

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 150-163.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024174
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
郭楠1( ), 杜鹉辰2, 纪守坤1, 刘建1, 崔素倩3, 袁辉4, 韩旭5, 刘计双6, 高立杰1(
), 杜鹉辰2, 纪守坤1, 刘建1, 崔素倩3, 袁辉4, 韩旭5, 刘计双6, 高立杰1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-14
修回日期:2024-07-25
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-02-19
通讯作者:
高立杰
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: gaolijie1975@163.com基金资助:
Nan GUO1( ), Wu-chen DU2, Shou-kun JI1, Jian LIU1, Su-qian CUI3, Hui YUAN4, Xu HAN5, Ji-shuang LIU6, Li-jie GAO1(
), Wu-chen DU2, Shou-kun JI1, Jian LIU1, Su-qian CUI3, Hui YUAN4, Xu HAN5, Ji-shuang LIU6, Li-jie GAO1( )
)
Received:2024-05-14
Revised:2024-07-25
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-02-19
Contact:
Li-jie GAO
摘要:
为了探究施肥和补播量对退化山地草甸牧草的营养物质含量及瘤胃发酵参数的影响,筛选最适宜的老芒麦、扁穗冰草、垂穗披碱草和紫花苜蓿混播组合,设置4个施肥量(0、3.6、7.2和10.8 t·hm-2)和4个播种量(0、3.4、4.6和5.7 kg·hm-2),对4种混播草地:老芒麦+垂穗披碱草+紫花苜蓿(EEM)、老芒麦+扁穗冰草+紫花苜蓿(EAM)、扁穗冰草+垂穗披碱草+紫花苜蓿(AEM)和老芒麦+扁穗冰草+垂穗披碱草+紫花苜蓿(EAEM)的干物质产量、营养物质含量进行测定,并通过体外发酵研究施肥和补播量对混播牧草组合瘤胃发酵参数的影响。结果表明:与未施肥相比,施肥显著提高了各混播处理的干物质产量(DMY)和相对饲喂价值(RFV)(P<0.05),显著降低了各混播处理的中性洗涤纤维(NDF)和酸性洗涤纤维(ADF)含量(P<0.05);在4.6 kg·hm-2的补播量处理下,补播显著提高了EEM混播处理的DMY和RFV(P<0.05),显著降低了EEM混播处理的NDF和ADF含量;EEM、EAM、AEM在4.6 kg·hm-2处理下,瘤胃液中氨态氮(NH3-N)和丙酸含量显著高于其他补播处理(P<0.05)。主成分分析结果显示,施肥和播种量分别为10.8 t·hm-2、5.7 kg·hm-2的EEM混播组合综合得分最高。响应面分析结果表明,AEM混播组合的预测产量最高,EEM次之,EEM混播组合的预测综合得分最高。基于产量和综合评价,在施肥和补播量分别为10.8 t·hm-2和5.7 kg·hm-2的老芒麦+垂穗披碱草+紫花苜蓿组合效果最好。
郭楠, 杜鹉辰, 纪守坤, 刘建, 崔素倩, 袁辉, 韩旭, 刘计双, 高立杰. 施肥和补播对山地草甸牧草营养及瘤胃发酵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 150-163.
Nan GUO, Wu-chen DU, Shou-kun JI, Jian LIU, Su-qian CUI, Hui YUAN, Xu HAN, Ji-shuang LIU, Li-jie GAO. Effects of different fertilization and reseeding rates on the nutrient content of forage in a mountain meadow and its rumen fermentation parameters[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(4): 150-163.

图1 不同施肥、补播量对各混播组合干物质产量和牧草营养物质含量的影响A: EEM; B: EAM; C: AEM; D: EAEM; PF: P施肥Fertilizer; PR: P补播Reseeding; PF×R: P施肥Fertilizer×补播Reseeding. 同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),同列不同大写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences (P<0.05); Different capital letters in the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05); 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Effect of different fertilizer application and reseeding rate on dry matter yield and forage nutrient content
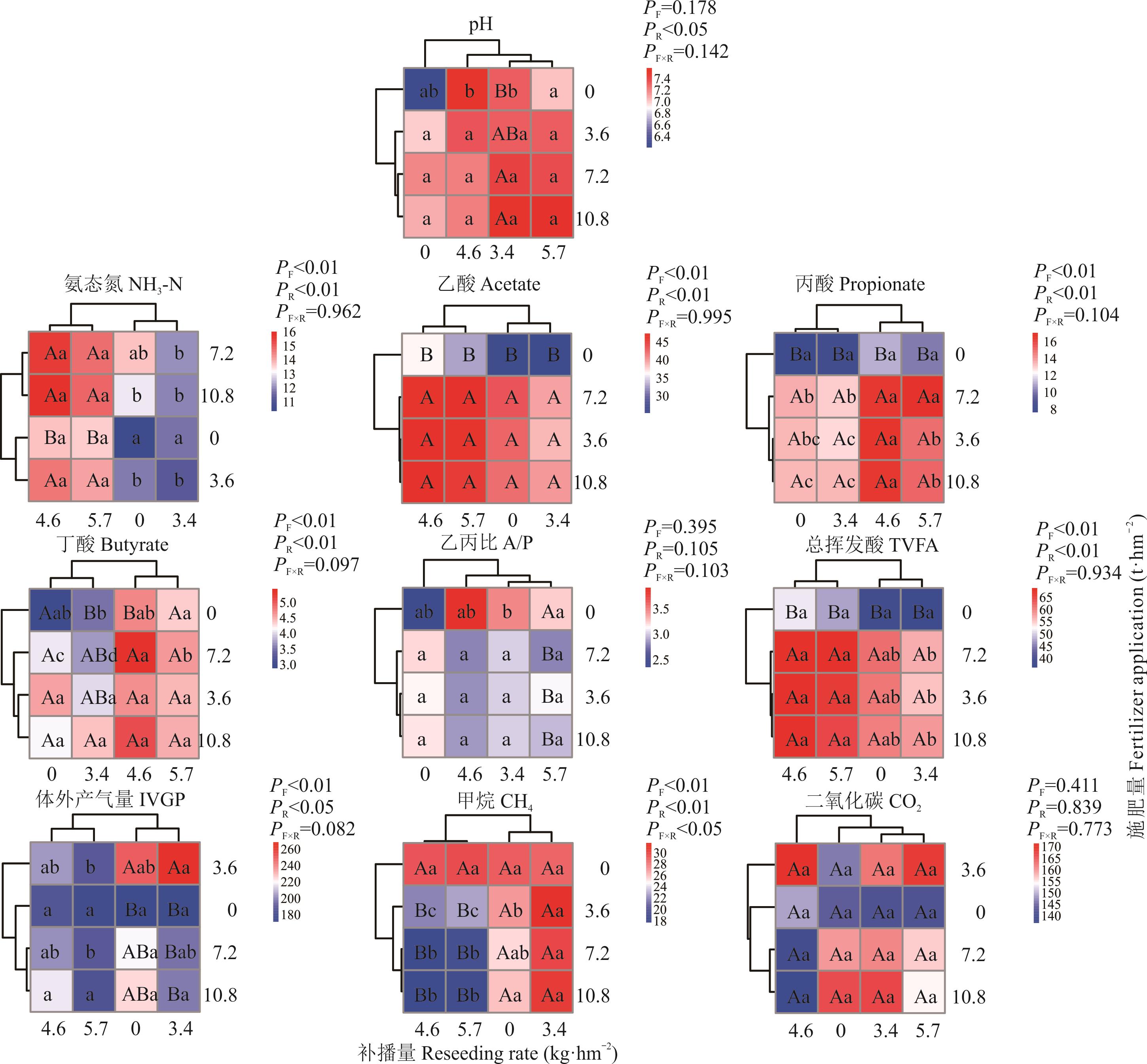
图2 不同施肥量、补播量对EEM混播组合牧草瘤胃发酵参数的影响
Fig.2 Effect of different fertilizer application and reseeding rate on rumen fermentation parameters of EEM mixed forage

图3 不同施肥、补播量对EAM混播组合牧草瘤胃体外发酵参数的影响
Fig.3 Effect of different fertilizer application and reseeding rate on rumen fermentation parameters of EAM mixed forage
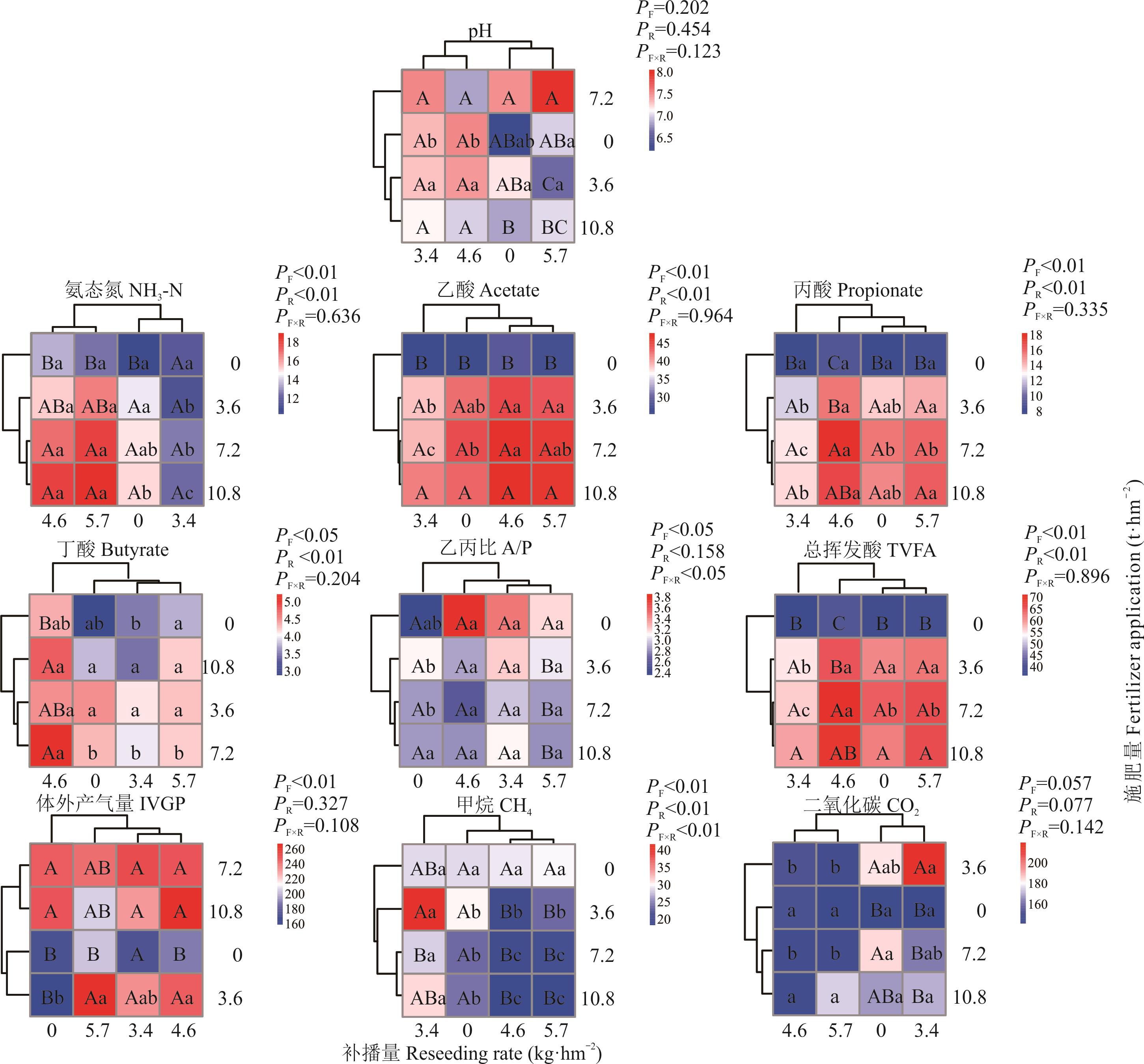
图4 不同施肥、补播量对AEM混播组合牧草瘤胃发酵参数的影响
Fig.4 Effect of different fertilizer application and reseeding rate on rumen fermentation parameters of AEM mixed forage
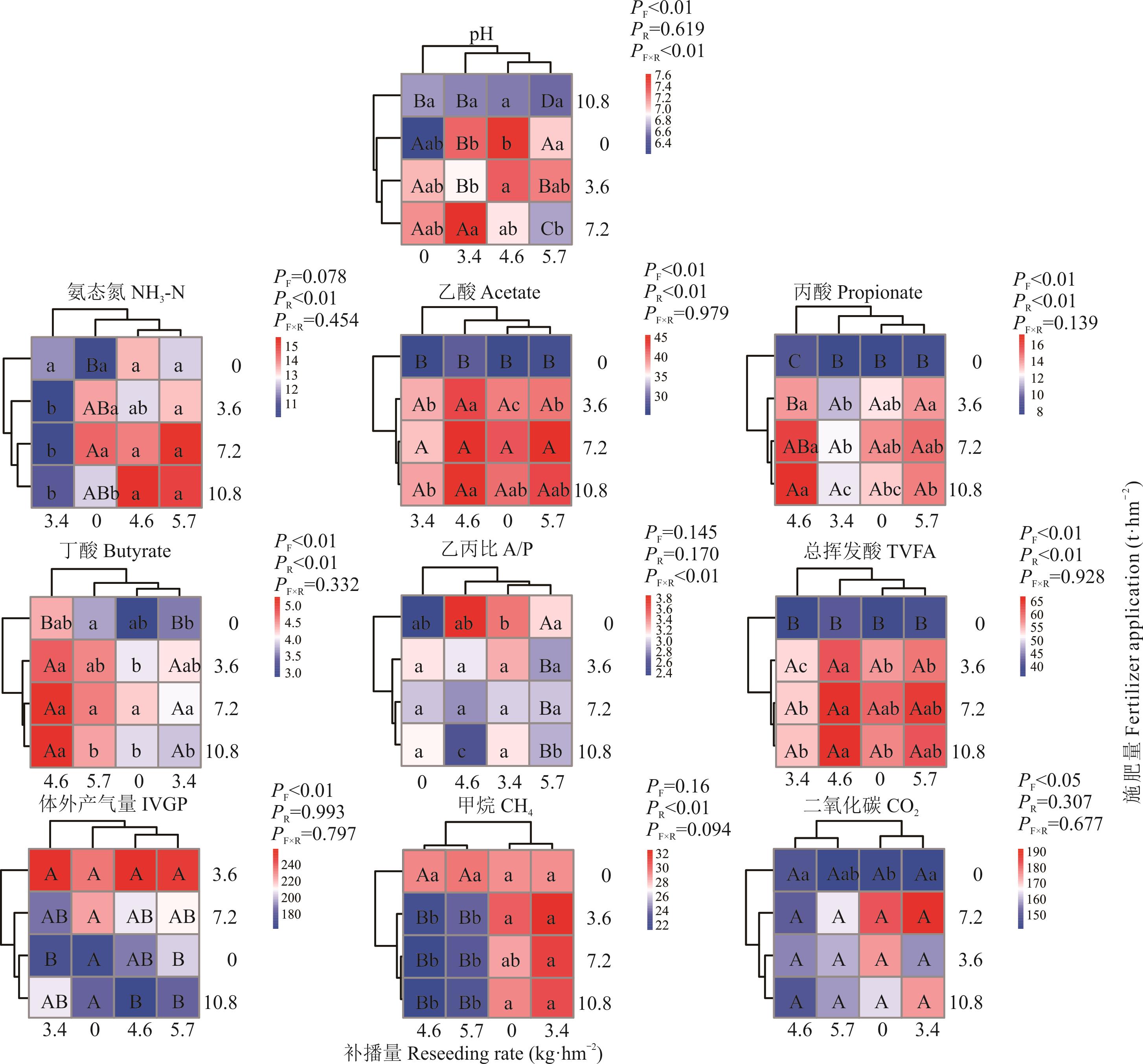
图5 不同施肥、补播量对EAEM混播组合牧草瘤胃体外发酵参数的影响
Fig.5 Effect of different fertilizer application and reseeding rate on rumen fermentation parameters of forage mixed with EAEM
| 混播组合Mixed sowing combination | 施肥量 Fertilizer application (t·hm-2) | 补播量 Reseeding rate (kg·hm-2) | 混播组合Mixed sowing combination | 施肥量 Fertilizer application (t·hm-2) | 补播量 Reseeding rate (kg·hm-2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 0 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 5.7 | ||||
| EEM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 | AEM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 |
| 3.6 | -0.72 | -1.89 | 1.06 | 0.39 | 3.6 | -0.04 | -1.72 | 1.74 | 1.17 | ||
| 7.2 | -0.37 | -1.48 | 1.52 | 1.13 | 7.2 | 0.58 | -0.59 | 2.66 | 1.90 | ||
| 10.8 | 0 | 3.40 | 4.60 | 5.70 | 10.8 | 0.33 | -0.50 | 2.59 | 1.90 | ||
| EAM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 | EAEM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 |
| 3.6 | -1.80 | -2.75 | -0.12 | -0.62 | 3.6 | -1.43 | -1.87 | 0.66 | 0.09 | ||
| 7.2 | -1.36 | -2.68 | 0.87 | 0.19 | 7.2 | -0.85 | -1.48 | 1.57 | 1.02 | ||
| 10.8 | -1.42 | -1.91 | 0.60 | -0.15 | 10.8 | -1.07 | -1.71 | 1.52 | 1.53 | ||
表1 不同处理的综合得分
Table 1 Composite scores for different treatments
| 混播组合Mixed sowing combination | 施肥量 Fertilizer application (t·hm-2) | 补播量 Reseeding rate (kg·hm-2) | 混播组合Mixed sowing combination | 施肥量 Fertilizer application (t·hm-2) | 补播量 Reseeding rate (kg·hm-2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 0 | 3.4 | 4.6 | 5.7 | ||||
| EEM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 | AEM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 |
| 3.6 | -0.72 | -1.89 | 1.06 | 0.39 | 3.6 | -0.04 | -1.72 | 1.74 | 1.17 | ||
| 7.2 | -0.37 | -1.48 | 1.52 | 1.13 | 7.2 | 0.58 | -0.59 | 2.66 | 1.90 | ||
| 10.8 | 0 | 3.40 | 4.60 | 5.70 | 10.8 | 0.33 | -0.50 | 2.59 | 1.90 | ||
| EAM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 | EAEM | 0 | -5.32 | -7.20 | -1.94 | -3.25 |
| 3.6 | -1.80 | -2.75 | -0.12 | -0.62 | 3.6 | -1.43 | -1.87 | 0.66 | 0.09 | ||
| 7.2 | -1.36 | -2.68 | 0.87 | 0.19 | 7.2 | -0.85 | -1.48 | 1.57 | 1.02 | ||
| 10.8 | -1.42 | -1.91 | 0.60 | -0.15 | 10.8 | -1.07 | -1.71 | 1.52 | 1.53 | ||

图6 施肥量和补播量对牧草综合评价的影响响应曲面越陡,等高线越密集,表示影响越显著;等高线越接近椭圆,表示两个因素的交互作用越强。The steeper the response surface and the denser the contours are, the more significant they are, and the closer the contours are to the ellipse, the stronger the interaction between the two factors.
Fig.6 Effect of fertilizer application and reseeding rate on the comprehensive evaluation
| 1 | Leal V N, Santos D D C, Paim T D P, et al. Economic results of forage species choice in crop-livestock integrated systems. Agriculture, 2023, 13(3): 637. |
| 2 | Zhao G S, Ren L J, Ye Z L, et al. Vegetation dynamics in response to climate change and human activities in a typical alpine region in the Tibetan Plateau. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(19): 12359. |
| 3 | Wang H S, Song M L, Wang Y Q, et al. Effects of different restoration methods on Ligularia virgaurea and toxic weed dominated degraded grassland community. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(4): 32-39. |
| 王宏生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 等. 不同恢复措施对黄帚橐吾及毒害草型退化草地群落的影响. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(4): 32-39. | |
| 4 | Nie H Y, Gao J X. Research progress on the ecological impact and spreading mechanism of weeds on degraded grassland. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(7): 101-113. |
| 聂华月, 高吉喜. 退化草地杂草生态影响及蔓延机制研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(7): 101-113. | |
| 5 | Song M H, Yu F H. Reduced compensatory effects explain the nitrogen-mediated reduction in stability of an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. New Phytologist, 2015, 207(1): 70-77. |
| 6 | Scotton M, Rossetti V. Effects of fertilisation on grass and forb gamic reproduction in semi-natural grasslands. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 19146. |
| 7 | Cao W X, Li W, Li X L, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on plant community structure and soil nutrient in alpine meadow-steppe. Journal of Desert Research, 2015, 35(3): 658-666. |
| 曹文侠, 李文, 李小龙, 等. 施氮对高寒草甸草原植物群落和土壤养分的影响. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(3): 658-666. | |
| 8 | Zhang H J, Zheng K F, Gu S S, et al. Grass-legume mixture with rhizobium inoculation enhanced the restoration effects of organic fertilizer. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(5): 1114. |
| 9 | Tian L, Yang W, Ji S A, et al. Artificial reseeding improves multiple ecosystem functions in an alpine sandy meadow of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 2023, 34(7): 2052-2060. |
| 10 | Shang Z H, Ma Y S, Long R J, et al. Effect of fencing, artificial seeding and abandonment on vegetation composition and dynamics of ‘black soil land’ in the headwaters of the Yangtze and the Yellow Rivers of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 2008, 19(5): 554-563. |
| 11 | Yang Z Z, Zhang C P, Dong Q M, et al. Effects of reseeding on plant community composition and diversity of moderately degraded alpine grassland in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(5): 1071-1077. |
| 杨增增, 张春平, 董全民, 等. 补播对中度退化高寒草地群落特征和多样性的影响. 草地学报, 2018, 26(5): 1071-1077. | |
| 12 | He J S, Bu H Y, Hu X W, et al. Close-to-nature restoration of degraded alpine grasslands: Theoretical basis and technical approach. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(34): 3898-3908. |
| 贺金生, 卜海燕, 胡小文, 等. 退化高寒草地的近自然恢复: 理论基础与技术途径. 科学通报, 2020, 65(34): 3898-3908. | |
| 13 | Zhang Q, Ma L, Zhang Z H, et al. Ecological restoration of degraded grassland in Qinghai-Tibet alpine region: Degradation status, restoration measures, effects and prospects. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(20): 7441-7451. |
| 张骞, 马丽, 张中华, 等. 青藏高寒区退化草地生态恢复: 退化现状、恢复措施、效应与展望. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 7441-7451. | |
| 14 | Tahir M, Li C H, Zeng T, et al. Mixture composition influenced the biomass yield and nutritional quality of legume-grass pastures. Agronomy, 2022, 12(6): 1449. |
| 15 | Cinar S, Hatipoglu R, Avci M, et al. Quality characteristics of the mixtures of some warm season perennial grasses with alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under irrigated conditions in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2018, 16(5): 7139-7154. |
| 16 | Menke K H, Raab L, Salewsli A, et al. The estimation of the digestibility and metabolizable energy content of ruminant feeding stuffs from the gas production when they are incubated with rumen liquor in-vitro. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1979, 93(1): 217-222. |
| 17 | Guo L N, Yao D D, Li D X, et al. Effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from rumen fluid and feces of dairy cows on fermentation quality, microbial community, and in-vitro digestibility of alfalfa silage. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10: 2998. |
| 18 | Van Soest P J, Robertson J B, Lewis B A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science, 1991, 74(10): 3583-3597. |
| 19 | Mirzaei-Aghsaghali A, Maheri-Sis N, Mirza-Aghazadeh A, et al. Estimation of quality indices of iranian alfalfa varieties using in vivo and in-situ methods. Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advances, 2012, 6(8): 1022-1027. |
| 20 | Wang Y Q, Wu J T, Lv M X, et al. Metabolism characteristics of lactic acid bacteria and the expanding applications in food industry. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 612285. |
| 21 | Minski D M E A, Dall A M, Rios E, et al. Nutritive value and herbage mass in hybrids of Paspalum plicatulum×Paspalum guenoarum fertilized with nitrogen or in mixture with temperate legumes. Grassland Science, 2020, 66(4): 261-270. |
| 22 | Peng Y, Sun J Y, Ma S J, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on production performance and nutritive value of pasture species in Northern Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 52-64. |
| 彭艳, 孙晶远, 马素洁, 等. 氮磷添加对藏北人工牧草生产性能和品质的评价. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 52-64. | |
| 23 | Wang Y Q, Song M L, Wang H S, et al. Effects of nitrogen addition on vegetation and forage nutritional quality of degraded alpine grasslands. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(12): 2742-2751. |
| 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 王宏生, 等. 添加氮素对退化高寒草地植被及营养品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(12): 2742-2751. | |
| 24 | Symanowicz B, Skorupka W, Becher M, et al. The effect of alfalfa mineral fertilization and times of soil sampling on enzymatic activity. Agronomy, 2021, 11(7): 1335. |
| 25 | McDonald I, Baral R, Min D. Effects of alfalfa and alfalfa-grass mixtures with nitrogen fertilization on dry matter yield and forage nutritive value. Journal of Animal Science and Technology, 2021, 63(2): 305-318. |
| 26 | Šidlauskaitė G, Kemešytė V, Toleikienė M, et al. Plant diversity, functional group composition and legumes effects versus fertilisation on the yield and forage quality. Sustainability, 2022, 14(3): 1182. |
| 27 | Zhang C, Wang M, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of root cutting and organic fertilizer application on aboveground biomass and soil nutrients in the mowing grassland of Leymus chinensis meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(1): 220-228. |
| 张楚, 王淼, 张宇, 等. 切根与施有机肥对羊草草甸草原打草场地上生物量与土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(1): 220-228. | |
| 28 | Yue L N, Shi S L, Qi J, et al. Effects of no-tillage reseeding on productivity and nutritional quality of degraded grassland in northern China. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(11): 2583-2590. |
| 岳丽楠, 师尚礼, 祁娟, 等. 免耕补播对北方退化草地生产力及营养品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(11): 2583-2590. | |
| 29 | Hou Y R, Ren Y P, Li X S, et al. Effects of reseeding alfalfa against community of degraded mountain meadow steppe in northern Tianshan Mountain. Grass-Feeding Livestock, 2016(2): 44-47. |
| 侯钰荣, 任玉平, 李学森, 等. 补播紫花苜蓿对天山北坡退化山地草甸草原群落的影响. 草食家畜, 2016(2): 44-47. | |
| 30 | Mack G, EI B N, Sporri M, et al. Perceived feasibility of sward management options in permanent grassland of alpine regions and expected effects on delivery of ecosystem services. Environment Development and Sustainability, 2024, 26: 4579-4601. |
| 31 | Hakl J, Kunzová E, Tocauerová Š, et al. Impact of long-term manure and mineral fertilization on yield and nutritive value of lucerne (Medicago sativa) in relation to changes in canopy structure. European Journal of Agronomy, 2021, 123: 126219. |
| 32 | Zhang R, Yang W, Wang W, et al. Effects of reseeding on forage nutrition and physical and chemical properties of degraded alpine meadow soils. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(6): 1059-1068. |
| 张冉, 杨蔚, 王文, 等. 补播对退化高寒草甸牧草养分及土壤理化性质的影响. 草业科学, 2022, 39(6): 1059-1068. | |
| 33 | Yin W, Tian H N, Yang G Z, et al. Reseeding experiment of several legume herbage natural grassland in the south bank of Qinghai Lake. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary, 2019(12): 117-120. |
| 尹卫, 田海宁, 杨国柱, 等. 青海湖南岸地区几种豆科牧草天然草地补播试验. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2019(12): 117-120. | |
| 34 | Duchene O, Vian J, Celette F. Intercropping with legume for agroecological cropping systems: Complementarity and facilitation processes and the importance of soil microorganisms: A review. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 240: 148-161. |
| 35 | Wang P, Chen B, Gu X M, et al. Evaluation of the adaptability of different forage varieties growing on meadow grassland. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary, 2022, 41(5): 248-252. |
| 王鹏, 陈斌, 顾新民, 等. 不同牧草品种在草甸草原生长的适应性评价. 畜牧兽医杂志, 2022, 41(5): 248-252. | |
| 36 | Wendling M, Büchi L, Amossé C, et al. Specific interactions leading to transgressive over yielding in cover crop mixtures. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 241: 88-99. |
| 37 | Ye T, Wu X J, Lu Y X, et al. Effect of planting ratio on the stability of forage yield and population density in two alfalfa-grass mixtures. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. |
| 叶婷, 吴晓娟, 芦奕晓, 等. 混播比例对两种苜蓿混播草地产量和种群密度稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 127-137. | |
| 38 | Zheng W, Jianaerguli, Tang G R, et al. Determination and comparison of community stability in different legume-grass mixes. Acta Prataculturae sinica, 2015, 24(3): 155-167. |
| 郑伟, 加娜尔古丽, 唐高溶, 等. 不同混播方式下豆禾混播草地群落稳定性的测度与比较. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 155-167. | |
| 39 | Ma Q H, Wu Y H, Liu Y N, et al. Interspecific interaction and productivity in a dryland wheat/alfalfa strip intercropping. Field Crops Research, 2024, 309: 109335. |
| 40 | Liu X D, Jiao Y, Zhao X Y, et al. Root architecture of forage species varies with intercropping combinations. Agronomy, 2023, 13(9): 2223. |
| 41 | Han J Q, Dong Y Y, Zhang M. Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Applied Soil Ecology, 2021, 165: 103966. |
| 42 | Pan H, Chen M M, Feng H J, et al. Organic and inorganic fertilizers respectively drive bacterial and fungal community compositions in a fluvo-aquic soil in northern China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2020, 198: 104540. |
| 43 | Fang Y F, Cao Z W, Sun H S, et al. Effects of fertilization and reseeding interaction on yield and quality of degraded grassland in Songnen plain. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2023(6): 167-174. |
| 方玉凤, 曹志伟, 孙洪升, 等. 施肥和补播互作对松嫩平原退化草地产量、品质的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023(6): 167-174. | |
| 44 | Wang Y, Wang Z, Kang Y, et al. Assessing the win-win situation of forage production and soil organic carbon through a short-term active restoration strategy in alpine grasslands. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2024, 14: 1290808. |
| 45 | Fan Q S, Wanapat M, Hou F J. Chemical composition of milk and rumen microbiome diversity of yak, impacting by herbage grown at different phenological periods on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Animals, 2020, 10(6): 1030. |
| 46 | Dijkstra J, Ellis J L, Kebreab E, et al. Ruminal pH regulation and nutritional consequences of low pH. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2012, 172(1/2): 22-33. |
| 47 | Liu H J, Xu T W, Xu S X, et al. Effect of dietary concentrate to forage ratio on growth performance, rumen fermentation and bacterial diversity of Tibetan sheep under barn feeding on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Peer J, 2019, 7: e7462. |
| 48 | Ferri C M, Stritzler N P, Pagella J H. Nitrogen fertilization on rye pasture: Effect on forage chemical composition, voluntary intake, digestibility and rumen degradation. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2004, 190(5): 347-354. |
| 49 | Ta N, Gui R, Wei R H, et al. Dynamic changes of grazing sheep body gains and ruminal fermentation parameters on sandy recovering grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(5): 45-50. |
| 塔娜, 桂荣, 魏日华, 等. 沙地恢复草场放牧绵羊体增重及瘤胃发酵参数动态变化. 草业学报, 2010, 19(5): 45-50. | |
| 50 | Cappellozza B I, Bohnert D W, Reis M M, et al. Influence of amount and frequency of protein supplementation to steers consuming low-quality, cool-season forage: Intake, nutrient digestibility, and ruminal fermentation. Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 99(6): skab112. |
| 51 | Zhao H B, Lv F, Liu G H, et al. Effects of starters with different NDF/starch ratio on rumen fermentation parameters and rumen microorganisms in lambs. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2023, 10: 1064774. |
| 52 | Suarez-Mena F X, Heinrichs A J, Jones C M, et al. Straw particle size in calf starters: Effects on digestive system development and rumen fermentation. Journal of Dairy Science, 2016, 99(1): 341-353. |
| 53 | Shen H, Lu Z, Xu Z, et al. Associations among dietary non-fiber carbohydrate, ruminal microbiota and epithelium G-protein-coupled receptor, and histone deacetylase regulations in goats. Microbiome, 2017, 5(1): 123. |
| 54 | Zhong R Z, Fang Y, Xia S H, et al. Rumen methane output and fermentation characteristics of gramineous forage and leguminous forage at differing harvest dates determined using an in-vitro gas production technique. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2016, 15(2): 414-423. |
| [1] | 金有顺, 侯扶江. 放牧家畜养分消化率的测定[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 200-212. |
| [2] | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [3] | 赵京东, 乌云娜, 宋彦涛. 短期围封对辽西北退化草地群落牧草品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 51-61. |
| [4] | 赵京东, 宋彦涛, 徐鑫磊, 乌云娜. 施氮和刈割对辽西北退化草地牧草产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 36-48. |
| [5] | 徐鑫磊, 宋彦涛, 赵京东, 乌云娜. 施肥和刈割对呼伦贝尔草甸草原牧草品质的影响及其与植物多样性的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 1-10. |
| [6] | 李晨, Ahmad Anum Ali, 张剑搏, 梁泽毅, 丁学智, 阎萍. 冷季牦牛和黄牛采食行为、血清生化指标与瘤胃发酵参数的比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 162-169. |
| [7] | 陈冬冬, 王彦荣, 韩云华. 灌溉次数和施肥量对甘肃引黄灌区紫花苜蓿种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 154-163. |
| [8] | 李小冬, 蔡璐, 张瑜, 王茜, 莫本田, 韩永芬, 王小利. AtmiR156a调控菊苣营养生长与品质[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 160-166. |
| [9] | 高金龙, 孟宝平, 杨淑霞, 冯琦胜, 崔霞, 梁天刚. 基于HJ-1A卫星数据的高寒草地氮素评估-以青海省贵南县及玛沁县高寒草地为例[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 11-20. |
| [10] | 杨帆,张宇,余爱,魏志远,唐树梅,漆智平. 配方施肥对热研2号柱花草产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(2): 264-270. |
| [11] | 塔娜,桂荣,魏日华,赵山志. 沙地恢复草场放牧绵羊体增重及瘤胃发酵参数动态变化[J]. 草业学报, 2010, 19(5): 45-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||