

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 191-202.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024084
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王新友( ), 王小兰, 张万昌, 李颖, 马永玲, 王晓寅, 王建刚, 王海青, 岳贝凡, 刘永福, 王永宏, 刘珊, 白美婷(
), 王小兰, 张万昌, 李颖, 马永玲, 王晓寅, 王建刚, 王海青, 岳贝凡, 刘永福, 王永宏, 刘珊, 白美婷( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-17
修回日期:2024-05-16
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
白美婷
作者简介:E-mail: 675132057@qq.com基金资助:
Xin-you WANG( ), Xiao-lan WANG, Wan-chang ZHANG, Ying LI, Yong-ling MA, Xiao-yin WANG, Jian-gang WANG, Hai-qing WANG, Bei-fan YUE, Yong-fu LIU, Yong-hong WANG, Shan LIU, Mei-ting BAI(
), Xiao-lan WANG, Wan-chang ZHANG, Ying LI, Yong-ling MA, Xiao-yin WANG, Jian-gang WANG, Hai-qing WANG, Bei-fan YUE, Yong-fu LIU, Yong-hong WANG, Shan LIU, Mei-ting BAI( )
)
Received:2024-03-17
Revised:2024-05-16
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Mei-ting BAI
摘要:
为筛选出适宜陇东南部林缘山区栽培的青贮玉米品种,并确定其合理的栽培方式,本试验先以5份青贮玉米品种为研究对象,通过田间试验比较了不同品种在该地区的生产性能和营养成分含量,并采用灰色关联度分析法进行综合评价发现:铁研53表现最好,可作为主推品种。再以优势品种铁研53为材料,分别探究了不同施氮量(0、70、140、210 和280 kg N·hm-2)和不同种植密度(60000、67500、75000、82500和90000株·hm-2)对铁研53产量和品质的影响。结果表明:铁研53产量在施氮210 kg N·hm-2 时达到最大,为38.80 t·hm-2,施氮280 kg N·hm-2时产量并未随施氮量的增加而显著增加,但其营养品质在施氮280 kg N·hm-2时最好。铁研53随密度的增加产量增加,在密度为90000株·hm-2时产量最高;虽然种植密度为75000株·hm-2时粗蛋白含量达到最高,但粗蛋白产量在种植密度为90000株·hm-2时达到最高。为兼顾产量和利润,本研究通过拟合施氮量与产量和经济效益的关系,初步推荐该地区铁研53的适宜施氮量为280.74 kg N·hm-2。另外,综合考虑产量和品质,推荐铁研53种植密度为90000 株·hm-2。
王新友, 王小兰, 张万昌, 李颖, 马永玲, 王晓寅, 王建刚, 王海青, 岳贝凡, 刘永福, 王永宏, 刘珊, 白美婷. 陇东南部林缘山区青贮玉米品种筛选及其高效栽培研究[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 191-202.
Xin-you WANG, Xiao-lan WANG, Wan-chang ZHANG, Ying LI, Yong-ling MA, Xiao-yin WANG, Jian-gang WANG, Hai-qing WANG, Bei-fan YUE, Yong-fu LIU, Yong-hong WANG, Shan LIU, Mei-ting BAI. Selection of optimal varieties of silage maize and methods for cultivation in mountainous forest-margin areas of southeast Gansu Province[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(1): 191-202.
土层 Soil layer (cm) | 含水量 Water content (%) | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductivity (ms·cm-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkalized-nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 26.55 | 7.67 | 1812.17 | 22.76 | 228.20 | 1.43 | 121.57 | 518.49 |
| 20~40 | 24.79 | 7.56 | 1648.17 | 21.51 | 189.47 | 1.23 | 87.87 | 435.87 |
| 40~60 | 20.45 | 7.37 | 1287.33 | 14.50 | 113.87 | 1.04 | 40.91 | 253.26 |
表1 试验地土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of soil in the experiment field
土层 Soil layer (cm) | 含水量 Water content (%) | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductivity (ms·cm-1) | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Alkalized-nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 | 26.55 | 7.67 | 1812.17 | 22.76 | 228.20 | 1.43 | 121.57 | 518.49 |
| 20~40 | 24.79 | 7.56 | 1648.17 | 21.51 | 189.47 | 1.23 | 87.87 | 435.87 |
| 40~60 | 20.45 | 7.37 | 1287.33 | 14.50 | 113.87 | 1.04 | 40.91 | 253.26 |
| 品种Variety | 来源Sources of varieties |
|---|---|
| 北农青贮208 Beinong silage 208 | 河南省大京九种业有限公司Henan Dajingjiu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. |
| 京科青贮932 Jingke silage 932 | 北京顺鑫农科种业科技有限公司Beijing Shunxin Nongke Seed Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 铁研53 Tie Yan 53 | 北京禾佳源农业科技股份有限公司Beijing Hejiayuan Agricultural Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 北京佰青源畜牧业科技发展有限公司Beijing Baiqingyuan Animal Husbandry Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 北京大京九农业开发有限公司Beijing Dajingjiu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. |
表2 供试青贮玉米品种
Table 2 Varieties of silage maize
| 品种Variety | 来源Sources of varieties |
|---|---|
| 北农青贮208 Beinong silage 208 | 河南省大京九种业有限公司Henan Dajingjiu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. |
| 京科青贮932 Jingke silage 932 | 北京顺鑫农科种业科技有限公司Beijing Shunxin Nongke Seed Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 铁研53 Tie Yan 53 | 北京禾佳源农业科技股份有限公司Beijing Hejiayuan Agricultural Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 文玉3号Wenyu No.3 | 北京佰青源畜牧业科技发展有限公司Beijing Baiqingyuan Animal Husbandry Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 | 北京大京九农业开发有限公司Beijing Dajingjiu Agricultural Development Co., Ltd. |
指标 Indexes | 北农青贮208 Beinong silage 208 | 京科青贮932 Jingke silage 932 | 铁研53 Tie Yan 53 | 文玉3号 Wenyu No.3 | 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 324.04±14.35a | 242.48±12.29d | 299.04±10.98bc | 290.29±14.73c | 316.90±5.69ab |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 30.85±1.85a | 23.88±0.73c | 32.52±1.98a | 26.03±0.69bc | 27.75±0.49b |
| 叶长Leaf length (cm) | 72.86±1.96ab | 59.94±4.33c | 77.33±2.79a | 68.10±3.89b | 72.72±2.03ab |
| 叶宽Leaf width (cm) | 10.38±0.47b | 10.03±0.47b | 11.75±0.38a | 10.21±0.35b | 9.01±0.34c |
| 鲜草产量Fresh yield (t·hm-2) | 96.92±9.07ab | 70.20±5.83c | 113.23±3.65a | 90.99±6.32bc | 87.65±5.91bc |
| 干草产量Dry yield (t·hm-2) | 22.47±1.96abc | 18.46±1.85c | 26.59±0.81ab | 29.21±3.42a | 20.06±1.47bc |
| 干鲜比Dry to fresh ratio | 0.23±0.00b | 0.26±0.01b | 0.24±0.01b | 0.35±0.12a | 0.23±0.00b |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 5.07±0.38a | 4.19±0.27a | 4.88±0.33a | 4.46±0.18a | 4.50±0.21a |
| 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 1.14±0.12a | 0.77±0.09a | 1.30±0.08a | 1.30±0.17a | 0.90±0.07a |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 61.06±2.36a | 58.82±9.00a | 60.53±4.54a | 62.85±1.43a | 60.25±1.93a |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 28.84±2.35ab | 24.49±1.49b | 28.34±1.29ab | 32.72±0.84a | 30.04±1.15a |
| 淀粉Starch (%) | 11.55±3.30a | 16.50±2.80a | 17.12±4.63a | 16.01±2.04a | 15.58±2.81a |
| 粗灰分Crude ash (%) | 5.20±0.16a | 4.44±0.55a | 4.59±0.31a | 5.51±0.34a | 5.19±0.33a |
表3 不同青贮玉米品种生产性能
Table 3 Production performance of different silage maize varieties
指标 Indexes | 北农青贮208 Beinong silage 208 | 京科青贮932 Jingke silage 932 | 铁研53 Tie Yan 53 | 文玉3号 Wenyu No.3 | 豫青贮23 Yu silage 23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height (cm) | 324.04±14.35a | 242.48±12.29d | 299.04±10.98bc | 290.29±14.73c | 316.90±5.69ab |
| 茎粗Stem diameter (mm) | 30.85±1.85a | 23.88±0.73c | 32.52±1.98a | 26.03±0.69bc | 27.75±0.49b |
| 叶长Leaf length (cm) | 72.86±1.96ab | 59.94±4.33c | 77.33±2.79a | 68.10±3.89b | 72.72±2.03ab |
| 叶宽Leaf width (cm) | 10.38±0.47b | 10.03±0.47b | 11.75±0.38a | 10.21±0.35b | 9.01±0.34c |
| 鲜草产量Fresh yield (t·hm-2) | 96.92±9.07ab | 70.20±5.83c | 113.23±3.65a | 90.99±6.32bc | 87.65±5.91bc |
| 干草产量Dry yield (t·hm-2) | 22.47±1.96abc | 18.46±1.85c | 26.59±0.81ab | 29.21±3.42a | 20.06±1.47bc |
| 干鲜比Dry to fresh ratio | 0.23±0.00b | 0.26±0.01b | 0.24±0.01b | 0.35±0.12a | 0.23±0.00b |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 5.07±0.38a | 4.19±0.27a | 4.88±0.33a | 4.46±0.18a | 4.50±0.21a |
| 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 1.14±0.12a | 0.77±0.09a | 1.30±0.08a | 1.30±0.17a | 0.90±0.07a |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 61.06±2.36a | 58.82±9.00a | 60.53±4.54a | 62.85±1.43a | 60.25±1.93a |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 28.84±2.35ab | 24.49±1.49b | 28.34±1.29ab | 32.72±0.84a | 30.04±1.15a |
| 淀粉Starch (%) | 11.55±3.30a | 16.50±2.80a | 17.12±4.63a | 16.01±2.04a | 15.58±2.81a |
| 粗灰分Crude ash (%) | 5.20±0.16a | 4.44±0.55a | 4.59±0.31a | 5.51±0.34a | 5.19±0.33a |
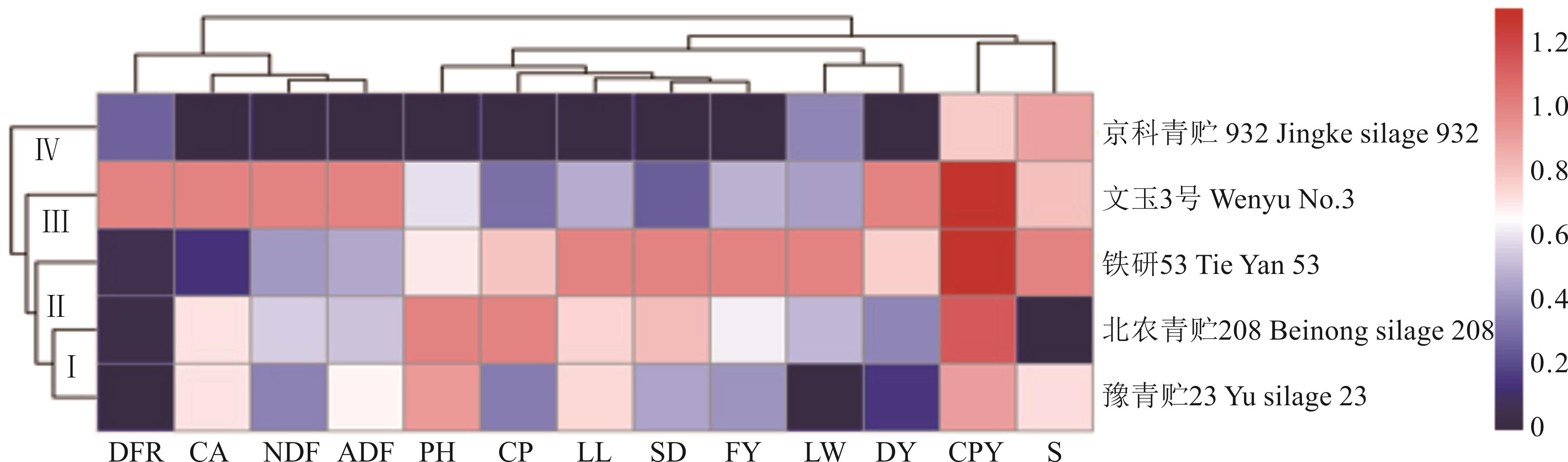
图1 不同青贮玉米品种性状指标比较DFR: 干鲜比Dry to fresh ratio; CA: 粗灰分Crude ash; NDF: 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber; ADF: 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber; PH: 株高Plant height; CP: 粗蛋白Crude protein; LL: 叶长Leaf length; SD: 茎粗Stem diameter; FY: 鲜草产量Fresh yield; LW: 叶宽Leaf width; DY: 干草产量Dry yield; CPY: 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield; S: 淀粉Starch.
Fig.1 Comparison of features indexes of different silage maize varieties
| 指标Indexes | N0 | N70 | N140 | N210 | N280 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎干重Dry weight of the stem (t·hm-2) | 7.56±0.76c | 9.60±0.97bc | 12.60±0.18ab | 16.20±2.35a | 13.90±1.56ab |
| 叶干重Dry weight of leaves (t·hm-2) | 7.89±0.67a | 7.74±0.58a | 8.37±0.17a | 9.00±0.80a | 9.36±0.52a |
| 穗干重Dry weight of ear (t·hm-2) | 9.23±1.26b | 12.59±0.99ab | 11.16±1.60ab | 13.61±0.42a | 13.29±0.41a |
| 总干重Total dry weight (t·hm-2) | 24.68±2.10c | 29.93±2.02bc | 32.09±1.74ab | 38.80±2.53a | 36.55±2.32ab |
| 粗灰分Crude ash (%) | 4.75±0.33a | 5.08±0.06a | 5.28±0.29a | 4.54±0.30a | 5.04±0.50a |
| 粗脂肪Ether extract (%) | 1.23±0.13b | 1.39±0.11ab | 1.58±0.11a | 1.66±0.14a | 1.70±0.11a |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 4.74±0.59c | 5.43±0.31bc | 5.64±0.45bc | 6.38±0.27ab | 7.15±0.58a |
| 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 1.17±0.07c | 1.63±0.01b | 1.81±0.02b | 2.48±0.06a | 2.61±0.09a |
| 淀粉Starch (%) | 17.27±2.44a | 17.02±2.34a | 17.28±2.46a | 18.97±2.40a | 19.50±3.81a |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 61.55±5.89a | 57.95±2.70ab | 51.34±2.73ab | 45.84±7.82b | 45.20±6.39b |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 31.88±1.90a | 29.72±1.83a | 28.96±2.00ab | 28.39±1.44ab | 24.79±2.27b |
表4 不同施氮处理对铁研53产量和品质的影响
Table 4 Effects of different nitrogen application treatments on yield and quality of Tie Yan 53
| 指标Indexes | N0 | N70 | N140 | N210 | N280 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎干重Dry weight of the stem (t·hm-2) | 7.56±0.76c | 9.60±0.97bc | 12.60±0.18ab | 16.20±2.35a | 13.90±1.56ab |
| 叶干重Dry weight of leaves (t·hm-2) | 7.89±0.67a | 7.74±0.58a | 8.37±0.17a | 9.00±0.80a | 9.36±0.52a |
| 穗干重Dry weight of ear (t·hm-2) | 9.23±1.26b | 12.59±0.99ab | 11.16±1.60ab | 13.61±0.42a | 13.29±0.41a |
| 总干重Total dry weight (t·hm-2) | 24.68±2.10c | 29.93±2.02bc | 32.09±1.74ab | 38.80±2.53a | 36.55±2.32ab |
| 粗灰分Crude ash (%) | 4.75±0.33a | 5.08±0.06a | 5.28±0.29a | 4.54±0.30a | 5.04±0.50a |
| 粗脂肪Ether extract (%) | 1.23±0.13b | 1.39±0.11ab | 1.58±0.11a | 1.66±0.14a | 1.70±0.11a |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 4.74±0.59c | 5.43±0.31bc | 5.64±0.45bc | 6.38±0.27ab | 7.15±0.58a |
| 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 1.17±0.07c | 1.63±0.01b | 1.81±0.02b | 2.48±0.06a | 2.61±0.09a |
| 淀粉Starch (%) | 17.27±2.44a | 17.02±2.34a | 17.28±2.46a | 18.97±2.40a | 19.50±3.81a |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 61.55±5.89a | 57.95±2.70ab | 51.34±2.73ab | 45.84±7.82b | 45.20±6.39b |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 31.88±1.90a | 29.72±1.83a | 28.96±2.00ab | 28.39±1.44ab | 24.79±2.27b |
| 指标Indexes | D6 | D6.75 | D7.5 | D8.25 | D9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎干重Dry weight of the stem (t·hm-2) | 9.30±1.53b | 10.42±1.82ab | 9.31±1.34b | 10.68±1.17ab | 14.00±0.38a |
| 叶干重Dry weight of leaves (t·hm-2) | 8.44±1.04ab | 8.27±0.61ab | 8.04±0.99b | 8.26±1.21ab | 11.51±1.06a |
| 穗干重Dry weight of ear (t·hm-2) | 11.73±0.52ab | 11.06±1.00b | 12.44±1.86ab | 12.43±1.38ab | 15.29±1.20a |
| 总干重Total dry weight (t·hm-2) | 29.47±2.95b | 29.75±3.25b | 29.79±4.16ab | 31.37±2.62ab | 40.80±1.79a |
| 粗灰分Crude ash (%) | 4.00±0.02a | 4.22±0.26a | 4.29±0.18a | 4.28±0.32a | 4.48±0.52a |
| 粗脂肪Ether extract (%) | 1.55±0.15b | 1.75±0.10ab | 1.78±0.15ab | 2.08±0.08a | 1.78±0.14ab |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 4.94±0.05b | 4.95±0.25b | 5.73±0.22a | 5.28±0.28ab | 5.06±0.24b |
| 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 1.46±0.14b | 1.47±0.08b | 1.71±0.13ab | 1.66±0.10b | 2.06±0.04a |
| 淀粉Starch (%) | 13.44±0.69b | 14.01±0.96ab | 13.89±0.65b | 17.13±1.32a | 14.38±0.87ab |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 51.94±5.35a | 54.58±4.05a | 55.74±5.08a | 64.10±1.76a | 62.72±3.50a |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 24.67±1.59a | 26.22±2.42a | 25.37±1.12a | 29.25±1.73a | 27.62±0.72a |
表5 不同种植密度对铁研53产量和品质的影响
Table 5 Effect of different planting densities on yield and quality of Tie Yan 53
| 指标Indexes | D6 | D6.75 | D7.5 | D8.25 | D9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎干重Dry weight of the stem (t·hm-2) | 9.30±1.53b | 10.42±1.82ab | 9.31±1.34b | 10.68±1.17ab | 14.00±0.38a |
| 叶干重Dry weight of leaves (t·hm-2) | 8.44±1.04ab | 8.27±0.61ab | 8.04±0.99b | 8.26±1.21ab | 11.51±1.06a |
| 穗干重Dry weight of ear (t·hm-2) | 11.73±0.52ab | 11.06±1.00b | 12.44±1.86ab | 12.43±1.38ab | 15.29±1.20a |
| 总干重Total dry weight (t·hm-2) | 29.47±2.95b | 29.75±3.25b | 29.79±4.16ab | 31.37±2.62ab | 40.80±1.79a |
| 粗灰分Crude ash (%) | 4.00±0.02a | 4.22±0.26a | 4.29±0.18a | 4.28±0.32a | 4.48±0.52a |
| 粗脂肪Ether extract (%) | 1.55±0.15b | 1.75±0.10ab | 1.78±0.15ab | 2.08±0.08a | 1.78±0.14ab |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (%) | 4.94±0.05b | 4.95±0.25b | 5.73±0.22a | 5.28±0.28ab | 5.06±0.24b |
| 粗蛋白产量Crude protein yield (t·hm-2) | 1.46±0.14b | 1.47±0.08b | 1.71±0.13ab | 1.66±0.10b | 2.06±0.04a |
| 淀粉Starch (%) | 13.44±0.69b | 14.01±0.96ab | 13.89±0.65b | 17.13±1.32a | 14.38±0.87ab |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (%) | 51.94±5.35a | 54.58±4.05a | 55.74±5.08a | 64.10±1.76a | 62.72±3.50a |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (%) | 24.67±1.59a | 26.22±2.42a | 25.37±1.12a | 29.25±1.73a | 27.62±0.72a |
| 1 | Khan N A, Yu P Q, Ali M, et al. Nutritive value of maize silage in relation to dairy cow performance and milk quality. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2015, 95(2): 238-252. |
| 2 | Fang Y J, Zhang X C, Yu X F, et al. Effects of vertical rotary subsoiling with combined organic and inorganic fertilization on water use efficiency and yield of forage maize in a semi-arid area. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(4): 1327-1336. |
| 方彦杰, 张绪成, 于显枫, 等. 半干旱区立式深旋耕和有机无机肥配施对饲用玉米水分利用效率和产量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(4): 1327-1336. | |
| 3 | Liu C Q, Han L, Li T T, et al. The security of feed grains supply in China from the perspective of a big food concept. Chinese Rural Economy, 2023(1): 33-57. |
| 刘长全, 韩磊, 李婷婷, 等. 大食物观下中国饲料粮供给安全问题研究. 中国农村经济, 2023(1): 33-57. | |
| 4 | Yan J J, Luo G Q, Zhang Y. Agglomeration evolution and mechanism of feed grain production in China: Based on dynamic spatial Durbin model. Feed Research, 2024(1): 175-180. |
| 颜姣姣, 罗国庆, 张翼. 我国青贮玉米生产的集聚演变及其作用机制——基于动态空间杜宾模型. 饲料研究, 2024(1): 175-180. | |
| 5 | Wang X Y. Research on the application of forage maize and the progress in its cultivation measures. Feed Industry. (2024-01-04)[2024-03-16]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1169.S.20240104.1302.005. |
| 王新友. 青贮玉米应用现状以及其栽培措施研究进展. 饲料工业. (2024-01-04)[2024-03-16]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1169.S.20240104.1302.005. | |
| 6 | Liu Y H, Guo M, Jia S L, et al. Advance on the factors effecting on maize forage nutritive value. Crops, 2018(2): 6-10. |
| 刘颖慧, 郭明, 贾树利, 等. 影响青贮玉米品质因素研究进展. 作物杂志, 2018(2): 6-10. | |
| 7 | Wu Y Q, Wang W, Zhao L, et al. Effect of nitrogen application and density on yield and quality of mainly planted maize varieties in southwest China. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2022, 30(5): 99-107, 115. |
| 吴元奇, 王伟, 赵丽, 等. 施氮量与密度对西南地区主栽青贮玉米品种产量和品质的影响. 玉米科学, 2022, 30(5): 99-107, 115. | |
| 8 | Chen Q, Wang L Y, Zhao X L, et al. Effect of nitrogen application rate and planting density on yield and quality of silage maize varieties. China Feed, 2024(1): 141-148. |
| 陈琦, 汪兰英, 赵小林, 等. 施氮量和种植密度对青贮玉米产量和品质的影响. 中国饲料, 2024(1): 141-148. | |
| 9 | Wu Y, Yi J. Visualization analysis of silage maize research field in China based on knowledge map. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2021, 29(1): 184-190. |
| 吴园, 易婧. 基于知识图谱的我国青贮玉米研究领域可视化分析. 玉米科学, 2021, 29(1): 184-190. | |
| 10 | Dong Y, Li X Y, Yan F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of 12 silage maize varieties in Qiqihar area. Seed, 2023, 42(9): 68-72. |
| 董扬, 李旭业, 闫锋, 等. 齐齐哈尔地区12个青贮玉米品种综合评价. 种子, 2023, 42(9): 68-72. | |
| 11 | Yue H W, Wei J W, Wang G C, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of silage maize hybrids in the Huanghuaihai plain based on mega-environments delineated using envirotyping techniques. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 120-138. |
| 岳海旺, 魏建伟, 王广才, 等. 基于环境型鉴定技术划分生态区综合评价黄淮海青贮玉米品种. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 120-138. | |
| 12 | Liang W W, Zhang H H, Zhang X Z, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of 23 silage maize varieties in the Changji, Xinjiang. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(10): 2180-2190. |
| 梁维维, 张荟荟, 张学洲, 等. 新疆昌吉地区23份青贮玉米品种综合评价. 草业科学, 2022, 39(10): 2180-2190. | |
| 13 | Li S J, Yuan L, Qi Z Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on yield and silage quality of different silage corn varieties. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2023, 54(7): 2092-2100. |
| 李淑君, 袁亮, 祁志云, 等. 不同青贮玉米品种产量和青贮品质的综合评价. 南方农业学报, 2023, 54(7): 2092-2100. | |
| 14 | Wang Y C, Lu G X, Deng H, et al. Evaluation and screening of agricultural characters of silage maize varieties based on principal component analysis. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1725-1732. |
| 王英成, 芦光新, 邓晖, 等. 基于主成分分析的青贮玉米品种农艺性状评价及筛选研究. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1725-1732. | |
| 15 | Jiang C Z, Shou N, Gao W, et al. A multivariate evaluation of production performance and nutritional quality of different varieties of silage maize in the dry plateau area of Longdong. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 216-228. |
| 蒋丛泽, 受娜, 高玮, 等. 陇东旱塬区不同青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养品质综合评价. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 216-228. | |
| 16 | Wang H N, Qin W N, Jiao T, et al. Evaluation of milk yield, agronomic traits, and nutritional quality of different green-feeding maize varieties in Gansu Province. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(6): 1617-1628. |
| 王虎宁, 秦伟娜, 焦婷, 等. 甘肃不同青饲玉米品种产量、农艺性状及营养品质评定. 草业科学, 2023, 40(6): 1617-1628. | |
| 17 | Gao W. Study on the regulating effect of nitrogen (N) rate and planting density on production, water and N utilization of forage maize. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2023. |
| 高玮. 施氮量和密度调控青贮玉米生产及水氮利用的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2023. | |
| 18 | Wang J, Li Y, Jia Q M, et al. Effects of planting density and nitrogen application on yield, quality and water use efficiency of silage maize in Hexi irrigation region. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 60-73. |
| 王佳, 李阳, 贾倩民, 等. 种植密度与施氮对河西灌区青贮玉米产量与品质及水分利用效率的影响. 西北农业学报, 2021, 30(1): 60-73. | |
| 19 | Wang Y, Shi Y Q, Liu C, et al. Combined effect of water and nitrogen application on yield and silage quality of silage maize. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(11): 2247-2254. |
| 王晔, 石雅琪, 刘呈, 等. 水氮互作对青贮玉米产量和青贮品质的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(11): 2247-2254. | |
| 20 | Wang J. Effects of planting method, density and nitrogen rate on yield, quality and water and nitrogen utilization of forage maize in Hexi region. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. |
| 王佳. 种植模式、密度和施氮对河西地区饲用玉米产量、品质及水氮利用的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. | |
| 21 | You Y L, Li Y, Zhao H M, et al. Effects of sowing date and planting density on production performance and forage quality of silage corn. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2615-2624. |
| 游永亮, 李源, 赵海明, 等. 播期和种植密度对青贮玉米生产性能和饲用品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2615-2624. | |
| 22 | Dong S, Wang H, Jia Q M, et al. Effects of irrigation modes and planting patterns on the growth, yield and economic benefits of silage maize in Hexi region. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(4): 1111-1120. |
| 董姗, 王皓, 贾倩民, 等. 灌溉模式与种植方式对河西地区青贮玉米生长、产量和经济效益的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(4): 1111-1120. | |
| 23 | Bai X C, Zhang J H, Feng K L, et al. Effects of chemical fertilizer reduction and application of organic manure on the yield and nutritive value of Zea mays and soil microbial activity. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(2): 348-354. |
| 白雪纯, 张君红, 冯魁亮, 等. 化肥减量配施有机肥对青贮玉米产量、营养价值及土壤微生物活性的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(2): 348-354. | |
| 24 | Xu J, Yu D B, Feng B B, et al. Effects of different organic chicken manure fertilizers on the yield and quality of watermelon-silage maize and benefit analysis. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2020, 25(10): 89-97. |
| 徐军, 虞德兵, 冯彬彬, 等. 不同来源鸡粪有机肥对西瓜-青贮玉米产量、品质的影响及效益分析. 中国农业大学学报, 2020, 25(10): 89-97. | |
| 25 | Xiong B, Wang C, Zhang L, et al. Effects of organic fertilizer substituting chemical fertilizer on the growth and quality of summer silage maize in Beijing suburbs. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(3): 141-147. |
| 熊波, 王琛, 张莉, 等. 有机肥替代化肥对京郊夏播青贮玉米生长与饲料品质的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(3): 141-147. | |
| 26 | Yang Y, Gong S S, Jin H M, et al. Effects of biogas slurry derived from cow dung on the yield and quality of wheat and silage maize. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2023, 39(2): 264-272. |
| 杨月, 宫少硕, 靳红梅, 等. 奶牛场沼液施用对小麦及青贮玉米植株产量和品质的影响. 生态与农村环境学报, 2023, 39(2): 264-272. | |
| 27 | Dong Z X, He R H, Kuang J Y, et al. Effects of intercropping Dolichos lablab with silage maize on the yield and quality of mixed forage in the Chengdu Plain, China. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(8): 1587-1595. |
| 董志晓, 何润濠, 况鉴洋, 等. 成都平原青贮玉米间作拉巴豆对混合饲草产量及品质的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(8): 1587-1595. | |
| 28 | Li Y J, Ma P J, Wu J H, et al. Effects of interplanting with Dolichos lablab on agronomic traits and yield of two varieties of silage maize. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(9): 209-216. |
| 李亚娇, 马培杰, 吴佳海, 等. 不同品种青贮玉米与拉巴豆套种对青贮玉米农艺性状及产量的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(9): 209-216. | |
| 29 | Cheng G L, Qiu J, Wang X G, et al. Changes of agronomic traits, biomass yield and quality of national silage maize combinations (varieties). Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. |
| 成广雷, 邱军, 王晓光, 等. 我国青贮玉米组合(品种)的农艺性状、生物产量和品质变化. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(4): 30-37. | |
| 30 | Wang X Y, Wang D B, Qu Z. Study on the sustainable development of grassland animal husbandry in the combination zone of agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry-A case study of S village in Qingshui county, Gansu province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(16): 210-213. |
| 王新友, 王多斌, 屈展. 农林牧结合地带草地畜牧业可持续发展探讨——以甘肃省清水县S村为例. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(16): 210-213. | |
| 31 | Wang X Y, Qu Z. Investigation and development prospect of grass livestock balance in Shanmen forest farm of Xiaolongshan forest area. China Cattle Science, 2021, 47(3): 46-49. |
| 王新友, 屈展. 小陇山林区山门林场草畜平衡现状调查及发展展望. 中国牛业科学, 2021, 47(3): 46-49. | |
| 32 | Lu W R, Yuan X H, Liu J Z, et al. Screening of different silage maize varieties in the Qingshui area. Feed Research. (2023-12-28)[2024-03-16]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2114.S.20231227.1534.002. |
| 路婉茹, 袁想红, 刘建忠, 等. 清水地区不同青贮玉米品种的筛选. 饲料研究. (2023-12-28)[2024-03-16]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2114.S.20231227.1534.002. | |
| 33 | Wu R X, Yang L, He Y F, et al. Determination of crude ash content in feed: GB/T 6438-2007. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2007. |
| 武润仙, 杨林, 何一帆, 等. 饲料中粗灰分的测定: GB/T 6438-2007. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. | |
| 34 | Xiao Z M, Fan X, Ma D X, et al. Determination of crude protein in feed: GB/T 6432-2018. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018. |
| 肖志明, 樊霞, 马东霞, 等. 饲料中粗蛋白的测定: GB/T 6432-2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 35 | Zhang F P, Zhang Y, Zhang R, et al. Determination of neutral detergent fiber (NDF) in feeds: GB/T 20806-2022. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2022. |
| 张凤枰, 张芸, 张茹, 等. 饲料中中性洗涤纤维(NDF)的测定: GB/T 20806-2022. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. | |
| 36 | Li H L, Zhao C H, Jia Q, et al. Determination of acid detergent fiber in feed: NY/T 1459-2007. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2007. |
| 李会玲, 赵彩会, 贾青, 等. 饲料中酸性洗涤纤维的测定: NY/T 1459-2007. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. | |
| 37 | Huang T, Wang S S, Gao J F, et al. Determination of starch in feeds—Polarimetry: GB/T 20194-2018. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018. |
| 黄婷, 王思思, 高俊峰, 等. 动物饲料中淀粉含量的测定 旋光法: GB/T 20194-2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 38 | Cao J, Wu Z F, Chen X J, et al. Selection and comprehensive evaluation of suitable silage maize varieties in Jiuquan. Feed Research, 2023, 46(16): 121-125. |
| 曹健, 武志锋, 陈学俊, 等. 酒泉适宜青贮玉米品种综合评价与筛选. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(16): 121-125. | |
| 39 | Li H F, Zhou B W, Zhang M, et al. Adaptability evaluation of different oat varieties introduced in the Hulunbuir region. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 等. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. | |
| 40 | Ochieng’ I O, Gitari H I, Mochoge B, et al. Optimizing maize yield, nitrogen efficacy and grain protein content under different N forms and rates. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2021, 21(3): 1867-1880. |
| 41 | Shou N, Gao W, Shen Y Y, et al. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on yield and water use efficiency of silage maize. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(7): 1351-1361. |
| 受娜, 高玮, 沈禹颖, 等. 不同施氮量对青贮玉米产量及水分利用效率的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(7): 1351-1361. | |
| 42 | Gan S P, Yang X G, Ma Y Q, et al. Introduction and cultivation of the mid-late silage maize ‘Tieyan53’ in Qinghai Province. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(5): 927-934. |
| 甘淑萍, 杨学贵, 马玉清, 等. 青海省中晚熟青贮玉米‘铁研53’的引种栽培. 草业科学, 2021, 38(5): 927-934. | |
| 43 | Anniina L, Auvo S, Seija J, et al. Yield, quality and nitrogen use of forage maize under different nitrogen application rates in two boreal locations. Agronomy, 2022, 12(4): 887. |
| 44 | Morris T F, Murrell T S, Beegle D B, et al. Strengths and limitations of nitrogen rate recommendations for corn and opportunities for improvement. Agronomy Journal, 2018, 110(1): 1-37. |
| 45 | Miguez F E, Poffenbarger H. How can we estimate optimum fertilizer rates with accuracy and precision? Agricultural & Environmental Letters, 2022, 7(1): e20075. |
| 46 | Hu Y Q, Xu K W, Long L, et al. Effect of high plant density on yield of maize variety ‘Zhenghong No.6’. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(7): 154-162. |
| 胡月秋, 徐开未, 龙玲, 等. 玉米“正红6号”的密植效应. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 154-162. | |
| 47 | Zhang X, Su Y J, Wang Y, et al. Effect of variety and density on silage maize biomass and agronomic traits. Feed Research, 2022, 45(15): 88-93. |
| 张晓, 苏亚军, 王瑛, 等. 品种和密度对青贮玉米生物量与农艺性状的影响. 饲料研究, 2022, 45(15): 88-93. | |
| 48 | Zhang Q Z, Pan J B, Nan Z J, et al. Effect of planting densities on qualities of silage corn. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 2007, 22(2): 10-12. |
| 张秋芝, 潘金豹, 南张杰, 等. 不同种植密度对青贮玉米品质的影响. 北京农学院学报, 2007, 22(2): 10-12. | |
| 49 | Sun J Y, Gao J L, Wang Z G, et al. Effect of planting density on forage yield and nutritive value of different maize varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(6): 1733-1742. |
| 孙继颖, 高聚林, 王志刚, 等. 不同类型青贮玉米饲用产量及营养价值对密度调控的响应. 草地学报, 2019, 27(6): 1733-1742. |
| [1] | 卜祥琪, 李姗姗, 段莹娜, 王迎春, 郑琳琳. 一氧化氮对盐碱胁迫下盐地碱蓬抗逆性及饲用品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 60-69. |
| [2] | 李中利, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 高玮, 受娜, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区5个饲用甜高粱品种生产适宜性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 50-62. |
| [3] | 徐寿霞. 基于meta分析的丛枝菌根对小麦产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 192-204. |
| [4] | 李鸿飞, 周帮伟, 张淼, 施树楠, 李志坚. 不同燕麦品种在呼伦贝尔地区的引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 60-72. |
| [5] | 岳海旺, 魏建伟, 王广才, 刘朋程, 陈淑萍, 卜俊周. 基于环境型鉴定技术划分生态区综合评价黄淮海青贮玉米品种[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 120-138. |
| [6] | 孟超楠, 赵玉洁, 陈佳欣, 张旖璐, 王彦佳, 冯丽荣, 孙玉刚, 郭长虹. 2株青贮玉米根际固氮菌的筛选鉴定及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 174-185. |
| [7] | 张瑞, 安雪姣, 李建烨, 卢曾奎, 牛春娥, 徐振飞, 张金霞, 耿智广, 岳耀敬, 杨博辉. 湖羊及其不同杂交组合生长性能、产肉性能及肌肉品质比较分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 186-197. |
| [8] | 张峰硕, 季秋蓉, 何婷莉, 苏曲杨昂毛, 王志有, 侯生珍, 桂林生. 低蛋白日粮中不同比例氨基酸对藏羊背腰最长肌肉品质、氨基酸和脂肪酸组成以及维生素和矿物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 198-208. |
| [9] | 张永亮, 滕泽, 郝凤, 于铁峰, 张玉霞. 苜蓿混播方式及比例对混播草地生产力和稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 185-197. |
| [10] | 白宇飞, 尹航, 杨海波, 冯振华, 李斐. 无人机多光谱和RGB影像融合的苜蓿产量估测[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 45-58. |
| [11] | 曹秭琦, 赵小庆, 张向前, 伍建辉, 张帆, 刘丹, 路战远, 任永峰. 施钾水平对北方风沙区油莎豆生长、块茎品质及产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 73-83. |
| [12] | 吕帅磊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 刘蕊, 赵鑫, 刘佳, 徐昌旭, 曹卫东. 江西红壤绿肥季施用磷矿粉的磷素效应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 149-160. |
| [13] | 侯铭辉, 孙延亮, 杨开鑫, 齐军仓, 张前兵. 基于响应曲面法确定水培大麦饲草高产优质的氮磷钾养分投入量[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 172-185. |
| [14] | 王凤宇, 梁国玲, 胡泽龙, 刘文辉. 地理因子对青藏高原野生垂穗披碱草表型及种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 198-214. |
| [15] | 高兴发, 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 杨敏, 徐树花, 朱孟. 干旱条件下乌蒙山区冬闲田燕麦引种适应性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 215-227. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||