

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 95-104.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020036
收稿日期:2020-02-05
修回日期:2020-03-11
出版日期:2020-12-28
发布日期:2020-12-28
通讯作者:
王德利
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail:wangd@nenu.edu.cn基金资助:
Ying-kui WANG1( ), Yu-rong YANG2, De-li WANG1,2(
), Yu-rong YANG2, De-li WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2020-02-05
Revised:2020-03-11
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
De-li WANG
摘要:
丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)通过影响植物地上及地下离子吸收分配来增强植物耐盐碱能力的机理尚不明确,采用盆栽试验,选取松嫩草地的优势种羊草作为试验材料,研究不同盐碱梯度下接种AMF对羊草体内无机阳离子吸收、运输和分配的影响。试验结果表明:1)盐碱胁迫会增加羊草体内Na+含量,减少K+、Ca2+和Mg2+含量,增强地下到地上部分Na+的运输,抑制K+、Ca2+和Mg2+的运输,改变羊草体内地上和地下的离子分配;2)盐碱胁迫条件下,AMF抑制了羊草对Na+的吸收,促进了其对K+、Ca2+和Mg2+的吸收,同时提高了根系对Na+的截留能力,通过调节羊草体内的无机离子运输比和阳离子运输选择比,维持其体内的离子平衡,从而提高耐盐碱性;3)盐碱胁迫程度增加改变了AMF的盐碱适应性,使其菌丝侵染率及菌丝密度显著降低,泡囊侵染率显著升高,AMF可以利用泡囊存储更多的盐碱离子来减轻盐碱胁迫对羊草根系的破坏作用。可见,在盐碱胁迫下,AMF能够通过抑制羊草吸收Na+,利用泡囊结构帮助其根系截留Na+,以及促进K+、Ca2+和Mg2+的吸收来调节羊草体内地上和地下的离子分配,进而增强羊草的盐碱耐受性。由此,可以利用羊草-AMF共生体改良草地盐碱化,同时为研究AMF对其他植物的耐盐碱机理提供了有效参考。
王英逵, 杨玉荣, 王德利. 盐碱胁迫下AMF对羊草的离子吸收和分配作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 95-104.
Ying-kui WANG, Yu-rong YANG, De-li WANG. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on ion absorption and distribution in Leymus chinensis under saline-alkaline stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(12): 95-104.
盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductance (μs·cm-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (%) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | K+ (g·kg-1) | Na+ (g·kg-1 ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 8.35±0.02c | 267.8±14.9c | 0.23±0.03a | 1.01±0.09a | 0.05±0.01a | 0.05±0.03c |
| M | 9.52±0.05b | 410.4±44.3b | 0.16±0.02b | 0.82±0.14a | 0.03±0.01ab | 0.14±0.02b |
| S | 10.39±0.05a | 559.0±48.3a | 0.09±0.01c | 0.71±0.10a | 0.02±0.01b | 0.25±0.03a |
表1 不同盐碱梯度的土壤特征
Table 1 Soil characteristics with different saline-alkaline gradients
盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | pH | 电导率 Electrical conductance (μs·cm-1) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (%) | 全磷 Total phosphorus (g·kg-1) | K+ (g·kg-1) | Na+ (g·kg-1 ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 8.35±0.02c | 267.8±14.9c | 0.23±0.03a | 1.01±0.09a | 0.05±0.01a | 0.05±0.03c |
| M | 9.52±0.05b | 410.4±44.3b | 0.16±0.02b | 0.82±0.14a | 0.03±0.01ab | 0.14±0.02b |
| S | 10.39±0.05a | 559.0±48.3a | 0.09±0.01c | 0.71±0.10a | 0.02±0.01b | 0.25±0.03a |
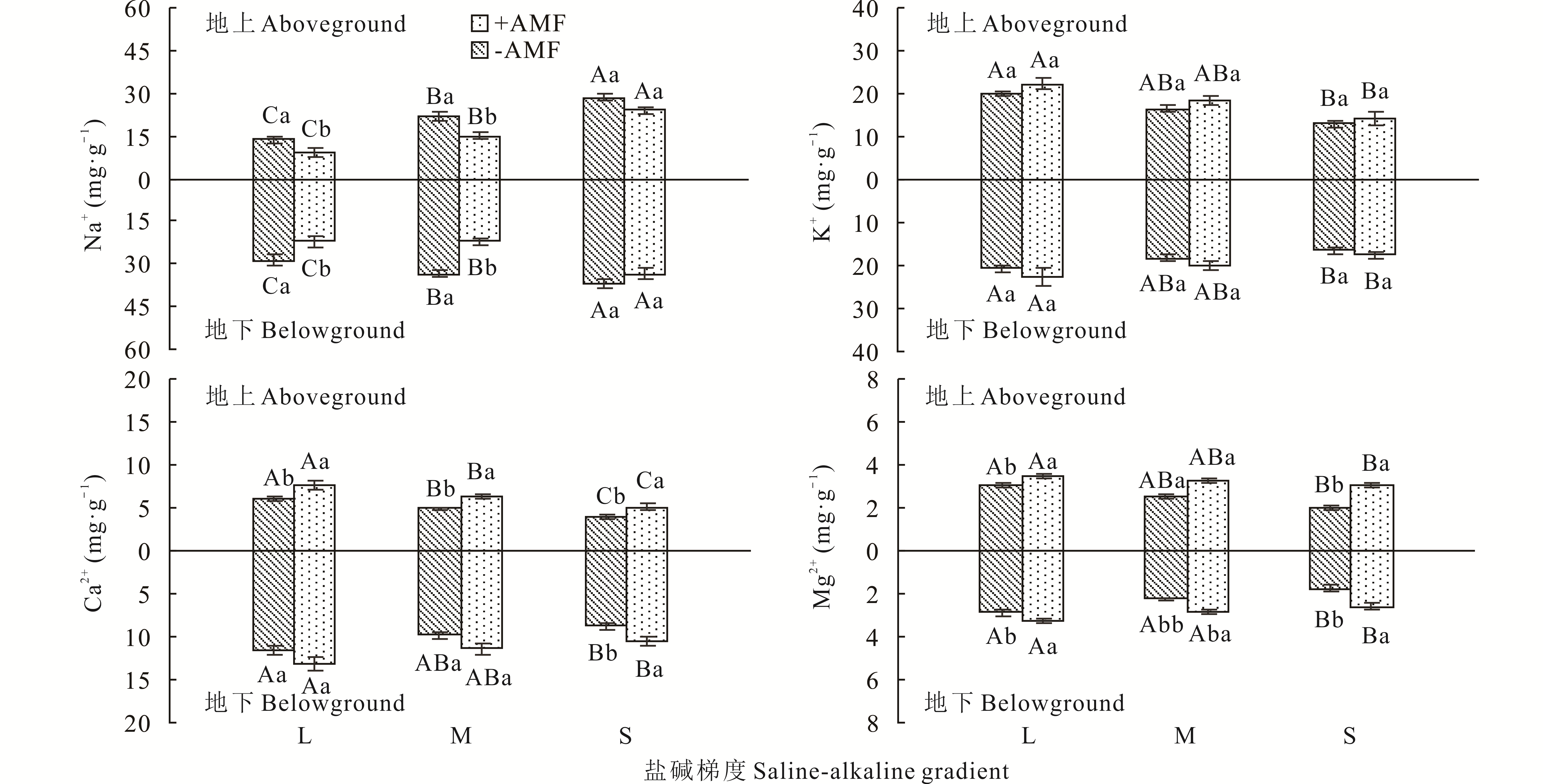
图1 不同盐碱梯度下AMF对羊草地上和地下Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+吸收分配的影响
Fig.1 Effects of AMF on Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ absorption and distribution in aboveground and belowground of L. chinensis under different saline-alkaline gradients
项目 Item | 盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理 Treatment | K+/Na+ | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上Aboveground | L | -AMF | 1.49±0.11Aa | 0.45±0.02Ab | 0.23±0.02Ab |
| +AMF | 2.62±0.46Aa | 0.88±0.11Aa | 0.40±0.05Aa | ||
| M | -AMF | 0.78±0.05Bb | 0.23±0.02Bb | 0.12±0.01Bb | |
| +AMF | 1.25±0.13Ba | 0.44±0.05Ba | 0.22±0.02Ba | ||
| S | -AMF | 0.47±0.04Ca | 0.14±0.02Cb | 0.07±0.01Bb | |
| +AMF | 0.62±0.07Ba | 0.21±0.01Ca | 0.13±0.01Ca | ||
| 地下 Belowground | L | -AMF | 0.73±0.05Aa | 0.41±0.02Ab | 0.10±0.01Ab |
| +AMF | 1.04±0.12Aa | 0.60±0.04Aa | 0.15±0.01Aa | ||
| M | -AMF | 0.55±0.02Ba | 0.30±0.02Bb | 0.07±0.00Bb | |
| +AMF | 0.71±0.06Ba | 0.40±0.03Ba | 0.10±0.01Ba | ||
| S | -AMF | 0.45±0.03Ba | 0.24±0.02Bb | 0.05±0.00Bb | |
| +AMF | 0.53±0.04Ba | 0.32±0.02Ba | 0.08±0.00Ca |
表2 不同盐碱梯度下AMF对羊草地上和地下K+/Na+、Ca2+/Na+、Mg2+/Na+的影响
Table 2 Effects of AMF on K+/Na+, Ca2+/Na+, Mg2+/Na+ in aboveground and belowground of L. chinensis under saline-alkaline gradients
项目 Item | 盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理 Treatment | K+/Na+ | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上Aboveground | L | -AMF | 1.49±0.11Aa | 0.45±0.02Ab | 0.23±0.02Ab |
| +AMF | 2.62±0.46Aa | 0.88±0.11Aa | 0.40±0.05Aa | ||
| M | -AMF | 0.78±0.05Bb | 0.23±0.02Bb | 0.12±0.01Bb | |
| +AMF | 1.25±0.13Ba | 0.44±0.05Ba | 0.22±0.02Ba | ||
| S | -AMF | 0.47±0.04Ca | 0.14±0.02Cb | 0.07±0.01Bb | |
| +AMF | 0.62±0.07Ba | 0.21±0.01Ca | 0.13±0.01Ca | ||
| 地下 Belowground | L | -AMF | 0.73±0.05Aa | 0.41±0.02Ab | 0.10±0.01Ab |
| +AMF | 1.04±0.12Aa | 0.60±0.04Aa | 0.15±0.01Aa | ||
| M | -AMF | 0.55±0.02Ba | 0.30±0.02Bb | 0.07±0.00Bb | |
| +AMF | 0.71±0.06Ba | 0.40±0.03Ba | 0.10±0.01Ba | ||
| S | -AMF | 0.45±0.03Ba | 0.24±0.02Bb | 0.05±0.00Bb | |
| +AMF | 0.53±0.04Ba | 0.32±0.02Ba | 0.08±0.00Ca |
| 盐碱梯度Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理Treatment | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | -AMF | 0.47±0.02Ca | 0.97±0.02Aa | 0.52±0.01Ab | 1.07±0.01Aa |
| +AMF | 0.41±0.03Ca | 0.99±0.02Aa | 0.59±0.01Aa | 1.07±0.02Ca | |
| M | -AMF | 0.64±0.02Ba | 0.91±0.02Ba | 0.50±0.01Ab | 1.11±0.04Aa |
| +AMF | 0.52±0.03Bb | 0.91±0.02Ba | 0.55±0.01Ba | 1.13±0.01Ba | |
| S | -AMF | 0.77±0.01Aa | 0.79±0.01Ca | 0.45±0.02Ba | 1.15±0.05Aa |
| +AMF | 0.71±0.01Ab | 0.81±0.02Ca | 0.48±0.01Ca | 1.18±0.02Aa |
表3 不同盐碱梯度下AMF对羊草体内无机阳离子地下到地上运输比的影响
Table 3 Effects of AMF on transportation from belowground to aboveground ratio of inorganic cationsin L. chinensis under saline-alkaline gradients
| 盐碱梯度Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理Treatment | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | -AMF | 0.47±0.02Ca | 0.97±0.02Aa | 0.52±0.01Ab | 1.07±0.01Aa |
| +AMF | 0.41±0.03Ca | 0.99±0.02Aa | 0.59±0.01Aa | 1.07±0.02Ca | |
| M | -AMF | 0.64±0.02Ba | 0.91±0.02Ba | 0.50±0.01Ab | 1.11±0.04Aa |
| +AMF | 0.52±0.03Bb | 0.91±0.02Ba | 0.55±0.01Ba | 1.13±0.01Ba | |
| S | -AMF | 0.77±0.01Aa | 0.79±0.01Ca | 0.45±0.02Ba | 1.15±0.05Aa |
| +AMF | 0.71±0.01Ab | 0.81±0.02Ca | 0.48±0.01Ca | 1.18±0.02Aa |
| 盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理Treatment | K+/Na+ | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | -AMF | 2.06±0.08Aa | 1.11±0.04Ab | 2.27±0.10Aa |
| +AMF | 2.45±0.20Aa | 1.46±0.11Aa | 2.66±0.20Aa | |
| M | -AMF | 1.42±0.06Bb | 0.78±0.04Bb | 1.73±0.05Bb |
| +AMF | 1.75±0.08Ba | 1.07±0.05Ba | 2.18±0.12Ba | |
| S | -AMF | 1.04±0.02Ca | 0.58±0.03Cb | 1.50±0.07Ba |
| +AMF | 1.14±0.04Ca | 0.67±0.01Ca | 1.65±0.05Ca |
表4 不同盐碱梯度下AMF对羊草体内阳离子运输选择比的影响
Table 4 Effects of AMF on cations transport selectivity ratioin L. chinensis under saline-alkaline gradients
| 盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理Treatment | K+/Na+ | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | -AMF | 2.06±0.08Aa | 1.11±0.04Ab | 2.27±0.10Aa |
| +AMF | 2.45±0.20Aa | 1.46±0.11Aa | 2.66±0.20Aa | |
| M | -AMF | 1.42±0.06Bb | 0.78±0.04Bb | 1.73±0.05Bb |
| +AMF | 1.75±0.08Ba | 1.07±0.05Ba | 2.18±0.12Ba | |
| S | -AMF | 1.04±0.02Ca | 0.58±0.03Cb | 1.50±0.07Ba |
| +AMF | 1.14±0.04Ca | 0.67±0.01Ca | 1.65±0.05Ca |
盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理 Treatment | 菌丝侵染率 Hyphae colonization (%) | 丛枝侵染率 Arbuscular colonization (%) | 泡囊侵染率 Vesicle colonization (%) | 孢子密度 Spore density (No.·100 g-1) | 菌丝密度 Hyphae density (cm·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | +AMF | 69.10±3.53A | 11.90±0.78A | 8.29±0.85C | 704.15±52.32A | 113.81±3.21A |
| M | 51.62±2.83B | 12.95±0.82A | 11.94±1.45B | 682.20±75.25A | 98.01±4.48B | |
| S | 36.22±1.93C | 11.30±0.96A | 15.71±1.14A | 659.86±27.38A | 82.24±6.33C |
表5 不同盐碱梯度下AMF定殖特征
Table 5 The colonization characteristics of AMF under different saline-alkaline gradients
盐碱梯度 Saline-alkaline gradient | 处理 Treatment | 菌丝侵染率 Hyphae colonization (%) | 丛枝侵染率 Arbuscular colonization (%) | 泡囊侵染率 Vesicle colonization (%) | 孢子密度 Spore density (No.·100 g-1) | 菌丝密度 Hyphae density (cm·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | +AMF | 69.10±3.53A | 11.90±0.78A | 8.29±0.85C | 704.15±52.32A | 113.81±3.21A |
| M | 51.62±2.83B | 12.95±0.82A | 11.94±1.45B | 682.20±75.25A | 98.01±4.48B | |
| S | 36.22±1.93C | 11.30±0.96A | 15.71±1.14A | 659.86±27.38A | 82.24±6.33C |
| 1 | Wang D L, Guo J X. Restoration theory and technology of Songnen saline-alkaline grasslands. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. |
| 王德利, 郭继勋. 松嫩盐碱化草地的恢复理论与技术. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. | |
| 2 | Wang D. How the salinization and alkalization impacted the characteristics of soil celluloytic microorganism in Songnen grassland. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2017. |
| 王丹. 松嫩草地盐碱化对土壤纤维素降解菌特性的影响. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2017. | |
| 3 | Zhang J L, Li H R, Guo S Y, et al. Research advances in higher plant adaptation to salt stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(12): 220-236. |
| 张金林, 李惠茹, 郭姝媛, 等. 高等植物适应盐逆境研究进展. 草业学报, 2015, 24(12): 220-236. | |
| 4 | Munns R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell and Environment, 2002, 25(2): 239-250. |
| 5 | Zhang Y, Wang P, Yang Y, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve reestablishment of Leymus chinensis in bare saline-alkaline soil: Implication on vegetation restoration of extremely degraded land. Journal of Arid Environments, 2011, 75(9): 773-778. |
| 6 | Ba L, Ning J, Wang D, et al. The relationship between the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and grazing in a meadow steppe. Plant and Soil, 2012, 352(1/2): 143-156. |
| 7 | Van d H, Marcel G A, Klironomos J N. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature, 1998, 396(6706): 69-72. |
| 8 | Asensio D, Rapparini F, Peñuelas J. AM fungi root colonization increases the production of essential isoprenoids vs. nonessential isoprenoids especially under drought stress conditions or after jasmonic acid application. Phytochemistry, 2012, 77: 149-161. |
| 9 | Heikham E, Thokchom S D, Samta G, et al. Mitigation of salinity stress in plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Current understanding and new challenges. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 470. |
| 10 | Sohrabi Y, Heidari G, Weisany W, et al. Changes of antioxidative enzymes, lipid peroxidation and chlorophyll content in chickpea types colonized by different Glomus species under drought stress. Symbiosis, 2012, 56(1): 5-18. |
| 11 | Zhu X C, Song F B, Liu S Q, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on photosynthesis and water status of maize under high temperature stress. Plant and Soil, 2011, 346(1/2): 189-199. |
| 12 | Hashem A, Alqarawi A A, Radhakrishnan R, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi regulate the oxidative system, hormones and ionic equilibrium to trigger salt stress tolerance in Cucumis sativus L. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2018, 25(6): 1102-1114. |
| 13 | Pavithra D, Yapa N. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation enhances drought stress tolerance of plants. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2018, 7: 490-494. |
| 14 | Mathur S, Sharma M P, Jajoo A. Improved photosynthetic efficacy of maize (Zea mays) plants with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) under high temperature stress. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 2018, 180: 149-154. |
| 15 | Vogel-Mikuš K, Drobne D, Regvar M. Zn, Cd and Pb accumulation and arbuscular mycorrhizal colonisation of pennycress Thlaspi praecox Wulf. (Brassicaceae) from the vicinity of a lead mine and smelter in Slovenia. Environmental Pollution, 2005, 133(2): 233-242. |
| 16 | Luo Q Y, Wang X J, Li Y Y, et al. Mechanism of biological control to plant diseases using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(19): 5997-6005. |
| 罗巧玉, 王晓娟, 李媛媛, 等. AM真菌在植物病虫害生物防治中的作用机制. 生态学报, 2013, 33(19): 5997-6005. | |
| 17 | Zhang Y F, Wang P, Bi Q, et al. The effect of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth of Leymus chinensis under saline stress of different intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(17): 5467-5476. |
| 张义飞, 王平, 毕琪, 等. 不同强度盐胁迫下AM真菌对羊草生长的影响. 生态学报, 2016, 36(17): 5467-5476. | |
| 18 | Feng G, Bai D S, Yang M Q, et al. Influence of inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and salinity tolerance parameters of maize plants. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2000, 26(6): 743-750. |
| 冯固, 白灯莎, 杨茂秋, 等. 盐胁迫下AM真菌对玉米生长及耐盐生理指标的影响. 作物学报, 2000, 26(6): 743-750. | |
| 19 | He X L, Zhao L L, Li Y P. Effects of AM fungi on the growth and protective enzymes of cotton under NaCl stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 188-193. |
| 贺学礼, 赵丽莉, 李英鹏. NaCl胁迫下AM真菌对棉花生长和叶片保护酶系统的影响. 生态学报, 2005, 25(1): 188-193. | |
| 20 | Chang W, Sui X, Fan X X, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis modulates antioxidant response and ion distribution in salt-stressed Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 652. |
| 21 | Wang Y N, Tao S, Hua X Y, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and physiological metabolism of Leymus chinensis under salt-alkali stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(6): 2187-2194. |
| 王英男, 陶爽, 华晓雨, 等. 盐碱胁迫下AM真菌对羊草生长及生理代谢的影响. 生态学报, 2018, 38(6): 2187-2194. | |
| 22 | Li J D, Zheng H Y. Studies on improving saline-alkaline grassland in Songnen Plain. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 1995, 1: 110-115. |
| 李建东,郑慧莹. 松嫩平原盐碱化草地改良治理的研究. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 1995, 1: 110-115. | |
| 23 | Lin J, Wang Y, Sun S, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth, photosynthesis and photosynthetic pigments of Leymus chinensis seedlings under salt-alkali stress and nitrogen deposition. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 576: 234-241. |
| 24 | Jiang S C. Research on the distribution patterns of soil water and salinity and revegetation of bare saline-alkali patches in Songnen Grassland. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2010. |
| 姜世成. 松嫩盐碱化草地水盐分布格局及盐碱裸地植被快速恢复技术研究. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2010. | |
| 25 | Zhang W, Feng Y J. Physico-chemical properties and ecological recovery of saline-alkali soil in the Songnen Plain. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2009, 46(1): 169-172. |
| 张巍, 冯玉杰. 松嫩平原盐碱土理化性质与生态恢复. 土壤学报, 2009, 46(1): 169-172. | |
| 26 | Zhang K, Zhang D Y, Wang L, et al. Study on the ionic absorption and transport in Salicornia europaea L. growing in natural habitats in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Research, 2007, 24(4): 480-486. |
| 张科, 张道远, 王雷, 等. 自然生境下盐角草的离子吸收-运输特征. 干旱区研究, 2007, 24(4): 480-486. | |
| 27 | Wang S M. Effects of salt stress on the characteristics of ion absorption and distribution in Puccinellia tenuiflora. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 1996, 4(3): 186-193. |
| 王锁民. 不同程度盐胁迫对碱茅离子吸收与分配的影响. 草地学报, 1996, 4(3): 186-193. | |
| 28 | Koske R E. Physiological and genetical aspects of mycorrhizae, V. Gianinazzi-Pearson, S. Gianinazzi (Eds.)//In: Proceedings of 1st European symposium on mycorrhizae. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 1988, 90(3): 509. |
| 29 | Giovannetti M, Mosse B. An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytologist, 2006, 84(3): 489-500. |
| 30 | Gerdemann J W, Nicolson T H. Spores of mycorrhizal endogone species extracted from soil by wet sieving and decanting. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 1963, 46(2): 235-244. |
| 31 | Xu P L. The role and mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on arsenate tolerance of Medicago truncatula. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 许鹏亮. 丛枝菌根真菌对蒺藜状苜蓿抗砷酸能力的影响及其机制. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. | |
| 32 | De Herralde F, Biel C, Savé R, et al. Effect of water and salt stresses on the growth, gas exchange and water relations in Argyranthemum coronopifolium plants. Plant Science, 1998, 139(1): 9-17. |
| 33 | Zhou J G, Hu H L, Zeng K, et al. Study on osmotic adjustment on inorganic ions of cucumber seedling under NaCl stress. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 39(2): 79-82. |
| 周俊国, 扈惠灵, 曾凯, 等. NaCl胁迫下黄瓜幼苗无机离子的渗透调节效应. 河南农业科学, 2010, 39(2): 79-82. | |
| 34 | Zhang H J, Zhang N, Yang R C, et al. Growth, ion distribution and salt-tolerance mechanism of eggplant seedlings under salt stress. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2013, 18(4): 77-83. |
| 张海军, 张娜, 杨荣超, 等. NaCl胁迫对茄子幼苗生长和K+、Na+和Ca2+分布的影响及耐盐机理. 中国农业大学学报, 2013, 18(4): 77-83. | |
| 35 | Che Y M, Tang J, Chen K, et al. Effects of nitric oxide on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and photosynthetic characteristics of maize seedling under salt stress. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2009, 17(3): 91-94. |
| 车永梅, 唐静, 陈康, 等. 一氧化氮对盐胁迫下玉米幼苗叶绿素荧光参数和光合特性的影响. 玉米科学, 2009, 17(3): 91-94. | |
| 36 | Wang Q Z, Liu Q, Gao Y N, et al. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. |
| 王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 等. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. | |
| 37 | Yang F, Ding F, Du T Z. Absorption and allocation characteristics of K+, Ca2+, Na+ and Cl- in different organs of Broussonetia papyrifera seedlings under NaCl stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(4): 767-772. |
| 杨帆, 丁菲, 杜天真. 盐胁迫下构树幼苗各器官中K+、Ca2+、Na+和Cl-含量分布及吸收特征. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(4): 767-772. | |
| 38 | Cao Y P, Dai P, Dai S Y, et al. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on seedling growth and Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ contents and distribution in asparagus under salt stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(6): 1699-1704. |
| 曹岩坡, 代鹏, 戴素英, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对盐胁迫下芦笋幼苗生长及体内Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+含量和分布的影响. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(6): 1699-1704. | |
| 39 | Zheng Q S, Wang R L, Liu Y L. Effects of Ca2+ on absorption and distribution of ions in salt-treated cotton seedlings. Acta Photophysiologica Sinica, 2001, 27(4): 325-330. |
| 郑青松, 王仁雷, 刘友良. 钙对盐胁迫下棉苗离子吸收分配的影响. 植物生理学报, 2001, 27(4): 325-330. | |
| 40 | Gosling P, Hodge A, Goodlass G, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic farming. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2006, 113(1/4): 17-35. |
| 41 | Juniper S, Abbott L. Soil salinity delays germination and limits growth of hyphae from propagules of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza, 2006, 16(5): 371-379. |
| 42 | Hart M M, Reader R J. Taxonomic basis for variation in the colonization strategy of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytologist, 2002, 153(2): 335-344. |
| 43 | Copeman R H, Martin C A, Stutz J C. Tomato growth in response to salinity and mycorrhizal fungi from saline or nonsaline soil. Horticultural Science, 1996, 31(3): 313-318. |
| 44 | Trimble M R, Knowles N R. Influence of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus on growth, carbohydrate partitioning and mineral nutrition of greenhouse cucumber (Cucurnis sativus L.) plants during establishment. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 1995, 75(1): 239-250. |
| [1] | 郭丰辉, 丁勇, 马文静, 李贤松, 李西良, 侯向阳. 母体放牧经历对羊草克隆后代干旱敏感性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 119-126. |
| [2] | 张丽星, 海春兴, 常耀文, 高晓媚, 高文邦, 解云虎. 羊草及芨芨草草原和西北针茅草原土壤质量评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 68-79. |
| [3] | 李倩, 李晓霞, 程丽琴, 陈双燕, 齐冬梅, 杨伟光, 高利军, 新巴音, 刘公社. 羊草LcCBF6基因的表达特性和功能研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 105-115. |
| [4] | 李聪聪, 周亚星, 谷强, 杨明新, 朱传鲁, 彭子原, 薛凯, 赵新全, 王艳芬, 纪宝明, 张静. 三江源区典型高寒草地丛枝菌根真菌多样性及构建机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 46-58. |
| [5] | 漫静, 唐波, 邓波, 李佳欢, 何玉娟, 张佳良. 羊草根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 59-71. |
| [6] | 邢易梅, 蕫理, 战力峰, 才华, 杨圣秋, 孙娜. 混合接种摩西球囊霉和根瘤菌对紫花苜蓿耐碱能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 136-145. |
| [7] | 李茹霞, 耿元波. 应用13C同位素标记法区分羊草草原生态系统呼吸[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 56-70. |
| [8] | 贾红梅, 方千, 张秫华, 严铸云, 柳敏. AM真菌对丹参生长及根际土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 83-92. |
| [9] | 赵昕, 吴子龙, 张浩, 杨旭钊, 韩超, 高杰. 峰峰矿区煤矸石山周边植物丛枝菌根真菌的侵染及Cd含量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 78-87. |
| [10] | 伏兵哲, 周燕飞, 李雪, 倪彪, 高雪芹. 宁夏引黄灌区羊草水肥耦合效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 98-108. |
| [11] | 白乌云, 侯向阳, 武自念, 田春育, 丁勇. 羊草不同地理种群表型变异及其对根茎克隆繁殖的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 86-94. |
| [12] | 高亚敏, 罗慧琴, 姚拓, 张建贵, 李海云, 杨琰珊, 兰晓君. 高寒退化草地委陵菜根围丛枝菌根菌(AMF)分离鉴定及促生效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 145-154. |
| [13] | 李文彬, 宁楚涵, 李伟, 李峰, 郭绍霞. 菲和芘胁迫下AMF和PGPR对高羊茅生理生态的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 84-94. |
| [14] | 任伟忠, 高艳霞, 李秋凤, 曹玉凤, 李建国. 全株玉米青贮、谷草和羊草组合全混合日粮饲喂干奶前期奶牛对其围产期生产性能和血液生化及免疫指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 124-136. |
| [15] | 秦燕, 刘文辉, 何峰, 仝宗永, 李向林. 施肥与切根对退化羊草草原土壤理化性质和酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 5-14. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||