

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 168-180.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020600
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
张梦1,4( ), 史鹏飞2, 李本银1, 刘春增1(
), 史鹏飞2, 李本银1, 刘春增1( ), 郑春风1, 张成兰1, 郭晓彦2, 张丽霞2, 吕玉虎2, 何春梅5, 曹卫东3(
), 郑春风1, 张成兰1, 郭晓彦2, 张丽霞2, 吕玉虎2, 何春梅5, 曹卫东3( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-30
修回日期:2021-03-15
出版日期:2022-03-20
发布日期:2022-01-15
通讯作者:
刘春增,曹卫东
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: liucz321@aliyun.com, caoweidong@caas.cn基金资助:
Meng ZHANG1,4( ), Peng-fei SHI2, Ben-yin LI1, Chun-zeng LIU1(
), Peng-fei SHI2, Ben-yin LI1, Chun-zeng LIU1( ), Chun-feng ZHENG1, Cheng-lan ZHANG1, Xiao-yan GUO2, Li-xia ZHANG2, Yu-hu LV2, Chun-mei HE5, Wei-dong CAO3(
), Chun-feng ZHENG1, Cheng-lan ZHANG1, Xiao-yan GUO2, Li-xia ZHANG2, Yu-hu LV2, Chun-mei HE5, Wei-dong CAO3( )
)
Received:2020-12-30
Revised:2021-03-15
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-01-15
Contact:
Chun-zeng LIU,Wei-dong CAO
摘要:
对70份当地和引入紫云英种质资源在豫南地区种植的表型性状和结实特征进行研究,结果表明,供试紫云英均可在豫南地区完成扩繁,19个调查性状的变异系数(CV)介于1.3%~73.2%,其中冠层面积(CV=45.9%~73.2%)、始荚高度(CV=46.0%~52.9%)、生殖分枝数和生殖分枝比率(CV=34.6%~48.4%)、二级分枝数(CV=41.2%~41.3%)、返青期株高(CV=30.2%~39.2%)、种子产量(CV=24.4%~35.7%)变异性较高。信紫1号、XYHY-1等6个当地资源在越冬期和返青期叶片呈现紫红色。种子产量与返青期株高、盛花期株高、越冬期冠层大小、始荚高度、结荚层数、种子千粒重显著正相关;种子千粒重与返青期株高、盛花期株高、越冬期冠层大小、始荚高度、结荚层数、生殖分枝比率显著正相关,与出苗至盛花期天数、全氮和全磷含量显著负相关。引入资源平均种子产量为1015.5 kg·hm-2,当地资源平均种子产量为1096.5 kg·hm-2。与冬油菜和冬小麦相比,大部分紫云英种质资源在豫南地区繁种具有较高的经济效益,适合移栽稻接茬。
张梦, 史鹏飞, 李本银, 刘春增, 郑春风, 张成兰, 郭晓彦, 张丽霞, 吕玉虎, 何春梅, 曹卫东. 70份紫云英种质资源表型多样性及其在豫南地区的结实特征[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 168-180.
Meng ZHANG, Peng-fei SHI, Ben-yin LI, Chun-zeng LIU, Chun-feng ZHENG, Cheng-lan ZHANG, Xiao-yan GUO, Li-xia ZHANG, Yu-hu LV, Chun-mei HE, Wei-dong CAO. Phenotypic diversity and podding characteristics of 70 Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) germplasm lines cultivated in Southern Henan[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(3): 168-180.
编号 No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Source | 编号 No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Source | 编号 No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 兵库Bingku | 日本Japan | 25 | 余浅紫26 Yuqianzi 26 | 浙江Zhejiang | 49 | 南京节庄种Nanjing-Jiezhuang | 江苏Jiangsu |
| 2 | 75-388 | 江西 Jiangxi | 26 | 浙22 Zhe 22 | 浙江Zhejiang | 50 | 南桥Nanqiao | 上海Shanghai |
| 3 | 75-110 | 湖南 Hunan | 27 | 浙72-554 Zhe 72-554 | 浙江Zhejiang | 51 | 青浦Qingpu | 上海Shanghai |
| 4 | 隆西Longxi | 湖南 Hunan | 28 | 茅山Maoshan | 浙江Zhejiang | 52 | 当涂Dangtu | 安徽Anhui |
| 5 | 萍宁3号Pingning No.3 | 广西 Guangxi | 29 | 浙江5号Zhejiang No.5 | 浙江Zhejiang | 53 | 弋江籽Yijiangzi | 安徽Anhui |
| 6 | 川西Chuanxi | 四川Sichuan | 30 | 平湖大叶Pinghudaye | 浙江Zhejiang | 54 | 闽紫7号Minzi No.7 | 福建Fujian |
| 7 | 赣紫75-3-51 Ganzi 75-3-51 | 江西Jiangxi | 31 | 浙紫62-18 Zhezi 62-18 | 浙江Zhejiang | 55 | XYHY-1 | 河南Henan |
| 8 | 余干Yugan | 江西Jiangxi | 32 | 浙71-107 Zhe 71-107 | 浙江Zhejiang | 56 | XYHY-2 | 河南Henan |
| 9 | 宜春Yichun | 江西Jiangxi | 33 | 宁绿1号Ninglv No.1 | 浙江Zhejiang | 57 | XYHY-3 | 河南Henan |
| 10 | 南昌Nanchang | 江西Jiangxi | 34 | 闽紫1号Minzi No.1 | 福建Fujian | 58 | XYHY-4 | 河南Henan |
| 11 | 湘肥73-1 Xiangfei 73-1 | 湖南Hunan | 35 | 闽紫82 Minzi 82 | 福建Fujian | 59 | DSHS-1 | 河南Henan |
| 12 | 长沙Changsha | 湖南Hunan | 36 | 闽紫83(4) Minzi 83(4) | 福建Fujian | 60 | DSHS-2 | 河南Henan |
| 13 | 湘肥1号Xiangfei No.1 | 湖南Hunan | 37 | 闽紫84(10) Minzi 84(10) | 福建Fujian | 61 | DSHS-3 | 河南Henan |
| 14 | 湘肥3号Xiangfei No.3 | 湖南Hunan | 38 | 闽紫84(34) Minzi 84(34) | 福建Fujian | 62 | DSHS-4 | 河南Henan |
| 15 | 湘肥70-1-3 Xiangfei 70-1-3 | 湖南Hunan | 39 | 闽紫84(28) Minzi 84(28) | 福建Fujian | 63 | DSHS-5 | 河南Henan |
| 16 | 湘肥72-2 Xiangfei 72-2 | 湖南Hunan | 40 | 闽紫84(13) Minzi 84(13) | 福建Fujian | 64 | DSHS-6 | 河南Henan |
| 17 | 乐平Leping | 江西Jiangxi | 41 | 闽紫2号Minzi No.2 | 福建Fujian | 65 | DSHS-7 | 河南Henan |
| 18 | 湖南70-3 Hunan 70-3 | 湖南Hunan | 42 | 闽紫3号Minzi No.3 | 福建Fujian | 66 | ZDY-1 | 河南Henan |
| 19 | 醴陵Liling | 湖南Hunan | 43 | 闽紫4号Minzi No.4 | 福建Fujian | 67 | ZDY-2 | 河南Henan |
| 20 | 宁乡紫 Ningxiangzi | 湖南Hunan | 44 | 闽紫5号Minzi No.5 | 福建Fujian | 68 | QYJH1 | 河南Henan |
| 21 | 澧县Lixian | 湖南Hunan | 45 | 闽紫6号Minzi No.6 | 福建Fujian | 69 | LDYZD1 | 河南Henan |
| 22 | 华容Huarong | 湖南Hunan | 46 | 苏州Suzhou | 江苏Jiangsu | 70 | 信紫1号Xinzi No.1 | 河南Henan |
| 23 | 宁波大桥Ningbodaqiao | 浙江Zhejiang | 47 | 茜墩Qiandun | 江苏Jiangsu | |||
| 24 | 宁绿2号Ninglv No.2 | 浙江Zhejiang | 48 | 斜塘紫Xietangzi | 江苏Jiangsu |
表1 70份紫云英种质资源
Table 1 Materials of 70 A. sinicus germplasm lines
编号 No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Source | 编号 No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Source | 编号 No. | 种质名称 Germplasm name | 来源地 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 兵库Bingku | 日本Japan | 25 | 余浅紫26 Yuqianzi 26 | 浙江Zhejiang | 49 | 南京节庄种Nanjing-Jiezhuang | 江苏Jiangsu |
| 2 | 75-388 | 江西 Jiangxi | 26 | 浙22 Zhe 22 | 浙江Zhejiang | 50 | 南桥Nanqiao | 上海Shanghai |
| 3 | 75-110 | 湖南 Hunan | 27 | 浙72-554 Zhe 72-554 | 浙江Zhejiang | 51 | 青浦Qingpu | 上海Shanghai |
| 4 | 隆西Longxi | 湖南 Hunan | 28 | 茅山Maoshan | 浙江Zhejiang | 52 | 当涂Dangtu | 安徽Anhui |
| 5 | 萍宁3号Pingning No.3 | 广西 Guangxi | 29 | 浙江5号Zhejiang No.5 | 浙江Zhejiang | 53 | 弋江籽Yijiangzi | 安徽Anhui |
| 6 | 川西Chuanxi | 四川Sichuan | 30 | 平湖大叶Pinghudaye | 浙江Zhejiang | 54 | 闽紫7号Minzi No.7 | 福建Fujian |
| 7 | 赣紫75-3-51 Ganzi 75-3-51 | 江西Jiangxi | 31 | 浙紫62-18 Zhezi 62-18 | 浙江Zhejiang | 55 | XYHY-1 | 河南Henan |
| 8 | 余干Yugan | 江西Jiangxi | 32 | 浙71-107 Zhe 71-107 | 浙江Zhejiang | 56 | XYHY-2 | 河南Henan |
| 9 | 宜春Yichun | 江西Jiangxi | 33 | 宁绿1号Ninglv No.1 | 浙江Zhejiang | 57 | XYHY-3 | 河南Henan |
| 10 | 南昌Nanchang | 江西Jiangxi | 34 | 闽紫1号Minzi No.1 | 福建Fujian | 58 | XYHY-4 | 河南Henan |
| 11 | 湘肥73-1 Xiangfei 73-1 | 湖南Hunan | 35 | 闽紫82 Minzi 82 | 福建Fujian | 59 | DSHS-1 | 河南Henan |
| 12 | 长沙Changsha | 湖南Hunan | 36 | 闽紫83(4) Minzi 83(4) | 福建Fujian | 60 | DSHS-2 | 河南Henan |
| 13 | 湘肥1号Xiangfei No.1 | 湖南Hunan | 37 | 闽紫84(10) Minzi 84(10) | 福建Fujian | 61 | DSHS-3 | 河南Henan |
| 14 | 湘肥3号Xiangfei No.3 | 湖南Hunan | 38 | 闽紫84(34) Minzi 84(34) | 福建Fujian | 62 | DSHS-4 | 河南Henan |
| 15 | 湘肥70-1-3 Xiangfei 70-1-3 | 湖南Hunan | 39 | 闽紫84(28) Minzi 84(28) | 福建Fujian | 63 | DSHS-5 | 河南Henan |
| 16 | 湘肥72-2 Xiangfei 72-2 | 湖南Hunan | 40 | 闽紫84(13) Minzi 84(13) | 福建Fujian | 64 | DSHS-6 | 河南Henan |
| 17 | 乐平Leping | 江西Jiangxi | 41 | 闽紫2号Minzi No.2 | 福建Fujian | 65 | DSHS-7 | 河南Henan |
| 18 | 湖南70-3 Hunan 70-3 | 湖南Hunan | 42 | 闽紫3号Minzi No.3 | 福建Fujian | 66 | ZDY-1 | 河南Henan |
| 19 | 醴陵Liling | 湖南Hunan | 43 | 闽紫4号Minzi No.4 | 福建Fujian | 67 | ZDY-2 | 河南Henan |
| 20 | 宁乡紫 Ningxiangzi | 湖南Hunan | 44 | 闽紫5号Minzi No.5 | 福建Fujian | 68 | QYJH1 | 河南Henan |
| 21 | 澧县Lixian | 湖南Hunan | 45 | 闽紫6号Minzi No.6 | 福建Fujian | 69 | LDYZD1 | 河南Henan |
| 22 | 华容Huarong | 湖南Hunan | 46 | 苏州Suzhou | 江苏Jiangsu | 70 | 信紫1号Xinzi No.1 | 河南Henan |
| 23 | 宁波大桥Ningbodaqiao | 浙江Zhejiang | 47 | 茜墩Qiandun | 江苏Jiangsu | |||
| 24 | 宁绿2号Ninglv No.2 | 浙江Zhejiang | 48 | 斜塘紫Xietangzi | 江苏Jiangsu |
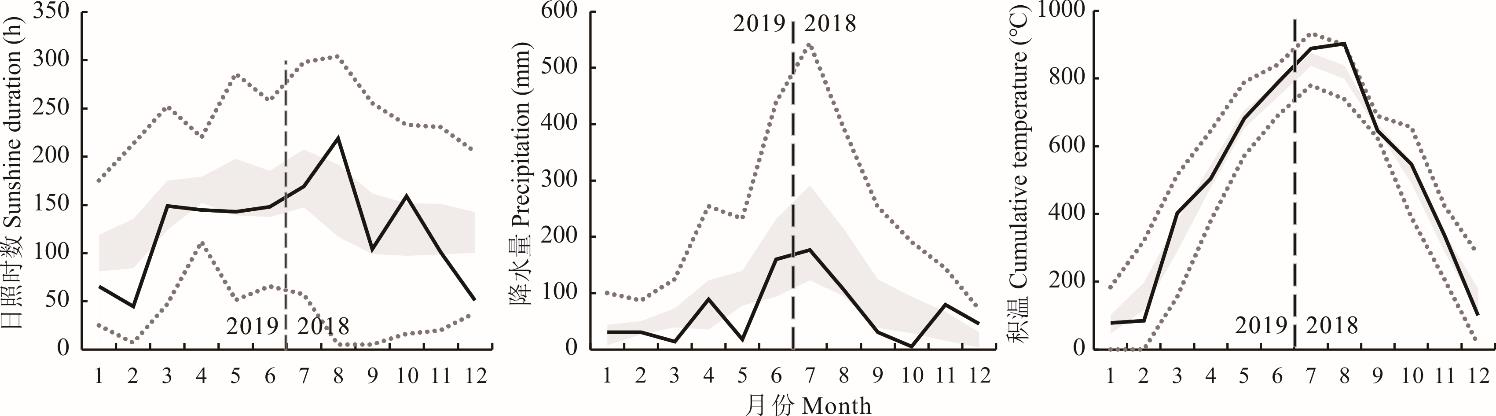
图1 试验区气候条件灰色区域为试验地区1986-2017年气象数据中25%~75%的两个四分位区间,虚线为1.5倍四分位距(interquartile range,IQR)的异常值临界线,黑色实线为2018年7月至2019年6月试验地气象数据。所示日照时数、降水量和积温原始数据均来自国家气象科学数据中心第57297号气象站,该气象站距试验点44 km。The grey area is the interquartile ranges between 25% and 75% of the meteorological data from 1986 to 2017 in the test area. The dash line is the critical boundary (whisker) of the outlier at 1.5×interquartile range (IQR). The solid line shows the weather data from July 2018 to June 2019. The original data of sunshine duration, precipitation and cumulative temperature were all obtained from the No. 57297 meteorological station of National Meteorological Data Center, which was 44 km away from the test site.
Fig.1 Weather condition of the experimental site
性状 Traits | 来源 Sources | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 均值/众数? Mean/mode | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (CV, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出苗期Emerging period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 10-15 | 10-18 | 10-18 | - |
| 引入 IR | 10-13 | 10-20 | 10-18 | - | |
| 返青期Spring regreening period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 03-23 | 03-30 | 03-26 | - |
| 引入IR | 03-25 | 04-02 | 03-28 | - | |
| 盛花期Full-bloom period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 04-06 | 04-14 | 04-06 | - |
| 引入 IR | 04-08 | 04-17 | 04-11 | - | |
| 成熟期Mature period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 05-19 | 05-29 | 05-23 | - |
| 引入IR | 05-19 | 05-30 | 05-29 | - | |
| 出苗期至盛花期天数Emerging to full-bloom (d) | 当地LR | 170 | 178 | 173b | 1.54 |
| 引入 IR | 172 | 181 | 176a | 1.33 | |
| 出苗期至成熟期天数Emerging to maturity (d) | 当地LR | 213 | 223 | 217b | 1.49 |
| 引入IR | 213 | 223 | 220a | 1.38 |
表2 不同紫云英的生育期情况
Table 2 Fertility period of different A. sinicus germplasm resources
性状 Traits | 来源 Sources | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 均值/众数? Mean/mode | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (CV, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出苗期Emerging period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 10-15 | 10-18 | 10-18 | - |
| 引入 IR | 10-13 | 10-20 | 10-18 | - | |
| 返青期Spring regreening period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 03-23 | 03-30 | 03-26 | - |
| 引入IR | 03-25 | 04-02 | 03-28 | - | |
| 盛花期Full-bloom period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 04-06 | 04-14 | 04-06 | - |
| 引入 IR | 04-08 | 04-17 | 04-11 | - | |
| 成熟期Mature period (月-日Month-day) | 当地LR | 05-19 | 05-29 | 05-23 | - |
| 引入IR | 05-19 | 05-30 | 05-29 | - | |
| 出苗期至盛花期天数Emerging to full-bloom (d) | 当地LR | 170 | 178 | 173b | 1.54 |
| 引入 IR | 172 | 181 | 176a | 1.33 | |
| 出苗期至成熟期天数Emerging to maturity (d) | 当地LR | 213 | 223 | 217b | 1.49 |
| 引入IR | 213 | 223 | 220a | 1.38 |
性状 Traits | 来源 Sources | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 均值/众数? Mean/mode | 变异系数 CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 返青期株高 Height at returning-green period (cm) | 当地LR | 10.6 | 37.0 | 24.3a | 30.2 |
| 引入 IR | 5.0 | 39.4 | 21.1a | 39.2 | |
| 盛花期株高Height at full-bloom period (cm) | 当地LR | 42.8 | 78.8 | 57.5a | 17.1 |
| 引入IR | 36.5 | 113.4 | 64.7a | 24.4 | |
| 一级分枝数Number of 1st order branch | 当地LR | 3.2 | 7.6 | 5.6b | 23.2 |
| 引入 IR | 3.4 | 12.0 | 7.1a | 23.5 | |
| 二级分枝数Number of 2nd order branch | 当地LR | 1.4 | 6.4 | 3.9b | 41.2 |
| 引入IR | 1.6 | 16.4 | 6.7a | 41.3 | |
| 苗期冠层面积Canopy area at seedling period (mm2·plant-1) | 当地LR | 33.3 | 675.9 | 239.1a | 65.5 |
| 引入 IR | 35.0 | 1104.2 | 353.2a | 73.2 | |
| 越冬期冠层面积Canopy area at wintering period (mm2·plant-1) | 当地LR | 220.5 | 4177.1 | 2043.1a | 49.6 |
| 引入IR | 417.5 | 7944.0 | 2646.0a | 68.3 | |
| 返青期冠层面积Canopy area at returning-green period (mm2·plant-1) | 当地LR | 3216.3 | 18397.3 | 9512.9a | 45.9 |
| 引入 IR | 1196.7 | 16460.5 | 7360.7a | 49.0 | |
| 茎色Stem color | 当地LR | 2 | 5 | 5 | - |
| 引入IR | 2 | 5 | 4 | - | |
| 叶色Leaf color | 当地LR | 1 | 5 | 1 | - |
| 引入 IR | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | |
| 全氮含量 Total N (g·kg-1) | 当地LR | 15.3 | 27.6 | 21.1b | 16.3 |
| 引入IR | 14.4 | 33.1 | 23.8a | 15.6 | |
| 全磷含量 Total P (g·kg-1) | 当地LR | 1.3 | 3.2 | 2.0a | 26.3 |
| 引入 IR | 1.0 | 3.5 | 1.9a | 26.5 | |
| 全钾含量 Total K (g·kg-1) | 当地LR | 24.9 | 37.2 | 30.3b | 12.8 |
| 引入IR | 20.2 | 46.3 | 33.4a | 16.9 |
表3 不同紫云英的农艺性状及养分含量
Table 3 Main agronomic characters and nutrient content of A. sinicus germplasm resources
性状 Traits | 来源 Sources | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 均值/众数? Mean/mode | 变异系数 CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 返青期株高 Height at returning-green period (cm) | 当地LR | 10.6 | 37.0 | 24.3a | 30.2 |
| 引入 IR | 5.0 | 39.4 | 21.1a | 39.2 | |
| 盛花期株高Height at full-bloom period (cm) | 当地LR | 42.8 | 78.8 | 57.5a | 17.1 |
| 引入IR | 36.5 | 113.4 | 64.7a | 24.4 | |
| 一级分枝数Number of 1st order branch | 当地LR | 3.2 | 7.6 | 5.6b | 23.2 |
| 引入 IR | 3.4 | 12.0 | 7.1a | 23.5 | |
| 二级分枝数Number of 2nd order branch | 当地LR | 1.4 | 6.4 | 3.9b | 41.2 |
| 引入IR | 1.6 | 16.4 | 6.7a | 41.3 | |
| 苗期冠层面积Canopy area at seedling period (mm2·plant-1) | 当地LR | 33.3 | 675.9 | 239.1a | 65.5 |
| 引入 IR | 35.0 | 1104.2 | 353.2a | 73.2 | |
| 越冬期冠层面积Canopy area at wintering period (mm2·plant-1) | 当地LR | 220.5 | 4177.1 | 2043.1a | 49.6 |
| 引入IR | 417.5 | 7944.0 | 2646.0a | 68.3 | |
| 返青期冠层面积Canopy area at returning-green period (mm2·plant-1) | 当地LR | 3216.3 | 18397.3 | 9512.9a | 45.9 |
| 引入 IR | 1196.7 | 16460.5 | 7360.7a | 49.0 | |
| 茎色Stem color | 当地LR | 2 | 5 | 5 | - |
| 引入IR | 2 | 5 | 4 | - | |
| 叶色Leaf color | 当地LR | 1 | 5 | 1 | - |
| 引入 IR | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | |
| 全氮含量 Total N (g·kg-1) | 当地LR | 15.3 | 27.6 | 21.1b | 16.3 |
| 引入IR | 14.4 | 33.1 | 23.8a | 15.6 | |
| 全磷含量 Total P (g·kg-1) | 当地LR | 1.3 | 3.2 | 2.0a | 26.3 |
| 引入 IR | 1.0 | 3.5 | 1.9a | 26.5 | |
| 全钾含量 Total K (g·kg-1) | 当地LR | 24.9 | 37.2 | 30.3b | 12.8 |
| 引入IR | 20.2 | 46.3 | 33.4a | 16.9 |

图3 紫云英种质资源冠层图像图像统一采集于2019年3月27日(返青期)。The image was collected on March 27, 2019 during the spring regreening period.
Fig.3 The canopy images of the A. sinicus germplasm lines
| 性状Traits | 来源Sources | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 均值Mean | 变异系数CV(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 始荚高度Height of the first pod (cm) | 当地LR | 5.0 | 22.0 | 11.9a | 46.0 |
| 引入IR | 4.7 | 41.2 | 13.1a | 52.9 | |
| 始荚柄长Peduncle length of the first pod (cm) | 当地LR | 12.6 | 18.0 | 15.3a | 10.4 |
| 引入 IR | 10.4 | 19.2 | 15.1a | 14.7 | |
| 结荚层数Number of reproductive node sites per branch | 当地LR | 6.8 | 13.2 | 10.6a | 16.9 |
| 引入IR | 5.3 | 14.0 | 10.8a | 15.7 | |
| 生殖分枝数Number of reproductive branch | 当地LR | 0.8 | 4.0 | 2.3a | 44.3 |
| 引入 IR | 0.4 | 5.6 | 2.3a | 48.4 | |
| 生殖分枝比率Reproductive branch ratio (%) | 当地LR | 19.2 | 87.5 | 48.6a | 34.6 |
| 引入IR | 11.8 | 100.0 | 43.1a | 42.8 | |
| 种子千粒重1000-seed weight (g) | 当地LR | 1.9 | 3.6 | 3.1a | 11.8 |
| 引入 IR | 2.6 | 3.7 | 3.3a | 8.6 | |
| 种子产量Seed yield (kg·hm-2) | 当地LR | 562.5 | 1644.0 | 1096.5a | 24.4 |
| 引入IR | 346.5 | 1941.0 | 1015.5a | 35.7 |
表4 不同紫云英的结实特征
Table 4 Podding characters of different A. sinicus germplasm resources
| 性状Traits | 来源Sources | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 均值Mean | 变异系数CV(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 始荚高度Height of the first pod (cm) | 当地LR | 5.0 | 22.0 | 11.9a | 46.0 |
| 引入IR | 4.7 | 41.2 | 13.1a | 52.9 | |
| 始荚柄长Peduncle length of the first pod (cm) | 当地LR | 12.6 | 18.0 | 15.3a | 10.4 |
| 引入 IR | 10.4 | 19.2 | 15.1a | 14.7 | |
| 结荚层数Number of reproductive node sites per branch | 当地LR | 6.8 | 13.2 | 10.6a | 16.9 |
| 引入IR | 5.3 | 14.0 | 10.8a | 15.7 | |
| 生殖分枝数Number of reproductive branch | 当地LR | 0.8 | 4.0 | 2.3a | 44.3 |
| 引入 IR | 0.4 | 5.6 | 2.3a | 48.4 | |
| 生殖分枝比率Reproductive branch ratio (%) | 当地LR | 19.2 | 87.5 | 48.6a | 34.6 |
| 引入IR | 11.8 | 100.0 | 43.1a | 42.8 | |
| 种子千粒重1000-seed weight (g) | 当地LR | 1.9 | 3.6 | 3.1a | 11.8 |
| 引入 IR | 2.6 | 3.7 | 3.3a | 8.6 | |
| 种子产量Seed yield (kg·hm-2) | 当地LR | 562.5 | 1644.0 | 1096.5a | 24.4 |
| 引入IR | 346.5 | 1941.0 | 1015.5a | 35.7 |

图4 紫云英主要性状间的相关性SY: 种子产量Seed yield; TKW: 千粒重1000 seeds weight; RR: 生殖分枝比率Reproductive branch ratio; RB: 生殖分枝数The number of reproductive branch; LNP: 结荚层数Number of reproductive node sites per branch; PLB: 始荚柄长Peduncle length of the first pod; HBO: 始荚高度Height of the first pod; TK: 全钾含量Total potassium content; TP: 全磷含量Total phosphorus content; TN: 全氮含量Total nitrogen content; CL: 叶片颜色Leaf color; CS: 茎秆颜色Stem color; CAR: 返青期冠层面积Canopy area at spring regreening period; CAW: 越冬期冠层面积Canopy area at wintering period; CAS: 苗期冠层面积Canopy area at seedling period; SB: 二级分枝数2nd order branch number; FB: 一级分枝数1st order branch number; HRG: 返青期株高Height at spring regreening period; HF: 盛花期株高Height at full-bloom period; EMP: 出苗至成熟天数Days of emerging to maturity; EFP: 出苗至盛花天数Days of emerging to full-bloom. 下同The same below.
Fig.4 The relationships between traits of the A. sinicus germplasm lines

图5 紫云英种质资源及性状特征聚类关系*: 当地资源Local resource;**: 目前豫南地区推广品种信紫1号Xinzi No.1, a recommended cultivar in Southern Henan region. Ⅰ: 6, 8, 11, 1, 9, 69, 5, 64; Ⅱ: 7, 10, 63, 50, 60; Ⅲ: 51, 41, 45, 25, 59, 52, 53, 4, 2, 47; Ⅳ: 16, 30, 37, 13, 33; Ⅴ: 31, 19, 43, 54, 62; Ⅵ: 56, 57, 70, 55, 58; Ⅶ: 3, 18, 65, 24, 20, 23, 14, 15; Ⅷ: 48, 44, 68, 66, 67, 36, 39; Ⅸ: 29, 17, 35, 21, 38, 26, 27; Ⅹ: 28, 12, 22, 40, 61, 46, 49, 34, 32, 42.
Fig.5 Clustering relations between different traits and germplasm lines of A. sinicus
| 1 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 2 | Xie Z J, Zhou C H, He Y Q, et al. A review of Astragalus sinicus in paddy fields in south China since 2000s. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(8): 185-196. |
| 谢志坚, 周春火, 贺亚琴, 等. 21世纪我国稻区种植紫云英的研究现状及展望. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 185-196. | |
| 3 | Lin X J, Cao W D, Wu Y Q, et al. Advance in Astragalus sinicus research. Pratacultural Science, 2011, 28(1): 135-140. |
| 林新坚, 曹卫东, 吴一群, 等. 紫云英研究进展. 草业科学, 2011, 28(1): 135-140. | |
| 4 | Lu Y H, Liao Y L, Zhou X, et al. Adaptability comparison of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) varieties for double-rice cropping system in Hunan. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2014(24): 3-6. |
| 鲁艳红, 廖育林, 周兴, 等. 湖南省双季稻区紫云英品种适宜性比较.湖南农业科学, 2014(24): 3-6. | |
| 5 | He C M, Liu C L, Wang L M, et al. Comparative study on local cultivars of Astragalus sinicus L.. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2020, 41(3): 441-448. |
| 何春梅, 刘彩玲, 王利民, 等. 紫云英地方种质资源品种比较试验. 热带作物学报, 2020, 41(3): 441-448. | |
| 6 | Zhong S. Discuss on the effective anthesis period, development of pod and seed and proper time for harvest of Chinese milk vetch for seed reservation. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 1978(6): 24-29, 46. |
| 钟山. 留种紫云英有效开花期、荚粒发育过程和收种适期的探讨. 浙江农业科学, 1978(6): 24-29, 46. | |
| 7 | Lin D H, Gu R S. Milk vetch in China. Fuzhou: Fujian Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 林多胡, 顾荣申. 中国紫云英. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 2000. | |
| 8 | Huang Q H, Xu X L, Xu C X, et al. Effect of applying B, Zn and Mo fertilizer on seed yield of milk vetch in hilly upland red soil. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2013(2): 75-79. |
| 黄庆海, 徐小林, 徐昌旭, 等. 丘陵旱地红壤上施用硼、锌和钼肥对紫云英种子产量的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013(2): 75-79. | |
| 9 | Su J P, Liu C P, Xu C X, et al. High-yielding cultivation techniques for stock seed of Ganzi No. 2. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2011, 23(8): 19-21. |
| 苏金平, 刘成鹏, 徐昌旭, 等. 赣紫2号的留种高产配套栽培技术研究. 江西农业学报, 2011, 23(8): 19-21. | |
| 10 | Liao Y L, Lu Y H, Nie J, et al. Effects of rice combine harvester application to harvesting Chinese milk vetch seed. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2014(18): 12-14, 17. |
| 廖育林, 鲁艳红, 聂军, 等. 水稻联合收割机收获紫云英种子的应用效果研究. 湖南农业科学, 2014(18): 12-14, 17. | |
| 11 | Qin Z G, Liu W, Li X K, et al. Effect of seeding rate on seed yield and its components of Chinese milk vetch. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 54(20): 4960-4962, 4968. |
| 秦自果, 刘威, 李小坤, 等. 播种量对紫云英种子产量及其构成因素的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2015, 54(20): 4960-4962, 4968. | |
| 12 | You Z Y, Gao X M, Wu H C, et al. Calculation of the loss rate of machine-harvested during Chinese milk vetch seed harvesting. Seed, 2019, 38(7): 140-143. |
| 游兆延, 高学梅, 吴惠昌, 等. 紫云英种子收获期机收损失率测算. 种子, 2019, 38(7): 140-143. | |
| 13 | Liu Y, Guo X S, Wang Y Q, et al. Comparative study on new Chinese milk vetch cultivars with high yield and high quality. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(6): 2448-2449, 2451. |
| 刘英, 郭熙盛, 王允青, 等. 紫云英新品种高产优质比较研究. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(6): 2448-2449, 2451. | |
| 14 | Liu C Z, Lv Y H, Pan Z L, et al. Breeding of Xinzi No.1, a new Chinese milk vetch cultivar with high yield and high quality. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2010(11): 42-44. |
| 刘春增, 吕玉虎, 潘兹亮, 等. 高产优质紫云英新品种信紫1号的选育. 河南农业科学, 2010(11): 42-44. | |
| 15 | Zhang M, Li B Y, Liu C Z, et al. A study of stratified maturity characteristics of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus) pods and their seed yield. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(2): 64-72. |
| 张梦, 李本银, 刘春增, 等. 紫云英荚果分层成熟特性及其种子产量研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 64-72. | |
| 16 | Zhou G, Gao S, Chang D, et al. Using milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) to promote rice straw decomposition by regulating enzyme activity and bacterial community. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 319: 124215. |
| 17 | Gao S, Zhou G, Rees R M, et al. Green manuring inhibits nitrification in a typical paddy soil by changing the contributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Applied Soil Ecology, 2020, 156: 103698. |
| 18 | Cao W D. Descriptors and data standard for green manure. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2007. |
| 曹卫东. 绿肥种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2007. | |
| 19 | Lu R K. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis method. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 20 | Belwal T, Singh G, Jeandet P, et al. Anthocyanins, multi-functional natural products of industrial relevance: Recent biotechnological advances. Biotechnology Advances, 2020, 43: 107600. |
| 21 | Zhang B, Li M, Jiang M S, et al. Relationship between anthocyanin accumulation and response to low temperature stress in foxtail millet. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(11): 2607-2613. |
| 张彬, 李萌, 蒋茂双, 等. 花青素积累与谷子低温胁迫响应的关系. 核农学报, 2020, 34(11): 2607-2613. | |
| 22 | Zhu H, Zhang T J, Zheng J, et al. Anthocyanins function as a light attenuator to compensate for insufficient photoprotection mediated by nonphotochemical quenching in young leaves of Acmenaacuminatissima in winter. Photosynthetica, 2018, 56(1): 445-454. |
| 23 | Liu X J, Ma K P. Plant functional traits-concepts, applications and future directions. Science in China (Series C), 2015, 45(4): 325-339. |
| 刘晓娟, 马克平. 植物功能性状研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2015, 45(4): 325-339. | |
| 24 | Westoby M. A leaf-height-seed (LHS) plant ecology strategy scheme. Plant Soil, 1998, 199(2): 213-227. |
| 25 | Liu C Z, Li B Y, Zhang M, et al. Influence of pod maturing states on pod drop and seed yield of Chinese milk vetch. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(2): 413-420. |
| 刘春增, 李本银, 张梦, 等. 紫云英荚果成熟度对落荚及种子产量的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(2): 413-420. | |
| 26 | Yin W L, Song H Y, Sun Q D. Research report on the development of staple crop industry in Xinyang-A case study on rice, wheat and rapeseed case. Farm Produce Market Weekly, 2019(8): 45-47. |
| 尹为玲, 宋宏亚, 孙全东. 河南信阳市大宗农作物产业发展调研报告-以水稻、小麦和油菜产业发展为例. 农产品市场周刊, 2019(8): 45-47. | |
| 27 | Xue C Y, Liu R H, Wu Q. Effect of climate warming on rice growing stages in Xinyang. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2010, 31(3): 353-357. |
| 薛昌颖, 刘荣花, 吴骞. 气候变暖对信阳地区水稻生育期的影响. 中国农业气象, 2010, 31(3): 353-357. | |
| 28 | Liu C Z, Lv Y H, Li B Y, et al. Effects of sowing date on Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) growth, yield and nutrients accumulation. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2018(1): 127-133. |
| 刘春增, 吕玉虎, 李本银, 等. 不同播期对紫云英“信紫1号”生长状况、产量及养分积累的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018(1): 127-133. |
| [1] | 任文静, 吕玉虎, 周国朋, 常单娜, 向春阳, 曹卫东. 一个紫云英F4重组自交系群体的农艺性状与养分吸收评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(2): 101-110. |
| [2] | 王飞, 刘彩玲, 何春梅, 李清华, 刘玉洁, 黄毅斌. 适宜磷、钾肥配比及稻秆半量还田提高紫云英产量与养分截获[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 81-89. |
| [3] | 张帆, 杨茜. 紫云英与双季稻秸秆协同利用影响稻田土壤钾循环与平衡[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 72-80. |
| [4] | 刘芳, 陈震, 徐雯, 储志英, 管永祥, 吴桂成, 还静, 孙政国. 不同稻茬土壤对紫云英根瘤生长特性的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 153-161. |
| [5] | 张梦, 李本银, 刘春增, 吕玉虎, 张成兰, 陈雪青, 曹卫东. 紫云英荚果分层成熟特性及其种子产量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 64-72. |
| [6] | 郑春风, 刘春增, 李本银, 吕玉虎, 潘兹亮, 曹卫东. 叶面喷硼对紫云英结实特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 192-199. |
| [7] | 谢志坚, 周春火, 贺亚琴, 宋涛, 于洋, 吴佳. 21世纪我国稻区种植紫云英的研究现状及展望[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 185-196. |
| [8] | 常单娜, 刘春增, 李本银, 吕玉虎, 潘兹亮, 高嵩涓, 曹卫东. 翻压紫云英对稻田土壤还原物质变化特征及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 133-144. |
| [9] | 王艳秋, 高嵩涓, 曹卫东, 李景环, 聂军, 徐昌旭, 白金顺, 曾闹华, 周国朋. 多年冬种紫云英对两种典型双季稻田土壤肥力及硝化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 180-189. |
| [10] | 万水霞, 唐杉, 蒋光月, 李帆, 郭熙盛, 王允青, 曹卫东. 紫云英与化肥配施对土壤微生物特征和作物产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 109-117. |
| [11] | 谢志坚,徐昌旭,刘光荣,曹卫东. 不同剂量苄·丁和二氯喹啉酸对紫云英生长环境及其养分吸收累积的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(5): 201-207. |
| [12] | 林新坚,兰忠明,张辉,王飞,何春梅. 不同紫云英基因型根系分泌物中有机酸成分分析[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4): 146-152. |
| [13] | 王飞,林诚,李清华,何春梅,林新坚,李昱. 亚热带单季稻区紫云英不同翻压量下有机碳和养分释放特征[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(4): 319-324. |
| [14] | 吴一群,张辉,林新坚,兰忠明,张伟光,曹卫东. 不同土壤田间含水量对紫云英生长及生理代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1): 156-161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||