

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 119-130.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022044
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
刘建新( ), 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 欧晓彬, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜
), 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 欧晓彬, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜
收稿日期:2022-01-22
修回日期:2022-03-09
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-12-01
通讯作者:
刘建新
作者简介:E-mail: liujx1964@163.com基金资助:
Jian-xin LIU( ), Rui-rui LIU, Xiu-li LIU, Xiao-bin OU, Hai-yan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI
), Rui-rui LIU, Xiu-li LIU, Xiao-bin OU, Hai-yan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI
Received:2022-01-22
Revised:2022-03-09
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2022-12-01
Contact:
Jian-xin LIU
摘要:
信号硫化氢缓解植物盐碱胁迫机理备受关注。为探讨外源硫化氢对盐碱胁迫下植物氨基酸代谢的调控机制,采用盆栽土培试验,以裸燕麦品种‘定莜9号’为材料,设置盆土不添加盐碱和添加3.00 g·kg-1盐碱(摩尔比NaCl︰Na2SO4︰Na2CO3︰NaHCO3=12︰8︰1︰9)与抽穗期叶面喷蒸馏水和喷50 μmol·L-1硫化氢供体硫氢化钠(NaHS)溶液,共4个处理。研究其对叶片中总氨基酸、丙二醛含量和籽粒产量的影响;运用液相色谱和质谱检测,采用主成分分析22种组成蛋白质的氨基酸中差异氨基酸,解析外源硫化氢对氨基酸代谢途径的调控效应。结果表明:在裸燕麦叶片中未检出高半胱氨酸。喷施NaHS溶液对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片中总氨基酸含量下降的缓解效应不显著,对盐碱胁迫诱导的丙二醛含量的升高和籽粒产量的下降有显著的缓解作用。主成分分析结果显示:盐碱胁迫下,喷施NaHS可显著下调裸燕麦叶片中α-酮戊二酸族的鸟氨酸和草酰乙酸族的天冬酰胺含量;显著上调α-酮戊二酸族的谷氨酰胺、脯氨酸、精氨酸和丙酮酸族的亮氨酸及芳香族的酪氨酸含量,对甘氨酸、丝氨酸(3-磷酸甘油酸族)、色氨酸、苯丙氨酸(芳香族)、丙氨酸、缬氨酸(丙酮酸族)、γ-氨基丁酸、组氨酸、谷氨酸(α-酮戊二酸族)、异亮氨酸、苏氨酸、甲硫氨酸、赖氨酸、天冬氨酸(草酰乙酸族)含量无显著影响。表明外源硫化氢参与盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦氨基酸代谢途径的调控,它能够缓解盐碱胁迫造成的氧化伤害和同化物积累抑制。
刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 欧晓彬, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. 盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢对裸燕麦叶片氨基酸代谢过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 119-130.
Jian-xin LIU, Rui-rui LIU, Xiu-li LIU, Xiao-bin OU, Hai-yan JIA, Ting BU, Na LI. Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on amino acid metabolism in naked oat leaves under saline-alkali stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 119-130.

图1 盐碱胁迫下外源H2S对裸燕麦叶片总氨基酸含量的影响CK:无盐碱胁迫下喷水对照;SA:盐碱胁迫下喷水;SA+NaHS:盐碱胁迫下喷施NaHS;NaHS:无盐碱胁迫下喷施NaHS。数值为8次重复的平均值±标准差,不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。CK: Control of spraying water under no salt-alkali stress; SA: Spraing water under salt-alkali stress; SA+NaHS: Spraying NaHS under salt-alkali stress; NaHS: Spraying NaHS under no salt-alkali stress. Values were means±standard deviations of eight independent replications. The different letters indicate significant differences among the treatments at P<0.05. The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on total amino acid content in naked oat leaves under salt-alkali stress
氨基酸 Amino acid | CK | SA | SA+NaHS | NaHS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 差异倍数 Log2FC | 置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 差异倍数 Log2FC | 置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 差异倍数 Log2FC | |
| Gly | 32.858~39.705 | 17.389~24.236 | -0.802 | 20.351~27.198 | 0.192 | 23.493~30.340 | -0.431 |
| Ala | 330.409~389.297 | 230.053~288.941 | -0.472 | 219.962~278.850 | -0.057 | 329.797~388.685 | -0.002 |
| GABA | 499.214~565.512 | 398.812~465.110 | -0.302 | 409.664~475.962 | 0.036 | 541.339~607.637 | 0.110 |
| Ser | 116.555~139.956 | 66.621~90.022 | -0.712 | 65.348~88.749 | -0.024 | 127.607~151.008 | 0.119 |
| Pro | 38.321~44.476 | 30.165~36.319 | -0.317 | 33.173~39.328 | 0.125 | 35.335~41.490 | -0.108 |
| Val | 115.921~131.910 | 89.601~105.590 | -0.344 | 86.784~102.773 | -0.042 | 103.425~119.414 | -0.153 |
| Thr | 133.017~145.292 | 91.378~103.653 | -0.513 | 86.568~98.842 | -0.073 | 115.345~127.619 | -0.196 |
| Ile | 83.684~93.354 | 68.262~77.932 | -0.276 | 70.137~79.807 | 0.037 | 73.122~82.792 | -0.183 |
| Leu | 209.488~238.520 | 187.562~216.594 | -0.149 | 204.842~233.873 | 0.118 | 195.379~224.411 | -0.094 |
| Asn | 47.533~62.169 | 24.772~39.408 | -0.773 | 10.285~24.921 | -0.866 | 30.160~44.796 | -0.549 |
| Orn | 1.208~1.487 | 1.285~1.565 | 0.081 | 0.303~0.582 | -1.687 | 0.559~0.838 | -0.948 |
| Asp | 115.014~138.558 | 113.078~136.621 | -0.022 | 102.951~126.495 | -0.122 | 133.492~157.036 | 0.196 |
| Hcy | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Gln | 495.752~561.061 | 463.632~528.940 | -0.090 | 526.960~592.268 | 0.173 | 445.254~510.562 | -0.145 |
| Lys | 514.520~588.630 | 473.475~547.585 | -0.112 | 518.119~592.229 | 0.121 | 494.387~568.497 | -0.054 |
| Glu | 11.005~12.342 | 2.031~3.367 | -2.113 | 2.647~3.984 | 0.297 | 1.094~2.431 | -2.728 |
| Met | 69.670~81.173 | 66.807~78.310 | -0.056 | 70.161~81.663 | 0.065 | 68.094~79.597 | -0.030 |
| His | 19.891~23.804 | 17.354~21.266 | -0.178 | 17.304~21.217 | -0.004 | 20.035~23.948 | 0.009 |
| Phe | 140.783~163.773 | 132.287~155.277 | -0.083 | 140.298~163.288 | 0.078 | 144.945~167.935 | 0.039 |
| Arg | 28.871~54.286 | 81.632~107.047 | 1.182 | 102.889~128.304 | 0.293 | 52.335~77.750 | 0.646 |
| Tyr | 117.855~135.378 | 95.177~112.700 | -0.285 | 107.457~124.980 | 0.161 | 110.622~128.144 | -0.085 |
| Trp | 36.264~44.057 | 31.483~39.277 | -0.183 | 33.592~41.386 | 0.084 | 37.702~45.496 | 0.051 |
表1 不同处理下裸燕麦叶片中个别氨基酸含量的置信区间及差异倍数
Table 1 Confidence interval and fold change (FC) for the content of individual amino acids in naked oat leaves under different treatments
氨基酸 Amino acid | CK | SA | SA+NaHS | NaHS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 差异倍数 Log2FC | 置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 差异倍数 Log2FC | 置信区间 Confidence interval (μg·g-1 FW) | 差异倍数 Log2FC | |
| Gly | 32.858~39.705 | 17.389~24.236 | -0.802 | 20.351~27.198 | 0.192 | 23.493~30.340 | -0.431 |
| Ala | 330.409~389.297 | 230.053~288.941 | -0.472 | 219.962~278.850 | -0.057 | 329.797~388.685 | -0.002 |
| GABA | 499.214~565.512 | 398.812~465.110 | -0.302 | 409.664~475.962 | 0.036 | 541.339~607.637 | 0.110 |
| Ser | 116.555~139.956 | 66.621~90.022 | -0.712 | 65.348~88.749 | -0.024 | 127.607~151.008 | 0.119 |
| Pro | 38.321~44.476 | 30.165~36.319 | -0.317 | 33.173~39.328 | 0.125 | 35.335~41.490 | -0.108 |
| Val | 115.921~131.910 | 89.601~105.590 | -0.344 | 86.784~102.773 | -0.042 | 103.425~119.414 | -0.153 |
| Thr | 133.017~145.292 | 91.378~103.653 | -0.513 | 86.568~98.842 | -0.073 | 115.345~127.619 | -0.196 |
| Ile | 83.684~93.354 | 68.262~77.932 | -0.276 | 70.137~79.807 | 0.037 | 73.122~82.792 | -0.183 |
| Leu | 209.488~238.520 | 187.562~216.594 | -0.149 | 204.842~233.873 | 0.118 | 195.379~224.411 | -0.094 |
| Asn | 47.533~62.169 | 24.772~39.408 | -0.773 | 10.285~24.921 | -0.866 | 30.160~44.796 | -0.549 |
| Orn | 1.208~1.487 | 1.285~1.565 | 0.081 | 0.303~0.582 | -1.687 | 0.559~0.838 | -0.948 |
| Asp | 115.014~138.558 | 113.078~136.621 | -0.022 | 102.951~126.495 | -0.122 | 133.492~157.036 | 0.196 |
| Hcy | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Gln | 495.752~561.061 | 463.632~528.940 | -0.090 | 526.960~592.268 | 0.173 | 445.254~510.562 | -0.145 |
| Lys | 514.520~588.630 | 473.475~547.585 | -0.112 | 518.119~592.229 | 0.121 | 494.387~568.497 | -0.054 |
| Glu | 11.005~12.342 | 2.031~3.367 | -2.113 | 2.647~3.984 | 0.297 | 1.094~2.431 | -2.728 |
| Met | 69.670~81.173 | 66.807~78.310 | -0.056 | 70.161~81.663 | 0.065 | 68.094~79.597 | -0.030 |
| His | 19.891~23.804 | 17.354~21.266 | -0.178 | 17.304~21.217 | -0.004 | 20.035~23.948 | 0.009 |
| Phe | 140.783~163.773 | 132.287~155.277 | -0.083 | 140.298~163.288 | 0.078 | 144.945~167.935 | 0.039 |
| Arg | 28.871~54.286 | 81.632~107.047 | 1.182 | 102.889~128.304 | 0.293 | 52.335~77.750 | 0.646 |
| Tyr | 117.855~135.378 | 95.177~112.700 | -0.285 | 107.457~124.980 | 0.161 | 110.622~128.144 | -0.085 |
| Trp | 36.264~44.057 | 31.483~39.277 | -0.183 | 33.592~41.386 | 0.084 | 37.702~45.496 | 0.051 |

图2 盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢对裸燕麦叶片中3-磷酸甘油酸、α-酮戊二酸、丙酮酸、芳香族和草酰乙酸途径氨基酸含量的影响
Fig.2 Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the content of individual amino acids in the 3-phosphoglycerate, α-ketoglutarate, pyruvate, aromatic, and oxaloacetate pathways in naked oat leaves under saline-alkali stress
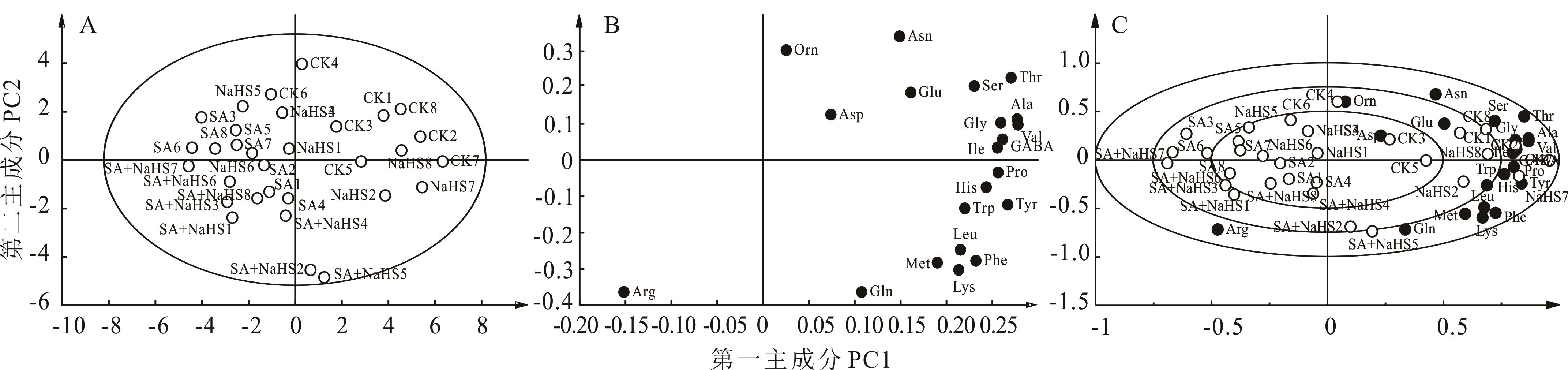
图3 不同处理下裸燕麦叶片氨基酸含量的主成分分析得分图(A)、载荷图(B)和双标图(C)Gly:甘氨酸 L-Glycine; Ala: 丙氨酸 L-Alanine; GABA: γ-氨基丁酸 4-Aminobutyric acid; Ser: 丝氨酸 L-Serine; Pro: 脯氨酸 L-Proline; Val: 缬氨酸 L-Valine; Thr: 苏氨酸 L-Threonine; Ile: 异亮氨酸 L-Isoleucine; Leu:亮氨酸 L-Leucine; Asn: 天冬酰胺 L-Asparagine; Orn: 鸟氨酸盐酸盐 L-Ornithine hydrochloride; Asp: 天冬氨酸L-Aspartic acid; Hcy: 高半胱氨酸 DL-Homocysteine; Gln: 谷氨酰胺L-Glutamine; Lys: 赖氨酸 L-Lysine; Glu: 谷氨酸L-Glutamic acid; Met: 甲硫氨酸L-Methionine; His: 组氨酸 L-Histidine; Phe: 苯丙氨酸 L-Phenylalanine; Arg: 精氨酸L-Arginine; Tyr: 酪氨酸L-Tyrosine; Trp: 色氨酸 L-Tryptophan.下同 The same below.
Fig.3 Principal component analysis scores plot (A), loading plot (B), and biplot (C) of amino acid content in naked oat leaves under different treatments
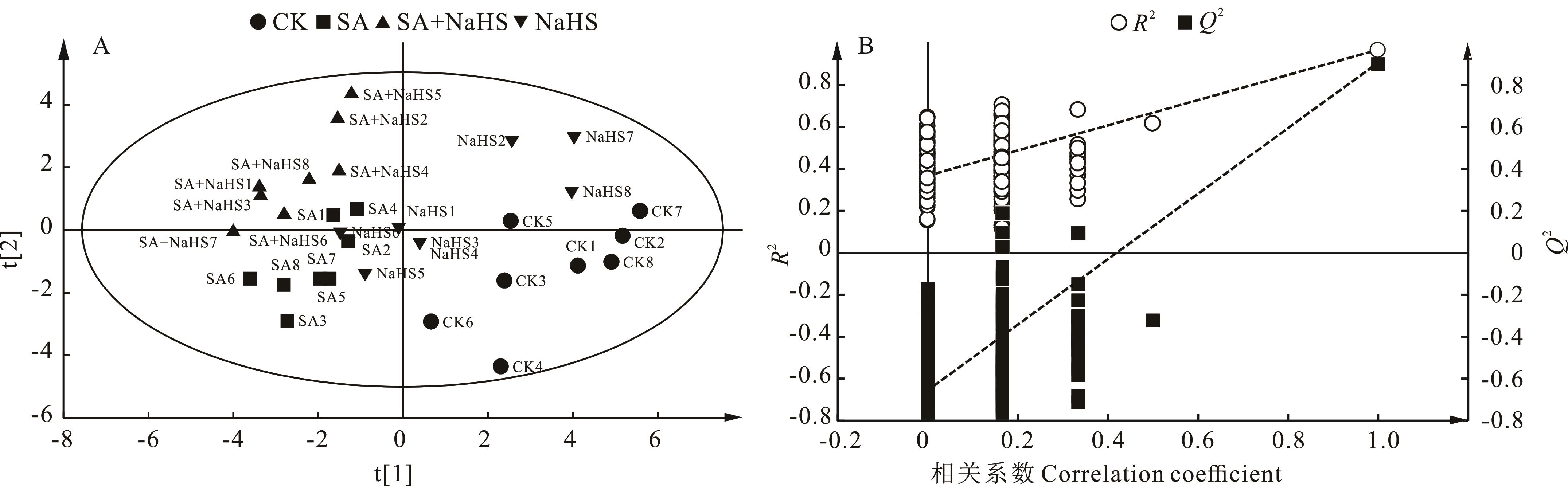
图4 不同处理下裸燕麦叶片氨基酸PLS-DA得分图及200次模型的置换检验t[1]:第一预测主成分 First predictor principal component. t[2]:第二预测主成分 Second predictive principal component.
Fig.4 PLS-DA score plot of naked oat leaves under different treatment and 200 permutation test of the model
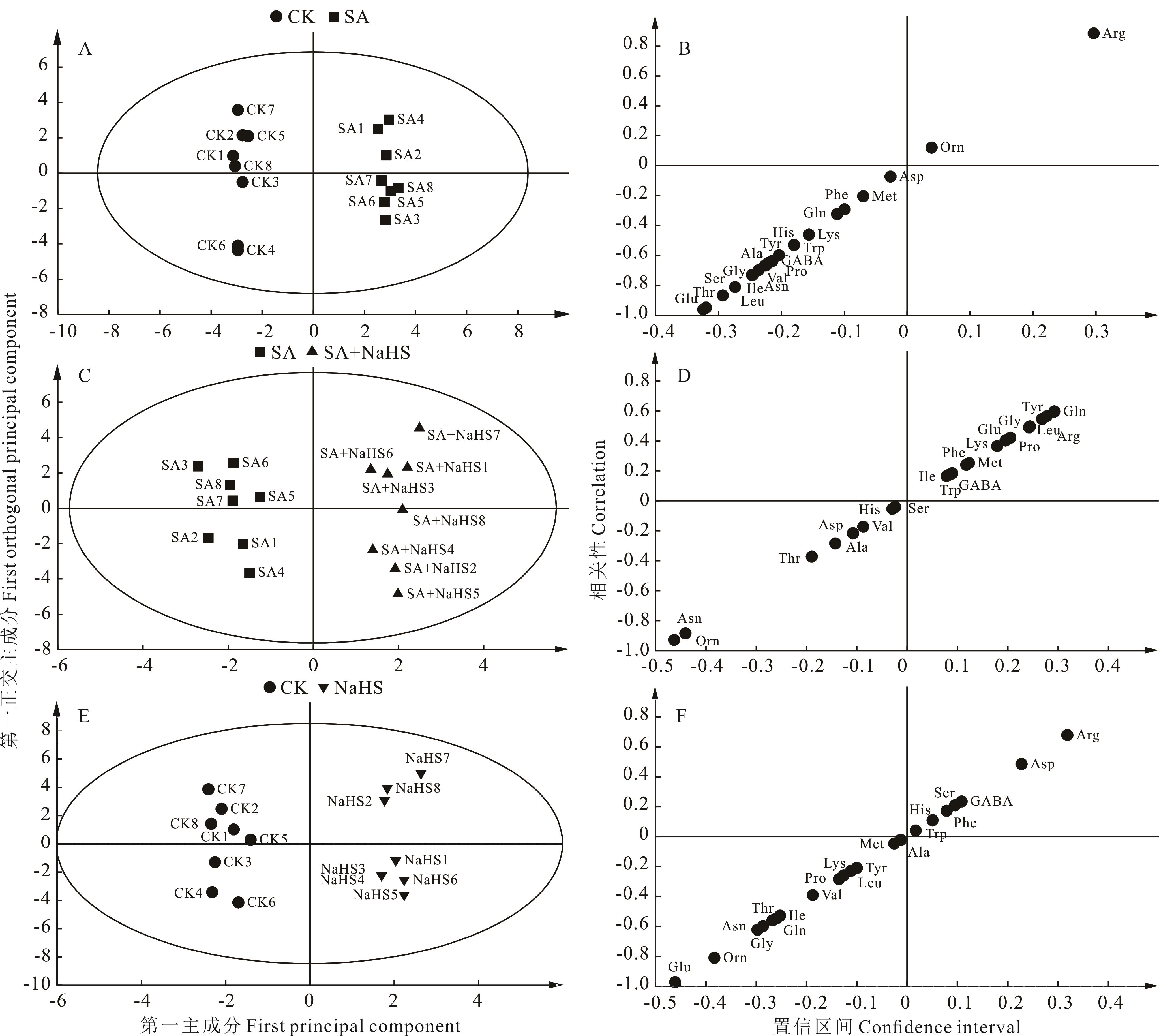
图5 不同处理下裸燕麦叶片氨基酸含量OPLS-DA得分图(A、C、E)和S形图(B、D、F)A,B: CK vs. SA; C,D: SA vs. SA+NaHS; E,F: CK vs. NaHS.
Fig.5 OPLS-DA score plot (A, C, E) and S-plot (B, D, F) of amino acid contents in naked oat leaves under different treatment
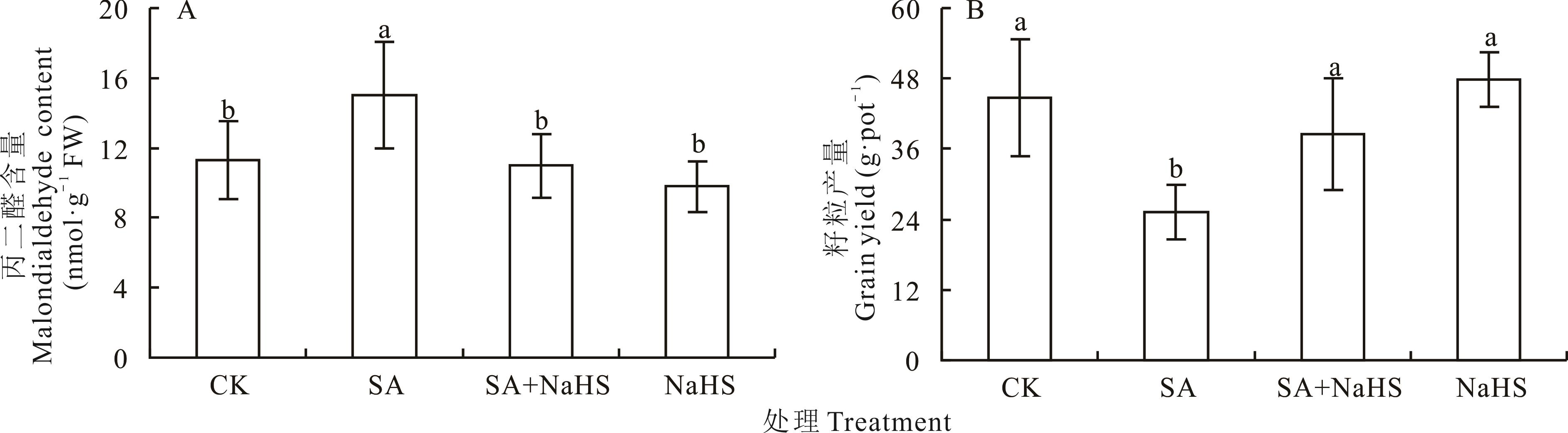
图6 盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢对裸燕麦叶片丙二醛含量和籽粒产量的影响
Fig.6 Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on malondialdehyde content in leaves and grain yield of naked oat under salt-alkali stress
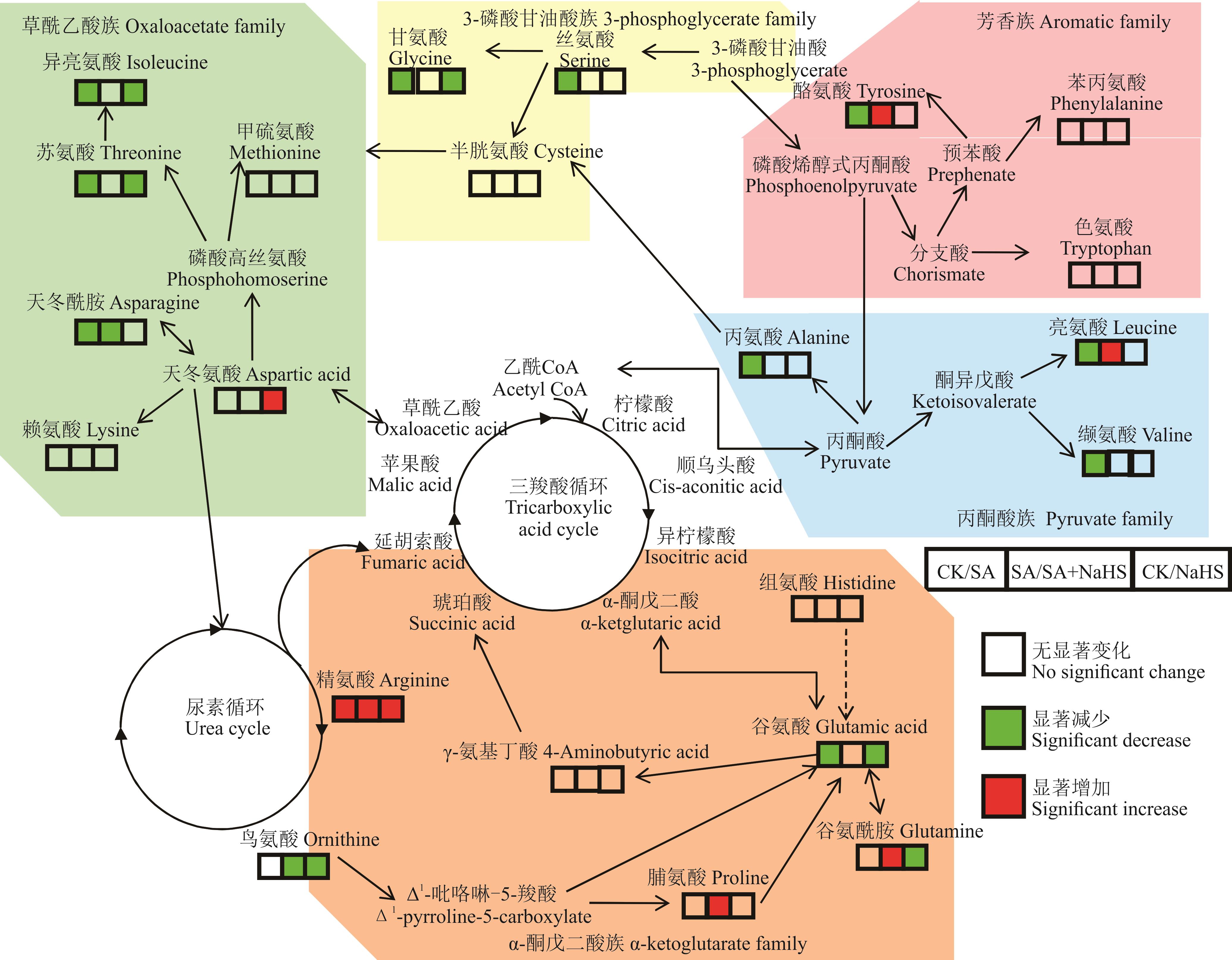
图7 OPLS-DA分析提出盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢调控裸燕麦叶片氨基酸代谢途径
Fig.7 Exogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates amino acid metabolism pathways in naked oat leaves under saline-alkali stress obtained from OPLS-DA analysis
| 1 | Zhang Y, Shi Y, Hu X H, et al. Effects of exogenous spermidine on the nitrogen metabolism and main mineral elements contents of tomato seedlings under saline-alkali stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2013, 24(5): 1401-1408. |
| 张毅, 石玉, 胡晓辉, 等. 外源Spd对盐碱胁迫下番茄幼苗氮代谢及主要矿质元素含量的影响. 应用生态学报, 2013, 24(5): 1401-1408. | |
| 2 | Fu Y S, Cui J Z, Chen G D, et al. Expression of Na+/H+ antiporter gene KsNHX1 in Kochia sieversiana under saline-alkali stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(6): 1629-1634. |
| 付寅生, 崔继哲, 陈广东, 等. 盐碱胁迫下碱地肤Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白基因KsNHX1表达分析. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(6): 1629-1634. | |
| 3 | Yan Y Q, Wang W J, Zhu H, et al. Effects of salt alkali stress on osmoregulation substance and active oxygen metabolism of Qingshan poplar (Populus pseudo cathayana×P. deltoides). Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(9): 2085-2091. |
| 闫永庆, 王文杰, 朱虹, 等. 混合盐碱胁迫对青山杨渗透调节物质及活性氧代谢的影响. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(9): 2085-2091. | |
| 4 | Liu J X, Liu R R, Jia H Y, et al. Regulation of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on osmotic stress in leaves of naked oat seedlings under saline alkali mixed stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(12): 3989-3997. |
| 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 等. 外源H2S对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗叶片渗透胁迫的调节作用. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(12): 3989-3997. | |
| 5 | Liu J X, Wang J C, Liu X L, et al. Effect of exogenous H2O2 on proline accumulation and metabolic pathway in leaves of oat seedlings under complex saline alkali stress. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2016, 36(3): 427-433. |
| 刘建新, 王金成, 刘秀丽, 等. 外源H2O2对混合盐碱胁迫下燕麦幼苗叶片脯氨酸积累和代谢途径的影响. 植物研究, 2016, 36(3): 427-433. | |
| 6 | Kumar S G, Reddy A M, Sudhakar C. NaCl effects on proline metabolism in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) with contrasting salt tolerance. Plant Science, 2003, 165(6): 1245-1251. |
| 7 | Yan H, Peng X B, Xue J J. Effects of NaCl stress on leaf photosynthesis characteristics and free amino acid metabolism of Heyedysarum scoparium. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(7): 1790-1796. |
| 燕辉, 彭晓邦, 薛建杰. NaCl胁迫对花棒叶片光合特性及游离氨基酸代谢的影响. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(7): 1790-1796. | |
| 8 | Rai V K. Role of amino acids in plant responses to stresses. Biologia Plantarum, 2002, 45(4): 481-487. |
| 9 | Yang Z Y, Zhao L Y, Xu Z D. Impacts of salt stress on the growth and physiological characteristics of Rosa rugosa. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(8): 1993-1998. |
| 杨志莹, 赵兰勇, 徐宗大. 盐胁迫对玫瑰生长和生理特性的影响. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(8): 1993-1998. | |
| 10 | Wu Z H, Yang C W, Yang M Y. Photosynthesis, photosystem Ⅱ efficiency, amino acid metabolism and ion distribution in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to alkaline stress. Photosynthetica, 2014, 52(1): 157-160. |
| 11 | Aidoo M K, Quansah L, Galkin E, et al. A combination of stomata deregulation and a distinctive modulation of amino acid metabolism are associated with enhanced tolerance of wheat varieties to transient drought. Metabolomics, 2017, 13: 138-150. |
| 12 | Jin Z P, Pei Y X. Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide in plants: pleasant exploration behind its unpleasant odour. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015, 2015: 1-6. |
| 13 | Mostofa M G, Saegusa D, Fujita M, et al. Hydrogen sulfide regulates salt tolerance in rice by maintaining Na+/K+ balance, mineral homeostasis and oxidative metabolism under excessive salt stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 1055-1068. |
| 14 | Chen J, Wang W H, Wu F H, et al. Hydrogen sulfide enhances salt tolerance through nitric oxide mediated maintenance of ion homeostasis in barley seedling roots. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12516-12534. |
| 15 | Huang H, Guo S S, Chen L C, et al. Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the antioxidant characteristics of tea plant (Camellia sinensis) under salt stress.Plant Physiology Journal, 2017, 53(3): 497-504. |
| 黄菡, 郭莎莎, 陈良超, 等. 外源硫化氢对盐胁迫下茶树抗氧化特性的影响. 植物生理学报, 2017, 53(3): 497-504. | |
| 16 | Shan C, Liu H, Zhao L, et al. Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on the redox states of ascorbate and glutathione in maize leaves under salt stress. Biologia Plantarum, 2013, 58(1): 169-173. |
| 17 | Liu J X, Liu R R, Jia H Y, et al. Effects of exogenous hydrogensulfide on growth and physiological characteristics of naked oat seedlings under saline alkali mixed stress. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2021, 41(2): 245-253. |
| 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 等. 外源H2S对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗生长和生理特性的影响. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(2): 245-253. | |
| 18 | Liu J X, Liu R R, Jia H Y, et al. Effects of spraying NaHS at different growth stages on osmotic adjustment substance and antioxidant activity in leaves of naked oat under saline alkali stress. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(11): 3620-3632. |
| 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 等. 不同时期喷施NaHS对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片渗透调节物质和抗氧化活性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(11): 3620-3632. | |
| 19 | Zheng D S, Zhang Z W. Discussion on the origin and taxonomy of naked oat (Avena nuda L.). Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2011, 12(5): 667-670. |
| 郑殿升, 张宗文. 大粒裸燕麦(莜麦) (Avena nuda L.)起源及分类问题的探讨. 植物遗传资源学报, 2011, 12(5): 667-670. | |
| 20 | Micek P, Kulig B, Woźnica P, et al. The nutritive value for ruminants of faba bean (Vicia faba) seeds and naked oat (Avena nuda) grain cultivated in an organic farming system. Journal of Animal Science, 2012, 21: 773-786. |
| 21 | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000: 192-194, 260-261. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000: 192-194, 260-261. | |
| 22 | Ben B B, Xu W H, Zou D Y, et al. Study on metabonomics of wheat grain under different fertilization conditions.Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2021, 41(2): 212-219. |
| 贲蓓倍, 徐维红, 邹德玉, 等. 不同施肥条件下的小麦籽粒代谢组学研究. 麦类作物学报, 2021, 41(2): 212-219. | |
| 23 | Hartzendorf T, Rolletschek H. Effects of NaCl salinity on amino acid and carbohydrate contents of Phragmites australis. Aquatic Botany, 2001, 69: 195-208. |
| 24 | Guo R, Zhou J, Yang F, et al. Effects of alkaline stress on metabonomic responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum Linn) leaves. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(2): 250-259. |
| 郭瑞, 周际, 杨帆, 等. 碱胁迫对小麦(Triticum aestivum Linn)叶片代谢过程的影响. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(2): 250-259. | |
| 25 | Deng R L, Xu H R, Cao Y F, et al. The molecular basis of ammonium transporters in plants. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2007, 13(3): 512-519. |
| 邓若磊, 徐海荣, 曹云飞, 等. 植物吸收铵态氮的分子生物学基础. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, 13(3): 512-519. | |
| 26 | Chen P, Yang W X, Min X W, et al. Hydrogen sulfide alleviates salinity stress in Cyclocarya paliurus by maintaining chlorophyll fluorescence and regulating nitric oxide level and antioxidant capacity. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2021, 167: 738-747. |
| 27 | Deng Y Q, Bao J, Yuan F, et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates salt stress in wheat seedlings by decreasing Na+ content. Plant Growth Regulation, 2016, 79: 391-399. |
| 28 | Zhu Y W, Che Y M, Zhao F G, et al. H2S functions in growth regulation in rice (Oryza sativa) seedling and metabolism modulating of reactive oxygen under alkaline stress. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2018, 26(7): 1124-1131. |
| 祝一文, 车永梅, 赵方贵, 等. 碱胁迫下H2S参与活性氧代谢和水稻幼苗生长的调控. 农业生物技术学报, 2018, 26(7): 1124-1131. | |
| 29 | Ren X M, Jiang J L, Sun W, et al. Proteomic analysis of cucumber seedling response to high salt stress by exogenous H2S. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 2236-2248. |
| 任绪明, 蒋景龙, 孙旺, 等. 外源H2S影响黄瓜幼苗响应高盐胁迫的蛋白质组学分析. 西北植物学报, 2018, 38(12): 2236-2248. | |
| 30 | Keutgen A J, Pawelzik E. Contribution of amino acids to strawberry fruit quality and their relevance as stress indicators under NaCl salinity. Food Chemistry, 2008, 111(3): 642-647. |
| 31 | Rossi S, Chapman C, Yuan B, et al. Improved heat tolerance in creeping bentgrass by γ aminobutyric acid, proline, and inorganic nitrogen associated with differential regulation of amino acid metabolism. Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 93(2): 231-242. |
| 32 | Bokhary S U F, Wang L, Zheng Y H, et al. Pre-storage hot water treatment enhances chilling tolerance of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) squash by regulating arginine metabolism. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2020, 166: 111229. |
| 33 | Kakkar R K, Bhadur S, Rai V K, et al. Amelioration of NaCl stress by arginine in rice seedlings: Changes in endogenous polyamines. Biologia Plantarum,2000, 43(3): 419-422. |
| 34 | Kovács Z, Simon S L, Sovány C, et al. Differential effects of cold acclimation and abscisic acid on free amino acid composition in wheat. Plant Science, 2011, 180(1): 61-68. |
| 35 | Zeng Z J, Zeng Y, Yan L, et al. Effects of boron deficiency/toxicity on the growth and proline metabolism of cotton seedlings. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1616-1623. |
| 曾紫君, 曾钰, 闫磊, 等. 低硼及高硼胁迫对棉花幼苗生长与脯氨酸代谢的影响. 作物学报, 2021, 47(8): 1616-1623. | |
| 36 | Dai H, Xiao C, Liu H, et al. Combined NMR and LC-MS analysis reveals the metabonomic changes in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge induced by water depletion.Journal of Proteome Research, 2010, 9(3): 1460-1475. |
| 37 | Heinemann B, Hildebrandt T M. The role of amino acid metabolism in signaling and metabolic adaptation to stress induced energy deficiency in plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 72(13): 4634-4645. |
| [1] | 李瑞强, 王玉祥, 孙玉兰, 张磊, 陈爱萍. 盐胁迫对5份无芒雀麦苗期生长和生理生化的影响及综合性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-111. |
| [2] | 苗阳阳, 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民. 碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 107-117. |
| [3] | 沈吉成, 王蕾, 赵彩霞, 叶发慧, 吕士凯, 刘德梅, 刘瑞娟, 张怀刚, 陈文杰. 77份裸燕麦品种籽粒相关性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 156-167. |
| [4] | 王星宇, 程静, 高生, 李默涵, 杨满霞, 葛军勇, 周海涛, 李云霞, 臧华栋, 左文博. 应用AMMI模型和GGE双标图评价裸燕麦品种在华北高寒区的适应性[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 76-84. |
| [5] | 周倩倩, 张亚见, 张静, 殷涂童, 盛下放, 何琳燕. 产硫化氢细菌的筛选及阻控苜蓿吸收铅和改良土壤的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 44-52. |
| [6] | 聂秀美, 慕平, 赵桂琴, 何海鹏, 吴文斌, 蔺豆豆, 苏伟娟, 张丽睿. 贮藏年限对裸燕麦种带真菌和真菌毒素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 106-120. |
| [7] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [8] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. NaHS引发提高裸燕麦种子活力的生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 135-142. |
| [9] | 范朕连, 贾阳杰, 范远, 宋慧平, 冯政君. 盐碱土施用硅钙渣对披碱草生长的影响及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 93-101. |
| [10] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 刘秀丽, 卜婷, 李娜. 外源半胱氨酸缓解裸燕麦镧胁迫的生理机制[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 122-131. |
| [11] | 申午艳, 冯政君, 秦文芳, 范远. 盐碱胁迫下黑麦草生长及离子微区分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 52-63. |
| [12] | 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 王金成, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕. 镉胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗对外源H2O2的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 125-134. |
| [13] | 赵颖, 魏小红, 赫亚龙, 赵枭飞, 韩厅, 岳凯, 辛夏青, 宿梅飞, 马文静, 骆巧娟. 混合盐碱胁迫对藜麦种子萌发和幼苗抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 156-167. |
| [14] | 王茜, 李志坚, 李晶, 周帮伟. 不同类型燕麦农艺和饲草品质性状分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 149-158. |
| [15] | 麻莹, 王晓苹, 姜海波, 石德成. 盐碱胁迫下碱地肤体内的有机酸积累及其草酸代谢特点[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 158-165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||