

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 163-173.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024142
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-04-23
修回日期:2024-06-17
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
曹静,徐国伟
作者简介:gwxu2007@163.com基金资助:
Hao-jing LI( ), Dan-ke ZHANG, Hai-run LI, Jing CAO(
), Dan-ke ZHANG, Hai-run LI, Jing CAO( ), Guo-wei XU(
), Guo-wei XU( )
)
Received:2024-04-23
Revised:2024-06-17
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Jing CAO,Guo-wei XU
摘要:
氮肥施用对水稻生长发育及品质形成具有重要影响,为明确施氮对不同食味品质水稻根系生长及分泌有机酸的影响,以郑稻C42(优质食味)和徐稻3号(一般食味)为供试品种进行盆栽试验,设置4个氮肥施用量,分别为0、120、240、360 kg·hm-2(以N0、N120、N240、N360表示),测定水稻根长、根表面积、根系氧化力、根系伤流量、根系伤流液中玉米素和玉米素核苷(Z+ZR)含量、脱落酸含量(ABA)、有机酸总量,为优质食味稻米栽培提供参考。结果表明:随着施氮量的增加,水稻根表面积、根系氧化力、Z+ZR含量、有机酸总量先增加后降低,两品种在N240处各指标达到最高值。与不施氮肥相比,抽穗期徐稻3号在N240时上述指标分别增加了148.0%、48.5%、16.0%与86.5%,郑稻C42在N240时分别增加了103.7%、72.5%、17.8%与98.0%。ABA含量随施氮量增加先降低后增加,在N240处达到最低值。不同食味品种间比较发现,郑稻C42的根系氧化力、根系伤流量、根系伤流液中Z+ZR含量和有机酸总量高于徐稻3号,平均增加40.7%、74.7%、9.7%和34.1%。郑稻C42的根长、根表面积均小于徐稻3号。相关分析可知,根表面积、根系氧化力、根系伤流量、根系伤流液中Z+ZR含量和有机酸总量与直链淀粉含量呈显著或极显著负相关,而与胶稠度呈显著或极显著正相关;幼穗分化始期根系伤流液中ABA含量与直链淀粉含量呈极显著正相关,而与胶稠度呈极显著负相关。综上,N240下不同食味品种根系生长及分泌功能较强。优质食味郑稻C42的根长、根表面积较小,而根系生理活性及根系伤流液中Z+ZR含量与有机酸总量较高。研究结果可以为不同食味水稻栽培及氮肥管理提供理论依据。
李浩晶, 张丹珂, 李海润, 曹静, 徐国伟. 施氮对不同食味品质水稻根系生长及分泌有机酸的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 163-173.
Hao-jing LI, Dan-ke ZHANG, Hai-run LI, Jing CAO, Guo-wei XU. Effect of nitrogen application rates on root growth and organic acid secretion in two rice varieties with different eating quality[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 163-173.
| 品种Cultivar | 处理Treatment | 分蘖盛期Mid-tillering | 幼穗分化始期Panicle initiation | 抽穗期Heading | 成熟期Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
徐稻3号 Xudao 3 | N0 | 105.77e | 142.55c | 205.13d | 230.36d |
| N120 | 201.81bc | 282.83b | 352.53b | 244.71cd | |
| N240 | 253.49a | 340.70a | 465.08a | 276.83b | |
| N360 | 211.09bc | 335.27a | 357.15b | 235.32d | |
| 平均值Mean | 193.04 | 275.34 | 344.98 | 246.81 | |
郑稻C42 Zhengdao C42 | N0 | 136.47d | 192.77c | 213.57d | 207.02e |
| N120 | 159.49d | 311.42ab | 238.29c | 264.58bc | |
| N240 | 223.46b | 333.26a | 347.41b | 305.37a | |
| N360 | 195.79c | 330.70a | 353.24b | 322.97a | |
| 平均值Mean | 178.81 | 292.04 | 288.13 | 274.99 | |
| 方差分析Variance analysis (ANOVA) | |||||
| 品种Cultivar (C) | 6.16** | 2.36* | 179.04** | 35.79** | |
| 施氮量Nitrogen (N) | 73.88** | 103.31** | 396.65** | 27.81** | |
| 品种×施氮量C×N | 7.75** | 1.86* | 64.90** | 18.27** | |
表1 施氮对不同食味品质水稻根长的影响
Table 1 Effect of nitrogen rates on root length of rice varieties with different eating qualities (m·hill-1)
| 品种Cultivar | 处理Treatment | 分蘖盛期Mid-tillering | 幼穗分化始期Panicle initiation | 抽穗期Heading | 成熟期Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
徐稻3号 Xudao 3 | N0 | 105.77e | 142.55c | 205.13d | 230.36d |
| N120 | 201.81bc | 282.83b | 352.53b | 244.71cd | |
| N240 | 253.49a | 340.70a | 465.08a | 276.83b | |
| N360 | 211.09bc | 335.27a | 357.15b | 235.32d | |
| 平均值Mean | 193.04 | 275.34 | 344.98 | 246.81 | |
郑稻C42 Zhengdao C42 | N0 | 136.47d | 192.77c | 213.57d | 207.02e |
| N120 | 159.49d | 311.42ab | 238.29c | 264.58bc | |
| N240 | 223.46b | 333.26a | 347.41b | 305.37a | |
| N360 | 195.79c | 330.70a | 353.24b | 322.97a | |
| 平均值Mean | 178.81 | 292.04 | 288.13 | 274.99 | |
| 方差分析Variance analysis (ANOVA) | |||||
| 品种Cultivar (C) | 6.16** | 2.36* | 179.04** | 35.79** | |
| 施氮量Nitrogen (N) | 73.88** | 103.31** | 396.65** | 27.81** | |
| 品种×施氮量C×N | 7.75** | 1.86* | 64.90** | 18.27** | |
| 品种Cultivar | 处理Treatment | 分蘖盛期Mid-tillering | 幼穗分化始期Panicle initiation | 抽穗期Heading | 成熟期Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
徐稻3号 Xudao 3 | N0 | 0.15f | 0.27d | 0.25e | 0.24d |
| N120 | 0.20d | 0.46c | 0.42c | 0.31c | |
| N240 | 0.30a | 0.58ab | 0.62a | 0.45a | |
| N360 | 0.26b | 0.55b | 0.55b | 0.38b | |
| 平均值Mean | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.35 | |
郑稻C42 Zhengdao C42 | N0 | 0.17ef | 0.22e | 0.27e | 0.22d |
| N120 | 0.19de | 0.42c | 0.34d | 0.36b | |
| N240 | 0.27b | 0.63a | 0.55b | 0.38b | |
| N360 | 0.23c | 0.54b | 0.47c | 0.37b | |
| 平均值Mean | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.33 | |
| 方差分析Variance analysis (ANOVA) | |||||
| 品种Cultivar (C) | 6.57** | 1.40 | 15.13** | 11.77** | |
| 施氮量Nitrogen (N) | 100.81** | 174.18** | 116.61** | 253.65** | |
| 品种×施氮量C×N | 4.57* | 3.20* | 3.03 | 26.35** | |
表2 施氮对不同食味品质水稻根表面积的影响
Table 2 Effect of nitrogen rates on root surface of rice varieties with different eating qualities (m2·hill-1)
| 品种Cultivar | 处理Treatment | 分蘖盛期Mid-tillering | 幼穗分化始期Panicle initiation | 抽穗期Heading | 成熟期Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
徐稻3号 Xudao 3 | N0 | 0.15f | 0.27d | 0.25e | 0.24d |
| N120 | 0.20d | 0.46c | 0.42c | 0.31c | |
| N240 | 0.30a | 0.58ab | 0.62a | 0.45a | |
| N360 | 0.26b | 0.55b | 0.55b | 0.38b | |
| 平均值Mean | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.35 | |
郑稻C42 Zhengdao C42 | N0 | 0.17ef | 0.22e | 0.27e | 0.22d |
| N120 | 0.19de | 0.42c | 0.34d | 0.36b | |
| N240 | 0.27b | 0.63a | 0.55b | 0.38b | |
| N360 | 0.23c | 0.54b | 0.47c | 0.37b | |
| 平均值Mean | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.33 | |
| 方差分析Variance analysis (ANOVA) | |||||
| 品种Cultivar (C) | 6.57** | 1.40 | 15.13** | 11.77** | |
| 施氮量Nitrogen (N) | 100.81** | 174.18** | 116.61** | 253.65** | |
| 品种×施氮量C×N | 4.57* | 3.20* | 3.03 | 26.35** | |
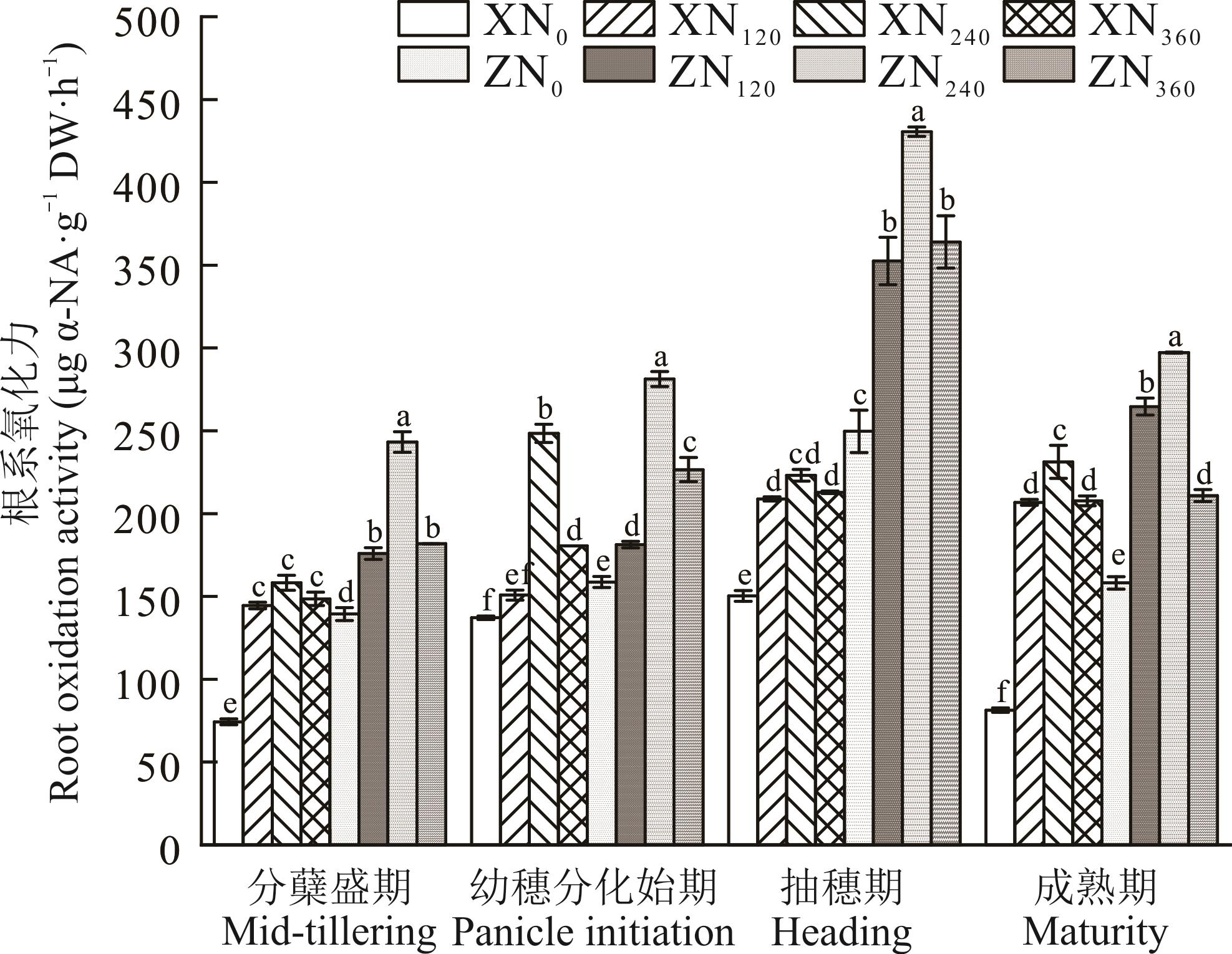
图1 施氮对不同食味品质水稻根系氧化力的影响X: 徐稻3号;Z: 郑稻C42。同一生育时期不同字母表示不同处理在0.05水平差异显著。下同。X: Xudao 3; Z: Zhengdao C42. Different letters in the same stage indicate significant differences among different treatments at 0.05 level. The same below.
Fig.1 Effect of nitrogen rates on root oxidation activity of rice varieties with different eating qualities
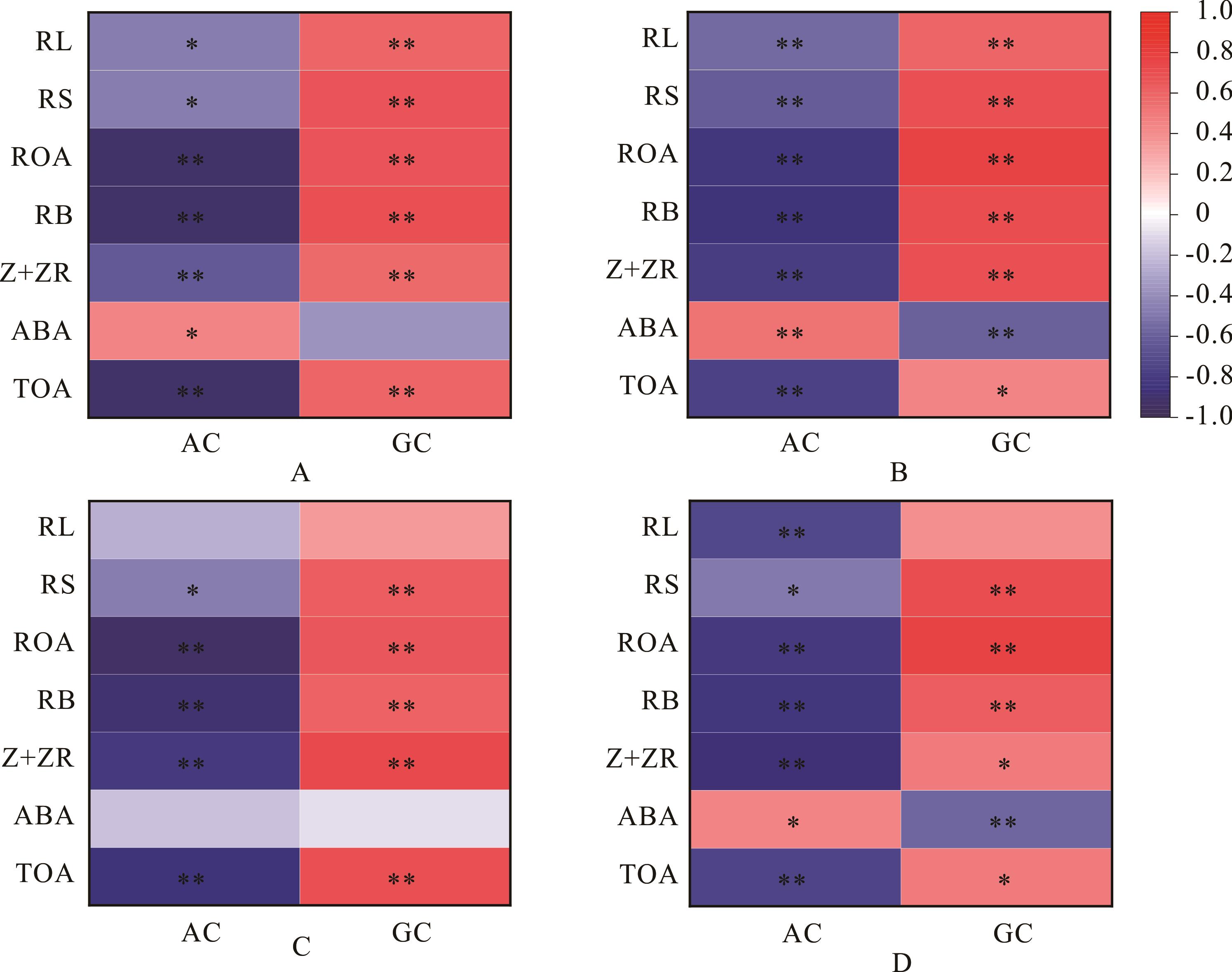
图6 不同食味品质水稻根系特性与蒸煮食味品质间的关系RL: 根长 Root length; RS: 根表面积 Root surface area; ROA: 根系氧化力 Root oxidation activity; RB: 根系伤流量 Root bleeding sap; Z+ZR: 根系伤流液中玉米素和玉米素核苷含量 Contents of zeatin and zeatin riboside in root bleeding sap; ABA: 根系伤流液中脱落酸含量Contents of abscisic acid in root bleeding sap; TOA: 根系伤流液中有机酸总量Total organic acid in root bleeding sap; AC: 直链淀粉含量 Amylose content; GC: 胶稠度 Gel consistency. A: 分蘖盛期 Mid-tillering; B: 幼穗分化始期 Panicle initiation; C: 抽穗期 Heading stage; D: 成熟期或花后20 d Maturity or 20 days after anthesis. *: P≤0.05; **: P≤0.01.
Fig.6 The relationship between root index and eating qualities of rice
| 1 | Sundus Z, Xu J. Recent advances to enhance nutritional quality of rice. Rice Science, 2023, 30(6): 523-536. |
| 2 | Liu J X, Fan X W, Li X Y, et al. Responses of different agricultural structures to nitrogen loss and agricultural green development in Northwest China. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2024, 367: 108956. |
| 3 | Chen G Y, Duan Q, Wu C Y, et al. Optimizing rice yield, quality and nutrient use efficiency through combined application of nitrogen and potassium. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1335744. |
| 4 | Febina M, Deepa J, Maya R, et al. Physicochemical properties, eating and cooking quality and genetic variability: A comparative analysis in selected rice varieties of South India. Food Production, Processing and Nutrition, 2023, 5(1): 1-12. |
| 5 | Dou Z, Yang Q, Guo H L, et al. A comparative study of grain quality and physicochemical properties of premium japonica rice from three typical production regions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1270388. |
| 6 | Xu Y Q, Guan X Y, Han Z Y, et al. Combined effect of nitrogen fertilizer application and high temperature on grain quality properties of cooked rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 874033. |
| 7 | Guo X Q, Wang L Q, Zhu G L, et al. Impacts of inherent components and nitrogen fertilizer on eating and cooking quality of rice: a review. Foods, 2023, 12(13): 2495. |
| 8 | Wu H, Zhang Y, Wang C, et al. Effects of cultivation optimization on root characteristics and starch properties of rice at grain filling stage in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(2): 478-492. |
| 吴昊, 张瑛, 王琛, 等. 栽培优化对长江下游水稻灌浆期根系特征和稻米淀粉特性的影响. 作物学报, 2024, 50(2): 478-492. | |
| 9 | Shang Z X, Bian J B, Chen S J, et al. Relationship between rice root system and rice quality under different fertilization treatments. Journal of Tianjin Agricultural University, 2020, 27(4): 1-6. |
| 尚振西, 边嘉宾, 陈帅君, 等. 不同施肥处理下水稻根系与稻米品质的关系研究. 天津农学院学报, 2020, 27(4): 1-6. | |
| 10 | Yang J C, Zhang J H, Huang Z L, et al. Correlation of cytokinin levels in the endosperms and roots with cell number and cell division activity during endosperm development in rice. Annals of Botany, 2002, 90(3): 369-377. |
| 11 | Sun X S, Bian X Y, Wang J D, et al. Loss of RSR1 function increases the abscisic acid content and improves rice quality performance at high temperature. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 256(Pt1): 128426. |
| 12 | Jing W J, Gu H Z, Zhang X X, et al. Response of grain quality and root characteristics to irrigation methods during mid-season indica rice varieties improvement. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(5): 505-519. |
| 景文疆, 顾汉柱, 张小祥, 等. 中籼水稻品种改良过程中米质和根系特征对灌溉方式的响应. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(5): 505-519. | |
| 13 | Yang J C, Chang E H, Zhang W J, et al. Relationship between root chemical signals and grain quality of rice. Agricultural Sciences in China, 2007, 6(1): 47-57. |
| 14 | Zhang Y J, Ma P, Wang Z Q, et al. Water-nitrogen coupling influence on rhizosphere environment and root morphology of rice under wheat straw return.Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(6): 924-936. |
| 张宇杰, 马鹏, 王志强, 等. 麦秆还田下水氮耦合对水稻根际环境及根系形态的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(6): 924-936. | |
| 15 | Liu H J. Experimental analysis of high-quality japonica rice varieties in Henan Province in 2021. Henan Agriculture, 2022(29): 33-34. |
| 刘海静. 2021年河南省优质粳稻品种展示试验分析. 河南农业, 2022(29): 33-34. | |
| 16 | Wang J K, Liu C, Guo R L, et al. Characteristics of japonica rice cultivar Xudao 3 and its cultivation technique for yield of 700 kg/667 m2. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 34(2): 31-32. |
| 王健康, 刘超, 郭荣良, 等. 中粳稻徐稻3号的特征特性及大面积产量700 kg/667 m2栽培技术. 江苏农业科学, 2006, 34(2): 31-32. | |
| 17 | Chen Y Y, Fan P S, Mo Z W, et al. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer affects grain field, nitrogen recovery efficiency, and root characteristics in direct-seeded rice in South China. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 40(1): 379-387. |
| 18 | Hou D, Liu K, Liu S, et al. Enhancing root physiology for increased yield in water-saving and drought-resistance rice with optimal irrigation and nitrogen. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 15: 1370297. |
| 19 | Xu G W, Li S, Zhao Y F, et al. Effects of straw returning and nitrogen fertilizer application on root secretion and nitrogen utilization of rice. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(2): 140-146. |
| 徐国伟, 李帅, 赵永芳, 等. 秸秆还田与施氮对水稻根系分泌物及氮素利用的影响研究. 草业学报, 2014, 23(2): 140-146. | |
| 20 | Zhao C, Chen M Y, Li X F, et al. Effects of soil types and irrigation modes on rice root morphophysiological traits and grain quality. Agronomy, 2021, 11(1): 120. |
| 21 | Xin W, Zhang L N, Gao J P, et al. Adaptation mechanism of roots to low and high nitrogen revealed by proteomic analysis. Rice, 2021, 14(1): 1-14. |
| 22 | Liu K, Chen Y, Li S Y, et al. Differing responses of root morphology and physiology to nitrogen application rates and their relationships with grain yield in rice. The Crop Journal, 2023, 11(2): 618-627. |
| 23 | Xu L, You H, Zhang O L, et al. Genetic effects of soluble starch synthase IV-2 and it with ADPglucose pyrophorylase large unit and pullulanase on rice qualities. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 46. |
| 24 | Saini R, Manjaiah M K, Chobhe A K, et al. Root morphological characteristics of five rice genotypes with different nitrogen use efficiency. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change, 2023, 13(10): 3690-3697. |
| 25 | Fei L W, Yang S C, Ma A, et al. Grain chalkiness is reduced by coordinating the biosynthesis of protein and starch in fragrant rice (Oryza sativa L.) grain under nitrogen fertilization. Field Crops Research, 2023, 302: 109098. |
| 26 | Liu L J, Wang K J, Bian J L, et al. Differences in yield response to nitrogen fertilizer among rice cultivars and their relationship with root morphology and physiology. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2014, 40(11): 1999-2007. |
| 刘立军, 王康君, 卞金龙, 等. 水稻产量对氮肥响应的品种间差异及其与根系形态生理的关系. 作物学报, 2014, 40(11): 1999-2007. | |
| 27 | Yu X J, Hu B J, Yuan H, et al. Effects of amino acid value-added urea on rice growth and root exudates. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 39(9): 1834-1842. |
| 于雪娇, 胡冰洁, 袁宏, 等. 氨基酸增值尿素对水稻生长和根系分泌物的影响. 江苏农业学报, 2023, 39(9): 1834-1842. | |
| 28 | Xu G W, Lu D K, Wang H Z, et al. Coupling effect of alternate wetting and drying irrigation and nitrogen rate on organic acid in rice root secretion at heading stage. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(4): 516-525. |
| 徐国伟, 陆大克, 王贺正, 等. 施氮和干湿灌溉对水稻抽穗期根系分泌有机酸的影响.中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(4): 516-525. | |
| 29 | Aulakh S M, Wassmann R, Bueno C, et al. Characterization of root exudates at different growth stages of ten rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Plant Biology, 2001, 3(2): 139-148. |
| 30 | Liu F, Yang Z N, Yang R Q, et al. Effects of rice root traits and organic acid secretion on thallium absorption capacity. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 46(7): 73-78. |
| 刘芳, 杨钊楠, 杨睿祺, 等. 水稻根系性状和有机酸分泌对铊吸收能力的影响. 广东农业科学, 2019, 46(7): 73-78. | |
| 31 | Tang J, Xu H Y, Wang C Q, et al. Effect of cadmium stress on root growth and organic acids and amino acid secretion of three rice varieties. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2016, 42(2): 118-124. |
| 唐杰, 徐浩洋, 王昌全, 等. 镉胁迫对3个水稻品种(系)根系生长及有机酸和氨基酸分泌的影响. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(2): 118-124. | |
| 32 | Liu L J, Chang E H, Xiong Y W, et al. Relationships of organic acid and polyamines exudated from roots with grain cooking quality and protein components in rice. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agricultural and Life Science Edition), 2014, 35(3): 48-53. |
| 刘立军, 常二华, 熊溢伟, 等. 水稻根系分泌物有机酸、多胺与稻米蒸煮品质及蛋白质组分的关系. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2014, 35(3): 48-53. | |
| 33 | Du S Y, Fang Y T, Lu J W. Progress on effects of root exudates on nutrient uptake and utilization of crops. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023, 42(2): 147-157. |
| 杜思垚, 方娅婷, 鲁剑巍. 根系分泌物对作物养分吸收利用的影响研究进展. 华中农业大学学报, 2023, 42(2): 147-157. | |
| 34 | Ma Z H, Gao M H, Cheng H T, et al. Differences in rice component distribution across layers and their relationship with taste. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2023, 104(3): 1824-1832. |
| 35 | Cui R L, Zhou T Y, Shu C C, et al. Effects of salt stress on grain quality and starch properties of high-quality rice cultivars. Agronomy, 2024, 14(3): 444. |
| 36 | Li Y Y, Zhao X H, Hao W M, et al. Effects of different phosphorus fertilizer rates on grain yield, grain quality and root growth of rice with different phosphorus sensitivity. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023(12): 219-226. |
| 李雨阳, 赵喜辉, 郝威名, 等. 施磷量对不同磷敏感型水稻产量、品质及根系生长的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023 (12): 219-226. | |
| 37 | Wu H, Gu H Z, Wang C, et al. Research progress on relationship between roots of rice and efficient absorption and utilization of nitrogen fertilizer. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(20): 9-14. |
| 吴昊, 顾汉柱, 王琛, 等. 水稻根系与氮肥高效吸收利用关系研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(20): 9-14. | |
| 38 | Zhu A, Gao J, Huang J, et al. Advances in morphology and physiology of root and their relationships with grain quality in rice. Crops, 2020(2): 1-8. |
| 朱安, 高捷, 黄健, 等. 水稻根系形态生理及其与稻米品质关系的研究进展. 作物杂志, 2020(2): 1-8. |
| [1] | 王新友, 王小兰, 张万昌, 李颖, 马永玲, 王晓寅, 王建刚, 王海青, 岳贝凡, 刘永福, 王永宏, 刘珊, 白美婷. 陇东南部林缘山区青贮玉米品种筛选及其高效栽培研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 191-202. |
| [2] | 吕帅磊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 刘蕊, 赵鑫, 刘佳, 徐昌旭, 曹卫东. 江西红壤绿肥季施用磷矿粉的磷素效应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 149-160. |
| [3] | 黄丽娟, 孙镕基, 高文婧, 张志飞, 陈桂华. 全株水稻表面优势乳酸菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 117-125. |
| [4] | 徐蕊, 王峥, 王仪明, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿对轮作水稻产量和蔗糖代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 129-140. |
| [5] | 钱文武, 郭鹏, 朱慧森, 张士敏, 李德颖. 草地早熟禾叶片表皮特征、解剖结构及光合特性对不同施氮量的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 131-143. |
| [6] | 高玮, 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 施氮量对饲用高粱干物质积累、分配及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. |
| [7] | 吴永杰, 丁浩, 邵涛, 赵杰, 董东, 代童童, 尹雪敬, 宗成, 李君风. 酶制剂对水稻秸秆青贮发酵品质及体外消化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 167-177. |
| [8] | 李君风, 赵杰, 唐小月, 代童童, 董东, 宗成, 邵涛. 瘤胃纤维素降解菌系对灭菌水稻秸秆结构性碳水化合物降解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 85-95. |
| [9] | 米永伟, 龚成文, 邵武平, 彭云霞. 覆膜对高寒阴湿区土壤水热与当归根系生长的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 66-75. |
| [10] | 黄丽琴, 李松桥, 袁振中, 唐晶, 闫景彩, 唐启源. 全株水稻与平菇菌糠共发酵料对浏阳黑山羊屠宰性能、肉品质和器官指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [11] | 王红林, 左艳春, 严旭, 周晓康, 寇晶, 杨希智, 郭俊英, 蒲军, 张浩仁, 杜周和. 刈割高度与施氮量对饲料桑全株产量及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 203-211. |
| [12] | 张帆, 杨茜. 紫云英与双季稻秸秆协同利用影响稻田土壤钾循环与平衡[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 72-80. |
| [13] | 舒新月, 江波, 马丽, 郑爱萍. 不同侵染时间点稻粒黑粉病菌的转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 190-202. |
| [14] | 康彩睿, 谢军红, 李玲玲, 王嘉男, 郭喜军, 彭正凯, 王进斌, Setor kwami Fudjoe, 王林林. 种植密度与施氮量对陇中旱农区玉米产量及光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 141-149. |
| [15] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 常雯雯. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||