

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 126-139.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023102
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王宝1( ), 谢占玲1,2(
), 谢占玲1,2( ), 郭璟1, 唐永鹏3, 孟清1, 彭清青1, 杨家宝1, 董德誉1, 徐鸿雁1, 高太侦4, 张凡5, 段迎珠6
), 郭璟1, 唐永鹏3, 孟清1, 彭清青1, 杨家宝1, 董德誉1, 徐鸿雁1, 高太侦4, 张凡5, 段迎珠6
收稿日期:2023-04-04
修回日期:2023-05-11
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-06-20
通讯作者:
谢占玲
作者简介:E-mail: xiezhanling2012@126.com基金资助:
Bao WANG1( ), Zhan-ling XIE1,2(
), Zhan-ling XIE1,2( ), Jing GUO1, Yong-peng TANG3, Qing MENG1, Qing-qing PENG1, Jia-bao YANG1, De-yu DONG1, Hong-yan XU1, Tai-zhen GAO4, Fan ZHANG5, Ying-zhu DUAN6
), Jing GUO1, Yong-peng TANG3, Qing MENG1, Qing-qing PENG1, Jia-bao YANG1, De-yu DONG1, Hong-yan XU1, Tai-zhen GAO4, Fan ZHANG5, Ying-zhu DUAN6
Received:2023-04-04
Revised:2023-05-11
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-06-20
Contact:
Zhan-ling XIE
摘要:
本研究以分离自青藏高原植物内生真菌(3株青霉和1株木霉)浸种燕麦,以未接种培养基为无菌株对照(CK),探究轻度、中度和重度干旱胁迫下其对燕麦生长、生理及根系内生真菌群落结构的影响。浸种后的种子置于培养皿中发芽,在正常条件下生长30 d后,在不同渗透胁迫处理下生长10 d,添加50 mL的聚乙二醇溶液模拟不同梯度干旱胁迫:5%、10%、15%(轻度胁迫);20%、25%(中度胁迫);30%、35%(重度胁迫),以无菌水作为未胁迫对照(0%)。结果表明,随着胁迫的加剧,燕麦幼苗的株高、鲜重、干重和叶绿素含量普遍下降,而过氧化物酶活性和丙二醛、脯氨酸含量随着内生真菌处理的不同而变化很大。真菌浸种燕麦,盆栽40 d根系Illumina Miseq结果共获得192944条有效序列,包括1140个OTU,隶属于9门-15纲-34目-56科-148属;与对照相比,浸种改变了燕麦根系内生真菌群落结构;真菌浸种提高了担子菌门红菇科的相对丰度,优势属为乳菇属,而对照的优势属为链格孢属。主成分分析将浸种所用的青霉属和木霉属菌株分为3类,分别为促生菌株、增强抗逆性菌株和增加微生物多样性的菌株;白木霉增加了根系内生真菌多样性,而青霉属、鹅掌青霉促进燕麦生长及抗逆性。本研究揭示了青藏高原内生真菌浸种通过促进燕麦生长,降低干旱造成的氧化损伤及改变根系内生真菌群落结构,增强了燕麦对干旱胁迫的响应能力。
王宝, 谢占玲, 郭璟, 唐永鹏, 孟清, 彭清青, 杨家宝, 董德誉, 徐鸿雁, 高太侦, 张凡, 段迎珠. 真菌发酵液浸种燕麦对其抗旱性及根际真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 126-139.
Bao WANG, Zhan-ling XIE, Jing GUO, Yong-peng TANG, Qing MENG, Qing-qing PENG, Jia-bao YANG, De-yu DONG, Hong-yan XU, Tai-zhen GAO, Fan ZHANG, Ying-zhu DUAN. Effects of seed soaking of Avena sativa in fungal fermentation broth on rhizosphere fungal community structure and drought resistance of oats[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 126-139.
菌株 Strains | 物种 Species | 寄主植物 Host plants | 分离地区 Separating regions | 分离部位 Separation part | NCBI登录号 NCBI accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 204 | 鹅掌青霉Penicillium goetzii | 麻花艽Gentiana straminea | 泽库Zeku | 根Root | MT558933.1 |
| 132 | 皮落青霉Penicillium crustosum | 黄芪Astragalus propinquus | 甘德Gande | 叶Leaves | MZ901027.1 |
| 303 | 青霉Penicillium spp. | 长芒嵩草Kobresia longearistita | 天峻Tianjun | 茎Stem | HQ607963.1 |
| 227 | 白木霉Trichoderma alni | 繁缕Stellaria media | 泽库Zeku | 根Root | KX632522.1 |
表1 供试菌株来源及登录号
Table 1 Source and registration number of test strains
菌株 Strains | 物种 Species | 寄主植物 Host plants | 分离地区 Separating regions | 分离部位 Separation part | NCBI登录号 NCBI accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 204 | 鹅掌青霉Penicillium goetzii | 麻花艽Gentiana straminea | 泽库Zeku | 根Root | MT558933.1 |
| 132 | 皮落青霉Penicillium crustosum | 黄芪Astragalus propinquus | 甘德Gande | 叶Leaves | MZ901027.1 |
| 303 | 青霉Penicillium spp. | 长芒嵩草Kobresia longearistita | 天峻Tianjun | 茎Stem | HQ607963.1 |
| 227 | 白木霉Trichoderma alni | 繁缕Stellaria media | 泽库Zeku | 根Root | KX632522.1 |

图1 内生真菌浸种对燕麦种子萌发的影响227为白木霉、303为青霉、132为皮落青霉、204为鹅掌青霉。A、B、C、D、E依次为PEG浓度0%、5%、15%、20%、25%。不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。227 is T. alni, 303 is Penicillium spp., 132 is P. crustosum, 204 is P. goetzii. A, B, C, D, E were PEG concentration of 0%, 5%, 15%, 20%, 25%. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference (P<0.05), the same below. 重度干旱胁迫(30%、35% PEG)下种子未萌发。Seeds didn’t germinate under severe drought stress (30%, 35% PEG).
Fig.1 Effects of seed soaking with endophytic fungi on oat seed germination
菌株 Strain | 操作分类单元 Operational taxonomic unit | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Pielou指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 44 | 0.61±0.09a | 2.43±1.36a | 0.24±0.13a |
| 227 | 62 | 0.46±0.16a | 2.02±0.42a | 0.18±0.02a |
| 303 | 47 | 0.50±0.11a | 2.33±0.51a | 0.23±0.06a |
| 132 | 31 | 0.57±0.17a | 2.11±0.72a | 0.29±0.14a |
| 204 | 41 | 0.61±0.11a | 1.92±0.33a | 0.21±0.07a |
表2 内生真菌浸种后燕麦根系真菌群落的α-多样性分析
Table 2 α-diversity analysis of oat root fungal community after soaking
菌株 Strain | 操作分类单元 Operational taxonomic unit | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Pielou指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 44 | 0.61±0.09a | 2.43±1.36a | 0.24±0.13a |
| 227 | 62 | 0.46±0.16a | 2.02±0.42a | 0.18±0.02a |
| 303 | 47 | 0.50±0.11a | 2.33±0.51a | 0.23±0.06a |
| 132 | 31 | 0.57±0.17a | 2.11±0.72a | 0.29±0.14a |
| 204 | 41 | 0.61±0.11a | 1.92±0.33a | 0.21±0.07a |
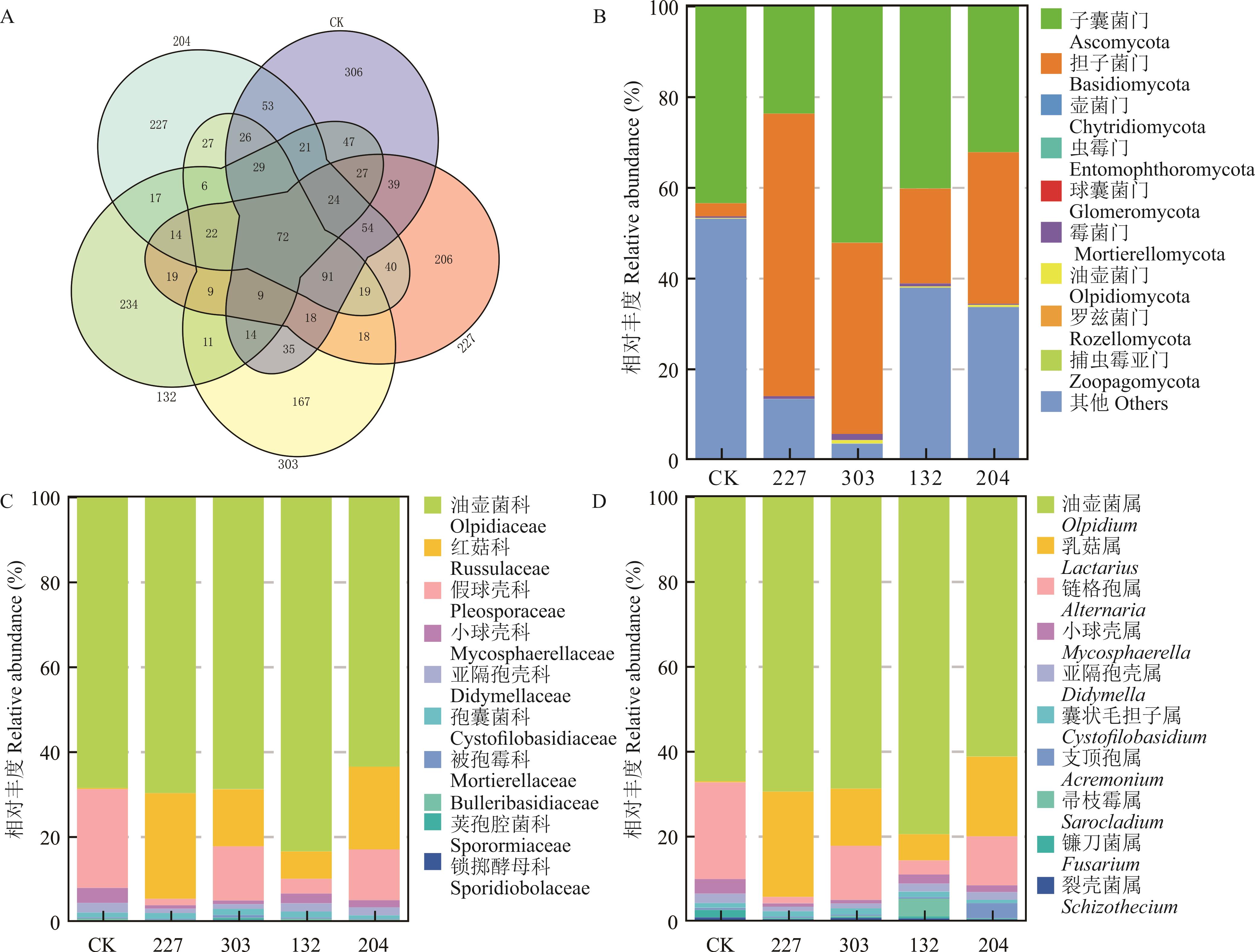
图4 内生真菌浸种对燕麦根系真菌群落结构的影响A为总的OTU数,B为门水平,C为科水平(相对丰度≥1%),D为属水平(相对丰度较高前10属)。A is the total number of OTUs, B is the phylum level, C is the family level (relative abundance≥1%), and D is the genus level (the top 10 genera with higher relative abundance).
Fig.4 Effects of seed soaking with endophytic fungi on the fungal community structure of oat roots
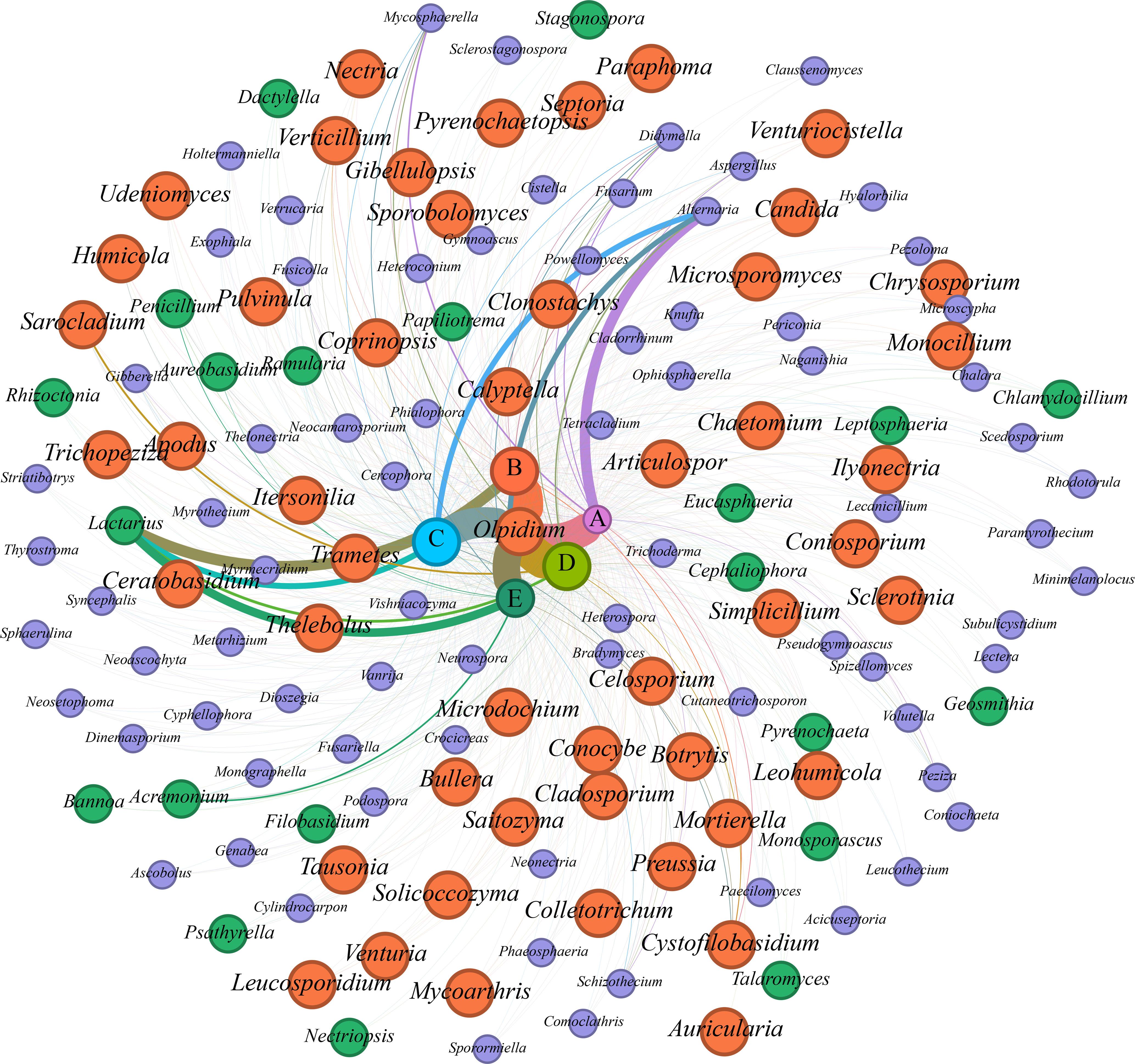
图5 属水平燕麦根系真菌群落网络A: 对照CK; B: 白木霉T. alni; C: 青霉Penicillium spp.; D: 皮落青霉P. crustosum; E: 鹅掌青霉P. goetzii. Cladosporium: 枝孢属; Mycosphaerella: 球腔菌属; Ramularia: 柱隔孢属; Septoria: 壳针孢属; Sphaerulina: 亚球壳属; Aureobasidium: 短梗霉属; Pyrenochaeta: 须壳孢属; Pyrenochaetopsis: 拟棘壳孢属; Didymella: 亚隔孢壳属; Heterospora: 异孢菌属; Leptosphaeria: 小球腔菌属; Stagonospora: 壳多孢属; Periconia: 黑团孢属; Paraphoma: 异茎点霉属; Phaeosphaeria: 暗壳腔菌属; Alternaria: 链格孢属; Neocamarosporium: 新菌孢子菌属; Thyrostroma: 葡萄座腔菌属; Preussia: 光黑壳属; Sporormiella: 孢子菌属; Cyphellophora: 黑色附球孢菌属; Coniosporium: 梨孢霉属; Exophiala: 外瓶霉属; Heteroconium: 异锥孢属; Minimelanolocus: 拟折孢属; Phialophora: 瓶霉属; Bradymyces: 延霉菌属; Aspergillus: 曲霉属; Penicillium: 青霉属; Talaromyces: 篮状菌属; Gymnoascus: 裸囊菌属; Chrysosporium: 金孢属; Verrucaria: 疣孢漆斑菌属; Articulospor: 阿替古菌属; Claussenomyces: 克劳森酵母属; Crocicreas: 胶被盘菌属; Tetracladium: 刺毛四枝孢菌; Chalara: 鞘孢属; Leohumicola: 耐热丝菌属; Mycoarthris: 奇异变形杆菌属; Cistella: 小毛盘菌属; Microscypha: 小单孢属; Pezoloma: 盘霜霉属; Botrytis: 葡萄孢属; Sclerotinia: 核盘菌属; Pseudogymnoascus: 假裸囊菌属; Thelebolus: 寡囊盘菌属; Dactylella: 隔指孢属; Hyalorbilia: 品圆盘菌属; Ascobolus: 粪盘菌属; Cephaliophora: 头束霉属; Peziza: 盘菌属; Genabea: 囊被块菌属; Pulvinula: 垫盘菌属; Candida: 假丝酵母菌属; Dinemasporium: 丁孢子虫属; Coniochaeta: 锥毛壳属; Colletotrichum: 刺盘孢属; Lectera: 勒克氏菌属; Verticillium: 轮枝孢属; Clonostachys: 枝穗霉属; Metarhizium: 绿僵菌属; Paecilomyces: 拟青霉属; Simplicillium: 菌褶轮枝菌属; Monocillium: 单链孢属; Trichoderma: 木霉属; Acremonium: 枝顶孢属; Chlamydocillium: 衣藻属; Fusariella: 柄小镰孢; Sarocladium: 帚枝霉属; Cylindrocarpon: 柱孢霉属; Fusarium: 镰刀菌属; Gibberella: 赤霉菌属; Ilyonectria: 土赤壳属; Nectria: 丛赤壳属; Neonectria: 新丛赤壳属; Thelonectria: 乳突赤壳属; Volutella: 周刺座霉属; Eucasphaeria: 真星藻属; Myrothecium: 漆斑霉属; Paramyrothecium: 拟漆斑菌属; Striatibotrys: 葡萄穗霉属; Scedosporium: 赛多孢子菌属; Chaetomium: 毛壳属; Humicola: 腐质霉属; Cercophora: 尾孢菌属; Podospora: 柄孢壳属; Schizothecium: 裂褶菌属; Neurospora: 脉孢菌属; Microdochium: 微杆菌属; Conocybe: 锥盖伞属; Coprinopsis: 鬼伞属; Psathyrella: 小脆柄菇属; Calyptella: 帽形菌属; Ceratobasidium: 角担菌属; Rhizoctonia: 丝核菌属; Trametes: 栓菌属; Subulicystidium: 锥囊菌属; Lactarius: 乳菇属; Microsporomyces: 小孢子属; Leucosporidium: 白冬孢酵母属; Rhodotorula: 红酵母属; Sporobolomyces: 掷孢酵母属; Itersonilia: 锁霉属; Tausonia: 毛壳属; Udeniomyces: 乌登霉菌属; Filobasidium: 线黑粉酵母属; Bullera: 布勒掷孢酵母属; Dioszegia: 宙斯沸耳属; Vishniacozyma: 维希尼克氏酵母属; Cutaneotrichosporon: 皮肤皮状新丝孢酵母; Spizellomyces: 棘孢霉属; Mortierella: 被孢霉属; Olpidium: 油壶菌属; Syncephalis: 集珠霉属; Bannoa: 坂野酵母属; Nectriopsis: 丛赤壳属; Auricularia: 木耳属.
Fig.5 Fungal community network of A. sativa root at genus level

图6 内生真菌对燕麦的主成分分析(A)及相关性分析(B)204为鹅掌青霉、132为皮落青霉、303为青霉、227为白木霉。30%、35%为PEG浓度。1、2、3为试验重复。204 is P. goetzii, 132 is P. crustosum, 303 is Penicillium spp., and 227 is T. alni. 30%, 35% were PEG concentration. 1, 2 and 3 are experimental replicates. C、D、E、F、G、H、I、J、K、L、M、N、O依次为株高、根长、鲜重、干重、丙二醛、过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶、脯氨酸、可溶性糖、叶绿素、辛普森指数、香浓指数和均匀度指数。C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O were plant height, root length, fresh weight, dry weight, malonaldehyde, peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, proline, soluble sugar, chlorophyll, Simpson index, Shannon index and Pielou index. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01: ***: P<0.001.
Fig.6 Principal component analysis (A) and correlation analysis (B) of endophytic fungi on oat
| 1 | Wu Y S, Lu Y, Zhu Z B, et al. The endophytic fungi and their secondary metabolites with antifungal activities in medicinal plants. World Notes on Antibiotics, 2019, 40(4): 309-315. |
| 武艳霜, 陆悦, 朱作斌, 等. 药用植物中具有抗真菌活性的内生真菌及其次级代谢产物的研究. 国外医药(抗生素分册), 2019, 40(4): 309-315. | |
| 2 | Badawy A A, Alotaibi M O, Abdelaziz A M, et al. Enhancement of seawater stress tolerance in barley by the endophytic fungus Aspergillus ochraceus. Metabolites, 2021, 11(7): 428. |
| 3 | Li E, Hu H R, Li J N, et al. Research progress on endophytic fungi improving plant resistance to salt stress. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2019, 35(11): 169-178. |
| 李娥, 胡华冉, 李蛟男, 等. 内生真菌提高植物抵御盐胁迫的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2019, 35(11): 169-178. | |
| 4 | Yao R L, Gan C Y, Xiang D Y. Physiological responses to drought stress in Toona sinensis and Bischofia javanica seedlings colonized by Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Guangxi Forestry Science, 2013, 42(4): 295-299. |
| 姚瑞玲, 甘春雁, 项东云. 丛枝菌根化香椿、秋枫幼苗对PEG-6000溶液生理响应. 广西林业科学, 2013, 42(4): 295-299. | |
| 5 | Vitti A, Pellegrini E, Nali C, et al. Trichoderma harzianum T-22 induces systemic resistance in tomato infected by cucumber mosaic virus. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 10(7): 1520. |
| 6 | Rojas X, Guo J, Leff J W, et al. Infection with a shoot-specific fungal endophyte (Epichloë) alters tall fescue soil microbial communities. Microbial Ecology, 2016, 72(1): 197-206. |
| 7 | Oses-Pedraza R, Torres-Díaz C, Lavín P, et al. Root endophytic Penicillium promotes growth of Antarctic vascular plants by enhancing nitrogen mineralization. Extremophiles, 2020, 24(5): 721-732. |
| 8 | Jin Y Y, Chen Z J, Wang T, et al. Effects of Epichloe endophyte and field management practices on the abundance and diversity of the soil fungal community. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 142-152. |
| 金媛媛, 陈振江, 王添, 等. 内生真菌和田间管理措施对土壤真菌群落丰度和多样性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 142-152. | |
| 9 | Wang T, Wei S F, Wei Q, et al. Diversity of endophytic fungi from leaves of Cinnamomum longepaniculatum N. Chao ex H.W. Li in Yibin, Sichuan, China. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2007, 129(3): 300-302, 307. |
| 王涛, 魏淑芳, 魏琴, 等. 油樟叶内生真菌的多样性研究. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 129(3): 300-302, 307. | |
| 10 | Ngo M T, Nguyen M V, Han J W, et al. In vitro and in vivo antifungal activity of sorbicillinoids produced by Trichoderma longibrachiatum. Journal of Fungi, 2021, 7(6): 428. |
| 11 | Gómez-Muñoz B, Jensen L S, Neergaard A D, et al. Effects of Penicillium bilaii on maize growth are mediated by available phosphorus. Plant and Soil, 2018, 431(1): 159-173. |
| 12 | Masunaga A, Sato Y, Kadofuku T, et al. A case of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and interleukin 6 receptor-producing mediastinal mature cystic teratoma with somatic-type malignancy. Pathology International, 2011, 61(4): 243-247. |
| 13 | Zhang F, Wang Y, Liu C, et al. Trichoderma harzianum mitigates salt stress in cucumber via multiple responses. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 170(15): 436-445. |
| 14 | Wang T J, Zhao L J, Zhang X. Discussion on the method of ecotope comprehensive evaluation for Tibet Plateau ecological shelter zone. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 498(9): 112-116. |
| 王铁军, 赵礼剑, 张溪. 青藏高原生态屏障区生态环境综合评价方法探讨. 测绘通报, 2018, 498(9): 112-116. | |
| 15 | Yuan F D, Zhang X, Wei Y Q. Evaluation of ecological environment vulnerability in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological barrier zone. Geospatial Information, 2018, 16(4): 67-69. |
| 袁烽迪, 张溪, 魏永强. 青藏高原生态屏障区生态环境脆弱性评价研究. 地理空间信息, 2018, 16(4): 67-69. | |
| 16 | Jiang Z H, Zhou H, Zhang D G, et al. Diversity of endophytic fungi of Oxytropis ochrocephala in different altitude gradients on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1526-1536. |
| 姜哲浩, 周恒, 张德罡, 等. 青藏高原不同海拔梯度黄花棘豆内生真菌多样性研究. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1526-1536. | |
| 17 | Liu K Q. Effects of water stress on growth and yield components of oat. Xining: Qinghai University, 2020. |
| 刘凯强. 水分胁迫对燕麦生长发育及产量构成的影响. 西宁: 青海大学, 2020. | |
| 18 | Xu T, Cui Z H, Zhong J, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria from oats in alpine region of Qinghai. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(2): 205-208. |
| 徐婷, 崔占鸿, 钟瑾, 等. 青海省部分地区人工种植燕麦青贮乳酸菌的筛选. 江苏农业科学, 2015, 43(2): 205-208. | |
| 19 | Mao Y J, Xie Z L, Xu H Y, et al. Study on the plant diversity of Floccularia luteovirens community under different altitude gradients. Journal of Qinghai University, 2022, 40(1): 1-9. |
| 毛玉晶, 谢占玲, 徐鸿雁, 等. 不同海拔梯度下黄绿卷毛菇群落植物多样性研究. 青海大学学报, 2022, 40(1): 1-9. | |
| 20 | Gao X, Nimazhaxi, Liu G Y, et al. Effects of PEG simulation drought stress on growth characteristics of spring rapeseed (Brassica campestris L.) at bud stage. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 47(7): 9-17. |
| 高雪, 尼玛扎西, 刘国一, 等. PEG模拟干旱胁迫对白菜型春油菜芽期生长特性的影响. 广东农业科学, 2020, 47(7): 9-17. | |
| 21 | Yu J, Jiao P P. Inhibition of seed germination of Ammmopiptanthus nanus (M. Pop.) Cheng f. under simulated drought stress with polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000). Genomics and Applied Biology, 2010, 29(2): 355-360. |
| 于军, 焦培培. 聚乙二醇(PEG6000)模拟干旱胁迫抑制矮沙冬青种子的萌发. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2010, 29(2): 355-360. | |
| 22 | Zhang H. Identification indexes, evaluation methods of rice drought-resistance and its application. Chengdu: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 张鸿. 水稻抗旱性鉴定指标、评价方法及其应用研究. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2018. | |
| 23 | Wang Q M, Yan L, Hu X Q, et al. Effects of tea grey blight on the community structure of endophytic fungi in tea leaves. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2021, 61(9): 2949-2961. |
| 王桥美, 严亮, 胡先奇, 等. 茶轮斑病对茶树叶片内生真菌群落结构的影响. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(9): 2949-2961. | |
| 24 | Zhong R, Xia C, Ju Y W, et al. A foliar Epichloë endophyte and soil moisture modified belowground arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal biodiversity associated with Achnatherum inebrians. Plant and Soil, 2021, 458(4): 105-122. |
| 25 | Zhang M M, Wu J, Hao X L, et al. The studying of species diversity of different forest types in typical hilly and gully areas of southern Shanxi. Journal of Shanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 36(4): 23-28. |
| 张咪咪, 吴洁, 郝小玲, 等. 晋南典型丘陵沟壑区不同林地类型物种多样性研究. 山西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 36(4): 23-28. | |
| 26 | Zhao M L, Zhao W J, Guo Y T, et al. Effects of drought stress and rewatering on growth and leaf photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Helianthus tuberosus. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2019, 28(4): 49-57. |
| 赵孟良, 赵文菊, 郭怡婷, 等. 干旱胁迫及复水对菊芋生长及叶片光合和生理特性的影响. 植物资源与环境学报, 2019, 28(4): 49-57. | |
| 27 | Wang X J, Yan S J. Drought stress affects physiological characteristics of tomato seedlings. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2022, 35(6): 76-80. |
| 王新军, 阎世江. 干旱胁迫对番茄幼苗生理特性的影响. 中国瓜菜, 2022, 35(6): 76-80. | |
| 28 | Yin X L, Shi Y, Li W S, et al. Photosynthetic physiological response to drought stress in sugar beet at seedling stage. Crops, 2022, 10(29): 152-158. |
| 尹希龙, 石杨, 李王胜, 等. 甜菜幼苗光合生理对干旱胁迫的响应. 作物杂志, 2022, 10(29): 152-158. | |
| 29 | Anisimov M M, Chaikina E L, Smetanina O F. Influence of the metabolites of the marine algicolous fungus Penicillium sp. on seedling root growth of agricultural plants. Natural Product Communications, 2016, 11(9): 1261-1262. |
| 30 | Saia S, Corrado G, Vitaglione P, et al. An endophytic fungi-based biostimulant modulates volatile and non-volatile secondary metabolites and yield of greenhouse basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) through variable mechanisms dependent on salinity stress level. Pathogens, 2021, 10(7): 797. |
| 31 | Khan M S, Gao J, Munir I, et al. Characterization of endophytic fungi, Acremonium sp., from Lilium davidii and analysis of its antifungal and plant growth-promoting effects. BioMed Research International, 2021. DOI:10.1155/2021/9930210. |
| 32 | Han L, Zhou X, Zhao Y T. Colonization of endophyte Acremonium sp. D212 in Panax notoginseng and rice mediated by auxin and jasmonic acid. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2020, 62(9): 1433-1451. |
| 33 | Li W R, Zhang S Q, Ding S Y, et al. Root morphological variation and water use in alfalfa under drought stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(19): 5140-5150. |
| 李文娆, 张岁岐, 丁圣彦, 等. 干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿根系形态变化及与水分利用的关系. 生态学报, 2010, 30(19): 5140-5150. | |
| 34 | Hirayama T, Shinozaki K. Research on plant abiotic stress responses in the post-genome era: past, present and future. Plant, 2010, 61(6): 1041-1052. |
| 35 | Li K, Shi C, He F Y, et al. Effects of endophyte infection on growth and physiological characteristics of Melica transsilvanica under Pb stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. |
| 李柯, 施宠, 何飞焱, 等. Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草生长及生理的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. | |
| 36 | Ahlem N, Rania A B A, Hayfa J K, et al. Ability of endophytic fungi associated with Withania somnifera L. to control Fusarium crown and root rot and to promote growth in tomato. Brazillian Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 50: 481-494. |
| 37 | Rut I, Clin M, Capr L, et al. Cladosporium sp. isolate as fungal plant growth promoting agent. Agronomy, 2021, 11(2): 392. |
| 38 | Wang C Y. Effects of simulated acid rain on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Paris polyphylla var. chinensis. Tropical Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 43(6): 28-32. |
| 王春燕. 模拟酸雨对华重楼生理生化特性的影响. 热带农业工程, 2019, 43(6): 28-32. | |
| 39 | Zhao L F, Xu Y J, Shao X, et al. Two endophytic Bacillus strains from soybean nodules affect superoxide dismutase and peroxidase activities in soybean seedlings under salt stress. Microbiology China, 2022, 49(5): 1664-1677. |
| 赵龙飞, 徐亚军, 邵璇, 等. 两株内生芽孢杆菌对盐胁迫下大豆幼苗超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化物酶活性影响. 微生物学通报, 2022, 49(5): 1664-1677. | |
| 40 | Khodabin G, Tahmasebi-Sarvestani Z, Rad A H S, et al. Effect of drought stress on certain morphological and physiological characteristics of a resistant and a sensitive canola cultivar. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2020, 17(2): e1900399. |
| 41 | Liu W, Yu K, He T, et al. The low temperature induced physiological responses of Avena nuda L., a cold-tolerant plant species. Scientific World Journal, 2013, 11: 658793. |
| 42 | Wang Y, Liu Z T, Gao G L, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on seed germination, seedling growth of Caragana korshinskii and Ammopiptanthus mongolicus under drought stress. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 73-81. |
| 王雨, 刘振婷, 高广磊, 等. 干旱胁迫下枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)对柠条(Caragana korshinskii)和沙冬青(Ammopiptanthus mongolicus)种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 73-81. | |
| 43 | Shang C H, Zhou Z Y, Cui W X, et al. Identification and expression analysis of proline accumulation related gene families in soybean under drought stress. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2022, 10(29): 1793-1806. |
| 商成慧, 周泽宇, 崔文雪, 等. 大豆脯氨酸积累相关基因家族鉴定及干旱胁迫表达分析. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 10(29): 1793-1806. | |
| 44 | Ding Z H, Fu L L, Yan Y, et al. Evolution analysis of P5CR and expression analysis of P5CR genes in cassava. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018, 34(3): 105-112. |
| 丁泽红, 付莉莉, 颜彦, 等. P5CR基因的进化及其在木薯中的表达分析. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(3): 105-112. | |
| 45 | Sandhya V, Ali S Z, Grover M, et al. Effect of plant growth promoting Pseudomonas spp. on compatible solutes, antioxidant status and plant growth of maize under drought stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 2010, 62: 21-30. |
| 46 | Königshofer H, Löppert H G. Regulation of invertase activity in different root zones of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings in the course of osmotic adjustment under water deficit conditions. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 183(1): 130-137. |
| 47 | Yuan Y H, Fan H B, Huang Q R, et al. Influence of long-term fertilization on photosynthesis, part of protective enzyme activities in leaves and the yield of rice. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2011, 38(2): 299-304. |
| 袁颖红, 樊后保, 黄欠如, 等. 长期不同施肥对水稻叶片光合特性和部分保护酶活性及产量的影响. 安徽农业大学学报, 2011, 38(2): 299-304. | |
| 48 | Du T Y, He H Y, Zhang Q, et al. Positive effects of organic fertilizers and biofertilizers on soil microbial community composition and walnut yield. Applied Soil Ecology, 2022, 175: 104457. |
| 49 | Kuang J L, Han S, Chen Y J, et al. Root-associated fungal community reflects host spatial co-occurrence patterns in a subtropical forest. ISME Communications, 2021, 1(1): 65. |
| [1] | 张婷婷, 刘宇乐, 陈红, 许凌欣, 陈祥伟, 王恩姮, 严俊鑫. 不同外源物质对盐、碱及干旱胁迫下草木樨种子萌发、幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 122-132. |
| [2] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [3] | 魏娜, 敬文茂, 许尔文, 王荣新, 赵晶忠, 马雪娥, 张吉宇, 刘文献. 白花草木樨MaERF058基因耐旱功能验证[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 159-169. |
| [4] | 杜文盼, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 杨莉, 张建贵, 史怡超, 张官禄. 根系分隔方式对燕麦/豌豆间作地上生物量、土壤养分及根系性状的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 25-36. |
| [5] | 桑瑞娟, 崔超杰, 何云, 张晓霞, 姚晋, 董春阳, 孙浩, 史莹华, 朱晓艳, 李德锋. 豫北地区18个秋播饲用燕麦品种抗倒伏特性及生产性能评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 74-85. |
| [6] | 张昭, 伏莹莹, 孙浩文, 孙逢雪, 闫慧芳. 不同品种燕麦种子活力鉴定与耐贮藏性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 165-174. |
| [7] | 曾露婧, 王国华. 干旱及复水对荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 41-57. |
| [8] | 李硕, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 李雯. 基于转录组测序的狗牙根抗旱根系关键代谢途径分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 186-198. |
| [9] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [10] | 慕平, 柴继宽, 苏玮娟, 章海龙, 赵桂琴. 燕麦不同组合正、反交杂种后代的表型及遗传参数分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 73-86. |
| [11] | 冯琴, 何小莉, 王斌, 王腾飞, 倪旺, 马霞, 明雪花, 邓建强, 兰剑. 宁夏引黄灌区燕麦与箭筈豌豆的混播效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 107-119. |
| [12] | 鲍根生, 李媛, 冯晓云, 张鹏, 孟思宇. 高寒区氮添加和间作种植互作对燕麦和豌豆根系构型影响的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 73-84. |
| [13] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 王静, 吴勇, 童长春. 连续间作下的紫花苜蓿/燕麦根系与碳氮代谢特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 85-96. |
| [14] | 罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184. |
| [15] | 黄丽娟, 孙镕基, 高文婧, 张志飞, 陈桂华. 全株水稻表面优势乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 117-125. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||