

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 80-91.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023229
尹仲毅1( ), 马黎华1,2(
), 马黎华1,2( ), 李兆磊1,2, 冯桦1,2, 蒋先军1(
), 李兆磊1,2, 冯桦1,2, 蒋先军1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-04
修回日期:2023-08-11
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
马黎华,蒋先军
作者简介:jiangxj@swu.edu.cn基金资助:
Zhong-yi YIN1( ), Li-hua MA1,2(
), Li-hua MA1,2( ), Zhao-lei LI1,2, Hua FENG1,2, Xian-jun JIANG1(
), Zhao-lei LI1,2, Hua FENG1,2, Xian-jun JIANG1( )
)
Received:2023-07-04
Revised:2023-08-11
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Li-hua MA,Xian-jun JIANG
摘要:
近年来,西南地区高温天气频发,高温带来稻田土壤温度的升高,进而带来稻田生境的改变。为了探究高温条件对紫色水稻土壤水、热、盐的影响,以及不同耕作模式下稻田对高温的应对策略,选取垄作(RT)、水旱平作(CT)、冬水田(FPF)3种耕作模式,针对不同耕作模式下0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~40 cm、40~60 cm,4个土层的土壤温度、土壤含水率和土壤电导率进行了连续两年(2021-2022年)的原位监测。结果表明:在常温条件下,3种耕作模式0~40 cm土层的土壤温度无显著差异(P>0.05),土壤含水率与土壤电导率存在显著差异;在高温条件下,3种耕作模式土壤温度与土壤含水率在4个土层中均差异显著(P<0.05),土壤温度与土壤含水率均为RT>FPF>CT,土壤电导率为CT>FPF>RT。常温与高温条件下,3种耕作模式的土壤温度与电导率均呈显著正相关关系。高温会导致土壤温度,土壤电导率和土壤含水率耦合关系的改变。高温条件下,垄作稻田的土壤含水率最高,土壤电导率最低,体现了对高温条件更好的适应性。
尹仲毅, 马黎华, 李兆磊, 冯桦, 蒋先军. 高温条件对不同耕作模式紫色水稻土水、热、盐的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 80-91.
Zhong-yi YIN, Li-hua MA, Zhao-lei LI, Hua FENG, Xian-jun JIANG. Impact of high temperature on soil water, heat and salt in purple paddy fields under different tillage patterns[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 80-91.
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 全钾 Total K (g·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 容重 Density (g?cm-3) | 孔隙度 Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPF | 34.1 | 2.23 | 128 | 1.46 | 15.3 | 20.1 | 104.3 | 1.22 | 50.2 |
| RT | 32.1 | 2.27 | 196 | 1.79 | 30.3 | 22.7 | 82.0 | 1.25 | 49.8 |
| CT | 24.1 | 1.66 | 139 | 1.07 | 26.3 | 19.3 | 92.3 | 1.32 | 47.6 |
表1 3种耕作模式的土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Selected soil properties under different tillage systems
处理 Treatment | 有机质 Organic matter (g·kg-1) | 全氮 Total N (g·kg-1) | 碱解氮 Available N (mg·kg-1) | 全磷 Total P (g·kg-1) | 速效磷 Available P (mg·kg-1) | 全钾 Total K (g·kg-1) | 速效钾 Available K (mg·kg-1) | 容重 Density (g?cm-3) | 孔隙度 Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPF | 34.1 | 2.23 | 128 | 1.46 | 15.3 | 20.1 | 104.3 | 1.22 | 50.2 |
| RT | 32.1 | 2.27 | 196 | 1.79 | 30.3 | 22.7 | 82.0 | 1.25 | 49.8 |
| CT | 24.1 | 1.66 | 139 | 1.07 | 26.3 | 19.3 | 92.3 | 1.32 | 47.6 |
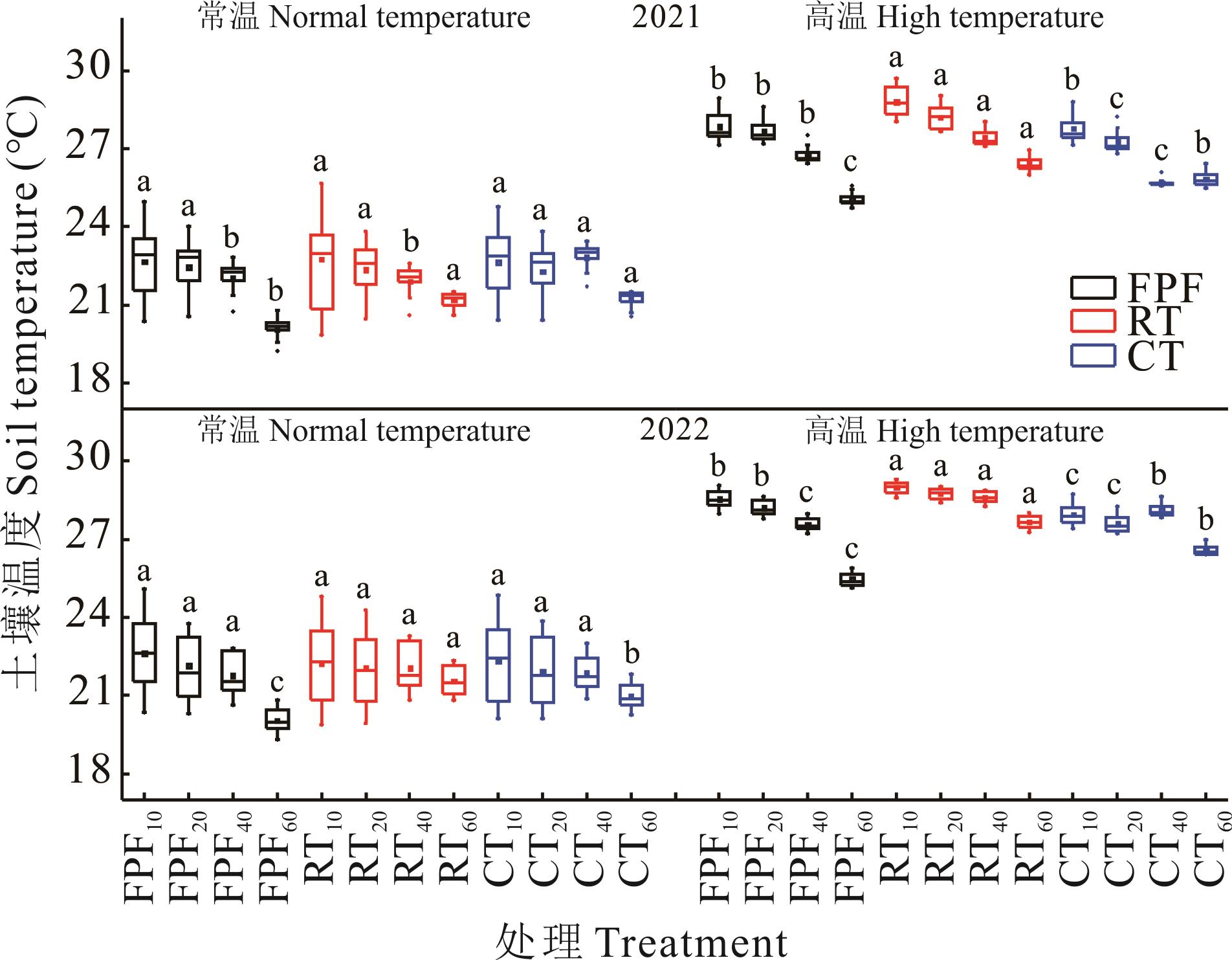
图3 3种耕作模式在不同温度下各土层的土壤温度变化FPF: 冬水田Flooded paddy field; RT: 垄作Ridge tillage; CT: 水旱平作Conventional paddy-upland rotation tillage. 下标数字10、20、40和60分别代表0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~40 cm和40~60 cm土层。The subscripts 10, 20, 40 and 60 represent 0-10 cm, 10-20 cm, 20-40 cm and 40-60 cm soil layers, respectively. 不同小写字母代表同一土层不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Values with different lowercase letters represent significant differences among different tillage treatments of the same soil layer (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.3 Changes in soil temperature under different air temperature with tillage treatments and soil depths
大气温度 Air temperature | 对比项目 Comparison items | 相关系数Correlation coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT | CT | FPF | ||
常温 Normal temperature | 温度与含水率Temperature and water content | -0.905** | -0.753** | -0.561** |
| 温度与电导率Temperature and conductivity | 0.954** | 0.919** | 0.845** | |
高温 High temperature | 温度与含水率Temperature and water content | 0.249** | 0.079 | -0.023 |
| 温度与电导率Temperature and conductivity | 0.616** | 0.717** | 0.499** | |
表2 3种耕作模式在常温与高温下土壤温度与土壤含水率和土壤电导率的相关性
Table 2 Correlation of soil temperature, soil water content and soil conductivity under different air temperature with tillage treatments
大气温度 Air temperature | 对比项目 Comparison items | 相关系数Correlation coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT | CT | FPF | ||
常温 Normal temperature | 温度与含水率Temperature and water content | -0.905** | -0.753** | -0.561** |
| 温度与电导率Temperature and conductivity | 0.954** | 0.919** | 0.845** | |
高温 High temperature | 温度与含水率Temperature and water content | 0.249** | 0.079 | -0.023 |
| 温度与电导率Temperature and conductivity | 0.616** | 0.717** | 0.499** | |

图6 3种耕作模式在常温与高温下土壤温度与土壤含水率和土壤电导率的相关性分析
Fig.6 Correlation analysis of soil temperature, soil water content and soil conductivity under normal and high temperature with tillage treatments

图7 3种耕作模式在常温与高温下大气温度与土壤温度的相关性分析
Fig.7 Correlation analysis of air temperature and soil temperature under normal and high temperature with tillage treatments
| 1 | Wang Z L, Liu C X, Jiang Q X, et al. Effects of climate warming on the key process and index of black soil carbon and nitrogen cycle during freezing period. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(4): 1967-1978. |
| 王子龙, 刘传兴, 姜秋香, 等. 气候变暖对冻结期黑土碳氮循环关键过程及指标的影响. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 1967-1978. | |
| 2 | Shu Z K, Li W X, Zhang J Y, et al. Historical changes and future trends of extreme precipitation and high temperature in China. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(5): 116-125. |
| 舒章康, 李文鑫, 张建云, 等. 中国极端降水和高温历史变化及未来趋势. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(5): 116-125. | |
| 3 | Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis//Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. USA: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1535. |
| 4 | Sun Z X, Zhang Q, Sun R, et al. Characteristics of the extreme high temperature and drought and their main impacts in southwestern China of 2022. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2022, 40(5): 764-770. |
| 孙昭萱, 张强, 孙蕊, 等. 2022年西南地区极端高温干旱特征及其主要影响. 干旱气象, 2022, 40(5): 764-770. | |
| 5 | Zhang H L, Liu S C, Su X Y, et al. Effects of exogenous SA and DPI on the stomatal closure of wheat leaves under heat and high light stress during grain filling stage. Crops, 2014(3): 67-71. |
| 张欢玲, 刘淑春, 苏小雨, 等. 外源SA和DPI对灌浆期高温强光下小麦叶片气孔开闭的影响. 作物杂志, 2014(3): 67-71. | |
| 6 | Zhu Y, Huang L, Dang C H, et al. Effects of high temperature on leaf stomatal traits and gas exchange parameters of blueberry. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(1): 218-225. |
| 朱玉, 黄磊, 党承华, 等. 高温对蓝莓叶片气孔特征和气体交换参数的影响. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(1): 218-225. | |
| 7 | Zhen B, Zhou X G, Lu H F, et al. Effect of interaction of high temperature at jointing stage and waterlogging on growth and development of rice. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(21): 105-111. |
| 甄博, 周新国, 陆红飞, 等. 拔节期高温与涝交互胁迫对水稻生长发育的影响. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(21): 105-111. | |
| 8 | Wang P, Zhang Z, Song X, et al. Temperature variations and rice yields in China: historical contributions and future trends. Climatic Change, 2014, 124(4): 777-789. |
| 9 | Zhang Z, Chen Y, Wang C Z, et al. Future extreme temperature and its impact on rice yield in China. International Journal of Climatology, 2017, 37(14): 4814-4827. |
| 10 | Feng B P, Zhang Z Y, Zhang J F, et al. Review of effect of temperature on soil water movement. Advances in Water Science, 2002(5): 643-648. |
| 冯宝平, 张展羽, 张建丰, 等. 温度对土壤水分运动影响的研究进展. 水科学进展, 2002(5): 643-648. | |
| 11 | Tian Y, Shi C P, Malo C U, et al. Long-term soil warming decreases microbial phosphorus utilization by increasing abiotic phosphorus sorption and phosphorus losses. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 864-874. |
| 12 | Liu Y Z. Advances in impacts of climate change on rice in China. Advances in Resources Research, 2022, 2(2): 67-76. |
| 13 | Hou R J, Li T X, Fu Q, et al. Research on the distribution of soil water, heat, salt and their response mechanisms under freezing conditions. Soil and Tillage Research, 2020, 196: 104486. |
| 14 | Wang R S, Kang Y H, Wan S Q, et al. Salt distribution and the growth of cotton under different drip irrigation regimes in a saline area. Agricultural Water Management, 2011, 100(1): 58-69. |
| 15 | Qi Z J, Feng H, Zhang T B, et al. Effects of mulch and tillage methods on soil water and temperature as well as corn yield in Hetao irrigation district. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(20): 108-113. |
| 齐智娟, 冯浩, 张体彬, 等. 覆膜耕作方式对河套灌区土壤水热效应及玉米产量的影响. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(20): 108-113. | |
| 16 | Peng Z Y, Huang J S, Wu J W, et al. Salt movement of seasonal freezing-thawing soil under autumn irrigation condition. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(6): 77-81. |
| 彭振阳, 黄介生, 伍靖伟, 等. 秋浇条件下季节性冻融土壤盐分运动规律. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(6): 77-81. | |
| 17 | Sun K, Wang C X, Wu C T, et al. Effects of autumn tillage on water, heat and salt transport in seasonal frozen thawed soil. Water Saving Irrigation, 2021(7): 46-50, 59. |
| 孙开, 王春霞, 吴晨涛, 等. 秋耕对季节性冻融土壤水热盐运移规律的影响. 节水灌溉, 2021(7): 46-50, 59. | |
| 18 | Li X W, Jin M G, Zhou N Q, et al. Inter-dripper variation of soil water and salt in a mulched drip irrigated cotton field: Advantages of 3-D modeling. Soil and Tillage Research, 2018, 184: 186-194. |
| 19 | Wang Y L, Mao X M, Chen S, et al. Experiments and simulation of soil moisture, temperature and salinity dynamics and oil sunflower growth in saline border irrigated farmland. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(8): 76-86. |
| 王雅丽, 毛晓敏, 陈帅, 等. 咸水畦灌农田土壤水热盐动态及油葵生长的试验与模拟. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(8): 76-86. | |
| 20 | Ren Z H, Yu J, Shi J G. Effects of PAM no-till planting on soil moisture, soil temperature, soil salinity and the growth of sunflower seedlings. Water Saving Irrigation, 2014(8): 7-11. |
| 任志宏, 于健, 史吉刚. 施用PAM免耕种植对土壤水热盐及向日葵幼苗生长的影响. 节水灌溉, 2014(8): 7-11. | |
| 21 | Guo H J, Fu Z Q, Li C, et al. Research progress on the application of ridge rice field in ecological cultivation. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(7): 2416-2425. |
| 郭慧娟, 傅志强, 李超, 等. 垄作稻田在生态种养中的应用研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(7): 2416-2425. | |
| 22 | Liu S Z, Gao W D, Ren T S. Evaluating the stability of black soil water content in northeast China under no tillage and ridge tillage using least limiting water range. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(10): 107-115. |
| 刘淑珍, 高伟达, 任图生. 利用最小水分限制范围评价东北黑土区免耕和垄作的土壤水分稳定性. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(10): 107-115. | |
| 23 | Fu Y L, Wang S S, Li Y B. Effects of straw mulching and water control on growth and yield of summer maize under ridge and furrow irrigation. Water Saving Irrigation, 2021(11): 74-82. |
| 傅渝亮, 汪顺生, 李彦彬. 秸秆覆盖和水分控制条件对垄作沟灌夏玉米生长和产量的影响. 节水灌溉, 2021(11): 74-82. | |
| 24 | Lu Y, Wang L, Han X L, et al. Water-salt transporting law of alkali-saline soil of greenhouse under ridging, plastic mulching and drip irrigation. Water Saving Irrigation, 2018(10): 27-32. |
| 陆阳, 王乐, 韩小龙, 等. 垄作覆膜滴灌条件下温室盐碱土壤水盐运移规律研究. 节水灌溉, 2018(10): 27-32. | |
| 25 | Jin W, Wang H, Chen Y W, et al. Movement of soil water and salt of drip irrigation under different ridge cultivation methods with root domain restrictions. Northern Horticulture, 2021(9): 93-103. |
| 靳韦, 王昊, 陈永伟, 等. 不同垄作根域限制栽培方式对滴灌土壤水盐运移的影响. 北方园艺, 2021(9): 93-103. | |
| 26 | Jiang X J, Xie D T. Combining ridge with no-tillage in lowland rice-based cropping system: long-term effect on soil and rice yield. Pedosphere, 2009, 19(4): 515-522. |
| 27 | Yao B L, Li G Y, Wang F. Effects of winter irrigation and soil surface mulching during freezing-thawing period on soil water-heat-salt for cotton fields in south Xinjiang. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(7): 114-120. |
| 姚宝林, 李光永, 王峰. 冻融期灌水和覆盖对南疆棉田水热盐的影响. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(7): 114-120. | |
| 28 | Sun G F, Qu Z Y, Du B, et al. Water-heat-salt effects of mulched drip irrigation maize with different irrigation scheduling in Hetao irrigation district. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(12): 144-152. |
| 孙贯芳, 屈忠义, 杜斌, 等. 不同灌溉制度下河套灌区玉米膜下滴灌水热盐运移规律. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(12): 144-152. | |
| 29 | Lu X H, Shi H B, Li R P, et al. Effect of autumn irrigation after mulching on water-heat-salt and yield of following spring maize. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 148-154. |
| 卢星航, 史海滨, 李瑞平, 等. 覆盖后秋浇对翌年春玉米生育期水热盐及产量的影响. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 148-154. | |
| 30 | Liu Z Q, Li B R. The influence of high temperature weather in Chongqing on rice seed setting and its counter measures. South China Agriculture, 2014, 8(31): 20-21. |
| 刘宗钱, 李白荣. 重庆市高温天气对水稻结实的影响及对策探讨. 南方农业, 2014, 8(31): 20-21. | |
| 31 | Tang Y H, Gao Y H. The research of Chongqing’s high temperature classification index and its regularity. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University, 2003, 25(1): 88-91. |
| 唐云辉, 高阳华. 重庆市高温分类与指标及其发生规律研究. 西南农业大学学报, 2003, 25(1): 88-91. | |
| 32 | Liang W J, Zhang X P, Sun S X, et al. Conservation tillage positively influences the microflora and microfauna in the black soil of Northeast China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2015, 149(6): 46-52. |
| 33 | Chivenge P P, Murwira H K, Giller K E, et al. Long-term impact of reduced tillage and residue management on soil carbon stabilization: Implications for conservation agriculture on contrasting soils. Soil and Tillage Research, 2007, 94(2): 328-337. |
| 34 | Chang S Y, Li R Y, Xie X J, et al. Effects of warming at different growth stages on rice yield and nitrogen and phosphorus contents. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(3): 754-763. |
| 常少燕, 李仁英, 谢晓金, 等. 不同生育期增温对水稻产量及氮、磷含量的影响. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(3): 754-763. | |
| 35 | Tan X Z, Shao D G, Liu H H. Simulating soil water regime in lowland paddy fields under different water managements using HYDRUS-1D. Agricultural Water Management, 2014, 132: 69-78. |
| 36 | Wu Y, Jia Z K, Ren X L, et al. Effects of ridge and furrow rainwater harvesting system combined with irrigation on improving water use efficiency of maize (Zea mays L.) in semi-humid area of China. Agricultural Water Management, 2015, 158: 1-9. |
| 37 | Sun J, Liu M, Li L J, et al. Effects of different tillage systems on soil hydrothermal regimes in rain-fed field of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(6): 1539-1547. |
| 孙建, 刘苗, 李立军, 等. 不同耕作方式对内蒙古旱作农田土壤水热状况的影响. 生态学报, 2010, 30(6): 1539-1547. | |
| 38 | Gu X B, Li Y N, Du Y D. Effects of ridge-furrow film mulching and nitrogen fertilization on growth, seed yield and water productivity of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in northwestern China. Agricultural Water Management, 2018, 200: 60-70. |
| 39 | Lin D, Wang F, Xu Z Q, et al. Appropriate winter and spring irrigations for salt leaching in typical cotton field of southern Xinjiang based on SHAW model. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2023, 54(1): 326-338. |
| 林栋, 王峰, 许尊秋, 等. 基于SHAW模型的南疆典型棉田适宜冬春灌盐分淋洗策略. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(1): 326-338. | |
| 40 | Liu H D, Liu J, Zhao Y, et al. Effects of Haloxylon ammodendron and Calligonum mongolicum on water-heat-salt dynamics in sandy soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(3): 169-175, 181. |
| 刘海东, 刘娇, 赵英, 等. 梭梭和沙拐枣对风沙土壤水热盐动态的影响. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(3): 169-175, 181. | |
| 41 | Ma L H, Wan Q H, Wang Z C, et al. Comparative study on yield and organ multi-factor responses of rice under different tillage modes. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(11): 119-128. |
| 马黎华, 万琪慧, 王振昌, 等. 不同耕作模式下水稻产量与器官多要素响应的比较研究. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(11): 119-128. | |
| 42 | Wan Q H, Ma L H, Jiang X J. Root characteristics and accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in rice plants cultivated under three different systems. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 44-52. |
| 万琪慧, 马黎华, 蒋先军. 垄作免耕对水稻根系特性和氮磷钾养分累积的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 44-52. |
| [1] | 卫宏健, 贺文员, 王越, 唐明, 陈辉. 丛枝菌根真菌与褪黑素对多年生黑麦草耐热性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(12): 126-138. |
| [2] | 甘凤玲, 韦杰, 李沙沙. 紫色土埂坎典型草本根系摩阻特性对土壤含水率的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 28-37. |
| [3] | 米永伟, 龚成文, 邵武平, 彭云霞. 覆膜对高寒阴湿区土壤水热与当归根系生长的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 66-75. |
| [4] | 吴路遥, 张建国, 常闻谦, 张少磊, 常青. 三种荒漠植物叶绿素荧光参数日变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 203-213. |
| [5] | 张茹, 李建平, 彭文栋, 王芳, 李志刚. 柠条枝条覆盖对宁夏荒漠草原土壤水热及补播牧草生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 58-67. |
| [6] | 汪智宇, 李莹, 刘金平, 伍德, 苟蓉. 高温冲击对受丝茅入侵的细叶结缕草现实和潜在竞争力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 106-118. |
| [7] | 王日明, 王志强, 向佐湘. γ-氨基丁酸对高温胁迫下黑麦草光合特性及碳水化合物代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(2): 168-178. |
| [8] | 周旭姣, 王琦, 张登奎, 尹鑫卫, 李晓玲, 刘青林, 贾生海. 垄沟集雨种植对土壤水热效应及紫花苜蓿产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 60-74. |
| [9] | 李小冬, 尚以顺, 武语迪, 王学敏, 熊先勤, 陈光吉, 孙方, 张文, 蔡一鸣. 紫花苜蓿MsMBF1c基因在拟南芥中表达提高转基因植株的耐热性[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 187-198. |
| [10] | 李小冬, 莫本田, 牟琼, 娄芬, 陈文贵, 陈光吉, 张瑜, 韩永芬. 紫花苜蓿高温诱导启动子pMsMBF 1c 的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 128-137. |
| [11] | 安婵, 乔建霞, 商建英, 李金升, 赵天赐, 唐士明, 邵新庆, 黄顶, 王堃, 刘克思. 人造湖对毗邻退化草地土壤含水量、电导率和pH的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8): 21-29. |
| [12] | 于景金, 范宁丽, 李冉, 杨志民. 高浓度CO2对热胁迫条件下高羊茅生长和抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 113-122. |
| [13] | 周泉, 邢毅, 马淑敏, 张小短, 陈娇, 石超, 王龙昌. 西南旱地不同种植模式下土壤呼吸及水热因子对极端低温的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 37-44. |
| [14] | 李娟, 雷霞, 钟理, 王小利, 杨春燕, 吴佳海. 高温胁迫对高羊茅航天诱变新品系生理特性研究及综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(3): 121-131. |
| [15] | 漆永红, 岳德成, 曹素芳, 李敏权. 全膜双垄沟播玉米土壤含水率和温度及杂草去除效应[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(11): 176-184. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||