

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 13-23.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023150
于双1( ), 李小伟1,2(
), 李小伟1,2( ), 王瑞霞3, 杨君珑1, 马龙1
), 王瑞霞3, 杨君珑1, 马龙1
收稿日期:2023-05-08
修回日期:2023-06-08
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2023-12-27
通讯作者:
李小伟
作者简介:.E-mail: lxwbq@126.com基金资助:
Shuang YU1( ), Xiao-wei LI1,2(
), Xiao-wei LI1,2( ), Rui-xia WANG3, Jun-long YANG1, Long MA1
), Rui-xia WANG3, Jun-long YANG1, Long MA1
Received:2023-05-08
Revised:2023-06-08
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Xiao-wei LI
摘要:
为探讨柠条固沙林林下草本群落演替序列与环境因子的关系,调查了灵武白芨滩不同种植年限(3、5、10、20、30、40、50、60和70年)柠条林下草本群落,测定了土壤理化性质,采用双向指示种分析(TWINSPAN)、除趋势对应分析(DCA)和冗余分析(RDA)的方法对群落进行数量分类和排序,并分析群落演替序列与环境因子间的关系。结果表明:1)应用TWINSPAN将9个样地的27个样方划分为4个群落类型:蒙古虫实+沙蓬群落→沙鞭+白沙蒿群落→狗尾草+藜群落→猪毛蒿+短花针茅群落。2)DCA 排序与TWINSPAN分类结果一致,DCA 排序进一步印证了TWINSPAN分类的合理性。3)通过冗余分析(RDA)显示,土壤有机质含量和土壤pH值是影响林下草本植物群落演替的主要环境因子,解释量分别为19.3%和13.6%,贡献率分别达37.5%和26.5%(P<0.05)。本研究对揭示白芨滩固沙林林下草本群落演替规律和驱动因素具有重要意义,结果可为荒漠化治理及白芨滩自然保护区的科学管理提供理论依据。
于双, 李小伟, 王瑞霞, 杨君珑, 马龙. 灵武白芨滩不同年限柠条固沙林林下草本群落演替规律及机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 13-23.
Shuang YU, Xiao-wei LI, Rui-xia WANG, Jun-long YANG, Long MA. Succession mechanism and dynamics in artificial Caragana korshinskii sand-fixing forests of different ages in Baijitan of Lingwu[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 13-23.

图1 不同种植年限柠条样地分布S3: 种植3年3 years of planting; S5: 种植5年5 years of planting; S10: 种植10年10 years of planting; S20: 种植20年20 years of planting; S30: 种植30年30 years of planting; S40: 种植40年40 years of planting; S50: 种植50年50 years of planting; S60: 种植60年60 years of planting; S70: 种植70年70 years of planting.
Fig.1 Distribution of C. korshinskii sample plot with different planting years
林龄 Forest age (yrs) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 林下草本植物 Understory herbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 37°40′ | 106°46′ | 1213.88 | 0.16 | 蒙古虫实Corispermum mongolicum、沙蓬Agriophyllum squarrosum、雾冰藜Bassia dasyphylla |
| 5 | 38°03′ | 106°51′ | 1255.95 | 0.65 | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、猪毛蒿Artemisia scoparia、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、香青兰Dracocephalum moldavica |
| 10 | 38°02′ | 106°48′ | 1227.35 | 0.53 | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、画眉草Eragrostis pilosa |
| 20 | 37°55′ | 106°50′ | 1308.89 | 0.82 | 沙鞭Psammochloa villosa、地锦Parthenocissus tricuspidata、砂蓝刺头Echinops gmelini、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、白沙蒿Artemisia sphaerocephala、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草Setaria viridis、锋芒草Tragus racemosus、阿尔泰狗娃花Heteropappus altaicus |
| 30 | 38°02′ | 106°33′ | 1307.64 | 0.54 | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草S. viridis、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、地锦P. tricuspidata、藜Chenopodium album、砂蓝刺头E. gmelini、猪毛蒿A. scoparia、香青兰D. moldavica、地捎瓜Cynanchum thesioides、银柴胡Stellaria dichotoma var. lanceolata、草木樨状黄芪Astragalus melilotoides、阿尔泰狗娃花H. altaicus、叉枝鸦葱Scorzonera divaricata |
| 40 | 38°10′ | 106°39′ | 1324.16 | 0.51 | 阿尔泰狗娃花H. altaicus、狗尾草S. viridis、画眉草E. pilosa、乳浆大戟Euphorbia esula、兴安胡枝子Lespedeza davurica、短花针茅Stipa breviflora、锋芒草T. racemosus、地锦P. tricuspidata、猪毛蒿A. scoparia、甘草Glycyrrhiza uralensis、香青兰D. moldavica、藜C. album、虎尾草Setaria viridis、条叶车前Plantago lessingii、丝叶山苦荬Ixeridium graminifolium、砂蓝刺头E. gmelini |
| 50 | 38°11′ | 106°41′ | 1326.34 | 0.71 | 雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、猪毛蒿A. scoparia、地锦P. tricuspidata、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草S. viridis、藜C. album、蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、香青兰D. moldavica、蒺藜Tribulus terrestris、白沙蒿A. sphaerocephala、中华小苦荬Ixeridium chinense |
| 60 | 38°10′ | 106°52′ | 1320.46 | 0.82 | 藜C. album、刺藜Teloxys aristata、香青兰D. moldavica、中华小苦荬I. chinense、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草S. viridis、阿尔泰狗娃花H. altaicus、沙生大戟Euphorbia kozlovii、乳苣Mulgedium tataricu、白沙蒿A. sphaerocephala、短花针茅S. breviflora、九顶草Enneapogon desvauxii |
| 70 | 38°08′ | 106°15′ | 1315.48 | 0.88 | 藜C. album、刺藜T. aristata、画眉草E. pilosa、砂蓝刺头E. gmelini、香青兰D. moldavica、地锦P. tricuspidata、青海天门冬Asparagus cochinchinensis、马齿苋Portulaca oleracea、赖草Leymus secalinus、草瑞香Diarthron linifolium、中华小苦荬I. chinense、鹅绒藤Cynanchum chinense、猪毛蒿A. scoparia |
表1 样地概况
Table 1 General situation of the sample plot
林龄 Forest age (yrs) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 经度 Longitude (E) | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 林下草本植物 Understory herbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 37°40′ | 106°46′ | 1213.88 | 0.16 | 蒙古虫实Corispermum mongolicum、沙蓬Agriophyllum squarrosum、雾冰藜Bassia dasyphylla |
| 5 | 38°03′ | 106°51′ | 1255.95 | 0.65 | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、猪毛蒿Artemisia scoparia、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、香青兰Dracocephalum moldavica |
| 10 | 38°02′ | 106°48′ | 1227.35 | 0.53 | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、画眉草Eragrostis pilosa |
| 20 | 37°55′ | 106°50′ | 1308.89 | 0.82 | 沙鞭Psammochloa villosa、地锦Parthenocissus tricuspidata、砂蓝刺头Echinops gmelini、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、白沙蒿Artemisia sphaerocephala、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草Setaria viridis、锋芒草Tragus racemosus、阿尔泰狗娃花Heteropappus altaicus |
| 30 | 38°02′ | 106°33′ | 1307.64 | 0.54 | 蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草S. viridis、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、地锦P. tricuspidata、藜Chenopodium album、砂蓝刺头E. gmelini、猪毛蒿A. scoparia、香青兰D. moldavica、地捎瓜Cynanchum thesioides、银柴胡Stellaria dichotoma var. lanceolata、草木樨状黄芪Astragalus melilotoides、阿尔泰狗娃花H. altaicus、叉枝鸦葱Scorzonera divaricata |
| 40 | 38°10′ | 106°39′ | 1324.16 | 0.51 | 阿尔泰狗娃花H. altaicus、狗尾草S. viridis、画眉草E. pilosa、乳浆大戟Euphorbia esula、兴安胡枝子Lespedeza davurica、短花针茅Stipa breviflora、锋芒草T. racemosus、地锦P. tricuspidata、猪毛蒿A. scoparia、甘草Glycyrrhiza uralensis、香青兰D. moldavica、藜C. album、虎尾草Setaria viridis、条叶车前Plantago lessingii、丝叶山苦荬Ixeridium graminifolium、砂蓝刺头E. gmelini |
| 50 | 38°11′ | 106°41′ | 1326.34 | 0.71 | 雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、猪毛蒿A. scoparia、地锦P. tricuspidata、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草S. viridis、藜C. album、蒙古虫实C. mongolicum、香青兰D. moldavica、蒺藜Tribulus terrestris、白沙蒿A. sphaerocephala、中华小苦荬Ixeridium chinense |
| 60 | 38°10′ | 106°52′ | 1320.46 | 0.82 | 藜C. album、刺藜Teloxys aristata、香青兰D. moldavica、中华小苦荬I. chinense、雾冰藜B. dasyphylla、画眉草E. pilosa、狗尾草S. viridis、阿尔泰狗娃花H. altaicus、沙生大戟Euphorbia kozlovii、乳苣Mulgedium tataricu、白沙蒿A. sphaerocephala、短花针茅S. breviflora、九顶草Enneapogon desvauxii |
| 70 | 38°08′ | 106°15′ | 1315.48 | 0.88 | 藜C. album、刺藜T. aristata、画眉草E. pilosa、砂蓝刺头E. gmelini、香青兰D. moldavica、地锦P. tricuspidata、青海天门冬Asparagus cochinchinensis、马齿苋Portulaca oleracea、赖草Leymus secalinus、草瑞香Diarthron linifolium、中华小苦荬I. chinense、鹅绒藤Cynanchum chinense、猪毛蒿A. scoparia |
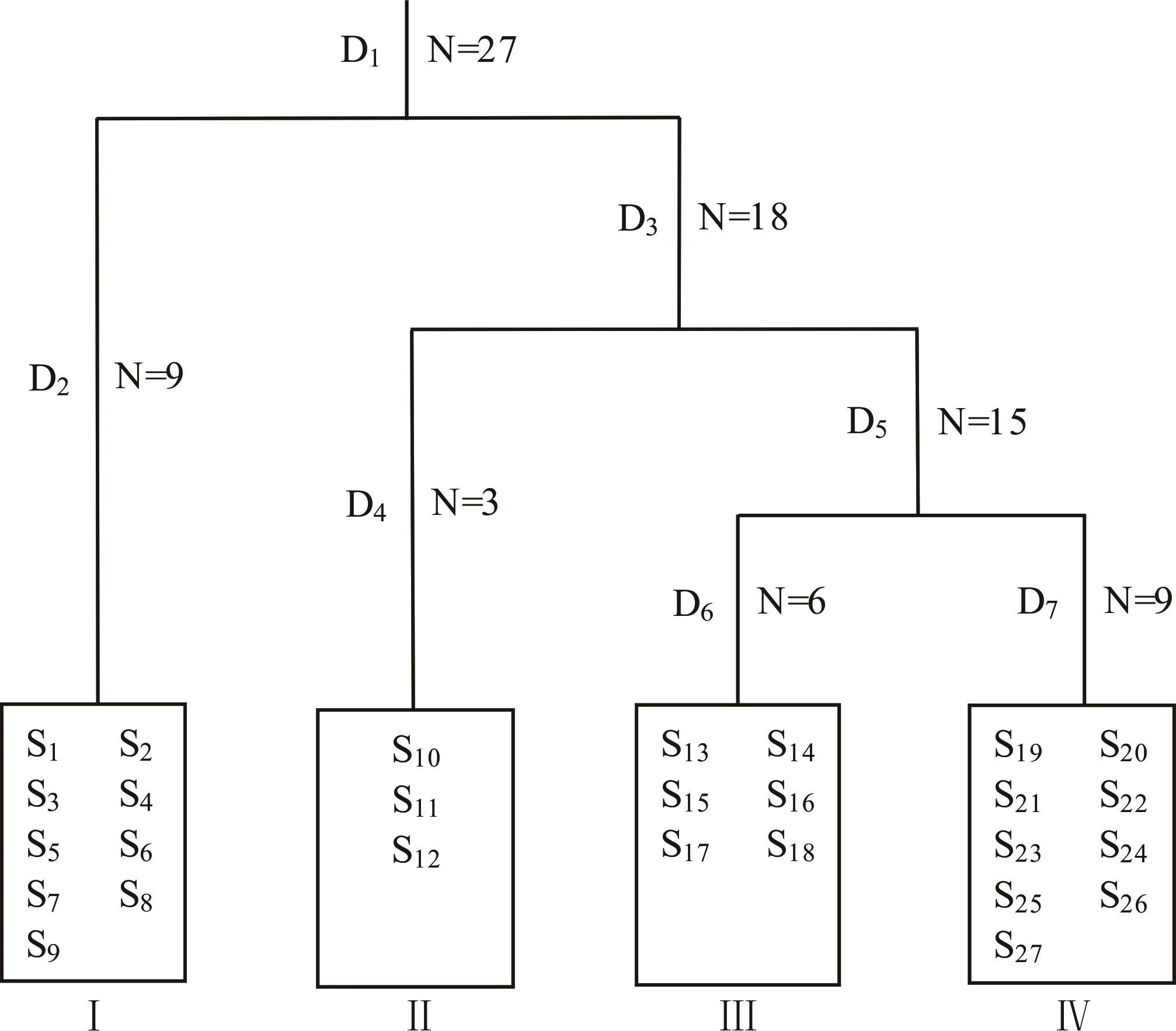
图2 不同种植年限柠条林下草本植物群落TWINSPAN分类结果树状示意图N: 处理数Treatment number; D: 分类等级Classification grade; S: 样方编号Quadrat number; 3年Years: S1, S2, S3; 5年Years: S4, S5, S6; 10年Years: S7, S8, S9; 20年Years: S10, S11, S12; 30年Years: S13, S14, S15; 40年Years: S16, S17, S18; 50年Years: S19, S20, S21; 60年Years: S22, S23, S24; 70年Years: S25, S26, S27.
Fig.2 TWINSPAN classification results tree schematic diagram of herb plant communities under C. korshinskii in different planting years
群丛 Association | 林龄 Forest age (yrs) | 盖度 Coverage (%) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (%) | pH | 土壤有机质 Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (mg·g-1) | 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 3 | 14.11±2.35b | 1.52±0.02ab | 5.53±0.63a | 8.08±0.03b | 2.74±0.45c | 0.06±0.01g | 0.11±0.01d |
| 5 | 11.56±2.94b | 1.51±0.05ab | 4.44±0.12abc | 8.13±0.06b | 2.22±0.38c | 0.06±0.01g | 0.12±0.01c | |
| 10 | 10.40±1.33b | 1.52±0.01ab | 3.19±0.42bcd | 8.06±0.05b | 2.87±0.32c | 0.11±0.01ef | 0.13±0.01b | |
| Ⅱ | 20 | 11.53±2.90b | 1.55±0.03a | 4.77±0.63ab | 8.18±0.04b | 3.36±0.31c | 0.11±0.01ef | 0.13±0.01b |
| Ⅲ | 30 | 34.05±3.12ab | 1.50±0.08ab | 5.87±1.18a | 8.52±0.02a | 7.45±0.63b | 0.13±0.01de | 0.13±0.01b |
| 40 | 36.62±6.06ab | 1.44±0.05b | 3.48±0.24bcd | 8.49±0.02a | 6.28±0.56b | 0.15±0.01d | 0.13±0.01b | |
| Ⅳ | 50 | 78.71±8.67a | 1.52±0.03ab | 3.11±0.18bcd | 8.46±0.02a | 6.45±0.30b | 0.18±0.01c | 0.13±0.01b |
| 60 | 60.56±5.24ab | 1.54±0.02a | 2.91±0.21cd | 8.37±0.08a | 6.71±1.84b | 0.21±0.02b | 0.14±0.01a | |
| 70 | 70.81±6.56a | 1.50±0.01ab | 2.45±0.86d | 8.40±0.06a | 10.98±1.39a | 0.27±0.01a | 0.14±0.01a |
表2 林下草本层群落分类主要特征描述
Table 2 Description of main characteristics of community classification of understory herb layer
群丛 Association | 林龄 Forest age (yrs) | 盖度 Coverage (%) | 土壤容重 Soil bulk density (g·cm-3) | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (%) | pH | 土壤有机质 Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 土壤全氮 Soil total nitrogen (mg·g-1) | 土壤全磷 Soil total phosphorus (mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 3 | 14.11±2.35b | 1.52±0.02ab | 5.53±0.63a | 8.08±0.03b | 2.74±0.45c | 0.06±0.01g | 0.11±0.01d |
| 5 | 11.56±2.94b | 1.51±0.05ab | 4.44±0.12abc | 8.13±0.06b | 2.22±0.38c | 0.06±0.01g | 0.12±0.01c | |
| 10 | 10.40±1.33b | 1.52±0.01ab | 3.19±0.42bcd | 8.06±0.05b | 2.87±0.32c | 0.11±0.01ef | 0.13±0.01b | |
| Ⅱ | 20 | 11.53±2.90b | 1.55±0.03a | 4.77±0.63ab | 8.18±0.04b | 3.36±0.31c | 0.11±0.01ef | 0.13±0.01b |
| Ⅲ | 30 | 34.05±3.12ab | 1.50±0.08ab | 5.87±1.18a | 8.52±0.02a | 7.45±0.63b | 0.13±0.01de | 0.13±0.01b |
| 40 | 36.62±6.06ab | 1.44±0.05b | 3.48±0.24bcd | 8.49±0.02a | 6.28±0.56b | 0.15±0.01d | 0.13±0.01b | |
| Ⅳ | 50 | 78.71±8.67a | 1.52±0.03ab | 3.11±0.18bcd | 8.46±0.02a | 6.45±0.30b | 0.18±0.01c | 0.13±0.01b |
| 60 | 60.56±5.24ab | 1.54±0.02a | 2.91±0.21cd | 8.37±0.08a | 6.71±1.84b | 0.21±0.02b | 0.14±0.01a | |
| 70 | 70.81±6.56a | 1.50±0.01ab | 2.45±0.86d | 8.40±0.06a | 10.98±1.39a | 0.27±0.01a | 0.14±0.01a |
群丛 Association | 林龄 Forest age (yrs) | 丰富度指数 Richness index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 3 | 3.44±0.11c | 0.67±0.01c | 1.16±0.05cd | 0.94±0.01a |
| 5 | 3.00±0.19cd | 0.51±0.02d | 0.87±0.09d | 0.81±0.02b | |
| 10 | 1.11±0.11d | 0.04±0.03e | 0.06±0.02e | 0.08±0.03c | |
| Ⅱ | 20 | 5.67±0.80b | 0.70±0.06bc | 1.44±0.11bc | 0.85±0.04ab |
| Ⅲ | 30 | 8.00±0.33a | 0.82±0.01a | 1.85±0.08a | 0.90±0.02ab |
| 40 | 7.00±1.45ab | 0.75±0.05abc | 1.65±0.12ab | 0.87±0.02ab | |
| Ⅳ | 50 | 7.56±0.48ab | 0.77±0.02abc | 1.76±0.06ab | 0.88±0.02ab |
| 60 | 7.00±0.96ab | 0.78±0.03ab | 1.70±0.10ab | 0.90±0.02ab | |
| 70 | 6.11±0.40ab | 0.76±0.01abc | 1.56±0.06ab | 0.87±0.01ab |
表3 柠条固沙林林下植物群落的物种多样性
Table 3 Species diversities of plant communities under the C. korshinskii forest
群丛 Association | 林龄 Forest age (yrs) | 丰富度指数 Richness index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Pielou指数 Pielou index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 3 | 3.44±0.11c | 0.67±0.01c | 1.16±0.05cd | 0.94±0.01a |
| 5 | 3.00±0.19cd | 0.51±0.02d | 0.87±0.09d | 0.81±0.02b | |
| 10 | 1.11±0.11d | 0.04±0.03e | 0.06±0.02e | 0.08±0.03c | |
| Ⅱ | 20 | 5.67±0.80b | 0.70±0.06bc | 1.44±0.11bc | 0.85±0.04ab |
| Ⅲ | 30 | 8.00±0.33a | 0.82±0.01a | 1.85±0.08a | 0.90±0.02ab |
| 40 | 7.00±1.45ab | 0.75±0.05abc | 1.65±0.12ab | 0.87±0.02ab | |
| Ⅳ | 50 | 7.56±0.48ab | 0.77±0.02abc | 1.76±0.06ab | 0.88±0.02ab |
| 60 | 7.00±0.96ab | 0.78±0.03ab | 1.70±0.10ab | 0.90±0.02ab | |
| 70 | 6.11±0.40ab | 0.76±0.01abc | 1.56±0.06ab | 0.87±0.01ab |
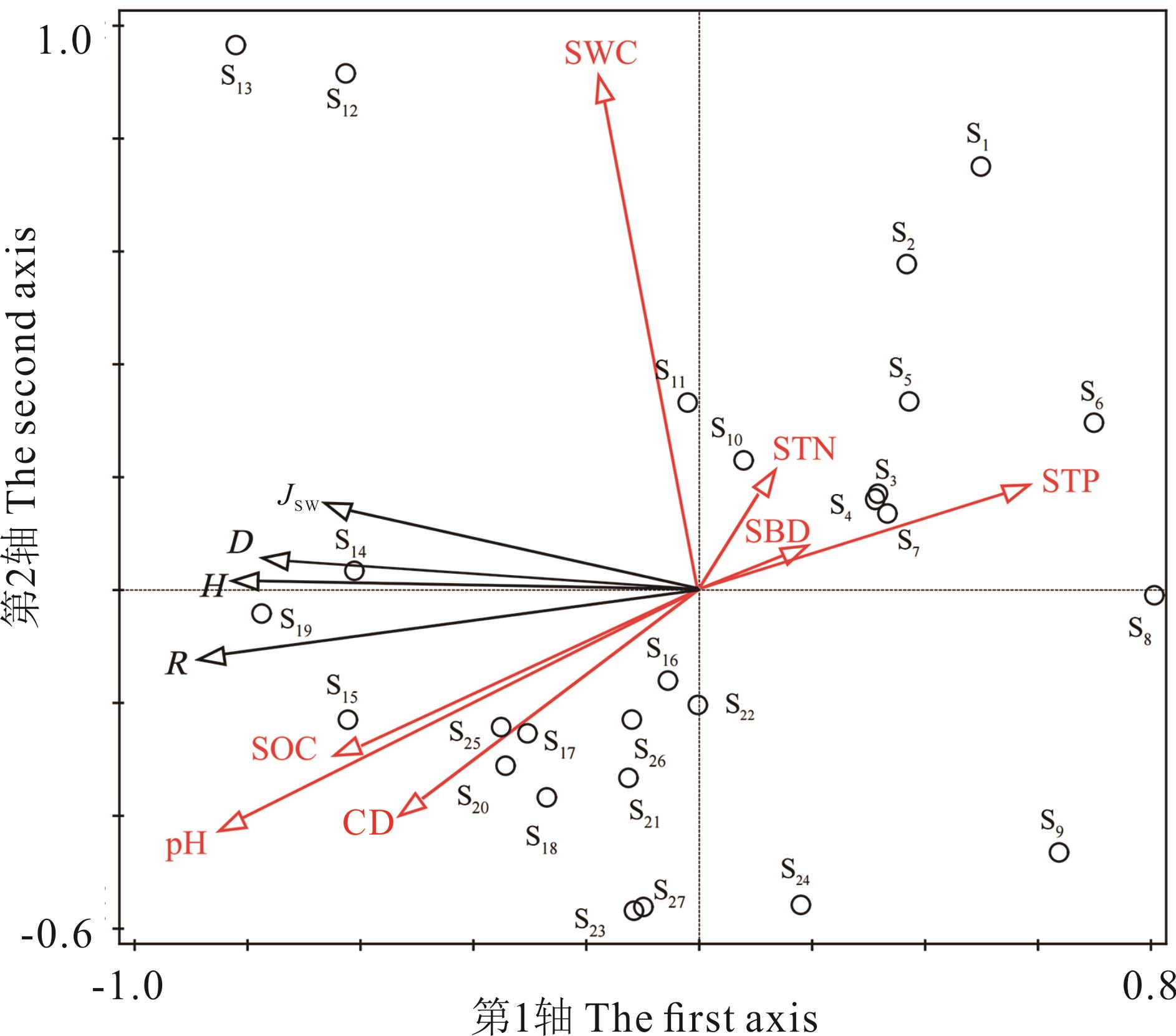
图4 林下草本层冗余分析(RDA)排序R: 草本植物物种丰富度指数Richness index of herbaceous plants; H: 草本植物Shannon-Wiener多样性指数Shannon-Wiener diversity index of herbaceous plants; D: 草本植物Simpson指数Simpson index of herbaceous plants; Jsw: 草本植物Pielou指数Pielou index of herbaceous plants; SOC: 土壤有机质Soil organic carbon; STN: 土壤全氮Soil total nitrogen; STP: 土壤全磷Soil total phosphorus; SBD: 土壤容重Soil bulk density; SWC: 土壤含水量Soil moisture content; pH: 土壤pH Soil pH; CD: 郁闭度Canopy density.
Fig.4 Redundancy analysis biplot of understory herb layer
环境因子 Environmental factors | 解释量 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 所有典范轴的显著性检验 Test of significance of all canonical axes | 0.044 | |||
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture | 5.5 | 10.7 | 2.1 | 0.158 |
| 土壤容重Soil bulk density | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.890 |
| pH | 13.6 | 26.5 | 4.9 | 0.032* |
| 有机质Soil organic carbon | 19.3 | 37.5 | 6.0 | 0.010* |
| 全氮Soil total nitrogen | 1.5 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 0.458 |
| 全磷Soil total phosphorus | 4.2 | 8.1 | 1.7 | 0.204 |
| 郁闭度Canopy density | 7.2 | 14.1 | 2.9 | 0.096 |
| 特征参数Characteristic parameter | RDA1 | RDA2 | RDA3 | RDA4 |
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 0.5038 | 0.0098 | 0.0008 | 0.0001 |
| 累计解释变异Explained variation | 50.38 | 51.37 | 51.41 | 51.41 |
| 多样性-环境因子相关系数 Diversity-environmental factor correlation coefficient | 0.980 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
表4 冗余分析(RDA)排序及蒙特卡洛置换检验结果
Table 4 Results by redundancy analysis (RDA) ordination with the first two axes and Monte Carlo permutation test
环境因子 Environmental factors | 解释量 Explains (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 所有典范轴的显著性检验 Test of significance of all canonical axes | 0.044 | |||
| 土壤含水量Soil moisture | 5.5 | 10.7 | 2.1 | 0.158 |
| 土壤容重Soil bulk density | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.890 |
| pH | 13.6 | 26.5 | 4.9 | 0.032* |
| 有机质Soil organic carbon | 19.3 | 37.5 | 6.0 | 0.010* |
| 全氮Soil total nitrogen | 1.5 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 0.458 |
| 全磷Soil total phosphorus | 4.2 | 8.1 | 1.7 | 0.204 |
| 郁闭度Canopy density | 7.2 | 14.1 | 2.9 | 0.096 |
| 特征参数Characteristic parameter | RDA1 | RDA2 | RDA3 | RDA4 |
| 特征值Eigenvalues | 0.5038 | 0.0098 | 0.0008 | 0.0001 |
| 累计解释变异Explained variation | 50.38 | 51.37 | 51.41 | 51.41 |
| 多样性-环境因子相关系数 Diversity-environmental factor correlation coefficient | 0.980 | 0.999 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 1 | Zhao L J, Xiao H L, Liu X H, et al. Seasonal variation characteristics of leaf carbon isotope discrimination δ13C and N concentration of C. korshinskii and A. ordosica. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2005, 26(Supple1): 213-219. |
| 赵良菊, 肖洪浪, 刘晓宏, 等. 沙坡头油蒿和柠条叶片δ13C和N含量的季节变化特征. 地球学报, 2005, 26(增刊1): 213-219. | |
| 2 | Li X F, Li J, Wang X C, et al. Simulation of water productivity and soil desication of Caragana microphylla shrub land on semi-arid hilly region of the loess plateau. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2007, 25(3): 113-119. |
| 李小芳, 李军, 王学春, 等. 半干旱黄土丘陵区柠条林水分生产力和土壤干燥化效应模拟研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 2007, 25(3): 113-119. | |
| 3 | Wang M B, Li H J, Chai B F. Water ecophysiological characterristics of Caragana korshinskii. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 1996, 20(6): 494-501. |
| 王孟本, 李洪建, 柴宝峰. 柠条(Caragana korshinskii)的水分生理生态学特性. 植物生态学报, 1996, 20(6): 494-501. | |
| 4 | Bao J T. Study on water use characteristics of main sand-fixing shrubs in Shapotou area. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. |
| 鲍婧婷. 沙坡头地区主要固沙灌木的水分利用特征研究. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015. | |
| 5 | An S S, Huang Y M. Study on the ameliorate benefits of Caragana korshinskii shrubwood to soil properties in loess hilly area. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2006, 42(1): 70-74. |
| 安韶山, 黄懿梅. 黄土丘陵区柠条林改良土壤作用的研究. 林业科学, 2006, 42(1): 70-74. | |
| 6 | Zhang F, Chen Y M, Wang Y F, et al. Effects of Caragana korshinskii plantation on soil physical properties and organic matter in semi-arid loess hilly region. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 17(3): 105-109. |
| 张飞, 陈云明, 王耀凤, 等. 黄土丘陵半干旱区柠条林对土壤物理性质及有机质的影响. 水土保持研究, 2010, 17(3): 105-109. | |
| 7 | Zhang L Z, Niu W, Niu Y, et al. Impact of Caragana Fabr. plantation on plant community and soil properities of saline-alkali wasteland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(9): 4693-4699. |
| 张丽珍, 牛伟, 牛宇, 等. 柠条对盐碱地植被组成及土壤特性的影响. 生态学报, 2009, 29(9): 4693-4699. | |
| 8 | Whigham D F. Ecology of woodland herbs in temperate deciduous forests. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2004, 35(1): 583-621. |
| 9 | Margaret B, Gargiullo. The herbaceous layer in forests of eastern north America. The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society, 2005, 132(1): 169-171. |
| 10 | Li G, Liang Y, Cao L X. Effects of different vegetation restoration patterns on soil erosion in secondary Pinus massoniana pure forest. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 10(6): 25-31. |
| 李钢, 梁音, 曹龙熹. 次生马尾松林下植被恢复措施的水土保持效益. 中国水土保持科学, 2012, 10(6): 25-31. | |
| 11 | Zhang Y, Zhou Q H, Xu J Y, et al. Effects of forest ages on the diversity of understory plants and soil seed bank of Pinus massoniana plantations. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| 张洋, 周清慧, 许骄阳, 等. 林龄对马尾松人工林林下植物与土壤种子库多样性的影响. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. | |
| 12 | Gou Q Q, Liu J, Wang G H, et al. Changes of herbaceous plant composition and niche characteristics in different-aged artificial Caragana korshinskii forest in sandy-hilly region of northwest Shanxi Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(22): 9069-9090. |
| 缑倩倩, 刘婧, 王国华, 等. 晋西北丘陵风沙区柠条林下草本植物群落组成和种群生态位变化特征. 生态学报, 2022, 42(22): 9069-9090. | |
| 13 | Cui J, Huang J J, Chen Y M, et al. Biodiversity of herbaceous species under Caragana microphylla plantations in loess hilly region. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2018, 33(3): 14-20. |
| 崔静, 黄佳健, 陈云明, 等. 黄土丘陵区人工柠条林下草本植物物种多样性研究. 西北林学院学报, 2018, 33(3): 14-20. | |
| 14 | Qin L. Statistical ecology. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 2009. |
| 覃林. 统计生态学. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2009. | |
| 15 | Hill M O. TWINSPAN: A FORTRAN program for arranging multivariate data in an ordered two-way table by classification of individual and attributes. New York: Cornell University Press, 1979. |
| 16 | Scudeller V V, Martins F R, Shepherd G J. Distribution and abundance of arboreal species in the Atlantic ombrophilous dense forest in southeaster Brazil. Plant Ecology, 2001, 152(2): 185-199. |
| 17 | Liu L, Bai Y, She W, et al. A nurse shrub species helps associated herbaceous plants by preventing shade-induced evaporation in a desert ecosystem. Land Degradation and Development, 2020, 32(4): 1796-1808. |
| 18 | Bachar A, Soares M I, Gillor O. The effect of resource islands on abundance and diversity of bacteria in arid soils. Microbial Ecology, 2012, 63(3): 694-700. |
| 19 | Cao Y, Li Y, Li C, et al. Relationship between presence of the desert shrub Haloxylon ammodendron and microbial communities in two soils with contrasting textures. Applied Soil Ecology, 2016, 103: 93-100. |
| 20 | Ma Q L, Zhang J C, Chen F, et al. Mechanism and dynamics for succession of artificial Hedysarum scoparium sand-binding forests at the southern edge of Tengger Desert. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 206-215. |
| 马全林, 张锦春, 陈芳, 等. 腾格里沙漠南缘花棒(Hedysarum scoparium)人工固沙林演替规律与机制. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 206-215. | |
| 21 | Li X R, Zhang Z S, Liu Y B, et al. Long-term ecological research guides ecological restoration and recovery in sandy areas of northern China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(7): 790-797. |
| 李新荣, 张志山, 刘玉冰, 等. 长期生态学研究引领中国沙区的生态重建与恢复. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(7): 790-797. | |
| 22 | Ou J, Didi M G, Zhang S L, et al. Diversity of understory shrubs and herbs in Pinus armandii plantation with different canopy densities. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2020, 41(6): 56-63. |
| 欧江, 地地木古, 张时林, 等. 不同郁闭度华山松人工林林下灌木和草本多样性. 四川林业科技, 2020, 41(6): 56-63. | |
| 23 | Su Y Z, Zhao H L. Soil properties and plant species in an age sequence of Caragana microphylla plantations in the Horqin Sandy Land, north China. Ecological Engineering, 2003, 20(3): 223-235. |
| 24 | Ma Z W, Xie Z L, Duan X F, et al. Plant-soil relationship and plant niche in the Yellow River Delta National Natural Reserve, China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2012, 48(5): 801-811. |
| 马宗文, 谢正磊, 段晓峰, 等. 黄河三角洲自然保护区植物与土壤因子关系及生态位分析. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(5): 801-811. | |
| 25 | Wu Y Q, Zhang J F, Du S S, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of soil moisture in dunes with different vegetation coverage in southern margin of the Mu US Sandy land. Journal of Desert Research, 2015, 35(6): 1612-1619. |
| 伍永秋, 张健枫, 杜世松, 等. 毛乌素沙地南缘不同活性沙丘土壤水分时空变化. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(6): 1612-1619. | |
| 26 | Fenu G, Carboni M, Acosta A T R, et al. Environmental factors influencing coastal vegetation pattern: new insights from the Mediterr-anean Basin. Folia Geobotanica, 2013, 48(1): 493-508. |
| 27 | Lange M, Eisenhauer N, Sierra C A, et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6707. |
| 28 | Jobbagy E G, Jacks R B. Paterns and mechanisms of soil acidification in the conversion of grasslands to forests. Biogeochemistry, 2003, 64(2): 205-229. |
| 29 | Farley K A, Kelly E F. Effects of afforestation of a Paramo grassland on soil nutrient status. Forest Ecology and Management, 2004, 195(3): 281-290. |
| 30 | Schuster B, Diekmann M. Changes in species density along the soil pH gradient-evidence from German plant communities. Folia Geobotanica, 2003, 38(4): 367-379. |
| 31 | Liu S. Relationship between the distribution of plant communities and soil factors in the northwest of Liaoning. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 刘莎. 辽西北草地群落分布与土壤因子的关系. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2017. | |
| 32 | Song C Y, Guo K. Relationship between plant community and soil on the inter-dune lowland in the middle of Otingdag sand land. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(1): 40-49. |
| 宋创业, 郭柯. 浑善达克沙地中部丘间低地植物群落分布与土壤环境关系. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(1): 40-49. | |
| 33 | Tripathi B M, Stegen J C, Kim M, et al. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME Journal, 2018, 12(4): 1072-1083. |
| 34 | Feng Y Z, Chen R R, Stegen J C, et al. Two key features influencing community assembly processes at regional scale: Initial state and degree of change in environmental conditions. Molecular Ecology, 2018, 27(24): 5238-5251. |
| [1] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [2] | 苏金娟, 刘永萍, 刘丽燕, 吴天忠, 王梅. 新疆阿勒泰地区典型植物群落数量分类与排序分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 50-67. |
| [3] | 吕自立, 刘彬, 常凤, 马紫荆, 曹秋梅. 巴音布鲁克高寒草甸物种多样性与系统发育多样性沿海拔梯度分布格局及驱动因子[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 12-22. |
| [4] | 郭文章, 井长青, 邓小进, 陈宸, 赵苇康, 侯志雄, 王公鑫. 新疆天山北坡荒漠草原碳通量特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 1-12. |
| [5] | 金玲, 陆颖, 马红彬, 谢应忠, 沈艳. 内蒙古鄂托克前旗荒漠草原植物群落的数量分类与排序[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 12-21. |
| [6] | 杨鑫, 曹文侠, 鱼小军, 汪海斌, 郝媛媛. 基于近20年MODIS NDVI日数据的青海省草地资源动态监测及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 1-14. |
| [7] | 张敏, NIPAPAN Kanjana, 李铷, 傅杨, 汤东生. 环境因子对云南扁穗雀麦种子萌发和出苗的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 143-151. |
| [8] | 孙思思, 吴战平, 肖启涛, 于飞, 古书鸿, 方荻, 李浪, 赵兴炳. 云贵高原草地生态系统CO2通量变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 184-191. |
| [9] | 王磊, 宋乃平, 陈林, 杨新国, 王兴. 荒漠草原土壤粗质化和养分减少伴随多年生群落转变为一年生群落[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 183-189. |
| [10] | 陈乙实, 孙海荣, 李娜娜, 靳省飞, 车昭碧, 曹佳敏, 鲁为华. 绵羊放牧绢蒿荒漠草地植物群落多样性及其环境解释[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 1-11. |
| [11] | 孙丽坤, 刘光琇, 张宝贵, 章高森. 环境因子对中国柽柳遗传变异的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 178-186. |
| [12] | 聂明鹤, 沈艳, 饶丽仙. 宁夏典型草原区退耕草地群落演替序列与环境解释[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 11-20. |
| [13] | 佘淑凤,胡玉福,舒向阳,严星,李智,王琴,何佳,贾安都. 川西北高寒沙地不同年限高山柳林下优势植物碳、氮、磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 123-130. |
| [14] | 陆姣云,段兵红,杨梅,杨晗,杨惠敏. 植物叶片氮磷养分重吸收规律及其调控机制研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 178-188. |
| [15] | 范顺祥, 郑建伟, 魏士凯, 黄选瑞, 张志东. 河北省森林草原区主要草本植物功能群适宜分布预测[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 24-32. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||