

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 181-190.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021459
李娜娜1( ), 刘同歌1, 黄志慧1, 郑宝江2, 张玉红1(
), 刘同歌1, 黄志慧1, 郑宝江2, 张玉红1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-12-10
修回日期:2022-03-09
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-10-01
通讯作者:
张玉红
作者简介:E-mail: pzhangyh@126.com基金资助:
Na-na LI1( ), Tong-ge LIU1, Zhi-hui HUANG1, Bao-jiang ZHENG2, Yu-hong ZHANG1(
), Tong-ge LIU1, Zhi-hui HUANG1, Bao-jiang ZHENG2, Yu-hong ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2021-12-10
Revised:2022-03-09
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2022-10-01
Contact:
Yu-hong ZHANG
摘要:
旨在探究盐胁迫下菥蓂生理生态及次生代谢产物的响应,为进一步研究在盐碱地上耐盐植株的种植奠定理论基础。以菥蓂为试验材料,采用水培的方式进行培养,设置5个NaCl浓度梯度(0、50、100、150、200 mmol·L-1)来模拟不同强度盐胁迫条件,分别在处理1、5、10、15 d采集菥蓂叶片,测定其生理生化指标,光合参数和次生代谢产物含量。结果表明:菥蓂叶片中SOD、POD、CAT活性在盐胁迫1~15 d时均随盐浓度的升高呈先增后减的趋势,均在NaCl浓度为100 mmol·L-1时,酶活性达到最高。丙二醛含量随盐浓度的升高先增后减;菥蓂叶片可溶性糖和脯氨酸含量随盐浓度的升高和胁迫时间的延长而增加,可溶性蛋白含量随盐浓度的升高先增后减;菥蓂叶片中叶绿素a、叶绿素b、总叶绿素含量、叶绿素荧光参数、净光合速率和蒸腾速率随盐浓度的升高基本呈下降趋势,下降幅度逐渐增大;菥蓂叶片中总黄铜、总酚、黑芥子苷的含量随盐浓度的升高呈先增后减的趋势。由此可见,菥蓂对盐胁迫有较高的耐受性,在50~100 mmol·L-1盐胁迫环境中能正常生长,该结果可为后续菥蓂耐盐机制的研究提供理论依据。
李娜娜, 刘同歌, 黄志慧, 郑宝江, 张玉红. 草本资源植物菥蓂对盐胁迫下生理生态及次生代谢产物响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 181-190.
Na-na LI, Tong-ge LIU, Zhi-hui HUANG, Bao-jiang ZHENG, Yu-hong ZHANG. Physiological ecological and secondary metabolic responses of the herbaceous resource plant Thlaspi arvense to salt stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(11): 181-190.
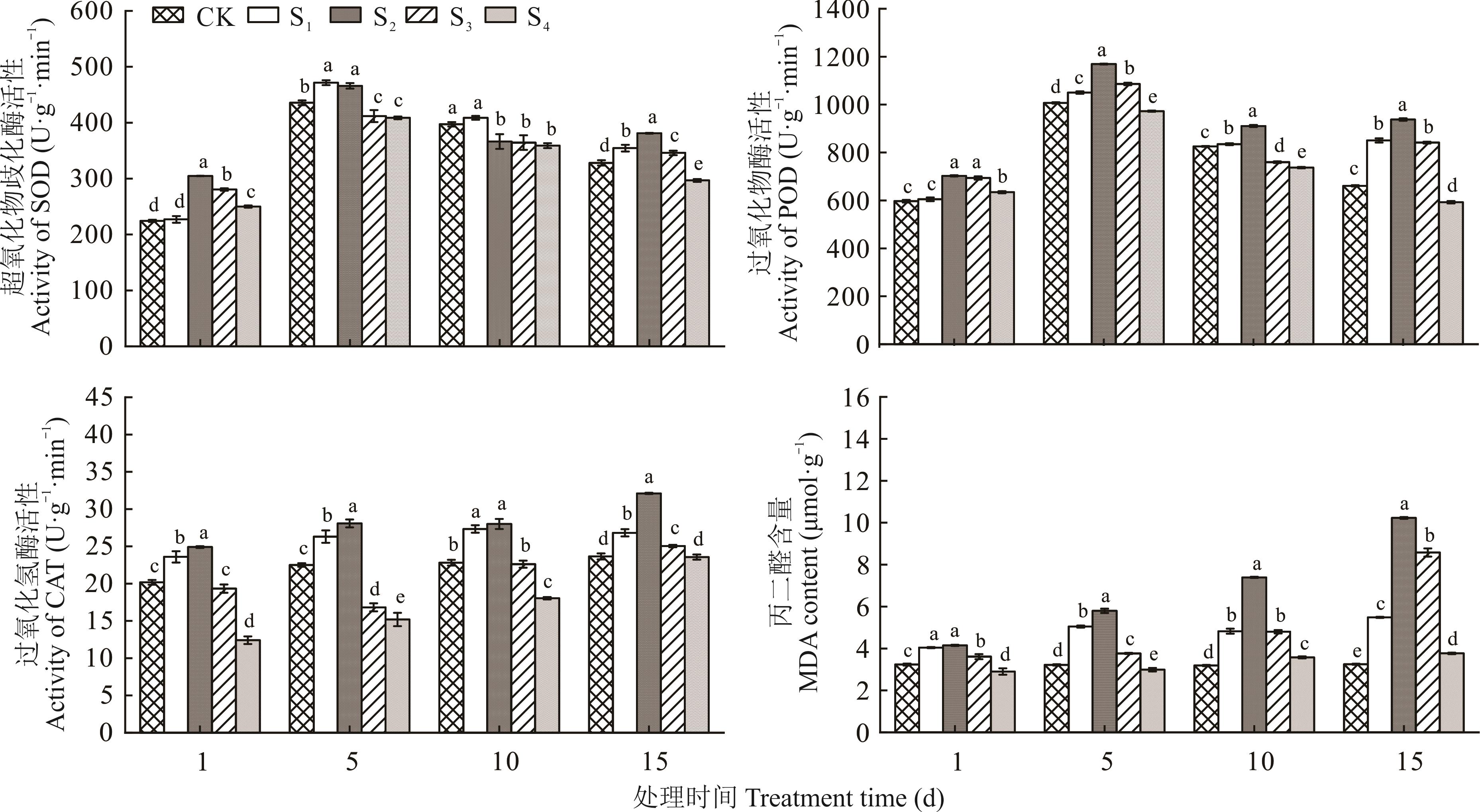
图2 NaCl胁迫对菥蓂叶片抗氧化酶活性和MDA含量的影响不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference among different treatments at P<0.05, the same below.
Fig.2 Effect of NaCl stress on antioxidant enzyme activity and MDA content of T. arvense
| 1 | Yang W P, Ma R, Yang Y Y, et al. Effects of NaCl treatment on leaf traits of Lycium ruthenicum. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(4): 35-41. |
| 杨万鹏, 马瑞, 杨永义, 等.不同浓度NaCl处理对黑果枸杞叶片性状的影响. 生态科学, 2019, 38(4): 35-41. | |
| 2 | Wang X P, Geng S J, Cao D H, et al. Physiological responses and adaptive strategies of tomato plants to salt and alkali stresses. Scientia Horticulturae, 2011, 130(1): 248-255. |
| 3 | Li J J, Ma J J, Guo H L, et al. Growth and physiological responses of two phenotypically distinct accessions of centipedegrass (Eremochloa ophiuroides (Munro) Hack.) to salt stress. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 126: 1-10. |
| 4 | Guo Q Q, Wu P, Chen B J, et al. Preliminary study on the effect of sodium salt stress on the tolerance of pepper with different pungency degree. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 46(4): 69-74, 87. |
| 郭茜茜, 吴鹏, 陈柏杰, 等. 钠盐胁迫对不同辣度辣椒的耐受性影响研究初探. 东北农业科学, 2021, 46(4): 69-74, 87. | |
| 5 | Wang G Y, Cai L G, Zhang J J, et al. Research on characteristics of Thlaspi arvenus L. which adapt to the arid environment. Journal of Changchun Normal University (Natural Science), 2009, 28(4): 54-56. |
| 王光野, 蔡立格, 张静菊, 等. 菥蓂(Thlaspi arvenus L.)抗旱适应结构研究. 长春师范学院学报(自然科学版), 2009, 28(4): 54-56. | |
| 6 | Hojilla-Evangelista M P, Evangelista R L, Isbell T A, et al. Effects of cold-pressing and seed cooking on functional properties of protein in pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) seed and press cakes. Industrial Crops & Products, 2013, 45: 223-229. |
| 7 | Dose H L, Eberle C A, Forcella F, et al. Early planting dates maximize winter annual field pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) yield and oil content. Industrial Crops & Products, 2017, 97: 477-483. |
| 8 | Zhang Z Z. Biological characteristics and processing of edible pennycress. Special Economic Animals and Plants, 2005, 8(8): 25. |
| 张宗舟. 食用菥蓂的生物学特性与加工. 特种经济动植物, 2005, 8(8): 25. | |
| 9 | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 Edition, Volume 1). Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020: 321. |
| 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(2020年版,一部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 321. | |
| 10 | Li C X. Study on the antidepressant and memory impairment of polyphenolic compound from extracts of Thlaspi arvenus L. seeds. Medical Information, 2011, 24(7): 4634. |
| 李春晓. 多酚类化合物菥蓂子提取物抗抑郁及记忆障碍研究. 医学信息, 2011, 24(7): 4634. | |
| 11 | Zhao R, Yang X Y, Li M Z, et al. Biodiesel preparation from Thlaspi arvense L. seed oil utilizing a novel ionic liquid core-shell magnetic catalyst. Industrial Crops & Products, 2021, 162: 113316. |
| 12 | Zanetti F, Isbell T A, Gesch R W, et al. Turning a burden into an opportunity: Pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) new oilseed crop for biofuel production. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2019, 130: 105354. |
| 13 | Gao J F. Plant physiology experiment guidance. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版, 2006. | |
| 14 | Hu W Y, Wang X L, Xuan Y S. Determination of chlorophyll content by dimethyl sulfoxide. Liaoning Agricultural Science, 1984(1): 38-41. |
| 胡文玉, 王兴理, 玄英淑. 二甲基亚砜法测定叶绿素含量. 辽宁农业科学, 1984(1): 38-41. | |
| 15 | Fu L Z, Zhao L M, Liu Q, et al. Effects of nitrogen forms on main phytochemical content and antioxidant activity in root tubers of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2021, 56(8): 633-639. |
| 付立忠, 赵利梅, 刘骞, 等. 氮素形态对三叶青块根主要化学成分含量及抗氧化活性的影响. 中国药学杂志, 2021, 56(8): 633-639. | |
| 16 | Chen Y, Zhou M, Wu L P, et al. Determination of sinigrin in Thlaspi arvense by HPLC. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2012, 27(1): 94-95. |
| 陈玉, 周旻, 伍丽萍, 等. HPLC测定菥蓂子中的黑芥子苷. 华西药学杂志, 2012, 27(1): 94-95. | |
| 17 | Zhou Y. Research on germination, ionic balance and soluble sugars content of Glycine max under saline stress. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2014. |
| 周妍. 盐胁迫对大豆种子萌发、离子平衡及可溶性糖含量影响的研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2014. | |
| 18 | Xu Z Q, Zhang Y, Yang X K. Optimization research of quality and saline-alkaline resistance of Helianthus tuberosus L. species in the Western Jilin Province. Forest Engineering, 2019, 35(6): 6-15. |
| 徐子棋, 张瑜, 杨献坤. 吉林省西部菊芋品质及耐盐碱性优选研究. 森林工程, 2019, 35(6): 6-15. | |
| 19 | Wei X X, Jiang M Y, Zhang W T, et al. Plant regeneration of the stem bud proliferation pathway of Thymus dahuricus. Forest Engineering, 2019, 35(4): 22-27, 31. |
| 魏晓雪, 姜明月, 张文天, 等. 兴安百里香茎芽增殖途径的植株再生. 森林工程, 2019, 35(4): 22-27, 31. | |
| 20 | Gu H, Li L, Ouyang Q X, et al. Effects of salt stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of three sweet Osmanthus fragrans varieties. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2020, 39(10): 28-34. |
| 顾恒, 李玲, 欧阳绮霞, 等. 盐胁迫对3个桂花品种生长和生理特性的影响. 中国野生植物资源, 2020, 39(10): 28-34. | |
| 21 | Guo D. Effects of different salt stress on photosynthesis of Euonymus kiautschoicus and Euonymus japonicus. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 21(6): 138-141. |
| 郭栋. 不同盐处理对攀援卫矛和大叶黄杨生理效应的影响. 天津农业科学, 2015, 21(6): 138-141. | |
| 22 | Cui X S, Li X X, Wang F, et al. Comparative analysis of light response characteristics of Perilla from different provenances. Forest Engineering, 2020, 36(2): 20-24, 34. |
| 崔新爽, 李晓雪, 王菲, 等. 不同种源紫苏光响应特征比较分析. 森林工程, 2020, 36(2): 20-24, 34. | |
| 23 | Yu W C, Yu Y, Wang C, et al. Mechanism by which salt stress induces physiological responses and regulates tanshinone synthesis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 164: 10-20. |
| 24 | Li Z J, Zuo Y M, Song M Y, et al. Effects of salt stress on growth physiological indexes and salt tolerance threshold of Taraxacum mongolicum Hand-Mazz. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2020, 43(7): 1558-1562. |
| 李赵嘉, 左永梅, 宋明月, 等. 盐胁迫对大叶蒲公英生长生理指标及耐盐阈值的影响. 中药材, 2020, 43(7): 1558-1562. | |
| 25 | Jiang Y T, Li Y M, Chen C X, et al. Effects of salt stress on physiological characteristics of Begonia semperflorens Link et Otto seedlings. Northern Horticulture, 2020(16): 62-69. |
| 姜云天, 李玉梅, 陈晨霞, 等. 盐胁迫对四季秋海棠幼苗生理特性的影响. 北方园艺, 2020(16): 62-69. | |
| 26 | Zhang K, Li M N, Cao S H, et al. Response of Carex rigescens to different NaCl concentrations and its salinity threshold calculation. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(3): 479-487. |
| 张昆, 李明娜, 曹世豪, 等. 白颖苔草对不同浓度NaCl胁迫的响应及其耐盐阈值. 草业科学, 2017, 34(3): 479-487. | |
| 27 | Mambetale A, Nurbulat L, Gao L L, et al. Effect of salt stress on growth and physiological characteristics of sea island cotton and upland cotton cultivars. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(4): 465-473. |
| 阿曼古丽·买买提阿力, 拉扎提·努尔布拉提, 高丽丽, 等. 盐胁迫对海岛棉和陆地棉幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 植物学报, 2017, 52(4): 465-473. | |
| 28 | AbdElgawad H, Zinta G, Hegab M M, et al. High salinity induces different oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in maize seedlings organs. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 276. |
| 29 | Chen Y Q, Su K Q, Li C J. Effects of NaCl stress on seeding growth and physiological responses of Achnatherum inebrians and Festuca arundinacea. Grassland and Turf, 2021, 41(3): 32-40. |
| 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 李春杰. 盐胁迫对2种冷季型草坪草幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 草原与草坪, 2021, 41(3): 32-40. | |
| 30 | Xu J Z, Zhu L, Li Y M, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on physiological and biochemical characteristies in mustard seedling. Henan Science, 2015, 33(3): 389-393. |
| 徐俊芝, 朱磊, 李严曼, 等. 盐胁迫对芥菜幼苗生理生化特性的影响. 河南科学, 2015, 33(3): 389-393. | |
| 31 | He L C, Wang K, Wei X Y, et al. Antioxidant enzyme activities and SNP/InDel analysis of cotton varieties differring in salt tolerance. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 30(5): 980-985. |
| 何林池, 王康, 魏小云, 等. 耐盐差异性不同棉花品种的抗氧化酶活性及SNP/InDel分析. 江苏农业学报, 2014, 30(5): 980-985. | |
| 32 | Chen L, Zhang X L, Gao Z, et al. Effect of lanthanum nitrate spraying on osmotic regulating substance accumulation in navel orange leaves. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(29): 1-6. |
| 陈璐, 张小丽, 高柱, 等. 喷施硝酸镧对脐橙叶片渗透调节物质的影响. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(29): 1-6. | |
| 33 | Jin H X, Shen X Y, Chen R R, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on morphological and physiological characteristics of Magnolia denudate Desr. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2021, 41(4): 596-603. |
| 金荷仙, 沈徐悦, 陈蓉蓉, 等. NaCl胁迫对白玉兰形态及生理特性的影响. 植物研究, 2021, 41(4): 596-603. | |
| 34 | Li Y J, Li J, Xu P, et al. Physiological responses of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. seedlings to drought stress. Arid Zone Research, 2014, 31(4): 756-762. |
| 李永洁, 李进, 徐萍, 等. 黑果枸杞幼苗对干旱胁迫的生理响应. 干旱区研究, 2014, 31(4): 756-762. | |
| 35 | Su Y, Pei Y, He S Y, et al. Experimental study on the physiological response of Lonicera cearulea L. to salt stress. Science and Technology of Tianjin Agriculture and Forestry, 2021(1): 1-4. |
| 苏雅, 裴毅, 何松燕, 等. 蓝果忍冬对盐胁迫的生理响应研究试验研究. 天津农林科技, 2021(1): 1-4. | |
| 36 | Chen Y L, Li X, Zhao W Z, et al. Physiological response of Thuarea involuta under salt stress. Guihaia, 2021, 41(2): 225-232. |
| 陈意兰, 李昕, 赵文忠, 等. 蒭雷草对盐胁迫的生理响应. 广西植物, 2021, 41(2): 225-232. | |
| 37 | Lu S, Mao C Y, Xiao H X. Effects of nitrogen on photosynthetic capacity of Orychophragmcs violaceus tissue culture seedling by chlorophyll fluorescence method. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017(10): 37-40. |
| 鲁珊, 毛彩云, 肖荷霞. 应用叶绿素荧光法鉴定氮素对诸葛菜组培苗光合能力的影响. 黑龙江农业科学, 2017(10): 37-40. | |
| 38 | Santos C V. Regulation of chlorophyll biosynthesis and degradation by salt stress in sunflower leaves. Scientia Horticulturae, 2004, 103(1): 93-99. |
| 39 | Han Z P, Guo S R, Feng J Q, et al. Effect of salinity on plant growth, photosynthetic pigments and proline content in leaves of watermelon seedings. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2008, 31(2): 32-36. |
| 韩志平, 郭世荣, 冯吉庆, 等. 盐胁迫对西瓜幼苗生长、叶片光合色素和脯氨酸含量的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 2008, 31(2): 32-36. | |
| 40 | Rong X F, Xu F, Huang X H, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on photosynthesis characteristics of Ginkgo biloba. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 52(4): 842-845. |
| 容晓峰, 许锋, 黄小花, 等. NaCl胁迫对银杏光合作用的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(4): 842-845. | |
| 41 | Tu L Y. Effects of water stress on the physiology and main secondary metabolites of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2019. |
| 屠玲艳. 水分胁迫对三叶青生理及主要次生代谢产物的影响. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2019. | |
| 42 | Hong S R, Chen X Y, Li W L, et al. Effects of salt stress on physiological characteristics and secondary metabolites of plantlets of two cultivars of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg in Huaiyu Mountain. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 53(9): 38-45. |
| 洪森荣, 陈轩宇, 李文丽, 等. 盐胁迫对怀玉山三叶青2个栽培种试管苗生理特性和次生代谢产物的影响. 山东农业科学, 2021, 53(9): 38-45. |
| [1] | 谢文辉, 黄莉娟, 赵丽丽, 王雷挺, 赵文武. 钙盐胁迫对3份葛藤种质种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 220-233. |
| [2] | 刘亚男, 于人杰, 高燕丽, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 武志海, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿膜联蛋白MtANN2基因的表达模式及盐胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 124-134. |
| [3] | 王志恒, 魏玉清, 赵延蓉, 王悦娟. 基于转录组学比较研究甜高粱幼苗响应干旱和盐胁迫的生理特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 71-84. |
| [4] | 陈倩, 徐晓芸, 汪军成, 姚立蓉, 司二静, 杨轲, 韦晓玲, 马小乐, 李葆春, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄, 王化俊. 基于全长转录组的盐生草WRKY基因家族的鉴定及其盐胁迫响应模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 146-157. |
| [5] | 张鹏, 任茜, 孟思宇, 魏小星, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对盐胁迫下紫花针茅种子萌发和幼苗生长的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 110-121. |
| [6] | 陆安桥, 张峰举, 许兴, 王学琴, 姚姗. 盐胁迫对湖南稷子苗期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 84-93. |
| [7] | 汪芳珍, 杨成行, 何子华, 林子茹, 曾浩源, 马清. 盐处理下旱生植物沙芥蛋白激酶相关基因的差异表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 116-124. |
| [8] | 田甜, 王海江, 王金刚, 朱永琪, 史晓艳, 李维弟, 李文瑞玉. 盐胁迫下施加氮素对饲用油菜有机渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [9] | 项洪涛, 郑殿峰, 何宁, 李琬, 王曼力, 王诗雅. 植物对低温胁迫的生理响应及外源脱落酸缓解胁迫效应的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 208-219. |
| [10] | 王苗苗, 周向睿, 梁国玲, 赵桂琴, 焦润安, 柴继宽, 高雪梅, 李娟宁. 5份燕麦材料苗期耐盐性综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 143-154. |
| [11] | 黄勇, 郭猛, 张红瑞, 周艳, 李贺敏, 高致明, 王盼盼. 盐胁迫对石竹种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 105-111. |
| [12] | 王桔红, 史生晶, 陈文, 甘桂媚, 陈赛娜, 李张伟. 枯草芽孢杆菌和3种放线菌对盐胁迫下鬼针草和鳢肠种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 112-120. |
| [13] | 何建军, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 边秀秀, 司二静, 杨轲, 王化俊, 马小乐, 李葆春, 尚勋武, 孟亚雄. 干旱和盐胁迫对盐生植物盐生草种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 129-140. |
| [14] | 李珍, 云岚, 石子英, 王俊, 张晨, 郭宏宇, 盛誉. 盐胁迫对新麦草种子萌发及幼苗期生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 119-129. |
| [15] | 伍国强, 李辉, 雷彩荣, 蔺丽媛, 金娟, 李善家. 添加KCl对高盐胁迫下红豆草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 45-55. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||