

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 150-158.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020462
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2020-10-14
修回日期:2020-11-18
出版日期:2021-08-30
发布日期:2021-08-30
通讯作者:
宋梅玲
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: songml16@126.com基金资助:
Mei-ling SONG( ), Yu-qin WANG, Hong-sheng WANG, Gen-sheng Bao
), Yu-qin WANG, Hong-sheng WANG, Gen-sheng Bao
Received:2020-10-14
Revised:2020-11-18
Online:2021-08-30
Published:2021-08-30
Contact:
Mei-ling SONG
摘要:
禾草内生真菌对于提高宿主植物对生物和非生物胁迫的耐性发挥着积极作用,然而,禾草内生真菌共生体凋落物分解对于草地生态系统养分循环的影响仍不清楚。本研究以紫花针茅为研究对象,比较带内生真菌(E+)与不带内生真菌(E-)植株凋落物分解过程中重量及全氮、木质素和纤维素含量,以及木质素∶N、纤维素∶N与全氮、木质素和纤维素残留率的变化,以期揭示内生真菌在紫花针茅凋落物分解过程中发挥的作用。主要结果如下:E+紫花针茅凋落物分解速率高于E-,具有更短的分解周期;随着时间的延长,紫花针茅凋落物木质素含量和木质素∶N由E+显著高于E-逐渐变为二者之间差异不显著,纤维素含量、纤维素∶N和纤维素残留率则逐渐变为E+显著低于E-;另外,随着分解时间延长,E+和E-凋落物全氮含量呈上升趋势,而全氮残留率呈现出下降-上升-下降的趋势,且后期E+显著低于E-。因此,内生真菌不同程度地促进了紫花针茅凋落物全氮、木质素和纤维素的降解。
宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对高寒草地紫花针茅凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 150-158.
Mei-ling SONG, Yu-qin WANG, Hong-sheng WANG, Gen-sheng Bao. Effect of Epichloë endophyte on the litter decomposition of Stipa purpurea in alpine grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 150-158.
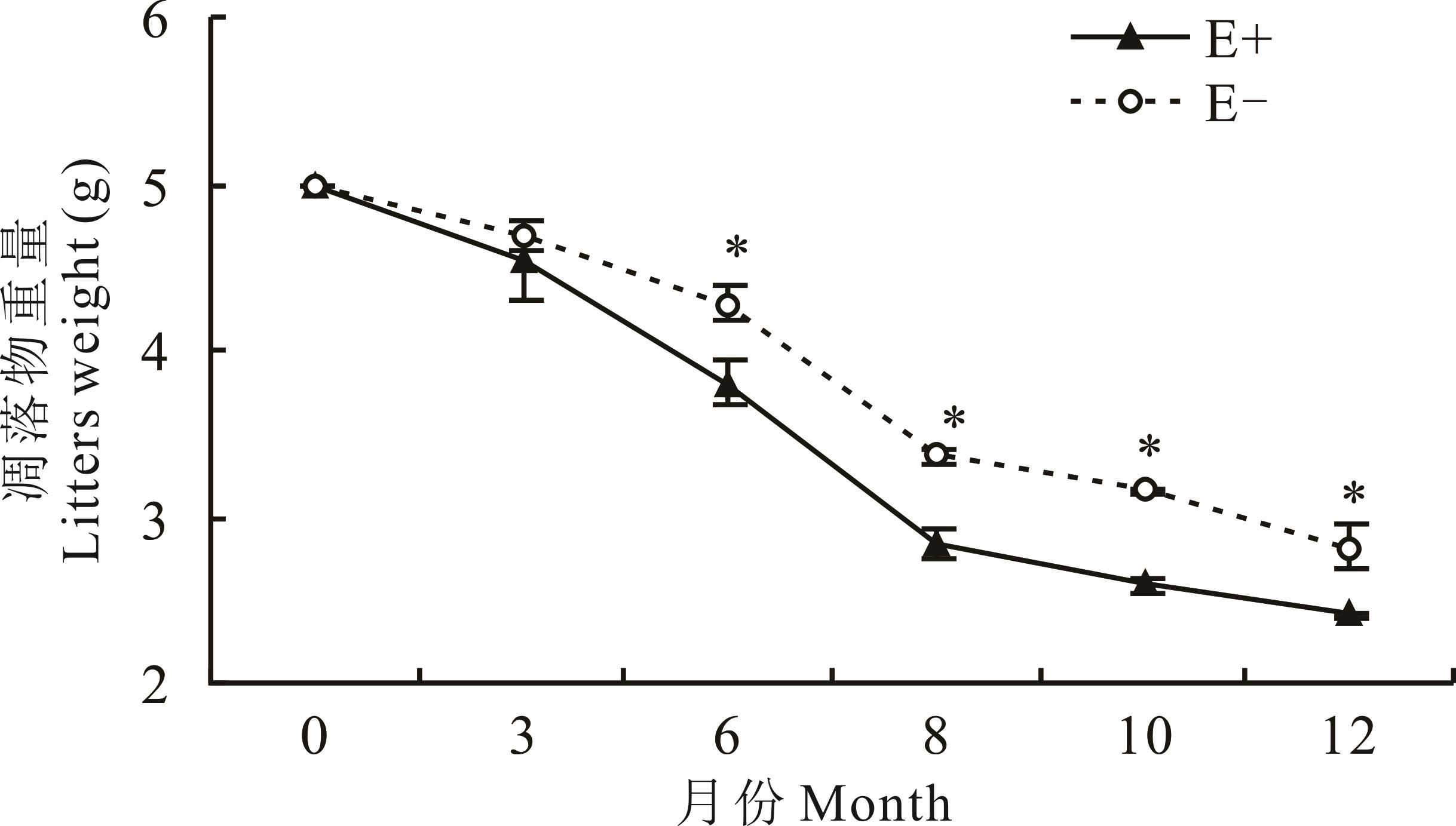
图1 E+和E-紫花针茅凋落物重量随时间的变化*表示相同时间内E+和E-之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。* indicates significant difference (P<0.05) between E+ and E- at same time. The same below.
Fig.1 The change of E+ and E- S. purpurea litters weight over time
项目 Item | df | 凋落物重量Litters weight | 全氮含量Total N content | 木质素含量Lignin content | 纤维素含量Cellulose content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| 内生真菌Endophyte (E) | 1 | 35.47 | <0.001 | 13.71 | 0.001 | 1.10 | 0.305 | 15.93 | 0.001 |
| 时间Times (T) | 5 | 185.61 | <0.001 | 90.42 | <0.001 | 37.19 | <0.001 | 151.65 | <0.001 |
| E×T | 5 | 2.52 | 0.057 | 6.72 | <0.001 | 0.80 | 0.560 | 1.24 | 0.323 |
表1 内生真菌在不同的时间对紫花针茅凋落物重量以及全氮、木质素和纤维素含量的重复度量方差分析
Table 1 Repeated measures ANOVA for the effects of endophyte at different times on litter weight, total N, lignin and cellulose contents of S. purpurea litters
项目 Item | df | 凋落物重量Litters weight | 全氮含量Total N content | 木质素含量Lignin content | 纤维素含量Cellulose content | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| 内生真菌Endophyte (E) | 1 | 35.47 | <0.001 | 13.71 | 0.001 | 1.10 | 0.305 | 15.93 | 0.001 |
| 时间Times (T) | 5 | 185.61 | <0.001 | 90.42 | <0.001 | 37.19 | <0.001 | 151.65 | <0.001 |
| E×T | 5 | 2.52 | 0.057 | 6.72 | <0.001 | 0.80 | 0.560 | 1.24 | 0.323 |
凋落物种类 Litter | 回归方程 Regression equation | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R2) | 分解系数 Decomposition coefficient (k) | 分解50%时间 Time of 50% decomposed (a) | 分解95%时间 Time of 95% decomposed (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E+ | y=0.9752e-0.793t | 0.904 | 0.793 | 0.84 | 3.75 |
| E- | y=1.0058e-0.616t | 0.929 | 0.616 | 1.14 | 4.87 |
表2 E+和E-紫花针茅凋落物分解特征参数
Table 2 Decomposition characteristics parameters of E+ and E- S. purpurea litters
凋落物种类 Litter | 回归方程 Regression equation | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R2) | 分解系数 Decomposition coefficient (k) | 分解50%时间 Time of 50% decomposed (a) | 分解95%时间 Time of 95% decomposed (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E+ | y=0.9752e-0.793t | 0.904 | 0.793 | 0.84 | 3.75 |
| E- | y=1.0058e-0.616t | 0.929 | 0.616 | 1.14 | 4.87 |
项目 Item | df | 木质素∶氮 Lignin∶N | 纤维素∶氮 Cellulose∶N | 氮残留率 N residual rate | 木质素残留率 Lignin residual rate | 纤维素残留率 Cellulose residual rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| 内生真菌Endophyte (E) | 1 | 0.77 | 0.388 | 8.73 | 0.007 | 5.29 | 0.030 | 0.64 | 0.432 | 5.23 | 0.031 |
| 时间Times (T) | 5 | 46.85 | <0.001 | 72.81 | <0.001 | 6.58 | 0.001 | 137.85 | <0.001 | 201.59 | <0.001 |
| E×T | 5 | 0.69 | 0.637 | 0.65 | 0.666 | 1.57 | 0.207 | 1.65 | 0.186 | 0.40 | 0.846 |
表3 内生真菌在不同的时间对紫花针茅凋落物木质素∶氮和纤维素∶氮比值以及全氮、木质素和纤维素残留率的重复度量方差分析
Table 3 Repeated measures ANOVA for the effects of endophyte at different times on lignin∶N ratio, cellulose∶N ratio, and total N, lignin and cellulose residual rates of S. purpurea litters
项目 Item | df | 木质素∶氮 Lignin∶N | 纤维素∶氮 Cellulose∶N | 氮残留率 N residual rate | 木质素残留率 Lignin residual rate | 纤维素残留率 Cellulose residual rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| 内生真菌Endophyte (E) | 1 | 0.77 | 0.388 | 8.73 | 0.007 | 5.29 | 0.030 | 0.64 | 0.432 | 5.23 | 0.031 |
| 时间Times (T) | 5 | 46.85 | <0.001 | 72.81 | <0.001 | 6.58 | 0.001 | 137.85 | <0.001 | 201.59 | <0.001 |
| E×T | 5 | 0.69 | 0.637 | 0.65 | 0.666 | 1.57 | 0.207 | 1.65 | 0.186 | 0.40 | 0.846 |
| 1 | Swift M J, Heal O W, Anderson J M. Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Studies in Ecology, 1979, 5(14): 2772-2774. |
| 2 | Jiang Y F, Yin X Q, Wang F B. The influence of litter mixing on decomposition and soil fauna assemblages in a Pinus koraiensis mixed broadleaved forest of the Changbai Mountains, China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2013, 55: 28-39. |
| 3 | Schlesinger W H, Bernhardt E S. Biogeochemistry: An analysis of global change. New York: Academic Press, 2013. |
| 4 | Couteaux M M, Bottner P, Berg B. Litter decomposition, climate and litter quality. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 1995, 10: 63-66. |
| 5 | Berg B, Berg M P, Bottner P, et al. Litter mass-loss rates in pine forests of Europe and eastern united-states-some relationships with climate and litter quality. Biogeochemistry, 1993, 20(3): 127-159. |
| 6 | Rodriguez R J, Henson J, Van Volkenburgh E, et al. Stress tolerance in plants via habitat-adapted symbiosis. The ISME Journal, 2008, 2(4): 404-416. |
| 7 | Saikkonen K, Gundel P E, Helander M. Chemical ecology mediated by fungal endophytes in grasses. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2013, 39: 962-968. |
| 8 | Siegel M R, Latch G C M, Johnson M C. Fungal endophytes of grasses. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 1987, 25(1): 293-315. |
| 9 | Nan Z B, Li C J. Roles of the grass-Neotyphodium association in pastoral agriculture systems. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(3): 605-616. |
| 南志标, 李春杰. 禾草-内生真菌共生体在草地农业系统中的作用. 生态学报, 2004, 24(3): 605-616. | |
| 10 | Schardl C L, Leuchtmann A, Spiering M J. Symbioses of grasses with seedborne fungal endophytes. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2004, 55: 315-340. |
| 11 | Hu C X. Effects of N, P and tryptophan on growth and ergot alkaloid content in Achnatherum inebrians symbiotic with Neotyphodium gansuense. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. |
| 胡春霞. 氮、磷和色氨酸对醉马草内生真菌共生体生长及麦角生物碱含量的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. | |
| 12 | Hector A, Beale A J, Minns A, et al. Consequences of the reduction of plant diversity for litter decomposition: Effects through litter quality and microenvironment. Oikos, 2000, 90(2): 357-371. |
| 13 | Gartner T B, Cardon Z G. Decomposition dynamics in mixed-species leaf litter. Oikos, 2004, 104(2): 230-246. |
| 14 | Omacini M, Chaneton E J, Ghersa C M, et al. Do foliar endophytes affect grass litter decomposition? A microcosm approach using Lolium multiflorum. Oikos, 2004, 104(3): 581-590. |
| 15 | Saikkonen K, Mikola J, Helander M. Endophytic phyllosphere fungi and nutrient cycling in terrestrial ecosystems. Current Science, 2015, 109(1): 121-126. |
| 16 | Liu W S, Dong M, Song Z P, et al. Genetic diversity patern of Stipa purpurea populations in the hinterland of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Annals of Applied Biology, 2009, 154(1): 57-65. |
| 17 | Duan M J, Gao Q Z, Wan Y F, et al. Effect of grazing on community characteristics and species diversity of Stipa purpurea alpine grassland in Northern Tibet. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(14): 3892-3900. |
| 段敏杰, 高清竹, 万运帆, 等. 放牧对藏北紫花针茅高寒草原植物群落特征的影响. 生态学报, 2010, 30(14): 3892-3900. | |
| 18 | Bao G S, Li C J. Isolation and identification of endophytes infecting Stipa purpurea, a dominant grass in meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(3): 32-42. |
| 鲍根生, 李春杰. 青藏高原高寒草地优势禾草-紫花针茅内生真菌分离和鉴定. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 32-42. | |
| 19 | Yang Y, Li X, Kong X X, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals diversified adaptation of Stipa purpurea along a drought gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 2014, 15(3): 295-307. |
| 20 | Bao G S. Effects of the hemiparasitic plant Pedicularis kansuensis on growth and photosynthetic properties of Stipa purpurea-Epichloë symbiosis. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2015. |
| 鲍根生. 甘肃马先蒿寄生对紫花针茅内生真菌共生体生长和光合特性的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2015. | |
| 21 | Li C J, Nan Z B, Liu Y, et al. Methodology of endophyte detection of drunken horse grass (Achnatherum inebrians). Edible Fungi of China, 2008, 27(supple): 16-19. |
| 李春杰, 南志标, 刘勇, 等. 醉马草内生真菌检测方法的研究. 中国食用菌, 2008, 27(增刊): 16-19. | |
| 22 | Li C J. Biological and ecological characteristics of Achnatherum inebrians/Neotyphodium endophyte symbiont. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2005. |
| 李春杰. 醉马草-内生真菌共生体生物学与生态学特性的研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2005. | |
| 23 | Olson J S. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology, 1963, 44: 322-331. |
| 24 | Rowland A P, Roberts J D. Lignin and cellulose fractionation in decomposition studies using acid-detergent fibre methods. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1994, 25: 269-277. |
| 25 | Thormann M N, Currah R S, Bayley S E. Succession of microfungal assemblages in decomposing peatland plants. Plant and Soil, 2003, 250(2): 323-333. |
| 26 | Fryar S C, Yuen T K, Hyde K D, et al. The influence of competition between tropical fungi on wood colonization in streams. Microbial Ecology, 2001, 41(3): 245-251. |
| 27 | Terekhova V A, Semenova T A. The structure of micromycete communities and their synecologic interactions with basidiomycetes during plant debris decomposition. Microbiology, 2005, 74(1): 91-96. |
| 28 | He X B, Han G M, Lin Y H, et al. Diversity and decomposition potential of endophytes in leaves of a Cinnamomum camphora plantation in China. Ecological Research, 2012, 27(2): 273-284. |
| 29 | Yu W C, Song X L, Xiu W M, et al. Effects of additional nitrogen on litter decomposition in Stipa Baicalensis grassland. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(5): 49-60. |
| 于雯超, 宋晓龙, 修伟明, 等. 氮素添加对贝加尔针茅草原凋落物分解的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(5): 49-60. | |
| 30 | Gurmesa G A, Lu X, Gundersen P, et al. High retention of 15 N-labeled nitrogen deposition in a nitrogen saturated old-grown tropical forest. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(11): 3608-3620. |
| 31 | Bell-Dereske L, Gao X D, Masiello C A, et al. Plant-fungal symbiosis affects litter decomposition during primary succession. Oikos, 2017, 126(6): 801-811. |
| 32 | Lemons A, Clay K, Rudgers J A. Connecting plant-microbial interactions above and belowground: A fungal endophyte affects decomposition. Oecologia, 2005, 145(4): 595-604. |
| 33 | Siegrist J A, McCulley R L, Bush L P, et al. Alkaloids may not be responsible for endophyte associated reductions in tall fescue decomposition rates. Functional Ecology, 2010, 24(2): 460-468. |
| 34 | Gundel P E, Helander M, Garibaldi L A, et al. Role of foliar fungal endophytes in litter decomposition among species and population origins. Fungal Ecology, 2016, 21: 50-56. |
| 35 | Melillo J M, Aber J D, Muratore J F. Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology, 1982, 63(3): 621-626. |
| 36 | Li C L. Litter decomposition of Elymus nutans and its response to UV-B on the eastern alpine meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. |
| 李传龙. 青藏高原东部高寒草甸垂穗披碱草凋落物分解对UV-B的响应. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2010. | |
| 37 | Chapin F S, Matson P A, Mooney H A. Terrestrial decomposition//In: Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology. New York: Springer, 2002: 151-175. |
| 38 | Song X Z, Jiang H, Zhang H L, et al. Elevated UV-B radiation did not affect decomposition rates of needles of two coniferous species in subtropical China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2011, 47: 343-348. |
| 39 | Ma Z L, Gao S, Yang W Q, et al. Degradation characteristics of lignin and cellulose of foliar litter at different rainy stages in subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(1): 122-129. |
| 马志良, 高顺, 杨万勤, 等. 亚热带常绿阔叶林区凋落叶木质素和纤维素在不同雨热季节的降解特征. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(1): 122-129. | |
| 40 | Cortez J, Garnier E, Pérez-Harguindeguy N, et al. Plant traits, litter quality and decomposition in a Mediterranean old-field succession. Plant and Soil, 2007, 296(1/2): 19-34. |
| 41 | Melillo J M, Aber J D, Linkins A E, et al. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics along the decay continuum: Plant litter to soil organic matter. Plant and Soil, 1989, 115(2): 189-198. |
| 42 | Zhang L L. Study on decomposition of 15 common plant litter in Tibetan alpine meadow. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 张丽莉. 青藏高原高寒草甸15种常见植物凋落物分解研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 43 | Gao H Y. Decomposition characteristics of common plant litters in the Stipa breviflora desert grassland of Inner Mongolia. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 高海燕. 内蒙古短花针茅荒漠草原常见植物凋落物分解特征. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. | |
| 44 | Sjöberg G, Nilsson S I, Persson T, et al. Degradation of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin in decomposing spruce needle litter in relation to N. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2004, 36: 1761-1768. |
| 45 | Fang H, Mo J M. Effects of nitrogen deposition on forest litter decomposition. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(9): 3127-3136. |
| 方华, 莫江明. 氮沉降对森林凋落物分解的影响. 生态学报, 2006, 26(9): 3127-3136. | |
| 46 | Sinsabaugh R L, Carreiro M M, Repert D A. Allocation of extracellular enzymatic activity in relation to litter composition, N deposition, and mass loss. Biogeochemistry, 2002, 60(1): 1-24. |
| 47 | Frey S D, Knorr M, Parrent J L, et al. Chronic N enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 2004, 196: 159-171. |
| 48 | Gallardo A, Merino J. Leaf decomposition in two Mediterranean ecosystems of southwest Spain: Influence of substrate quality. Ecology, 1993, 74(1): 152-161. |
| 49 | Song X G, Hu T X, Xian J R, et al. Responses of litter decomposition and nutrient release to simulated nitrogen deposition in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in Southwestern Sichuan. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(10): 2167-2172. |
| 宋学贵, 胡庭兴, 鲜骏仁, 等. 川西南常绿阔叶林凋落物分解及养分释放对模拟氮沉降的响应. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(10): 2167-2172. | |
| 50 | Yang J J. Litter decomposition characteristics in different habitats in extreme arid area. Alar: Tarim University, 2020. |
| 杨晶晶. 极端干旱区不同生境下凋落物分解特征研究. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2020. | |
| 51 | Enriquez S, Duarte C M, Jensen K, et al. Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: The importance of detritus C∶N∶P content. Oecologia, 1993, 94: 457-471. |
| 52 | Shi Y, Dai C C, Wu Y C, et al. Study on the degradation of wheat straw by endophytic fungi. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2004, 24(1): 144-149. |
| 史央, 戴传超, 吴耀春, 等. 植物内生真菌强化还田秸秆降解的研究. 环境科学学报, 2004, 24(1): 144-149. | |
| 53 | Peng X W, Chen H Z. Lipid accumulation and cellulose decomposition of endophytic fungi isolated from Taxus mairei. Mycosystema, 2005, 24(3): 457-461. |
| 彭小伟, 陈洪章. 南方红豆杉内生真菌产油及降解纤维素的研究. 菌物学报, 2005, 24(3): 457-461. |
| [1] | 刘佳丽, 范建容, 张茜彧, 杨超, 徐富宝, 张晓雪, 梁博. 高寒草地生长季/非生长季植被盖度遥感反演[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 15-26. |
| [2] | 李春杰, 郎鸣晓, 陈振江, 王正凤, 陈泰祥. 禾草-内生真菌人工接种技术研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 179-189. |
| [3] | 李淑琴, 陈振江, 陈泰祥, 李秀璋, 慕彪彪, 李春杰. 基于CNKI数据库的禾草与非禾草内生真菌文献计量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 121-132. |
| [4] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [5] | 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 杨明新, 朱传鲁, 彭子原, 薛凯, 赵新全, 王艳芬, 纪宝明, 张静. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| [6] | 陈红, 马文明, 周青平, 杨智, 刘超文, 刘金秋, 杜中曼. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其铁铝氧化物分异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 73-84. |
| [7] | 崔雪莲, 夏超. 外源脱落酸对醉马草内生真菌共生体幼苗建植过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 70-80. |
| [8] | 岳可欣, 龚吉蕊, 于上媛, 宝音陶格涛, 杨波, 王彪, 朱趁趁, 张子荷, 矢佳昱. 氮添加下典型草原凋落物质量和土壤酶活性对凋落物分解速率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 71-82. |
| [9] | 李秀璋, 宋辉, 张宗豪, 徐海峰, 刘欣, 李玉玲, 李春杰. 甘肃内生真菌基因组密码子使用的偏好性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 67-77. |
| [10] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 刘静, 王宏生. 不同密度甘肃马先蒿寄生和内生真菌互作对紫花针茅内源激素及生物碱含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 147-156. |
| [11] | 李柯, 施宠, 何飞焱, 李昊宇. Pb胁迫下内生真菌侵染对德兰臭草生长及生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 112-120. |
| [12] | 何雅丽, 陈振江, 魏学凯, 张海娟, 刘阳, 刘辉, 李春杰. 喷施茉莉酮酸甲酯及感染内生真菌促进醉马草抗虫性的生理作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 121-129. |
| [13] | 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 李春杰. 甘肃马先蒿寄生对禾草内生真菌共生体共生关系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 42-51. |
| [14] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 王宏生. 狼毒防除对高寒草地群落植物养分重吸收的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 47-57. |
| [15] | 马碧花, 蔺伟虎, 高敏, 王兴迪, 田沛. 干旱胁迫下水杨酸和内生真菌对多年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 135-144. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||