
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 94-110.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023379
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ya-jing MENG( ), Guo-qiang WU(
), Guo-qiang WU( ), Ming WEI
), Ming WEI
Received:2023-10-11
Revised:2023-12-04
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-06-20
Contact:
Guo-qiang WU
Ya-jing MENG, Guo-qiang WU, Ming WEI. Genome-wide identification of the Beta vulgaris ABF (BvABF) gene family and analysis of the expression pattern in sugar beet under ABA treatment[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 94-110.
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) | 反向引物 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | GCCGAATACCTTGCTTGATGCT | 58.2 | GAATTTCCGCATCCTCGCCAT | 58.4 |
| BvABF2 | CTCAATTGGCAGTTTCAACCAC | 54.7 | CTCAACAGTCTTCTCGACCAC | 55.4 |
| BvABF3 | CTGGAGTTGGAAGTTGTCCAATA | 54.3 | AGCATGGCGTTTTCTTTCGTT | 49.3 |
| BvABF4 | AATGCACAATTAAAGCAAGCC | 51.6 | GCCCTGCTTAGTATTACCTGT | 54.0 |
| BvABF5 | ACTACCTAGGACGCTTAGTCA | 54.2 | GTGATCTCCCCAAGTGTCTG | 55.4 |
| BvABF6 | CTGTGTGATAAGCCCAATTCG | 53.8 | AATTCATTGTGGTAAGCCTGT | 51.5 |
| BvACTIN | ACTGGTATTGTGCTTGACTC | 51.9 | ATGAGATAATCAGTGAGATC | 44.8 |
Table 1 The primers used in this study
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物 Forward primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) | 反向引物 Reverse primer sequence (5′-3′) | 溶解温度 Melting temperature (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | GCCGAATACCTTGCTTGATGCT | 58.2 | GAATTTCCGCATCCTCGCCAT | 58.4 |
| BvABF2 | CTCAATTGGCAGTTTCAACCAC | 54.7 | CTCAACAGTCTTCTCGACCAC | 55.4 |
| BvABF3 | CTGGAGTTGGAAGTTGTCCAATA | 54.3 | AGCATGGCGTTTTCTTTCGTT | 49.3 |
| BvABF4 | AATGCACAATTAAAGCAAGCC | 51.6 | GCCCTGCTTAGTATTACCTGT | 54.0 |
| BvABF5 | ACTACCTAGGACGCTTAGTCA | 54.2 | GTGATCTCCCCAAGTGTCTG | 55.4 |
| BvABF6 | CTGTGTGATAAGCCCAATTCG | 53.8 | AATTCATTGTGGTAAGCCTGT | 51.5 |
| BvACTIN | ACTGGTATTGTGCTTGACTC | 51.9 | ATGAGATAATCAGTGAGATC | 44.8 |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 位置 Locus | CDS (bp) | 蛋白长度 Protein length (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | Bv1_011670_nwdc | Bvchr1.sca004:3786136..3794120(-) | 813 | 270 | 29.49 | 5.55 | -0.607 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF2 | Bv3_064480_rnwf | Bvchr3.sca011:690504..695203(-) | 1002 | 333 | 36.54 | 9.27 | -0.807 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF3 | Bv6_134230_aref | Bvchr6.sca003:2686565..2693985(+) | 723 | 240 | 26.69 | 9.35 | -0.697 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF4 | Bv7_159570_afnu | Bvchr7.sca001:3838771..3848492(-) | 1356 | 451 | 49.19 | 8.30 | -0.793 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF5 | Bv7_169340_mcdu | Bvchr7.sca021:1716062..1720374(-) | 1470 | 489 | 51.59 | 9.49 | -0.655 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF6 | Bv9_207080_uszh | Bvchr9.sca010:874741..883695(+) | 795 | 264 | 29.46 | 6.92 | -0.653 | 细胞核Nucleus |
Table 2 Identification of BvABF gene family members in sugar beet
基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 位置 Locus | CDS (bp) | 蛋白长度 Protein length (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | GRAVY | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | Bv1_011670_nwdc | Bvchr1.sca004:3786136..3794120(-) | 813 | 270 | 29.49 | 5.55 | -0.607 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF2 | Bv3_064480_rnwf | Bvchr3.sca011:690504..695203(-) | 1002 | 333 | 36.54 | 9.27 | -0.807 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF3 | Bv6_134230_aref | Bvchr6.sca003:2686565..2693985(+) | 723 | 240 | 26.69 | 9.35 | -0.697 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF4 | Bv7_159570_afnu | Bvchr7.sca001:3838771..3848492(-) | 1356 | 451 | 49.19 | 8.30 | -0.793 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF5 | Bv7_169340_mcdu | Bvchr7.sca021:1716062..1720374(-) | 1470 | 489 | 51.59 | 9.49 | -0.655 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| BvABF6 | Bv9_207080_uszh | Bvchr9.sca010:874741..883695(+) | 795 | 264 | 29.46 | 6.92 | -0.653 | 细胞核Nucleus |
| 基序Motif | 序列长度Sequence length (aa) | 基序序列Motif sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | 49 | VDKVVERRQKRMIKNRESAARSRARKQAYTVELESEVSQLEEENEELRK |
| Motif 2 | 45 | RQVSIYSLTLDEFQNTLGGLGKDFGSMNMDEFLKNIWTAEENQSV |
| Motif 3 | 26 | SLPRQGSLTLPRHLSRKTVDEVWREI |
| Motif 4 | 24 | PKRZATLGEMTLEDFLVKAGVVRE |
| Motif 5 | 12 | KYQLRRTSSAPF |
| Motif 6 | 10 | PPPHQHPPHH |
| Motif 7 | 11 | MTAFIDGHHNP |
| Motif 8 | 6 | FFAFDN |
| Motif 9 | 6 | NHIDEN |
| Motif 10 | 9 | TKECFKQQM |
Table 3 Sequence information of 10 conserved motifs of BvABF in sugar beet
| 基序Motif | 序列长度Sequence length (aa) | 基序序列Motif sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | 49 | VDKVVERRQKRMIKNRESAARSRARKQAYTVELESEVSQLEEENEELRK |
| Motif 2 | 45 | RQVSIYSLTLDEFQNTLGGLGKDFGSMNMDEFLKNIWTAEENQSV |
| Motif 3 | 26 | SLPRQGSLTLPRHLSRKTVDEVWREI |
| Motif 4 | 24 | PKRZATLGEMTLEDFLVKAGVVRE |
| Motif 5 | 12 | KYQLRRTSSAPF |
| Motif 6 | 10 | PPPHQHPPHH |
| Motif 7 | 11 | MTAFIDGHHNP |
| Motif 8 | 6 | FFAFDN |
| Motif 9 | 6 | NHIDEN |
| Motif 10 | 9 | TKECFKQQM |
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 Alpha helix (%) | β-折叠 Beta fold (%) | β-转角 Beta turn (%) | 无规卷曲 Random coil (%) | 二级结构组成分布 Distribution of secondery structure elements (aa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | 55.93 | 15.19 | 2.22 | 26.67 | 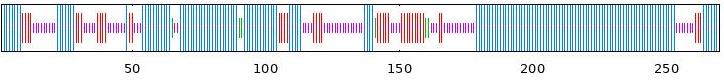 |
| BvABF2 | 33.03 | 6.91 | 1.20 | 58.86 | 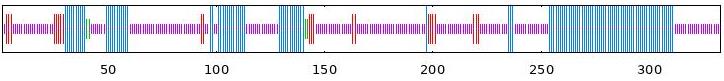 |
| BvABF3 | 30.83 | 7.08 | 0.00 | 62.08 |  |
| BvABF4 | 33.48 | 5.99 | 1.33 | 59.20 | 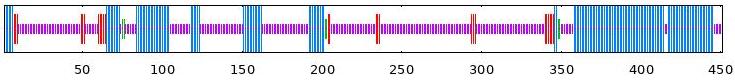 |
| BvABF5 | 26.99 | 10.84 | 2.25 | 59.92 | 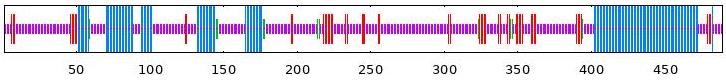 |
| BvABF6 | 44.32 | 4.92 | 2.65 | 48.11 |  |
Table 4 Prediction of secondary structure of the BvABF proteins in sugar beet
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋 Alpha helix (%) | β-折叠 Beta fold (%) | β-转角 Beta turn (%) | 无规卷曲 Random coil (%) | 二级结构组成分布 Distribution of secondery structure elements (aa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | 55.93 | 15.19 | 2.22 | 26.67 |  |
| BvABF2 | 33.03 | 6.91 | 1.20 | 58.86 |  |
| BvABF3 | 30.83 | 7.08 | 0.00 | 62.08 |  |
| BvABF4 | 33.48 | 5.99 | 1.33 | 59.20 |  |
| BvABF5 | 26.99 | 10.84 | 2.25 | 59.92 |  |
| BvABF6 | 44.32 | 4.92 | 2.65 | 48.11 |  |
基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义替换 Non-synonymous substitution (dN) | 同义替换 Synonymous substitution (dS) | dN/dS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | BvABF2 | 0.6972 | 27.9790 | 0.0249 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF3 | 0.8324 | 6.9155 | 0.1204 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF4 | 0.6323 | 60.5700 | 0.0104 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF5 | 0.5167 | 54.6018 | 0.0095 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF6 | 0.7298 | 58.7015 | 0.0124 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF3 | 0.7702 | 10.6805 | 0.0721 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF4 | 0.5773 | 31.4895 | 0.0183 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF5 | 0.5274 | 23.5223 | 0.0224 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF6 | 0.4581 | 3.1932 | 0.1434 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF4 | 0.6850 | 53.4818 | 0.0128 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF5 | 0.7556 | 55.0648 | 0.0137 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF6 | 0.9365 | 64.0495 | 0.0146 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF5 | 0.6265 | 23.8488 | 0.0263 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF6 | 0.5877 | 55.3501 | 0.0106 |
| BvABF5 | BvABF6 | 0.5938 | 60.9069 | 0.0097 |
Table 5 The ratio of dN and dS of the BvABF genes in sugar beet
基因1 Gene 1 | 基因2 Gene 2 | 非同义替换 Non-synonymous substitution (dN) | 同义替换 Synonymous substitution (dS) | dN/dS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BvABF1 | BvABF2 | 0.6972 | 27.9790 | 0.0249 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF3 | 0.8324 | 6.9155 | 0.1204 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF4 | 0.6323 | 60.5700 | 0.0104 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF5 | 0.5167 | 54.6018 | 0.0095 |
| BvABF1 | BvABF6 | 0.7298 | 58.7015 | 0.0124 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF3 | 0.7702 | 10.6805 | 0.0721 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF4 | 0.5773 | 31.4895 | 0.0183 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF5 | 0.5274 | 23.5223 | 0.0224 |
| BvABF2 | BvABF6 | 0.4581 | 3.1932 | 0.1434 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF4 | 0.6850 | 53.4818 | 0.0128 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF5 | 0.7556 | 55.0648 | 0.0137 |
| BvABF3 | BvABF6 | 0.9365 | 64.0495 | 0.0146 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF5 | 0.6265 | 23.8488 | 0.0263 |
| BvABF4 | BvABF6 | 0.5877 | 55.3501 | 0.0106 |
| BvABF5 | BvABF6 | 0.5938 | 60.9069 | 0.0097 |
| 1 | Zhang H M, Zhu J H, Gong Z Z, et al. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2022, 23(2): 104-119. |
| 2 | Yoshida T, Mogami J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling in response to osmotic stress in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2014, 21: 133-139. |
| 3 | Soma F, Takahashi F, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, et al. Cellular phosphorylation signaling and gene expression in drought stress responses: ABA-dependent and ABA-independent regulatory systems. Plants, 2021, 10(4): 756. |
| 4 | Choi H, Hong J, Ha J, et al. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(3): 1723-1730. |
| 5 | Zhao G Y, Cheng Q, Zhao Y T, et al. The abscisic acid-responsive element binding factors MAPKKK18 module regulates abscisic acid-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2023, 299(4): 103060. |
| 6 | Yu Z D, Ding F, Feng Y R, et al. ABA promotes sulfite stress tolerance by ABF4-mediated upregulation of SOX expression. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 203: 105070. |
| 7 | Zhang C W, Zhou Q, Liu W S, et al. BrABF3 promotes flowering through the direct activation of CONSTANS transcription in pak choi. The Plant Journal, 2022, 111(1): 134-148. |
| 8 | Zeng Z, Lyu T, Lyu Y M. LoSWEET14, a sugar transporter in lily, is regulated by transcription factor LoABF2 to participate in the ABA signaling pathway and enhance tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in tobacco. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(23): 15093. |
| 9 | Song J, Sun P P, Kong W N, et al. SnRK2.4-mediated phosphorylation of ABF2 regulates ARGININE DECARBOXYLASE expression and putrescine accumulation under drought stress. New Phytologist, 2023, 238(1): 216-236. |
| 10 | Wu L, Liu X, Zhang M Y, et al. Self S-RNase inhibits ABF-LRX signaling to arrest pollen tube growth to achieve self-incompatibility in pear. The Plant Journal, 2023, 113(3): 595-609. |
| 11 | Hou Z H, Zhang X Z, Tang Y M, et al. GmSAP5, a soybean A20/AN1 domain-containing stress-associated protein gene activated by GmAREB3, increases drought stress resistance in soybean by mediating ABA signaling. The Crop Journal, 2022, 10(6): 1601-1610. |
| 12 | Zhang H J, Mao L L, Xin M, et al. Overexpression of GhABF3 increases cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) tolerance to salt and drought. BMC Plant Biology, 2022, 22(1): 313. |
| 13 | Yang Q S, Wu X Y, Gao Y H, et al. PpyABF3 recruits the COMPASS-like complex to regulate bud dormancy maintenance via integrating ABA signaling and GA catabolism. New Phytologist, 2023, 237(1): 192-203. |
| 14 | Kou S, Chen Y, Liu T T, et al. Crosstalk of putrescine synthetic pathway with abscisic acid signaling pathway in cold tolerance of potato. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 204: 105085. |
| 15 | Cheng H K, Pan G Y, Zhou N, et al. Calcium-dependent protein kinase 5 (CPK5) positively modulates drought tolerance through phosphorylating ABA-responsive element binding factors in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant Science, 2021, 315: 111125. |
| 16 | Wei X B, Wei X P, Guan W L, et al. ABA-responsive transcription factor ABF1-1 promotes JA biosynthesis to accelerate suberin polyphenolic formation in wounded kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis). Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2022, 187: 111850. |
| 17 | Jiang Y Q, Wu X, Shi M, et al. The miR159‐MYB33‐ABI5 module regulates seed germination in Arabidopsis. Physiologia Plantarum, 2022, 174(2): e13659. |
| 18 | Chang H C, Tsai M C, Wu S S, et al. Regulation of ABI5 expression by ABF3 during salt stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Botanical Studies, 2019, 60(1): 16. |
| 19 | Finkelstein R, Gampala S S L, Lynch T J, et al. Redundant and distinct functions of the ABA response loci ABA-INSENSITIVE (ABI) 5 and ABRE-BINDING FACTOR (ABF) 3. Plant Molecular Biology, 2005, 59(2): 253-267. |
| 20 | Fernando V C D, Khateeb W A, Belmonte M F, et al. Role of Arabidopsis ABF1/3/4 during det1 germination in salt and osmotic stress conditions. Plant Molecular Biology, 2018, 97(1/2): 149-163. |
| 21 | Kobayashi F, Maeta E, Terashima A, et al. Positive role of a wheat HvABI5 ortholog in abiotic stress response of seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 2008, 134(1): 74-86. |
| 22 | Huang X S, Liu J H, Chen X J. Overexpression of PtrABF gene, a bZIP transcription factor isolated from Poncirus trifoliata, enhances dehydration and drought tolerance in tobacco via scavenging ROS and modulating expression of stress-responsive genes. BMC Plant Biology, 2010, 10: 230. |
| 23 | Xu Z J, Wang F, Ma Y B, et al. Transcription factor SlAREB1 is involved in the antioxidant regulation under saline-alkaline stress in tomato. Antioxidants, 2022, 11(9): 1673. |
| 24 | Kim S Y. The role of ABF family bZIP class transcription factors in stress response. Physiologia Plantarum, 2006, 126(4): 519-527. |
| 25 | Mirzaei K, Bahramnejad B, Fatemi S. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bZIP gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Gene, 2020, 24: 100257. |
| 26 | Fiallos-Salguero M S, Li J, Li Y, et al. Identification of AREB/ABF gene family involved in the response of ABA under salt and drought stresses in jute (Corchorus olitorius L.). Plants, 2023, 12(5): 1161. |
| 27 | Ji L X, Wang J, Ye M X, et al. Identification and characterization of the Populus AREB/ABF subfamily. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2013, 55(2): 177-186. |
| 28 | Pan X J, Wang C L, Liu Z S, et al. Identification of ABF/AREB gene family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and functional analysis of ABF/AREB in response to ABA and abiotic stresses. PeerJ, 2023, 11: e15310. |
| 29 | Rui L, Yang Y Y, Zheng P F, et al. Genome-wide analysis of MdABF subfamily and functional identification of MdABF1 in drought tolerance in apple. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 199: 104904. |
| 30 | Liu X J, Cheng R W, Chen Y, et al. Identification and characterization of the AREB/ABF/ABI5 gene family in sandalwood (Santalum album L.) and its potential role in drought stress and ABA treatment. Forests, 2023, 14(8): 1691. |
| 31 | Guo S J, Sun Y, Zheng H Y, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of ABF/AREB/ ABI5 gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2023, 31(4): 667-681. |
| 郭树娟, 孙月, 郑昊元, 等. 小麦ABF/AREB/ABI5基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 2023, 31(4): 667-681. | |
| 32 | Zhang H F, Liu W Z, Zhang Y P, et al. Identification, expression and interaction analyses of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CPK) genes in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 211. |
| 33 | Yong X, Zheng T C, Zhuo X K, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterisation, and evolution of ABF/AREB subfamily in nine Rosaceae species and expression analysis in mei (Prunus mume). PeerJ, 2021, 9: e10785. |
| 34 | Que F, Wang G L, Huang Y, et al. Genomic identification of group A bZIP transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stress in carrot. Genetics and Molecular Research, 2015, 14(4): 13274-13288. |
| 35 | Kerr T C C, Abdel-Mageed H, Kang M Y, et al. Functional characterization of the ABF gene family in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). bioRxiv, 2017: 186015. |
| 36 | Zandkarimi H, Ebadi A, Salami S A, et al. Analyzing the expression profile of AREB/ABF and DREB/CBF genes under drought and salinity stresses in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0134288. |
| 37 | Vysotskii D A, de Vries-van Leeuwen I J, Souer E, et al. ABF transcription factors of Thellungiella salsuginea: structure, expression profiles and interaction with 14-3-3 regulatory proteins. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2013, 8(1): e22672. |
| 38 | Hu H B. Study of high yield and high efficiency cultivation technology of sugar beet in Xinjiang. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2014. |
| 胡华兵. 新疆甜菜高产高效种植技术研究. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2014. | |
| 39 | Yolcu S, Alavilli H, Ganesh P, et al. An insight into the abiotic stress responses of cultivated beets (Beta vulgaris L.). Plants, 2021, 11(1): 12. |
| 40 | Skorupa M, Gołębiewski M, Kurnik K, et al. Salt stress vs. salt shock-the case of sugar beet and its halophytic ancestor. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 57. |
| 41 | Dohm J C, Minoche A E, Holtgräwe D, et al. The genome of the recently domesticated crop plant sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Nature, 2014, 505(7484): 546-549. |
| 42 | Wu G Q, Li Z Q, Cao H, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the WRKY genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under alkaline stress. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e7817. |
| 43 | Yang X H, Wu G Q, Wei M, et al. Genome-wide identification of BvHAK gene family in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) and their expression analysis under salt treatments. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 38(10): 3773-3789. |
| 杨小涵, 伍国强, 魏明, 等. 甜菜 BvHAK 基因家族全基因组鉴定及其在盐处理下的表达分析. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(10): 3773-3789. | |
| 44 | Wu G Q, Liu Z X, Xie L L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the BvSnRK2 genes family in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under salt conditions. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 40: 519-532. |
| 45 | Genies L, Orjollet D, Carasco L, et al. Uptake and translocation of cesium by Arabidopsis thaliana in hydroponics conditions: Links between kinetics and molecular mechanisms. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 138: 164-172. |
| 46 | Guan R, Xu S, Lu Z M, et al. Genomic characterization of bZIP transcription factors related to andrographolide biosynthesis in Andrographis paniculata. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 223(Pt A): 1619-1631. |
| 47 | Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D412-D419. |
| 48 | Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P. SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D458-D460. |
| 49 | Lu S N, Wang J Y, Chitsaz F, et al. CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Research, 2020, 48(D1): D265-D268. |
| 50 | Waterhouse A M, Procter J B, Martin D M A, et al. Jalview Version 2——a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(9): 1189-1191. |
| 51 | Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, et al. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2018, 35(6): 1547. |
| 52 | Subramanian B, Gao S, Lercher M J, et al. Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(W1): W270-W275. |
| 53 | Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, et al. ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, 31(13): 3784-3788. |
| 54 | Chou K C, Shen H B. Plant-mPLoc: a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS One, 2010, 5(6): e11335. |
| 55 | Hu B, Jin J P, Guo A Y, et al. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics, 2015, 31(8): 1296-1297. |
| 56 | Jing Z B, Fu H Q. Identification of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor and analysis of expression responses to biotic and abiotic stresses in kiwifruit (Actinidia lind L.). European Journal of Horticultural Science, 2018, 83(4): 212-223. |
| 57 | Bailey T L, Williams N, Misleh C, et al. MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, 34(suppl_2): W369-W373. |
| 58 | Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194-1202. |
| 59 | Tu M X, Wang X H, Huang L, et al. Expression of a grape bZIP transcription factor, VqbZIP39, in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana confers tolerance of multiple abiotic stresses. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 2016, 125: 537-551. |
| 60 | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, 30(1): 325-327. |
| 61 | Goldman N, Yang Z. A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1994, 11(5): 725-736. |
| 62 | Cao H L, Wang L, Yue C, et al. Isolation and expression analysis of 18 CsbZIP genes implicated in abiotic stress responses in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2015, 97: 432-442. |
| 63 | Szklarczyk D, Gable A L, Nastou K C, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Research, 2021, 49(D1): D605-D612. |
| 64 | Wu G Q, Xie L L, Wang J L, et al. Genome-wide identification of CIPK genes in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) and their expression under NaCl stress. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2022, 42(1): 260-274. |
| 65 | Swift M L. GraphPad prism, data analysis, and scientific graphing. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1997, 37(2): 411-412. |
| 66 | Schwechheimer C, Bevan M. The regulation of transcription factor activity in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 1998, 3(10): 378-383. |
| 67 | Samad A F A, Sajad M, Nazaruddin N, et al. MicroRNA and transcription factor: key players in plant regulatory network. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 565. |
| 68 | Jakoby M, Weisshaar B, Dröge-Laser W, et al. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends in Plant Science, 2002, 7(3): 106-111. |
| 69 | Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Reports, 2013, 32(3): 959-970. |
| 70 | Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, et al. Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8(120): 161. |
| 71 | Raghavendra A S, Gonugunta V K, Christmann A, et al. ABA perception and signaling. Trends in Plant Science, 2010, 15(7): 395-401. |
| 72 | Kang J, Choi H, Im M, et al. Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper proteins that mediate stress-responsive abscisic acid signaling. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(2): 343-357. |
| 73 | Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, et al. Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2000, 97(21): 11632-11637. |
| 74 | Hsieh T H, Li C W, Su R C, et al. A tomato bZIP transcription factor, SlAREB, is involved in water deficit and salt stress response. Planta, 2010, 231(6): 1459-1473. |
| 75 | Hong L, Hu B, Liu X, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a new stress-related AREB gene from Arachis hypogaea. Biologia Plantarum, 2013, 57(1): 56-62. |
| 76 | Wang J Y, Li Q, Mao X G, et al. Wheat transcription factor TaAREB3 participates in drought and freezing tolerances in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2016, 12(2): 257-269. |
| 77 | Schindler U, Menkens A E, Beckmann H, et al. Heterodimerization between light-regulated and ubiquitously expressed Arabidopsis GBF bZIP proteins. The EMBO Journal, 1992, 11(4): 1261-1273. |
| 78 | Nijhawan A, Jain M, Tyagi A K, et al. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiology, 2008, 146(2): 333-350. |
| 79 | Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Sayama H, et al. AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. The Plant Journal, 2010, 61(4): 672-685. |
| 80 | Bensmihen S, Rippa S, Lambert G, et al. The homologous ABI5 and EEL transcription factors function antagonistically to fine-tune gene expression during late embryogenesis. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(6): 1391-1403. |
| 81 | Chinnusamy V, Novella S R, Park S Y, et al. In vitro reconstitution of an ABA signaling pathway. Nature, 2009, 462(7273): 660-664. |
| 82 | Furihata T, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, et al. Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2006, 103(6): 1988-1993. |
| 83 | Li H L, Duan L H, Fang S M, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of AREB1 from red bean and kidney bean. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(8): 1559-1564. |
| 李海龙, 段立华, 方淑梅, 等. 红小豆与芸豆AREB1基因生物信息学分析. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(8): 1559-1564. | |
| 84 | Amparo R D, Branco C, Arenas J, et al. Analysis of selection in protein-coding sequences accounting for common biases. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2021, 22(5): bbaa431. |
| 85 | Zhang J Z. Positive selection, not negative selection, in the pseudogenization of rcsA in Yersinia pestis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 2008, 105(42): E69-E70. |
| 86 | Kim S Y, Thomas T L. A family of novel basic leucine zipper proteins binds to seed-specification elements in the carrot Dc3 gene promoter. Journal of Plant Physiology, 1998, 152(6): 607-613. |
| 87 | Kim S Y, Chung H J, Thomas T L. Isolation of a novel class of bZIP transcription factors that interact with ABA-responsive and embryo-specification elements in the Dc3 promoter using a modified yeast one-hybrid system. The Plant Journal, 1997, 11(6): 1237-1251. |
| 88 | Fode B, Siemsen T, Thurow C, et al. The Arabidopsis GRAS protein SCL14 interacts with class Ⅱ TGA transcription factors and is essential for the activation of stress-inducible promoters. The Plant Cell, 2008, 20(11): 3122-3135. |
| 89 | Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu J K. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(10): 444-451. |
| 90 | Chen W J, Zhu T. Networks of transcription factors with roles in environmental stress response. Trends in Plant Science, 2004, 9(12): 591-596. |
| 91 | Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiologia Plantarum, 2013, 147(1): 15-27. |
| 92 | Hossain M A, Cho J I, Han M, et al. The ABRE-binding bZIP transcription factor OsABF2 is a positive regulator of abiotic stress and ABA signaling in rice. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2010, 167(17): 1512-1520. |
| [1] | Li-fen HAO, Xiao-yang XU, Yu JI, Rui WANG, De-bao WU, Yu-yu LI, Ke-jian LIN. Comparison of the dynamic morphological and physiological characteristics of twin seeds during the germination of field sandbur [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(9): 40-50. |
| [2] | Jin-zhu GAO, Dong-hao ZHAO, Le GAO, Xi-hao SU, Xue-qing HE. Effects of cerium nitrate and abscisic acid treatment on alfalfa seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [3] | Shi-yang ZHANG, Feng-min LIU, Jun-tao CUI, Lei HE, Yue-yan FENG, Wei-li ZHANG. Effects of three exogenous substances on the physiological and fluorescence characteristics of Stylosanthes guianensis under low-temperature stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 85-99. |
| [4] | Yan-peng LI, Na WEI, Qing-yan ZHAI, Hang LI, Ji-yu ZHANG, Wen-xian LIU. Genome-wide identification of members of the TCP gene family in Melilotus albus and their expression patterns under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 101-111. |
| [5] | Zhen-song LI, Li-qiang WAN, Shuo LI, Xiang-lin LI. Response of alfalfa root architecture and physiological characteristics to drought and rehydration [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 189-196. |
| [6] | Hong-tao XIANG, Dian-feng ZHENG, Ning HE, Wan LI, Man-li WANG, Shi-ya WANG. Research progress on the physiological response of plants to low temperature and the amelioration effcectiveness of exogenous ABA [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 208-219. |
| [7] | CUI Xue-lian, XIA Chao. Effect of exogenous abscisic acid on seedling establishment of Epichloё gansuensis-Achnatherum inebrians symbiont [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(7): 70-80. |
| [8] | LI Si-zhong, ZHANG Li-ming, GAO Wei-shi, BAI Xiao-shan, LIU Jun, DONG Xin-jiu, YANG Hong-ze, SHA Hong, GAO Yan. Effects of re-watering after drought on leaf photosynthetic light response characteristics of sugar beet [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 198-204. |
| [9] | WU Guo-Qiang, FENG Rui-Jun, LI Shan-Jia, WANG Chun-Mei, JIAO Qi, LIU Hai-Long. Effects of salt treatments on growth and osmoregulatory substance accumulation in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(4): 169-177. |
| [10] | LI Yue, WAN Li-Qiang, LI Xiang-Lin. Progress in understanding relationships between the physiological mechanisms of endogenous abscisic acid and drought resistance of alfalfa [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(11): 195-205. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jia-ning,LIU Kun. Mechanisms for plants detecting the optimum time and place to germinate [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(1): 328-338. |
| [12] | XU Chun-bo, MI Fu-gui, WANG Yong, LI Xing-you, ZHAO Hai-xia. Factors influencing plant regeneration systems in mature embryo culture of Agropyron [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 18(1): 80-85. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||