
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 174-183.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024516
Qin-lin SUN1,2( ), Tian-xing WEI1,2(
), Tian-xing WEI1,2( ), Hao LI3, Xiao-man YE1,2, Ling ZHU1,2
), Hao LI3, Xiao-man YE1,2, Ling ZHU1,2
Received:2024-12-27
Revised:2025-03-12
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-10-09
Contact:
Tian-xing WEI
Qin-lin SUN, Tian-xing WEI, Hao LI, Xiao-man YE, Ling ZHU. Allelopathic effects of Hippophae rhamnoides leaf and root extracts on five plant species[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(11): 174-183.
受体植物 Receptor plant | 方差变异来源 ANOVA source | 种子萌发指标 Seed germination indicator | 幼苗生长指标 Seedling growth indicator | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发芽率Germination rate | 茎长Stem length | 根长Root length | 鲜重Fresh weight | ||
| 侧柏P. orientalis | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.685 |
| AD | <0.001 | 0.104 | 0.129 | 0.230 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | 0.354 | <0.001 | 0.354 | |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.288 |
| AD | <0.001 | 0.328 | <0.001 | 0.047 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.012 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.012 |
| AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.271 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | AP | 0.010 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 |
| AD | <0.001 | 0.987 | <0.001 | 0.003 | |
| AP×AD | 0.004 | 0.211 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
Table 1 Variance analysis (P) of the effects of different concentrations of H. rhamnoides leaf and root extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of 5 species of chestnut-irrigation plants
受体植物 Receptor plant | 方差变异来源 ANOVA source | 种子萌发指标 Seed germination indicator | 幼苗生长指标 Seedling growth indicator | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发芽率Germination rate | 茎长Stem length | 根长Root length | 鲜重Fresh weight | ||
| 侧柏P. orientalis | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.685 |
| AD | <0.001 | 0.104 | 0.129 | 0.230 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | 0.354 | <0.001 | 0.354 | |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.288 |
| AD | <0.001 | 0.328 | <0.001 | 0.047 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.012 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | AP | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.012 |
| AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.271 | |
| AP×AD | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | AP | 0.010 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 |
| AD | <0.001 | 0.987 | <0.001 | 0.003 | |
| AP×AD | 0.004 | 0.211 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
项目 Items | 受体植物 Receptor plant | 叶浸提液浓度Leaf extract concentration | 根浸提液浓度Root extract concentration | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0.1 g·L-1 | 0.5 g·L-1 | 1.0 g·L-1 | 2.5 g·L-1 | 5.0 g·L-1 | 10.0 g·L-1 | 0.1 g·L-1 | 0.5 g·L-1 | 1.0 g·L-1 | 2.5 g·L-1 | 5.0 g·L-1 | 10.0 g·L-1 | ||
发芽率 Germination rate | 侧柏P. orientalis | -0.140 | -0.211 | -0.070 | -0.158 | -0.105 | -0.096 | -0.096 | -0.053 | -0.193 | -0.149 | -0.167 | -0.088 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.000 | -0.163 | -0.138 | -0.110 | -0.080 | -0.110 | -0.100 | -0.050 | -0.090 | -0.180 | -0.170 | 0.024 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.160 | 0.357 | 0.370 | 0.492 | 0.563 | 0.344 | 0.380 | 0.400 | 0.330 | 0.232 | -0.111 | -0.429 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | -0.100 | -0.038 | -0.100 | -0.169 | 0.015 | 0.097 | 0.037 | -0.123 | -0.150 | -0.192 | 0.088 | -0.031 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | -0.302 | -0.295 | -0.257 | -0.267 | -0.270 | -0.333 | -0.393 | -0.310 | -0.460 | -0.298 | -0.413 | -0.413 | |
茎长 Stem length | 侧柏P. orientalis | -0.043 | -0.037 | -0.017 | 0.037 | 0.096 | 0.070 | -0.002 | -0.010 | 0.001 | 0.040 | 0.048 | 0.026 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | -0.128 | -0.203 | -0.111 | -0.074 | -0.047 | -0.027 | -0.204 | -0.132 | -0.021 | -0.050 | 0.009 | 0.034 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.081 | 0.106 | 0.140 | 0.095 | 0.072 | 0.007 | -0.066 | 0.053 | 0.093 | -0.032 | -0.178 | -0.151 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | 0.283 | 0.223 | 0.153 | 0.224 | 0.268 | 0.158 | 0.214 | 0.303 | 0.210 | 0.202 | 0.084 | 0.030 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | -0.048 | -0.151 | -0.281 | -0.225 | -0.347 | -0.303 | -0.147 | -0.128 | -0.208 | -0.258 | -0.269 | -0.331 | |
根长 Root length | 侧柏P. orientalis | -0.016 | -0.145 | -0.061 | 0.078 | 0.245 | 0.256 | 0.163 | 0.230 | 0.107 | 0.103 | 0.265 | 0.169 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.027 | -0.234 | -0.258 | -0.145 | -0.177 | -0.160 | -0.271 | -0.082 | -0.030 | 0.101 | 0.201 | 0.221 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.024 | 0.130 | 0.090 | -0.056 | -0.403 | -0.588 | -0.400 | -0.270 | -0.212 | -0.231 | -0.245 | -0.413 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | 0.259 | 0.360 | 0.192 | 0.103 | 0.077 | -0.070 | 0.113 | 0.106 | 0.197 | 0.045 | 0.014 | 0.041 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | -0.224 | -0.290 | -0.722 | -0.683 | -0.806 | -0.721 | -0.601 | -0.669 | -0.692 | -0.721 | -0.733 | -0.851 | |
鲜重 Fresh weight | 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.012 | 0.093 | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.066 | 0.110 | 0.070 | 0.084 | 0.087 | 0.045 | 0.068 | 0.056 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.013 | -0.222 | -0.128 | -0.087 | -0.172 | -0.122 | -0.260 | -0.047 | -0.067 | -0.081 | 0.042 | -0.012 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.144 | 0.138 | 0.171 | 0.160 | -0.046 | 0.032 | -0.047 | 0.158 | 0.074 | -0.015 | 0.006 | 0.083 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | 0.013 | 0.087 | 0.127 | 0.160 | 0.124 | 0.165 | 0.141 | 0.201 | 0.172 | 0.176 | 0.168 | -0.024 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | 0.007 | -0.047 | -0.082 | 0.067 | -0.039 | -0.016 | 0.085 | 0.065 | 0.015 | -0.016 | 0.005 | 0.167 | |
Table 2 Allelopathic effect index of different concentrations and different parts of H. rhamnoides extract on germination rate, stem length, root length and fresh weight of 5 species of chestnut-irrigation plants
项目 Items | 受体植物 Receptor plant | 叶浸提液浓度Leaf extract concentration | 根浸提液浓度Root extract concentration | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0.1 g·L-1 | 0.5 g·L-1 | 1.0 g·L-1 | 2.5 g·L-1 | 5.0 g·L-1 | 10.0 g·L-1 | 0.1 g·L-1 | 0.5 g·L-1 | 1.0 g·L-1 | 2.5 g·L-1 | 5.0 g·L-1 | 10.0 g·L-1 | ||
发芽率 Germination rate | 侧柏P. orientalis | -0.140 | -0.211 | -0.070 | -0.158 | -0.105 | -0.096 | -0.096 | -0.053 | -0.193 | -0.149 | -0.167 | -0.088 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.000 | -0.163 | -0.138 | -0.110 | -0.080 | -0.110 | -0.100 | -0.050 | -0.090 | -0.180 | -0.170 | 0.024 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.160 | 0.357 | 0.370 | 0.492 | 0.563 | 0.344 | 0.380 | 0.400 | 0.330 | 0.232 | -0.111 | -0.429 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | -0.100 | -0.038 | -0.100 | -0.169 | 0.015 | 0.097 | 0.037 | -0.123 | -0.150 | -0.192 | 0.088 | -0.031 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | -0.302 | -0.295 | -0.257 | -0.267 | -0.270 | -0.333 | -0.393 | -0.310 | -0.460 | -0.298 | -0.413 | -0.413 | |
茎长 Stem length | 侧柏P. orientalis | -0.043 | -0.037 | -0.017 | 0.037 | 0.096 | 0.070 | -0.002 | -0.010 | 0.001 | 0.040 | 0.048 | 0.026 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | -0.128 | -0.203 | -0.111 | -0.074 | -0.047 | -0.027 | -0.204 | -0.132 | -0.021 | -0.050 | 0.009 | 0.034 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.081 | 0.106 | 0.140 | 0.095 | 0.072 | 0.007 | -0.066 | 0.053 | 0.093 | -0.032 | -0.178 | -0.151 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | 0.283 | 0.223 | 0.153 | 0.224 | 0.268 | 0.158 | 0.214 | 0.303 | 0.210 | 0.202 | 0.084 | 0.030 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | -0.048 | -0.151 | -0.281 | -0.225 | -0.347 | -0.303 | -0.147 | -0.128 | -0.208 | -0.258 | -0.269 | -0.331 | |
根长 Root length | 侧柏P. orientalis | -0.016 | -0.145 | -0.061 | 0.078 | 0.245 | 0.256 | 0.163 | 0.230 | 0.107 | 0.103 | 0.265 | 0.169 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.027 | -0.234 | -0.258 | -0.145 | -0.177 | -0.160 | -0.271 | -0.082 | -0.030 | 0.101 | 0.201 | 0.221 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.024 | 0.130 | 0.090 | -0.056 | -0.403 | -0.588 | -0.400 | -0.270 | -0.212 | -0.231 | -0.245 | -0.413 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | 0.259 | 0.360 | 0.192 | 0.103 | 0.077 | -0.070 | 0.113 | 0.106 | 0.197 | 0.045 | 0.014 | 0.041 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | -0.224 | -0.290 | -0.722 | -0.683 | -0.806 | -0.721 | -0.601 | -0.669 | -0.692 | -0.721 | -0.733 | -0.851 | |
鲜重 Fresh weight | 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.012 | 0.093 | 0.036 | 0.046 | 0.066 | 0.110 | 0.070 | 0.084 | 0.087 | 0.045 | 0.068 | 0.056 |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.013 | -0.222 | -0.128 | -0.087 | -0.172 | -0.122 | -0.260 | -0.047 | -0.067 | -0.081 | 0.042 | -0.012 | |
| 刺槐R. pseudoacacia | 0.144 | 0.138 | 0.171 | 0.160 | -0.046 | 0.032 | -0.047 | 0.158 | 0.074 | -0.015 | 0.006 | 0.083 | |
| 柠条C. korshinskii | 0.013 | 0.087 | 0.127 | 0.160 | 0.124 | 0.165 | 0.141 | 0.201 | 0.172 | 0.176 | 0.168 | -0.024 | |
| 沙棘H. rhamnoides | 0.007 | -0.047 | -0.082 | 0.067 | -0.039 | -0.016 | 0.085 | 0.065 | 0.015 | -0.016 | 0.005 | 0.167 | |
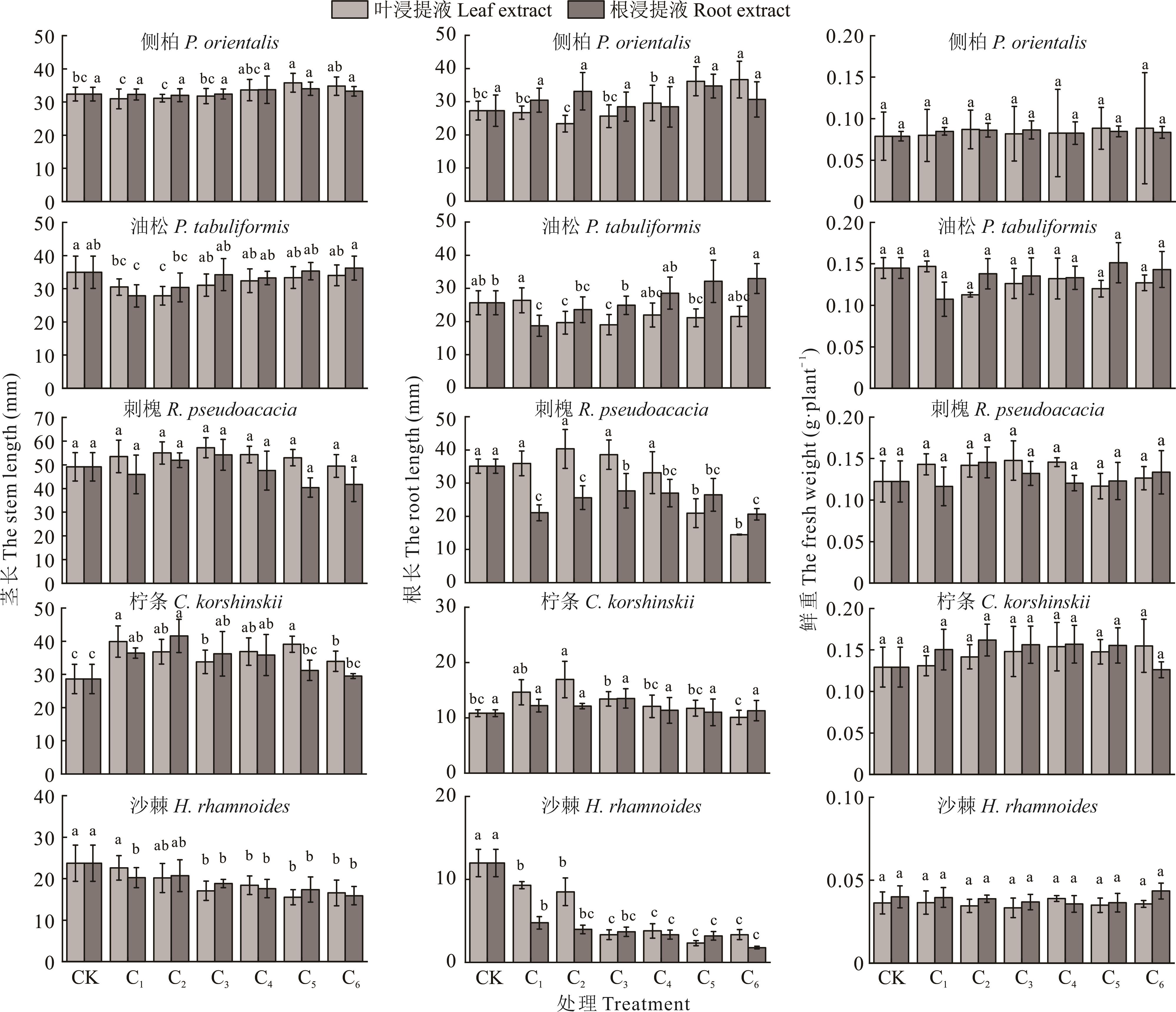
Fig.2 Effects of different concentrations of H. rhamnoides leaf and root extracts on stem length, root length, and fresh weight of 5 species of chestnut-irrigation plants
| [1] | Wang X Y, Li Y Q, Gong X W, et al. Storage, pattern and driving factors of soil organic carbon in an ecologically fragile zone of northern China. Geoderma, 2019, 343: 155-165. |
| [2] | Sun J F, Li G D, Zhang Y, et al. Identification of priority areas for afforestation in the Loess Plateau region of China. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 140: 108998. |
| [3] | Zhang X X, Liu Z W, Zhu Z H, et al. Impacts of mixed litter decomposition from Robinia pseudoacacia and other tree species on C loss and nutrient release in the Loess Plateau of China. Journal of Forestry Research, 2016, 27(3): 525-532. |
| [4] | Li H J, Niu X, Wang B, et al. Coupled coordination of ecosystem services and landscape patterns: Take the Grain for Green Project in the Wuling Mountain Area as an example. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(13): 4316-4326. |
| 李慧杰, 牛香, 王兵, 等. 生态系统服务功能与景观格局耦合协调度研究:以武陵山区退耕还林工程为例. 生态学报, 2020, 40(13): 4316-4326. | |
| [5] | Wang Z Y, Yu Q R, Guo L, et al. Quantifying the impact of the Grain-for-Green Program on ecosystem health in the typical agro-pastoral ecotone: A case study in the Xilin Gol League, Inner Mongolia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(16): 5631. |
| [6] | Liu Q F, Zhang Q, Yan Y Z, et al. Ecological restoration is the dominant driver of the recent reversal of desertification in the Mu Us Desert (China). Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 268: 122241. |
| [7] | Williams R A. Mitigating biodiversity concerns in Eucalyptus plantations located in South China. Journal of Biosciences and Medicines, 2015, 3: 1-8. |
| [8] | Sasikumar K, Vijayalakshmi C, Parthiban K T, et al. Allelopathic effects of four Eucalyptus species on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Tropical Forest Science, 2004, 16(4): 419-428. |
| [9] | Wang H Y, Liu J G, Yuan H C, et al. Effects of three extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica. Forest Engineering, 2023, 39(3): 30-39. |
| 王浩宇, 刘建功, 袁泓昌, 等. 3种浸提液对樟子松种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 森林工程, 2023, 39(3): 30-39. | |
| [10] | Yang S Y, Wang J R, Zhu Y Y, et al. Effects of mixed plantation of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Phoebe chekiangensis on root exudates and community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2024, 60(9): 59-68. |
| 杨淑雅, 王镜如, 朱滢滢, 等. 杉木与浙江楠混交对根系分泌物和丛枝菌根真菌群落结构的影响. 林业科学, 2024, 60(9): 59-68. | |
| [11] | Liu Z L, Wang Q C, Hao L F. Interspecific allelopathic effect of different organs, aqueous extracts of Betula platyphylla and Larix olgensis on their seed germination and seedling growth. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(12): 3138-3144. |
| 刘忠玲, 王庆成, 郝龙飞. 白桦、落叶松不同器官水浸液对种子萌发和播种苗生长的种间化感作用. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(12): 3138-3144. | |
| [12] | Yang L X, Wang P, Kong C H, et al. Effect of larch (Larix gmelini Rupr.) root exudates on manchurian walnut (Juglans mandshurica Maxim.) growth and soil juglone in a mixed-species plantation. Plant and Soil, 2010, 329(1/2): 249-258. |
| [13] | Xu Y, Chen X, Ding L, et al. Allelopathy and allelochemicals in grasslands and forests. Forests, 2023, 14(3): 562. |
| [14] | Reigosa M J, Pedrol N, Conzalez L, et al. Allelopathy: A physiological process with ecological implications. Dordrecht: Springer, 2006. |
| [15] | Lin X, Li X R, Li C Y, et al. Allelopathic effects of water leaching from different parts and rhizosphere soil on seed germination and seedling growth of Radix astragali. Chinese Traditional Medicine, 2024(4): 833-838. |
| 林鑫, 李昕蓉, 李成义, 等. 红芪不同部位及根际土水浸液对其种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感作用. 中药材, 2024(4): 833-838. | |
| [16] | Deng W H, Zhao X R, Zhang J Q, et al. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from Artemisia ordosica on four associated herbaceous plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(15): 5670-5678. |
| 邓文红, 赵欣蕊, 张俊琦, 等. 沙蒿(Artemisia ordosica)水浸提液对4种伴生草本植物的化感作用. 生态学报, 2019, 39(15): 5670-5678. | |
| [17] | Wang Y T, Geng G. Allelopathy between plants and its research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(23): 17-22. |
| 王月彤, 耿贵. 植物间化感作用及其研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(23): 17-22. | |
| [18] | Fan J B, Xia J F, Yuan C P, et al. Study and experiences on seabuckthorn plantation and management in Mu Us Sandy Land. International Sea Buckthorn Research and Development, 2008, 6(3): 28-30. |
| 范军波, 夏静芳, 袁成平, 等. 毛乌素沙地人工种植沙棘及管理经验浅谈. 国际沙棘研究与开发, 2008, 6(3): 28-30. | |
| [19] | Wang X, Bi Y L, Wang Y, et al. Effects of planting density of Hippophae rhamnoides and inoculation of AMF on understory vegetation growth and soil improvement. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2023, 59(10): 138-149. |
| 王晓, 毕银丽, 王义, 等. 沙棘林密度和丛枝菌根真菌接种对林下植物和土壤性状的影响. 林业科学, 2023, 59(10): 138-149. | |
| [20] | Zhou W J, Wei T X, Liu G Q, et al. Coupling relationship between Hippophae rhamnoides community and soil factor in typical returning farmland to forest area in northern Shaanxi Province. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 18(2): 1-9. |
| 周文洁, 魏天兴, 刘广全, 等. 陕北典型退耕地沙棘群落与土壤因子的耦合关系. 中国水土保持科学, 2020, 18(2): 1-9. | |
| [21] | Wang X, Wei T X, Zhu J Z, et al. Allelopathic effect of Pinus tabuliformis root in loess hilly area. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2015, 37(4): 82-89. |
| 王仙, 魏天兴, 朱金兆, 等. 黄土丘陵区油松根系化感效应研究. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(4): 82-89. | |
| [22] | Zhu L, Wei T X, Yu H, et al. Allelopathic potential of Robinia pseudoacacia root system and rhizosphere soil on 7 species of arbor, shrub, and grass plants. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(9): 1406-1415. |
| 朱玲, 魏天兴, 于欢, 等. 刺槐根系和根际土对7种乔灌草植物的化感潜力. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1406-1415. | |
| [23] | Ma S W, Guo J Y, Lan D M, et al. Study on community restoration characteristics of different conversions of croplands to forestlands in Wuqi County. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 23(6): 204-209. |
| 马少薇, 郭建英, 蓝登明, 等. 吴起县不同退耕还林地群落恢复特征研究. 水土保持研究, 2016, 23(6): 204-209. | |
| [24] | Bruce W G, Richardson D. Bioassays for allelopathy: Measuring treatment responses with independent controls. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 1988, 14(1): 181-187. |
| [25] | Wang X Q, Zhang R Q, Wang J X, et al. The effects of leaf extracts of four tree species on Amygdalus pedunculata seedlings growth. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 11(1): 587579. |
| [26] | Lin W H, Zhan C A, Chen H Y, et al. Effects of allelopathy among tree species. World Forestry Research, 2011, 24(5): 13-17. |
| 林文欢, 詹潮安, 陈红跃, 等. 林木种间的化感作用. 世界林业研究, 2011, 24(5): 13-17. | |
| [27] | Jia L M, Zhai M P, Yin W L, et al. The study on allelopathy in the mixture of Pinus tabulaeformis and Quercus liaotungensis. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 1995, 31(6): 491-498. |
| 贾黎明, 翟明普, 尹伟伦, 等. 油松、辽东栎混交林中生化他感作用的研究. 林业科学, 1995, 31(6): 491-498. | |
| [28] | Zheng L, Feng Y L. Allelopathic effects of Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. on seed germination and seedling growth in ten herbaceous species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(10): 2782-2787. |
| 郑丽, 冯玉龙. 紫茎泽兰叶片化感作用对10种草本植物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 生态学报, 2005, 25(10): 2782-2787. | |
| [29] | An G Q, Li J M, Lu H F, et al. Nitrogen-dependent luteolin effect on Microcystis growth and microcystin-pollution risk-novel mechanism insights unveiled by comparative proteomics and gene expression. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 311(10): 119848. |
| [30] | Yang K X, Wu X H, Zheng F P, et al. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts of the invasive plant Acmella radicans on seed germination and seedling growth of four weeds. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(12): 3759-3767. |
| 杨轲欣, 吴晓涵, 郑凤萍, 等. 白花金钮扣水提液对4种杂草种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用研究. 草地学报, 2023, 31(12): 3759-3767. | |
| [31] | Zhao Z, Xue D Z, Liu X P, et al. Studies of the relationship between Pinus tabulaeformis and some tree species of the mixed forest. Journal of Northwest Forestry College, 1995, 10(S1): 62-66. |
| 赵忠, 薛德自, 刘西平, 等. 几种混交树种根、叶对油松生长的影响. 西北林学院学报, 1995, 10(S1): 62-66. | |
| [32] | Chen L P, Fan X T, Ma D W, et al. Allelopathic effects of Galinsoga parviflora Cav. on antioxidant enzyme systems in rape seedlings. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 21(2): 332-334. |
| 陈丽萍, 范雪涛, 马丹炜, 等. 入侵植物辣子草对油菜幼苗抗氧化系统的化感效应. 西南农业学报, 2008, 21(2): 332-334. | |
| [33] | Yuan S A, Guo F, Tang C P, et al. Allelopathic effects of the aqueous extracts of Hippophae rhamnoides L. subsp. sinensis on the germination of its seeds. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(5): 116-121. |
| 袁思安, 郭峰, 唐翠平, 等. 中国沙棘浸提液对其种子萌发的化感效应. 干旱区资源与环境, 2015, 29(5): 116-121. | |
| [34] | Li H. Allelopathic effects of Hippophae rhamnoides L. in the restoration of vegetation in the farming-pastoral ecotone of the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019. |
| 李豪. 陕北黄土高原农牧交错区植被恢复中沙棘的化感效应研究. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. | |
| [35] | Gao G L, Ding G D, Zhao Y Y, et al. Fractal approach to estimating changes in soil properties following the establishment of Caragana korshinskii shelterbelts in Ningxia, NW China. Ecological Indicators, 2014, 43: 236-243. |
| [36] | Xia Z C, Kong C H, Chen L C, et al. A broadleaf species enhances an autotoxic conifers growth through belowground chemical interactions. Ecology, 2016, 97: 2283-2292. |
| [1] | Cong ZHAO, Wen-hui WU, Juan-ling WANG, Gai-mei LIANG, Na-na LI, Xue-fang HUANG. Allelopathic effects of cabbage leaf on germination and seedling stages of three crops [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(9): 65-77. |
| [2] | Xiao-xi ZHANG, Jia-wei HU, Xing WANG, Jiang-wen LI, Kai-xuan LIU, Ling-su CHEN, Yu-xin DONG, Zi-quan WANG, Jin-qiang CHEN. Allelopathic effects of Rhus typhina tillering seedlings on seed germination and seedling growth of three common turf species [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 47-59. |
| [3] | Yu-ying WANG, Pei-fang CHONG, Jian-xi ZHANG, Hang-hang LIU, Xin-guang BAO, Xue-ying WANG. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina on seedling growth [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 99-110. |
| [4] | Gui-lian SHAN, Zu-yan MA, Jia-yi LI, Yang LIU, Yong XIE, Jia LIU, Xiao-hui CHU. Effects of Euphorbia jolkinii on physiology and endogenous hormone content of alfalfa seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 153-161. |
| [5] | Wei-jie LI, Li WANG, Jing-yong MA, Zi-kui WANG. Effects of a cover crop on deep soil water and root characteristics in a dryland apple orchard on the Loess Plateau [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 63-74. |
| [6] | Jin-hui CHEN, Hui-yan MA, Yu CHEN, He HE. A study of chemicals released as volatiles or by rain leaching from Ipomoea cairica and their allelopathic effects [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(2): 88-100. |
| [7] | Di ZHANG, Li-fei REN, Guang-bin LIU, Fu-qing LUO, Wen-hao ZHANG, Tian-zuo WANG. Comparative metabolite profiling of alfalfa seeds dried at different temperatures [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 158-166. |
| [8] | Xiao-hong LIU, Yun CHEN, Zhe-hao YAN, Han TANG, Jiao-jiao QIANG, Yue QI, Yi-zhi DU. The effects of grass hedgerow roots on shear strength and scouring resistance of root-soil complexes in the purple soil region [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(11): 98-107. |
| [9] | LIANG Jun, QUAN Xiao-long, ZHANG Jie-xue, SHI Hui-lan, DUAN Zhong-hua, QIAO You-ming. Potential allelopathic effects of water extracts of three grasses on germination of their own seeds and seedling growth [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(7): 81-89. |
| [10] | ZHOU Tao, CHEN Yun, WANG Run-ze, LI Tie, TANG Han, ZHAI Ting-ting, LIU Xiao-hong. Effect of planting grasses and adding polyacrylamide on the shear performance and erodibility-resistance of purple soil in barren hillsides [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(3): 62-73. |
| [11] | HE Ping, DENG Yu-jun, HU Xiao-yin, PAN Hui-min, DENG Hong-ping. Potential allelopathic effect of Aster subulatus on Triticum aestivum and Brassica chinensis [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 101-109. |
| [12] | DONG Fang-Hui, LIU Ying, LENG Jia-Ming, YU Wei-Li, ZHAO Yu. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from Xanthium spinosum on seed germination and seedling growth of Lactuca sativa var. longifolia [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(2): 146-160. |
| [13] | WANG Run-Ze, CHEN Yun, LI Tie, ZHOU Tao, HE Bing-Hui, LIU Xiao-Hong, LIU Zhi-Peng, SHAN Zhi-Jie. Impacts of polyacrylamide and grass root systems on micro-aggregates of purple soil in barren hillside badlands [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(12): 13-23. |
| [14] | ZHAO Xin-Mei, WANG Jun, MO Jing-Jing, YANG Shui-Ping, WEN Ming-Xia, ZHANG Xue, ZHAO Jian, CHEN Da-Xia, JIANG Wei. Allelopathic effects of leaf-stem litter water aqueous extracts of three plant species on tobacco seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(9): 37-45. |
| [15] | MA Jin-Xing, TU De-Peng, KOU Jian-Cun, LIU Fang. Effects of drying temperature on water loss and germination rates of leguminous forage seeds [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(8): 56-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||