

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 68-80.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020150
收稿日期:2020-03-31
修回日期:2020-08-10
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2021-03-09
通讯作者:
龚春梅
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: gcm228@nwafu.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhi-peng CHANG1( ), Ying-ying SUN1, Jia-yang LI1, Chun-mei GONG2(
), Ying-ying SUN1, Jia-yang LI1, Chun-mei GONG2( )
)
Received:2020-03-31
Revised:2020-08-10
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2021-03-09
Contact:
Chun-mei GONG
摘要:
干旱胁迫严重影响植物的生长发育甚至生存状态,是限制我国西北荒漠植被恢复的主要非生物胁迫因素之一。实验室前期研究发现随黄土高原由南向北降水减少,柠条苯丙烷生物合成是差异表达最显著的代谢途径。本研究遂以柠条苯丙烷合成途径中木质素合成酶基因CkCAD为研究对象,生信分析表明该基因开放阅读框全长1074 bp,编码357个氨基酸;蛋白序列比对发现柠条CkCAD与非洲相思豆、蒺藜苜蓿、大豆和花生的亲缘关系较近,相似度均在80%以上,其中与非洲相思豆ApCAD最为相似。蛋白质偏酸性且为亲水性蛋白,无跨膜结构域,亚细胞定位于细胞质中。通过农杆菌介导法利用过表达载体pCAMBIA1302将柠条CkCAD转入野生型拟南芥中。在筛选获得T3代纯合阳性植株后进行抗旱性分析。对T3代过表达CkCAD拟南芥进行实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)和Western blot检测发现CkCAD及其酶蛋白在拟南芥中呈稳定表达。相较于野生型拟南芥,T3代过表达CkCAD拟南芥叶脉长度和叶脉密度更大,脉岛长径、脉岛短径更短,脉岛密度更大,叶脉更为发达且木质素含量更高。同时发现干旱处理下T3代过表达植株的叶片萎蔫程度、丙二醛含量、相对电导率均低于野生型植株,而相对含水量则高于野生型植株。从而证实干旱胁迫下柠条木质素合成酶基因CkCAD可以促进木质素合成进而提高过表达拟南芥植株的抗旱性。
畅志鹏, 孙莹莹, 李佳阳, 龚春梅. 柠条CkCAD基因的克隆转化及其抗旱功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 68-80.
Zhi-peng CHANG, Ying-ying SUN, Jia-yang LI, Chun-mei GONG. Cloning and transformation of the CkCAD gene in Caragana korshinskii and analysis of its drought resistance function[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(3): 68-80.
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| 1302-CkCAD-F | GGACTCTTGACCATGATGGGTAGCCTTGAATCGG |
| 1302-CkCAD-R | CTTCTCCTTTACTAGCTGATCAAGTTTACTGCCTTTGAC |
| Atactin-F | CACTACCGCAGAACGGGAAA |
| Atactin-R | GCGATGGCTGGAACAGAACC |
| CkCAD-F | TCTCTCCCCATACACCTACA |
| CkCAD-R | CCTTCTCTTTCCAAAACTCC |
| AtCAD-F | TAGAAGCAGGAGAAAAG |
| AtCAD-R | CAGGAACCATAGGATAA |
表1 柠条CkCAD转化和定量所用引物
Table 1 Primers for C. korshinskiiCkCAD conversion and quantification in this study
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| 1302-CkCAD-F | GGACTCTTGACCATGATGGGTAGCCTTGAATCGG |
| 1302-CkCAD-R | CTTCTCCTTTACTAGCTGATCAAGTTTACTGCCTTTGAC |
| Atactin-F | CACTACCGCAGAACGGGAAA |
| Atactin-R | GCGATGGCTGGAACAGAACC |
| CkCAD-F | TCTCTCCCCATACACCTACA |
| CkCAD-R | CCTTCTCTTTCCAAAACTCC |
| AtCAD-F | TAGAAGCAGGAGAAAAG |
| AtCAD-R | CAGGAACCATAGGATAA |
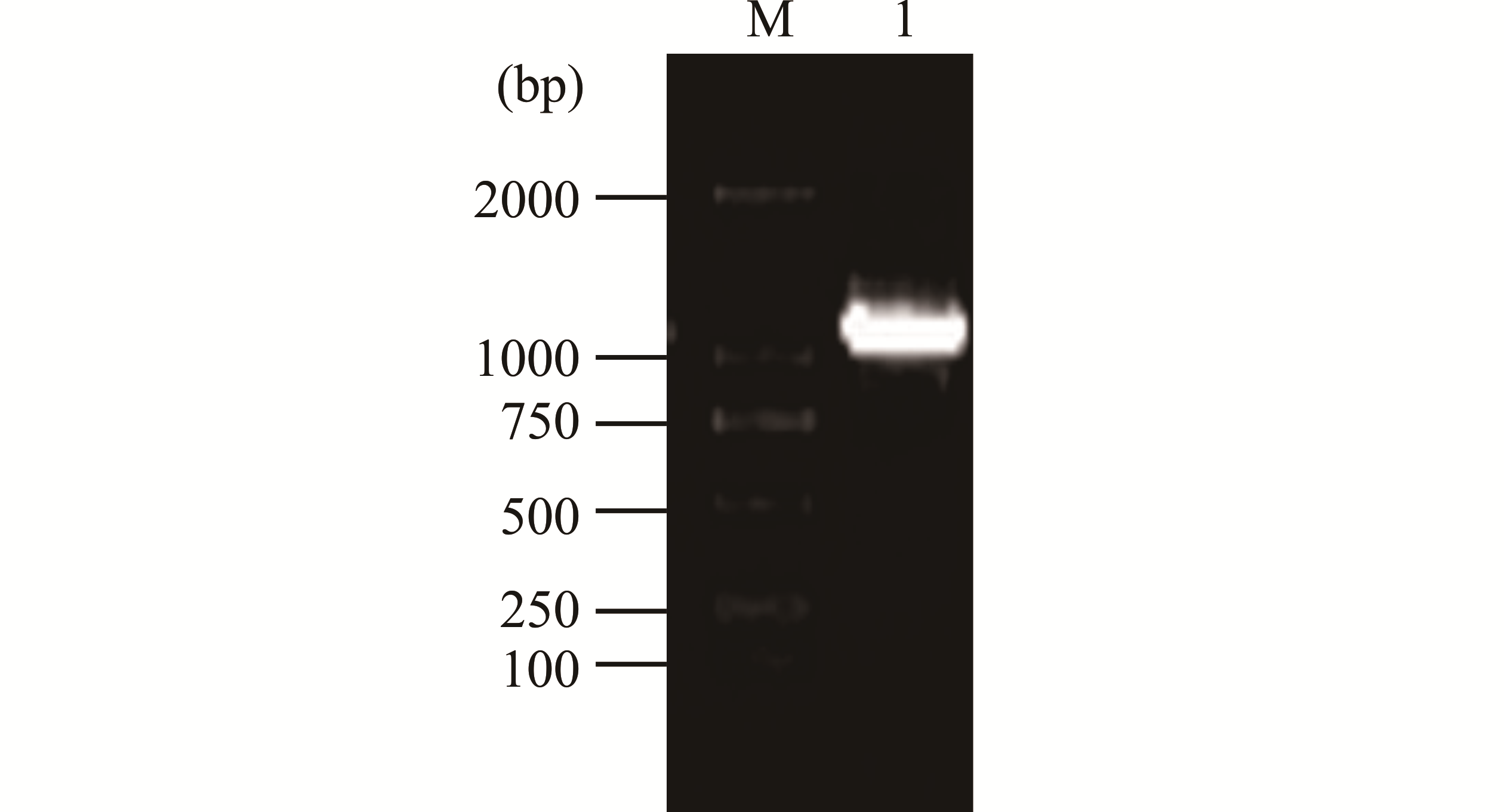
图1 柠条CkCAD序列扩增条带M为D2000 DNA maker条带;1为扩增CkCAD的DNA片段。M is the D2000 DNA maker band; 1 is the amplified DNA fragment of CkCAD.
Fig.1 Amplified bands of C. korshinskii CkCAD sequence

图2 柠条CkCAD与其他物种系统发育进化树及氨基酸序列比对结果A: 柠条CkCAD与其他物种中同源CAD系统发育进化树C. korshinskii CkCAD and other species homologous CAD phylogenetic tree;B: 柠条CkCAD与其他物种中同源CAD氨基酸序列比对结果C. korshinskii CkCAD and other species homologous CAD amino acid sequence alignment results。MsCAD: 紫花苜蓿肉桂醇脱氢酶M.sativa cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; MtCAD:蒺藜苜蓿肉桂醇脱氢酶M.truncatula cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; CaCAD:鹰嘴豆肉桂醇脱氢酶C.arietinum cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; ApCAD:非洲相思豆肉桂醇脱氢酶A.precatorius arietinum cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; AhCAD:花生肉桂醇脱氢酶A.hypogaea cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; VuCAD:豇豆肉桂醇脱氢酶Vigna unguiculata cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; GmCAD:大豆肉桂醇脱氢酶G.max cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase; GsCAD:野大豆肉桂醇脱氢酶Glycine soja cinnamoyl alcohol dehydrogenase. 灰色部分为氨基酸序列相同部分,黑色部分为氨基酸序列差异部分。The gray part is the same part of the amino acid sequence, and the black part is the difference part of the amino acid sequence.
Fig.2 Phylogenetic tree and amino acid sequence comparison of C. korshinskii CkCAD and other species

图3 柠条CkCAD蛋白质结构及亚细胞定位预测A: 保守结构域分析 Conserved domain analysis; B: 蛋白质二级结构 Protein secondary structure; C:蛋白质三级结构 Protein tertiary structure;D:亚细胞定位预测结果 Subcellular location prediction results.
Fig.3 CkCAD protein structure and subcellular localization prediction of C. korshinskii

图4 pCAMBIA1302-35S::CkCAD过表达载体的构建A: pCAMBIA1302-35S::CkCAD过表达载体示意图;B: pCAMBIA1302-35S::CkCAD过表达载体的酶切鉴定结果。A: pCAMBIA1302-35S:: CkCAD overexpression vector schematic diagram; B: Restriction digestion identification result of pCAMBIA1302-35S::CkCAD overexpression vector.M为D15000 DNA maker; 1为pCAMBIA1302-35S::CkCAD过表达载体Bam HI酶切条带。M is D15000 DNA maker; 1 is the pCAMBIA1302-35S:: CkCAD overexpression vector Bam HI digested band.
Fig.4 Construction of pCAMBIA1302-35S::CkCAD overexpression vector

图6 柠条CkCAD能够在转基因拟南芥中稳定表达A: CAD基因在野生型和过表达拟南芥株系#1、#3和#4中的定量结果。B: 野生型和过表达拟南芥植株中GFP标签的蛋白免疫印迹结果。CkCAD-GFP为过表达拟南芥株系#1、#3和#4中CkCAD与GFP(绿色荧光蛋白)形成的融合蛋白,GFP为绿色荧光蛋白。WT表示野生型拟南芥,#1、#3、#4表示3个转CkCAD拟南芥株系,**代表差异显著(P<0.01),下同。A: Quantitative results of CAD genes in wild-type and overexpressing Arabidopsis lines # 1, # 3, and # 4. B: Western blot results of GFP tags in wild-type and overexpressing Arabidopsis plants. CkCAD-GFP is a fusion protein formed by CkCAD and GFP (green fluorescent protein) in overexpressing Arabidopsis strains #1, #3 and #4, GFP is green fluorescent protein. WT represent wild-type Arabidopsis, #1, #3, #4 represent three CkCADArabidopsis lines, the asterisk represents significant difference (P<0.01), the same below.
Fig.6 C. korshinskiiCkCAD can be stably expressed in transgenic Arabidopsis

图8 干旱胁迫下野生型及转CkCAD拟南芥植株株高和叶面积的变化趋势
Fig.8 Variation trend of plant height and leaf area of wild-type and CkCAD transformed Arabidopsis plants under drought stress
| 1 | Gao L F. The expression of related genes CkERF2 and CkCOV1 in leaf vascular development during responding drought in Caragana korshinskii. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2018. |
| 高丽芳. 叶脉发育相关基因CkERF2和CkCOV1在柠条叶脉响应干旱中的表达研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. | |
| 2 | Ning P B, Zhou Y L, Gao L F, et al. Unraveling the microRNA of Caragana korshinskii along a precipitation gradient on the Loess Plateau, China, using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS One, 2017, 12(2): e0172017. |
| 3 | Li Y J, Zhao Z, Sun D X. Hydrological physiological characteristics of Caragana korshinskii under water stress. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2008, 23(3): 1-4. |
| 李彦瑾, 赵忠, 孙德祥.干旱胁迫下柠条锦鸡儿的水分生理特征. 西北林学院报, 2008, 23(3): 1-4. | |
| 4 | Yao H, Zhao X Y, Li X M. Physiological response of 3 kinds of Caragana plant seedlings on continuous drought. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(9): 3915-3917. |
| 姚华, 赵晓英, 李晓梅. 3种锦鸡儿属植物幼苗对持续干旱的生理响应.安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(9): 3915-3917. | |
| 5 | Wang J J. The drought adaption of leaf functional traits in Caragana korshinskii KOM. under water gradient. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2015. |
| 王佳佳. 水分梯度下柠条锦鸡儿叶功能属性的干旱适应性研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015. | |
| 6 | Wei L L. Mechanism analysis of cold and drought tolerance of the transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing DREB1 from Caragana korshinskii Kom. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 魏丽丽. 过表达柠条锦鸡儿CkDREB1基因的拟南芥抗旱和抗冷的机理分析.呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2013. | |
| 7 | Xia J X, Liu Y J, Yao S B, et al. Characterization and expression profiling of Camellia sinensis cinnamate 4-hydroxylase genes in phenylpropanoid pathways. Genes, 2017, 8(8): 193. |
| 8 | Turner S R, Somerville C R. Collapsed xylem phenotype of Arabidopsis identifies mutants deficient in cellulose deposition in the secondary cell wall. The Plant Cell, 1997, 9(5): 689-701. |
| 9 | Xue C, Yao J L, Xue Y S, et al. PbrMYB169 positively regulates lignification of stone cells in pear fruit. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2019, 70(6): 1801-1814. |
| 10 | Santos A B d, Bottcher A, Kiyota E, et al. Water stress alters lignin content and related gene expression in two sugarcane genotypes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(19): 4708-4720. |
| 11 | Liu F R, Xie L F, Yao Z Y, et al. Equipment B: Caragana korshinskii phenylalanine ammonialyase is up-regulated in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway in response to drought stress. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 2019, 33(1): 842-854. |
| 12 | Cass C L, Peraldi A, Dowd P F, et al. Effects of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) knockdown on cell wall composition, biomass digestibility, and biotic and abiotic stress responses in Brachypodium. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2015, 66(14): 4317-4335. |
| 13 | Sun Y Y. Study on drought response of genes related to lignin synthesis in Caragana korshinskii. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2018. |
| 孙莹莹. 柠条锦鸡儿木质素合成基因的干旱响应研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. | |
| 14 | Clough S J, Bent A F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium‐mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 1998, 16(6): 735-743. |
| 15 | Xu C, Wang Y D, Yu Y C, et al. Degradation of MONOCULM 1 by APC/C TAD1 regulates rice tillering. Nature Communications, 2012, 3(1): 1-9. |
| 16 | Zhang X H, Liu T J, Duan M M, et al. De novo transcriptome analysis of Sinapis alba in revealing the glucosinolate and phytochelatin pathways. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 259. |
| 17 | Ganguly D R, Crisp P A, Eichten S R, et al. The Arabidopsis DNA methylome is stable under transgenerational drought stress. Plant Physiology, 2017, 175(4): 1893-1912. |
| 18 | Marshall D M, Muhaidat R, Brown N J, et al. Cleome, a genus closely related to Arabidopsis, contains species spanning a developmental progression from C3 to C4 photosynthesis. The Plant Journal, 2007, 51(5): 886-896. |
| 19 | Hatfield R, Fukushima R S. Can lignin be accurately measured? Crop Science, 2005, 45(3): 832-839. |
| 20 | Kou X H, He Y L, Li Y F, et al. Effect of abscisic acid (ABA) and chitosan/nano-silica/sodium alginate composite film on the color development and quality of postharvest Chinese winter jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao). Food Chemistry, 2019, 270: 385-394. |
| 21 | Wang J B, Ding B, Guo Y L, et al. Overexpression of a wheat phospholipase D gene, TaPLDα, enhances tolerance to drought and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta, 2014, 240(1): 103-115. |
| 22 | Zhou W F, Liu F R, Yao Z Y, et al. Growth adaptation characteristics of three Salsola species with different photosynthetic systems. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 78-90. |
| 周文菲, 刘芙蓉, 姚甄业, 等. 猪毛菜属 3 种不同光合型物种的生长适应特征比较. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 78-90. | |
| 23 | Tang H M, Liu S Z, Hill‐Skinner S, et al. The maize brown midrib2 (bm2) gene encodes a methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase that contributes to lignin accumulation. The Plant Journal, 2014, 77(3): 380-392. |
| 24 | Wang J H, Feng J J, Jia W T, et al. Genome-wide identification of sorghum bicolor laccases reveals potential targets for lignin modification. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 714. |
| 25 | Mottiar Y, Vanholme R, Boerjan W, et al. Designer lignins: Harnessing the plasticity of lignification. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 37: 190-200. |
| 26 | Wang P, Dudareva N, Morgan J A, et al. Genetic manipulation of lignocellulosic biomass for bioenergy. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2015, 29: 32-39. |
| 27 | Coleman H D, Park J Y, Nair R, et al. RNAi-mediated suppression of p-coumaroyl-CoA 3′-hydroxylase in hybrid poplar impacts lignin deposition and soluble secondary metabolism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2008, 105(11): 4501-4506. |
| 28 | Amrhein N, Frank G, Lemm G, et al. Inhibition of lignin formation by L-alpha-aminooxy-beta-phenylpropionic acid, an inhibitor of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. European Journal of Cell Biology, 1983, 29(2): 139-144. |
| 29 | Smart C C, Amrhein N. The influence of lignification on the development of vascular tissue in Vigna radiata L. Protoplasma, 1985, 124(1/2): 87-95. |
| 30 | Li Z, Peng Y, Ma X. Different response on drought tolerance and post-drought recovery between the small-leafed and the large-leafed white clover (Trifolium repens L.) associated with antioxidative enzyme protection and lignin metabolism. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2013, 35(1): 213-222. |
| 31 | Cheng X, Li G, Ma C, et al. Comprehensive genome-wide analysis of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) laccase gene (PbLAC) family and functional identification of PbLAC1 involved in lignin biosynthesis. PLoS One, 2019, 14: e0210892. |
| 32 | Zhong R, Taylor J J, Ye Z H. Disruption of interfascicular fiber differentiation in an Arabidopsis mutant. The Plant Cell, 1997, 9(12): 2159-2170. |
| 33 | Lens F, Tixier A, Cochard H, et al. Embolism resistance as a key mechanism to understand adaptive plant strategies. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2013, 16(3): 287-292. |
| 34 | Adams H D, Zeppel M J, Anderegg W R, et al. A multi-species synthesis of physiological mechanisms in drought-induced tree mortality. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2017, 1(9): 1285-1291. |
| 35 | Anderegg W R, Klein T, Bartlett M, et al. Meta-analysis reveals that hydraulic traits explain cross-species patterns of drought-induced tree mortality across the globe. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(18): 5024-5029. |
| 36 | Pereira L, Domingues-Junior A P, Jansen S, et al. Is embolism resistance in plant xylem associated with quantity and characteristics of lignin? Trees, 2017(33): 1-10. |
| 37 | Jansen S, Choat B, Pletsers A. Morphological variation of intervessel pit membranes and implications to xylem function in angiosperms. American Journal of Botany, 2009, 96(2): 409-419. |
| 38 | Li S, Lens F, Espino S, et al. Intervessel pit membrane thickness as a key determinant of embolism resistance in angiosperm xylem. Iawa Journal, 2016, 37(2): 152-171. |
| 39 | Dória L C, Podadera D S, del Arco M, et al. Insular woody daisies (Argyranthemum, Asteraceae) are more resistant to drought‐induced hydraulic failure than their herbaceous relatives. Functional Ecology, 2018, 32(6): 1467-1478. |
| 40 | Dória L C, Meijs C, Podadera D S, et al. Embolism resistance in stems of herbaceous Brassicaceae and Asteraceae is linked to differences in woodiness and precipitation. Annals of Botany, 2018, 20: 1-13. |
| 41 | Xu T, Zhao C Z, Han L, et al. Correlation between vein density and water use efficiency of Salix matsudana in Zhangye wetland, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(7): 761-769. |
| 徐婷, 赵成章, 韩玲, 等. 张掖湿地旱柳叶脉密度与水分利用效率的关系. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(7): 761-769. | |
| 42 | Sack L, Scoffoni C. Leaf venation: Structure, function, development, evolution, ecology and applications in the past, present and future. New Phytologist, 2013, 198(4): 983-1000. |
| 43 | Nardini A, Raimondo F, Lo Gullo M A, et al. Leafminers help us understand leaf hydraulic design. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2010, 33(7): 1091-1100. |
| [1] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [2] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 贾瑜琀. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. |
| [3] | 张雪婷, 王新永, 杨文雄, 柳娜, 杨长刚. 河西绿洲灌区节水抗旱型玉米品种的评价方法探讨[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 134-148. |
| [4] | 常海涛, 刘任涛, 陈蔚, 张安宁, 左小安. 内蒙古乌拉特荒漠草原红砂灌丛林引入柠条后地面节肢动物群落结构分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 188-197. |
| [5] | 杨柳慧, 尹航, 黄沁梅, 张彦妮, 何淼, 周蕴薇. 细叶百合LpWRKY20基因对非生物胁迫的响应及抗旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 193-202. |
| [6] | 姜红岩, 滕珂, 檀鹏辉, 尹淑霞. 日本结缕草ZjZFN1基因对拟南芥的转化及其耐旱性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(4): 129-138. |
| [7] | 吴娟子, 钱晨, 刘智微, 潘玉梅, 钟小仙. 基于转录组测序分析象草木质素合成的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 150-161. |
| [8] | 郭星, 谢飞, 闫倩倩, 曹秀文, 杨帆. 黄腐酸对白龙江干旱河谷5种苗木抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 86-94. |
| [9] | 刘婷婷, 陈道钳, 王仕稳, 殷俐娜, 邓西平. 不同品种高粱幼苗在干旱复水过程中的生理生态响应[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(6): 100-110. |
| [10] | 许翩翩, 王建柱. 三种常见边坡植物对模拟干旱环境抗旱性能的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 36-47. |
| [11] | 史经昂, 张兵, 肖晓琳, 马晶晶, 杨向阳, 刘建秀. 结缕草肉桂醇脱氢酶基因家族全基因组序列鉴定和表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 111-119. |
| [12] | 孙毅, 闫兴富. 不同生境下柠条种子出苗及幼苗生长特[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(7): 186-195. |
| [13] | 汪毅, 郭海林, 陈静波, 宗俊勤, 李丹丹, 姜亦巍, 刘建秀. 国审品种‘苏植1号’杂交结缕草抗旱性初步评价与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 30-39. |
| [14] | 于景金, 李冉, 刘梦娴, 杨志民. 暖季型与冷季型草坪草差异响应干旱及旱后复水的生理生态机制[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 86-93. |
| [15] | 孙艳茹,石屹,陈国军,闫慧峰. PEG模拟干旱胁迫下8种绿肥作物萌发特性与抗旱性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 89-98. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||