

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 94-102.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020210
魏志敏( ), 孙斌, 方成, 代子雯, 刘满强, 焦加国, 胡锋, 李辉信, 徐莉(
), 孙斌, 方成, 代子雯, 刘满强, 焦加国, 胡锋, 李辉信, 徐莉( )
)
收稿日期:2020-05-12
修回日期:2020-08-25
出版日期:2021-05-20
发布日期:2021-04-16
通讯作者:
徐莉
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: xuli602@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhi-min WEI( ), Bin SUN, Cheng FANG, Zi-wen DAI, Man-qiang LIU, Jia-guo JIAO, Feng HU, Hui-xin LI, Li XU(
), Bin SUN, Cheng FANG, Zi-wen DAI, Man-qiang LIU, Jia-guo JIAO, Feng HU, Hui-xin LI, Li XU( )
)
Received:2020-05-12
Revised:2020-08-25
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-04-16
Contact:
Li XU
摘要:
利用前期筛选的具有优良固氮活性的巨大芽孢杆菌菌株N3和豌豆根瘤菌菌株Vic5,研究单一及复合接种对毛叶苕子的促生效果及对土壤性质的影响。结果表明:相比不接菌处理CK,单一接种N3能显著提高毛叶苕子根瘤固氮酶活性,单一接种Vic5能显著提高毛叶苕子地上部生物量、结瘤数和根瘤固氮酶活性,Vic5处理下毛叶苕子地上部生物量、结瘤数、根瘤固氮酶活性及根系形态学指标包括根系总长、根表面积、根体积及根尖数较N3处理分别增加了72.55%、121.20%、47.22%、21.46%、50.48%、53.85%和47.42%。相比CK,接种N3处理土壤全磷、速效磷和速效钾含量显著提高,Vic5处理土壤铵态氮和硝态氮含量显著提高,复合接菌处理下土壤有机质和全氮含量显著提高。接种N3能显著提高土壤固氮酶活性,接种Vic5能显著提高土壤基础呼吸、微生物量碳、氮含量和土壤固氮酶活性,复合接种处理下土壤基础呼吸强度最大、微生物量碳、氮含量最高,土壤固氮酶活性最高,用乙炔还原法测得固氮酶活性为C2H4 53.77 nmol·g-1·h-1。综上所述,相比单一接种,复合接种自生固氮菌N3和豌豆根瘤菌Vic5表现出对毛叶苕子更优的促生作用和对土壤具有更好的改良作用,可为后期毛叶苕子专性生物菌肥的开发利用奠定基础。
魏志敏, 孙斌, 方成, 代子雯, 刘满强, 焦加国, 胡锋, 李辉信, 徐莉. 根瘤菌与固氮菌联合对毛叶苕子的促生效果[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 94-102.
Zhi-min WEI, Bin SUN, Cheng FANG, Zi-wen DAI, Man-qiang LIU, Jia-guo JIAO, Feng HU, Hui-xin LI, Li XU. Co-inoculation with rhizobia and azotobacter affects the growth of Vicia villosa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 94-102.
处理 Treatment | 地上部生物量 The aboveground biomass (g·plant-1) | 地下部生物量 The underground biomass (g·plant-1) | 结瘤数 Nodule numbers (No.·plant-1) | 根瘤固氮酶活性 The nodule nitrogenase activity (μmol·h-1·g-1·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.60±0.50c | 0.40±0.10b | 37.70±2.10c | 116805.20±9131.10d |
| N3 | 5.10±0.10c | 0.60±0.10b | 41.00±1.70c | 177071.30±11525.10c |
| Vic5 | 8.80±0.60b | 1.40±0.10a | 87.00±4.00b | 260681.70±1974.10b |
| N3+Vic5 | 9.70±0.30a | 1.50±0.20a | 118.00±14.90a | 360103.10±31450.10a |
表1 不同处理对毛叶苕子植株的影响
Table 1 Effects of different treatments on V. villosa
处理 Treatment | 地上部生物量 The aboveground biomass (g·plant-1) | 地下部生物量 The underground biomass (g·plant-1) | 结瘤数 Nodule numbers (No.·plant-1) | 根瘤固氮酶活性 The nodule nitrogenase activity (μmol·h-1·g-1·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.60±0.50c | 0.40±0.10b | 37.70±2.10c | 116805.20±9131.10d |
| N3 | 5.10±0.10c | 0.60±0.10b | 41.00±1.70c | 177071.30±11525.10c |
| Vic5 | 8.80±0.60b | 1.40±0.10a | 87.00±4.00b | 260681.70±1974.10b |
| N3+Vic5 | 9.70±0.30a | 1.50±0.20a | 118.00±14.90a | 360103.10±31450.10a |
处理 Treatment | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Root number (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 296.80±11.20d | 46.80±2.20c | 0.40±0.10c | 142.00±26.20c |
| N3 | 370.40±29.70c | 52.30±1.40c | 0.52±0.10c | 194.00±9.00b |
| Vic5 | 449.90±12.70b | 78.70±8.40b | 0.80±0.20b | 286.00±16.40b |
| N3+Vic5 | 608.40±36.30a | 95.60±1.30a | 1.20±0.10a | 341.00±9.20a |
表2 不同处理对毛叶苕子根系的影响
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on the root of V. villosa
处理 Treatment | 根长 Root length (cm) | 根表面积 Root surface area (cm2) | 根体积 Root volume (cm3) | 根尖数 Root number (No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 296.80±11.20d | 46.80±2.20c | 0.40±0.10c | 142.00±26.20c |
| N3 | 370.40±29.70c | 52.30±1.40c | 0.52±0.10c | 194.00±9.00b |
| Vic5 | 449.90±12.70b | 78.70±8.40b | 0.80±0.20b | 286.00±16.40b |
| N3+Vic5 | 608.40±36.30a | 95.60±1.30a | 1.20±0.10a | 341.00±9.20a |
| 处理Treatment | pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | NO3--N (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.48±0.04a | 26.99±1.41b | 1.39±0.02b | 0.74±0.02b | 2.60±0.30c | 6.00±0.50c | 47.83±1.23b | 120.71±4.45c |
| N3 | 7.47±0.03a | 28.08±0.84ab | 1.42±0.01b | 0.84±0.04a | 2.90±0.10c | 7.20±0.60bc | 53.56±2.16a | 133.20±5.84a |
| Vic5 | 7.43±0.05a | 29.16±1.05ab | 1.44±0.05ab | 0.76±0.01b | 3.80±0.10b | 8.20±0.60b | 49.74±1.94b | 123.37±3.56bc |
| N3+Vic5 | 7.40±0.03a | 29.71±0.58a | 1.48±0.04a | 0.83±0.06a | 5.00±0.60a | 9.60±1.20a | 50.90±1.73ab | 129.57±2.01ab |
表3 不同处理对土壤性质的影响
Table 3 Effects of different treatments on soil properties
| 处理Treatment | pH | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | NH4+-N (mg·kg-1) | NO3--N (mg·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.48±0.04a | 26.99±1.41b | 1.39±0.02b | 0.74±0.02b | 2.60±0.30c | 6.00±0.50c | 47.83±1.23b | 120.71±4.45c |
| N3 | 7.47±0.03a | 28.08±0.84ab | 1.42±0.01b | 0.84±0.04a | 2.90±0.10c | 7.20±0.60bc | 53.56±2.16a | 133.20±5.84a |
| Vic5 | 7.43±0.05a | 29.16±1.05ab | 1.44±0.05ab | 0.76±0.01b | 3.80±0.10b | 8.20±0.60b | 49.74±1.94b | 123.37±3.56bc |
| N3+Vic5 | 7.40±0.03a | 29.71±0.58a | 1.48±0.04a | 0.83±0.06a | 5.00±0.60a | 9.60±1.20a | 50.90±1.73ab | 129.57±2.01ab |
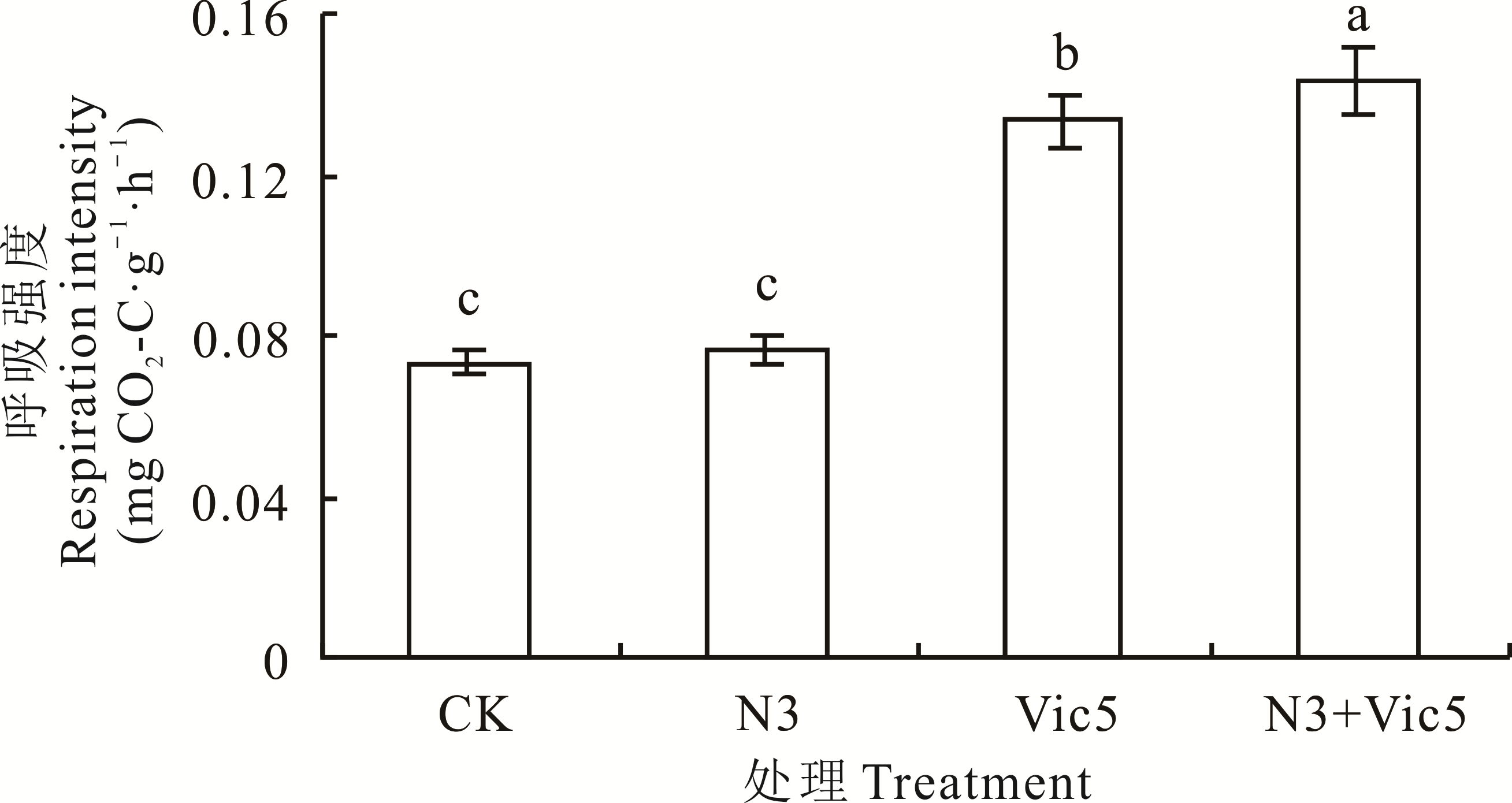
图1 不同处理对土壤基础呼吸的影响不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。The different letters indicate significant difference between treatments(P<0.05). The same blow.
Fig.1 Effects of different treatments on soil basal respiration
| 1 | Fan X, Duan Y, Duan H Y, et al. Influence of sowing date, seeding rate and fertilizer amount on grass and grain yield of hairy vetch. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012(6): 60-61, 69. |
| 范霞, 段玉, 段海燕, 等. 播种期、播种量和肥料用量对毛叶苕子产草量及籽实产量的影响. 内蒙古农业科技, 2012(6): 60-61, 69. | |
| 2 | Zhang J D, Bao X G, Wang T, et al. Effects of adding green fertilizer and reducing nitrogen fertilizer on wheat yield and soil fertility. Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 25(5): 998-1003. |
| 张久东, 包兴国, 王婷, 等. 增施绿肥与降低氮肥对小麦产量和土壤肥力的影响. 核农学报, 2011, 25(5): 998-1003. | |
| 3 | Liu J, Zhang J, Qin W J, et al. Decomposition and nutrient release characteristics of different Vicia villosa green manure applications in red soil uplands of South China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 29(10): 66-76. |
| 刘佳, 张杰, 秦文婧, 等. 红壤旱地毛叶苕子不同翻压量下腐解及养分释放特征. 草业学报, 2016, 25(10): 66-76. | |
| 4 | Xie S G, Han W B, Feng W Q, et al. The preliminary study on the effect of leguminous green manure on crop yield and economic benefits in hilly dry of Sichuan. Soil and Fertilizer in China, 2010(5): 82-85. |
| 谢树果, 韩文斌, 冯文强, 等. 豆科绿肥对四川丘陵旱地作物的产量及经济效益初探. 中国土壤与肥料, 2010(5): 82-85. | |
| 5 | Anugroho F, Kitou M, Nagumo F, et al. Potential growth of hairy vetch as a winter legume cover crops in subtropical soil conditions. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2010, 56: 254-262. |
| 6 | Garcia-Franco N, Albaladejo J, Almagro M, et al. Bene-ficial effects of reduced tillage and green manure on soil aggregation and stabilization of organic carbon in a medi-terranean agroecosystem. Soil and Tillage Research, 2015, 153: 66-75. |
| 7 | Song L, Liao W Y, Wang Y J, et al. Effects of interplanting green fertilizer on soil physical and chemical properties of tea gardens. Soil, 2016, 48(4): 675-679. |
| 宋莉, 廖万有, 王烨军, 等. 套种绿肥对茶园土壤理化性状的影响. 土壤, 2016, 48(4): 675-679. | |
| 8 | Yang B J, Huang G Q, Wang C, et al. Effects of winter planting green fertilizer on rice yield and soil fertility in paddy fields. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 2013, 21(10): 1209-1216. |
| 杨滨娟, 黄国勤, 王超, 等. 稻田冬种绿肥对水稻产量和土壤肥力的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(10): 1209-1216. | |
| 9 | Tejada M, Gonzalez J L, García-Martínez A M, et al. Effects of different green manures on soil biological pro-perties and maize yield. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99: 1758-1767. |
| 10 | Macguidwin A E, Knuteson D L, Connell T, et al. Manipulating inoculum densities of Verticillium dahliae and Pratylenchus penetrans with green manure amend-ments and solarization influence potato yield. Phytopa-Thology, 2012, 102: 519. |
| 11 | Yang Z P, Xu M G, Nie J, et al. Effects of long-term winter planting green manure on soil quality of red loam rice under double cropping rice cultivation and its evaluation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(3): 92-97, 102. |
| 杨曾平, 徐明岗, 聂军, 等. 长期冬种绿肥对双季稻种植下红壤性水稻土质量的影响及其评价. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(3): 92-97, 102. | |
| 12 | Yan Y L. Biological nitrogen fixation: To promote the reduction and efficiency of fertilizer application, promote green development of agriculture. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2019, 35(10): 6-7. |
| 燕永亮. 生物固氮: 促进化肥减施增效, 助力农业绿色发展. 生物技术通报, 2019, 35(10): 6-7. | |
| 13 | Wang Y H, Wang Y P. Field application of peanut rhizobia inoculation agent. China Agricultural Technology Extension, 2013, 29(11): 33-34. |
| 王艳辉, 王亚平. 花生接种根瘤菌剂田间应用效果. 中国农技推广, 2013, 29(11): 33-34. | |
| 14 | Gao Y M, Yao T, Li H Y, et al. Studies on the isolation and screening of rhizosphere promoting bacteria from the alpine meadow grasses and polygonum viviparum and their promoting characteristics. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(11): 114-123. |
| 高亚敏, 姚拓, 李海云, 等. 高寒草甸嵩草、珠芽蓼根际优良植物根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生特性研究. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 114-123. | |
| 15 | Zhang L, Yang Y H, Li Q, et al. Study on activation of inorganic phosphorus in soil by azotobacter. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(7): 2157-2164. |
| 张亮, 杨宇虹, 李倩, 等. 自生固氮菌活化土壤无机磷研究. 生态学报, 2013, 33(7): 2157-2164. | |
| 16 | Zhang L, Yuan L, Huang J G. Mobilization of potassium in soils by azotobacter. Acta Pedologica Sinaca, 2015, 52(2): 399-405. |
| 张亮, 袁玲, 黄建国. 自生固氮菌对土壤钾的活化作用. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(2): 399-405. | |
| 17 | Han M, Zhang H L, Guo S S, et al. Rhizobia inoculation effects on the root Vicia villosa nodulation ability of green manure crops. China Seed Industry, 2011(S2): 41-42. |
| 韩梅, 张宏亮, 郭石生, 等. 接种根瘤菌对绿肥作物毛苕子结瘤能力的影响. 中国种业, 2011(S2): 41-42. | |
| 18 | Fu P. Rhizobium influence on nitrogen fixation of nodule Vicia sativa L. Pratacultural Science, 2016, 33(4): 584-588. |
| 付萍. 根瘤菌对箭筈豌豆结瘤固氮的影响. 草业科学, 2016, 33(4): 584-588. | |
| 19 | Wei Z X, Zhuo M, Mima G C et al. Effects of alfalfa rhizobium inoculation on alfalfa growth and soil physicochemical properties in Xizang. Tibet Journal of Agricultureal Sciences, 2019,41(3): 1-5. |
| 韦泽秀, 卓玛, 米玛更才. 接种苜蓿根瘤菌对西藏苜蓿生长及土壤理化性质的影响. 西藏农业科技, 2019, 41(3): 1-5. | |
| 20 | Li Y P, Zhang M, Yuan M, et al. Effects of rhizobia and compound probiotics on the nodulation and growth of soybean. Soybean Science, 2017, 36(4): 583-591. |
| 李艳萍, 张敏, 袁梅, 等. 根瘤菌和复合促生菌对大豆结瘤和生长的影响. 大豆科学, 2017, 36(4): 583-591. | |
| 21 | Guan F Z, Qiu H D, Chen J C, et al. Research and development of rhizobia bacteriums. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2012, 31(3): 755-759. |
| 管凤贞, 邱宏端, 陈济琛, 等. 根瘤菌菌剂的研究与开发现状. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(3): 755-759. | |
| 22 | Li X X, Wang H D, Wang Z, et al. Effects of compound encapsulation agent on soybean growth and soil fertility. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2013, 44(2): 160-165. |
| 李晓旭, 王慧达, 王卓, 等. 复合包埋菌剂对大豆生长及土壤肥力的影响. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2013, 44(2): 160-165. | |
| 23 | Xue X Y, Feng R H, Guan D W, et al. Screening and mechanism of soybean rhizobia and growth-promoting bacteria. Soybean Science, 2011, 30(4): 613-620. |
| 薛晓昀, 冯瑞华, 关大伟, 等. 大豆根瘤菌与促生菌复合系筛选及机理研究. 大豆科学, 2011, 30(4): 613-620. | |
| 24 | Das S, De T K. Microbial assay of N2, fixation rate, a simple alternate for acetylene reduction assay. Methodsx, 2018(5): 909-914. |
| 25 | Lu R K. Methods of soil agricultural chemical analysis. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 26 | Vance E D, Brookes P C, Jenkinson D S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1987, 19(6): 703-707. |
| 27 | Liu L, Ma M C, Jiang X, et al. Effect of rhizobia and PGPR co-inoculant on soybean characteristics and soil enzyme activities. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(3): 644-654. |
| 刘丽, 马鸣超, 姜昕, 等. 根瘤菌与促生菌双接种对大豆生长和土壤酶活的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(3): 644-654. | |
| 28 | Dilfuza E, Li L, Kristina L, et al. A synergistic interaction between salt-tolerant Pseudomonas and Mesorhizobium strains improves growth and symbiotic performance of liquorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fish.) under salt stress. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2016, 100: 2829-2841. |
| 29 | Singh N, Singh G, Aggarwal N, et al. Yield enhancement and phosphorus economy in lentil (Lens culinaris medikus) with integrated use of phosphorus, rhizobium and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2018, 41(6): 737-748. |
| 30 | Otieno P E, Muthomi J W, Chemining G N, et al. Effect of rhizobia inoculation, farm yard manure and nitrogen fertilizer on nodulation and yield of food grain legumes. Journal of Biological Ences, 2009, 9(4): 305-312. |
| 31 | Wang H, Liu W, Jang Y, et al. Effect of rhizobia inoculation on soybean growth under different nitrogen levels. Soybean Science and Technology, 2012(1): 14-17. |
| 王浩, 刘伟, 姜妍, 等. 不同氮素水平下接种根瘤菌对大豆生长的影响. 大豆科技, 2012(1): 14-17. | |
| 32 | Mirza B S, Mirza M S, Bano A, et al. Coinoculation of chickpea with rhizobium isolates from roots and nodules and phytohormone-producing enterobacter strains. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 2007, 47(8): 1008-1015. |
| 33 | Jos L B, Alfredo C R, Luis H E. The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2003, 6(3): 280-287. |
| 34 | Xu L, Wei Z M, Sun B, et al. A strain of giant bacillus with nitrogen fixation capacity and its application. Jiangsu Province: CN110016445A, 2019-07-16. |
| 徐莉, 魏志敏, 孙斌, 等. 一株具有固氮能力的巨大芽孢杆菌及其应用. 江苏省: CN110016445A, 2019-07-16. | |
| 35 | Ma W B, Yao T, Rong L Y, et al. Effects of PGPR inoculum without exogenous nitrogen on the growth and root system characteristics of Vicia sativa L. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(3): 496-501. |
| 马文彬, 姚拓, 荣良燕, 等. 无外源氮素条件下接种促生菌对箭筈豌豆生长及根系特性影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(3): 496-501. | |
| 36 | Liu J, Li J, Ge C. Andvance in role mechanism of microbial fertilizer. Journal of Microbiology, 2001(1): 33-36, 46. |
| 刘健, 李俊, 葛诚. 微生物肥料作用机理的研究新进展. 微生物学杂志, 2001(1): 33-36, 46. | |
| 37 | Guo L Z, Ma J, Huang G B. Effects of rhizobia inoculation on yield and rhizosphere microorganism quantity of pea. Agricultural Modernization Research, 2010, 31(5): 630-633. |
| 郭丽琢, 马剑, 黄高宝. 根瘤菌接种对豌豆产量及根际微生物数量的影响. 农业现代化研究, 2010, 31(5): 630-633. | |
| 38 | Chen G Q. Some understandings on biological nitrogen fixation. Biology Teaching, 2008(8): 72. |
| 陈国庆. 关于生物固氮的几点认识. 生物学教学, 2008(8): 72. | |
| 39 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 40 | Hu C, Li H M, Wu H, et al. Effects of combined inoculation of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria and rhizobia on symbiotic nitrogen fixation of soybean and rhodopsin. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020, 39(4): 38-45. |
| 胡倡, 李慧明, 伍惠, 等. 解磷菌和根瘤菌复合接种对大豆和紫云英共生固氮的影响. 华中农业大学学报, 2020, 39(4): 38-45. | |
| 41 | Malinda S, Thilakarathna, Raizada, et al. A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of diverse rhizobia inoculants on soybean traits under field conditions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2017, 105: 177-196. |
| [1] | 陈永岗, 康文娟, 吴芳, 阿芸, 师尚礼, 张翠梅, 李自立. 硼对根瘤菌胞外多糖和吲哚乙酸分泌的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 42-51. |
| [2] | 贾雨雷, 廖真, 汪丽芳, 卜建超, 林标声, 林辉, 苏德伟, 鲁国东, 林占熺. 化肥减量配施菌草固氮菌肥对巨菌草生长、营养品质及土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 215-223. |
| [3] | 漫静, 唐波, 邓波, 李佳欢, 何玉娟, 张佳良. 羊草根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 59-71. |
| [4] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [5] | 何国兴, 宋建超, 温雅洁, 刘彩婷, 祁娟. 不同根瘤菌肥对紫花苜蓿生产力及土壤肥力的综合影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 109-120. |
| [6] | 康文娟, 师尚礼, 苗阳阳. 紫花苜蓿根瘤菌分子分型和生物型划分研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 88-101. |
| [7] | 严警, 夏丽, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 耐重金属苜蓿中华根瘤菌的筛选及其与能源植物联合富集铜的特性[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 102-111. |
| [8] | 高亚敏, 姚拓, 李海云, 罗慧琴, 张建贵, 杨琰珊, 刘婷. 高寒草甸嵩草、珠芽蓼根际优良植物根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 114-123. |
| [9] | 刘明, 陈远学, 陈强, 彭丹, 喻晓, 杨军伟, 徐开未. 翻压接种根瘤菌的紫花苕子对植烟土壤肥力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 162-169. |
| [10] | 谢志坚, 周春火, 贺亚琴, 宋涛, 于洋, 吴佳. 21世纪我国稻区种植紫云英的研究现状及展望[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 185-196. |
| [11] | 赵涛,马春晖,王栋,景永元,席琳乔. 冬小麦套种草木樨土壤中根瘤菌分布与土壤理化性质的相关性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 45-55. |
| [12] | 王登科, 于翔宇, 张学风, 黄蕾, 李晓婷, 贺治斌, 康林, 王党军, 姚露花, 郭彦军. 酸、铝和盐胁迫对夏季豆科绿肥作物种子萌发及根瘤菌抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 35-44. |
| [13] | 苗阳阳, 周彤, 师尚礼, 康文娟, 张运婷. 硼对根瘤菌在紫花苜蓿体内运移和定殖及对幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(4): 120-133. |
| [14] | 曾庆飞, 王茜, 陆瑞霞, 刘正书, 吴佳海, 王小利. 大豆根际促生菌的分离筛选及其对大豆和百脉根生长与品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1): 99-111. |
| [15] | 何树斌, 郭理想, 李菁, 王燚, 刘泽民, 程宇阳, 呼天明, 龙明秀. 丛枝菌根真菌与豆科植物共生体研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1): 187-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||