

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 164-184.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023105
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
罗颖( ), 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞(
), 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-04
修回日期:2023-05-24
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2023-12-12
通讯作者:
雷映霞
作者简介:E-mail: leiyingxia@hotmail.com基金资助:
Ying LUO( ), Cong LI, Pei WANG, Li-hua TIAN, Hui WANG, Qing-ping ZHOU, Ying-xia LEI(
), Cong LI, Pei WANG, Li-hua TIAN, Hui WANG, Qing-ping ZHOU, Ying-xia LEI( )
)
Received:2023-04-04
Revised:2023-05-24
Online:2024-02-20
Published:2023-12-12
Contact:
Ying-xia LEI
摘要:
为探讨在低氮胁迫下皮燕麦早期的形态、生理响应以及筛选出耐低氮皮燕麦品种,本研究以18种不同皮燕麦品种为材料,采用水培法,设置全氮(4 mmol·L-1,CK)和1/10 N(0.4 mmol·L-1,LN)两个氮浓度水平,在处理21 d后,对低氮胁迫下皮燕麦的7项形态指标和14项生理指标进行测定和分析;通过相关性分析、主成分降维分析提取影响因子,结合隶属函数分析和聚类分析进行综合评价。结果表明:1)低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的株高、地上部生物量、硝态氮含量、硝酸还原酶活性、谷氨酰胺合成酶活性、谷氨酸脱氢酶活性、可溶性糖含量与可溶性蛋白含量均呈下降趋势;谷氨酸合成酶活性、丙二醛含量、活性氧含量均呈上升趋势;根长、地下部生物量、根冠比变化趋势不尽相同;2)21项生理指标中有12对指标呈极显著相关性,根冠比(RSR)与地下部干重(RDW)呈极显著正相关关系,谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)与可溶性蛋白(SP)呈极显著负相关;3)低氮胁迫下皮燕麦的生物量、氮代谢因子、光合因子、抗氧化因子、渗透调节因子可作为评价耐低氮性的重要指标;4)18份皮燕麦可划分为3大类,青海甜燕麦和青海444这两份品种耐低氮能力较强,为耐低氮型品种,甜燕2号和青燕2号这两份皮燕麦品种的耐低氮能力较弱,为氮敏感型品种,其余材料耐低氮性居中。
罗颖, 李聪, 王沛, 田莉华, 汪辉, 周青平, 雷映霞. 低氮胁迫下不同皮燕麦品种早期的响应研究及耐低氮性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 164-184.
Ying LUO, Cong LI, Pei WANG, Li-hua TIAN, Hui WANG, Qing-ping ZHOU, Ying-xia LEI. Responses of different oat cultivars to low-nitrogen stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(2): 164-184.
序号 Number | 品种 Cultivar | 品种来源 Cultivar source | 序号 Number | 品种 Cultivar | 品种来源 Cultivar source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蒙燕1号 Mengyan No.1 | 内蒙古农牧业科学院Inner Mongolia Academy of Agricultural & Animal Husbandry Sciences | 10 | 太阳神Titan | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 2 | 青引1号 Qingyin No.1 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine | 11 | 青海444 Qinghai 444 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine |
| 3 | 枪手Shooter | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. | 12 | 美达Monida | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 4 | 燕王Forage plus | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. | 13 | 魅力Charisma | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 5 | 青燕2号 Qingyan No.2 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine | 14 | 领袖Souris | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 6 | 边锋Blade | 郑州华丰草业科技有限公司Zhengzhou Huafeng Grass Industry Technology Co., Ltd. | 15 | 青海甜燕麦 Qinghai sweet oat | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine |
| 7 | 骏马Cayuse | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. | 16 | 牧王Heymaker | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 8 | 莫妮卡Monica | 北京百斯特草业有限公司Beijing Best Grass Industry Co., Ltd. | 17 | 甜燕2号 Haywire | 北京佰青源畜牧业科技发展有限公司Beijing Baiqingyuan Animal Husbandry Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 9 | 甜燕70 Sweet oat 70 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine | 18 | 青燕1号 Qingyan No.1 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine |
表1 供试燕麦品种来源
Table 1 Cultivar source of oats
序号 Number | 品种 Cultivar | 品种来源 Cultivar source | 序号 Number | 品种 Cultivar | 品种来源 Cultivar source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蒙燕1号 Mengyan No.1 | 内蒙古农牧业科学院Inner Mongolia Academy of Agricultural & Animal Husbandry Sciences | 10 | 太阳神Titan | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 2 | 青引1号 Qingyin No.1 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine | 11 | 青海444 Qinghai 444 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine |
| 3 | 枪手Shooter | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. | 12 | 美达Monida | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 4 | 燕王Forage plus | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. | 13 | 魅力Charisma | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 5 | 青燕2号 Qingyan No.2 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine | 14 | 领袖Souris | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 6 | 边锋Blade | 郑州华丰草业科技有限公司Zhengzhou Huafeng Grass Industry Technology Co., Ltd. | 15 | 青海甜燕麦 Qinghai sweet oat | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine |
| 7 | 骏马Cayuse | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. | 16 | 牧王Heymaker | 北京正道生态科技有限公司Beijing Rytway Ecological Technology Co., Ltd. |
| 8 | 莫妮卡Monica | 北京百斯特草业有限公司Beijing Best Grass Industry Co., Ltd. | 17 | 甜燕2号 Haywire | 北京佰青源畜牧业科技发展有限公司Beijing Baiqingyuan Animal Husbandry Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd. |
| 9 | 甜燕70 Sweet oat 70 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine | 18 | 青燕1号 Qingyan No.1 | 青海省畜牧兽医科学院Qinghai Academy of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine |
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 地上部鲜重 Shoot fresh weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 地下部鲜重 Root fresh weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 地上部干重 Shoot dry weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends(%) | 地下部干重 Root dry weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CK | 67.57±4.37a | -2.58 | 27.77±10.73a | -28.23 | 0.10±0.04b | 20.00 | 6.89±2.04a | -30.62 | 0.72±0.23a | -18.06 | 0.60±0.16a | -20.00 | 0.06±0.02a | 0.00 |
| LN | 65.83±2.75a | 19.93±3.27b | 0.12±0.02a | 4.78±1.02b | 0.59±0.30a | 0.48±0.12b | 0.06±0.02a | ||||||||
| 2 | CK | 87.77±0.75a | -12.30 | 21.27±3.75a | -43.58 | 0.09±0.03a | -22.22 | 9.43±2.58a | -46.98 | 1.17±1.10a | -88.89 | 0.98±0.29a | -36.73 | 0.09±0.05a | -55.56 |
| LN | 76.97±17.45b | 12.00±3.36b | 0.07±0.01b | 5.00±2.74b | 0.13±0.02b | 0.62±0.37b | 0.04±0.02b | ||||||||
| 3 | CK | 67.67±3.71a | -21.19 | 22.90±9.47a | -17.34 | 0.22±0.11a | -36.36 | 3.71±0.75a | -24.26 | 0.49±0.02a | -28.57 | 0.28±0.06a | 0.00 | 0.06±0.01a | -33.33 |
| LN | 53.33±30.33b | 18.93±8.11b | 0.14±0.02a | 2.81±0.67b | 0.35±0.21b | 0.28±0.09a | 0.04±0.01b | ||||||||
| 4 | CK | 76.87±3.75a | -8.38 | 16.03±2.24a | -10.98 | 0.10±0.02a | -20.00 | 6.15±0.34a | -39.51 | 0.64±0.18a | -43.94 | 0.71±0.06a | -42.25 | 0.07±0.02a | -57.14 |
| LN | 70.43±3.35b | 14.27±3.51a | 0.08±0.06b | 3.72±1.18b | 0.33±0.12b | 0.41±0.14b | 0.03±0.01b | ||||||||
| 5 | CK | 86.50±9.55a | -2.66 | 31.40±9.64a | -54.78 | 0.09±0.03a | -33.33 | 11.51±2.04a | -51.22 | 1.02±0.45a | -67.65 | 1.03±0.21a | -44.66 | 0.09±0.03a | -66.67 |
| LN | 84.20±14.12a | 14.20±5.09b | 0.06±0.02b | 5.61±2.47b | 0.33±0.20b | 0.57±0.29b | 0.03±0.01b | ||||||||
| 6 | CK | 73.83±3.20a | -6.95 | 22.90±4.97b | 25.20 | 0.10±0.02b | 80.00 | 4.71±1.21a | -20.38 | 0.51±0.14b | 60.78 | 0.41±0.04a | -17.07 | 0.04±0.01b | 50.00 |
| LN | 68.70±3.46b | 28.67±15.47a | 0.18±0.06a | 3.75±0.88b | 0.82±0.23a | 0.34±0.11a | 0.06±0.02a | ||||||||
| 7 | CK | 73.00±2.42a | -8.95 | 22.70±4.61a | -3.83 | 0.14±0.05b | 57.14 | 7.73±0.19a | -69.73 | 0.99±0.13a | -38.38 | 0.54±0.14a | -66.67 | 0.07±0.01a | -42.86 |
| LN | 66.47±4.13b | 21.83±1.91a | 0.22±0.00a | 2.34±0.44b | 0.61±0.12b | 0.18±0.05b | 0.04±0.01b | ||||||||
| 8 | CK | 65.73±4.09a | -6.28 | 16.80±5.09b | 20.65 | 0.10±0.01b | 40.00 | 4.31±1.28a | -40.60 | 0.51±0.21a | -49.02 | 0.43±0.17a | -34.88 | 0.04±0.01a | 0.00 |
| LN | 61.60±2.82b | 20.27±3.66a | 0.14±0.04a | 2.56±0.20b | 0.26±0.08b | 0.28±0.06b | 0.04±0.01a | ||||||||
| 9 | CK | 74.40±10.67a | -9.85 | 20.57±8.06b | 40.35 | 0.08±0.02a | 0.00 | 4.47±1.75a | -26.17 | 0.39±0.24a | -20.51 | 0.33±0.14a | -3.03 | 0.03±0.02a | -33.33 |
| LN | 67.07±6.77b | 28.87±9.63a | 0.08±0.01a | 3.30±1.37b | 0.31±0.16a | 0.32±0.16a | 0.02±0.01b | ||||||||
| 10 | CK | 62.53±4.24a | -0.42 | 17.40±0.95a | -25.69 | 0.10±0.05b | 40.00 | 3.71±0.49a | -53.10 | 0.68±0.12a | -48.53 | 0.30±0.09a | -53.33 | 0.03±0.01a | -33.33 |
| LN | 62.27±2.99a | 12.93±5.37b | 0.14±0.04a | 1.74±0.58b | 0.35±0.13b | 0.14±0.05b | 0.02±0.01b | ||||||||
| 11 | CK | 84.9±5.04a | -10.92 | 15.93±3.77b | 43.94 | 0.04±0.01b | 150.00 | 8.10±1.22a | -18.52 | 0.44±0.14b | 111.36 | 1.02±0.15a | -27.45 | 0.04±0.01b | 100.00 |
| LN | 75.63±4.97b | 22.93±10.23a | 0.10±0.03a | 6.60±1.64a | 0.93±0.43a | 0.74±0.14b | 0.08±0.04a | ||||||||
| 12 | CK | 66.87±5.28a | -5.08 | 23.13±7.42a | -13.53 | 0.09±0.01a | 11.11 | 4.74±0.89a | -13.71 | 0.56±0.08a | -14.29 | 0.56±0.18a | -21.43 | 0.05±0.01a | -20.00 |
| LN | 63.47±1.97a | 20.00±1.82a | 0.10±0.03a | 4.09±0.67a | 0.48±0.04a | 0.44±0.07b | 0.04±0.01a | ||||||||
| 13 | CK | 70.90±4.89a | -5.12 | 32.27±21.84a | -12.40 | 0.10±0.07b | 50.00 | 5.69±0.97a | -8.61 | 0.93±0.77a | 18.28 | 0.71±0.14a | -25.35 | 0.06±0.03b | 33.33 |
| LN | 67.27±4.38a | 28.27±14.88a | 0.15±0.01a | 5.20±2.11a | 1.10±0.54a | 0.53±0.20b | 0.08±0.03a | ||||||||
| 14 | CK | 71.30±0.78a | -20.72 | 19.33±6.77a | -0.67 | 0.07±0.01b | 85.71 | 5.49±0.60a | -4.19 | 0.50±0.24b | 64.00 | 0.60±0.07a | -13.33 | 0.04±0.01b | 75.00 |
| LN | 56.53±39.09b | 19.20±4.99a | 0.13±0.02a | 5.26±0.59a | 0.82±0.26a | 0.52±0.10a | 0.07±0.02a | ||||||||
| 15 | CK | 83.40±0.80a | -5.31 | 21.17±4.99b | 42.32 | 0.06±0.00b | 83.33 | 7.20±0.68a | -12.22 | 0.51±0.08b | 33.33 | 0.73±0.10a | -19.18 | 0.04±0.01b | 75.00 |
| LN | 78.97±4.16a | 30.13±14.12a | 0.11±0.07a | 6.32±0.83a | 0.68±0.33a | 0.59±0.09b | 0.07±0.01a | ||||||||
| 16 | CK | 75.67±0.45a | -3.09 | 21.13±6.33a | -0.62 | 0.09±0.03b | 77.78 | 5.69±0.72a | -9.49 | 0.93±0.59a | 29.03 | 0.50±0.08a | -4.00 | 0.05±0.03b | 60.00 |
| LN | 73.33±8.90a | 21.00±14.25a | 0.16±0.02a | 5.15±2.67a | 1.20±1.07a | 0.48±0.28a | 0.08±0.05a | ||||||||
| 17 | CK | 80.40±5.84a | -27.36 | 29.27±13.01a | -55.93 | 0.11±0.07a | 0.00 | 5.76±0.95a | -45.49 | 0.98±0.72a | -67.35 | 0.59±0.11a | -50.85 | 0.06±0.03a | -50.00 |
| LN | 58.40±8.25b | 12.90±3.22b | 0.11±0.04a | 3.14±1.34b | 0.32±0.30b | 0.29±0.12b | 0.03±0.02b | ||||||||
| 18 | CK | 80.80±3.47a | -12.25 | 25.97±16.14a | -21.45 | 0.09±0.05a | -11.11 | 5.18±0.54a | -6.56 | 0.52±0.21a | -1.92 | 0.57±0.11a | -1.75 | 0.05±0.02a | -20.00 |
| LN | 70.90±1.40b | 20.40±0.75b | 0.08±0.03a | 4.84±0.74a | 0.51±0.16a | 0.56±0.09a | 0.04±0.01b |
表2 低氮胁迫下各皮燕麦品种的生长变化
Table 2 Effects of low nitrogen stress on the growth of different oat cultivars
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 地上部鲜重 Shoot fresh weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 地下部鲜重 Root fresh weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 地上部干重 Shoot dry weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends(%) | 地下部干重 Root dry weight (g) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CK | 67.57±4.37a | -2.58 | 27.77±10.73a | -28.23 | 0.10±0.04b | 20.00 | 6.89±2.04a | -30.62 | 0.72±0.23a | -18.06 | 0.60±0.16a | -20.00 | 0.06±0.02a | 0.00 |
| LN | 65.83±2.75a | 19.93±3.27b | 0.12±0.02a | 4.78±1.02b | 0.59±0.30a | 0.48±0.12b | 0.06±0.02a | ||||||||
| 2 | CK | 87.77±0.75a | -12.30 | 21.27±3.75a | -43.58 | 0.09±0.03a | -22.22 | 9.43±2.58a | -46.98 | 1.17±1.10a | -88.89 | 0.98±0.29a | -36.73 | 0.09±0.05a | -55.56 |
| LN | 76.97±17.45b | 12.00±3.36b | 0.07±0.01b | 5.00±2.74b | 0.13±0.02b | 0.62±0.37b | 0.04±0.02b | ||||||||
| 3 | CK | 67.67±3.71a | -21.19 | 22.90±9.47a | -17.34 | 0.22±0.11a | -36.36 | 3.71±0.75a | -24.26 | 0.49±0.02a | -28.57 | 0.28±0.06a | 0.00 | 0.06±0.01a | -33.33 |
| LN | 53.33±30.33b | 18.93±8.11b | 0.14±0.02a | 2.81±0.67b | 0.35±0.21b | 0.28±0.09a | 0.04±0.01b | ||||||||
| 4 | CK | 76.87±3.75a | -8.38 | 16.03±2.24a | -10.98 | 0.10±0.02a | -20.00 | 6.15±0.34a | -39.51 | 0.64±0.18a | -43.94 | 0.71±0.06a | -42.25 | 0.07±0.02a | -57.14 |
| LN | 70.43±3.35b | 14.27±3.51a | 0.08±0.06b | 3.72±1.18b | 0.33±0.12b | 0.41±0.14b | 0.03±0.01b | ||||||||
| 5 | CK | 86.50±9.55a | -2.66 | 31.40±9.64a | -54.78 | 0.09±0.03a | -33.33 | 11.51±2.04a | -51.22 | 1.02±0.45a | -67.65 | 1.03±0.21a | -44.66 | 0.09±0.03a | -66.67 |
| LN | 84.20±14.12a | 14.20±5.09b | 0.06±0.02b | 5.61±2.47b | 0.33±0.20b | 0.57±0.29b | 0.03±0.01b | ||||||||
| 6 | CK | 73.83±3.20a | -6.95 | 22.90±4.97b | 25.20 | 0.10±0.02b | 80.00 | 4.71±1.21a | -20.38 | 0.51±0.14b | 60.78 | 0.41±0.04a | -17.07 | 0.04±0.01b | 50.00 |
| LN | 68.70±3.46b | 28.67±15.47a | 0.18±0.06a | 3.75±0.88b | 0.82±0.23a | 0.34±0.11a | 0.06±0.02a | ||||||||
| 7 | CK | 73.00±2.42a | -8.95 | 22.70±4.61a | -3.83 | 0.14±0.05b | 57.14 | 7.73±0.19a | -69.73 | 0.99±0.13a | -38.38 | 0.54±0.14a | -66.67 | 0.07±0.01a | -42.86 |
| LN | 66.47±4.13b | 21.83±1.91a | 0.22±0.00a | 2.34±0.44b | 0.61±0.12b | 0.18±0.05b | 0.04±0.01b | ||||||||
| 8 | CK | 65.73±4.09a | -6.28 | 16.80±5.09b | 20.65 | 0.10±0.01b | 40.00 | 4.31±1.28a | -40.60 | 0.51±0.21a | -49.02 | 0.43±0.17a | -34.88 | 0.04±0.01a | 0.00 |
| LN | 61.60±2.82b | 20.27±3.66a | 0.14±0.04a | 2.56±0.20b | 0.26±0.08b | 0.28±0.06b | 0.04±0.01a | ||||||||
| 9 | CK | 74.40±10.67a | -9.85 | 20.57±8.06b | 40.35 | 0.08±0.02a | 0.00 | 4.47±1.75a | -26.17 | 0.39±0.24a | -20.51 | 0.33±0.14a | -3.03 | 0.03±0.02a | -33.33 |
| LN | 67.07±6.77b | 28.87±9.63a | 0.08±0.01a | 3.30±1.37b | 0.31±0.16a | 0.32±0.16a | 0.02±0.01b | ||||||||
| 10 | CK | 62.53±4.24a | -0.42 | 17.40±0.95a | -25.69 | 0.10±0.05b | 40.00 | 3.71±0.49a | -53.10 | 0.68±0.12a | -48.53 | 0.30±0.09a | -53.33 | 0.03±0.01a | -33.33 |
| LN | 62.27±2.99a | 12.93±5.37b | 0.14±0.04a | 1.74±0.58b | 0.35±0.13b | 0.14±0.05b | 0.02±0.01b | ||||||||
| 11 | CK | 84.9±5.04a | -10.92 | 15.93±3.77b | 43.94 | 0.04±0.01b | 150.00 | 8.10±1.22a | -18.52 | 0.44±0.14b | 111.36 | 1.02±0.15a | -27.45 | 0.04±0.01b | 100.00 |
| LN | 75.63±4.97b | 22.93±10.23a | 0.10±0.03a | 6.60±1.64a | 0.93±0.43a | 0.74±0.14b | 0.08±0.04a | ||||||||
| 12 | CK | 66.87±5.28a | -5.08 | 23.13±7.42a | -13.53 | 0.09±0.01a | 11.11 | 4.74±0.89a | -13.71 | 0.56±0.08a | -14.29 | 0.56±0.18a | -21.43 | 0.05±0.01a | -20.00 |
| LN | 63.47±1.97a | 20.00±1.82a | 0.10±0.03a | 4.09±0.67a | 0.48±0.04a | 0.44±0.07b | 0.04±0.01a | ||||||||
| 13 | CK | 70.90±4.89a | -5.12 | 32.27±21.84a | -12.40 | 0.10±0.07b | 50.00 | 5.69±0.97a | -8.61 | 0.93±0.77a | 18.28 | 0.71±0.14a | -25.35 | 0.06±0.03b | 33.33 |
| LN | 67.27±4.38a | 28.27±14.88a | 0.15±0.01a | 5.20±2.11a | 1.10±0.54a | 0.53±0.20b | 0.08±0.03a | ||||||||
| 14 | CK | 71.30±0.78a | -20.72 | 19.33±6.77a | -0.67 | 0.07±0.01b | 85.71 | 5.49±0.60a | -4.19 | 0.50±0.24b | 64.00 | 0.60±0.07a | -13.33 | 0.04±0.01b | 75.00 |
| LN | 56.53±39.09b | 19.20±4.99a | 0.13±0.02a | 5.26±0.59a | 0.82±0.26a | 0.52±0.10a | 0.07±0.02a | ||||||||
| 15 | CK | 83.40±0.80a | -5.31 | 21.17±4.99b | 42.32 | 0.06±0.00b | 83.33 | 7.20±0.68a | -12.22 | 0.51±0.08b | 33.33 | 0.73±0.10a | -19.18 | 0.04±0.01b | 75.00 |
| LN | 78.97±4.16a | 30.13±14.12a | 0.11±0.07a | 6.32±0.83a | 0.68±0.33a | 0.59±0.09b | 0.07±0.01a | ||||||||
| 16 | CK | 75.67±0.45a | -3.09 | 21.13±6.33a | -0.62 | 0.09±0.03b | 77.78 | 5.69±0.72a | -9.49 | 0.93±0.59a | 29.03 | 0.50±0.08a | -4.00 | 0.05±0.03b | 60.00 |
| LN | 73.33±8.90a | 21.00±14.25a | 0.16±0.02a | 5.15±2.67a | 1.20±1.07a | 0.48±0.28a | 0.08±0.05a | ||||||||
| 17 | CK | 80.40±5.84a | -27.36 | 29.27±13.01a | -55.93 | 0.11±0.07a | 0.00 | 5.76±0.95a | -45.49 | 0.98±0.72a | -67.35 | 0.59±0.11a | -50.85 | 0.06±0.03a | -50.00 |
| LN | 58.40±8.25b | 12.90±3.22b | 0.11±0.04a | 3.14±1.34b | 0.32±0.30b | 0.29±0.12b | 0.03±0.02b | ||||||||
| 18 | CK | 80.80±3.47a | -12.25 | 25.97±16.14a | -21.45 | 0.09±0.05a | -11.11 | 5.18±0.54a | -6.56 | 0.52±0.21a | -1.92 | 0.57±0.11a | -1.75 | 0.05±0.02a | -20.00 |
| LN | 70.90±1.40b | 20.40±0.75b | 0.08±0.03a | 4.84±0.74a | 0.51±0.16a | 0.56±0.09a | 0.04±0.01b |
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Photosynthesis rate (μmol·m-2·s-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 蒸腾速率 Transpiration rate (mmol·m-2·s-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 胞间CO2浓度 Internal CO2 concentration (μmol·m-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 气孔导度 Stomatal conductance (mol·m-2·s-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CK | 8.64±2.84a | -59.14 | 1.93±0.40a | -34.20 | 340.60±4.34a | -8.70 | 0.17±0.03a | -35.29 |
| LN | 3.53±0.19b | 1.27±0.10b | 310.97±13.65a | 0.11±0.01b | |||||
| 2 | CK | 10.00±0.14a | -45.40 | 2.97±0.04a | -37.37 | 338.57±5.98a | -10.36 | 0.18±0.00a | -11.11 |
| LN | 5.46±1.32b | 1.86±0.49b | 303.50±2.02b | 0.16±0.04a | |||||
| 3 | CK | 9.52±0.22a | -37.18 | 3.34±0.05a | -62.57 | 300.63±2.04a | -0.50 | 0.17±0.00a | -41.18 |
| LN | 5.98±2.81b | 1.25±0.53b | 299.13±6.32a | 0.10±0.04b | |||||
| 4 | CK | 12.39±1.95a | -27.85 | 4.38±0.18a | -30.82 | 328.99±1.38a | -4.72 | 0.26±0.03a | -7.69 |
| LN | 8.94±0.39b | 3.03±0.32b | 313.45±4.10a | 0.24±0.01a | |||||
| 5 | CK | 9.39±1.14a | -44.20 | 3.34±1.06a | -49.10 | 336.42±32.39a | -0.38 | 0.32±0.11a | -53.13 |
| LN | 5.24±0.04b | 1.70±0.10b | 335.13±2.83a | 0.15±0.01b | |||||
| 6 | CK | 7.05±1.78a | -23.97 | 2.92±0.26a | -62.67 | 349.66±7.19a | -15.91 | 0.26±0.03a | -65.38 |
| LN | 5.36±0.90b | 1.09±0.06b | 294.04±23.24b | 0.09±0.01b | |||||
| 7 | CK | 10.69±3.21a | -56.59 | 3.98±1.26a | -32.91 | 370.27±12.45a | -14.01 | 0.39±0.15a | -41.03 |
| LN | 4.64±0.25b | 2.67±0.62b | 318.39±4.38b | 0.23±0.06b | |||||
| 8 | CK | 7.72±2.15a | -52.85 | 3.71±0.67a | -71.43 | 355.40±4.38a | -10.01 | 0.34±0.08a | -76.47 |
| LN | 3.64±0.73b | 1.06±0.17b | 319.81±26.79b | 0.08±0.01b | |||||
| 9 | CK | 4.77±0.67a | -13.00 | 2.06±0.12a | -37.86 | 354.25±12.60a | -9.32 | 0.18±0.01a | -38.89 |
| LN | 4.15±1.31a | 1.28±0.03b | 321.24±9.35a | 0.11±0.00b | |||||
| 10 | CK | 5.76±0.98a | -12.15 | 2.31±2.04a | -37.23 | 324.94±26.20a | -0.57 | 0.21±0.21a | -42.86 |
| LN | 5.06±2.03a | 1.45±0.09b | 323.09±41.44a | 0.12±0.01b | |||||
| 11 | CK | 4.24±1.52a | -12.97 | 1.37±0.24a | -29.93 | 332.04±12.13a | -5.75 | 0.11±0.02a | -27.27 |
| LN | 3.69±0.47a | 0.96±0.08b | 312.95±7.67a | 0.08±0.01b | |||||
| 12 | CK | 8.61±0.24a | -31.71 | 1.75±0.12a | -17.14 | 309.24±2.86a | -3.57 | 0.15±0.01a | -26.67 |
| LN | 5.88±0.95b | 1.45±0.27a | 298.21±8.52a | 0.11±0.02b | |||||
| 13 | CK | 9.94±0.03a | -18.61 | 2.72±0.11a | -31.25 | 325.69±3.66a | -6.23 | 0.24±0.01a | -37.50 |
| LN | 8.09±2.13a | 1.87±0.44b | 305.40±1.54a | 0.15±0.04b | |||||
| 14 | CK | 7.09±2.93a | -44.57 | 1.51±0.75a | -41.06 | 297.28±7.27a | -0.33 | 0.13±0.07a | -46.15 |
| LN | 3.93±1.20b | 0.89±0.31b | 296.31±14.26a | 0.07±0.02b | |||||
| 15 | CK | 8.78±0.13a | -10.82 | 4.76±0.05a | -57.77 | 339.46±1.09a | -6.70 | 0.28±0.00a | -35.71 |
| LN | 7.83±1.09a | 2.01±0.49b | 316.72±26.10a | 0.18±0.05b | |||||
| 16 | CK | 9.47±0.24a | -64.52 | 2.68±0.08a | -77.61 | 298.54±2.36a | -10.75 | 0.16±0.00a | -75.00 |
| LN | 3.36±0.73b | 0.60±0.13b | 266.45±4.66b | 0.04±0.01b | |||||
| 17 | CK | 6.78±0.52a | -62.24 | 1.54±0.25a | -62.34 | 303.70±14.75a | -2.41 | 0.12±0.01a | -66.67 |
| LN | 2.56±0.41b | 0.58±0.05b | 296.39±9.02a | 0.04±0.00b | |||||
| 18 | CK | 6.03±0.78a | -3.32 | 1.30±0.06a | -36.92 | 293.10±6.50a | -18.27 | 0.10±0.01a | -40.00 |
| LN | 5.83±0.51a | 0.82±0.06b | 239.54±3.85b | 0.06±0.00b |
表3 低氮胁迫下各皮燕麦品种光合作用的变化
Table 3 Effects of low nitrogen stress on photosynthesis of different oat cultivars
品种 Cultivar | 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率 Photosynthesis rate (μmol·m-2·s-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 蒸腾速率 Transpiration rate (mmol·m-2·s-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 胞间CO2浓度 Internal CO2 concentration (μmol·m-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) | 气孔导度 Stomatal conductance (mol·m-2·s-1) | 变化趋势 Changing trends (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CK | 8.64±2.84a | -59.14 | 1.93±0.40a | -34.20 | 340.60±4.34a | -8.70 | 0.17±0.03a | -35.29 |
| LN | 3.53±0.19b | 1.27±0.10b | 310.97±13.65a | 0.11±0.01b | |||||
| 2 | CK | 10.00±0.14a | -45.40 | 2.97±0.04a | -37.37 | 338.57±5.98a | -10.36 | 0.18±0.00a | -11.11 |
| LN | 5.46±1.32b | 1.86±0.49b | 303.50±2.02b | 0.16±0.04a | |||||
| 3 | CK | 9.52±0.22a | -37.18 | 3.34±0.05a | -62.57 | 300.63±2.04a | -0.50 | 0.17±0.00a | -41.18 |
| LN | 5.98±2.81b | 1.25±0.53b | 299.13±6.32a | 0.10±0.04b | |||||
| 4 | CK | 12.39±1.95a | -27.85 | 4.38±0.18a | -30.82 | 328.99±1.38a | -4.72 | 0.26±0.03a | -7.69 |
| LN | 8.94±0.39b | 3.03±0.32b | 313.45±4.10a | 0.24±0.01a | |||||
| 5 | CK | 9.39±1.14a | -44.20 | 3.34±1.06a | -49.10 | 336.42±32.39a | -0.38 | 0.32±0.11a | -53.13 |
| LN | 5.24±0.04b | 1.70±0.10b | 335.13±2.83a | 0.15±0.01b | |||||
| 6 | CK | 7.05±1.78a | -23.97 | 2.92±0.26a | -62.67 | 349.66±7.19a | -15.91 | 0.26±0.03a | -65.38 |
| LN | 5.36±0.90b | 1.09±0.06b | 294.04±23.24b | 0.09±0.01b | |||||
| 7 | CK | 10.69±3.21a | -56.59 | 3.98±1.26a | -32.91 | 370.27±12.45a | -14.01 | 0.39±0.15a | -41.03 |
| LN | 4.64±0.25b | 2.67±0.62b | 318.39±4.38b | 0.23±0.06b | |||||
| 8 | CK | 7.72±2.15a | -52.85 | 3.71±0.67a | -71.43 | 355.40±4.38a | -10.01 | 0.34±0.08a | -76.47 |
| LN | 3.64±0.73b | 1.06±0.17b | 319.81±26.79b | 0.08±0.01b | |||||
| 9 | CK | 4.77±0.67a | -13.00 | 2.06±0.12a | -37.86 | 354.25±12.60a | -9.32 | 0.18±0.01a | -38.89 |
| LN | 4.15±1.31a | 1.28±0.03b | 321.24±9.35a | 0.11±0.00b | |||||
| 10 | CK | 5.76±0.98a | -12.15 | 2.31±2.04a | -37.23 | 324.94±26.20a | -0.57 | 0.21±0.21a | -42.86 |
| LN | 5.06±2.03a | 1.45±0.09b | 323.09±41.44a | 0.12±0.01b | |||||
| 11 | CK | 4.24±1.52a | -12.97 | 1.37±0.24a | -29.93 | 332.04±12.13a | -5.75 | 0.11±0.02a | -27.27 |
| LN | 3.69±0.47a | 0.96±0.08b | 312.95±7.67a | 0.08±0.01b | |||||
| 12 | CK | 8.61±0.24a | -31.71 | 1.75±0.12a | -17.14 | 309.24±2.86a | -3.57 | 0.15±0.01a | -26.67 |
| LN | 5.88±0.95b | 1.45±0.27a | 298.21±8.52a | 0.11±0.02b | |||||
| 13 | CK | 9.94±0.03a | -18.61 | 2.72±0.11a | -31.25 | 325.69±3.66a | -6.23 | 0.24±0.01a | -37.50 |
| LN | 8.09±2.13a | 1.87±0.44b | 305.40±1.54a | 0.15±0.04b | |||||
| 14 | CK | 7.09±2.93a | -44.57 | 1.51±0.75a | -41.06 | 297.28±7.27a | -0.33 | 0.13±0.07a | -46.15 |
| LN | 3.93±1.20b | 0.89±0.31b | 296.31±14.26a | 0.07±0.02b | |||||
| 15 | CK | 8.78±0.13a | -10.82 | 4.76±0.05a | -57.77 | 339.46±1.09a | -6.70 | 0.28±0.00a | -35.71 |
| LN | 7.83±1.09a | 2.01±0.49b | 316.72±26.10a | 0.18±0.05b | |||||
| 16 | CK | 9.47±0.24a | -64.52 | 2.68±0.08a | -77.61 | 298.54±2.36a | -10.75 | 0.16±0.00a | -75.00 |
| LN | 3.36±0.73b | 0.60±0.13b | 266.45±4.66b | 0.04±0.01b | |||||
| 17 | CK | 6.78±0.52a | -62.24 | 1.54±0.25a | -62.34 | 303.70±14.75a | -2.41 | 0.12±0.01a | -66.67 |
| LN | 2.56±0.41b | 0.58±0.05b | 296.39±9.02a | 0.04±0.00b | |||||
| 18 | CK | 6.03±0.78a | -3.32 | 1.30±0.06a | -36.92 | 293.10±6.50a | -18.27 | 0.10±0.01a | -40.00 |
| LN | 5.83±0.51a | 0.82±0.06b | 239.54±3.85b | 0.06±0.00b |
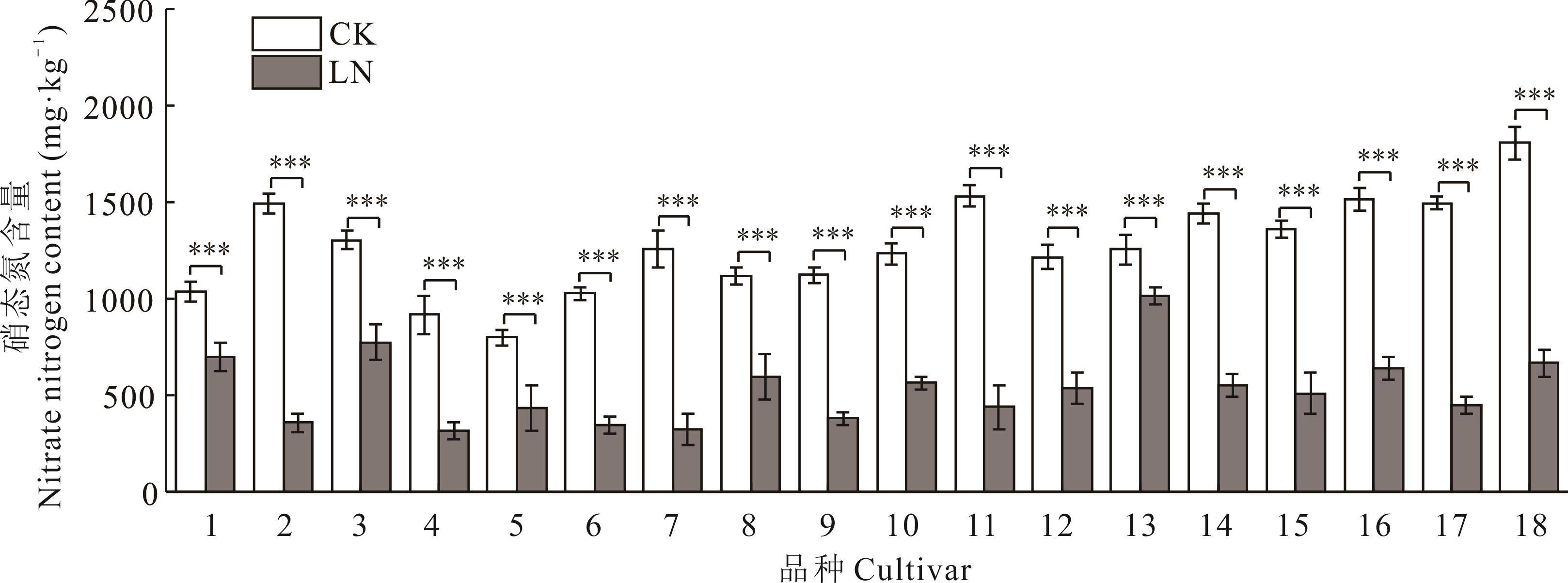
图1 不同皮燕麦品种的硝态氮含量在低氮胁迫下的变化1:蒙燕1号Mengyan No.1;2:青引1号Qingyin No.1;3:枪手Shooter;4:燕王Forage plus;5:青燕2号Qingyan No.2;6:边锋Blade;7:骏马Cayuse;8:莫妮卡Monica;9:甜燕70 Sweet oat 70;10:太阳神Titan;11:青海444 Qinghai 444;12:美达Monida;13:魅力Charisma;14:领袖Souris;15:青海甜燕麦Qinghai sweet oat;16:牧王Heymaker;17:甜燕2号Haywire;18:青燕1号Qingyan No.1. *表示同一品种的对照组与处理组在P<0.05水平显著相关,**表示同一品种的对照组与处理组在P<0.01水平极显著相关, ***表示同一品种的对照组与处理组在P<0.001水平极显著相关,下同。* means significant correlation at the level of P<0.05, ** means extremely significant correlation at the level of P<0.01, *** means extremely significant correlation at the level of P<0.001, the same below.
Fig.1 Changes of nitrate nitrogen content in different oat cultivars under low-nitrogen stress
品种 Cultivar | 株高 PH | 根长 RL | 根冠比 RSR | 地上部鲜重 SFW | 地下部鲜重 RFW | 地上部干重 SDW | 地下部干重 RDW | 净光合速率 Pn | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci | 气孔导度 Gs | 硝态氮 NO3--N | 硝酸还原酶 NR | 谷氨酰胺合成酶 GS | 谷氨酸合成酶 GOGAT | 谷氨酸脱氢酶 GDH | 超氧阴离子 O2·- | 过氧化氢 H2O2 | 丙二醛 MDA | 可溶性蛋白 SP | 可溶性糖 SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.974 | 0.718 | 1.200 | 0.694 | 0.819 | 0.800 | 1.000 | 0.409 | 0.658 | 0.913 | 0.647 | 0.672 | 0.403 | 0.555 | 1.806 | 0.649 | 1.626 | 1.048 | 1.402 | 0.617 | 0.920 |
| 2 | 0.877 | 0.564 | 0.778 | 0.530 | 0.111 | 0.633 | 0.444 | 0.546 | 0.626 | 0.896 | 0.889 | 0.239 | 0.834 | 0.803 | 3.038 | 0.805 | 1.883 | 1.049 | 1.047 | 0.934 | 0.810 |
| 3 | 0.788 | 0.827 | 0.636 | 0.757 | 0.714 | 1.000 | 0.667 | 0.628 | 0.374 | 0.995 | 0.588 | 0.593 | 0.559 | 0.449 | 1.340 | 0.684 | 1.054 | 1.098 | 1.387 | 0.763 | 0.938 |
| 4 | 0.916 | 0.890 | 0.800 | 0.605 | 0.516 | 0.577 | 0.429 | 0.722 | 0.692 | 0.953 | 0.923 | 0.344 | 0.552 | 1.056 | 1.486 | 0.947 | 1.346 | 1.160 | 1.257 | 0.766 | 0.599 |
| 5 | 0.973 | 0.452 | 0.667 | 0.487 | 0.324 | 0.553 | 0.333 | 0.558 | 0.509 | 0.996 | 0.469 | 0.545 | 0.835 | 0.490 | 2.097 | 0.624 | 1.515 | 1.707 | 2.826 | 0.784 | 0.483 |
| 6 | 0.931 | 1.252 | 1.800 | 0.796 | 1.608 | 0.829 | 1.500 | 0.760 | 0.373 | 0.841 | 0.346 | 0.337 | 0.674 | 0.385 | 1.757 | 0.796 | 1.258 | 1.398 | 1.157 | 0.842 | 0.409 |
| 7 | 0.911 | 0.962 | 1.571 | 0.303 | 0.616 | 0.333 | 0.571 | 0.434 | 0.671 | 0.860 | 0.590 | 0.258 | 0.558 | 0.073 | 2.429 | 0.232 | 1.119 | 1.360 | 1.197 | 0.983 | 0.457 |
| 8 | 0.937 | 1.207 | 1.400 | 0.594 | 0.510 | 0.651 | 1.000 | 0.472 | 0.286 | 0.900 | 0.235 | 0.532 | 0.631 | 0.592 | 1.643 | 0.454 | 1.419 | 1.735 | 1.682 | 0.729 | 0.759 |
| 9 | 0.901 | 1.404 | 1.000 | 0.738 | 0.795 | 0.970 | 0.667 | 0.870 | 0.621 | 0.907 | 0.611 | 0.338 | 0.786 | 0.674 | 2.223 | 0.471 | 2.210 | 1.454 | 1.741 | 0.822 | 0.860 |
| 10 | 0.996 | 0.743 | 1.400 | 0.469 | 0.515 | 0.467 | 0.667 | 0.878 | 0.628 | 0.994 | 0.571 | 0.458 | 0.365 | 0.512 | 1.242 | 0.855 | 1.042 | 1.401 | 1.578 | 0.692 | 0.627 |
| 11 | 0.891 | 1.439 | 2.500 | 0.815 | 2.114 | 0.725 | 2.000 | 0.870 | 0.701 | 0.943 | 0.727 | 0.286 | 0.688 | 0.965 | 1.656 | 0.533 | 1.361 | 1.174 | 1.017 | 0.430 | 0.690 |
| 12 | 0.949 | 0.865 | 1.111 | 0.863 | 0.857 | 0.786 | 0.800 | 0.683 | 0.829 | 0.964 | 0.733 | 0.441 | 0.487 | 0.915 | 1.738 | 0.944 | 1.421 | 2.000 | 1.029 | 0.402 | 0.670 |
| 13 | 0.949 | 0.876 | 1.500 | 0.914 | 1.183 | 0.746 | 1.333 | 0.814 | 0.688 | 0.938 | 0.625 | 0.809 | 0.637 | 0.810 | 1.251 | 0.508 | 1.369 | 1.115 | 2.541 | 0.553 | 0.774 |
| 14 | 0.793 | 0.993 | 1.857 | 0.958 | 1.640 | 0.867 | 1.750 | 0.554 | 0.589 | 0.997 | 0.538 | 0.382 | 0.470 | 0.756 | 2.262 | 0.526 | 1.138 | 1.126 | 1.196 | 0.406 | 0.666 |
| 15 | 0.947 | 1.423 | 1.833 | 0.878 | 1.333 | 0.808 | 1.750 | 0.892 | 0.422 | 0.933 | 0.643 | 0.374 | 0.477 | 0.698 | 1.402 | 0.280 | 1.899 | 2.401 | 1.146 | 0.584 | 0.930 |
| 16 | 0.969 | 0.994 | 1.778 | 0.905 | 1.290 | 0.960 | 1.600 | 0.355 | 0.224 | 0.893 | 0.250 | 0.423 | 0.740 | 0.820 | 2.337 | 0.848 | 1.049 | 1.157 | 1.041 | 0.482 | 0.768 |
| 17 | 0.726 | 0.441 | 1.000 | 0.545 | 0.327 | 0.492 | 0.500 | 0.378 | 0.377 | 0.976 | 0.333 | 0.298 | 0.717 | 0.911 | 1.252 | 0.694 | 1.230 | 1.233 | 2.076 | 0.292 | 0.654 |
| 18 | 0.877 | 0.786 | 0.889 | 0.934 | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.800 | 0.967 | 0.631 | 0.817 | 0.600 | 0.369 | 0.465 | 0.791 | 4.667 | 0.487 | 1.023 | 1.065 | 1.095 | 0.376 | 0.711 |
表4 18份皮燕麦材料各综合指标耐低氮系数
Table 4 The comprehensive index of 18 oat cultivars is resistant to low nitrogen coefficient
品种 Cultivar | 株高 PH | 根长 RL | 根冠比 RSR | 地上部鲜重 SFW | 地下部鲜重 RFW | 地上部干重 SDW | 地下部干重 RDW | 净光合速率 Pn | 蒸腾速率 Tr | 胞间CO2浓度 Ci | 气孔导度 Gs | 硝态氮 NO3--N | 硝酸还原酶 NR | 谷氨酰胺合成酶 GS | 谷氨酸合成酶 GOGAT | 谷氨酸脱氢酶 GDH | 超氧阴离子 O2·- | 过氧化氢 H2O2 | 丙二醛 MDA | 可溶性蛋白 SP | 可溶性糖 SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.974 | 0.718 | 1.200 | 0.694 | 0.819 | 0.800 | 1.000 | 0.409 | 0.658 | 0.913 | 0.647 | 0.672 | 0.403 | 0.555 | 1.806 | 0.649 | 1.626 | 1.048 | 1.402 | 0.617 | 0.920 |
| 2 | 0.877 | 0.564 | 0.778 | 0.530 | 0.111 | 0.633 | 0.444 | 0.546 | 0.626 | 0.896 | 0.889 | 0.239 | 0.834 | 0.803 | 3.038 | 0.805 | 1.883 | 1.049 | 1.047 | 0.934 | 0.810 |
| 3 | 0.788 | 0.827 | 0.636 | 0.757 | 0.714 | 1.000 | 0.667 | 0.628 | 0.374 | 0.995 | 0.588 | 0.593 | 0.559 | 0.449 | 1.340 | 0.684 | 1.054 | 1.098 | 1.387 | 0.763 | 0.938 |
| 4 | 0.916 | 0.890 | 0.800 | 0.605 | 0.516 | 0.577 | 0.429 | 0.722 | 0.692 | 0.953 | 0.923 | 0.344 | 0.552 | 1.056 | 1.486 | 0.947 | 1.346 | 1.160 | 1.257 | 0.766 | 0.599 |
| 5 | 0.973 | 0.452 | 0.667 | 0.487 | 0.324 | 0.553 | 0.333 | 0.558 | 0.509 | 0.996 | 0.469 | 0.545 | 0.835 | 0.490 | 2.097 | 0.624 | 1.515 | 1.707 | 2.826 | 0.784 | 0.483 |
| 6 | 0.931 | 1.252 | 1.800 | 0.796 | 1.608 | 0.829 | 1.500 | 0.760 | 0.373 | 0.841 | 0.346 | 0.337 | 0.674 | 0.385 | 1.757 | 0.796 | 1.258 | 1.398 | 1.157 | 0.842 | 0.409 |
| 7 | 0.911 | 0.962 | 1.571 | 0.303 | 0.616 | 0.333 | 0.571 | 0.434 | 0.671 | 0.860 | 0.590 | 0.258 | 0.558 | 0.073 | 2.429 | 0.232 | 1.119 | 1.360 | 1.197 | 0.983 | 0.457 |
| 8 | 0.937 | 1.207 | 1.400 | 0.594 | 0.510 | 0.651 | 1.000 | 0.472 | 0.286 | 0.900 | 0.235 | 0.532 | 0.631 | 0.592 | 1.643 | 0.454 | 1.419 | 1.735 | 1.682 | 0.729 | 0.759 |
| 9 | 0.901 | 1.404 | 1.000 | 0.738 | 0.795 | 0.970 | 0.667 | 0.870 | 0.621 | 0.907 | 0.611 | 0.338 | 0.786 | 0.674 | 2.223 | 0.471 | 2.210 | 1.454 | 1.741 | 0.822 | 0.860 |
| 10 | 0.996 | 0.743 | 1.400 | 0.469 | 0.515 | 0.467 | 0.667 | 0.878 | 0.628 | 0.994 | 0.571 | 0.458 | 0.365 | 0.512 | 1.242 | 0.855 | 1.042 | 1.401 | 1.578 | 0.692 | 0.627 |
| 11 | 0.891 | 1.439 | 2.500 | 0.815 | 2.114 | 0.725 | 2.000 | 0.870 | 0.701 | 0.943 | 0.727 | 0.286 | 0.688 | 0.965 | 1.656 | 0.533 | 1.361 | 1.174 | 1.017 | 0.430 | 0.690 |
| 12 | 0.949 | 0.865 | 1.111 | 0.863 | 0.857 | 0.786 | 0.800 | 0.683 | 0.829 | 0.964 | 0.733 | 0.441 | 0.487 | 0.915 | 1.738 | 0.944 | 1.421 | 2.000 | 1.029 | 0.402 | 0.670 |
| 13 | 0.949 | 0.876 | 1.500 | 0.914 | 1.183 | 0.746 | 1.333 | 0.814 | 0.688 | 0.938 | 0.625 | 0.809 | 0.637 | 0.810 | 1.251 | 0.508 | 1.369 | 1.115 | 2.541 | 0.553 | 0.774 |
| 14 | 0.793 | 0.993 | 1.857 | 0.958 | 1.640 | 0.867 | 1.750 | 0.554 | 0.589 | 0.997 | 0.538 | 0.382 | 0.470 | 0.756 | 2.262 | 0.526 | 1.138 | 1.126 | 1.196 | 0.406 | 0.666 |
| 15 | 0.947 | 1.423 | 1.833 | 0.878 | 1.333 | 0.808 | 1.750 | 0.892 | 0.422 | 0.933 | 0.643 | 0.374 | 0.477 | 0.698 | 1.402 | 0.280 | 1.899 | 2.401 | 1.146 | 0.584 | 0.930 |
| 16 | 0.969 | 0.994 | 1.778 | 0.905 | 1.290 | 0.960 | 1.600 | 0.355 | 0.224 | 0.893 | 0.250 | 0.423 | 0.740 | 0.820 | 2.337 | 0.848 | 1.049 | 1.157 | 1.041 | 0.482 | 0.768 |
| 17 | 0.726 | 0.441 | 1.000 | 0.545 | 0.327 | 0.492 | 0.500 | 0.378 | 0.377 | 0.976 | 0.333 | 0.298 | 0.717 | 0.911 | 1.252 | 0.694 | 1.230 | 1.233 | 2.076 | 0.292 | 0.654 |
| 18 | 0.877 | 0.786 | 0.889 | 0.934 | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.800 | 0.967 | 0.631 | 0.817 | 0.600 | 0.369 | 0.465 | 0.791 | 4.667 | 0.487 | 1.023 | 1.065 | 1.095 | 0.376 | 0.711 |

图9 18份皮燕麦材料低氮胁迫下各指标耐低氮系数相关性分析PH:株高, plant height;RL:根长, root length;RSR:根冠比, root-shoot ratio;SFW:地上部鲜重, shoot fresh weight;RFW:地下部鲜重, root fresh weight;SDW:地上部干重, shoot dry weight;RDW:地下部干重, root dry weight;Pn:净光合速率, photosynthesis rate;Tr:气孔导度, transpiration rate;Ci:胞间CO2浓度, internal CO2 concentration;Gs:蒸腾速率, transpiration rate;NO3--N:硝态氮;NR:硝酸还原酶, nitrate reductase;GS:谷氨酰胺合成酶, glutamine synthetase;GOGAT:谷氨酸合成酶, glutamate synthase;GDH:谷氨酸脱氢酶, glutamate dehydrogenase; O2·-:超氧阴离子;H2O2:过氧化氢;MDA:丙二醛, malondialdehyde;SP:可溶性蛋白, soluble protein;SS:可溶性糖, soluble sugar。下同The same below。 * 表示在P<0.05水平显著相关,**表示在P<0.01水平极显著相关,***表示在P<0.001水平极显著相关。* means significant correlation at the level of P<0.05, ** means extremely significant correlation at the level of P<0.01. *** means extremely significant correlation at the level of P<0.001.
Fig.9 Correlation analysis of low-nitrogen tolerance coefficient of each index under low nitrogen stress of 18 oat cultivars
变量 Variable | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 主成分3 Principal component 3 | 主成分4 Principal component 4 | 主成分5 Principal component 5 | 主成分6 Principal component 6 | 主成分7 Principal component 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下部干重Root dry weight | 0.878 | -0.247 | -0.241 | 0.035 | -0.128 | 0.051 | 0.010 |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight | 0.846 | 0.293 | -0.215 | -0.001 | 0.238 | -0.112 | 0.123 |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight | 0.791 | 0.033 | 0.075 | -0.073 | -0.370 | 0.114 | 0.186 |
| 根长Root length | 0.739 | -0.480 | 0.199 | 0.220 | 0.046 | 0.165 | -0.018 |
| 根冠比Root-shoot ratio | 0.693 | -0.459 | -0.103 | -0.013 | -0.396 | 0.110 | -0.046 |
| 地下部鲜重Root fresh weight | 0.643 | 0.224 | -0.152 | -0.051 | 0.588 | -0.168 | 0.149 |
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugar | -0.491 | -0.458 | 0.443 | 0.154 | 0.131 | -0.026 | 0.191 |
| 谷氨酰胺合成酶Glutamine synthetase | 0.382 | 0.688 | -0.023 | -0.025 | -0.010 | 0.450 | 0.149 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Internal CO2 concentration | -0.192 | 0.454 | -0.383 | 0.445 | -0.366 | 0.250 | -0.226 |
| 气孔导度Stomatal conductance | 0.033 | 0.529 | 0.749 | 0.178 | -0.125 | 0.047 | -0.101 |
| 蒸腾速率Transpiration rate | 0.005 | 0.441 | 0.665 | 0.160 | -0.329 | -0.171 | -0.083 |
| 净光合速率Photosynthesis rate | 0.462 | 0.141 | 0.467 | 0.284 | -0.035 | -0.130 | 0.060 |
| 谷氨酸合成酶Glutamate synthase | 0.042 | 0.034 | 0.403 | -0.604 | 0.446 | -0.279 | 0.027 |
| 过氧化氢H2O2 | 0.094 | -0.351 | 0.066 | 0.586 | -0.028 | 0.151 | -0.104 |
| 超氧阴离子O2·- | -0.001 | -0.037 | 0.418 | 0.555 | 0.500 | 0.407 | 0.008 |
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.297 | 0.337 | -0.100 | 0.347 | 0.599 | -0.062 | -0.294 |
| 硝酸还原酶Nitrate reductase | -0.272 | -0.177 | -0.068 | -0.089 | 0.396 | 0.649 | 0.376 |
| 硝态氮NO3--N | -0.051 | 0.217 | -0.476 | 0.531 | 0.096 | -0.556 | 0.180 |
| 谷氨酸脱氢酶Glutamate dehydrogenase | -0.168 | 0.532 | -0.088 | -0.161 | -0.247 | 0.144 | 0.591 |
| 株高Plant height | 0.038 | -0.279 | 0.244 | 0.463 | -0.136 | -0.360 | 0.585 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde | -0.513 | 0.037 | -0.400 | 0.454 | 0.063 | 0.009 | 0.112 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 4.658 | 2.702 | 2.559 | 2.291 | 2.049 | 1.561 | 1.180 |
| 贡献率Contribution (%) | 22.181 | 12.869 | 12.187 | 10.907 | 9.755 | 7.433 | 5.620 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution (%) | 22.181 | 35.049 | 47.236 | 58.144 | 67.899 | 75.332 | 80.952 |
表5 各综合指标系数及贡献率
Table 5 Coefficients and proportion rates of various comprehensive indicators
变量 Variable | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 主成分3 Principal component 3 | 主成分4 Principal component 4 | 主成分5 Principal component 5 | 主成分6 Principal component 6 | 主成分7 Principal component 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地下部干重Root dry weight | 0.878 | -0.247 | -0.241 | 0.035 | -0.128 | 0.051 | 0.010 |
| 地上部鲜重Shoot fresh weight | 0.846 | 0.293 | -0.215 | -0.001 | 0.238 | -0.112 | 0.123 |
| 地上部干重Shoot dry weight | 0.791 | 0.033 | 0.075 | -0.073 | -0.370 | 0.114 | 0.186 |
| 根长Root length | 0.739 | -0.480 | 0.199 | 0.220 | 0.046 | 0.165 | -0.018 |
| 根冠比Root-shoot ratio | 0.693 | -0.459 | -0.103 | -0.013 | -0.396 | 0.110 | -0.046 |
| 地下部鲜重Root fresh weight | 0.643 | 0.224 | -0.152 | -0.051 | 0.588 | -0.168 | 0.149 |
| 可溶性糖Soluble sugar | -0.491 | -0.458 | 0.443 | 0.154 | 0.131 | -0.026 | 0.191 |
| 谷氨酰胺合成酶Glutamine synthetase | 0.382 | 0.688 | -0.023 | -0.025 | -0.010 | 0.450 | 0.149 |
| 胞间二氧化碳浓度Internal CO2 concentration | -0.192 | 0.454 | -0.383 | 0.445 | -0.366 | 0.250 | -0.226 |
| 气孔导度Stomatal conductance | 0.033 | 0.529 | 0.749 | 0.178 | -0.125 | 0.047 | -0.101 |
| 蒸腾速率Transpiration rate | 0.005 | 0.441 | 0.665 | 0.160 | -0.329 | -0.171 | -0.083 |
| 净光合速率Photosynthesis rate | 0.462 | 0.141 | 0.467 | 0.284 | -0.035 | -0.130 | 0.060 |
| 谷氨酸合成酶Glutamate synthase | 0.042 | 0.034 | 0.403 | -0.604 | 0.446 | -0.279 | 0.027 |
| 过氧化氢H2O2 | 0.094 | -0.351 | 0.066 | 0.586 | -0.028 | 0.151 | -0.104 |
| 超氧阴离子O2·- | -0.001 | -0.037 | 0.418 | 0.555 | 0.500 | 0.407 | 0.008 |
| 可溶性蛋白Soluble protein | 0.297 | 0.337 | -0.100 | 0.347 | 0.599 | -0.062 | -0.294 |
| 硝酸还原酶Nitrate reductase | -0.272 | -0.177 | -0.068 | -0.089 | 0.396 | 0.649 | 0.376 |
| 硝态氮NO3--N | -0.051 | 0.217 | -0.476 | 0.531 | 0.096 | -0.556 | 0.180 |
| 谷氨酸脱氢酶Glutamate dehydrogenase | -0.168 | 0.532 | -0.088 | -0.161 | -0.247 | 0.144 | 0.591 |
| 株高Plant height | 0.038 | -0.279 | 0.244 | 0.463 | -0.136 | -0.360 | 0.585 |
| 丙二醛Malondialdehyde | -0.513 | 0.037 | -0.400 | 0.454 | 0.063 | 0.009 | 0.112 |
| 特征值Eigenvalue | 4.658 | 2.702 | 2.559 | 2.291 | 2.049 | 1.561 | 1.180 |
| 贡献率Contribution (%) | 22.181 | 12.869 | 12.187 | 10.907 | 9.755 | 7.433 | 5.620 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution (%) | 22.181 | 35.049 | 47.236 | 58.144 | 67.899 | 75.332 | 80.952 |
品种 Cultivar | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 主成分3 Principal component 3 | 主成分4 Principal component 4 | 主成分5 Principal component 5 | 主成分6 Principal component 6 | 主成分7 Principal component 7 | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | U(X4) | U(X5) | U(X6) | U(X7) | D值 D values | 耐低氮性排序 Low nitrogen tolerance ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.319 | 0.886 | -0.210 | 0.909 | 0.537 | -1.960 | -0.125 | 0.478 | 0.777 | 0.480 | 0.674 | 0.584 | 0.084 | 0.395 | 0.524 | 9 |
| 2 | -2.501 | 1.079 | 2.535 | -1.117 | 1.835 | 1.454 | 0.293 | 0.201 | 0.812 | 1.000 | 0.308 | 0.828 | 0.839 | 0.518 | 0.590 | 6 |
| 3 | -0.752 | 1.285 | -1.709 | 0.059 | 1.265 | -0.858 | -1.049 | 0.423 | 0.848 | 0.195 | 0.520 | 0.721 | 0.328 | 0.124 | 0.476 | 13 |
| 4 | -0.550 | 2.140 | 1.841 | -0.146 | -1.835 | 0.951 | 1.026 | 0.449 | 1.000 | 0.868 | 0.483 | 0.138 | 0.728 | 0.733 | 0.613 | 5 |
| 5 | -4.087 | -0.500 | -0.851 | 1.451 | 0.096 | 0.269 | 1.157 | 0.000 | 0.531 | 0.358 | 0.771 | 0.501 | 0.577 | 0.772 | 0.410 | 16 |
| 6 | 1.335 | -2.734 | -0.031 | -1.243 | -0.587 | 0.057 | 1.934 | 0.688 | 0.135 | 0.513 | 0.286 | 0.373 | 0.531 | 1.000 | 0.489 | 12 |
| 7 | -2.634 | -3.493 | 1.981 | -1.375 | -1.391 | -0.952 | -1.471 | 0.184 | 0.000 | 0.895 | 0.262 | 0.222 | 0.307 | 0.000 | 0.276 | 18 |
| 8 | -0.633 | -2.392 | -1.575 | 0.752 | 0.880 | -0.042 | -0.111 | 0.438 | 0.195 | 0.221 | 0.645 | 0.649 | 0.509 | 0.399 | 0.424 | 14 |
| 9 | 0.369 | -0.426 | 1.785 | 1.456 | 2.747 | 1.205 | 0.056 | 0.565 | 0.544 | 0.858 | 0.772 | 1.000 | 0.784 | 0.448 | 0.699 | 1 |
| 10 | -1.649 | 0.210 | 0.212 | 1.018 | -2.569 | -1.348 | 0.094 | 0.309 | 0.657 | 0.560 | 0.693 | 0.000 | 0.220 | 0.460 | 0.419 | 15 |
| 11 | 3.799 | -0.077 | 0.822 | -0.224 | -1.682 | 1.642 | -0.200 | 1.000 | 0.606 | 0.675 | 0.469 | 0.167 | 0.881 | 0.373 | 0.663 | 3 |
| 12 | 0.606 | 2.080 | 0.810 | 0.930 | -1.056 | -0.070 | 0.387 | 0.595 | 0.989 | 0.673 | 0.677 | 0.285 | 0.502 | 0.546 | 0.632 | 4 |
| 13 | 0.727 | 1.105 | -1.168 | 2.110 | -0.097 | -1.145 | 0.743 | 0.610 | 0.816 | 0.298 | 0.890 | 0.465 | 0.265 | 0.650 | 0.588 | 7 |
| 14 | 2.408 | 0.793 | -1.264 | -1.226 | -0.977 | 0.127 | -1.435 | 0.824 | 0.761 | 0.280 | 0.289 | 0.299 | 0.546 | 0.011 | 0.515 | 10 |
| 15 | 3.159 | -1.548 | 0.614 | 2.718 | 0.656 | 0.579 | -1.442 | 0.919 | 0.345 | 0.636 | 1.000 | 0.607 | 0.646 | 0.009 | 0.671 | 2 |
| 16 | 1.795 | -0.758 | -2.480 | -1.813 | 0.808 | 0.251 | 1.864 | 0.746 | 0.486 | 0.049 | 0.183 | 0.635 | 0.573 | 0.979 | 0.511 | 11 |
| 17 | -2.591 | 1.090 | -2.739 | -1.435 | -0.332 | 2.180 | -1.463 | 0.190 | 0.814 | 0.000 | 0.251 | 0.421 | 1.000 | 0.002 | 0.358 | 17 |
| 18 | 1.519 | 1.261 | 1.425 | -2.826 | 1.701 | -2.342 | -0.259 | 0.711 | 0.844 | 0.790 | 0.000 | 0.803 | 0.000 | 0.356 | 0.570 | 8 |
| 权重Weight | 0.274 | 0.159 | 0.151 | 0.135 | 0.121 | 0.092 | 0.069 |
表6 18份皮燕麦材料各综合指标值、权重、隶属函数值、D值及综合评价
Table 6 The comprehensive indicator values, index weight, membership function value, D values and comprehensive evaluation of 18 oat cultivars
品种 Cultivar | 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | 主成分3 Principal component 3 | 主成分4 Principal component 4 | 主成分5 Principal component 5 | 主成分6 Principal component 6 | 主成分7 Principal component 7 | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | U(X4) | U(X5) | U(X6) | U(X7) | D值 D values | 耐低氮性排序 Low nitrogen tolerance ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.319 | 0.886 | -0.210 | 0.909 | 0.537 | -1.960 | -0.125 | 0.478 | 0.777 | 0.480 | 0.674 | 0.584 | 0.084 | 0.395 | 0.524 | 9 |
| 2 | -2.501 | 1.079 | 2.535 | -1.117 | 1.835 | 1.454 | 0.293 | 0.201 | 0.812 | 1.000 | 0.308 | 0.828 | 0.839 | 0.518 | 0.590 | 6 |
| 3 | -0.752 | 1.285 | -1.709 | 0.059 | 1.265 | -0.858 | -1.049 | 0.423 | 0.848 | 0.195 | 0.520 | 0.721 | 0.328 | 0.124 | 0.476 | 13 |
| 4 | -0.550 | 2.140 | 1.841 | -0.146 | -1.835 | 0.951 | 1.026 | 0.449 | 1.000 | 0.868 | 0.483 | 0.138 | 0.728 | 0.733 | 0.613 | 5 |
| 5 | -4.087 | -0.500 | -0.851 | 1.451 | 0.096 | 0.269 | 1.157 | 0.000 | 0.531 | 0.358 | 0.771 | 0.501 | 0.577 | 0.772 | 0.410 | 16 |
| 6 | 1.335 | -2.734 | -0.031 | -1.243 | -0.587 | 0.057 | 1.934 | 0.688 | 0.135 | 0.513 | 0.286 | 0.373 | 0.531 | 1.000 | 0.489 | 12 |
| 7 | -2.634 | -3.493 | 1.981 | -1.375 | -1.391 | -0.952 | -1.471 | 0.184 | 0.000 | 0.895 | 0.262 | 0.222 | 0.307 | 0.000 | 0.276 | 18 |
| 8 | -0.633 | -2.392 | -1.575 | 0.752 | 0.880 | -0.042 | -0.111 | 0.438 | 0.195 | 0.221 | 0.645 | 0.649 | 0.509 | 0.399 | 0.424 | 14 |
| 9 | 0.369 | -0.426 | 1.785 | 1.456 | 2.747 | 1.205 | 0.056 | 0.565 | 0.544 | 0.858 | 0.772 | 1.000 | 0.784 | 0.448 | 0.699 | 1 |
| 10 | -1.649 | 0.210 | 0.212 | 1.018 | -2.569 | -1.348 | 0.094 | 0.309 | 0.657 | 0.560 | 0.693 | 0.000 | 0.220 | 0.460 | 0.419 | 15 |
| 11 | 3.799 | -0.077 | 0.822 | -0.224 | -1.682 | 1.642 | -0.200 | 1.000 | 0.606 | 0.675 | 0.469 | 0.167 | 0.881 | 0.373 | 0.663 | 3 |
| 12 | 0.606 | 2.080 | 0.810 | 0.930 | -1.056 | -0.070 | 0.387 | 0.595 | 0.989 | 0.673 | 0.677 | 0.285 | 0.502 | 0.546 | 0.632 | 4 |
| 13 | 0.727 | 1.105 | -1.168 | 2.110 | -0.097 | -1.145 | 0.743 | 0.610 | 0.816 | 0.298 | 0.890 | 0.465 | 0.265 | 0.650 | 0.588 | 7 |
| 14 | 2.408 | 0.793 | -1.264 | -1.226 | -0.977 | 0.127 | -1.435 | 0.824 | 0.761 | 0.280 | 0.289 | 0.299 | 0.546 | 0.011 | 0.515 | 10 |
| 15 | 3.159 | -1.548 | 0.614 | 2.718 | 0.656 | 0.579 | -1.442 | 0.919 | 0.345 | 0.636 | 1.000 | 0.607 | 0.646 | 0.009 | 0.671 | 2 |
| 16 | 1.795 | -0.758 | -2.480 | -1.813 | 0.808 | 0.251 | 1.864 | 0.746 | 0.486 | 0.049 | 0.183 | 0.635 | 0.573 | 0.979 | 0.511 | 11 |
| 17 | -2.591 | 1.090 | -2.739 | -1.435 | -0.332 | 2.180 | -1.463 | 0.190 | 0.814 | 0.000 | 0.251 | 0.421 | 1.000 | 0.002 | 0.358 | 17 |
| 18 | 1.519 | 1.261 | 1.425 | -2.826 | 1.701 | -2.342 | -0.259 | 0.711 | 0.844 | 0.790 | 0.000 | 0.803 | 0.000 | 0.356 | 0.570 | 8 |
| 权重Weight | 0.274 | 0.159 | 0.151 | 0.135 | 0.121 | 0.092 | 0.069 |
| 1 | Zou B K, Wang X M, Chu Z S, et al. Effects of nitrogen forms on growth and nitrogen assimilation and utilization of Buchloe dactyloides. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 118-127. |
| 邹博坤, 王欣铭, 褚章杉, 等. 氮素形态对野牛草生长及氮素吸收利用的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 118-127. | |
| 2 | Zhao Z Q, Shi Z K, Wang W, et al. Allocation of nitrogen and sucrose in maize seedling under low nitrogen stress. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(4): 783-796. |
| 赵泽群, 师赵康, 王雯, 等. 低氮胁迫下玉米幼苗氮素和蔗糖分配特性. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(4): 783-796. | |
| 3 | Wang H. Carbon-nitrogen metabolic responses and adaptive strategies to low-nitrogen stress in Glycine soja. Changchun: Changchun Normal University, 2020. |
| 王鹤. 低氮胁迫下野大豆幼苗碳氮代谢响应及适应机制研究. 长春: 长春师范大学, 2020. | |
| 4 | Yu F, Shi W M. Nitrogen use efficiencies of major grain crops in China in recent 10 years. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6): 1311-1324. |
| 于飞, 施卫明. 近10年中国大陆主要粮食作物氮肥利用率分析. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6): 1311-1324. | |
| 5 | Lv X M. Physiological and molecular response mechanisms of wheat to low nitrogen stress. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2020. |
| 吕雪梅. 小麦对低氮胁迫的生理与分子响应机制. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2020. | |
| 6 | Chen X P, Cui Z L, Fan M S, et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature, 2014, 514(7523): 486-489. |
| 7 | Boussadia O, Steppe K, Zgallai H, et al. Effects of nitrogen deficiency on leaf photosynthesis, carbohydrate status and biomass production in two olive cultivars Meski’ and Koroneiki’. Scientia Horticulturae, 2010, 123(3): 336-342. |
| 8 | Lu Y F. The policy change of chemical fertilizer reduction and its internal logic in China. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 2022(9): 74-85. |
| 陆钰凤. 中国化肥减量政策变迁及其内在逻辑. 农业经济问题, 2022(9): 74-85. | |
| 9 | Zhang B, Ren C Z. Advances in oat genomic research and molecular breeding. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 785-791. |
| 张波, 任长忠. 燕麦基因组学与分子育种研究进展. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 785-791. | |
| 10 | Yang C Q, Chang Y J, Yang J, et al. Research progress of oats production and breeding selection technology. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(5): 578-584. |
| 杨崇庆, 常耀军, 杨娇, 等. 燕麦生产及品种选育技术研究进展. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(5): 578-584. | |
| 11 | Yang L. Effects of ultrafine pulverization on quality and in vitro simulated digestion of oat flour. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 杨璐. 超微粉碎对燕麦粉品质影响及体外模拟消化研究. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. | |
| 12 | Zhang M F. Morphological, biochemical and molecular studies of oats kernel covering. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020. |
| 张鸣凡. 燕麦籽粒皮裸性的形态、生化和分子研究. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2020. | |
| 13 | Mu L H, Mu Y X, Chang K Q, et al. Correlation analysis of protein content with nutritional indexes and agronomic traits in oat cultivars with different skins. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(22): 86-88. |
| 穆兰海, 母养秀, 常克勤, 等. 不同皮燕麦品种蛋白质含量与营养指标及农艺性状的相关性分析. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(22): 86-88. | |
| 14 | Liu W H. Effects of planting dates on the growth characteristics of three naked oats varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(5): 1032-1040. |
| 刘文辉. 播期对三种裸燕麦品种生长特性的影响. 草地学报, 2016, 24(5): 1032-1040. | |
| 15 | Wang Q, Li Z J, Li J, et al. Evaluation of agronomic and forage quality traits of a range of oat cultivars. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 149-158. |
| 王茜, 李志坚, 李晶, 等. 不同类型燕麦农艺和饲草品质性状分析. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 149-158. | |
| 16 | Wu Y H, Liu W H, Liu K Q, et al. Effects of drought stress on leaf senescence and the active oxygen scavenging system of oat seedlings. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(10): 75-86. |
| 吴雨涵, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 等. 干旱胁迫对燕麦幼苗叶片光合特性及活性氧清除系统的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 75-86. | |
| 17 | Su W J, Zhao G Q, Ju Z L, et al. Effects of drought stress duration on physiological indexes of 6 oat germplasms at germination stage. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(3): 646-654. |
| 苏玮娟, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 等. 干旱胁迫时间对6份饲用燕麦种质萌发期生理指标的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(3): 646-654. | |
| 18 | Li L Y, Tan H X, Li J, et al. Screening of salt tolerant growth-promoting Bacillus strains and their effect on oat growth under salt stress. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(6): 1268-1276. |
| 李丽艳, 谭海霞, 李婧, 等. 耐盐促生芽孢杆菌的筛选及其对盐胁迫下燕麦生长的影响. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(6): 1268-1276. | |
| 19 | Hu J Y, Liu C, Li Z J, et al. Comparative study on yield and agronomic traits of different types of oat in western Jilin Province. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(10): 2247-2257. |
| 胡佳燕, 刘畅, 李志坚, 等. 不同类型皮燕麦在吉林省西部的产量与农艺性状的比较研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(10): 2247-2257. | |
| 20 | Sun R G. Effects of salt on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of oat for late growth period and germination. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2010. |
| 孙仁国. 盐胁迫对燕麦萌发及生长后期生理生化特性的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2010. | |
| 21 | Zhang Z L, Zhai W J, Li X F. Experimental supervision of plant physiology (The Fourth Edition). Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009: 30-227. |
| 张志良, 翟伟菁, 李小芳. 植物生理学实验指导(第4版). 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009: 30-227. | |
| 22 | Mu X H, Chen Q W, Wu X Y, et al. Gibberellins synthesis is involved in the reduction of cell flux and elemental growth rate in maize leaf under low nitrogen supply. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2018, 150(6): 198-208. |
| 23 | Jiang L L, Han L S, Han X R, et al. Effects of nitrogen on growth root morphological traits nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency of maize seedlings. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2011, 17(1): 247-253. |
| 姜琳琳, 韩立思, 韩晓日, 等. 氮素对玉米幼苗生长、根系形态及氮素吸收利用效率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1): 247-253. | |
| 24 | Chen Y, Wang Q, Chen X, et al. Effects of nitrogen deficiency stress on physiological characteristics of Festuca arundinacea at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(2): 9-15. |
| 陈莹, 王茜, 陈锡, 等. 低氮胁迫对高羊茅苗期生理特性的影响. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(2): 9-15. | |
| 25 | Markelz R J C, Strellner R S, Leakey A D B. Impairment of C4 photosynthesis by drought is exacerbated by limiting nitrogen and ameliorated by elevated [CO2] in maize. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(9): 3235-3246. |
| 26 | Zhao M L. Physiological characteristics and metabolomics reveal the tolerance mechanism to low nitrogen in Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc. seedling leaves. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2020. |
| 赵明丽. 低氮胁迫下野大豆(Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc.)幼苗叶片生理特性及代谢组学研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2020. | |
| 27 | Farquhar G D, Sharkey T D. Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 1982, 33(1): 317-345. |
| 28 | Xu D Q. Photosynthetic efficiency. Plant Physiology Communications, 1988(5): 3-9. |
| 许大全. 光合作用效率. 植物生理学通讯, 1988(5): 3-9. | |
| 29 | Li C F, Liu P, Wang K J, et al. Effect of nitrogen deficiency on yield and photosynthetic traits of cyto-plasmic male sterility maize. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008(4): 684-689. |
| 李从锋, 刘鹏, 王空军, 等. 缺氮对细胞质雄性不育玉米产量和光合特性的影响. 作物学报, 2008(4): 684-689. | |
| 30 | Li L, Huang J H, Chen Z W, et al. Progress of biological research on crops tolerant to low nitrogen. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2012, 28(2): 117-122. |
| 李梁, 黄剑华, 陈志伟, 等. 作物耐低氮的相关生物学研究进展. 上海农业学报, 2012, 28(2): 117-122. | |
| 31 | Fan L X, Hao N, Zhang T Y, et al. Physiology and molecular mechanism of low nitrogen tolerance in cucumber. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(5): 117-122. |
| 范莲雪, 郝宁, 张天怡, 等. 黄瓜耐低氮生理与分子机制. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(5): 117-122. | |
| 32 | Liu Y. Comparative study on leaf nutrient reabsorption of two different ecotypes of wild soybean and soybean seedings under low nitrogen stress. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2022. |
| 刘源. 低氮胁迫下两种生态型野大豆和大豆幼苗叶片养分再利用比较研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2022. | |
| 33 | Qin J. Studies on physiological and molecular mechanisms of highland barley in response to low nitrogen stress. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. |
| 秦娟. 青稞响应低氮胁迫的生理和分子机制研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. | |
| 34 | Wang F. Physiological response of highland barley to low nitrogen stress and studies on the mechanism of alternative respiratory pathway affecting low nitrogen tolerance. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016. |
| 王峰. 青稞对低氮胁迫的生理响应及交替呼吸途径影响低氮耐受性的机理研究. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016. | |
| 35 | Xiao J X, Zeng C Y, Peng M. Enzyme activity and expression analysis of glutamine synthetaseGS gene in cassava under low-nitrogen stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(1): 21-25. |
| 肖急祥, 曾长英, 彭明. 低氮条件下木薯谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)酶活及GS家族基因表达分析. 分子植物育种, 2016, 14(1): 21-25. | |
| 36 | Xu H C, Shang J, Liu M H, et al. Research progress of enzymes related to nitrogen metabolism. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(4): 17-20. |
| 徐洪超, 商靖, 刘铭荟, 等. 氮代谢相关酶的研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 2022, 50(4): 17-20. | |
| 37 | Liu Y F, Xue D S, Gong C J. Research progress of glutamine synthetase. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(5): 97-99. |
| 刘芸菲, 薛栋升, 宫春杰. 谷氨酰胺合成酶研究进展. 山东化工, 2021, 50(5): 97-99. | |
| 38 | Zhang Y P, Diao Q N, Cao Y Y, et al. Effect of exogenous SNP on the growth and enzymes related to nitrogen metabolism of melon seedlings under cold stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(5): 1692-1698. |
| 张永平, 刁倩楠, 曹燕燕, 等. 外源SNP对低温胁迫下甜瓜幼苗生长和氮代谢相关酶的影响. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(5): 1692-1698. | |
| 39 | Gu J J. Effects of salt stress on nitrogen metabolism and yield of rice. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 谷娇娇. 盐胁迫对水稻氮代谢及产量的影响. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019. | |
| 40 | Xie M L, Li Q, Zha L, et al. Effects of low nitrogen stress on the physiological and morphological traits of roots of different low nitrogen tolerance maize varieties at seedling stage. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2015, 23(8): 946-953. |
| 谢孟林, 李强, 查丽, 等. 低氮胁迫对不同耐低氮性玉米品种幼苗根系形态和生理特征的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(8): 946-953. | |
| 41 | Xu S H. Research advances of reactive oxygen species in plants under environmental stress. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 27(21): 29-32. |
| 徐松华. 逆境条件下植物体内活性氧代谢研究进展. 安徽农学通报, 2021, 27(21): 29-32. | |
| 42 | Zhao J J, Zhan W L, Zhou N. Research progress on the metabolisms of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal in plants under abiotic stresses. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2022, 53(8): 2099-2113. |
| 赵晶晶, 詹万龙, 周浓. 非生物胁迫下植物体内活性氧和丙酮醛代谢的研究进展. 南方农业学报, 2022, 53(8): 2099-2113. | |
| 43 | Li Y. Physiological responses of Pyrus betulaefolia to low potassium and analysis of its potassium uptake key genes. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 李岩. 杜梨对低钾胁迫的生理响应及其钾吸收关键基因的分析. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. | |
| 44 | Ye Y B, Ma G F, Pan Y Y, et al. Low nitrogen stress on growth and physiology of Cunninghamia lanceolata seedlings. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 2019, 39(6): 81-86. |
| 叶宇波, 马贵芳, 潘瑶瑶, 等. 低氮胁迫对杉木幼苗生长及生理的影响. 浙江林业科技, 2019, 39(6): 81-86. | |
| 45 | Liu Q, Wang Q C, Wang Z W, et al. Effectiveness of osmoregulation substance as an evaluation index of salt tolerance. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2014, 42(2): 78-82. |
| 刘强, 王庆成, 王占武, 等. 渗透调节物质作为植物抗盐性评价指标的有效性. 东北林业大学学报, 2014, 42(2): 78-82. | |
| 46 | Li Q, Luo Y H, Long W J, et al. Effect of low nitrogen stress on different low nitrogen tolerance maize cultivars seedling stage growth and physiological characteristics. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 204-212. |
| 李强, 罗延宏, 龙文靖, 等. 低氮胁迫对不同耐低氮性玉米品种苗期生长和生理特性的影响. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 204-212. | |
| 47 | Zhang C, Zhang Y Q, Lu Z J, et al. Effect of low nitrogen stress on the seedling growth and root physiological traits of Fagopyrum tataricum cultivars with different low-N treatments. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2017, 37(7): 1331-1339. |
| 张楚, 张永清, 路之娟, 等. 低氮胁迫对不同苦荞品种苗期生长和根系生理特征的影响. 西北植物学报, 2017, 37(7): 1331-1339. | |
| 48 | Wang N, Shi Z K, Xu S Y, et al. Dynamics of carbon and nitrogen balance during leaf senescence of maize seedlings induced by low nitrogen stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2022, 33(4): 1045-1054. |
| 王宁, 师赵康, 徐世英, 等. 低氮诱导玉米幼苗叶片衰老过程中碳氮平衡的动态变化. 应用生态学报, 2022, 33(4): 1045-1054. | |
| 49 | Lin D D, Zhao G Q, Ju Z L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of 15 oat varieties at the seedling stage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 等. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. | |
| 50 | Zhang C. The primary research about the screening of Fagopyrum tataricum genotypes to low nitrogen tolerance and physiological mechanisim. Taiyuan: Shanxi Normal University, 2018. |
| 张楚. 苦荞耐低氮基因型的筛选及其生理机制的初步研究. 太原: 山西师范大学, 2018. | |
| 51 | Li J W, Liu J H, Zhao B P, et al. Evaluation of salt tolerance of oat materials at seedling stage and selection of the relative index. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2022, 1-8. DOI:10.13327/j.jjlau.2021.1623. |
| 李俊伟, 刘景辉, 赵宝平, 等. 燕麦苗期耐盐性评价及鉴定指标筛选. 吉林农业大学学报, 2022, 1-8.DOI:10.13327/j.jjlau.2021.1623. |
| [1] | 康燕霞, 姜渊博, 齐广平, 银敏华, 马彦麟, 汪精海, 贾琼, 唐仲霞, 汪爱霞. 红豆草与无芒雀麦混播草地生产力提升的水分调控模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 115-128. |
| [2] | 王腾飞, 王斌, 邓建强, 李满有, 倪旺, 冯琴, 妥昀昀, 兰剑. 宁夏干旱区滴灌条件下拉巴豆不同播种量与甜高粱混播饲草生产性能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 30-40. |
| [3] | 徐宗昌, 鲁雪莉, 魏云冲, 孟晨, 张梦超, 张缘杨, 王萌, 王菊英, 张成省, 李义强. 航天诱变野大豆SP1群体苗期耐盐性鉴定与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(11): 168-178. |
| [4] | 王占军, 季波, 纪童, 蒋齐. 5种豆科牧草抗旱性研究与评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 187-199. |
| [5] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [6] | 李娜娜, 刘同歌, 黄志慧, 郑宝江, 张玉红. 草本资源植物菥蓂对盐胁迫下生理生态及次生代谢产物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 181-190. |
| [7] | 常利芳, 李欣, 郭慧娟, 乔麟轶, 张树伟, 陈芳, 畅志坚, 张晓军. 小偃麦衍生系表型遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 61-74. |
| [8] | 彭艳, 孙晶远, 马素洁, 王向涛, 孙磊, 魏学红. 氮磷添加对藏北人工牧草生产性能和品质的评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 52-64. |
| [9] | 张鹤山, 高秋, 张婷婷, 陆姣云, 田宏, 熊军波, 刘洋. 30份红三叶种质资源耐铜性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 117-128. |
| [10] | 蔺豆豆, 赵桂琴, 琚泽亮, 宫文龙. 15份燕麦材料苗期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 108-121. |
| [11] | 王红林, 左艳春, 严旭, 周晓康, 寇晶, 杨希智, 郭俊英, 蒲军, 张浩仁, 杜周和. 刈割高度与施氮量对饲料桑全株产量及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 203-211. |
| [12] | 姜慧新, 柏杉杉, 吴波, 宋静怡, 王国良. 22个燕麦品种在黄淮海地区的农艺性状与饲草品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 140-149. |
| [13] | 项洪涛, 郑殿峰, 何宁, 李琬, 王曼力, 王诗雅. 植物对低温胁迫的生理响应及外源脱落酸缓解胁迫效应的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 208-219. |
| [14] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙晓梵, 孙宗玖. 新疆不同生境狗牙根种质抗旱性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 155-169. |
| [15] | 张雪婷, 王新永, 杨文雄, 柳娜, 杨长刚. 河西绿洲灌区节水抗旱型玉米品种的评价方法探讨[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 134-148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||