

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 181-190.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021462
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
蒋晶晶1,3( ), 杜蕙1, 陈爱昌2(
), 杜蕙1, 陈爱昌2( ), 李雪萍1, 李敏权1, 漆永红1(
), 李雪萍1, 李敏权1, 漆永红1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-10
修回日期:2022-03-14
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2022-10-17
通讯作者:
陈爱昌,漆永红
作者简介:E-mail: aichang612@163.com基金资助:
Jing-jing JIANG1,3( ), Hui DU1, Ai-chang CHEN2(
), Hui DU1, Ai-chang CHEN2( ), Xue-ping LI1, Min-quan LI1, Yong-hong QI1(
), Xue-ping LI1, Min-quan LI1, Yong-hong QI1( )
)
Received:2021-12-10
Revised:2022-03-14
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2022-10-17
Contact:
Ai-chang CHEN,Yong-hong QI
摘要:
为了探究党参菌核病病原菌的种类和生物学特性,采用组织分离法分离病原物,通过形态特征和rDNA转录间隔区(rDNA-ITS)、RNA聚合酶Ⅱ第二大亚基基因(RPB2)进行病原菌种类鉴定,同时开展相关生物学特性研究。结果表明,引起甘肃省党参菌核病的病原菌为雪腐核盘菌和核盘菌,其中雪腐核盘菌为优势病原菌。生物学特性研究表明,雪腐核盘菌和核盘菌菌丝生长最适温度为20和25 ℃,菌核形成最适温度为15和25 ℃,菌丝生长最适pH均为6,菌核形成最适pH为6和7,最适培养基均为马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基。菌丝生长抑制法室内毒力测定表明,啶酰菌胺对两种病原菌的菌丝生长均有较好的抑制效果,EC50分别为0.2625、0.4165 mg·L-1。本研究在国内首次报道了雪腐核盘菌和核盘菌会引起党参菌核病。该研究结果可为该病害的诊断和综合防治提供较为可靠的理论基础和科学依据。
蒋晶晶, 杜蕙, 陈爱昌, 李雪萍, 李敏权, 漆永红. 甘肃省党参菌核病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 181-190.
Jing-jing JIANG, Hui DU, Ai-chang CHEN, Xue-ping LI, Min-quan LI, Yong-hong QI. Identification and biological characterization of the pathogens responsible for sclerotinia rot in Codonopsis pilosula[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(12): 181-190.
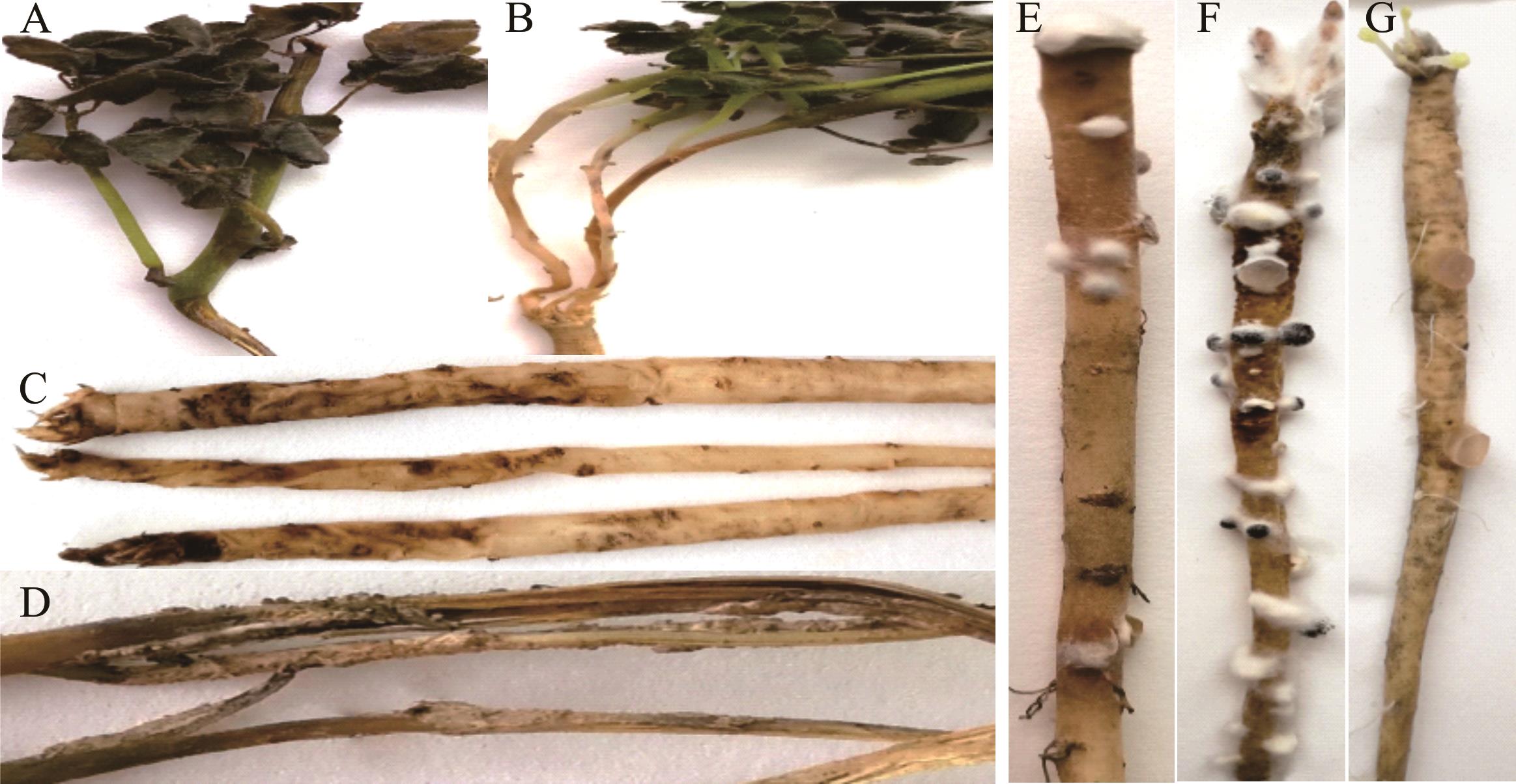

图1 党参菌核病发病症状及致病性测定A: 茎部症状The symptoms on stem; B: 茎基部症状The symptoms on basal stem; C: 根呈黄褐色水浸型软腐Yellow-brownish and water-soaked of roots; D: 茎表面形成黑色不规则菌核体Black and irregular sclerotia on stem surface; E~F: 党参离体根分别接种病原菌DS-RY-2和DS-JF-8 Symptoms of C. pilosulain vitro root inoculated with different isolates DS-RY-2 and DS-JF-8; G: 空白对照Control.
Fig.1 Symptom of C. pilosula sclerotinia rot and pathogenicity testing
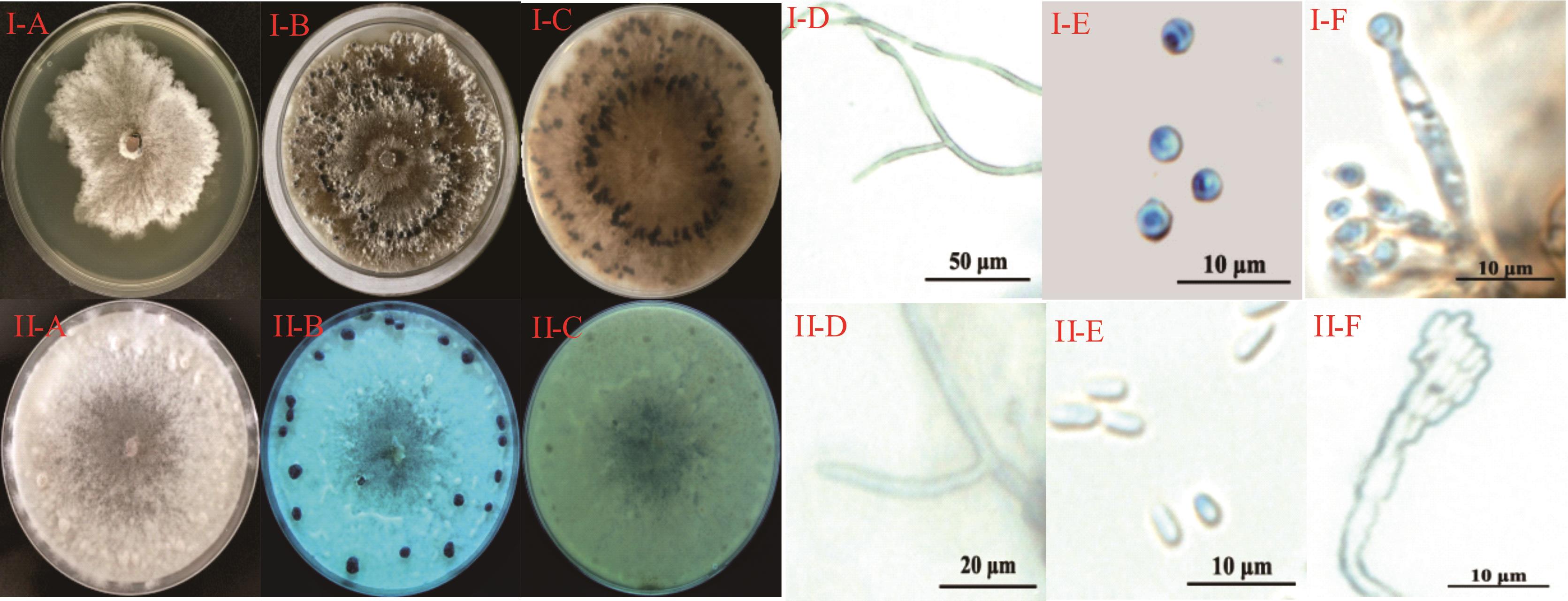
图2 党参菌核病病原菌的形态学特征I: 雪腐核盘菌的形态特征The colony morphology of the S. nivalis; Ⅰ-A, Ⅰ-B: 培养6和12 d 菌落形态Colony morphology after 6 and 12 d; Ⅰ-C: 培养12 d菌落背面Colony reverse after 12 d; I-D: 菌丝形态Mycelial morphology; Ⅰ-E: 小分生孢子Microconidia; Ⅰ-F: 小分生孢子着生在瓶状菌丝上Microconidia borne on hyphae. Ⅱ: 核盘菌的形态特征The colony morphology of the S. sclerotiorum; Ⅱ-A, Ⅱ-B: 培养6和15 d 菌落形态Colony morphology after 6 and 15 d; Ⅱ-C: 培养15 d菌落背面Colony reverse after 15 d; Ⅱ-D: 菌丝形态Mycelial morphology; Ⅱ-E: 小分生孢子Microconidia; Ⅱ-F: 小分生孢子成簇着生在菌丝上Microconidia are born in clusters on the hyphae.
Fig.2 The morphological characteristics of the pathogens causing C. pilosula sclerotinia rot
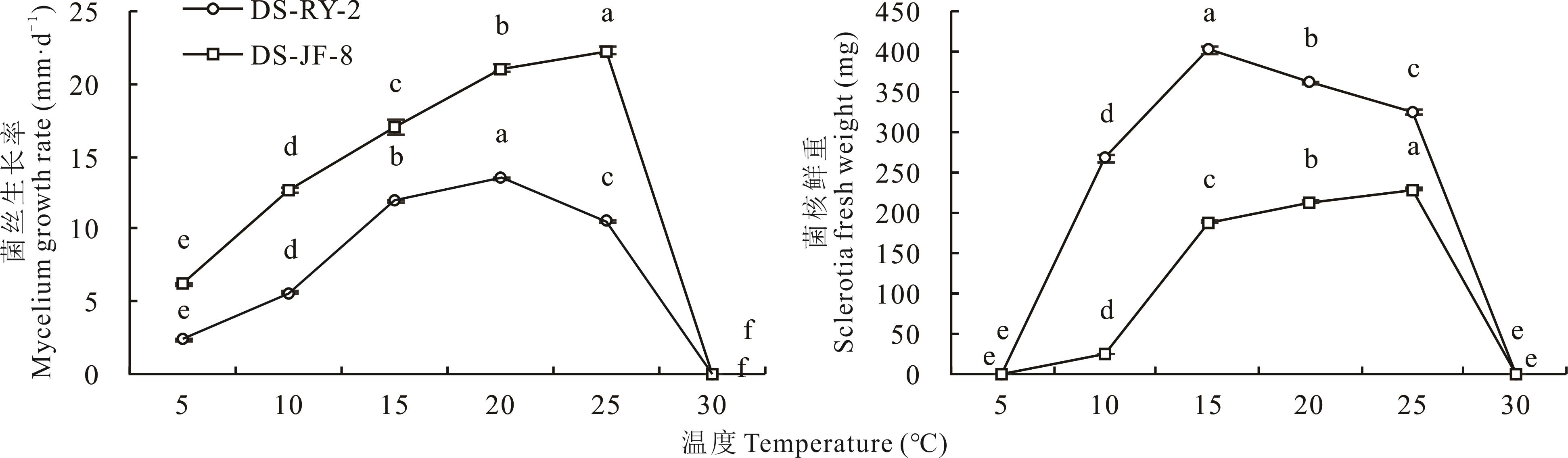
图5 不同温度对菌丝生长和菌核鲜重的影响不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.5 Effect of different temperature on mycelium growth and sclerotial fresh weight
病原菌 Pathogens | 回归方程 Regression equation | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R2) | EC50 (mg·L-1) | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval | 卡方值 Chi square | 自由度 df |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
雪腐核盘菌S. nivalis 核盘菌S. sclerotiorum | y=1.2003x+5.6973 y=1.1145x+5.4239 | 0.9948** 0.9741** | 0.2625 0.4165 | 0.152~0.454 0.254~0.634 | 1.17 1.52 | 9.49 9.49 |
表1 啶酰菌胺对雪腐核盘菌和核盘菌菌丝生长的抑制效果
Table 1 Inhibition of boscalid against mycelium growth of S. nivalis and S. sclerotiorum
病原菌 Pathogens | 回归方程 Regression equation | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient (R2) | EC50 (mg·L-1) | 95%置信区间 95% confidence interval | 卡方值 Chi square | 自由度 df |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
雪腐核盘菌S. nivalis 核盘菌S. sclerotiorum | y=1.2003x+5.6973 y=1.1145x+5.4239 | 0.9948** 0.9741** | 0.2625 0.4165 | 0.152~0.454 0.254~0.634 | 1.17 1.52 | 9.49 9.49 |
| 1 | National Pharmacopoeia Commission. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2015. |
| 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015. | |
| 2 | Jin P B, Hu J D, Mao G, et al. Effects of planting density on yield and secondary metabolite content of Codonopsis pilosula. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(3): 164-172. |
| 靳鹏博, 胡佳栋, 毛歌, 等. 栽培密度对党参产量和次生代谢物含量的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 164-172. | |
| 3 | Bai Y E, Zhang S S, Zhang R M, et al. Quality equivalence of Codonopsis radix-Codonopsis radix pieces-rice fried Codonopsis radix. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(12): 3228-3235. |
| 白云娥, 张沙沙, 张芮铭, 等. 党参药材-饮片-米炒党参的质量等同性探究. 中成药, 2020, 42(12): 3228-3235. | |
| 4 | Liu S B. Study on commercial grade specification and rational analysis correlation of Gansu Codonopsis pilosula. Lanzhou: Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 2016. |
| 刘书斌. 甘肃地产党参商品等级划分合理性分析及相关性的研究. 兰州: 甘肃中医药大学, 2016. | |
| 5 | Qi Y H, Li M Q, Cao S F, et al. Identification of Codonopsis pilosula crown rot disease and its sensitivity to fungicides. Journal of Agriculture, 2021, 11(2): 74-78. |
| 漆永红, 李敏权, 曹素芳, 等. 党参茎基腐病镰孢菌鉴定及其对杀菌剂的敏感性研究. 农学学报, 2021, 11(2): 74-78. | |
| 6 | Qi Y H, Li M Q, Cao S F, et al. Identification of a new Codonopsis pilosula root rot disease caused by Fusarium spp. Gansu Science and Technology, 2021, 37(1): 43-46. |
| 漆永红, 李敏权, 曹素芳, 等. 一种新的党参根腐病害镰孢菌鉴定. 甘肃科技, 2021, 37(1): 43-46. | |
| 7 | Yang K, Shi J, Yuan Y T, et al. Pathogen identification and cell physiological changes of Trifolium repens leaves infected with powdery mildew. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 92-104. |
| 杨凯, 史娟, 袁玉涛, 等. 白三叶草叶片感染白粉病的细胞生理变化及其病原鉴定. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 92-104. | |
| 8 | Huang Y P. Studies on the pathogens causing Angelica sinensis root rot. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2011. |
| 黄亚萍. 当归根腐病病原物研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2011. | |
| 9 | Staats M, Van Baarlen P, Van kan J A L. Molecular phylogeny of the plant pathogenic genus Botrytis and the evolution of host specificity. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2005, 22(2): 333-346. |
| 10 | Wang C H, Shang W J, Wang Q, et al. White rot of Panax quinquefolius caused by Sclerotinia nivalis. Plant Pathology, 2021, 70(9): 2034-2045. |
| 11 | Huang G Y. Pesticide trial technology and evaluation method. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. |
| 黄国洋. 农药试验技术与评价方法. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. | |
| 12 | Zhao C S, Li D W, Yang D, et al. Pathogenicity and biological characteristics of several pathogenic fungi isolated on Codonopsis pilosulain root rot disease-Codonopsis pilosulain root rot disease continue to report Ⅰ. Journal of Hubei Agricutural Science, 1989(6): 23-25. |
| 赵纯森, 李德望, 扬斗, 等. 党参根腐病病株上分离的几种病原真菌的致病性及其生物学特性-党参根腐病研究续报Ⅰ. 湖北农业科学, 1989(6): 23-25. | |
| 13 | Sun X R, Zhong C P, Zhang X M, et al. Identification and control of the root rot pathogen of Codonopsis pilosula in Dingxi of Gansu Province. Plant Protection, 2020, 46(5): 290-297. |
| 孙新荣, 仲彩萍, 张西梅, 等. 甘肃定西地区党参根腐病病原鉴定与防治研究. 植物保护, 2020, 46(5): 290-297. | |
| 14 | Chenault K D, Maas A L, Damicone J P, et al. Discovery and characterization of a molecular marker for Sclerotinia minor (Jagger) resistance in peanut. Euphytica, 2009, 166(3): 357-365. |
| 15 | Saito I. Sclerotinia nivalis, sp. nov., the pathogen of snow mold of herbaceous dicots in northern Japan. Mycoscience, 1997, 38(2): 227-236. |
| 16 | Lee C K, Lee S H, Choi Y J, et al. Sclerotinia rot of Aralia elata caused by Sclerotinia nivalis in Korea. Plant Pathology, 2010, 26(4): 426. |
| 17 | Zhou R J, Xu H J, Fu J F, et al. First report of sclerotinia rot of Chinese atractylodes caused by Sclerotinia nivalis in China. Plant Disease, 2012, 96(12): 1823. |
| 18 | Fan X, Zhang J, Yang L, et al. First report of Sclerotinia nivalis causing white mold disease on Sedum sarmentosum in China. Journal of Phytopathology, 2012, 160(10): 595-598. |
| 19 | Xu H J, Zhou R J, Fu J F, et al. Characterization of Sclerotinia nivalis causing sclerotinia rot of Pulsatilla koreana in China. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2015, 143: 1-9. |
| 20 | Guan Y M, Ma Y Y, Zhang L L, et al. Occurrence of postharvest snow rot caused by Sclerotinia nivalis on Asian ginseng in China. Plant Disease, 2022, 106(1): 322. |
| 21 | Liu C Y, Wang Y, Hao Y J, et al. Studies on the identification and the biological characteristic of the pathogen of bean sclerotinia rot in greenhouse. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2007, 23(12): 316-319. |
| 刘春艳, 王勇, 郝永娟, 等. 保护地菜豆菌核病病原鉴定及其生物学特性. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(12): 316-319. | |
| 22 | Liu T T, Gu Y L, Yang T S, et al. Identification and characterization of the pathogen of sclerotinia rot of Aeschynanthus pulche. Journal of Plant Protection, 2016, 43(4): 576-579. |
| 刘婷婷, 谷医林, 杨铁顺, 等. 口红吊兰菌核病病原鉴定及其生物学特性分析. 植物保护学报, 2016, 43(4): 576-579. | |
| 23 | Chen Y Q, Li M, Mou D K, et al. Studies on the identification and the major biological characteristic of the pathogen of sclerotinia rot on Salvia splendens. Journal of Anhui Agricutural Science, 2009, 37(13): 6067-6071. |
| 陈永强, 李梅, 牟登科, 等. 一串红菌核病病原鉴定及其主要生物学特性研究. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(13): 6067-6071. | |
| 24 | Huang H C, Kokko E G, Erickson R S. Infection of alfalfa pollen by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytoparasitica, 1997, 25(1): 17-24. |
| 25 | Young C S, Werner C P. Infection routes for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in apetalous and fully petalled winter oilseed rape. Plant Pathology, 2012, 61(4): 730-738. |
| 26 | Liu Y L. Effects of continuous cropping years on the growth of Codonopsis pilosula, soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021. |
| 刘垠霖. 连作年限对党参生长、土壤理化性状及酶活性的影响研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2021. | |
| 27 | Shi Z Q, Zhou M G, Ye Z Y. Study on resistance mechanism of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum to dimethachlon. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2000, 2(2): 47-51. |
| 石志琦, 周明国, 叶钟音. 核盘菌对菌核净的抗药性机制初探. 农药学学报, 2000, 2(2): 47-51. | |
| 28 | Wang K B, Pu T, Luo Y, et al. The synthesis and antifungal activity of nicotinamide derivatives. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2018, 33(2): 218-223. |
| 王凯博, 普特, 罗艳, 等. 烟酰胺类化合物的合成及其抑菌活性. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学), 2018, 33(2): 218-223. | |
| 29 | Zhang H Y, Li H Y, Meng Q L, et al. Effect of biological activity of boscalid on Sclerotinia sclerotiorum of sunflower. Journal of Agriculture, 2021, 11(1): 71-74, 90. |
| 张海洋, 李海燕, 孟庆林, 等. 啶酰菌胺对向日葵核盘菌生物活性的影响. 农学学报, 2021, 11(1): 71-74, 90. |
| [1] | 李晨芹, 李军乔, 王鑫慈, 牛永昆, 曲俊儒. 蕨麻根腐病病原菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 113-123. |
| [2] | 杨凯, 史娟, 袁玉涛, 王立婷. 白三叶草叶片感染白粉病的细胞生理变化及其病原鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 92-104. |
| [3] | 王琼, 段廷玉, 南志标. 箭筈豌豆炭疽病病原菌分离鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 127-136. |
| [4] | 王春明, 元维伟, 张小杰, 周天旺, 郭成, 金社林. 二月兰叶斑病病原甘蓝链格孢的分离鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 88-97. |
| [5] | 孙海荣, 车昭碧, 陈乙实, 鲁为华, 王树林, 李娜娜, 辛怀璐. 荒漠植物囊果草生物学特性及其种群分布格局的生态适应意义[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 198-207. |
| [6] | 李建宏, 李雪萍, 李昌宁, 韩冰, 徐万里, 姚拓. 一株植物根际促生菌Gnyt1的特性研究及分类地位的确定[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5): 55-67. |
| [7] | 丁爱强, 徐先英, 张雯, 刘江, 富丽, 付贵全. 不同退化程度柽柳灌丛的土壤理化和生物学特性[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 1-11. |
| [8] | 靳鹏博, 胡佳栋, 毛歌, 张志伟, 马存德, 梁宗锁, 董娟娥. 栽培密度对党参产量和次生代谢物含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 164-172. |
| [9] | 杨成德, 卞静, 陈泰祥, 陈秀蓉, 王涵琦, 杨小利, 王艳. 当归炭疽病菌的生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 139-144. |
| [10] | 贺春贵, 何振富, 王斐. 光敏型高丹草复种穴播高效栽培模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 70-80. |
| [11] | 李健, 李美, 高兴祥, 房锋, 董连红. 菟丝子生防菌“鲁保一号”生物学特性及T-DNA插入突变体库的构建[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(1): 142-148. |
| [12] | 李健, 李美, 高兴祥, 房锋, 董连红. 稗草生防菌BC-1的分离及生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 164-171. |
| [13] | 贾辉, 陈秀蓉, 芦光新, 孔雅丽, 杨成德. 纤维素降解细菌的筛选,生物学特性及降解效果[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 60-66. |
| [14] | 李健, 李岩, 高兴祥, 房锋, 李美. 马唐生防菌厚垣孢镰刀菌ZC201301的生物学特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 234-239. |
| [15] | 章武, 胡美姣, 高兆银, 李敏, 刘国道, 南志标. 草坪草红丝病与粉斑病病原菌生物学特性研究与杀菌剂室内毒力测定[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(12): 140-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||