

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 164-180.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020501
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
张家驹( ), 于洁, 李明娜, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才(
), 于洁, 李明娜, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才( )
)
收稿日期:2020-11-10
修回日期:2021-01-04
出版日期:2021-12-01
发布日期:2021-12-01
通讯作者:
龙瑞才
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: dragongodsgod@163.com基金资助:
Jia-ju ZHANG( ), Jie YU, Ming-na LI, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG(
), Jie YU, Ming-na LI, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG( )
)
Received:2020-11-10
Revised:2021-01-04
Online:2021-12-01
Published:2021-12-01
Contact:
Rui-cai LONG
摘要:
长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA, lncRNA)是一类长度大于200个核苷酸的功能性RNA分子,lncRNA在植物生长发育以及生物和非生物胁迫响应过程中发挥着重要作用。lncRNA常与microRNA(miRNA)关联发挥作用。本研究从蒺藜苜蓿中克隆一个预测的新lncRNA,该lncRNA与蒺藜苜蓿miR167c在染色体上位置重合,命名为Mt-lncRNA167,并推测Mt-lncRNA167作为Mt-miR167c的剪切前体发挥作用。靶基因预测分析结果表明,生长素响应因子6/8(auxin response factor 6/8)是miR167c的两个靶基因。表达模式分析表明,Mt-lncRNA167主要在叶中表达,Mt-lncRNA167和Mt-miR167c对100 mmol·L-1 NaCl、5% PEG 6000和4 ℃低温胁迫处理均有响应,与Mt-lncRNA167启动子顺式作用元件功能预测结果一致。在盐、干旱、低温胁迫条件下,Mt-lncRNA167与Mt-miR167c表达模式基本相同,与靶基因ARF6/8表达模式相反。Mt-lncRNA167与Mt-miR167c超表达转化拟南芥植株表现出生育缺陷的表型,即果荚和花丝显著缩短,花药不能正常释放花粉,花粉活力降低。盐和干旱胁迫下发芽率结果表明Mt-lncRNA167和Mt-miR167c超表达植株抗性优于野生型。此外,Mt-lncRNA167和Mt-miR167c超表达植株下胚轴显著长于野生型。综合以上,推测Mt-lncRNA167作为Mt-miR167c的前体发挥作用,Mt-miR167c抑制ARF6/8基因的表达,Mt-lncRNA167-Mt-miR167c-ARF6/8作用网络在蒺藜苜蓿抗逆和发育调控方面发挥重要作用。
张家驹, 于洁, 李明娜, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 龙瑞才. 蒺藜苜蓿lncRNA167及其剪切产物miR167c的鉴定和功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 164-180.
Jia-ju ZHANG, Jie YU, Ming-na LI, Jun-mei KANG, Qing-chuan YANG, Rui-cai LONG. Identification and functional analysis of lncRNA167 and its cleavage product miR167c in Medicago truncatula[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 164-180.
| 引物名称Primer | 正向引物序列Forward sequence (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列Reverse sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Mt-lncRNA167 | CAAATTCCAAACCCTAGCCAACT | AAGTTCCTTCCTTCAAAACCAAA |
| Pre-Mt-miR167c | TCTTTTCCTCAACTCTGCTATAT | CATAATCAACTTTTTTAAGAGCA |
| qRT-Mt-lncRNA167 | GTAGAAGCAGCTAGCATCACT | AACCTACAAAGGAGGCCAGT |
| qRT-Mt-miR167c | TGAAGCTGCCAGCATGATCTA | 试剂盒中反向引物 Reverse primer in kit |
| qRT-MtARF6 | AGAGGGGTGTAGAGTGTAAC | CAAAATAAGCAGAAAATGAC |
| qRT-MtARF8 | ATGATGTGCTTCTCCTTGGC | ATCTTCTGAATATCTTCCGG |
| qRT-AtARF6 | CCTCATGAAGGAGAGAAAAGAGT | AGCAGCAACCTGTTCACTGT |
| qRT-AtARF8 | TGTAGCTGTCTCAGGGTAACT | GGTCTGACCAAACTGAATGTCT |
| qRT-Mtactin | ACACTGTGCCAATCTATGAGGG | TTGTCCATCAGGAAGTTCATAGTTT |
| qRT-Atactin | TCCATCGATTGTTCACAGGA | TCACCACCACGAACCAGATA |
| U6 | CGCACAAATCGAGAAATGGTCC | 试剂盒中反向引物 Reverse primer in kit |
| 35S | AGAAAATCTTCGTCAACATGGTGGA | \ |
| GUS | TTCCTGATTATTGACCCACACTTTG | \ |
表1 本试验所用到的引物序列
Table 1 Primers used in the study
| 引物名称Primer | 正向引物序列Forward sequence (5′-3′) | 反向引物序列Reverse sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Mt-lncRNA167 | CAAATTCCAAACCCTAGCCAACT | AAGTTCCTTCCTTCAAAACCAAA |
| Pre-Mt-miR167c | TCTTTTCCTCAACTCTGCTATAT | CATAATCAACTTTTTTAAGAGCA |
| qRT-Mt-lncRNA167 | GTAGAAGCAGCTAGCATCACT | AACCTACAAAGGAGGCCAGT |
| qRT-Mt-miR167c | TGAAGCTGCCAGCATGATCTA | 试剂盒中反向引物 Reverse primer in kit |
| qRT-MtARF6 | AGAGGGGTGTAGAGTGTAAC | CAAAATAAGCAGAAAATGAC |
| qRT-MtARF8 | ATGATGTGCTTCTCCTTGGC | ATCTTCTGAATATCTTCCGG |
| qRT-AtARF6 | CCTCATGAAGGAGAGAAAAGAGT | AGCAGCAACCTGTTCACTGT |
| qRT-AtARF8 | TGTAGCTGTCTCAGGGTAACT | GGTCTGACCAAACTGAATGTCT |
| qRT-Mtactin | ACACTGTGCCAATCTATGAGGG | TTGTCCATCAGGAAGTTCATAGTTT |
| qRT-Atactin | TCCATCGATTGTTCACAGGA | TCACCACCACGAACCAGATA |
| U6 | CGCACAAATCGAGAAATGGTCC | 试剂盒中反向引物 Reverse primer in kit |
| 35S | AGAAAATCTTCGTCAACATGGTGGA | \ |
| GUS | TTCCTGATTATTGACCCACACTTTG | \ |

图1 Mt-lncRNA167与Mt-miR167c的鉴定A: Mt-lncRNA167与Mt-miR167c在染色体上的位置关系 The position relationship between Mt-lncRNA167 and Mt-miR167c on chromosome; B: Mt-miRNA167a/b/c的二级结构 Secondary structure of Mt-miRNA167a/b/c; C: At-miR167a/b/c/d和Mt-miRNA167a/b/c的多序列比对结果Multiple sequence alignment results of At-miR167a/b/c/d and Mt-miRNA167a/b/c.
Fig.1 Identification of Mt-lncRNA167 and Mt-miR167c
| 顺式作用元件Cis-acting element | 核心序列 Core sequence | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|
| TATA-box | TATATAA/ATTATA/TATA | 在转录开始-30左右的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start |
| CAAT-box | CAAT/CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域常见顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| MBS | CAACTG | MYB结合位点,受到干旱胁迫诱导MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 参与低温响应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness |
| TCCC-motif | TCTCCCT | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| I-box | GTATAAGGCC | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| Gap-box | CAAATGAA(A/G)A | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| chs-CMA1a | TTACTTAA | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| GA-motif | ATAGATAA | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
表2 Mt-lncRNA167的启动子顺式作用元件分析
Table 2 Cis-acting element analysis of promoter of Mt-lncRNA167
| 顺式作用元件Cis-acting element | 核心序列 Core sequence | 功能 Function |
|---|---|---|
| TATA-box | TATATAA/ATTATA/TATA | 在转录开始-30左右的核心启动子元件Core promoter element around -30 of transcription start |
| CAAT-box | CAAT/CAAAT | 启动子和增强子区域常见顺式作用元件Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| MBS | CAACTG | MYB结合位点,受到干旱胁迫诱导MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 参与低温响应的顺式作用元件Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness |
| TCCC-motif | TCTCCCT | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| I-box | GTATAAGGCC | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| Gap-box | CAAATGAA(A/G)A | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| chs-CMA1a | TTACTTAA | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
| GA-motif | ATAGATAA | 参与光响应的顺式作用元件Light responsive element |
靶基因符号 Gene symbol | 靶基因位置标签 Locus tag | 靶基因名称 Gene description | 与miRNA互补位点 Complementary sites with miRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC11413758 | MTR_3g064050 | 生长素响应因子8 Auxin response factor 8 | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 1683 UAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 1703 |
| LOC11446854 | MTR_2g018690 | 生长素响应因子6 Auxin response factor 6 | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 3316 GAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 3336 |
| LOC11442326 | MTR_5g066710 | E3泛素蛋白连接酶基因 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 11475 GAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 11495 |
| LOC11442155 | MTR_7g077700 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录中介蛋白基因 RNA polymerase Ⅱ transcription mediators | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 250 GAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 270 |
表3 psRNAtarget预测Mt-miR167c的靶基因
Table 3 Prediction of the target gene of Mt-miR167c by psRNAtarget
靶基因符号 Gene symbol | 靶基因位置标签 Locus tag | 靶基因名称 Gene description | 与miRNA互补位点 Complementary sites with miRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC11413758 | MTR_3g064050 | 生长素响应因子8 Auxin response factor 8 | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 1683 UAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 1703 |
| LOC11446854 | MTR_2g018690 | 生长素响应因子6 Auxin response factor 6 | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 3316 GAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 3336 |
| LOC11442326 | MTR_5g066710 | E3泛素蛋白连接酶基因 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 11475 GAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 11495 |
| LOC11442155 | MTR_7g077700 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录中介蛋白基因 RNA polymerase Ⅱ transcription mediators | miRNA 21 AUCUAGUACGACCGUCGAAGU 1 Target 250 GAGAUCAGGCUGGCAGCUUGU 270 |
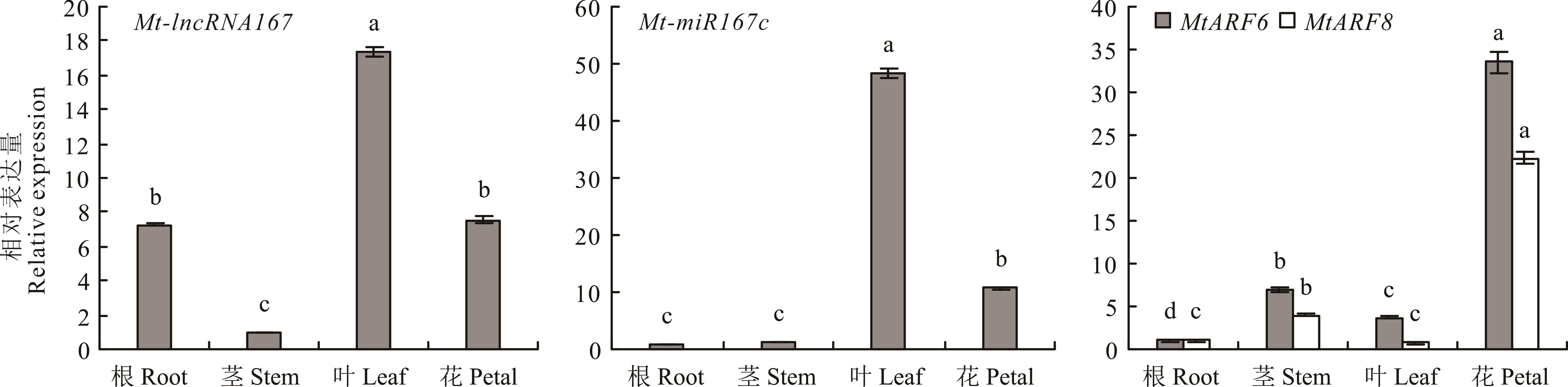
图4 Mt-lncRNA167、Mt-miR167c、MtARF6/8在不同组织中的表达标准差来自3个生物学重复,不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Bars represent the SD of three biological replicates and different lowercase letters indicate significant difference (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.4 The relative expression of Mt-lncRNA167, Mt-miR167c, MtARF6/8 in different tissues of M. truncatula

图5 Mt-lncRNA167、Mt-miR167c、MtARF6/8 在盐胁迫(100 mmol·L-1 NaCl)处理下的表达
Fig.5 The relative expression of Mt-lncRNA167, Mt-miR167c, MtARF6/8 under NaCl (100 mmol·L-1) treatment

图6 Mt-lncRNA167、Mt-miR167c、MtARF6/8 在低温胁迫(4 ℃)处理下的表达
Fig.6 The relative expression of Mt-lncRNA167, Mt-miR167c, MtARF6/8 under cold stress (4 ℃) treatment
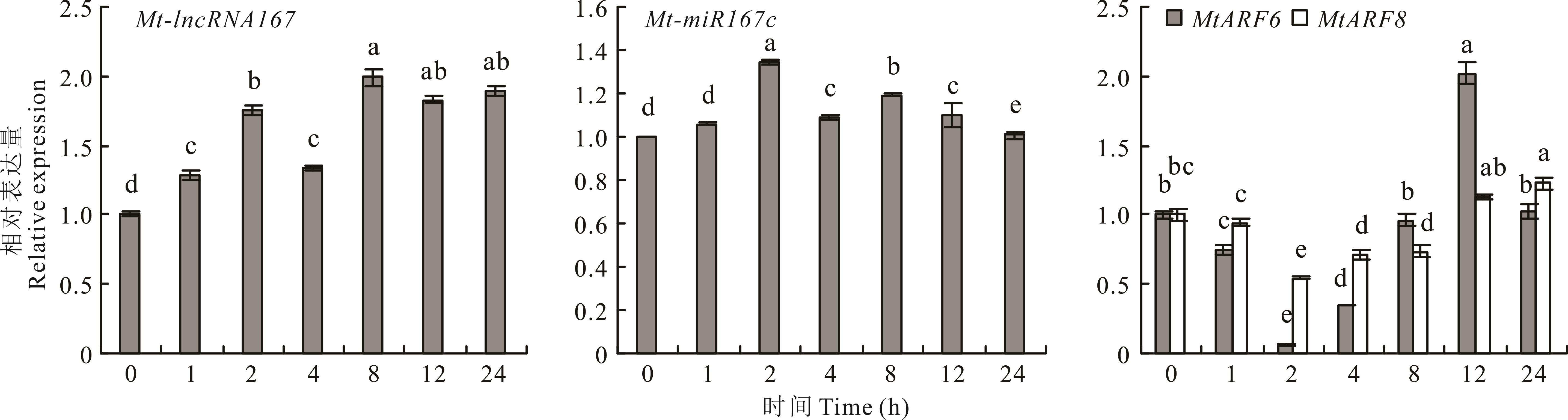
图7 Mt-lncRNA167、Mt-miR167c、MtARF6/8 在干旱胁迫(5% PEG 6000)处理下的表达
Fig.7 The relative expression of Mt-lncRNA167, Mt-miR167c, MtARF6/8 under drought (5% PEG 6000) treatment
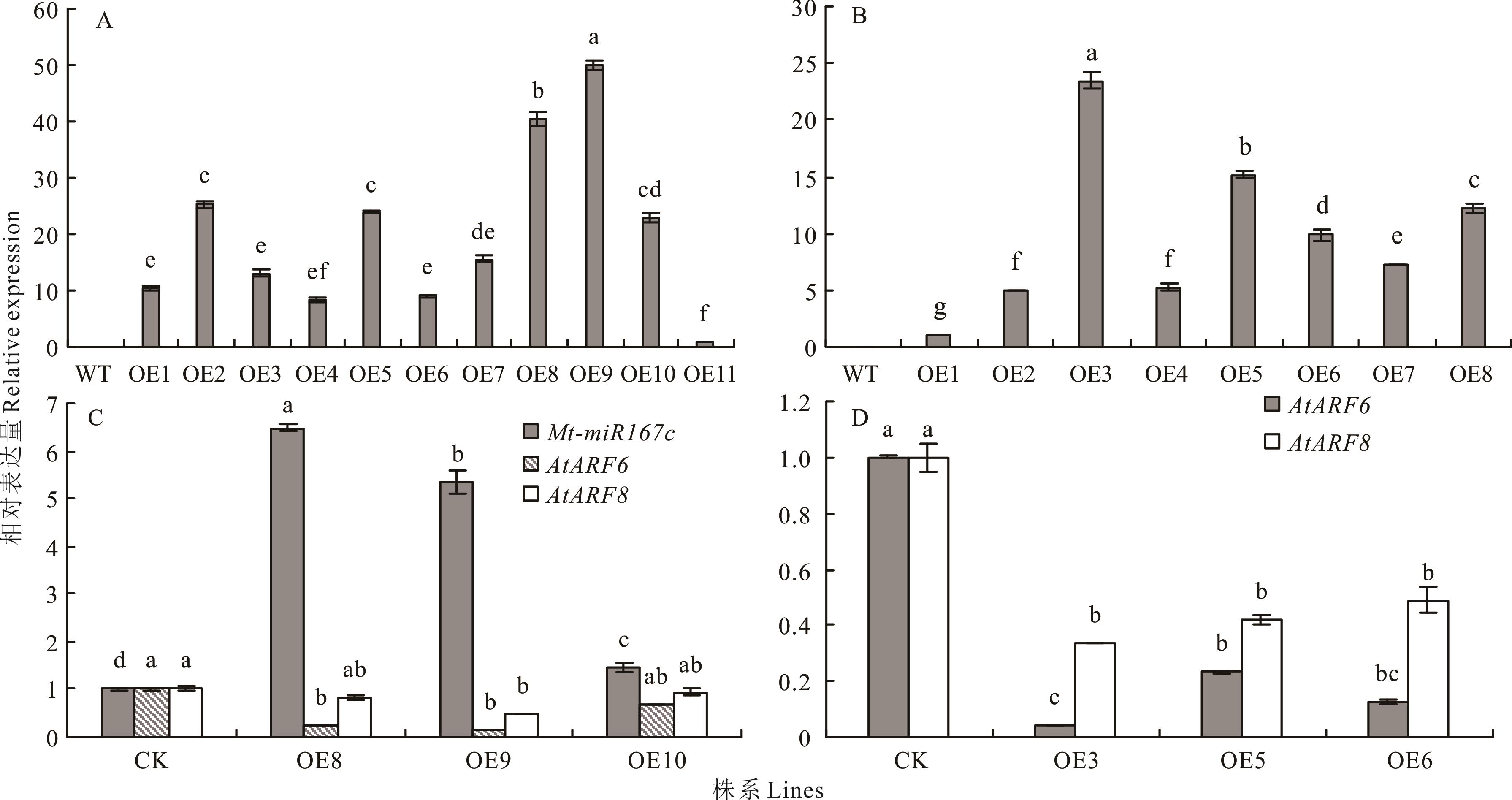
图8 超表达拟南芥中Mt-lncRNA167、Mt-miR167c的表达量分析A: 超表达拟南芥的Mt-lncRNA167相对表达量The relative expression level of Mt-lncRNA167 in the overexpressed Arabidopsis; B: 超表达拟南芥Mt-miR167c的相对表达量The relative expression level of Mt-miR167c in the overexpressed Arabidopsis; C: 超表达Mt-lncRNA167拟南芥中Mt-miR167c、AtARF6、AtARF8的相对表达量The relative expression levels of Mt-miR167c, AtARF6 and AtARF8 in overexpressed Mt-lncRNA167Arabidopsis; D: 超表达Mt-miR167c拟南芥中AtARF6、AtARF8的相对表达量The relative expression levels of AtARF6 and AtARF8 in overexpressed Mt-miR167cArabidopsis. WT: 野生型Wild type; OE1, 2, 3…: 超表达株系Overexpression line 1, 2, 3…; 下同The same below.
Fig.8 Analysis of the relative expression level of Mt-lncRNA167 and Mt-miR167c in the overexpressed Arabidopsis
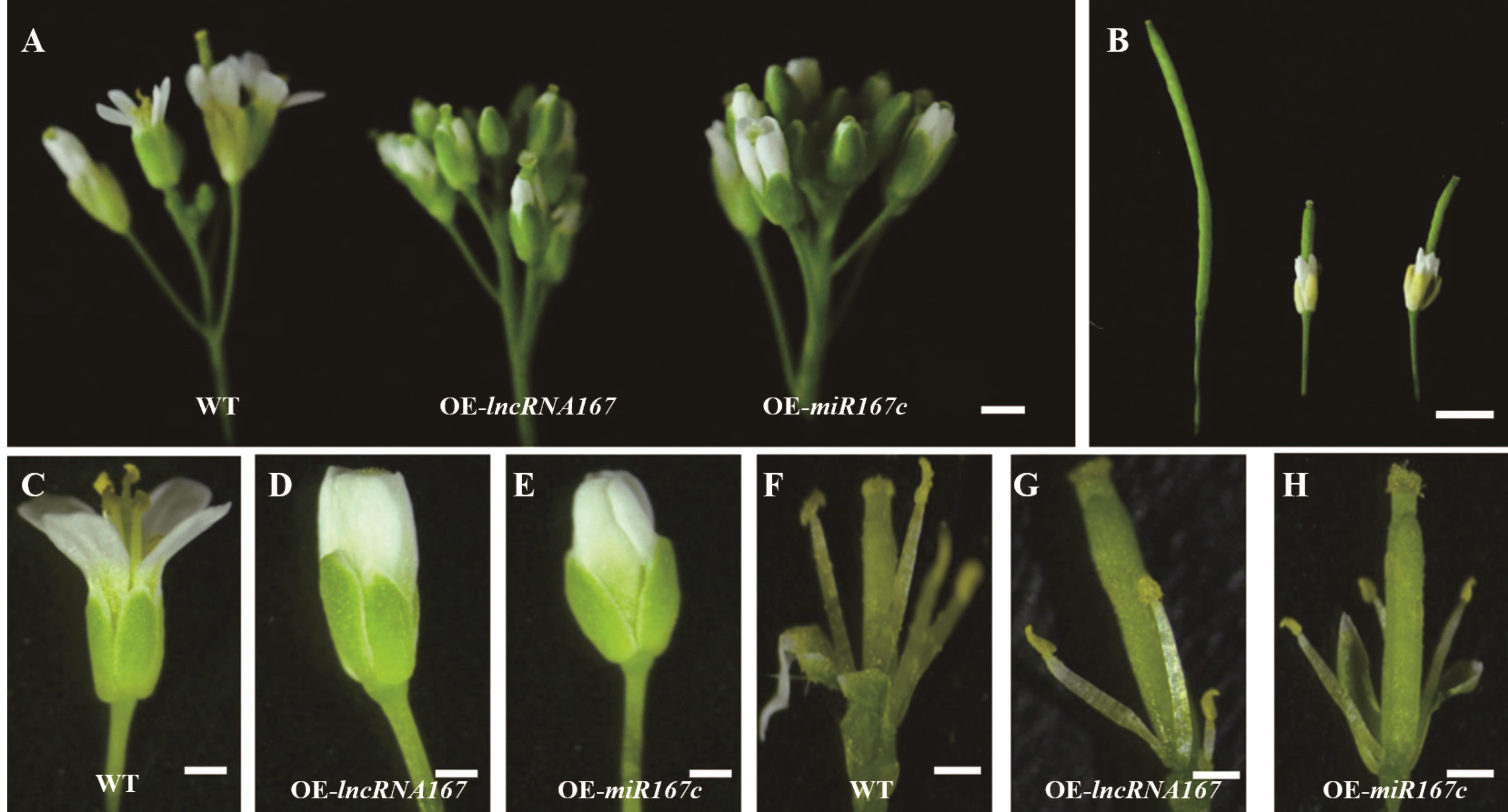

图9 Mt-lncRNA167、Mt-miR167c超表达拟南芥的花结构A: WT与超表达拟南芥的花序结构Inflorescence structure of WT and overexpressed Arabidopsis; B: WT与超表达拟南芥的角果Pod of WT and overexpressed Arabidopsis; C~E: WT与超表达拟南芥的花结构Flower structure of WT and overexpressed Arabidopsis; F~H: WT与超表达拟南芥的雄蕊和雌蕊Stamens and pistil of WT and overexpressed Arabidopsis; 图A和B标尺=1 mm Scales in A and B=1 mm; 图C~H标尺=0.5 mm Scales in C-H=0.5 mm.
Fig.9 The flower structure of overexpressed Mt-lncRNA167 and Mt-miR167cArabidopsis

图10 WT和超表达拟南芥的幼苗和下胚轴长度A: 1周龄拟南芥幼苗One-week old Arabidopsis seedlings; B: 1周龄拟南芥幼苗下胚轴长度The hypocotyl length of one-week old Arabidopsis seedlings; 标尺=1 mm Scale=1 mm.
Fig.10 Seeding and hypocotyl length of WT and overexpressed Arabidopsis
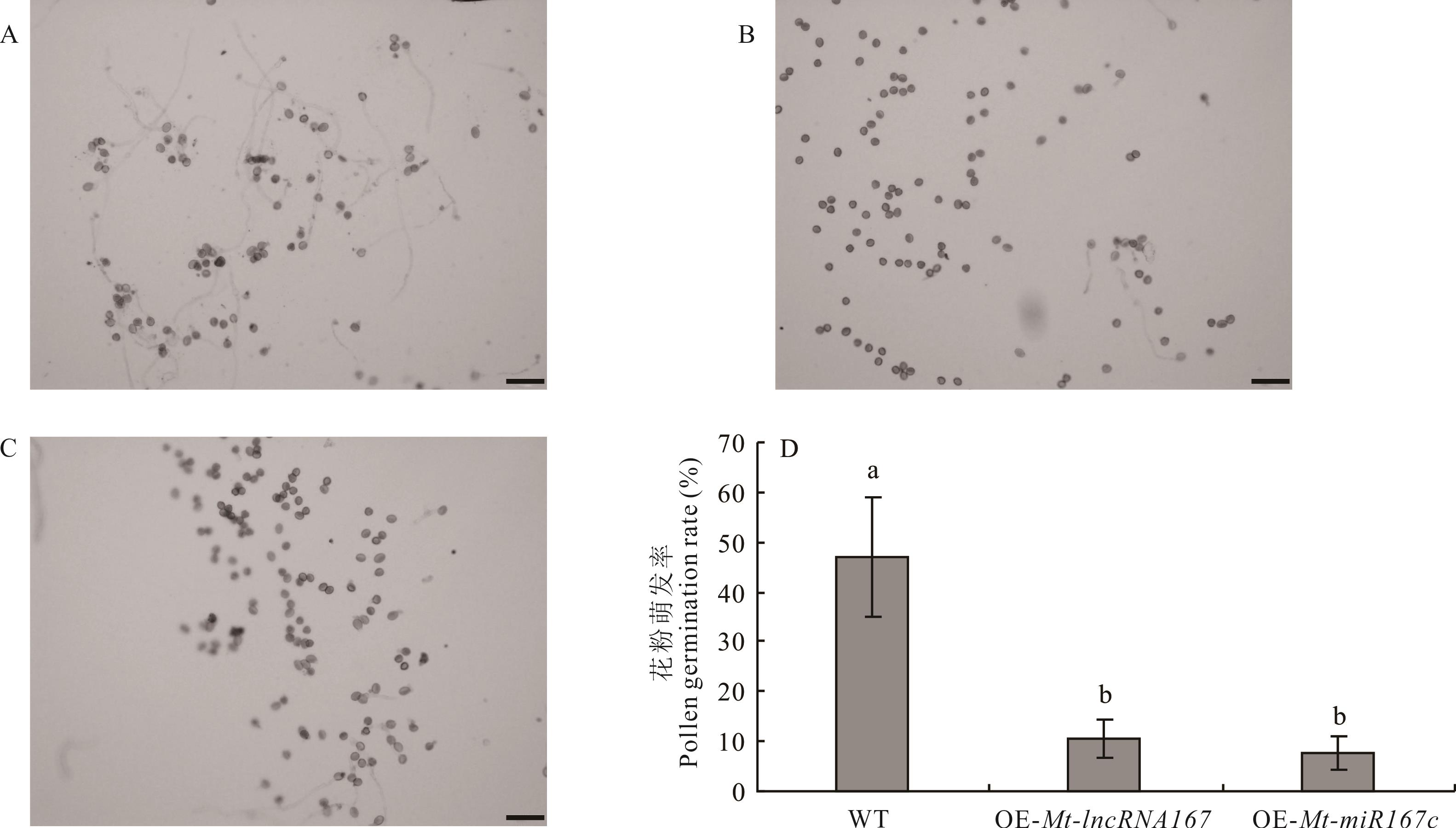
图11 拟南芥花粉的体外萌发A: WT花粉The pollen of WT; B: OE-Mt-lncRNA167植株花粉The pollen of OE-Mt-lncRNA167; C: OE-Mt-miR167c植株花粉The pollen of OE-Mt-miR167c; D: WT、OE-Mt-lncRNA167植株、OE-Mt-miR167c植株花粉萌发率统计Statistics of pollen germination rate of WT, OE-Mt-lncRNA167 and OE-Mt-miR167c plants; 标尺Scale=100 μm.
Fig.11 In vitro germination of Arabidopsis pollen
| 1 | Amor B B, Wirth S, Merchan F, et al. Novel long non-protein coding RNAs involved in Arabidopsis differentiation and stress responses. Genome Research, 2009, 19(1): 57-69. |
| 2 | Louro R, Smirnova A S, Verjovski-Almeida S. Long intronic noncoding RNA transcription: Expression noise or expression choice? Genomics, 2009, 93(4): 291-298. |
| 3 | Yang G D, Lu X Z, Yuan L J. LncRNA: A link between RNA and cancer. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 2014, 1839(11): 1097-1109. |
| 4 | Chekanova J A. Long non-coding RNAs and their functions in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2015, 27: 207-216. |
| 5 | Hang Y, Liu N, Wang J P, et al. Regulatory long non-coding RNA and its functions. Journal of Physiology & Biochemistry, 2012, 68(4): 611-618. |
| 6 | Flynn R A, Chang H Y. Long noncoding RNAs in cell-fate programming and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell, 2014, 14(6): 752-761. |
| 7 | Wang Y Q, Fan X D, Lin F, et al. Arabidopsis noncoding RNA mediates control of photomorphogenesis by red light. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(28): 10359-10364. |
| 8 | He H S, Cai L, Skogerbo G, et al. Profiling Caenorhabditis elegans non-coding RNA expression with a combined microarray. Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, 34(10): 2976-2983. |
| 9 | Deng F N, Zhang X P, Wang W, et al. Identification of Gossypium hirsutum long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) under salt stress. BMC Plant Biology, 2018, 18(1): 23. |
| 10 | Wang P F, Dai L M, Ai J, et al. Identification and functional prediction of cold-related long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in grapevine. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 1-15. |
| 11 | Ding Z H, Tie W W, Fu L L, et al. Strand-specific RNA-seq based identification and functional prediction of drought-responsive lncRNAs in cassava. BMC Genomics, 2019, 20(1): 214. |
| 12 | Lv Y D, Liang Z K, Ge M, et al. Genome-wide identification and functional prediction of nitrogen-responsive intergenic and intronic long non-coding RNAs in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Genomics, 2016, 17(1): 350. |
| 13 | Sun X, Zheng H X, Li J L, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals new lncRNAs responding to salt stress in sweet sorghum. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020, 8: 331. |
| 14 | Wan S Q, Zhang Y H, Duan M S, et al. Integrated analysis of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and mRNAs reveals the regulatory role of lncRNAs associated with salt resistance in Camellia sinensis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 218. |
| 15 | Fu L L, Ding Z H, Tan D G, et al. Genome-wide discovery and functional prediction of salt-responsive lncRNAs in duckweed. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 212. |
| 16 | Jannesar M, Seyedi S M, Jazi M M, et al. A genome-wide identification, characterization and functional analysis of salt-related long non-coding RNAs in non-model plant Pistacia vera L. using transcriptome high throughput sequencing. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 5585. |
| 17 | Ágyi Á, Havelda Z. Analysis of gradient-like expression of miR167 in Arabidopsis thaliana embryonic tissue. Journal of Plant Biology, 2013, 56(5): 336-344. |
| 18 | Liu H, Jia S H, Shen D F, et al. Four auxin response factor genes downregulated by microRNA167 are associated with growth and development in Oryza sativa. Functional Plant Biology, 2012, 39(9): 736-744. |
| 19 | Wu M F, Tian Q, Reed J W. Arabidopsis microRNA167 controls patterns of ARF6 and ARF8 expression, and regulates both female and male reproduction. Development, 2006, 133(21): 4211-4218. |
| 20 | Kinoshita N, Wang H, Kasahara H, et al. IAA-Ala resistant3, an evolutionarily conserved target of miR167, mediates Arabidopsis root architecture changes during high osmotic stress. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(9): 3590-3602. |
| 21 | Ru P, Xu L, Ma H, et al. Plant fertility defects induced by the enhanced expression of microRNA167. Cell Research, 2006, 16(5): 457-465. |
| 22 | Nagpal P, Ellis C M, Weber H, et al. Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development, 2005, 132(18): 4107-4118. |
| 23 | Gutierrez L, Bussell J D, Pâcurar D I, et al. Phenotypic plasticity of adventitious rooting in Arabidopsis is controlled by complex regulation of auxin response factor transcripts and microRNA abundance. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(10): 3119-3132. |
| 24 | Yao X Z, Chen J L, Zhou J, et al. An essential role for miRNA167 in maternal control of embryonic and seed development. Plant Physiology, 2019, 180(1): 453-464. |
| 25 | Liu N, Wu S, Van Houten J V, et al. Down-regulation of auxin response factors6 and 8 by microRNA167 leads to floral development defects and female sterility in tomato. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2014, 65(9): 2507-2520. |
| 26 | Xue L J, Zhang J J, Xue H W. Characterization and expression profiles of miRNAs in rice seeds. Nucleic Acids Research, 2009, 37(3): 916-930. |
| 27 | Peng T, Sun H Z, Qiao M M, et al. Differentially expressed microRNA cohorts in seed development may contribute to poor grain filling of inferior spikelets in rice. BMC Plant Biology, 2014, 14: 196. |
| 28 | Wei Y, Chen Z H, Chen G X, et al. Study of overexpressing miRNA167a to regulate the architecture in Oryza sativa. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2011, 9(4): 390-396. |
| 韦懿, 陈志辉, 陈国兴, 等. 超量表达水稻miRNA167a调控株型的研究. 分子植物育种, 2011, 9(4): 390-396. | |
| 29 | Wang Y N, Li K X, Chen L, et al. MicroRNA167-directed regulation of the auxin response factors GmARF8a and GmARF8b is required for soybean nodulation and lateral root development. Plant Physiology, 2015, 168(3): 984-999. |
| 30 | Sun Z F, Huang K, Han Z J, et al. Genome-wide identification of Arabidopsis long noncoding RNAs in response to the blue light. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 6229. |
| 31 | Quan M Y, Xiao L, Lu W J, et al. Association genetics in Populus reveal the allelic interactions of Pto-MIR167a and its targets in wood formation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 774. |
| 32 | Wang T Z, Liu M, Zhao M G, et al. Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in osmotic and salt stress in Medicago truncatula using genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biology, 2015, 15(1): 131. |
| 33 | Zhao M G, Wang T Z, Sun T Y, et al. Identification of tissue-specific and cold-responsive lncRNAs in Medicago truncatula by high-throughput RNA sequencing. BMC Plant Biology, 2020, 20(1): 99. |
| 34 | Sousa C, Johansson C, Charon C, et al. Translational and structural requirements of the early nodulin gene enod40, a short open reading frame containing RNA, for elicitation of a cell specific growth response in the alfalfa root cortex. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 2001, 21(1): 354-366. |
| 35 | Burleigh S H, Harrison M J. The down-regulation of Mt4-like genes by phosphate fertilization occurs systemically and involves phosphate translocation to the shoots. Plant Physiology, 1999, 119(1): 241-248. |
| 36 | Sun C L, Pan Y Y. Testing pollen character during pollen development in Arabidopsis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(3): 268-275. |
| 孙春丽, 潘延云. 拟南芥花粉活力的测定及其在花粉发育研究中的应用. 植物学通报, 2008, 25(3): 268-275. | |
| 37 | Franco-zorrilla J M, Valli A, Todesco M, et al. Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nature Genetics, 2007, 39(8): 1033-1037. |
| 38 | Gai Y P, Yuan S S, Zhao Y N, et al. A novel lncRNA, MuLnc1, associated with environmental stress in Mulberry (Morus multicaulis). Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 669. |
| 39 | Lu Y Y, Zhao X D, Liu Q, et al. lncRNA MIR100HG-derived miR-100 and miR-125b mediate cetuximab resistance via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Nature Medicine, 2017, 23: 1331-1341. |
| 40 | Tsang W P, Ng E K O, Ng S S M, et al. Oncofetal H19-derived miR-675 regulates tumor suppressor RB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis, 2010, 31(3): 350-358. |
| 41 | Mattick J S, Makunin I V. Non-coding RNA. Human Molecular Genetics, 2006, 15(1): R17-R29. |
| 42 | Reinhart B J, Weinstein E G, Rhoades M W, et al. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Development, 2002, 16(13): 1616-1626. |
| 43 | Ulmasov T, Murfett J, Hagen G, et al. Aux/IAA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. The Plant Cell, 1997, 9(11): 1963-1971. |
| 44 | Vernoux T, Brunoud G, Farcot E, et al. The auxin signalling network translates dynamic input into robust patterning at the shoot apex. Molecular Systems Biology, 2011, 7(1): 508. |
| 45 | Ye Y J, Wang J W, Wang W, et al. ARF family identification in Tamarix chinensis reveals the salt responsive expression of TcARF6 targeted by miR167. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e8829. |
| 46 | Zhang H Z, Huang S P, Yang R R, et al. Expression pattern and correlation analysis of the halophyte Halostachys caspica miR167d with predictive target gene ARF8 under salt stress. Xinjiang Agriculture Sciences, 2018, 55(11): 2080-2088. |
| 张慧珍, 黄世平, 杨瑞瑞, 等. 盐穗木miR167d和预测靶基因ARF8在盐胁迫下的表达与相关性分析. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(11): 2080-2088. | |
| 47 | Chang E T, Hideki M, Kanako H, et al. Disruption and overexpression of auxin response factor 8 gene of Arabidopsis affect hypocotyl elongation and root growth habit, indicating its possible involvement in auxin homeostasis in light condition. Plant Journal, 2010, 40(3): 333-343. |
| [1] | 王斌, 李满有, 王欣盼, 董秀, 庞军宝, 兰剑. 深松浅旋对半干旱区退化紫花苜蓿人工草地改良效果研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 107-117. |
| [2] | 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 刘文献. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| [3] | 尹晓凡, 魏娜, 郑淑文, 刘文献. 全基因组水平蒺藜苜蓿反转录转座子IRAP分子标记开发及应用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 131-144. |
| [4] | 李彦忠, 喻军强, 李明. 48个苜蓿品种对3种病害抗性的初步评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 62-75. |
| [5] | 赵颖, 辛夏青, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿氮代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 86-96. |
| [6] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静. 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 73-85. |
| [7] | 古丽娜扎尔·艾力null, 陶海宁, 王自奎, 沈禹颖. 基于APSIM模型的黄土旱塬区苜蓿——小麦轮作系统深层土壤水分及水分利用效率研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 22-33. |
| [8] | 周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52. |
| [9] | 张丹丹, 张元庆, 程景, 靳光, 李博, 王栋才, 徐芳, 孙锐锋. 不同粗饲料组合对晋南牛瘤胃体外发酵特性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 93-100. |
| [10] | 臧真凤, 白婕, 刘丛, 昝看卓, 龙明秀, 何树斌. 紫花苜蓿形态和生理指标响应干旱胁迫的品种特异性[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 73-81. |
| [11] | 索效军, 张年, 杨前平, 陶虎, 熊琪, 李晓锋, 张凤, 陈明新. 日粮添加花生秧和苜蓿草粉对波麻杂交羊增重性能、内脏器官发育及血液指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 146-154. |
| [12] | 谢展, 穆麟, 张志飞, 陈桂华, 刘洋, 高帅, 魏仲珊. 乳酸菌或有机酸盐与尿素复配添加对紫花苜蓿混合青贮的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 165-173. |
| [13] | 王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟. 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 186-199. |
| [14] | 张小芳, 魏小红, 刘放, 朱雪妹. PEG胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗内源激素对NO的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 160-169. |
| [15] | 候怡谣, 李霄, 龙瑞才, 杨青川, 康俊梅, 郭长虹. 过量表达紫花苜蓿MsHB7基因对拟南芥耐旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 170-179. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||