

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 106-122.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023490
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
黎泽斌2( ), 邱永争2, 刘延杰2, 喻金秋1, 王柏吉1, 刘千宁1, 王月1,2(
), 邱永争2, 刘延杰2, 喻金秋1, 王柏吉1, 刘千宁1, 王月1,2( ), 崔国文1(
), 崔国文1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-19
修回日期:2024-02-14
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
王月,崔国文
作者简介:cgw603@163.com基金资助:
Ze-bin LI2( ), Yong-zheng QIU2, Yan-jie LIU2, Jin-qiu YU1, Bai-ji WANG1, Qian-ning LIU1, Yue WANG1,2(
), Yong-zheng QIU2, Yan-jie LIU2, Jin-qiu YU1, Bai-ji WANG1, Qian-ning LIU1, Yue WANG1,2( ), Guo-wen CUI1(
), Guo-wen CUI1( )
)
Received:2023-12-19
Revised:2024-02-14
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Yue WANG,Guo-wen CUI
摘要:
油菜素内酯(brassinosteroid, BR)是一类类固醇激素,影响植物的各种发育和生理过程。油菜素唑抗性(BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT, BZR)转录因子(transcription factors)家族是油菜素内酯生物合成的正调节因子。BZR基因家族在植物生长发育的调节中发挥重要作用,同时参与多种抗逆功能。然而,在有“牧草之王”美誉的紫花苜蓿中,BZR基因家族的研究较少。本研究中,鉴定到紫花苜蓿共14个BZR基因,并且用生物信息学手段对其蛋白质理化性质、二级结构和三级结构、基因在染色体的定位、紫花苜蓿与相似物种的系统发育、基因结构、保守结构域、启动子顺式作用元件、基因之间共线性关系、BZR基因家族在6个不同组织中的表达量以及它们对非生物胁迫的响应进行分析,发现14个BZR家族的基因在紫花苜蓿6个组织中均有表达,分别有9、7、7个基因响应冷、盐、干旱胁迫,其中有3个基因(MsBZR05、MsBZR06、MsBZR12)对这3种胁迫都有响应。本研究为进一步探究BZR基因家族提供了候选基因。
黎泽斌, 邱永争, 刘延杰, 喻金秋, 王柏吉, 刘千宁, 王月, 崔国文. 紫花苜蓿BZR基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 106-122.
Ze-bin LI, Yong-zheng QIU, Yan-jie LIU, Jin-qiu YU, Bai-ji WANG, Qian-ning LIU, Yue WANG, Guo-wen CUI. Identification of the BZR gene family in alfalfa and analysis of its transcriptional responses to abiotic stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 106-122.
| 基因Gene | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| MsBZR05 | F: ACATTACTCCTTCCTGCCTTCT R: TTGATCCCAGCAAACCATTC |
| MsBZR06 | F: GAACGCATGGATGTGATAGG R: AGCCAGGACTTGGGTTGTAG |
| MsBZR12 | F: CCATTCATCCGCAACATAAC R: GAAAGAGGTGGCGTAACAGG |
| GAPDH | F: GGCTGCCATCAAGGAGGAAT R: TCCAAGCTCAGCCTCATCAAG |
表1 qRT-PCR 引物序列
Table 1 The primers sequences of qRT-PCR
| 基因Gene | 引物序列 Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| MsBZR05 | F: ACATTACTCCTTCCTGCCTTCT R: TTGATCCCAGCAAACCATTC |
| MsBZR06 | F: GAACGCATGGATGTGATAGG R: AGCCAGGACTTGGGTTGTAG |
| MsBZR12 | F: CCATTCATCCGCAACATAAC R: GAAAGAGGTGGCGTAACAGG |
| GAPDH | F: GGCTGCCATCAAGGAGGAAT R: TCCAAGCTCAGCCTCATCAAG |
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (D) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 疏水性 Hydrophobicity | 染色体 Chromosome | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsBZR01 | MS.gene24310.t1 | 249 | 27557.01 | 8.22 | -0.581 | Chr1.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR02 | MS.gene26935.t1 | 249 | 27540.01 | 8.82 | -0.595 | Chr1.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR03 | MS.gene062710.t1 | 249 | 27482.92 | 8.62 | -0.595 | Chr1.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR04 | MS.gene070724.t1 | 323 | 34856.61 | 8.44 | -0.705 | Chr2.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR05 | MS.gene070726.t1 | 316 | 34141.90 | 8.65 | -0.628 | Chr2.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR06 | MS.gene026895.t1 | 322 | 34700.43 | 8.14 | -0.693 | Chr2.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR07 | MS.gene059905.t1 | 280 | 29760.82 | 5.32 | -0.519 | Chr2.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR08 | MS.gene059906.t1 | 328 | 35427.26 | 8.64 | -0.718 | Chr2.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR09 | MS.gene63375.t1 | 316 | 34127.87 | 8.65 | -0.628 | Chr2.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR10 | MS.gene63376.t1 | 323 | 34856.61 | 8.44 | -0.705 | Chr2.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR11 | MS.gene047749.t1 | 323 | 35322.65 | 9.42 | -0.697 | Chr5.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR12 | MS.gene010465.t1 | 323 | 35322.65 | 9.42 | -0.697 | Chr5.2 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR13 | MS.gene89854.t1 | 323 | 35322.65 | 9.42 | -0.697 | Chr5.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR14 | MS.gene59331.t1 | 323 | 35322.67 | 9.42 | -0.704 | Chr5.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
表2 紫花苜蓿BZR基因家族信息
Table 2 Alfalfa BZR gene family information
基因名称 Gene name | 基因ID Gene ID | 氨基酸数目 Number of amino acids (aa) | 分子量 Molecular weight (D) | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 疏水性 Hydrophobicity | 染色体 Chromosome | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MsBZR01 | MS.gene24310.t1 | 249 | 27557.01 | 8.22 | -0.581 | Chr1.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR02 | MS.gene26935.t1 | 249 | 27540.01 | 8.82 | -0.595 | Chr1.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR03 | MS.gene062710.t1 | 249 | 27482.92 | 8.62 | -0.595 | Chr1.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR04 | MS.gene070724.t1 | 323 | 34856.61 | 8.44 | -0.705 | Chr2.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR05 | MS.gene070726.t1 | 316 | 34141.90 | 8.65 | -0.628 | Chr2.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR06 | MS.gene026895.t1 | 322 | 34700.43 | 8.14 | -0.693 | Chr2.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR07 | MS.gene059905.t1 | 280 | 29760.82 | 5.32 | -0.519 | Chr2.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR08 | MS.gene059906.t1 | 328 | 35427.26 | 8.64 | -0.718 | Chr2.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR09 | MS.gene63375.t1 | 316 | 34127.87 | 8.65 | -0.628 | Chr2.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR10 | MS.gene63376.t1 | 323 | 34856.61 | 8.44 | -0.705 | Chr2.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR11 | MS.gene047749.t1 | 323 | 35322.65 | 9.42 | -0.697 | Chr5.1 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR12 | MS.gene010465.t1 | 323 | 35322.65 | 9.42 | -0.697 | Chr5.2 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR13 | MS.gene89854.t1 | 323 | 35322.65 | 9.42 | -0.697 | Chr5.3 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
| MsBZR14 | MS.gene59331.t1 | 323 | 35322.67 | 9.42 | -0.704 | Chr5.4 | 细胞核Cell nucleus |
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋α-helix | β-转角β-turn | 无规则卷曲Random coil | 延伸链Extended chain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | |
| MsBZR01 | 51 | 20.48 | 12 | 4.82 | 156 | 62.65 | 30 | 12.05 |
| MsBZR02 | 52 | 20.16 | 14 | 5.13 | 160 | 62.02 | 32 | 12.40 |
| MsBZR03 | 53 | 21.29 | 12 | 4.82 | 165 | 66.27 | 19 | 7.63 |
| MsBZR04 | 50 | 15.48 | 13 | 4.02 | 238 | 73.68 | 22 | 6.81 |
| MsBZR05 | 51 | 16.14 | 13 | 4.11 | 221 | 69.94 | 31 | 9.81 |
| MsBZR06 | 54 | 16.77 | 16 | 4.97 | 227 | 70.50 | 25 | 7.76 |
| MsBZR07 | 39 | 13.93 | 10 | 3.57 | 201 | 71.79 | 30 | 10.71 |
| MsBZR08 | 50 | 15.24 | 14 | 4.27 | 246 | 75.00 | 18 | 5.49 |
| MsBZR09 | 47 | 14.87 | 18 | 5.70 | 218 | 68.99 | 18 | 5.70 |
| MsBZR10 | 50 | 15.48 | 13 | 4.02 | 238 | 73.68 | 22 | 6.81 |
| MsBZR11 | 58 | 17.96 | 18 | 5.57 | 222 | 68.73 | 18 | 5.57 |
| MsBZR12 | 58 | 17.96 | 18 | 5.57 | 222 | 68.73 | 25 | 7.74 |
| MsBZR13 | 58 | 17.96 | 18 | 5.57 | 222 | 68.73 | 25 | 7.74 |
| MsBZR14 | 48 | 14.86 | 19 | 5.88 | 224 | 69.35 | 32 | 9.91 |
表3 紫花苜蓿MsBZR蛋白质二级结构
Table 3 Secondary structure of alfalfa MsBZRprotein
蛋白名称 Protein name | α-螺旋α-helix | β-转角β-turn | 无规则卷曲Random coil | 延伸链Extended chain | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | 数量Number | 占比Ratio (%) | |
| MsBZR01 | 51 | 20.48 | 12 | 4.82 | 156 | 62.65 | 30 | 12.05 |
| MsBZR02 | 52 | 20.16 | 14 | 5.13 | 160 | 62.02 | 32 | 12.40 |
| MsBZR03 | 53 | 21.29 | 12 | 4.82 | 165 | 66.27 | 19 | 7.63 |
| MsBZR04 | 50 | 15.48 | 13 | 4.02 | 238 | 73.68 | 22 | 6.81 |
| MsBZR05 | 51 | 16.14 | 13 | 4.11 | 221 | 69.94 | 31 | 9.81 |
| MsBZR06 | 54 | 16.77 | 16 | 4.97 | 227 | 70.50 | 25 | 7.76 |
| MsBZR07 | 39 | 13.93 | 10 | 3.57 | 201 | 71.79 | 30 | 10.71 |
| MsBZR08 | 50 | 15.24 | 14 | 4.27 | 246 | 75.00 | 18 | 5.49 |
| MsBZR09 | 47 | 14.87 | 18 | 5.70 | 218 | 68.99 | 18 | 5.70 |
| MsBZR10 | 50 | 15.48 | 13 | 4.02 | 238 | 73.68 | 22 | 6.81 |
| MsBZR11 | 58 | 17.96 | 18 | 5.57 | 222 | 68.73 | 18 | 5.57 |
| MsBZR12 | 58 | 17.96 | 18 | 5.57 | 222 | 68.73 | 25 | 7.74 |
| MsBZR13 | 58 | 17.96 | 18 | 5.57 | 222 | 68.73 | 25 | 7.74 |
| MsBZR14 | 48 | 14.86 | 19 | 5.88 | 224 | 69.35 | 32 | 9.91 |
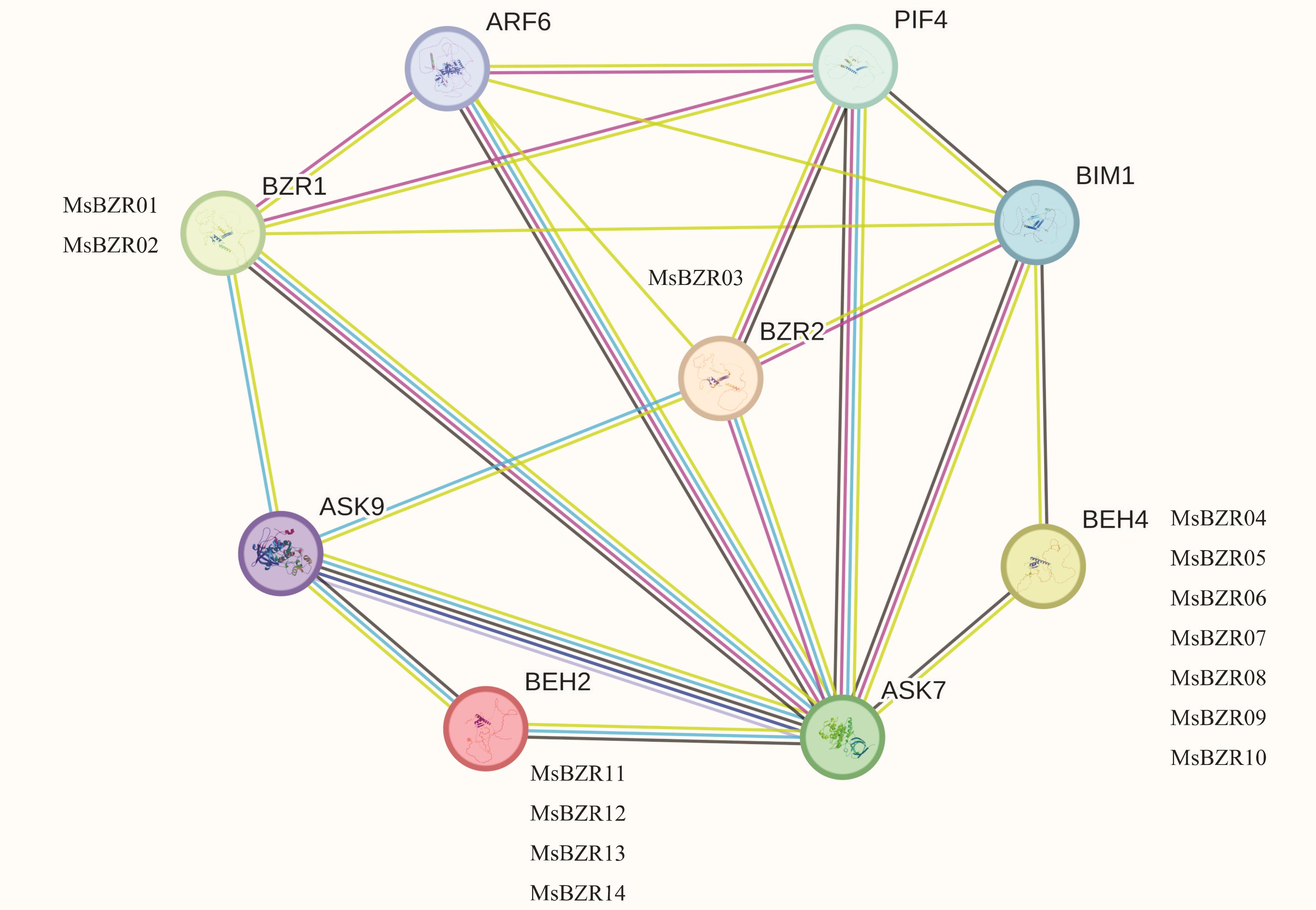
图8 紫花苜蓿中鉴定出的14个MsBZR蛋白与拟南芥中相关同源基因的蛋白相互作用网络较强的关联由较粗的线表示Stronger associations are represented by thicker lines.
Fig.8 Interaction network of 14 MsBZR proteins identified in alfalfa and proteins of related genes in A. thaliana
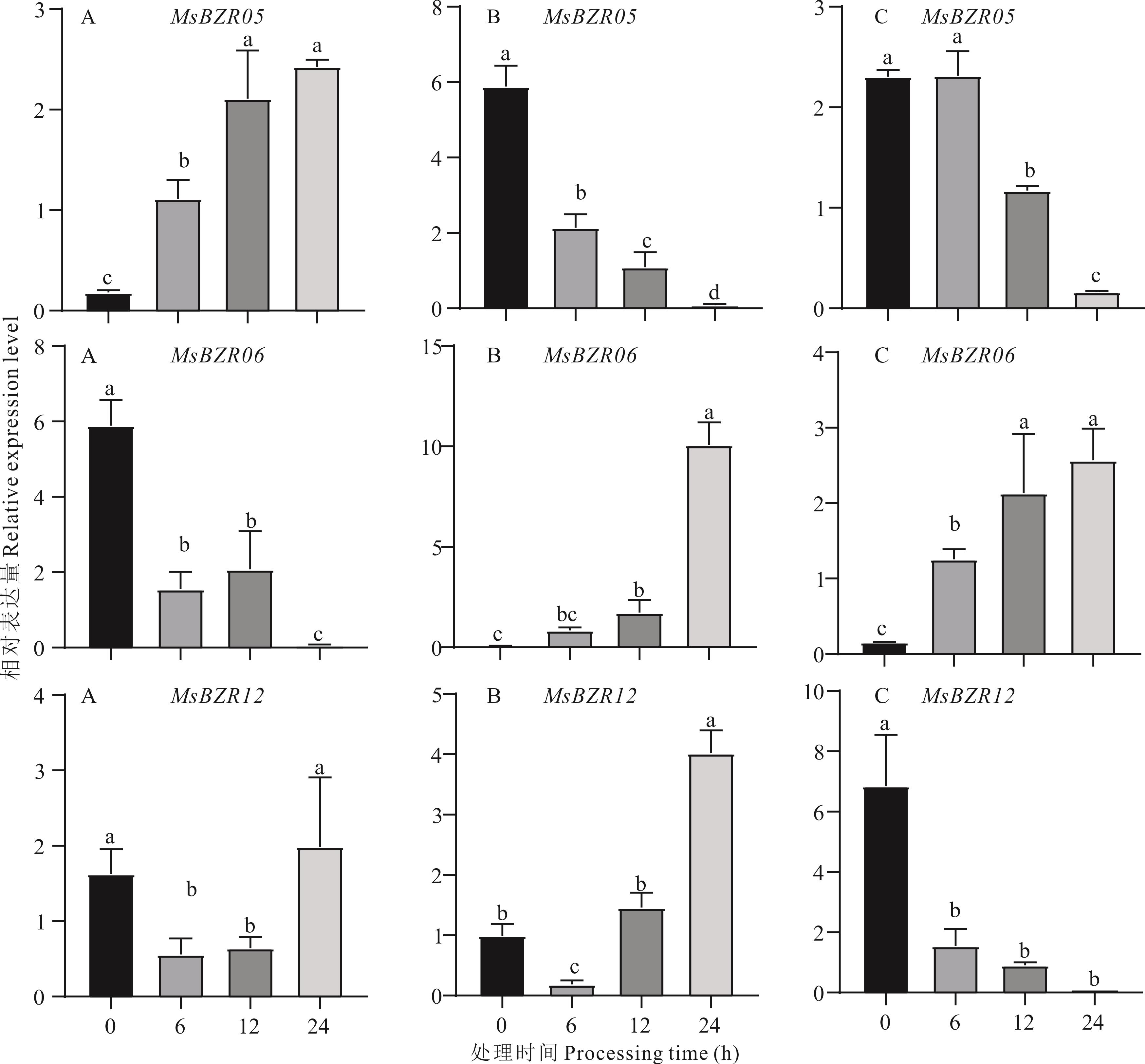
图 12 紫花苜蓿MsBZR05、MsBZR06、MsBZR12基因在冷、盐、干旱胁迫下的表达量A: 冷胁迫Cold stress; B: 盐胁迫Salt stress; C: 干旱胁迫Drought stress. 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences.
Fig.12 Expression levels of alfalfa MsBZR05, MsBZR06 and MsBZR12 genes under cold, salt, and drought stress
| 1 | Li J, Chory J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell, 1997, 90(5): 929-938. |
| 2 | Tanveer M, Shahzed B, Sharma A, et al. 24-epibrassinolide; an active brassinolide and its role in salt stress tolerance in plants: A review. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 130: 69-79. |
| 3 | Khripach V, Zhabinskii V, de Groot A. Twenty years of brassinosteroids: steroidal plant hormones warrant better crops for the XXI century. Annals of Botany, 2000, 86(3): 441-447. |
| 4 | Bajguz A, Hayat S. Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(1): 1-8. |
| 5 | Campos M L, de Almeida M, Rossi M L, et al. Brassinosteroids interact negatively with jasmonates in the formation of anti-herbivory traits in tomato. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2009, 60(15): 4347-4361. |
| 6 | Yang D H, Hettenhausen C, Baldwin I T, et al. BAK1 regulates the accumulation of jasmonic acid and the levels of trypsin proteinase inhibitors in Nicotiana attenuata’s responses to herbivory. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 62(2): 641-652. |
| 7 | Li L, Deng X W. It runs in the family: regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by the BZR1-BES1 class of transcription factors. Trends in Plant Science, 2005, 10(6): 266-268. |
| 8 | Yin Y, Vafeados D, Tao Y, et al. A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell, 2005, 120(2): 249-259. |
| 9 | Manoli, Alessandro, Trevisan, et al. Identification and characterization of the BZR transcription factor family and its expression in response to abiotic stresses in Zea mays L. Plant Growth Regulation, 2018, 84(3): 423-436. |
| 10 | Yu H Q, Feng W Q, Sun F, et al. Cloning and characterization of BES1/BZR1 transcription factor genes in maize. Plant Growth Regulation, 2018, 86(2): 235-249. |
| 11 | Kesawat M S, Kherawat B S, Singh A, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the brassinazole-resistant (BZR) gene family and its expression in the various developmental stage and stress conditions in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22: 8743. |
| 12 | Yin Y, Wang Z Y, Mora-Garcia, et al. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteriods to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell, 2002, 109(2): 181-191. |
| 13 | Sun Y, Fan X Y, Cao D M, et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Developmental Cell, 2010, 19(5): 765-777. |
| 14 | Wang Z Y, Nakano T, Gendron J, et al. Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Developmental Cell, 2002, 2(4): 505-513. |
| 15 | Arshad M, Feyissa B A, Amyot L, et al. MicroRNA156 improves drought stress tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) by silencing SPL13. Plant Science, 2017, 258: 122-136. |
| 16 | Chen H, Zeng Y, Yang Y, et al. Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2494. |
| 17 | Yin H, Yuan Y Y, Song T T, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of Medicago sativa L. YABBY gene family and its response to abiotic stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(2): 416-424. |
| 尹航, 袁玉莹, 宋婷婷, 等. 紫花苜蓿(Medicago sativa L.)YABBY基因家族的生物信息学分析及其对逆境胁迫的响应.分子植物育种, 2020, 18(2): 416-424. | |
| 18 | Liu H, Li X Y, He F, et al. Identification of the alfalfa SAUR gene family and its expression pattern under abiotic stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 等. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. | |
| 19 | Li X Y, Liu H, He F, et al. Identification and expression pattern of the WRKY transcription factor family in Medicago sativa. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 等. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. | |
| 20 | Chou K C, Shen H B. Cell-PLoc 2.0: an improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Natural Science, 2010, 2(10): 1090-1103. |
| 21 | Yin J L, Liu M Y, Ma D F, et al. Identification of circular RNAs and their targets during tomato fruit ripening. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2018, 136: 90-98. |
| 22 | Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2021, 38(7): 3022-3027. |
| 23 | Chen C, Wu Y, Li J, et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16(11): 1733-1742. |
| 24 | O’Rourke J A, Fu F, Bucciarelli B, et al. The Medicago sativa gene index 1.2: a web-accessible gene expression atlas for investigating expression differences between Medicago sativa subspecies. BMC Genomics, 2015, 16(1): 502. |
| 25 | Dong X, Deng H, Ma W, et al. Genome-wide identification of the MADS-box transcription factor family in autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and expression analysis under abiotic stress. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 603. |
| 26 | Sun F, Yu H, Qu J, et al. Maize ZmBES1/BZR1-5 decreases ABA sensitivity and confers tolerance to osmotic stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 996. |
| 27 | Liu D, Cui Y, Zhao Z, et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the BES/BZR gene family in wheat and foxtail millet. BMC Genomics, 2021, 22(1): 682. |
| 28 | Wang Z, Wang X, Zhang H, et al. A genome-wide association study approach to the identification of candidate genes underlying agronomic traits in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(3): 611-613. |
| 29 | Li X, Brummer E C. Applied genetics and genomics in alfalfa breeding. Agronomy, 2012, 2(1): 40-61. |
| 30 | Li Y, He L, Li J, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression profiling of the legume BZR transcription factor gene family. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1332. |
| 31 | Li C, Liu X J, Cai P, et al. Genome-wide identification and bioinformatics analysis of BZR gene family in pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.). Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022, 20(19): 6324-6330. |
| 李春, 刘小俊, 蔡鹏, 等. 中国南瓜BZR基因家族的全基因组鉴定及生物信息学分析. 分子植物育种, 2022, 20(19): 6324-6330. | |
| 32 | Jiang Q Q, Wang Y T, Hui Z M. Identification and expression analysis of BZR gene family in grapevine. Plant Physiology Journal, 2021, 57(6): 1218-1228. |
| 江倩倩, 王雨婷, 惠竹梅. 葡萄BZR基因家族的鉴定及表达分析. 植物生理学报, 2021, 57(6): 1218-1228. | |
| 33 | Du Q L, Liu J X, Chen M Q, et al. Identification of sorghum BR signal transcription factor BZR1 gene family and analysis of hormone response. Journal of Plant Protection, 2022, 49(3): 848-856. |
| 杜巧丽, 刘均霞, 陈美晴, 等. 高粱BR信号转录因子BZR1基因家族的鉴定及激素应答分析. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49(3): 848-856. | |
| 34 | Zhang Q, Yan X Y, Zuo C L, et al. Evolution and brassinosteroid response analysis of the BZR1 gene family in soybean. Journal of Hebei Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 47(6): 620-627. |
| 张晴, 严新悦, 左春柳, 等. 大豆BZR1基因家族进化与油菜素内酯响应分析. 河北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(6): 620-627. | |
| 35 | Chen X, Shen C Y, Mo F L, et al. Identification of BZR gene family in tomato and expression patterns analysis under abiotic stress. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2021, 52(11): 9-17. |
| 陈旭, 沈春洋, 莫福磊, 等. 番茄BZR基因家族鉴定及非生物胁迫下表达模式分析. 东北农业大学学报, 2021, 52(11): 9-17. | |
| 36 | Hernandez G C M, Finer J J. Identification and validation of promoters and cis-acting regulatory elements. Plant Science, 2014, 217: 109-119. |
| 37 | Li H, Ye K, Shi Y, et al. BZR1 positively regulates freezing tolerance via CBF-dependent and CBF-independent pathways in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(4): 545-559. |
| 38 | Wei N, Li Y P, Ma Y T, et al. Genome-wide identification of the alfalfa TCP gene family and analysis of gene transcription patterns in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under drought stress. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. |
| 魏娜, 李艳鹏, 马艺桐, 等. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿TCP基因家族的鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下表达模式分析. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 118-130. | |
| 39 | Cui C, Wang H, Hong L, et al. MtBZR1 plays an important role in nodule development in Medicago truncatula. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(12): 2941. |
| 40 | Luo S, Zhang G, Zhang Z, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of BZR gene family and associated responses to abiotic stresses in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23(1): 1-13. |
| 41 | Jia C G, Zhao S K, Bao T T, et al. Tomato BZR/BES transcription factor SlBZR1 positively regulates BR signaling and salt stress tolerance in tomato and Arabidopsis. Plant Science, 2021, 302: 110719. |
| 42 | Talaat N B, Ibrahim A S, Shawky B T. Enhancement of the expression of ZmBZR1 and ZmBES1 regulatory genes and antioxidant defense genes triggers water stress mitigation in maize (Zea mays L.) plants treated with 24-epibrassinolide in combination with spermine. Agronomy, 2022, 12(10): 2517. |
| 43 | Fan C, Guo G, Yan H, et al. Characterization of brassinazole resistant (BZR) gene family and stress induced expression in Eucalyptus grandis. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2018, 24: 821-831. |
| 44 | Chen X, Wu X, Qiu S, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the BZR transcription factor gene family in Nicotiana benthamiana. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(19): 10379. |
| 45 | Wang W, Su Y Q, Li G L, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression patterns of the BZR transcription factor family in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 1-12. |
| [1] | 崔红丽, 孙明哲, 贾博为, 孙晓丽. 蒺藜苜蓿OSCA基因家族鉴定及低温逆境表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 111-125. |
| [2] | 王晓彤, 李小红, 麻旭霞, 蔡文祺, 冯学丽, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿FBA基因家族成员的鉴定与分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 81-93. |
| [3] | 张盈盈, 胡丹丹, 马春晖, 张前兵. 苜蓿叶片结构和光合特性对菌磷添加的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 133-144. |
| [4] | 马圆, 刘欢, 赵桂琴, 王敬龙, 张然, 姚瑞瑞. 燕麦sHSP基因家族的鉴定及其响应高温及老化的表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 145-158. |
| [5] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [6] | 吴毅, 冯雅岚, 王添宁, 琚吉浩, 肖慧淑, 马超, 张均. 小麦及其祖先物种Hsp70基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 53-67. |
| [7] | 张震欢, 姚立蓉, 汪军成, 司二静, 张宏, 杨轲, 马小乐, 孟亚雄, 王化俊, 李葆春. 盐生草AKR基因家族成员的鉴定及根系盐胁迫响应基因HgAKR42639的耐盐分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 68-83. |
| [8] | 高金柱, 赵东豪, 高乐, 苏喜浩, 何学青. 硝酸铈与脱落酸处理对紫花苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 175-186. |
| [9] | 伍国强, 于祖隆, 魏明. PGPR调控植物响应逆境胁迫的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 203-218. |
| [10] | 谭英, 尹豪. 盐胁迫下根施AMF和褪黑素对紫花苜蓿生长、光合特征以及抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 64-75. |
| [11] | 王敏, 李莉, 贾蓉, 包爱科. 10种紫花苜蓿在低温胁迫下的生理特性及耐寒性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 76-88. |
| [12] | 孔海明, 宋家兴, 杨静, 李倩, 杨培志, 曹玉曼. 紫花苜蓿CAMTA基因家族鉴定及其在非生物胁迫下的表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 143-154. |
| [13] | 何升然, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 汪雪, 王静. 紫花苜蓿/甜高粱间作对根际土壤特性及微生物群落特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 92-105. |
| [14] | 刘昊, 李显炀, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 紫花苜蓿SAUR基因家族的鉴定及其在非生物胁迫中的表达模式研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 135-153. |
| [15] | 李显炀, 刘昊, 何飞, 王雪, 李明娜, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 陈林. 全基因组水平紫花苜蓿WRKY转录因子家族鉴定与表达模式分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 154-170. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||