

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 62-75.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021177
程分生1,3( ), 尤龙辉2,3(
), 尤龙辉2,3( ), 余锦林1,3, 徐惠昌1,3, 游惠明3, 聂森3, 李建民3, 叶功富3
), 余锦林1,3, 徐惠昌1,3, 游惠明3, 聂森3, 李建民3, 叶功富3
收稿日期:2021-05-07
修回日期:2021-06-16
出版日期:2021-10-19
发布日期:2021-10-19
通讯作者:
尤龙辉
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: m378384996@126.com基金资助:
Fen-sheng CHENG1,3( ), Long-hui YOU2,3(
), Long-hui YOU2,3( ), Jin-lin YU1,3, Hui-chang XU1,3, Hui-ming YOU3, Sen NIE3, Jian-min LI3, Gong-fu YE3
), Jin-lin YU1,3, Hui-chang XU1,3, Hui-ming YOU3, Sen NIE3, Jian-min LI3, Gong-fu YE3
Received:2021-05-07
Revised:2021-06-16
Online:2021-10-19
Published:2021-10-19
Contact:
Long-hui YOU
摘要:
为评价锥栗园生草法相比传统清耕法和施用化学除草剂法,果园土壤质量的绿肥恢复效益,本研究以福建典型的红壤丘陵山区锥栗园为研究对象,采用随机区组设计,将供试样地均分为面积0.3~0.5 hm2的若干试验小区,全园清除自然杂草后,设置撒播鼠茅草(Mode1)、黑麦草(Mode2)、光叶紫花苕(Mode3)3种生草处理,并以施用草甘膦(CK1)和清耕(CK2)处理为对照,每种处理3个重复,2年后,分析3种冷季型绿肥、清耕及施用草甘膦对锥栗园土壤理化性质、酶活性、微生物群落等指标的影响。结果表明:1)相较于清耕处理和喷施草甘膦处理,3种生草处理土壤碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾含量有明显提升,其中鼠茅草处理最高,分别为74.14、156.87和234.76 mg·kg-1;黑麦草处理土壤孔隙度最高,为56.03%;鼠茅草和黑麦草处理土壤蔗糖酶活性提升明显,分别为32.29和26.87 U·g-1。2)5种处理土壤共有优势细菌类群主要为放线菌门、变形菌门、绿弯菌门和酸杆菌门,相对丰度分别为24.9%~28.9%、20.9%~28.8%、13.7%~18.6%和10.8%~12.9%,共有优势真菌类群主要为子囊菌门和担子菌门,相对丰度分别为37.4%~73.7%和15.3%~54.4%。3)相较于清耕处理,3种生草处理细菌群落Chao1指数和Shannon指数均有所提升,真菌群落有所下降。4)相较于清耕处理和喷施草甘膦处理,3种生草处理土壤变形菌门、拟杆菌门和厚壁菌门细菌相对丰度均有所下降,绿弯菌门和浮酶菌门细菌则有所增加,生草促使锥栗园土壤细菌群落由快速生长型向缓慢生长型转变。5)5种处理细菌群落和真菌群落非计量多维尺度转换排序(NMDS)表明,土壤真菌群落分异程度高于细菌群落。6)相关分析(CA)和冗余分析(RDA)表明,生草处理通过改变土壤蔗糖酶、过氧化氢酶活性和碱解氮含量,喷施草甘膦处理通过改变土壤碳氮比,清耕处理通过限制土壤自然含水率改变真菌相关优势类群。综上,锥栗园短期人工生草对土壤理化性质和酶活性有一定程度的改善作用,生草处理与清耕处理和喷施草甘膦处理均会形成特异土壤真菌群落。
程分生, 尤龙辉, 余锦林, 徐惠昌, 游惠明, 聂森, 李建民, 叶功富. 冷季型绿肥对锥栗园土壤生化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 62-75.
Fen-sheng CHENG, Long-hui YOU, Jin-lin YU, Hui-chang XU, Hui-ming YOU, Sen NIE, Jian-min LI, Gong-fu YE. Effects of cold-season green manure on soil biochemical properties and the microbial community in a Castanea henryi orchard, China[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 62-75.
处理 Treatment | 砧木树龄Age of rootstock (a) | 接穗时间Scion time (a) | 林分密度 Stand density (plant·hm-2) | 平均树高 Average tree height (m) | 平均胸径 Mean diameter at breast height (cm) | 整地方式 Method of land preparation | 措施 Measures | 草被盖度 Coverage of grass cover (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 42 | 35 | 198.5 | 7.4 | 28.4 | 带状Stripline | 覆膜撒播鼠茅草Mulching with plastic film and sowing of V. myuros seed | 85 |
| Mode2 | 42 | 35 | 233.7 | 7.7 | 22.9 | 带状Stripline | 覆膜撒播黑麦草Mulching with plastic film and sowing of L. perenne seed | 85 |
| Mode3 | 42 | 35 | 240.8 | 7.1 | 30.4 | 带状Stripline | 覆膜撒播光叶紫花苕Mulching with plastic film and sowing of V. villosa seed | 80 |
| CK1 | 42 | 35 | 215.0 | 7.3 | 26.8 | 带状Stripline | 喷施草甘膦Spraying glyphosate | 10 |
| CK2 | 42 | 35 | 225.2 | 6.7 | 25.3 | 带状Stripline | 清耕Clean tillage | 10 |
表1 供试林分基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of tested stands
处理 Treatment | 砧木树龄Age of rootstock (a) | 接穗时间Scion time (a) | 林分密度 Stand density (plant·hm-2) | 平均树高 Average tree height (m) | 平均胸径 Mean diameter at breast height (cm) | 整地方式 Method of land preparation | 措施 Measures | 草被盖度 Coverage of grass cover (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 42 | 35 | 198.5 | 7.4 | 28.4 | 带状Stripline | 覆膜撒播鼠茅草Mulching with plastic film and sowing of V. myuros seed | 85 |
| Mode2 | 42 | 35 | 233.7 | 7.7 | 22.9 | 带状Stripline | 覆膜撒播黑麦草Mulching with plastic film and sowing of L. perenne seed | 85 |
| Mode3 | 42 | 35 | 240.8 | 7.1 | 30.4 | 带状Stripline | 覆膜撒播光叶紫花苕Mulching with plastic film and sowing of V. villosa seed | 80 |
| CK1 | 42 | 35 | 215.0 | 7.3 | 26.8 | 带状Stripline | 喷施草甘膦Spraying glyphosate | 10 |
| CK2 | 42 | 35 | 225.2 | 6.7 | 25.3 | 带状Stripline | 清耕Clean tillage | 10 |
| 处理Treatment | pH | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤自然含水率 Natural water content (%) | 孔隙度 Porosity (%) | 全碳/氮 Total carbon/ nitrogen | 碱解氮 Hydrolyzed nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 5.98±0.12bc | 1.29±0.08a | 26.40±2.12ab | 49.07±1.18bc | 18.85±1.28b | 74.14±2.16a | 156.87±28.22a | 234.76±6.95a |
| Mode2 | 6.07±0.04b | 1.10±0.07b | 27.31±1.24a | 56.03±1.66a | 16.12±1.71b | 61.36±5.66b | 151.31±28.02a | 209.82±18.19ab |
| Mode3 | 6.02±0.20bc | 1.24±0.06a | 24.49±2.21ab | 40.17±1.54d | 17.49±2.83b | 62.96±1.92b | 152.26±6.77a | 221.12±8.04a |
| CK1 | 6.35±0.01a | 1.25±0.02a | 22.12±2.75b | 46.87±1.36c | 31.60±4.56a | 47.10±2.73d | 108.34±7.26b | 176.37±11.24c |
| CK2 | 5.75±0.25c | 1.21±0.01a | 19.60±2.03c | 51.30±2.84b | 16.45±0.53b | 54.39±3.38c | 121.44±12.46b | 190.88±11.85b |
表2 5种土壤管理模式对锥栗园土壤理化性质的影响
Table 2 Effects of five soil management modes on soil physicochemical properties of C. henryi orchard
| 处理Treatment | pH | 容重 Bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤自然含水率 Natural water content (%) | 孔隙度 Porosity (%) | 全碳/氮 Total carbon/ nitrogen | 碱解氮 Hydrolyzed nitrogen (mg·kg-1) | 有效磷 Available phosphorus (mg·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available potassium (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 5.98±0.12bc | 1.29±0.08a | 26.40±2.12ab | 49.07±1.18bc | 18.85±1.28b | 74.14±2.16a | 156.87±28.22a | 234.76±6.95a |
| Mode2 | 6.07±0.04b | 1.10±0.07b | 27.31±1.24a | 56.03±1.66a | 16.12±1.71b | 61.36±5.66b | 151.31±28.02a | 209.82±18.19ab |
| Mode3 | 6.02±0.20bc | 1.24±0.06a | 24.49±2.21ab | 40.17±1.54d | 17.49±2.83b | 62.96±1.92b | 152.26±6.77a | 221.12±8.04a |
| CK1 | 6.35±0.01a | 1.25±0.02a | 22.12±2.75b | 46.87±1.36c | 31.60±4.56a | 47.10±2.73d | 108.34±7.26b | 176.37±11.24c |
| CK2 | 5.75±0.25c | 1.21±0.01a | 19.60±2.03c | 51.30±2.84b | 16.45±0.53b | 54.39±3.38c | 121.44±12.46b | 190.88±11.85b |
处理 Treatment | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 脲酶 Urease | 酸性磷酸酶 Acid phosphatase | 多酚氧化酶 Polyphenol oxidase | 纤维素酶 Cellulase | α-葡萄糖苷酶 α-glucosidase | β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 42.64±1.52a | 32.29±8.06a | 2.23±0.66a | 1.49±0.05a | 5.52±2.20a | 0.32±0.06a | 6.44±0.67a | 5.26±2.32ab |
| Mode2 | 26.80±2.84bc | 26.87±5.31a | 0.86±0.22b | 1.51±0.06a | 6.21±1.69a | 0.36±0.25a | 6.48±1.84a | 7.67±2.42a |
| Mode3 | 15.40±6.66d | 14.37±0.72c | 1.26±0.22b | 1.47±0.04a | 6.22±0.40a | 0.19±0.09a | 7.54±0.98a | 4.80±0.53b |
| CK1 | 33.42±6.57ab | 15.49±3.95bc | 0.62±0.18b | 1.47±0.04a | 3.87±0.72a | 0.53±0.13a | 4.22±0.16b | 5.04±2.11ab |
| CK2 | 21.37±7.82cd | 24.55±5.80ab | 2.35±0.74a | 1.45±0.12a | 5.91±0.63a | 0.17±0.03b | 5.76±0.48ab | 7.71±0.87a |
表3 5种土壤管理模式对锥栗园土壤酶活性的影响
Table 3 Effects of five soil management modes on soil enzyme activities of C. henryi orchard (U·g-1)
处理 Treatment | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | 蔗糖酶 Sucrase | 脲酶 Urease | 酸性磷酸酶 Acid phosphatase | 多酚氧化酶 Polyphenol oxidase | 纤维素酶 Cellulase | α-葡萄糖苷酶 α-glucosidase | β-葡萄糖苷酶 β-glucosidase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 42.64±1.52a | 32.29±8.06a | 2.23±0.66a | 1.49±0.05a | 5.52±2.20a | 0.32±0.06a | 6.44±0.67a | 5.26±2.32ab |
| Mode2 | 26.80±2.84bc | 26.87±5.31a | 0.86±0.22b | 1.51±0.06a | 6.21±1.69a | 0.36±0.25a | 6.48±1.84a | 7.67±2.42a |
| Mode3 | 15.40±6.66d | 14.37±0.72c | 1.26±0.22b | 1.47±0.04a | 6.22±0.40a | 0.19±0.09a | 7.54±0.98a | 4.80±0.53b |
| CK1 | 33.42±6.57ab | 15.49±3.95bc | 0.62±0.18b | 1.47±0.04a | 3.87±0.72a | 0.53±0.13a | 4.22±0.16b | 5.04±2.11ab |
| CK2 | 21.37±7.82cd | 24.55±5.80ab | 2.35±0.74a | 1.45±0.12a | 5.91±0.63a | 0.17±0.03b | 5.76±0.48ab | 7.71±0.87a |
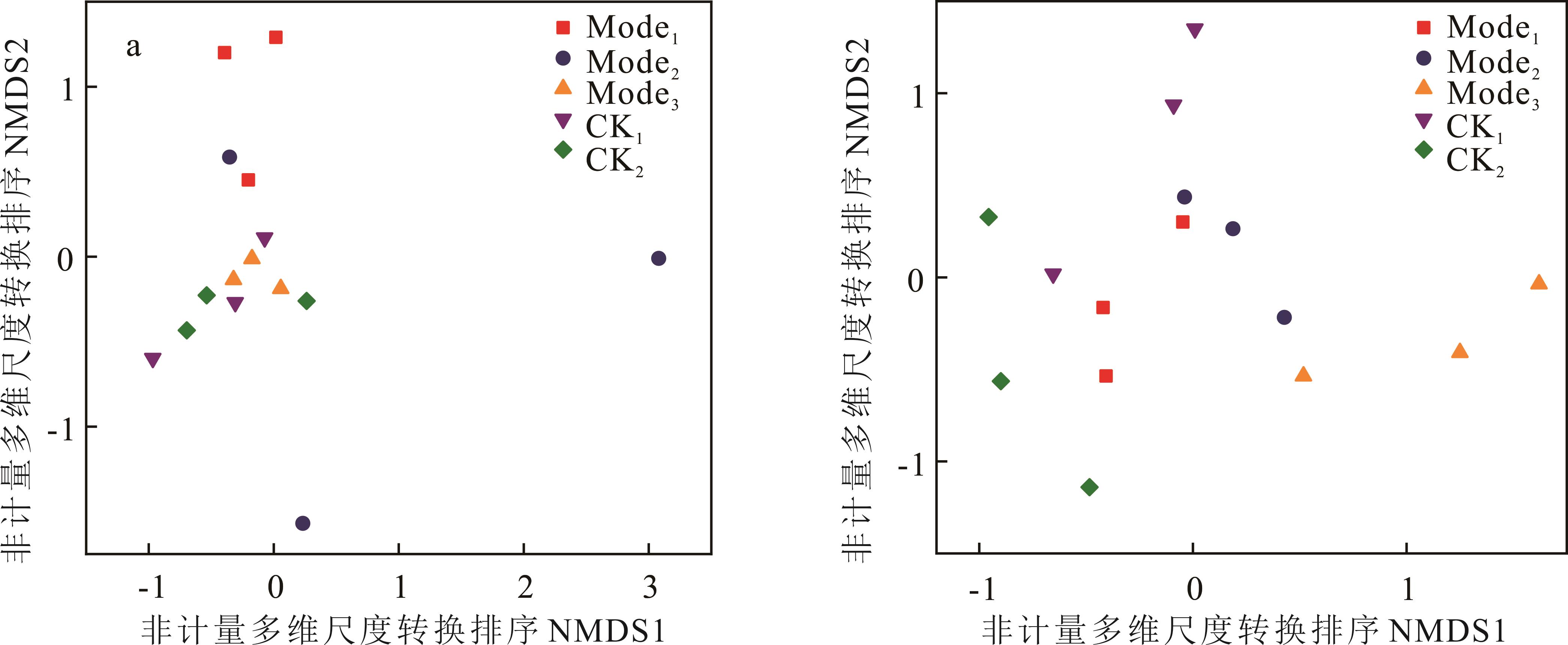
图3 土壤细菌、真菌群落结构的非计量多维尺度转换排序(NMDS)分析a表示细菌群落,b表示真菌群落。下同。 “a” is bacterial community, “b” is fungal community. The same below.
Fig.3 Non quantitative multidimensional scaling ordination (NMDS) analysis of soil bacterial and fungal community structure
类别 Type | 处理 Treatment | 操作分类单元 Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Goods_coverage指数 Goods_coverage index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | Mode1 | 7887±201a | 8627±158a | 9.19±0.98a | 0.996±0.0002a |
| Mode2 | 7400±957a | 8314±834a | 9.27±1.05a | 0.996±0.0004a | |
| Mode3 | 7845±385a | 8747±365a | 9.19±0.62a | 0.996±0.0001a | |
| CK1 | 7679±39a | 8478±95a | 9.03±0.22a | 0.996±0.0003a | |
| CK2 | 7465±122a | 8337±70a | 8.83±0.69a | 0.996±0.0001a | |
真菌 Fungus | Mode1 | 1653±463a | 1765±439a | 6.39±1.27a | 0.997±0.0003a |
| Mode2 | 1436±82a | 1572±112a | 6.73±0.94a | 0.998±0.0004a | |
| Mode3 | 1453±157a | 1532±181a | 6.46±1.40a | 0.997±0.0002a | |
| CK1 | 1516±510a | 1661±492a | 7.12±1.99a | 0.998±0.0003a | |
| CK2 | 1876±517a | 1982±557a | 7.31±1.55a | 0.997±0.0005a |
表4 锥栗园5种土壤管理模式土壤微生物多样性指数
Table 4 Soil microbial diversity index of five soil management models in C. henryi orchard
类别 Type | 处理 Treatment | 操作分类单元 Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | Shannon指数 Shannon index | Goods_coverage指数 Goods_coverage index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
细菌 Bacteria | Mode1 | 7887±201a | 8627±158a | 9.19±0.98a | 0.996±0.0002a |
| Mode2 | 7400±957a | 8314±834a | 9.27±1.05a | 0.996±0.0004a | |
| Mode3 | 7845±385a | 8747±365a | 9.19±0.62a | 0.996±0.0001a | |
| CK1 | 7679±39a | 8478±95a | 9.03±0.22a | 0.996±0.0003a | |
| CK2 | 7465±122a | 8337±70a | 8.83±0.69a | 0.996±0.0001a | |
真菌 Fungus | Mode1 | 1653±463a | 1765±439a | 6.39±1.27a | 0.997±0.0003a |
| Mode2 | 1436±82a | 1572±112a | 6.73±0.94a | 0.998±0.0004a | |
| Mode3 | 1453±157a | 1532±181a | 6.46±1.40a | 0.997±0.0002a | |
| CK1 | 1516±510a | 1661±492a | 7.12±1.99a | 0.998±0.0003a | |
| CK2 | 1876±517a | 1982±557a | 7.31±1.55a | 0.997±0.0005a |

图4 土壤环境因子与细菌门水平相对丰度相关系数热力图BD、WC、PO、TC/N、HN、AP和AK分别代表土壤容重、自然含水率、孔隙度、全碳/氮、碱解氮、有效磷和速效钾;Cat、Suc、Ure、Acp、PPo、Cel、α-G和β-G分别代表土壤过氧化氢酶、蔗糖酶、脲酶、酸性磷酸酶、多酚氧化酶、纤维素酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶和β-葡萄糖苷酶;“*”代表显著相关P<0.05。下同。BD、WC、PO、TC/N、HN、AP and AK represent bulk density, natural water content, porosity, total carbon/nitrogen, hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium; Cat、Suc、Ure、Acp、PPo、Cel、α-G and β-G represent catalase, sucrase, urease, acid phosphatase, polyphenol oxidase, cellulase, α-glucosidase and β-glucosidase; “*”represents significant correlation (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.4 Thermodynamic diagram of correlation coefficient between soil environmental factors and relative abundance of bacteria at phylum level

图5 土壤环境因子与真菌门水平相对丰度相关系数热力图
Fig.5 Thermodynamic diagram of correlation coefficient between soil environmental factors and relative abundance of fungi at phylum level
| 1 | Ma H Q, Jiang X B, Gong B C, et al. Dvance of researches on Castanea henryi and of further development in China. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 2013, 33(1): 62-67. |
| 马海泉, 江锡兵, 龚榜初, 等. 我国锥栗研究进展及发展对策. 浙江林业科技, 2013, 33(1): 62-67. | |
| 2 | Li C Z. Current situation and sustainable development countermeasures of Castanea henryi industry in Jianou. Modern Horticulture, 2012, 2: 6-8. |
| 李陈枝. 建瓯锥栗产业现状与可持续发展对策. 现代园艺, 2012, 2: 6-8. | |
| 3 | Gao Q G. Preliminary study on soil loss control measures and benefits of Castanea henryi landscape in Jianou City, Fujian Province. Subtropical Soil And Water Conservation, 2016, 28(1): 37-39. |
| 高清贵. 福建省建瓯市锥栗山水土流失防治措施及其效益初探. 亚热带水土保持, 2016, 28(1): 37-39. | |
| 4 | Drinkwater L E, Wagoner P, Sarrantonio M. Legumebased cropping systems have reduced carbon and nitrogen losses. Nature, 2006, 396: 262-265. |
| 5 | Luan H A, Wang X Y, Han S, et al. Effects of green manure planting on loss of soil nutrient in citrus orchard in Three Gorges Reservoi. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 30(2): 68-72. |
| 栾好安, 王晓雨, 韩上, 等. 三峡库区橘园种植绿肥对土壤养分流失的影响. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(2): 68-72. | |
| 6 | Yang L, Mao Y F, Hu Y L, et al. Effects of orchard grass on soil fertility and apple tree nutrition. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. |
| 杨露, 毛云飞, 胡艳丽, 等. 生草改善果园土壤肥力和苹果树体营养的效果. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. | |
| 7 | Fu X Q, Liu J R, Huang W X. Effects of natural grass on soil microbiology, nutrient and fruit quality of Nanfeng tangerine yard. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. |
| 付学琴, 刘琚珥, 黄文新. 南丰蜜橘园自然生草对土壤微生物和养分及果实品质的影响. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(8): 1551-1558. | |
| 8 | Zou X H, Huang B B, Gao Q G, et al. The control effect of soil erosion in Castanea henryi plantation in the North of Fujian Province. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 30(6): 47-55. |
| 邹显花, 黄彬彬, 高清贵, 等. 闽北锥栗林经营过程中的水土流失防治效果研究.水土保持学报, 2016, 30(6): 47-55. | |
| 9 | You L H. Effects of grass cultivation on physiological and biochemical characteristics of Castanea henryi leaves and physical and chemical properties of soil. Forestry Prospect and Design, 2020, 40(4): 13-19. |
| 尤龙辉. 生草栽培对锥栗叶片生理生化及土壤理化性质的影响. 林业勘察设计, 2020, 40(4): 13-19. | |
| 10 | Qian J F, Wu J S, Huang J Q. Effects of sod-cultural practices on soil nutrients and microbial diversity in the Carya cathayensis forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(15): 4324-4332. |
| 钱进芳, 吴家森, 黄坚钦. 生草栽培对山核桃林地土壤养分及微生物多样性的影响. 生态学报, 2014, 34(15): 4324-4332. | |
| 11 | Sun B, Zhao Q G, Zhang T L, et al. Soil quality and sustainable environment——Ⅲ. Biological indicators for soil quality assessment. Soils, 1997(5): 225-234. |
| 孙波, 赵其国, 张桃林, 等. 土壤质量与持续环境——Ⅲ.土壤质量评价的生物学指标. 土壤, 1997(5): 225-234. | |
| 12 | Xu Q F, Jiang P K, Wu Q F, et al. Effects of intensive management on soil microbial biomass and functional diversity in Castanea mollissima stands. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2007(3): 15-19. |
| 徐秋芳, 姜培坤, 邬奇峰, 等. 集约经营板栗林土壤微生物量碳与微生物多样性研究. 林业科学, 2007(3): 15-19. | |
| 13 | Jing Z B, Li T F, Long M X, et al. Effects of planted grasses on soil enzyme activities and microbial communities in a kiwifruit orchard. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(9): 1710-1718. |
| 井赵斌, 李腾飞, 龙明秀, 等. 生草对猕猴桃果园土壤酶活性和土壤微生物的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(9): 1710-1718. | |
| 14 | Caporaso J G, Lauber C L, Walters W A, et al. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108: 4516-4522. |
| 15 | Zhao S, Liu D Y, Ling N, et al. Bio-organic fertilizer application significantly reduces the Fusarium oxysporum population and alters the composition of fungi communities of watermelon fusarium wilt rhizosphere soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2014, 50: 765-774. |
| 16 | Nannipieri P, Giagnoni L, Landi L, et al. Role of phosphatase enzymes in soil. Phosphorus in Action, 2011: 215-243. |
| 17 | Abdulaki A A, Teasdale J R. A no-tillage tomato production system using hairy vetch and subterranean clover mulches. HortScience, 1993(28): 106-108. |
| 18 | Wang Y Q, Yuan L. Activation of insoluble phosphorus and its absorption by Sorghum dochna, Sorghum hybrid Sudan grass, and Dolichos lablab. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 33-43. |
| 王亚麒, 袁玲. 甜高粱、高丹草和拉巴豆对难溶性磷的活化与吸收. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 33-43. | |
| 19 | Yang Y H, Zhang S, Wang S, et al. Yield and nutrient concentration in common green manure crops and assessment of potential for nitrogen replacement in different regions of China. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. |
| 杨叶华, 张松, 王帅, 等. 中国不同区域常见绿肥产量和养分含量特征及替代氮肥潜力评估. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. | |
| 20 | Compant S, Reiter B, Sessitsch A, et al. Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by plant growth-promoting bacterium Burkholderia sp. strain PsJN. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(3): 1685-1693. |
| 21 | Niu H H, Wang S S, Jia H D, et al. Allelopathic effects of extracts of Vicia villosa on the germination of four forage seeds. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(9): 161-168. |
| 牛欢欢, 王森森, 贾宏定, 等. 光叶紫花苕子浸提液对4种牧草种子萌发过程的化感作用. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 161-168. | |
| 22 | Guo L, Zhang B B, Shen J H, et al. Effect of glyphosate and paraquat on root morphology and aboveground growth of Prunus persica seedlings. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(2): 524-532. |
| 郭磊, 张斌斌, 沈江海, 等. 草甘膦和百草枯对毛桃幼苗根系形态及地上部生长的影响. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(2): 524-532. | |
| 23 | Bardgett R D, Freeman C, Ostle N J. Microbial contributions to climate change through carbon cycle feedbacks. The ISME Journal, 2008, 2: 805-814. |
| 24 | Lipson D A, Schmidt S K. Seasonal changes in an alpine soil bacterial community in the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2004, 70: 2867-2879. |
| 25 | Xian W D, Zhang X T, Li W J. Research status and prospect on bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020, 60(9): 1801-1820. |
| 鲜文东, 张潇橦, 李文均. 绿弯菌的研究现状及展望. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(9): 1801-1820. | |
| 26 | Wang G H, Liu J J, Yu Z H, et al. Research progress of Acidobacteria ecology in soils. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(2): 14-20. |
| 王光华, 刘俊杰, 于镇华, 等. 土壤酸杆菌门细菌生态学研究进展. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(2): 14-20. | |
| 27 | Jones R T, Robeson M S, Lauber C L, et al. A comprehensive survey of soil Acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. The ISME Journal, 2009, 3: 442-453. |
| 28 | Leff J W, Jones S E, Prober S M, et al. Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112: 10967-10972. |
| 29 | Zhang S N, Yan D R, Huang H G, et al. Effects of short term fencing on soil microbial community structure in Ulmus pumila scattered woodla. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(9): 2860-2867. |
| 张胜男, 闫德仁, 黄海广, 等. 短期封育对科尔沁沙地榆树疏林土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(9): 2860-2867. | |
| 30 | Fei Y C, Huang Y, Zhang X, et al. Effects of different organic fertilizer treatments on the soil microbial community structure of a Camellia oleifera plantation in a purple soil area. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2020, 26(4): 919-927. |
| 费裕翀, 黄樱, 张筱, 等. 不同有机肥处理对紫色土油茶林土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2020, 26(4): 919-927. | |
| 31 | Zhang J, Zhang H W, Li X Y, et al. Research advances in soil fungal diversity and molecular ecology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2004, 10: 1958-1962. |
| 张晶, 张惠文, 李新宇, 等. 土壤真菌多样性及分子生态学研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2004, 10: 1958-1962. | |
| 32 | Hibbett D S, Binder M, Bischoff J F, et al. A higher level phylogenetic classification of the fungi. Mycological Research, 2007, 111: 509-547. |
| 33 | Egidi E, Delgadobaquerizo M, Plett J M, et al. A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2369. |
| 34 | Gu P W, Zhang G D, Wang H R, et al. Determination and control of the main pathogens of post harvest fruit and vegetables rot disease in Ningxia. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 33(1): 1-6. |
| 顾沛雯, 张光弟, 王华荣, 等. 果蔬采后致腐病菌检测及防治. 农业科学研究, 2012, 33(1): 1-6. | |
| 35 | Osorio N W, Habte M. Soil phosphate desorption induced by a phosphate-solubilizing fungus. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2014, 45(4): 451-460. |
| 36 | Siegel M R, Latch G C M. Expression of antifungal activity in agar culture by isolates of grass endophytes. Mycologia, 1991, 83: 529-537. |
| 37 | Li X Z, Fang A G, Li C J, et al. Advances in the researches on the effects of grass endophytes on other microbes. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(6): 1660-1671. |
| 李秀璋, 方爱国, 李春杰, 等.禾草内生真菌对其他微生物的影响研究进展. 生态学报, 2015, 35(6): 1660-1671. | |
| 38 | Wu J, Chen Y Y, Ye X Y, et al. Effects of herbicide glyphosate on microbial diversity in Castanea mollissima rhizosphere soil. Nonwood Forest Research, 2019, 37(3): 161-167,187. |
| 吴静, 陈岩岩, 叶项宇, 等. 除草剂草甘膦对板栗根际土壤微生物多样性的影响. 经济林研究, 2019, 37(3): 161-167,187. | |
| 39 | Liang B, Dong J, Sui F G, et al. Decomposition characteristics of a Vulpia myuros cover crop in an orchard soil and its effect on N supply. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(3): 245-250. |
| 梁斌, 董静, 隋方功, 等. 果园土壤中鼠茅草的降解特性及其对氮素供应的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 245-250. | |
| 40 | Zhao C Y, Wang Y Y, Dong Q J, et al. Influence of different irrigation and fertilization treatments on the growth of Vicia villosa Rothvar and later cropping maize and soil fertility. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(4): 161-166, 269. |
| 赵彩衣, 王媛媛, 董青君, 等. 不同水肥处理对苕子和后茬玉米生长及土壤肥力的影响. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(4): 161-166, 269. | |
| 41 | Druille M, Cabello M N, Omacini M, et al. Glyphosate reduces spore viability and root colonization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Applied Soil Ecology, 2013, 64: 99-103. |
| 42 | Cheng F S, You L H, Ye G F, et al. Carbon balance in an interplanting Pinus massoniana stand in subtropicl eroded red soil region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2021, 32(4): 1163-1174. |
| 程分生, 尤龙辉, 叶功富, 等. 亚热带红壤侵蚀区马尾松不同套种模式生态系统碳平衡. 应用生态学报, 2021, 32(4): 1163-1174. |
| [1] | 唐立涛, 毛睿, 王长庭, 李洁, 胡雷, 字洪标. 氮磷添加对高寒草甸植物群落根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. |
| [2] | 贺翔, 白梅梅, 徐长林, 宋美娟, 汪鹏斌, 鱼小军. 东祁连山小叶金露梅+杯腺柳灌丛草地植被和土壤对其自然恢复演替的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 12-24. |
| [3] | 孙忠超, 郭天斗, 于露, 马彦平, 赵亚楠, 李雪颖, 王红梅. 宁夏东部荒漠草原向灌丛地人为转变过程土壤粒径分形特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 34-45. |
| [4] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [5] | 张超, 闫瑞瑞, 梁庆伟, 娜日苏, 李彤, 杨秀芳, 包玉海, 辛晓平. 不同利用方式下草地土壤理化性质及碳、氮固持研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 90-98. |
| [6] | 李洁, 潘攀, 王长庭, 胡雷, 陈科宇, 杨文高. 三江源区不同建植年限人工草地根系动态特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 28-40. |
| [7] | 刘斯莉, 王长庭, 张昌兵, 胡雷, 唐立涛, 潘攀. 川西北高原3种禾本科牧草根系特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 41-53. |
| [8] | 车昭碧, 徐鹏飞, 郭亚亚, 曹佳敏, 黄星宇, 杨寒珺, 鲁为华. 北方蚁(Formica aquilonia)对山地草甸土壤种子库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 40-51. |
| [9] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [10] | 王琇瑜, 黄晓霞, 和克俭, 孙晓能, 吕曾哲舟, 张勇, 朱湄, 曾睿钦. 滇西北高寒草甸植物群落功能性状与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 6-17. |
| [11] | 宗文贞, 郭家昊, 贾云龙, 郑永兴, 杨旭, 胡芳弟, 王静. 单宁在植物-土壤氮循环中作用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 174-183. |
| [12] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [13] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [14] | 李争艳, 徐智明, 师尚礼, 贺春贵. 江淮地区不同轮茬作物对苜蓿产量及根际土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 28-39. |
| [15] | 常海涛, 赵娟, 刘佳楠, 刘任涛, 罗雅曦, 张静. 退耕还林与还草对土壤理化性质及分形特征的影响——以宁夏荒漠草原为例[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 14-25. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||