
ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S

Acta Prataculturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (12): 126-138.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023129
Hong-jian WEI( ), Wen-yuan HE, Yue WANG, Ming TANG, Hui CHEN(
), Wen-yuan HE, Yue WANG, Ming TANG, Hui CHEN( )
)
Received:2023-04-24
Revised:2023-06-08
Online:2023-12-20
Published:2023-10-18
Contact:
Hui CHEN
Hong-jian WEI, Wen-yuan HE, Yue WANG, Ming TANG, Hui CHEN. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and melatonin on the heat tolerance of perennial ryegrass[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(12): 126-138.
| 基因Gene | 上游引物序列Forward primer sequence (5'-3') | 下游引物序列Reverse primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| LpelF4A | AACTCAACTTGAAGTGTTGGAGTG | AGATCTGGTCCTGGAAAGAATATG |
| LpASMT1 | CAGCAGCATACTACACTCATACA | TCCAGCTGACCTTGAAGTAAC |
| LpASMT3 | CTCAAGTGGGTTATGTGTCTGT | CTACCACGGCATCGAAGATTAT |
| LpT5H | ATCAACACATTCGCCATGGG | AGCTTGTAGTCCGGATCCTTG |
| LpTDC1 | TGGCCAAGATGTTCGAAGAC | TGAAGCACACGAGAGCAAAG |
| LpTDC2 | TGCCAGTGAAGCAGTTCTTG | ATTCCTGCAATCTGGCATGC |
| LpSNAT | TCTTCAATATGCGGCGTCTG | ACCGTCTTTTCGCTTGCTTC |
| LpCOMT1 | TGAAGAACGCCATCGAGCTT | ACACACGGCAAAGCAATGTC |
| LpP5CS | TGCAAAAGCCGCAGAATGAG | ACTGTCTGTCACGAGAAGTTGG |
| LpPAL | GATGCTCGCAAAGAAGCTCG | TGGAAGAGATGAGGCCGAGA |
| LpPPO | TTCTCCTGCACTACCGCAAG | GGATCCGCTCGTGGAAGTAG |
Table 1 Primers used in the study
| 基因Gene | 上游引物序列Forward primer sequence (5'-3') | 下游引物序列Reverse primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| LpelF4A | AACTCAACTTGAAGTGTTGGAGTG | AGATCTGGTCCTGGAAAGAATATG |
| LpASMT1 | CAGCAGCATACTACACTCATACA | TCCAGCTGACCTTGAAGTAAC |
| LpASMT3 | CTCAAGTGGGTTATGTGTCTGT | CTACCACGGCATCGAAGATTAT |
| LpT5H | ATCAACACATTCGCCATGGG | AGCTTGTAGTCCGGATCCTTG |
| LpTDC1 | TGGCCAAGATGTTCGAAGAC | TGAAGCACACGAGAGCAAAG |
| LpTDC2 | TGCCAGTGAAGCAGTTCTTG | ATTCCTGCAATCTGGCATGC |
| LpSNAT | TCTTCAATATGCGGCGTCTG | ACCGTCTTTTCGCTTGCTTC |
| LpCOMT1 | TGAAGAACGCCATCGAGCTT | ACACACGGCAAAGCAATGTC |
| LpP5CS | TGCAAAAGCCGCAGAATGAG | ACTGTCTGTCACGAGAAGTTGG |
| LpPAL | GATGCTCGCAAAGAAGCTCG | TGGAAGAGATGAGGCCGAGA |
| LpPPO | TTCTCCTGCACTACCGCAAG | GGATCCGCTCGTGGAAGTAG |
处理 Treatments | 项目 Item | 株高 Shoot height (cm) | 地上部分鲜重 Shoot fresh weight (g·pot-1) | 地下部分鲜重 Root fresh weight (g·pot-1) | 地上部分干重 Shoot dry weight (g·pot-1) | 地下部分干重 Root dry weight (g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NM-NT | 17.07±1.51c | 8.68±1.14c | 3.66±0.26c | 1.36±0.11bc | 0.55±0.04c |
| NM-MT | 18.93±1.74b | 9.46±1.36b | 3.92±0.20b | 1.40±0.12b | 0.67±0.05b | |
| AM-NT | 19.60±1.18ab | 9.25±1.08b | 4.04±0.33b | 1.45±0.13b | 0.73±0.06ab | |
| AM-MT | 22.53±1.74a | 10.75±1.30a | 4.68±0.41a | 1.68±0.15a | 0.82±0.06a | |
| HT | NM-NT | 13.47±0.76e | 4.65±0.68f | 2.67±0.18e | 1.01±0.08e | 0.15±0.02f |
| NM-MT | 14.93±1.38d | 5.95±0.58e | 3.31±0.27d | 1.24±0.09d | 0.28±0.02e | |
| AM-NT | 15.24±1.43d | 6.38±0.71e | 3.22±0.24d | 1.19±0.10d | 0.32±0.03e | |
| AM-MT | 16.53±1.27c | 7.77±0.64d | 3.51±0.31c | 1.32±0.12c | 0.42±0.03d |
Table 2 Growth parameters of perennial ryegrass under different treatments
处理 Treatments | 项目 Item | 株高 Shoot height (cm) | 地上部分鲜重 Shoot fresh weight (g·pot-1) | 地下部分鲜重 Root fresh weight (g·pot-1) | 地上部分干重 Shoot dry weight (g·pot-1) | 地下部分干重 Root dry weight (g·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NM-NT | 17.07±1.51c | 8.68±1.14c | 3.66±0.26c | 1.36±0.11bc | 0.55±0.04c |
| NM-MT | 18.93±1.74b | 9.46±1.36b | 3.92±0.20b | 1.40±0.12b | 0.67±0.05b | |
| AM-NT | 19.60±1.18ab | 9.25±1.08b | 4.04±0.33b | 1.45±0.13b | 0.73±0.06ab | |
| AM-MT | 22.53±1.74a | 10.75±1.30a | 4.68±0.41a | 1.68±0.15a | 0.82±0.06a | |
| HT | NM-NT | 13.47±0.76e | 4.65±0.68f | 2.67±0.18e | 1.01±0.08e | 0.15±0.02f |
| NM-MT | 14.93±1.38d | 5.95±0.58e | 3.31±0.27d | 1.24±0.09d | 0.28±0.02e | |
| AM-NT | 15.24±1.43d | 6.38±0.71e | 3.22±0.24d | 1.19±0.10d | 0.32±0.03e | |
| AM-MT | 16.53±1.27c | 7.77±0.64d | 3.51±0.31c | 1.32±0.12c | 0.42±0.03d |
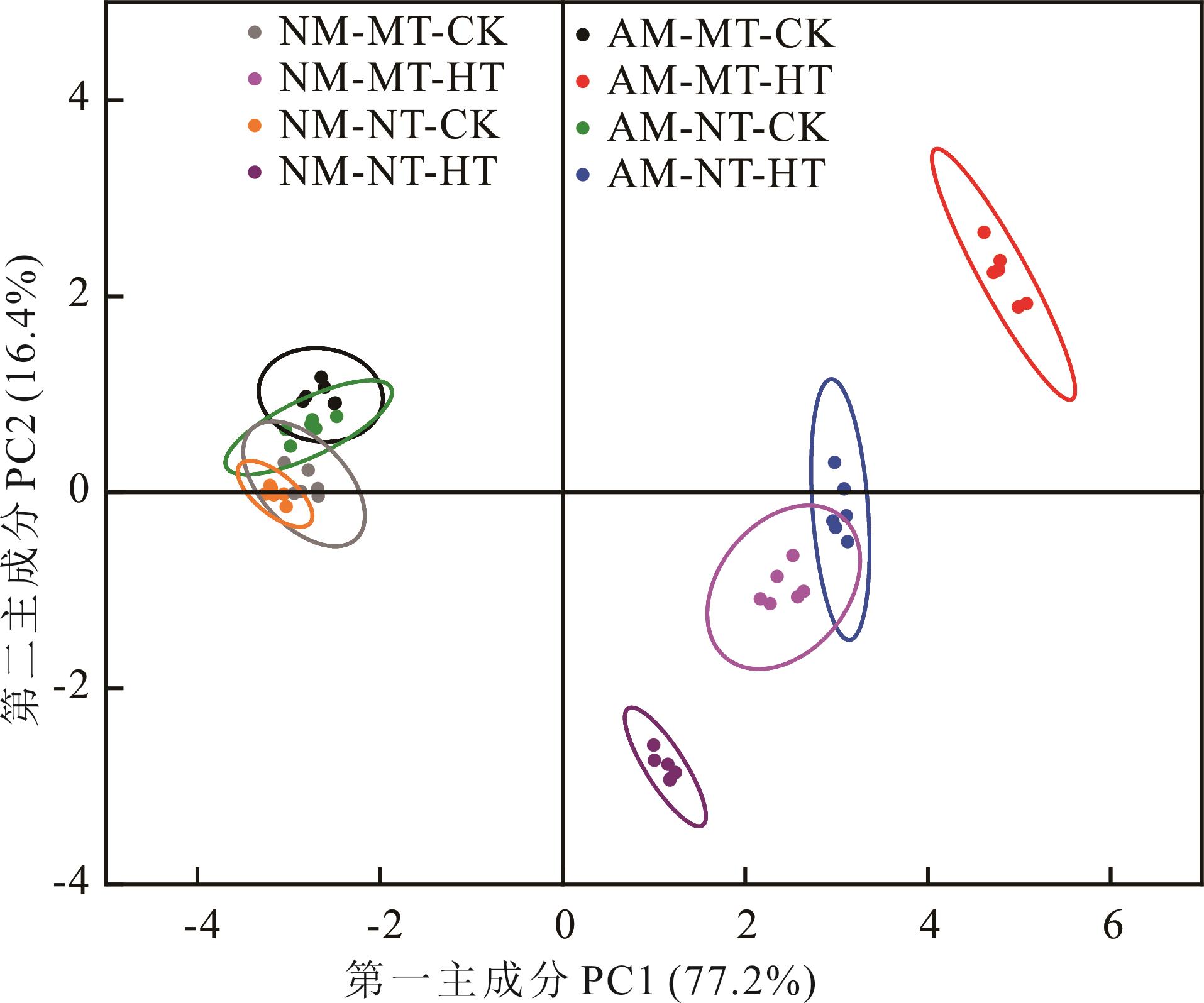
Fig.8 Principal component analysis of parameters related to antioxidant and osmoregulatory substances in perennial ryegrass under different treatments
| 1 | Yu X Q, Pijut P M, Byrne S, et al. Candidate gene association mapping for winter survival and spring regrowth in perennial ryegrass. Plant Science, 2015, 235: 37-45. |
| 2 | Wang Y, Dai Y, Tao X, et al. Heat shock factor genes of tall fescue and perennial ryegrass in response to temperature stress by RNA-Seq analysis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 6: 1226. |
| 3 | Mittler R, Zandalinas S I, Fichman Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2022, 23(10): 663-679. |
| 4 | Wei H J, Wang Y Q, Ding J, et al. Effects of silicon on performance quality and physiological metabolism of bermudagrass and zoysiagrass under wear stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(7): 1790-1800. |
| 卫宏健, 王咏琪, 丁杰, 等. 硅对磨损胁迫下狗牙根和结缕草表观质量与生理代谢的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(7): 1790-1800. | |
| 5 | Sun X F, Zhang Y L, Li P Y, et al. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on antioxidant activity and content of substances involved in osmotic adjustment in Cynodon dactylon under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. |
| 孙晓梵, 张一龙, 李培英, 等. 不同施氮量对干旱下狗牙根抗氧化酶活性及渗透调节物质含量的影响. 草业学报, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. | |
| 6 | Lu A X, Ling R, Chen S Y, et al. Physiological and biochemical responses of eight hydrangea cultivars to high temperature stress. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2022, 43(4): 816-828. |
| 陆艾鲜, 凌瑞, 陈生煜, 等. 高温胁迫下8个绣球品种的生理生化响应. 热带作物学报, 2022, 43(4): 816-828. | |
| 7 | Gao T T, Liu X M, Tan K X, et al. Introducing melatonin to the horticultural industry: Physiological roles, potential applications, and challenges. Horticulture Research, 2022, 9: uhac094. |
| 8 | Lee K, Choi G H, Back K. Cadmium-induced melatonin synthesis in rice requires light, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide: Key regulatory roles for tryptophan decarboxylase and caffeic acid O-methyltransferase. Journal of Pineal Research, 2017, 63(4): 12441. |
| 9 | Byeon Y, Park S, Lee H Y, et al. Elevated production of melatonin in transgenic rice seeds expressing rice tryptophan decarboxylase. Journal of Pineal Research, 2014, 56(3): 275-282. |
| 10 | Zhao H L, Zuo L, Zhang L, et al. Mitigation of exogenous melatonin on photoinhibition of tomato seedlings under chilling stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(1): 151-159. |
| 赵海亮, 左璐, 张璐, 等. 低温胁迫下外源褪黑素对番茄幼苗光抑制的缓解效应. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(1): 151-159. | |
| 11 | Gu X B, Lu L H, Song G H, et al. The mitigative effect of exogenous melatonin pretreatment on peach seedling growth under drought stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2022, 58(2): 309-318. |
| 古咸彬, 陆玲鸿, 宋根华, 等. 外源褪黑素预处理对干旱胁迫下桃苗生长的缓解效应. 植物生理学报, 2022, 58(2): 309-318. | |
| 12 | Arnao M B, Hernandez-Ruiz J. Melatonin: A new plant hormone and/or a plant master regulator? Trends in Plant Science, 2019, 24(1): 38-48. |
| 13 | Alam M N, Zhang L, Yang L, et al. Transcriptomic profiling of tall fescue in response to heat stress and improved thermotolerance by melatonin and 24-epibrassinolide. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19: 224. |
| 14 | Cheng C, Liu Y, Fang W, et al. iTRAQ-based proteomic and physiological analyses of mustard sprouts in response to heat stress. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(10): 6052-6062. |
| 15 | Parniske M. Arbuscular mycorrhiza: The mother of plant root endosymbioses. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(10): 763-775. |
| 16 | Chen J, Xie J, Tang M. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and drought resistance of Amorpha fruticosa under water stress. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2014, 36(6): 142-148. |
| 陈婕, 谢靖, 唐明. 水分胁迫下丛枝菌根真菌对紫穗槐生长和抗旱性的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 2014, 36(6): 142-148. | |
| 17 | Liu J Q, Li L, Yang H H, et al. Effect of melatonin on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of wheat under salt stress. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2022, 42(7): 857-863. |
| 刘佳奇, 李丽, 杨红红, 等. 盐胁迫下褪黑素对小麦种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2022, 42(7): 857-863. | |
| 18 | Wei H, Li X, He W, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis enhances perennial ryegrass growth during temperature stress through the modulation of antioxidant defense and hormone levels. Industrial Crops and Products, 2023, 195: 116412. |
| 19 | Wang Y Y, Zhao B, Li Y. Heat resistance of Rhododendron with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2019, 36(4): 733-740. |
| 王颖颖, 赵冰, 李莹. 丛枝菌根真菌对杜鹃花耐热性的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 2019, 36(4): 733-740. | |
| 20 | Nguyen H D, Csintalan Z, Posta K. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mitigate negative effects of combined drought and heat stress on tomato plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 132: 297-307. |
| 21 | Zhang X Y, Zhang H J, Zhang H Q, et al. Exogenous melatonin application enhances Rhizophagus irregularis symbiosis and induces the antioxidant response of Medicago truncatula under lead stress. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11: 516. |
| 22 | Ren Y, Che X R, Liang J W, et al. Brassinosteroids benefit plants performance by augmenting arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Microbiology Spectrum, 2021, 9(3): e0164521. |
| 23 | Zhang J, Shi Y, Zhang X, et al. Melatonin suppression of heat-induced leaf senescence involves changes in abscisic acid and cytokinin biosynthesis and signaling pathways in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 138: 36-45. |
| 24 | Koske R E, Gemma J N. A modified procedure for staining roots to detect VA mycorrhizas. Mycological Research, 1989, 92(4): 486-488. |
| 25 | Mcgonigle T P, Miller M H, Evans D G, et al. A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytologist, 1990, 115(3): 495-501. |
| 26 | Beyer W J, Fridovich I. Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: Some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Analytical Biochemistry, 1987, 161(2): 559-566. |
| 27 | Amako K, Chen G X, Asada K. Separate assays specific for ascorbate peroxidase and guaiacol peroxidase and for the chloroplastic and cytosolic lsozymes of ascorbate peroxidase in plants. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1994, 35: 497-504. |
| 28 | Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology, 1984, 105: 121-126. |
| 29 | Nakano Y, Asada K U. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1981, 22(5): 867-880. |
| 30 | Chen C T, Chen L, Lin C C, et al. Regulation of proline accumulation in detached rice leaves exposed to excess copper. Plant Science, 2001, 160(2): 283-290. |
| 31 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. | |
| 32 | Huang L K, Yan H D, Jiang X M, et al. Identification of candidate reference genes in perennial ryegrass for quantitative RT-PCR under various abiotic stress conditions. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e93724. |
| 33 | Shi H T, Qian Y Q, Tan D X, et al. Melatonin induces the transcripts of CBF/DREB1s and their involvement in both abiotic and biotic stresses in Arabidopsis. Journal of Pineal Research, 2015, 59(3): 334-342. |
| 34 | Liu D S, Yao L, Xu W R, et al. Research progress of melatonin in plant stress resistance. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 等. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. | |
| 35 | Liu T, Zhao F, Liu Z, et al. Identification of melatonin in Trichoderma spp. and detection of melatonin content under controlled-stress growth conditions from T. asperellum. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2016, 56(7): 838-843. |
| 36 | Chen X, Yang Y, Liu F Q. Research progress of plant melatonin. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(24): 17-24. |
| 陈贤, 杨勇, 刘凤权. 植物褪黑素的研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(24): 17-24. | |
| 37 | Byeon Y, Back K. Melatonin synthesis in rice seedlings in vivo is enhanced at high temperatures and under dark conditions due to increased serotonin N-acetyltransferase and N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase activities. Journal of Pineal Research, 2014, 56(2): 189-195. |
| 38 | Kang K, Lee K, Park S, et al. Enhanced production of melatonin by ectopic overexpression of human serotonin N-acetyltransferase plays a role in cold resistance in transgenic rice seedlings. Journal of Pineal Research, 2010, 49(2): 176-182. |
| 39 | Byeon Y, Lee H Y, Hwang O J, et al. Coordinated regulation of melatonin synthesis and degradation genes in rice leaves in response to cadmium treatment. Journal of Pineal Research, 2015, 58(4): 470-478. |
| 40 | Xiao X C, Liu M Y, Jiang M Q, et al. Whole-genome identification and expression analysis of SNAT, ASMT and COMT families of melatonin synthesis pathway in Dimocarpus longan. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| 肖学宸, 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 等. 龙眼褪黑素合成途径SNAT、ASMT和COMT家族基因鉴定及表达分析. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. | |
| 41 | Fu J J, Zhang S T, Jiang H N, et al. Melatonin-induced cold and drought tolerance is regulated by brassinosteroids and hydrogen peroxide signaling in perennial ryegrass. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2022, 196: 104815. |
| 42 | Ma T, Liu R J, Li M. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on heat-tolerance of Lactuca satica L. Plant Physiology Journal, 2015, 51(11): 1919-1926. |
| 马通, 刘润进, 李敏. 丛枝菌根真菌对生菜耐热性的效应. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(11): 1919-1926. | |
| 43 | Xing H S, Sun P F, Li F, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on heat tolerance of Lavandula angustifolia. Mycosystema, 2019, 38(5): 698-706. |
| 邢红爽, 孙鹏飞, 李峰, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌对薰衣草耐热性的影响. 菌物学报, 2019, 38(5): 698-706. | |
| 44 | Sies H, Jones D P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2020, 21(7): 363-383. |
| 45 | Tan Z Z, Zhang X X, Yang Z M. Research advances in heat resistance of cool-season turfgrasses. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 193-202. |
| 谭真真, 张夏香, 杨志民. 冷季型草坪草耐热性研究进展. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 193-202. | |
| 46 | Zhang X Y, Zhang H Q, Lou X, et al. Mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal Medicago truncatula roots exhibit differentially regulated NADPH oxidase and antioxidant response under Pb stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2019, 164: 10-19. |
| 47 | Qiu N W, Yang C C, Fu W C, et al. Protective effect of exogenous proline on PSII particles under high salinity and high temperature stresses. Plant Physiology Journal, 2013, 49(6): 586-590. |
| 邱念伟, 杨翠翠, 付文诚, 等. 高盐和高温胁迫下外源脯氨酸对PSII颗粒的保护作用. 植物生理学报, 2013, 49(6): 586-590. | |
| 48 | Zhao R X, Zhu H S, Cheng Y H, et al. Research progress on proline and its biosynthesis enzymes in plant. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 25(2): 90-97. |
| 赵瑞雪, 朱慧森, 程钰宏, 等. 植物脯氨酸及其合成酶系研究进展. 草业科学, 2008, 25(2): 90-97. | |
| 49 | Antoniou C, Chatzimichail G, Xenofontos R, et al. Melatonin systemically ameliorates drought stress-induced damage in Medicago sativa plants by modulating nitro-oxidative homeostasis and proline metabolism. Journal of Pineal Research, 2017, 62(4): 12401. |
| 50 | Fan Y H, Li Y X, Ma L L, et al. Effects of exogenous salicylic acid on antioxidant physiological characteristics of wheat flag leaves under high temperature stress at grain filling stage. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 36(9): 1878-1886. |
| 樊永惠, 李宇星, 马亮亮, 等. 灌浆期高温胁迫下外源水杨酸对小麦旗叶抗氧化生理特性的影响. 核农学报, 2022, 36(9): 1878-1886. | |
| 51 | Liang D, Shen Y Q, Ni Z Y, et al. Exogenous melatonin application delays senescence of kiwifruit leaves by regulating the antioxidant capacity and biosynthesis of flavonoids. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 426. |
| 52 | Jiao J Q, Jin M J, Liu H, et al. Application of melatonin in kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) alleviated chilling injury during cold storage. Scientia Horticulturae, 2022, 296: 110876. |
| 53 | Wang X Y, Yang L Z, Wang T, et al. Recent progress toward understanding the physiological function, purification, and enzymatic browning control of plant polyphenol oxidases. Food Science, 2020, 41(9): 222-237. |
| 王馨雨, 杨绿竹, 王婷, 等. 植物多酚氧化酶的生理功能、分离纯化及酶促褐变控制的研究进展. 食品科学, 2020, 41(9): 222-237. | |
| 54 | Garcia-Garrido J M, Ocampo J A. Regulation of the plant defence response in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2002, 53(373): 1377-1386. |
| 55 | Wang R M, Xiong X Y. Effect of temperature stress on growth and metabolism in perennial ryegrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(8): 81-90. |
| 王日明, 熊兴耀. 高温胁迫对黑麦草生长及生理代谢的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 81-90. | |
| 56 | Ma L, Xie X R, Liu J R, et al. Research progress of glycine betaine in plant stress resistance and its application in turfgrass. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2016, 24(5): 947-952. |
| 马莉, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣, 等. 甜菜碱与植物抗逆性研究进展及其在草坪上的应用. 草地学报, 2016, 24(5): 947-952. | |
| 57 | Ben Abdallah S, Aung B, Amyot L, et al. Salt stress (NaCl) affects plant growth and branch pathways of carotenoid and flavonoid biosyntheses in Solanum nigrum. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2016, 38(3): 72. |
| 58 | Misra N, Saxena P. Effect of salicylic acid on proline metabolism in lentil grown under salinity stress. Plant Science, 2009, 177(3): 181-189. |
| 59 | Park S, Byeon Y, Back K. Transcriptional suppression of tryptamine 5-hydroxylase, a terminal serotonin biosynthetic gene, induces melatonin biosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Journal of Pineal Research, 2013, 55(2): 131-137. |
| 60 | Zhao Q, Bao Y Y. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and two phenolic acids of Medicago sativa under various mixed salt-alkaline stresses. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2015, 35(9): 1829-1836. |
| 赵琦, 包玉英. 混合盐碱胁迫下丛枝菌根真菌对紫花苜蓿生长及2种酚酸含量的影响. 西北植物学报, 2015, 35(9): 1829-1836. |
| [1] | Ying JIANG, Hui-hong ZHANG, Chang WEI, Zheng-yang XU, Ying ZHAO, Fang LIU, Ge-zi LI, Xue-hai ZHANG, Hai-tao LIU. Effects of exogenous melatonin on root development and physiological and biochemical characteristics of maize seedlings under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 143-159. |
| [2] | Jia LIANG, Zhao-yang HU, Zhi-ming XIE, Liu-feng MA, Yun CHEN, Zhi-gang FANG. Exogenous melatonin alleviates the physiological effects of drought stress in sweet sorghum seedlings [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(7): 206-215. |
| [3] | Xiao-xia AN, Ying-ying ZHANG, Chun-hui MA, Man LI, Qian-bing ZHANG. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on alfalfa yield and phosphorus use efficiency [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(6): 71-84. |
| [4] | Jia-ming YAO, Huan-huan HAO, Jing ZHANG, Bin XU. The use of the tRNA-sgRNA/Cas9 system for gene editing in perennial ryegrass protoplasts [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 129-141. |
| [5] | Wen-ting GUO, Guo-hua WANG, Qian-qian GOU. Effects of sodium salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of three Chenopodiaceae annuals [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 128-141. |
| [6] | Yan-lan ZHAO, Xin-yi ZENG, Jin-chao GONG, Xiang-jun LI, Xu-xu LI, Shan LIU, Xin-quan ZHANG, Ji-qiong ZHOU. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the salt tolerance of Trifolium repens [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 179-188. |
| [7] | Jiao-yun LU, Hong TIAN, He-shan ZHANG, Jun-bo XIONG, Yang LIU, Zhen-nan WANG. Effects of H2O2 immersion on seed germination and seedling growth of alfalfa under salt stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(10): 141-152. |
| [8] | Jia-ming YAO, Yue HE, Huan-huan HAO, Xin-ru HUANG, Jing ZHANG, Bin XU. Characterization and transcriptional regulation analysis of the LpPIL5 gene in perennial ryegrass [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(9): 155-167. |
| [9] | Xiao-fan SUN, Yi-long ZHANG, Pei-ying LI, Zong-jiu SUN. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on antioxidant activity and content of substances involved in osmotic adjustment in Cynodon dactylon under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(6): 69-78. |
| [10] | Qing ZHANG, Jing XING, Jia-ming YAO, Ting-chao YIN, Xin-ru HUANG, Yue HE, Jing ZHANG, Bin XU. The role of a cytokinin signaling pathway type-B ARR transcription factor, LpARR10, in cadmium tolerance of perennial ryegrass [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [11] | Dong-rong HAN, Tuo YAO, Hai-yun LI, Shu-chao HUANG, Yan-shan YANG, Ya-min GAO, Chang-ning LI, Yin-cui ZHANG. Effects of combined application of microbial fertilizer and chemical fertilizer on the growth of Lolium perenne [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 136-143. |
| [12] | Li-qing ZHAO, Xiang-yong PENG, Jun-xiang LIU, Jin-mei MAO, Zhen-yuan SUN. Effects of reduced glutathione on the growth and photosynthesis of perennial ryegrass under lead stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(9): 97-104. |
| [13] | Hong SUN, Yu-long ZHENG, Yan-li LIN, Chao CHEN, Fu-yu YANG. Effects of biochar, phosphorus addition and AMF inoculation on switchgrass growth and soil properties under Cd stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(12): 71-80. |
| [14] | Tian TIAN, Hai-jiang WANG, Jin-gang WANG, Yong-qi ZHU, Xiao-yan SHI, Wei-di LI, Wen-rui-yu LI. Effects of nitrogen application on accumulation of organic osmotic regulating substances in forage rapeseed (Brassica napus) under salt stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(10): 125-136. |
| [15] | Dong LI, Hong-tao SHEN, Yan-fang WANG, Yue-hua WANG, Li-jun WANG, Shi-min ZHAO, Ling LIU. Effects of exogenous melatonin on photosynthetic carbon assimilation and endogenous hormones in tobacco seedlings under drought stress [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(1): 130-139. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||