

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 128-142.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023236
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-07-12
修回日期:2023-09-21
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-02-03
通讯作者:
孙颖
作者简介:E-mail: littlesuning@nefu.edu.cn基金资助:
Qiang LI( ), Fan KANG, Qing XUE, Bin CHEN, Ying SUN(
), Fan KANG, Qing XUE, Bin CHEN, Ying SUN( )
)
Received:2023-07-12
Revised:2023-09-21
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-02-03
Contact:
Ying SUN
摘要:
为探究CiMYB4在镉胁迫下的功能,以课题组已获得的过表达CiMYB4烟草(CiMYB4-S)、野菊(CiMYB4-OE)和抑制表达野菊(CiMYB4-Ri)为材料,在镉胁迫条件下分别测定其生长相关指标、抗氧化酶活性、光合指标、地上部及根系的镉含量,并对耐镉相关基因PCS1、GSH1、ABCC1、HMA3的表达模式进行分析。研究结果表明:镉处理后,CiMYB4-S和CiMYB4-OE株系的根长、茎粗、株高和叶长、叶宽显著大于野生型对照(WT)株系,丙二醛(MDA)含量显著降低,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性显著增强,叶片的光合能力和叶绿素含量显著增加,具有更强的镉富集和转运能力。同时,耐镉相关基因PCS1、GSH1、HMA3的表达水平显著提高;而CiMYB4-Ri株系的株高、地上部干重显著小于WT株系,MDA含量显著增加,SOD、POD、CAT活性显著降低,叶片的光合能力和叶绿素含量显著降低,镉富集和转运能力减弱。同时,耐镉相关基因PCS1、GSH1、HMA3的表达水平显著降低。上述结果表明CiMYB4能提高烟草和野菊对镉的耐受性。
李强, 康璠, 薛晴, 陈斌, 孙颖. 神农香菊R2R3-MYB转录因子CiMYB4在镉胁迫中的功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 128-142.
Qiang LI, Fan KANG, Qing XUE, Bin CHEN, Ying SUN. Functional analysis of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor CiMYB4 of Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum in response to cadmium stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(5): 128-142.
| 引物名称Primer name | 正向引物序列Forward primer sequence (5′→3′) | 反向引物序列Reverse primer sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| NtPCS1 | TGGTCTTGAATGCCCTTGC | GAGGCTCACAACAGTCCAACA |
| NtGSH1 | TGGGTTTGAGCAGTATGTGG | GCTGGTTGGCACCTTATTC |
| NtABCC1 | GCTTGATGCTGGACAGGTTG | TAAATACTGGGCATTTGCGGC |
| NtHMA3 | AGGGCAAGTCACAAGGCTAC | CAGCCCAGACCGTTGAATCT |
| HSC70-1 | AGGTGGAGACATGGGTGGTG | TCATTAGGCACACAGATCTCTG |
| CiPCS1 | TTTGGGAAGGTTGTGTGCCT | CCCTGCCAGCATGATAACCA |
| CiGSH1 | CCAGCCAAAATGGGAACGGA | GCAAACAGTGCCGTAGCAAT |
| CiABCC1 | TCGTCTAAGTGGCTATGCGG | AAGGCCACAAACCTCCCAAA |
| CiHMA3 | TCGTCTAAGTGGCTATGCGG | AAGGCCACAAACCTCCCAAA |
| EF1a | TTTTGGTATCTGGTCCTGGAG | CCATTCAAGCGACAGACTCA |
表1 引物
Table 1 The primers
| 引物名称Primer name | 正向引物序列Forward primer sequence (5′→3′) | 反向引物序列Reverse primer sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| NtPCS1 | TGGTCTTGAATGCCCTTGC | GAGGCTCACAACAGTCCAACA |
| NtGSH1 | TGGGTTTGAGCAGTATGTGG | GCTGGTTGGCACCTTATTC |
| NtABCC1 | GCTTGATGCTGGACAGGTTG | TAAATACTGGGCATTTGCGGC |
| NtHMA3 | AGGGCAAGTCACAAGGCTAC | CAGCCCAGACCGTTGAATCT |
| HSC70-1 | AGGTGGAGACATGGGTGGTG | TCATTAGGCACACAGATCTCTG |
| CiPCS1 | TTTGGGAAGGTTGTGTGCCT | CCCTGCCAGCATGATAACCA |
| CiGSH1 | CCAGCCAAAATGGGAACGGA | GCAAACAGTGCCGTAGCAAT |
| CiABCC1 | TCGTCTAAGTGGCTATGCGG | AAGGCCACAAACCTCCCAAA |
| CiHMA3 | TCGTCTAAGTGGCTATGCGG | AAGGCCACAAACCTCCCAAA |
| EF1a | TTTTGGTATCTGGTCCTGGAG | CCATTCAAGCGACAGACTCA |
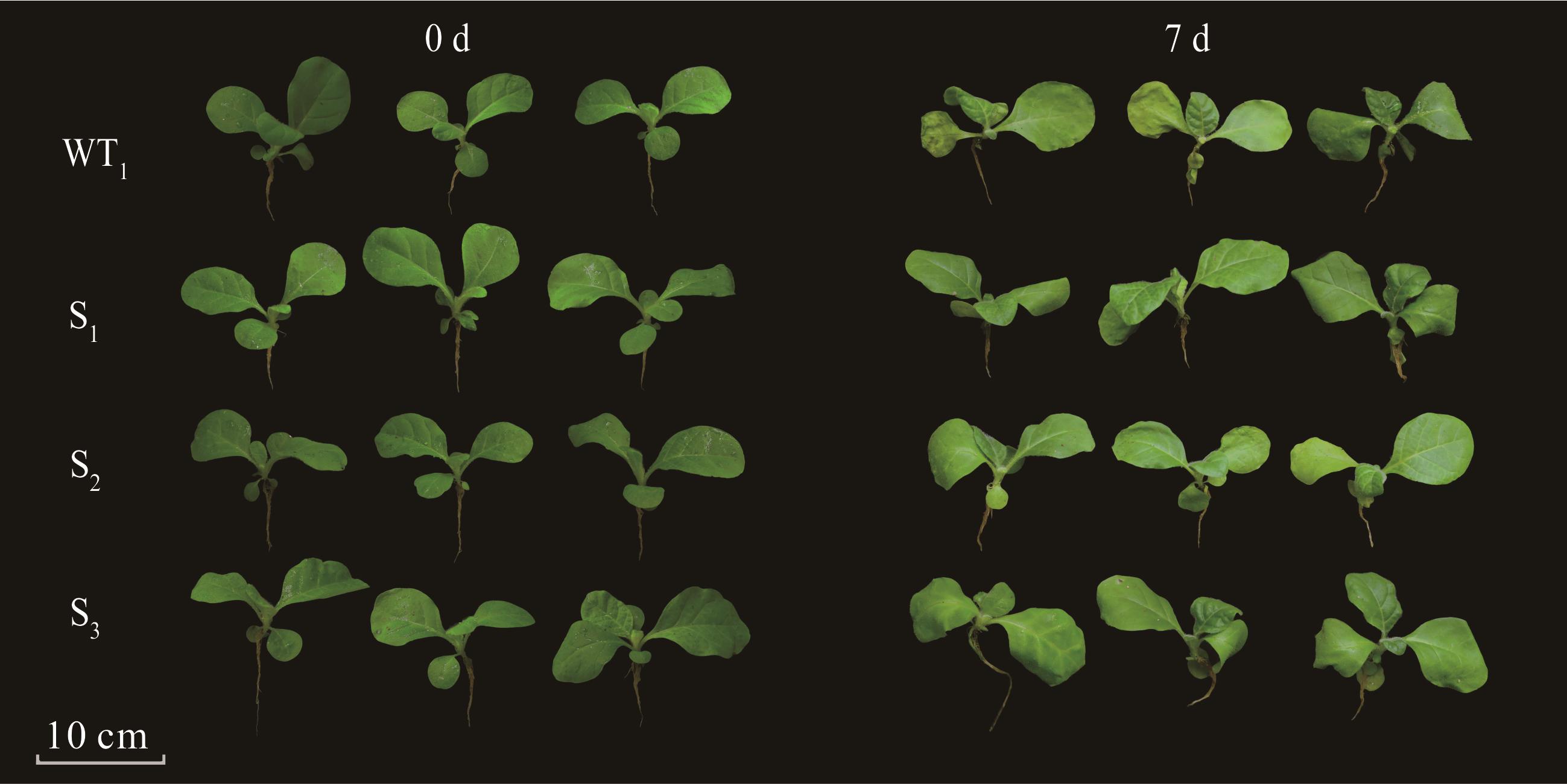

图1 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因烟草表型的影响WT1: 野生型烟草Wild tobacco; S1, S2, S3: 过表达CiMYB4烟草株系CiMYB4 overexpressing tobacco strains. 下同The same below.
Fig.1 Effects of Cd stress on phenotypes of CiMYB4 transgenic tobacco
项目 Item | 株系 Strain | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (cm) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (cm) | 干重Dry weight (g·plant-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部Above-ground | 根Root | |||||||
对照组 Control | WT1 | 10.24±0.41a | 5.50±0.18a | 0.37±0.06a | 8.83±0.65a | 4.57±0.11a | 0.87±0.16a | 0.21±0.02a |
| S1 | 10.09±0.25a | 5.51±0.27a | 0.39±0.03a | 9.03±0.85a | 4.60±0.15a | 0.85±0.12a | 0.20±0.06a | |
| S2 | 10.75±0.59a | 5.92±0.64a | 0.40±0.03a | 8.97±0.32a | 4.63±0.27a | 0.87±0.08a | 0.18±0.03a | |
| S3 | 10.32±0.56a | 5.51±0.40a | 0.38±0.02a | 8.94±0.68a | 4.45±0.12a | 0.86±0.23a | 0.19±0.02a | |
处理组 Treatment | WT1 | 9.25±0.26b | 4.62±0.25c | 0.33±0.04b | 7.85±1.05b | 3.65±0.14b | 0.75±0.14b | 0.14±0.02a |
| S1 | 9.80±0.30ab | 5.10±0.53b | 0.37±0.02a | 8.48±0.57a | 4.14±0.17a | 0.81±0.08ab | 0.15±0.04a | |
| S2 | 10.24±0.42a | 5.59±0.22a | 0.39±0.05a | 8.54±0.49a | 4.28±0.30a | 0.83±0.15ab | 0.17±0.02a | |
| S3 | 9.83±0.50ab | 5.11±0.32b | 0.38±0.02a | 8.62±0.82a | 3.97±0.15a | 0.83±0.09a | 0.16±0.05a | |
表2 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因烟草生长状态的影响
Table 2 Effects of Cd stress on the growth of CiMYB4 transgenic tobacco
项目 Item | 株系 Strain | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (cm) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (cm) | 干重Dry weight (g·plant-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部Above-ground | 根Root | |||||||
对照组 Control | WT1 | 10.24±0.41a | 5.50±0.18a | 0.37±0.06a | 8.83±0.65a | 4.57±0.11a | 0.87±0.16a | 0.21±0.02a |
| S1 | 10.09±0.25a | 5.51±0.27a | 0.39±0.03a | 9.03±0.85a | 4.60±0.15a | 0.85±0.12a | 0.20±0.06a | |
| S2 | 10.75±0.59a | 5.92±0.64a | 0.40±0.03a | 8.97±0.32a | 4.63±0.27a | 0.87±0.08a | 0.18±0.03a | |
| S3 | 10.32±0.56a | 5.51±0.40a | 0.38±0.02a | 8.94±0.68a | 4.45±0.12a | 0.86±0.23a | 0.19±0.02a | |
处理组 Treatment | WT1 | 9.25±0.26b | 4.62±0.25c | 0.33±0.04b | 7.85±1.05b | 3.65±0.14b | 0.75±0.14b | 0.14±0.02a |
| S1 | 9.80±0.30ab | 5.10±0.53b | 0.37±0.02a | 8.48±0.57a | 4.14±0.17a | 0.81±0.08ab | 0.15±0.04a | |
| S2 | 10.24±0.42a | 5.59±0.22a | 0.39±0.05a | 8.54±0.49a | 4.28±0.30a | 0.83±0.15ab | 0.17±0.02a | |
| S3 | 9.83±0.50ab | 5.11±0.32b | 0.38±0.02a | 8.62±0.82a | 3.97±0.15a | 0.83±0.09a | 0.16±0.05a | |

图2 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因烟草抗氧化指标的影响不同小写字母表示相同处理不同株系间的差异达到显著水平(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters represent that the difference among different strains of the same treatment has reached significant level (P<0.05),the same below.
Fig.2 Effects of Cd stress on antioxidant indexes of CiMYB4 transgenic tobacco
株系 Strain | 根系镉含量 Cd2+ content in the root (mg·kg-1) | 地上部镉含量 Cd2+ content in the shoot (mg·kg-1) | 根系富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the root | 地上部富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the shoot | 转运系数 Translocation factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT1 | 33.05±2.28b | 45.55±3.41c | 1.65±0.11c | 2.28±0.17b | 1.38±0.02b |
| S1 | 67.85±4.85a | 112.86±3.28a | 3.39±0.24b | 5.64±0.16b | 1.64±0.10a |
| S2 | 73.95±7.60a | 122.73±5.91a | 3.70±0.38a | 6.14±0.30a | 1.66±0.11a |
| S3 | 60.14±3.60a | 96.86±5.86b | 3.01±0.18c | 4.84±0.29a | 1.61±0.01b |
表3 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因烟草不同部位镉含量与富集系数和转运系数的影响
Table 3 Effects of Cd stress on Cd2+ content of root, stem and leaf, bioconcentration factor and translocation factor of CiMYB4 transgenic tobacco
株系 Strain | 根系镉含量 Cd2+ content in the root (mg·kg-1) | 地上部镉含量 Cd2+ content in the shoot (mg·kg-1) | 根系富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the root | 地上部富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the shoot | 转运系数 Translocation factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT1 | 33.05±2.28b | 45.55±3.41c | 1.65±0.11c | 2.28±0.17b | 1.38±0.02b |
| S1 | 67.85±4.85a | 112.86±3.28a | 3.39±0.24b | 5.64±0.16b | 1.64±0.10a |
| S2 | 73.95±7.60a | 122.73±5.91a | 3.70±0.38a | 6.14±0.30a | 1.66±0.11a |
| S3 | 60.14±3.60a | 96.86±5.86b | 3.01±0.18c | 4.84±0.29a | 1.61±0.01b |

图5 野生型与CiMYB4转基因烟草株系中耐镉相关基因的表达不同小写字母表示同一处理时间不同株系间差异达到显著水平(P<0.05),下同。Different lowercase letters represent that the difference among different strains has reached significant level under the same treatment time (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.5 Expression analyses of the genes related to cadmium-tolerant in the wild-type and CiMYB4 transgenic tobacco lines

图6 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因野菊表型的影响OE-2, OE-3: 过表达CiMYB4野菊株系CiMYB4 overexpressing C. indicum strains; WT2: 野生型野菊Wild C. indicum; Ri-1, Ri-2: 抑制表达CiMYB4野菊株系CiMYB4 RNAi C. indicum strains. 下同The same below.
Fig.6 Effects of Cd stress on phenotypes of CiMYB4 transgenic C. indicum
项目 Item | 株系 Strain | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (cm) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (cm) | 干重Dry weight (g·plant-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部 Above-ground | 根 Root | |||||||
对照组 Control | OE-2 | 16.02±0.85a | 11.54±0.79a | 0.21±0.02a | 3.53±0.36a | 2.79±0.17a | 0.95±0.08a | 0.36±0.04a |
| OE-3 | 15.86±0.60a | 12.33±1.25a | 0.19±0.01a | 3.65±0.57a | 2.93±0.43a | 0.94±0.05a | 0.37±0.04a | |
| WT2 | 16.36±0.44a | 11.46±0.55a | 0.22±0.02a | 2.58±0.23b | 2.10±0.23b | 0.90±0.04a | 0.37±0.05a | |
| Ri-1 | 15.86±0.65a | 11.54±0.82a | 0.19±0.02a | 2.60±0.26b | 2.11±0.41b | 0.90±0.09a | 0.37±0.04a | |
| Ri-2 | 15.87±0.95a | 11.79±0.78a | 0.20±0.01a | 2.55±0.14b | 2.08±0.13b | 0.91±0.11a | 0.38±0.04a | |
处理组 Treatment | OE-2 | 15.42±1.29a | 10.65±0.81ab | 0.16±0.02ab | 3.27±0.37a | 2.45±0.12a | 0.87±0.02ab | 0.32±0.03ab |
| OE-3 | 15.50±0.62a | 11.40±0.55a | 0.17±0.01a | 3.39±0.47a | 2.64±0.44a | 0.88±0.13a | 0.33±0.04a | |
| WT2 | 15.06±1.21b | 9.47±0.62bc | 0.15±0.01ab | 2.08±0.19b | 1.69±0.31b | 0.84±0.01b | 0.30±0.03ab | |
| Ri-1 | 14.76±0.36c | 9.51±0.47bc | 0.13±0.02bc | 1.98±0.22b | 1.54±0.27b | 0.80±0.06c | 0.26±0.04b | |
| Ri-2 | 14.63±0.48c | 9.25±1.01c | 0.12±0.02c | 1.92±0.32b | 1.50±0.15b | 0.78±0.03c | 0.28±0.04ab | |
表4 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因野菊生长的影响
Table 4 Effects of Cd stress on the growth of CiMYB4 transgenic C. indicum
项目 Item | 株系 Strain | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (cm) | 叶长 Leaf length (cm) | 叶宽 Leaf width (cm) | 干重Dry weight (g·plant-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
地上部 Above-ground | 根 Root | |||||||
对照组 Control | OE-2 | 16.02±0.85a | 11.54±0.79a | 0.21±0.02a | 3.53±0.36a | 2.79±0.17a | 0.95±0.08a | 0.36±0.04a |
| OE-3 | 15.86±0.60a | 12.33±1.25a | 0.19±0.01a | 3.65±0.57a | 2.93±0.43a | 0.94±0.05a | 0.37±0.04a | |
| WT2 | 16.36±0.44a | 11.46±0.55a | 0.22±0.02a | 2.58±0.23b | 2.10±0.23b | 0.90±0.04a | 0.37±0.05a | |
| Ri-1 | 15.86±0.65a | 11.54±0.82a | 0.19±0.02a | 2.60±0.26b | 2.11±0.41b | 0.90±0.09a | 0.37±0.04a | |
| Ri-2 | 15.87±0.95a | 11.79±0.78a | 0.20±0.01a | 2.55±0.14b | 2.08±0.13b | 0.91±0.11a | 0.38±0.04a | |
处理组 Treatment | OE-2 | 15.42±1.29a | 10.65±0.81ab | 0.16±0.02ab | 3.27±0.37a | 2.45±0.12a | 0.87±0.02ab | 0.32±0.03ab |
| OE-3 | 15.50±0.62a | 11.40±0.55a | 0.17±0.01a | 3.39±0.47a | 2.64±0.44a | 0.88±0.13a | 0.33±0.04a | |
| WT2 | 15.06±1.21b | 9.47±0.62bc | 0.15±0.01ab | 2.08±0.19b | 1.69±0.31b | 0.84±0.01b | 0.30±0.03ab | |
| Ri-1 | 14.76±0.36c | 9.51±0.47bc | 0.13±0.02bc | 1.98±0.22b | 1.54±0.27b | 0.80±0.06c | 0.26±0.04b | |
| Ri-2 | 14.63±0.48c | 9.25±1.01c | 0.12±0.02c | 1.92±0.32b | 1.50±0.15b | 0.78±0.03c | 0.28±0.04ab | |
株系 Strain | 根系镉含量 Cd2+ content in the root (mg·kg-1) | 地上部镉含量 Cd2+ content in the shoot (mg·kg-1) | 根系富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the root | 地上部富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the shoot | 转运系数 Translocation factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OE-2 | 1242.05±66.12b | 178.19±11.62ab | 24.84±1.32a | 3.56±0.23a | 0.14±0.01a |
| OE-3 | 1384.30±86.35a | 204.55±5.77a | 27.69±1.73a | 4.09±0.11a | 0.15±0.01a |
| WT2 | 1028.47±54.46c | 122.68±14.68b | 20.57±1.09b | 2.45±0.29b | 0.12±0.02a |
| Ri-1 | 936.22±9.26cd | 115.45±8.63c | 17.92±0.62c | 2.31±0.17b | 0.13±0.02a |
| Ri-2 | 754.78±28.56d | 98.72±8.72d | 15.10±0.58c | 1.97±0.19c | 0.13±0.01a |
表5 镉胁迫对CiMYB4转基因野菊不同部位镉含量与富集系数、转运系数的影响
Table 5 Effects of Cd stress on Cd2+ content of root, stem and leaf, bioconcentration factor and translocation factor of CiMYB4 transgenic C. indicum
株系 Strain | 根系镉含量 Cd2+ content in the root (mg·kg-1) | 地上部镉含量 Cd2+ content in the shoot (mg·kg-1) | 根系富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the root | 地上部富集系数 Bioconcentration factor of the shoot | 转运系数 Translocation factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OE-2 | 1242.05±66.12b | 178.19±11.62ab | 24.84±1.32a | 3.56±0.23a | 0.14±0.01a |
| OE-3 | 1384.30±86.35a | 204.55±5.77a | 27.69±1.73a | 4.09±0.11a | 0.15±0.01a |
| WT2 | 1028.47±54.46c | 122.68±14.68b | 20.57±1.09b | 2.45±0.29b | 0.12±0.02a |
| Ri-1 | 936.22±9.26cd | 115.45±8.63c | 17.92±0.62c | 2.31±0.17b | 0.13±0.02a |
| Ri-2 | 754.78±28.56d | 98.72±8.72d | 15.10±0.58c | 1.97±0.19c | 0.13±0.01a |
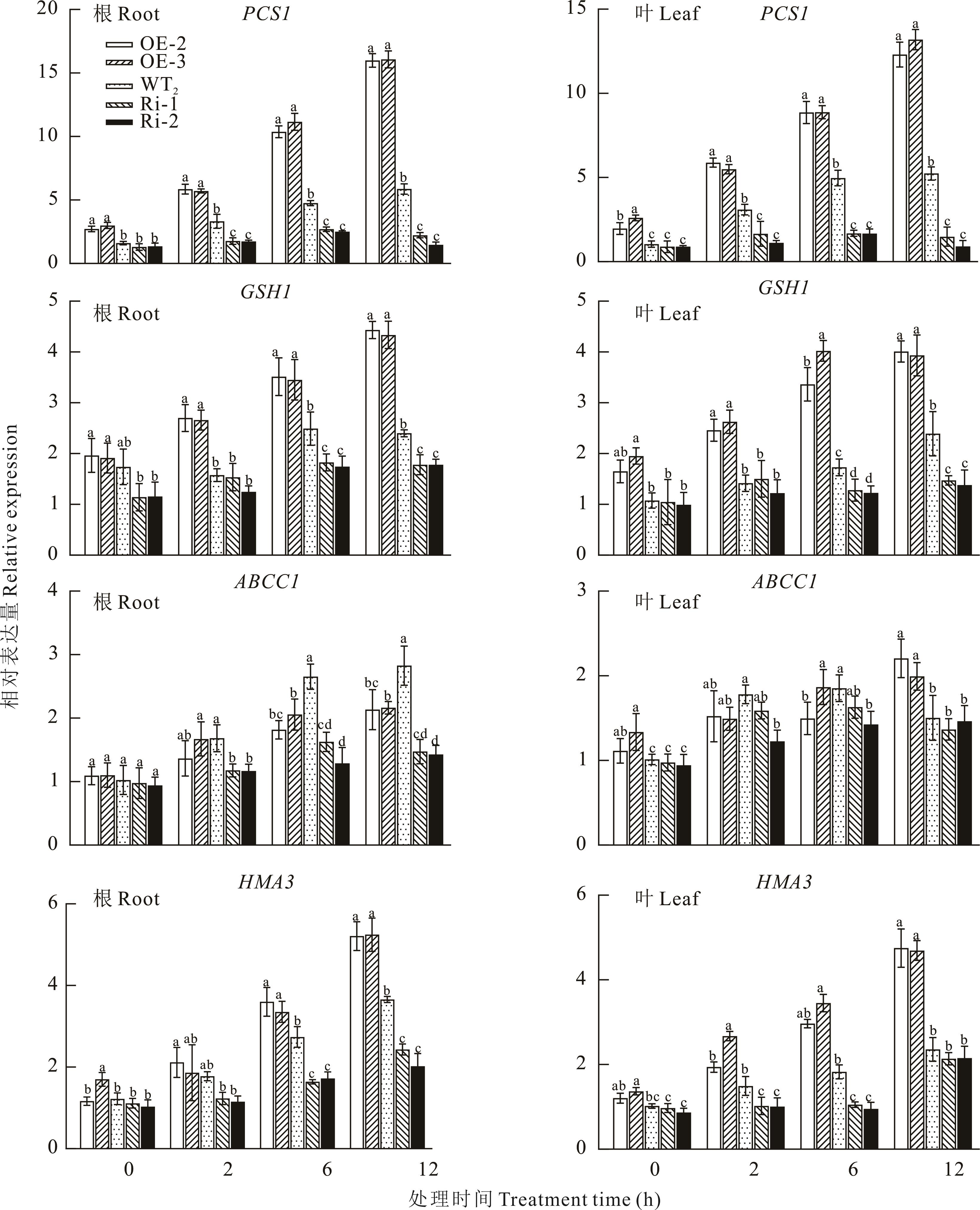
图10 野生型与CiMYB4转基因野菊株系中耐镉相关基因的表达
Fig.10 Expression analyses of the genes related to cadmium-tolerant in the wild-type and CiMYB4 transgenic lines C. indicum
| 1 | Satarug S, Garrett S H, Sens M A, et al. Cadmium, environmental exposure, and health outcomes. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2010, 118(2): 182-190. |
| 2 | Raza A, Habib M, Kakavand S N, et al. Phytoremediation of cadmium: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms. Biology, 2020, 9(7): 177. |
| 3 | Liu J X, Sun Z Y, Gou P, et al. Response of photosynthetic physiology of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) to Cd2+ stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(3): 191-197. |
| 刘俊祥, 孙振元, 勾萍, 等. 镉胁迫下多年生黑麦草的光合生理响应. 草业学报, 2012, 21(3): 191-197. | |
| 4 | Wang F, Kong W, Wong G, et al. AtMYB12 regulates flavonoids accumulation and abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2016, 291(4): 1545-1559. |
| 5 | Shen X J, Wang Y Y, Zhang Y X, et al. Overexpression of the wild soybean R2R3-MYB transcription factor GsMYB15 enhances resistance to salt stress and Helicoverpa armigera in transgenic Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018, 19(12): 3958. |
| 6 | Liu C, Zhang Y, Tan Y, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated SlMYBS2 mutagenesis reduces tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(21): 11423. |
| 7 | Yang A, Dai X, Zhang W H. A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold and dehydration tolerance in rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(7): 2541-2556. |
| 8 | Wei Q, Chen R, Wei X, et al. Genome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB family in wheat and functional characteristics of the abiotic stress responsive gene TaMYB344. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 1-16. |
| 9 | Yang J, Zhang B, Gu G, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the R2R3-MYB gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). BMC Genomics, 2022, 23(1): 432. |
| 10 | Wang Y, Wu J, Li J, et al. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor ThRAX2 recognized a new element MYB-T (CTTCCA) to enhance cadmium tolerance in Tamarix hispida. Plant Science, 2023, 329: 111574. |
| 11 | Zhu S, Shi W, Jie Y, et al. A MYB transcription factor, BnMYB2, cloned from ramie (Boehmeria nivea) is involved in cadmium tolerance and accumulation. PLoS One, 2020, 15(5): e0233375. |
| 12 | Agarwal P, Mehali M, Banerjee S, et al. MYB4 transcription factor, a member of R2R3-subfamily of MYB domain protein, regulates cadmium tolerance via enhanced protection against oxidative damage and increases expression of PCS1 and MT1C in Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 2020, 297: 110501. |
| 13 | Zhang P, Wang R, Ju Q, et al. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor MYB49 regulates cadmium accumulation. Plant Physiology, 2019, 180(1): 529-542. |
| 14 | Wu X S, Xu J, Zhang T J, et al. Research progress in chemical constituents of Chrysanthemum indicum and their quality assessment. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2015, 46(3): 443-452. |
| 吴雪松, 许浚, 张铁军, 等. 野菊的化学成分及质量评价研究进展. 中草药, 2015, 46(3): 443-452. | |
| 15 | Liu X J, Li Y, Su S L, et al. Status and prospects of resource utilization of non-medicinal parts of medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2020, 51(15): 4075-4081. |
| 刘夏进, 李懿, 宿树兰, 等. 药用菊非药用部位的资源化利用现状与展望. 中草药, 2020, 51(15): 4075-4081. | |
| 16 | Wang J J. Cloning of CiMYB4 Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum and genetic transformation of Chrysanthemum indicum. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2019. |
| 王霁佳. 神农香菊CiMYB4基因的克隆及对野菊的遗传转化. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019. | |
| 17 | Li M Y. Verification of drought tolerance function of CiMYB4 gene of Chrysanthemum indicum var. aromaticum and construction of RNAi vector. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2020. |
| 李梦雨. 神农香菊CiMYB4基因抗旱性功能验证及RNAi载体构建. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020. | |
| 18 | Li H S. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment. Bejing: Higher Education Press, 2000. |
| 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. | |
| 19 | Zhang X Y, Li L G, Guo J L, et al. Comparison and analysis of isolation methods of photosynthetic pigment of leaves in Cerasus humilis. Northern Horticulture, 2021(9): 104-110. |
| 张晓艳, 李连国, 郭金丽, 等. 欧李叶片光合色素提取方法的比较分析. 北方园艺, 2021(9): 104-110. | |
| 20 | Wang A, Wang M, Liao Q, et al. Characterization of Cd translocation and accumulation in 19 maize cultivars grown on Cd-contaminated soil: implication of maize cultivar selection for minimal risk to human health and for phytoremediation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23(6): 5410-5419. |
| 21 | Wang R, Xu Y L, Li Z F, et al. Identification and validation of tobacco reference genes for qRT-PCR based on microarray data. Tobacco Science & Technology, 2015, 48(2): 1-6. |
| 王燃, 许亚龙, 李泽锋, 等. 基于芯片数据的烟草qRT-PCR内参基因鉴定与验证. 烟草科技, 2015, 48(2): 1-6. | |
| 22 | Gu C, Chen S, Liu Z, et al. Reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR in Chrysanthemum subjected to biotic and abiotic stress. Molecular Biotechnology, 2011, 49(2): 192-197. |
| 23 | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| 24 | He L X, Huang Y X, Huang C Y, et al. Physiological response of Chamaecrista rotundifolia to cadmium exposure. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2): 198-204. |
| 何梨香, 黄运湘, 黄楚瑜, 等. 圆叶决明对镉胁迫的生理响应. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 198-204. | |
| 25 | Hu B Y, Fang Z G, Lou L Q, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of cadmium tolerance of 14 switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) cultivars in the seedling stage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(1): 27-36. |
| 胡冰钰, 方志刚, 娄来清, 等. 14份柳枝稷种质资源苗期耐镉性综合评价. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 27-36. | |
| 26 | Zhang C, Chen Y, Xu W, et al. Resistance of alfalfa and Indian mustard to Cd and the correlation of plant Cd uptake and soil Cd form. Environmental Science and Pollution Reseach, 2019, 26(14): 13804-13811. |
| 27 | Sun Y B, Zhou Q X, Wang L, et al. Cadmium tolerance and accumulation characteristics of Bidens pilosa L. as a potential Cd-hyperaccumulator. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(2/3): 808-814. |
| 28 | Mourato M, Reis R, Martins L L. Characterization of plant antioxidative system in response to abiotic stresses: A focus on heavy metal toxicity. Advances in Selected Plant Physiology Aspects, 2012, 12: 1-17. |
| 29 | Liu X S, Sun Y L, An X X, et al. Effects of phosphorus application and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria on the photosynthetic characteristics and biomass of alfalfa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 等. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. | |
| 30 | Zhao C D, Liu Y C, Yang Z, et al. Effects of different gradient phosphorus additions on photosynthetic characteristics of Vitex negundo seedlings. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2020, 49(6): 94-99. |
| 赵琛迪, 刘雅辰, 杨子, 等. 不同磷添加梯度对荆条幼苗光合特性的影响. 西部林业科学, 2020, 49(6): 94-99. | |
| 31 | Xin J P, Li W M, Qi X, et al. Effects of Cd on antioxidant enzyme activities, and leaf photosynthetic and fluorescence characteristics in Pontederia cordata. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(10): 23-34. |
| 辛建攀, 李文明, 祁茜, 等. 镉对梭鱼草叶片保护酶活性、光合及荧光特性的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 23-34. | |
| 32 | Jia L, Liu Z, Chen W, et al. Hormesis effects induced by cadmium on growth and photosynthetic performance in a hyperaccumulator, Lonicera japonica Thunb. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2015, 34(1): 13-21. |
| 33 | An M J, Wang H J, Fan H, et al. Effects of modifiers on the growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzymes of cotton under cadmium toxicity. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2019, 38: 1196-1205. |
| 34 | Sun J Y, Li Q, He M, et al. Bioaccumulation characteristics and physiological response of different ground-cover Chrysanthemum cultivars to cadmium. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2018, 40(1): 92-98. |
| 孙婕妤, 李强, 何淼, 等. 不同地被菊品种对镉的富集特性及生理响应. 吉林农业大学学报, 2018, 40(1): 92-98. | |
| 35 | Wang X J, Wang W B, Yang L, et al. Transport pathways of cadmium (Cd) and its regulatory mechanisms in plant. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(23): 7921-7929. |
| 王晓娟, 王文斌, 杨龙, 等. 重金属镉(Cd)在植物体内的转运途径及其调控机制. 生态学报, 2015, 35(23): 7921-7929. | |
| 36 | Zhang X Y, Ye Z B, Zhang Y Y. Advances in physiological and molecular mechanism of plant response to cadmium stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2021, 57(7): 14. |
| 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋. 植物响应镉胁迫的生理与分子机制研究进展. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(7): 14. | |
| 37 | Yamazaki S, Ueda Y, Mukai A, et al. Rice phytochelatin synthases OsPCS1 and OsPCS2 make different contributions to cadmium and arsenic tolerance. Plant Direct, 2018, 2(1): e00034. |
| 38 | Zhu S, Shi W, Jie Y. Overexpression of BnPCS1, a novel phytochelatin synthase gene from ramie (Boehmeria nivea) enhanced Cd tolerance, accumulation, and translocation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 1169. |
| 39 | Yang Z, Yang F, Liu J L, et al. Heavy metal transporters: Functional mechanisms, regulation, and application in phytoremediation. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 809: 151099. |
| 40 | Park J, Song W Y, Ko D, et al. The phytochelatin transporters AtABCC1 and AtABCC2mediate tolerance to cadmium and mercury. The Plant Journal, 2012, 69(2): 278-288. |
| 41 | Liu H, Zhao H, Wu L, et al. Heavy metal ATPase 3 (HMA3) confers cadmium hyper tolerance on the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. New Phytologist, 2017, 215(2): 687-698. |
| [1] | 韩金秀, 陈斌, 刘晏廷, 孟儒, 金利妍, 何淼. 神农香菊CibHLH1的鉴定及对光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(1): 89-101. |
| [2] | 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 殷庭超, 黄心如, 何悦, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [3] | 刘建新, 欧晓彬, 王金成, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕. 镉胁迫下裸燕麦幼苗对外源H2O2的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 125-134. |
| [4] | 李继伟, 悦飞雪, 王艳芳, 张亚梅, 倪瑞景, 王发园, 付国占, 刘领. 施用生物炭和AM真菌对镉胁迫下玉米生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 120-129. |
| [5] | 辛建攀, 李文明, 祁茜, 田如男. 镉对梭鱼草叶片保护酶活性、光合及荧光特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 23-34. |
| [6] | 董姬妃, 张帆, 胡雨寒, 李俊承, 李维, 王娴淑. 镉胁迫下增施氮对白三叶草生长的影响和镉毒害的缓解效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(9): 83-91. |
| [7] | 檀鹏辉, 袁丽丽, 樊波, 于安东, 董笛, 滕珂, 晁跃辉. 日本结缕草滞绿基因 ZjSGR 对烟草的转化及功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(5): 155-162. |
| [8] | 王玉萍, 常宏, 李成, 梁延超, 卢萧. Ca2+对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生长、光合特征和PSⅡ功能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(5): 40-48. |
| [9] | 李希铭, 宋桂龙. 镉胁迫对紫花苜蓿镉吸收特征及根系形态影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 178-186. |
| [10] | 何梨香, 黄运湘, 黄楚瑜, 刘利杉, 龙祥, 罗琳. 圆叶决明对镉胁迫的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2): 198-204. |
| [11] | 韩宝贺,朱宏. 镉胁迫对白三叶的富集能力、叶片显微结构及其生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(6): 167-175. |
| [12] | 刘柿良,石新生,潘远智,丁继军,何杨,王力. 镉胁迫对长春花生长,生物量及养分积累与分配的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(3): 154-. |
| [13] | 王芳,常盼盼,陈永平,彭云玲,方永丰,王汉宁. 外源NO对镉胁迫下玉米幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2013, 22(2): 178-186. |
| [14] | 陈良,隆小华,郑晓涛,刘兆普. 镉胁迫下两种菊芋幼苗的光合作用特征及镉吸收转运差异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6): 60-67. |
| [15] | 李源,李金娟,魏小红*. 镉胁迫下蚕豆幼苗抗氧化能力对外源NO和H2O2的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(6): 186-191. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 176
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 148
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||