan’; Gma: 大豆G. max; Ath: 拟南芥A. thaliana; Nta: 烟草N. tabacum.下同The same below.
Fig.2 Precursor sequence alignment analysis of miR397
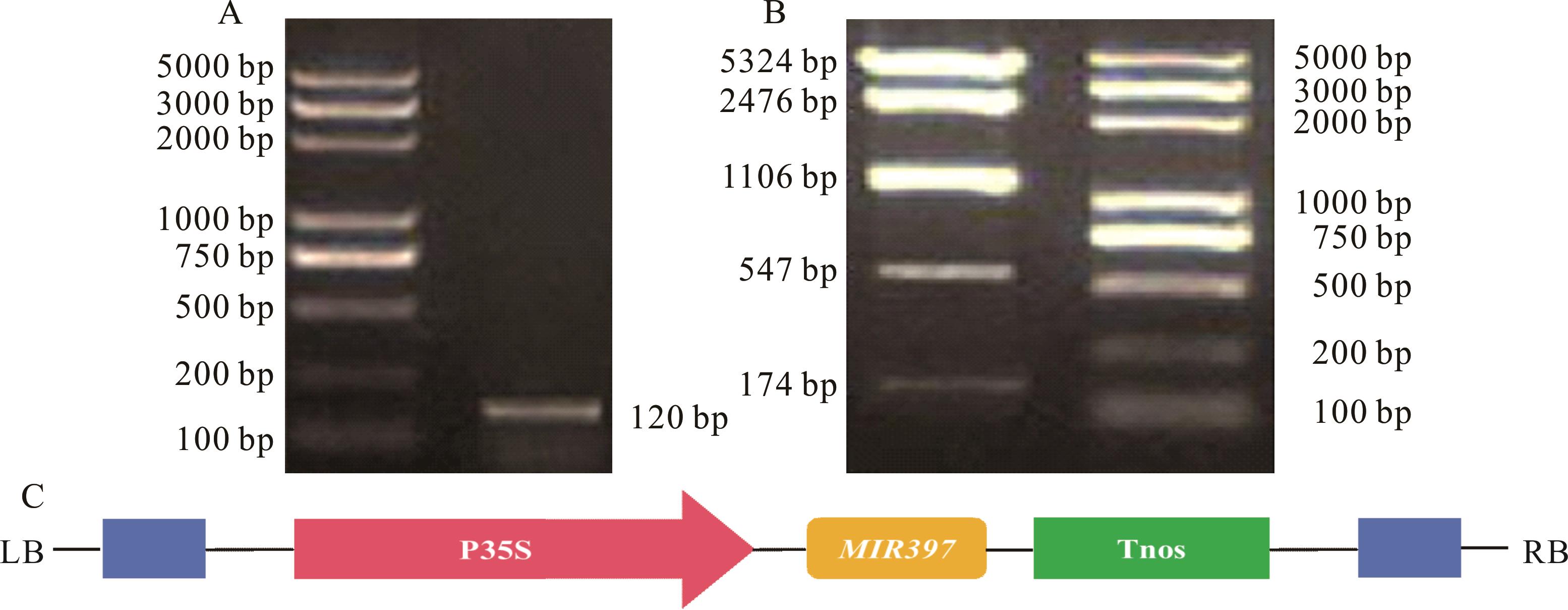
图5 重组表达载体pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p鉴定A: 阳性克隆菌液PCR鉴定PCR identification of pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p; B: pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p酶切鉴定Identification of pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p by enzyme digestion analysis; C: pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p表达载体构建Construction of pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p expression vector.
Fig.5 Identification of pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p
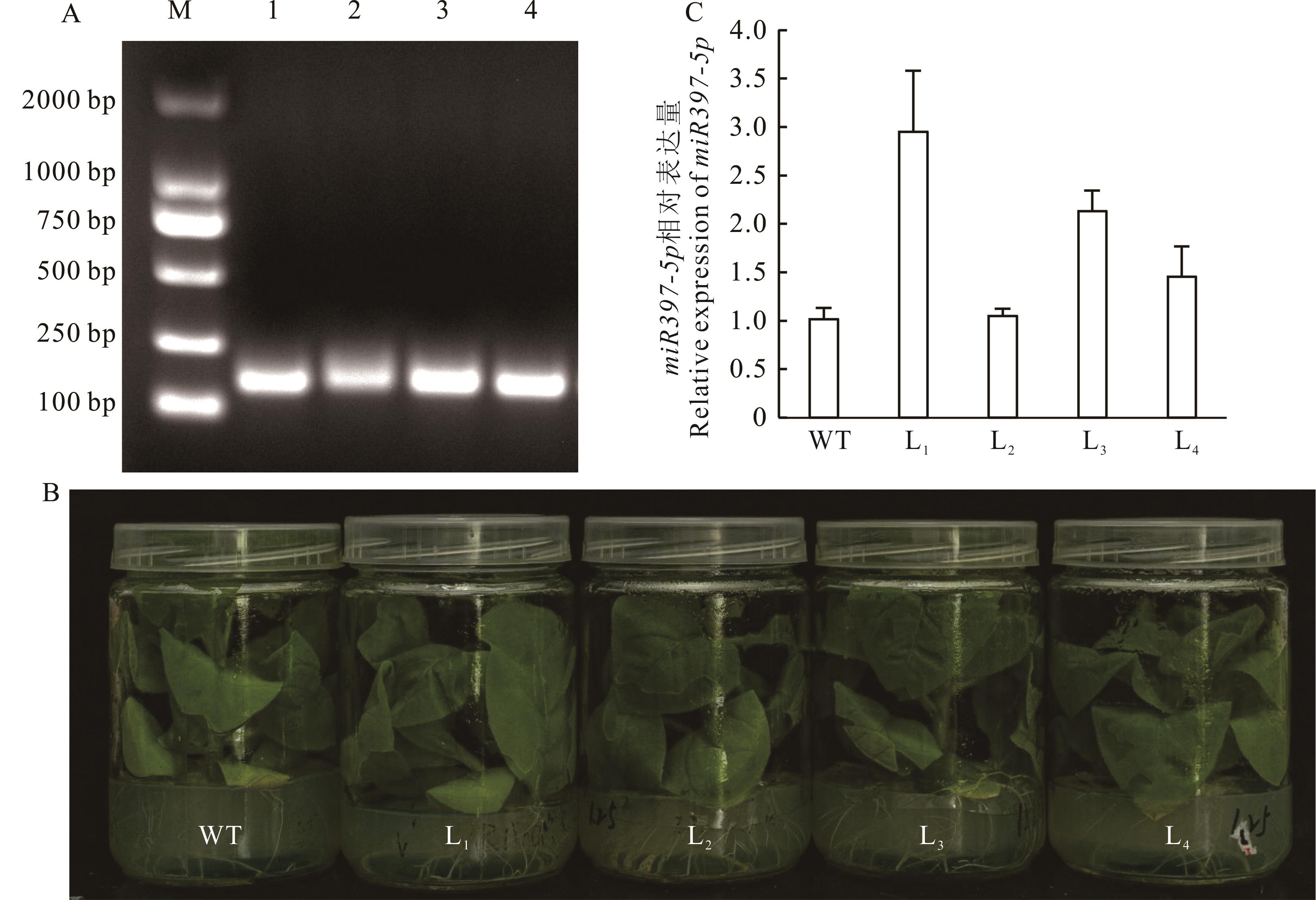
图6 pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p阳性植株鉴定A: 转基因烟草的PCR检测PCR detection of transgenic tobacco; B: 转基因烟草阳性植株Transgenic tobacco positive plants; C: 转基因烟草miR397-5p的表达分析Expression analysis of miR397-5p in transgenic tobacco.
Fig.6 Identification of pBWA(V)KS-miR397-5p positive plants

图7 干旱胁迫下野生型和过表达miR397-5p烟草生理响应不同大、小写字母分别表示野生型烟草和过表达miR397-5p烟草在不同处理时间对应各指标差异显著(P<0.05)。*表示野生型和过表达miR397-5p烟草在同一处理时间对应各指标差异显著。Different capital and lowercase letters indicate that wild-type tobacco and overexpressed miR397-5p tobacco have significant differences in each index at different treatment times (P<0.05). * denote wild-type and overexpressed miR397-5p tobacco have significant differences in each index at the same treatment time. 下同The same below.
Fig.7 Physiological response of wild type and miR397-5p-overexpressing tobacco under drought stress
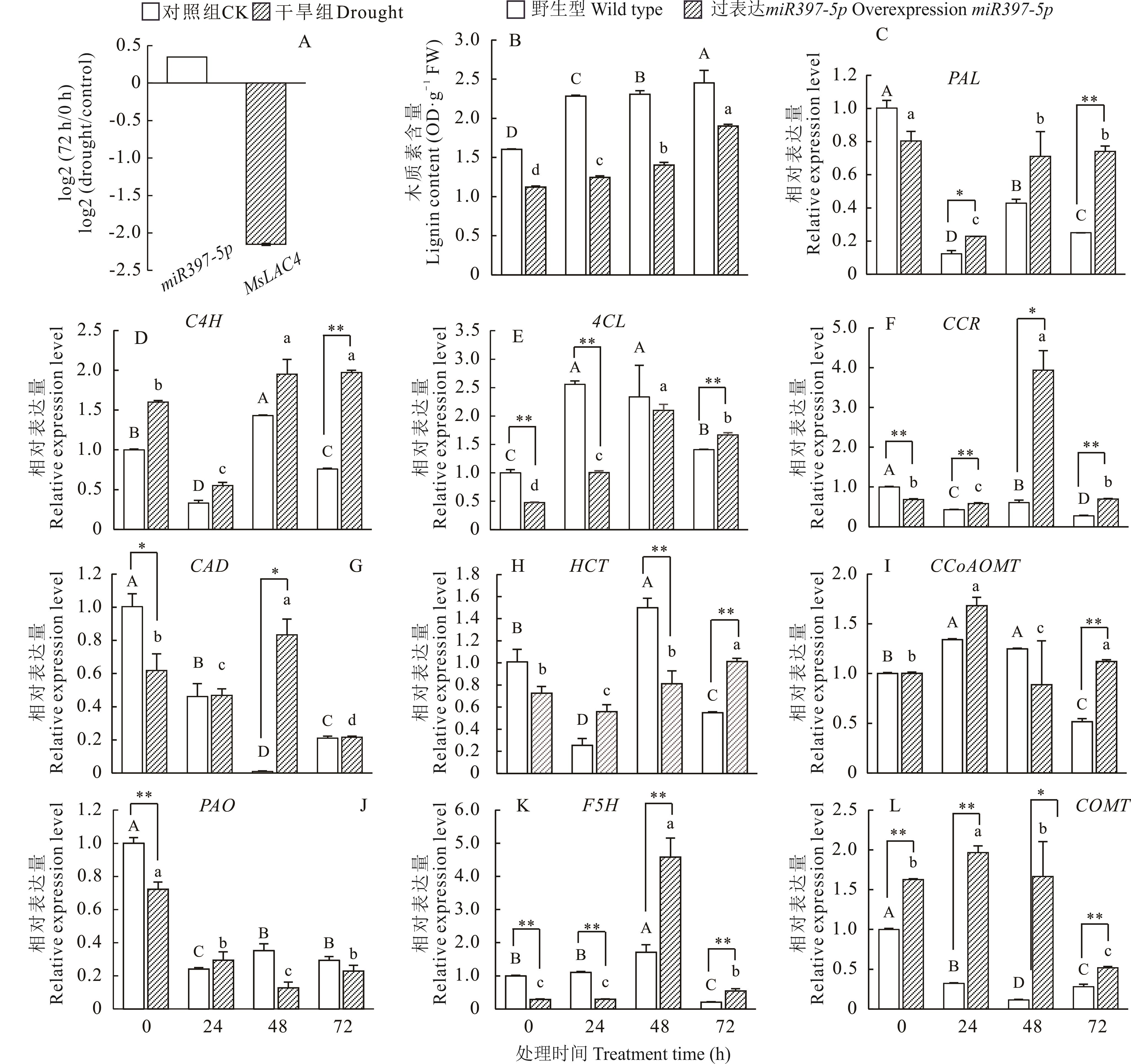
图8 干旱胁迫下野生型和过表达miR397-5p烟草木质素含量及相关基因表达量分析A: 干旱胁迫下偏关苜蓿miR397-5p及MsLAC4基因差异表达量Differential expression of miR397-5p and MsLAC4 genes in M. sativa cv. ‘Pianguan’ under drought stress; B: 野生型和过表达miR397-5p烟草中木质素含量Lignin content in wild-type and miR397-5p-overexpressing tobacco; C~L: 木质素代谢关键酶基因相对表达量Genes expression of lignin metabolism enzymes.
Fig.8 Analysis of lignin content and expression of related genes in wild-type and miR397-5p-overexpressing tobacco under drought stress
| 1 | Han Q F, Jia Z K, Wang J P. The analysis of current situation and development prospect of alfalfa industry at home and abroad. Pratacultural Science, 2005(3): 22-25. |
| 韩清芳, 贾志宽, 王俊鹏. 国内外苜蓿产业发展现状与前景分析. 草业科学, 2005(3): 22-25. | |
| 2 | Dong K H, Zhu H S, Tong L R, et al. Forage germplasm resources in Shanxi. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2010. |
| 董宽虎, 朱慧森, 佟莉蓉, 等. 山西牧草种质资源. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2010. | |
| 3 | Archana S, Deepti J, Jyotsna P, et al. Deciphering the role of miRNA in reprogramming plant responses to drought stress. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2022, 43(4): 11-15. |
| 4 | Sunkar R, Zhu J K. Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2004, 16(8): 2001-2019. |
| 5 | Kantar M, Lucas S J, Budak H. miRNA expression patterns of Triticum dicoccoides in response to shock drought stress. Planta, 2011, 233(3): 471-484. |
| 6 | Ferreira T H, Gentile A, Vilela R D, et al. microRNAs associated with drought response in the bioenergy crop sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). PLoS One, 2012, 7(10): e46703. |
| 7 | Xiang J, Lin P, Li X S, et al. Overexpression of tomato Sly-miR397 gene enhances drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(10): 51-58. |
| 向娟, 林鹏, 李兴盛, 等. 过表达番茄Sly-miR397基因增强拟南芥的耐旱性. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(10): 51-58. | |
| 8 | Yin J Q, Zhao R C. Identifying expression of new mall RNAs by microarrays. Methods, 2007, 43(2): 123-130. |
| 9 | Luo Y C, Zhou H, Li Y, et al. Rice embryogenic calli express a unique set of microRNAs, suggesting regulatory roles of microRNAs in plant post-embryogenic development. FEBS Letters, 2006, 580(21): 5111-5116. |
| 10 | Wang C Y, Zhang S C, Yu Y, et al. miR397b regulates both lignin content and seed number in Arabidopsis via modulating a laccase involved in lignin biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2014, 12(8): 1132-1142. |
| 11 | Ali S, Huang S L, Zhou J J, et al. miR397-LACs mediated cadmium stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Molecular Biology, 2023, 113(6): 415-430. |
| 12 | Cui W T, Zhuang Z H, Jiang P H, et al. Characterization, expression profiling, and biochemical analyses of the Cinnamoyl-CoA Reductase gene family for lignin synthesis in alfalfa plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(14): 7762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147762. |
| 13 | Halpin C. Lignin engineering to improve saccharification and digestibility in grasses. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2019, 56: 223-229. |
| 14 | Yan Y, Wang P, Liu Y, et al. MeRAV5 promotes drought stress resistance in cassava by modulating hydrogen peroxide and lignin accumulation. The Plant Journal, 2021, 107(3): 847-860. |
| 15 | Li D D, Yang J L, Pak S, et al. PuC3H35 confers drought tolerance by enhancing lignin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in the roots of Populus ussuriensis. The New Phytologist, 2021, 233(1): 390-408. |
| 16 | Río D C J, Rencoret J, Gutiérrez A, et al. Lignin monomers from beyond the canonical monolignol biosynthetic pathway: Another brick in the wall. ACS Sustainable Chemistry Engineering, 2020, 8(13): 4997-5012. |
| 17 | Bhatt P, Tiwari M, Parmarick P, et al. Insights into the catalytic mechanism of ligninolytic peroxidase and laccase in lignin degradation. Bioremediation Journal, 2022, 26(4): 281-291. |
| 18 | Sharma N K, Yadav S, Gupta S K, et al. microRNA397 regulates tolerance to drought and fungal infection by regulating lignin deposition in chickpea root. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2023, 46(11): 3501-3517. |
| 19 | Swetha C, Basu D, Pachamuthu K, et al. Major domestication related phenotypes in Indica rice are due to loss of miRNA mediated laccase silencing. The Plant Cell, 2018, 30(11): 2649-2662. |
| 20 | Rio D C, Ares M, Hannon G J, et al. Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harbor Protocols, 2010(6): 5439. |
| 21 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 22 | Gao J F, Sun Q, Cao C L, et al. Plant physiology experiment guide. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 15, 142, 144. |
| 高俊凤, 孙群, 曹翠玲, 等. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 15, 142, 144. | |
| 23 | Zou Q. Plant physiology experimental guidance. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 1-54. |
| 邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 1-54. | |
| 24 | Jiang H, Yan S C, Xue Y, et al. Effects of forest type on the activity of several defense proteins and content of secondary metabolites in larch needles. Forest Research, 2018, 31(3): 24-28. |
| 姜虹, 严善春, 薛羿, 等. 落叶松林型对其针叶内几种防御蛋白活力和次生代谢物含量的影响. 林业科学研究, 2018, 31(3): 24-28. | |
| 25 | Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(15): 4157-4168. |
| 26 | Wang L L, Zhao H S, Sun H Y, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of miR397 and miR1432 in Phyllostachys edulis under stresses. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2015, 51(6): 63-70. |
| 王丽丽, 赵韩生, 孙化雨, 等. 毛竹miR397和miR1432的克隆及其逆境胁迫响应表达分析. 林业科学, 2015, 51(6): 63-70. | |
| 27 | Shin S J, Lee J H, Kwon H B. Genome-wide identification and characterization of drought responsive microRNAs in Solanum tuberosum L. Genes & Genomics, 2017, 39(11): 1193-1203. |
| 28 | Luo M R, Liang W B, Yang Y, et al. Effects of drought stress on photosynthesis and chloroplast ultrastructure of Gardenia jasminoides. Economic Forest Research, 2021, 39(3): 165-174. |
| 罗孟容, 梁文斌, 杨艳, 等. 干旱胁迫对栀子光合作用及叶绿体超微结构的影响. 经济林研究, 2021, 39(3): 165-174. | |
| 29 | Khan R, Ma X H, Zhang J, et al. Circular drought-hardening confers drought tolerance via modulation of the antioxidant defence system, osmoregulation, and gene expression in tobacco. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 172(2): 1073-1088. |
| 30 | Xiang H T, Zheng D F, He N, et al. Research progress on the physiological response of plants to low temperature and the amelioration effectiveness of exogenous ABA. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 208-219. |
| 项洪涛, 郑殿峰, 何宁, 等. 植物对低温胁迫的生理响应及外源脱落酸缓解胁迫效应的研究进展. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 208-219. | |
| 31 | Li B, Liu C, Li H, et al. Analysis of the effect of exogenous calcium chloride on drought alleviation of ‘Longmu 807’ alfalfa seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 990-997. |
| 李波, 刘畅, 李红, 等. 外源氯化钙对‘龙牧 807’苜蓿幼苗干旱缓解效应分析. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 990-997. | |
| 32 | Melandri G, AbdElgawad H, Riewe D, et al. Biomarkers for grain yield stability in rice under drought stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2020, 71(2): 669-683. |
| 33 | Li X, Tian X H, Du W H. Screening on the drought resistance index and conditions for ×Triticale Wittmack at the seedling stage. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(3): 539-546. |
| 李雪, 田新会, 杜文华. 饲草型小黑麦苗期抗旱指标的筛选. 草业科学, 2017, 34(3): 539-546. | |
| 34 | Guo Y Y, Xu H M, Zhao Y Y, et al. Plant lignification and its regulation. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2020, 50(2): 111-122. |
| 郭亚玉, 许会敏, 赵媛媛, 等. 植物木质化过程及其调控的研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2020, 50(2): 111-122. | |
| 35 | Zhang S C, Ju C L, Wang X J. Arabidopsis laccase gene AtLAC4 regulates plant growth and responses to abiotic stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(4): 357-365. |
| 张盛春, 鞠常亮, 王小菁. 拟南芥漆酶基因AtLAC4参与生长及非生物胁迫响应. 植物学报, 2012, 47(4): 357-365. |
| [1] | 王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139. |
| [2] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [3] | 魏娜, 敬文茂, 许尔文, 王荣新, 赵晶忠, 马雪娥, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 白花草木樨MaERF058基因耐旱功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 159-169. |
| [4] | 曾露婧, 王国华. 干旱及复水对荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 41-57. |
| [5] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [6] | 姜瑛, 张辉红, 魏畅, 徐正阳, 赵颖, 刘芳, 李鸽子, 张雪海, 柳海涛. 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下玉米幼苗根系发育及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [7] | 王宝强, 马文静, 王贤, 朱晓林, 赵颖, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [8] | 张一龙, 李雯, 喻启坤, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 狗牙根叶与根氮代谢对不同干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 175-187. |
| [9] | 张浩, 胡海英, 李惠霞, 贺海明, 马霜, 马风华, 宋柯辰. 荒漠草原优势植物牛枝子对干旱胁迫的生理响应与转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 188-205. |
| [10] | 梁佳, 胡朝阳, 谢志明, 马刘峰, 陈芸, 方志刚. 外源褪黑素缓解甜高粱幼苗干旱胁迫的生理效应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [11] | 李艳鹏, 魏娜, 翟庆妍, 李杭, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 全基因组水平白花草木樨TCP基因家族的鉴定及在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [12] | 张一龙, 喻启坤, 李雯, 李培英, 孙宗玖. 不同抗旱性狗牙根地上地下表型特征及内源激素对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 163-178. |
| [13] | 王占军, 季波, 纪童, 蒋齐. 5种豆科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. |
| [14] | 刘牧野, 郭丽珠, 岳跃森, 武菊英, 范希峰, 肖国增, 滕珂. 干旱胁迫下不同性别野牛草生理及抗氧化酶基因表达差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 93-103. |
| [15] | 刘福, 陈诚, 张凯旋, 周美亮, 张新全. 日本百脉根LjbHLH34基因克隆及耐旱功能鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 178-191. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||