

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (1): 50-60.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023070
白旭琴2( ), 贾春云1(
), 贾春云1( ), 李文栓3,4, 李亚敏5, 刘长风2, 韩秀云1, 褚美函6, 巩宗强1, 李晓军1
), 李文栓3,4, 李亚敏5, 刘长风2, 韩秀云1, 褚美函6, 巩宗强1, 李晓军1
收稿日期:2023-03-06
修回日期:2023-04-24
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
贾春云
作者简介:E-mail: jiachunyun@iae.ac.cn基金资助:
Xu-qin BAI2( ), Chun-yun JIA1(
), Chun-yun JIA1( ), Wen-shuan LI3,4, Ya-min LI5, Chang-feng LIU2, Xiu-yun HAN1, Mei-han CHU6, Zong-qiang GONG1, Xiao-jun LI1
), Wen-shuan LI3,4, Ya-min LI5, Chang-feng LIU2, Xiu-yun HAN1, Mei-han CHU6, Zong-qiang GONG1, Xiao-jun LI1
Received:2023-03-06
Revised:2023-04-24
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-11-23
Contact:
Chun-yun JIA
摘要:
为了缓解紫花苜蓿的镉累积并实现富硒目的,探究了不同浓度镉胁迫下叶面喷施硒肥对紫花苜蓿生长特征及富硒降镉特性的影响。以草原三号和中苜一号紫花苜蓿为材料,采用叶面喷施硒肥的方式,在初花期测量紫花苜蓿的株高、生物量并检测根茎叶部位的总硒、硒代蛋氨酸(SeMet)、镉等含量,分析叶面喷施硒肥对紫花苜蓿富硒降镉效果的影响。结果表明,施加外源硒对紫花苜蓿的生长和富硒量均有促进作用,表现为两个品种紫花苜蓿的株高、生物量、总硒和SeMet含量均显著提高,镉含量、镉富集系数、镉转运系数均显著下降。相同喷施硒肥浓度下,低浓度镉污染促进紫花苜蓿的生长,高浓度镉污染则抑制紫花苜蓿的生长。镉浓度为1 mg·kg-1、施硒量为100 mg·kg-1时,紫花苜蓿中硒含量最高、镉含量最低,各组织中总硒、SeMet含量:叶>茎>根,镉含量:茎<叶<根。相同条件下, 中苜一号的生物量、总硒、SeMet含量均高于草原三号,镉含量低于草原三号,且在镉浓度为1 mg·kg-1、施硒量为50 mg·kg-1的条件下富硒降镉效果最佳。
白旭琴, 贾春云, 李文栓, 李亚敏, 刘长风, 韩秀云, 褚美函, 巩宗强, 李晓军. 叶面喷施硒肥对紫花苜蓿富硒降镉效果的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 50-60.
Xu-qin BAI, Chun-yun JIA, Wen-shuan LI, Ya-min LI, Chang-feng LIU, Xiu-yun HAN, Mei-han CHU, Zong-qiang GONG, Xiao-jun LI. An investigation of foliar spraying of selenium fertilizer for selenium enrichment and cadmium reduction in alfalfa[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(1): 50-60.
化学性状 Chemical property | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen | 速效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 总硒 Selenium (Se) | 锌 Zn | 铁 Fe | 镁 Mg | 锰 Mn | 镉 Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量Content (mg·kg-1) | 7.32 | 18020 | 1.84 | 0.89 | 2.57 | 0.02 | 11.81 | 12806.25 | 2634.38 | 420.94 | - |
表 1 土壤基本化学性质
Table 1 Chemical properties of soil
化学性状 Chemical property | pH | 有机质 Organic matter | 碱解氮 Alkaline hydrolysis nitrogen | 速效磷 Available P | 速效钾 Available K | 总硒 Selenium (Se) | 锌 Zn | 铁 Fe | 镁 Mg | 锰 Mn | 镉 Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量Content (mg·kg-1) | 7.32 | 18020 | 1.84 | 0.89 | 2.57 | 0.02 | 11.81 | 12806.25 | 2634.38 | 420.94 | - |

图1 镉胁迫下叶面施硒对紫花苜蓿株高和生物量的影响CY: 草原三号M. sativa cv. Caoyuan No.3; ZM: 中苜一号M. sativa cv. Zhongmu No.1. CK: 对照组Control group; Cd=1: 镉含量为1 mg·kg-1处理Cadmium content of 1 mg·kg-1 treatment; Cd=10: 镉含量为10 mg·kg-1处理Cadmium content of 10 mg·kg-1 treatment. 不同大写字母表示同一个品种同一施硒量不同镉处理下差异显著,不同小写字母表示同一个品种同一镉处理不同施硒量下差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among different cadmium treatments of the same variety and selenium application amount, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different selenium application amount of the same variety alfalfa and cadmium treatment (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.1 Effect of foliar spraying of selenium fertilizer on plant height and biomass of alfalfa under cadmium stress

图2 镉胁迫下叶面施硒对紫花苜蓿不同组织中硒含量的影响
Fig.2 Effect of foliar spraying of selenium fertilizer on selenium content in different organs of alfalfa under cadmium stress
组织 Organs | 施硒量 Selenium application amount (mg·kg-1) | 有机硒转化率Conversion rate of organic selenium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草原三号M. sativa cv. Caoyuan No.3 | 中苜一号M. sativa cv. Zhongmu No.1 | ||||||
| CK | Cd=1 | Cd=10 | CK | Cd=1 | Cd=10 | ||
根 Root | 0 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.36 |
| 50 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.65 | |
| 100 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.68 | |
茎 Stem | 0 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.34 |
| 50 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.74 | |
| 100 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.74 | |
叶 Leaf | 0 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.50 |
| 50 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.78 | |
| 100 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 0.84 | |
表2 有机硒转化率
Table 2 Conversion rate of organic selenium
组织 Organs | 施硒量 Selenium application amount (mg·kg-1) | 有机硒转化率Conversion rate of organic selenium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草原三号M. sativa cv. Caoyuan No.3 | 中苜一号M. sativa cv. Zhongmu No.1 | ||||||
| CK | Cd=1 | Cd=10 | CK | Cd=1 | Cd=10 | ||
根 Root | 0 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.36 |
| 50 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.65 | |
| 100 | 0.70 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.68 | |
茎 Stem | 0 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.34 |
| 50 | 0.75 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.74 | |
| 100 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.74 | |
叶 Leaf | 0 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.50 |
| 50 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.78 | |
| 100 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 0.84 | |
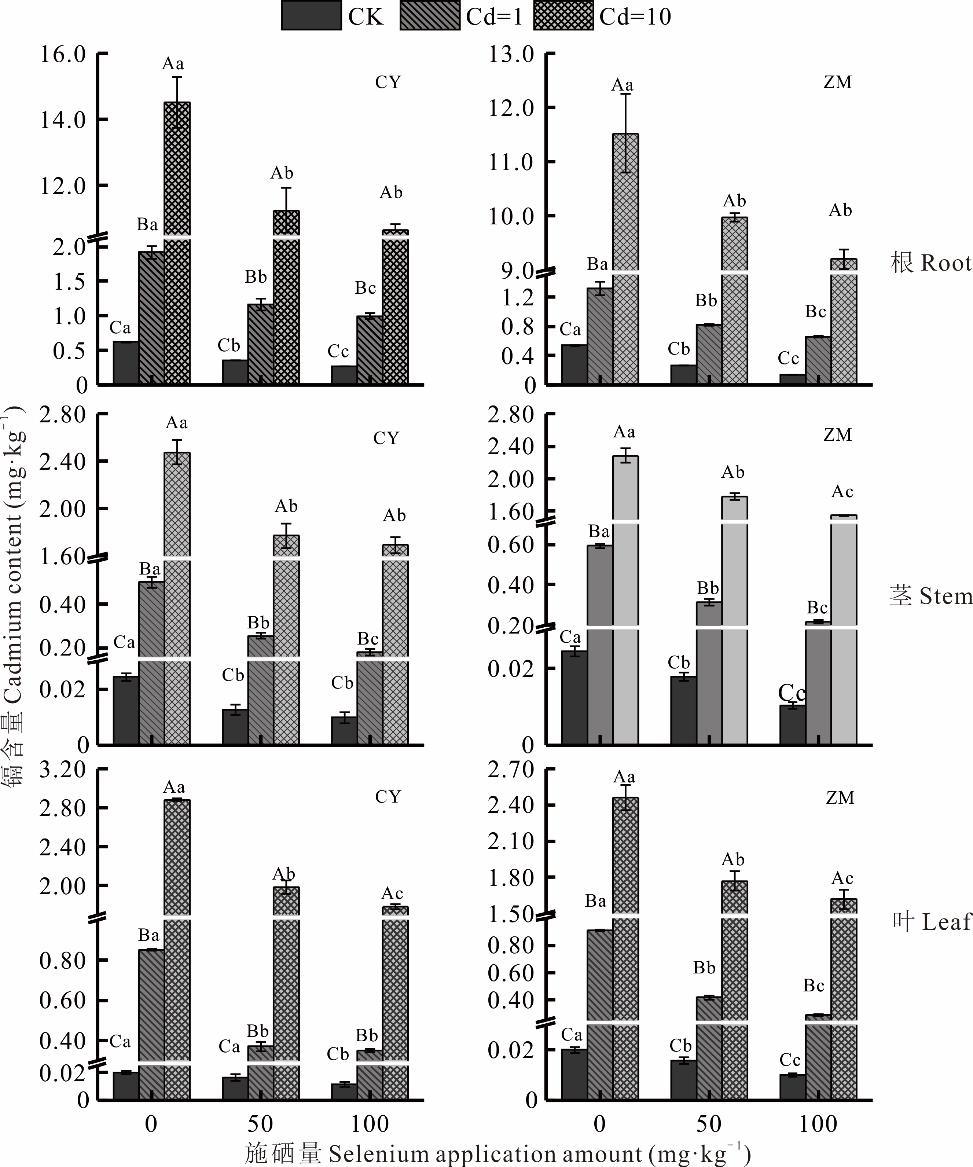
图3 镉胁迫下叶面施硒对紫花苜蓿不同部位镉含量的影响
Fig.3 Effect of foliar spraying of selenium fertilizer on cadmium content in different organs of alfalfa under cadmium stress
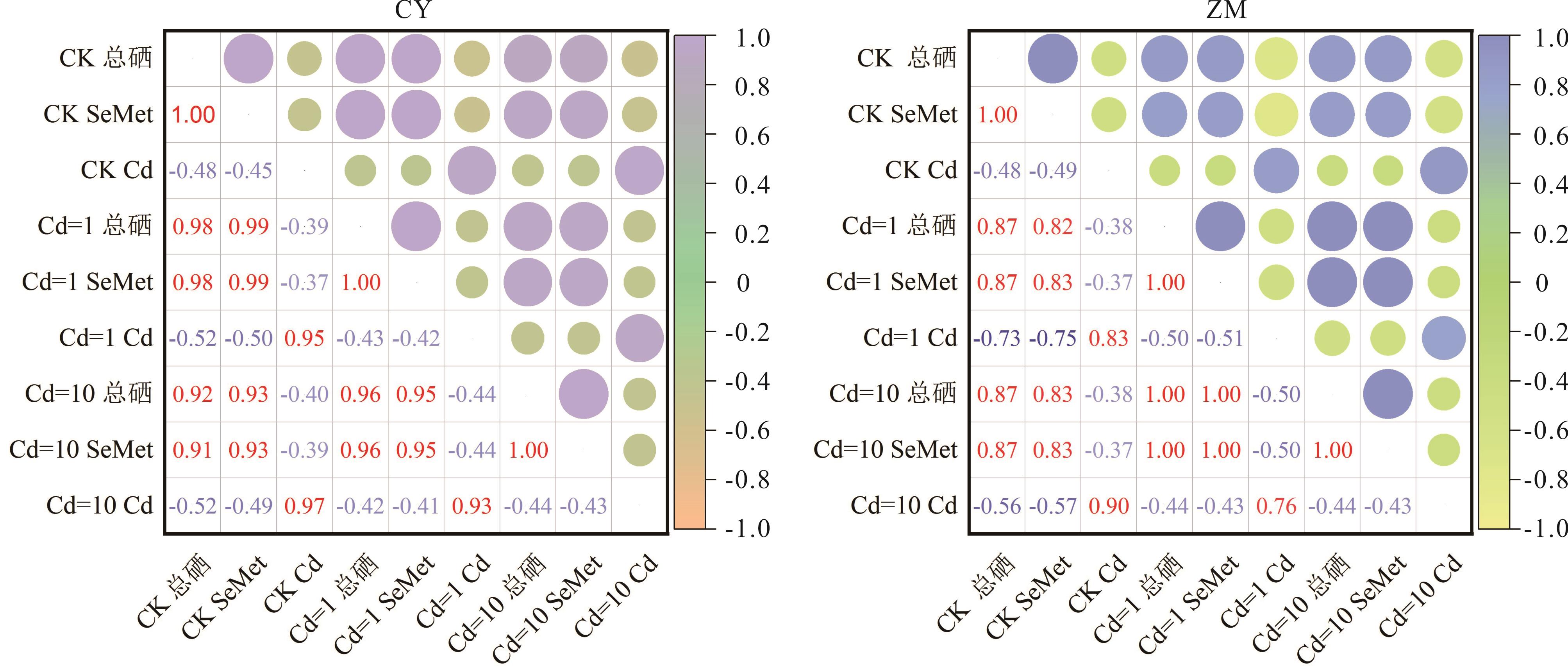
图5 紫花苜蓿总硒、SeMet、镉含量之间的相关性图中数字代表两个相交叉指标的相关性P值;其中正值代表显著正相关,负值代表显著负相关;圆形面积越大,颜色越深,代表相关系数越高。 The number in the figure represents the correlation P value of the two intersecting indicators; a positive value represents a significant positive correlation and a negative value represents a significant negative correlation; the larger the circle area, the darker the color, the higher the correlation coefficient. CK 总硒: 对照组中的总硒 Total selenium in control group; CK SeMet: 对照组中的SeMet SeMet in control group; CK Cd: 对照组中的Cd Cd in control group; Cd=1 总硒: 镉含量为1 mg·kg-1处理下的总硒 Cadmium content is 1 mg·kg-1 treatment of total selenium; Cd=1 SeMet: 镉含量为1 mg·kg-1处理下的SeMet Cadmium content is 1 mg·kg-1 treatment of SeMet; Cd=1 Cd: 镉含量为1 mg·kg-1处理下的Cd Cadmium content is 1 mg·kg-1 treatment of Cd; Cd=10 总硒: 镉含量为10 mg·kg-1处理下的总硒 Cadmium content is 10 mg·kg-1 treatment of total selenium; Cd=10 SeMet: 镉含量为10 mg·kg-1处理下的SeMet Cadmium content is 10 mg·kg-1 treatment of SeMet; Cd=10 Cd: 镉含量为10 mg·kg-1处理下的Cd Cadmium content is 10 mg·kg-1 treatment of Cd.
Fig.5 Correlation of total selenium, SeMet and cadmium content in alfalfa
| 1 | Lönnerdal B, Vargas-Fernández E, Whitacre M. Selenium fortification of infant formulas: does selenium form matter? Food & Function, 2017, 8(11): 3856-3868. |
| 2 | Avery J C, Hoffmann P R. Selenium, selenoproteins, and immunity. Nutrients, 2018, 10(9): 1203. |
| 3 | Pavlovic Z, Miletic I, Zekovic M, et al. Impact of selenium addition to animal feeds on human selenium status in Serbia. Nutrients, 2018, 10(2): 225. |
| 4 | Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M H M B, Raza A, et al. Selenium in plants: Boon or bane? Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2020, 178(1): 104170. |
| 5 | Pilon-Smits E A H. On the ecology of selenium accumulation in plants. Plants, 2019, 8(7): 197. |
| 6 | Schiavon M, Pilon-Smits E A. Selenium biofortification and phytoremediation phytotechnologies: A review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2017, 46(1): 10-19. |
| 7 | Schiavon M, Pilon-Smits E A. The fascinating facets of plant selenium accumulation-biochemistry, physiology, evolution and ecology. New Phytologist, 2017, 213(4): 1582-1596. |
| 8 | Ebrahimi N, Stoddard F L, Hartikainen H, et al. Plant species and growing season weather influence the efficiency of selenium biofortification. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2019, 114(2): 111-124. |
| 9 | Ke C Y, Xia L N, Wu X F, et al. Research application of selenium enrichment methods in plants. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines, 2009, 23(5): 79-81, 57. |
| 可成友, 夏丽娜, 吴晓芳, 等. 富硒方法在植物中的研究应用. 现代中药研究与实践, 2009, 23(5): 79-81, 57. | |
| 10 | Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia-Ur-Rehman M, et al. Effects of selenium on the uptake of toxic trace elements by crop plants: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 51(21): 2531-2566. |
| 11 | Ros G H, Van R A M D, Bussink D W, et al. Selenium fertilization strategies for bio-fortification of food: an agro-ecosystem approach. Plant and Soil, 2016, 404(1/2): 99-112. |
| 12 | Yan D P, Gong L, Yuan Y Y, et al. Effects of spraying foliar fertilizer on alfalfa growth, grass yield, and nutrient quality at different stages. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(5): 1255-1261. |
| 闫得朋, 巩林, 袁玉莹, 等. 不同时期喷施叶面肥对紫花苜蓿生长和、产草量营养品质的影响. 草地学报, 2018, 26(5): 1255-1261. | |
| 13 | Han B, Yu H Y, Chen X, et al. Effect of combined application of selenium and cobalt fertilizers on root morphology of alfalfa. Grassland and Turf, 2016, 36(5): 88-94. |
| 韩冰, 俞慧云, 陈曦, 等. 硒钴肥配施对紫花苜蓿根系形态的影响. 草原与草坪, 2016, 36(5): 88-94. | |
| 14 | Kompe Y O, Sagiroglu A. The effects of cadmium on the biochemical and physiological parameters of Eruca sativa. Acta Biologica Hungarica, 2016, 67(4): 393-402. |
| 15 | Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of marine ecology and environment status of China in 2021. (2022-05-26)[2023-01-18]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202205/P020220608338202870777.pdf. |
| 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 中国生态环境状况公报. (2022-05-26)[2023-01-18]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202205/P020220608338202870777.pdf. | |
| 16 | Riaz U, Aslam A, Zaman Q, et al. Cadmium contamination, bioavailability, uptake mechanism and remediation strategies in soil-plant-environment system: A critical review. Current Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 17(1): 49-60. |
| 17 | Wang Q H, Zheng Y, Li Q W, et al. Overview of combined bioremediation mechanism of contaminated soil. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(1): 246-256. |
| 王庆宏, 郑逸, 李倩玮, 等. 污染土壤生物联合修复机制研究进展. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(1): 246-256. | |
| 18 | Huang T Q, Jiang Z P, Huang Y F, et al. Effects of different foliar fertilizers containing Se on Se-enrichment and Cd-reduction in rice. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2017, 48(7): 1185-1189. |
| 黄太庆, 江泽普, 黄雁飞, 等. 不同配方含硒叶面肥对水稻富硒降镉的影响. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(7): 1185-1189. | |
| 19 | Hu H F, Wang Y H, Li M, et al. Effect of foliar selenium on the forage yield of alfalfa and selenium absorption characteristics. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(6): 1347-1350. |
| 胡华锋, 王彦华, 李明, 等. 叶面施硒对紫花苜蓿产草量及吸硒特性的影响. 草地学报, 2015, 23(6): 1347-1350. | |
| 20 | Zhang R, Zhao B P, Wang Y N, et al. Effects of different cadmium concentrations on photosynthetic characteristics and cadmium enrichment and transport coefficients of three oat varieties. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(8): 2089-2099. |
| 张茹, 赵宝平, 王永宁, 等. 不同镉浓度对3个燕麦品种光合特性及镉富集转运系数的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8): 2089-2099. | |
| 21 | Zhou X B, Shi W M, Yang L Z. Effect of foliar application of selenite on selenium accumulation and distribution in rice. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 73-78. |
| 周鑫斌, 施卫明, 杨林章. 叶面喷硒对水稻籽粒硒富集及分布的影响. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 73-78. | |
| 22 | Li Q Y, Yao X H, Liu L P, et al. Analysis of selenium speciation in broccoli by high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2023, 11(1): 1-13. |
| 李乾玉, 姚晓慧, 刘丽萍, 等. 高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法分析研究西兰花中硒形态. 岩矿测试, 2023, 11(1): 1-13. | |
| 23 | Liu W, Yin J J, Wu M C, et al. Selenium amino acids speciation in selenium-enriched agricultural products and their distribution in different protein components. Food & Machinery, 2022, 38(6): 45-51, 190. |
| 刘为, 尹金晶, 吴慕慈, 等. 富硒农产品中硒代氨基酸形态及其在不同蛋白组分中的分布. 食品与机械, 2022, 38(6): 45-51, 190. | |
| 24 | Huang H, Li M, Rizwan M, et al. Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 401: 123393. |
| 25 | Tang H, Liu Y, Gong X, et al. Effects of selenium and silicon on enhancing antioxidative capacity in ramie [Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.] under cadmium stress. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(13): 9999-10008. |
| 26 | Li J, Yang W, Guo A, et al. Combined foliar and soil selenium fertilizer increased the grain yield, quality, total Se, and organic Se content in naked oats. Journal of Cereal Science, 2021, 100(2): 103265. |
| 27 | Liu P, Song L, Hao S, et al. Effects of selenium application concentration, period and method on the selenium content and grain yield of Tartary buckwheat of different varieties. Journal of Science Food Agriculture, 2022, 102(15): 6868-6876. |
| 28 | Jiang S C, Du B, Wu Q X, et al. Selenium decreases the cadmium content in brown rice: foliar Se application to plants grown in Cd-contaminated soil. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2022, 22(1): 1033-1043. |
| 29 | Xu H, Yan J, Qin Y, et al. Effect of different forms of selenium on the physiological response and the cadmium uptake by rice under cadmium stress. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(19): 6991. |
| 30 | Liu C, Chang C, Fei Y, et al. Cadmium accumulation in edible flowering cabbages in the Pearl River Delta, China: Critical soil factors and enrichment models. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 233: 880-888. |
| 31 | Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, et al. A critical review on effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of cadmium in vegetables. Chemosphere, 2017, 182: 90-105. |
| 32 | Schieber M, Chandel N S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Current Biology, 2014, 24(10): R453- R462. |
| 33 | Dias M C, Monteiro C, Moutinho-Pereira J, et al. Cadmium toxicity affects photosynthesis and plant growth at different levels. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2012, 35(4): 1281-1289. |
| 34 | Cui J, Liu T, Li Y, et al. Selenium reduces cadmium uptake into rice suspension cells by regulating the expression of lignin synthesis and cadmium-related genes. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 644: 602-610. |
| 35 | Feng R, Wei C, Tu S. The roles of selenium in protecting plants against abiotic stresses. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013, 87: 58-68. |
| 36 | Guo Y K, Mao K, Cao H R, et al. Exogenous selenium (cadmium) inhibits the absorption and transportation of cadmium (selenium) in rice. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 268(Part A):115829. |
| 37 | Schiavon M, Lima L W, Jiang Y, et al. Effects of selenium on plant metabolism and implications for crops and consumers. Springer International Publising, 2017. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-56249-0_15. |
| 38 | Jiang P, Liu J, Chen M, et al. Exogenous selenium improves the physiological resistance of cucumber to cadmium stress. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 102(9): 455-472. |
| 39 | Liu S, Wu Z C, Zhao Y R, et al. Effects of selenium on the uptake and transport of trace elements by cadmium-stressed flowering Chinese cabbage. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(3): 431-439. |
| 刘帅, 吴志超, 赵亚荣, 等. 外源硒对镉胁迫下菜心Fe、Mn、Cu、Zn吸收与转运的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(3): 431-439. | |
| 40 | Wang L, Wu K, Liu Z, et al. Selenite reduced uptake/translocation of cadmium via regulation of assembles and interactions of pectins, hemicelluloses, lignins, callose and Casparian strips in rice roots. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 448: 130812. |
| 41 | Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T. Rice breaks ground for cadmium-free cereals. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2013, 16(3): 328-334. |
| 42 | Yuan S L, Yu Y, Wan Y N, et al. Mechanisms of selenium mitigating stress and accumulation of heavy metals in plants. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6): 545-550. |
| 袁思莉, 余垚, 万亚男, 等. 硒缓解植物重金属胁迫和累积的机制. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6): 545-550. |
| [1] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 马春晖, 张前兵. 菌磷耦合下紫花苜蓿的干物质产量及磷素空间分布特征[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 104-115. |
| [2] | 徐蕊, 王峥, 王仪明, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿对轮作水稻产量和蔗糖代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 129-140. |
| [3] | 王宝强, 马文静, 王贤, 朱晓林, 赵颖, 魏小红. 一氧化氮对干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗次生代谢产物的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 141-151. |
| [4] | 凌文卿, 张磊, 李珏, 冯启贤, 李妍, 周燚, 刘一佳, 阳伏林, 周晶. 布氏乳杆菌和不同糖类联用对紫花苜蓿青贮营养成分、发酵品质、瘤胃降解率及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 122-134. |
| [5] | 王少鹏, 刘佳, 洪军, 林积圳, 张义, 史昆, 王赞. 紫花苜蓿MsPPR1基因的克隆及抗旱功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 49-60. |
| [6] | 李超男, 王磊, 周继强, 赵长兴, 谢晓蓉, 刘金荣. 微塑料对紫花苜蓿生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 138-146. |
| [7] | 张振粉, 黄荣, 姚博, 张旺东, 杨成德, 陈秀蓉. 欧美进口紫花苜蓿可培养种带细菌及其对动植物的致病性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 161-172. |
| [8] | 张士敏, 赵娇阳, 朱慧森, 卫凯, 王永新. 硒对不同品种紫花苜蓿发芽阶段物质转化和形态建成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 79-90. |
| [9] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [10] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [11] | 孙守江, 唐艺涵, 马馼, 李曼莉, 毛培胜. 紫花苜蓿种子吸胀期胚根线粒体AsA-GSH循环对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 152-162. |
| [12] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| [13] | 杜江, 马振男, 王晨燕, 张丽, 王德富, 牛颜冰. 基于小RNA深度测序技术的苜蓿病毒病鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 115-125. |
| [14] | 王彦佳, 胡伯昂, 陈佳欣, 许丽婷, 姚琳, 冯丽荣, 郭长虹. 2株紫花苜蓿解钾菌的筛选鉴定及其对产量和品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 139-149. |
| [15] | 赵金梅, 殷国梅, 孙娟娟, 卫媛, 李薇, 郭茂伟, 刘思齐, 张佳琪. 抗寒锻炼中紫花苜蓿非结构性碳水化合物转化转运与抗寒性关系[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 181-188. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||