

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (2): 81-93.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024102
收稿日期:2024-04-02
修回日期:2024-05-08
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2024-11-27
通讯作者:
康文娟,师尚礼
作者简介:shishl@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yuan-yuan DU( ), Wen-juan KANG(
), Wen-juan KANG( ), Shang-li SHI(
), Shang-li SHI( ), Yi-lin HAN, Fu-qiang HE
), Yi-lin HAN, Fu-qiang HE
Received:2024-04-02
Revised:2024-05-08
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2024-11-27
Contact:
Wen-juan KANG,Shang-li SHI
摘要:
紫花苜蓿根瘤的形成发育及幼苗生长受到多重植物激素的调控。激素对外源根瘤菌的增殖和促生效应已有研究,但激素对内生根瘤菌的增殖及促生效应研究较少。因此,筛选出对根瘤菌SM12531f生长有促进作用的3-吲哚乙酸、6-苄氨基嘌呤和28-高油菜素内酯的浓度,然后用这3种浓度分别浸泡含有青色荧光蛋白标记的内生根瘤菌SM12531f的苜蓿种子并种植,分析外源激素对苜蓿植株组织中内生根瘤菌数量、植株结瘤及植株生长的影响。结果表明,3-吲哚乙酸、6-苄氨基嘌呤和28-高油菜素内酯这3种激素的最适浓度分别为14 mg·L-1、18 mg·L-1和2.97 mg·L-1。幼苗期对植株内生根瘤菌增殖、结瘤及生长有益的是6-苄氨基嘌呤和28-高油菜素内酯,且前者的促进效果更明显,前者内生根瘤菌在根部的定殖数量最多,在稀释100倍时定殖数量为1167 cfu·g-1、地上鲜重为1.99 g·株-1。同样在分枝期对植株有益的是6-苄氨基嘌呤,且内生根瘤菌在根部研磨液稀释100倍时定殖数量为833 cfu·g-1、地上鲜重为5.03 g·株-1。因此,对苜蓿内生根瘤菌增殖及苜蓿生长最适的激素是18 mg·L-1的6-苄氨基嘌呤,该发现对精准利用种子内生根瘤菌的结瘤固氮效应提供理论依据,为紫花苜蓿-根瘤菌共生育种奠定了基础。
杜媛媛, 康文娟, 师尚礼, 韩宜霖, 何富强. 外源激素对紫花苜蓿种子内生根瘤菌增殖及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(2): 81-93.
Yuan-yuan DU, Wen-juan KANG, Shang-li SHI, Yi-lin HAN, Fu-qiang HE. Effects of exogenous hormones on the proliferation of endophytic fluorescent labeled rhizobia in seeds and growth of the seedlings[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(2): 81-93.
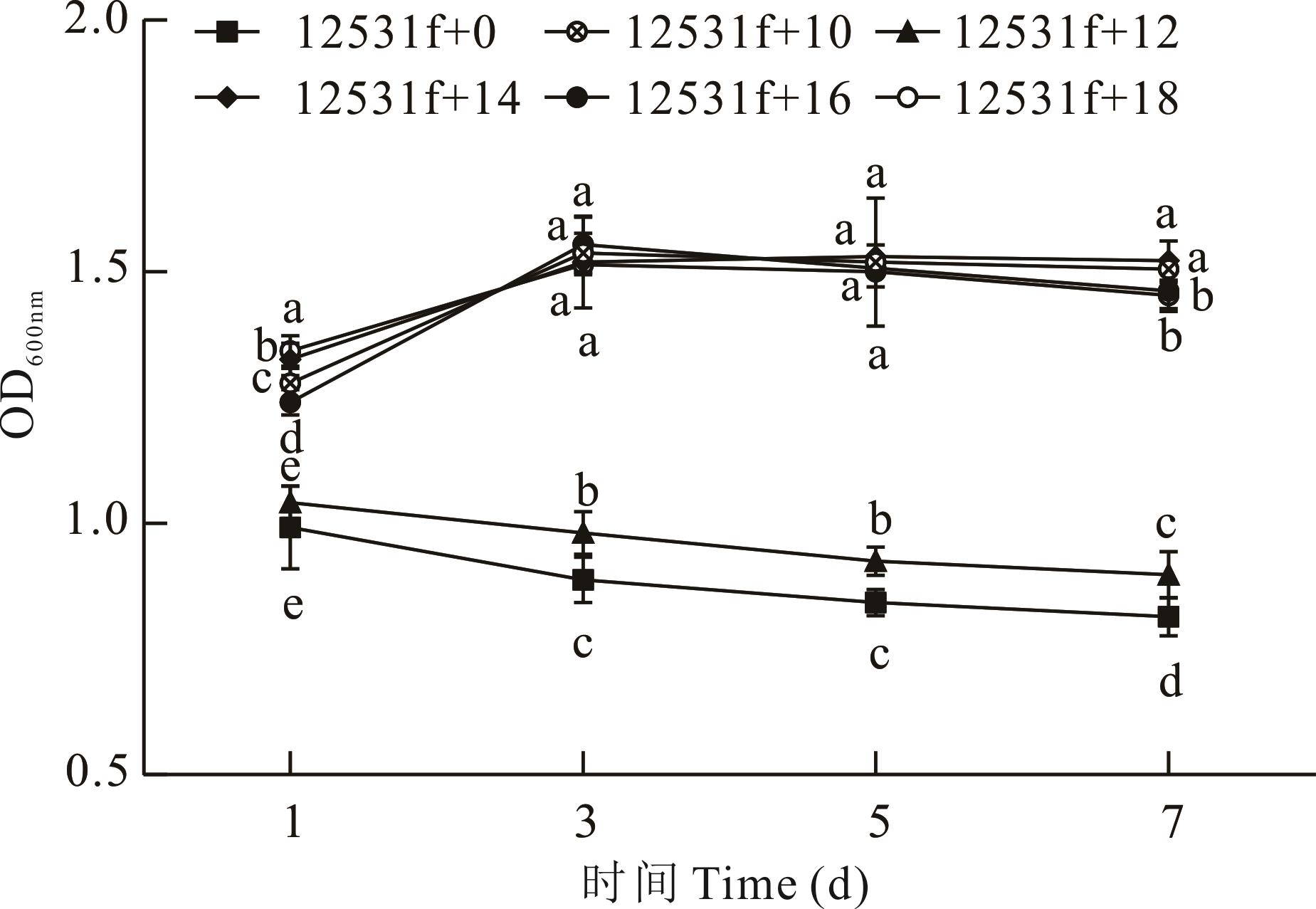
图1 3-吲哚乙酸处理对SM12531f增殖的影响图例为菌株名称+添加浓度,不同小写字母间表示差异显著(P<0.05),为同一检测时间的测定值(平均值±标准差),下同。The legend shows the name of the strain and the concentration added, the difference between different lowercase letters is significant (P<0.05), and the measured values at the same testing time (mean±standard deviation), the same below.
Fig.1 Effect of 3-indoleacetic acid treatment on the proliferation of SM12531f
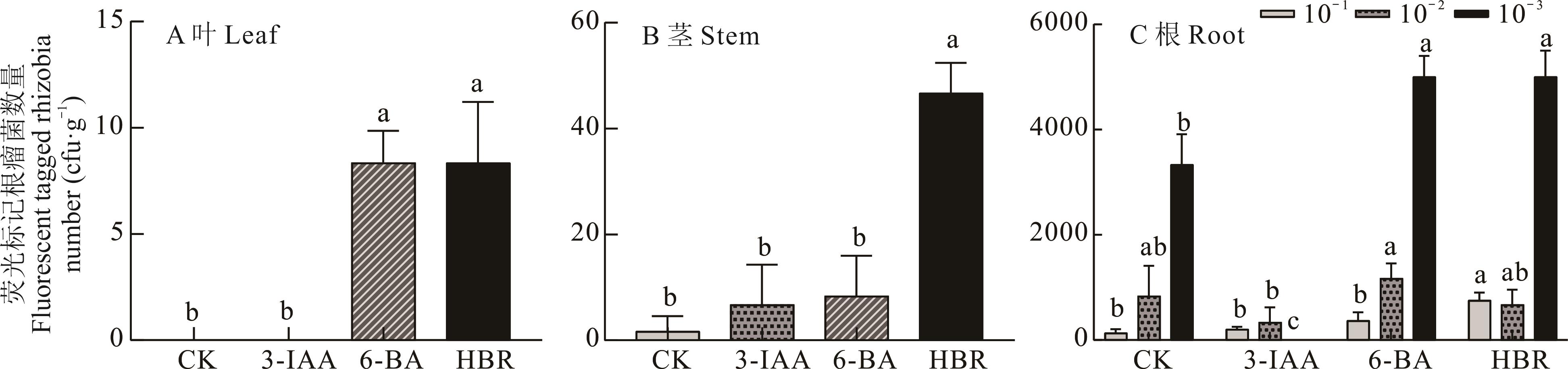
图4 幼苗期苜蓿植株组织内标记内生根瘤菌数量不同小写字母表示同一菌株不同激素处理下差异显著(P<0.05),下同。The different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the same strain under different hormone treatments (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.4 Number of endophytic rhizobia labeled in alfalfa plant tissues at seedling stage
处理 Treatment | 地上鲜重 Aboveground fresh weight | 地上干重 Aboveground dry weight | 地下鲜重 Underground fresh weight | 地下干重 Underground dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.73±0.08ab | 0.23±0.00b | 0.83±0.01b | 0.06±0.00c |
| 3-IAA | 1.62±0.21b | 0.29±0.05ab | 0.68±0.01d | 0.06±0.00c |
| 6-BA | 1.99±0.23a | 0.31±0.02a | 0.73±0.01c | 0.07±0.01b |
| HBR | 1.66±0.15ab | 0.29±0.03ab | 1.40±0.00a | 0.16±0.01a |
表1 幼苗期不同激素对苜蓿植株地上、地下干鲜重的影响
Table 1 The effect of different hormones on the aboveground and belowground dry and fresh weight of alfalfa plants during the seedling stage (g·plant-1)
处理 Treatment | 地上鲜重 Aboveground fresh weight | 地上干重 Aboveground dry weight | 地下鲜重 Underground fresh weight | 地下干重 Underground dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.73±0.08ab | 0.23±0.00b | 0.83±0.01b | 0.06±0.00c |
| 3-IAA | 1.62±0.21b | 0.29±0.05ab | 0.68±0.01d | 0.06±0.00c |
| 6-BA | 1.99±0.23a | 0.31±0.02a | 0.73±0.01c | 0.07±0.01b |
| HBR | 1.66±0.15ab | 0.29±0.03ab | 1.40±0.00a | 0.16±0.01a |
处理 Treatment | 地上干重 Aboveground dry weight | 地上鲜重 Aboveground fresh weight | 地下鲜重 Underground fresh weight | 地下干重 Underground dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.80±0.09ab | 4.28±0.47ab | 2.33±1.00b | 0.36±0.13a |
| 3-IAA | 0.39±0.10c | 2.06±0.48c | 1.19±0.19c | 0.21±0.12a |
| 6-BA | 0.95±0.19a | 5.03±1.20a | 3.91±0.20a | 0.46±0.23a |
| HBR | 0.51±0.20bc | 2.97±1.04bc | 2.19±0.14b | 0.29±0.12a |
表2 分枝期不同激素对苜蓿植株地上、地下干鲜重的影响
Table 2 Effects of different hormones during branching stage on dry and fresh weight of alfalfa plants above and below ground (g·plant-1)
处理 Treatment | 地上干重 Aboveground dry weight | 地上鲜重 Aboveground fresh weight | 地下鲜重 Underground fresh weight | 地下干重 Underground dry weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.80±0.09ab | 4.28±0.47ab | 2.33±1.00b | 0.36±0.13a |
| 3-IAA | 0.39±0.10c | 2.06±0.48c | 1.19±0.19c | 0.21±0.12a |
| 6-BA | 0.95±0.19a | 5.03±1.20a | 3.91±0.20a | 0.46±0.23a |
| HBR | 0.51±0.20bc | 2.97±1.04bc | 2.19±0.14b | 0.29±0.12a |
处理 Treatment | 单株叶片数 Leaf number per plant | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.00±2.00b | 31.66±2.15ab | 19.10±0.30a |
| 3-IAA | 19.00±1.73ab | 29.02±3.21b | 14.80±1.10b |
| 6-BA | 20.00±1.73a | 32.62±2.31a | 18.80±0.80a |
| HBR | 19.33±1.53ab | 29.64±1.09ab | 18.50±0.70a |
表3 幼苗期不同激素对苜蓿植株单株叶片数、株高以及根长的影响
Table 3 Effects of different hormones at seedling stage on leaf number, plant height and root length of alfalfa plant
处理 Treatment | 单株叶片数 Leaf number per plant | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 16.00±2.00b | 31.66±2.15ab | 19.10±0.30a |
| 3-IAA | 19.00±1.73ab | 29.02±3.21b | 14.80±1.10b |
| 6-BA | 20.00±1.73a | 32.62±2.31a | 18.80±0.80a |
| HBR | 19.33±1.53ab | 29.64±1.09ab | 18.50±0.70a |
处理 Treatment | 单株叶片数 Leaf number per plant | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 64.00±21.28a | 32.46±2.51a | 19.13±0.95a |
| 3-IAA | 33.67±5.13b | 35.04±2.05a | 19.23±3.02a |
| 6-BA | 53.33±9.24ab | 35.52±5.81a | 20.13±0.67a |
| HBR | 62.67±2.08a | 34.10±3.90a | 20.20±3.45a |
表4 分枝期不同激素对苜蓿植株单株叶片数、株高以及根长的影响
Table 4 Effects of different hormones at branching stage on leaf number, plant height and root length of alfalfa plant
处理 Treatment | 单株叶片数 Leaf number per plant | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 64.00±21.28a | 32.46±2.51a | 19.13±0.95a |
| 3-IAA | 33.67±5.13b | 35.04±2.05a | 19.23±3.02a |
| 6-BA | 53.33±9.24ab | 35.52±5.81a | 20.13±0.67a |
| HBR | 62.67±2.08a | 34.10±3.90a | 20.20±3.45a |
| 1 | Li Y. Development and utilization and biological characteristics of Medicago sativa L. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 35(1): 84-85,1287. |
| 李妍. 紫花苜蓿的生物学特性及开发利用. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(1): 84-85,1287. | |
| 2 | Wang X Y. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation system in plants. Friend of Chemical Industry, 2006(6): 41-42. |
| 王秀云. 植物的共生固氮体系. 化工之友, 2006(6): 41-42. | |
| 3 | Burgess B K, Lowe D J. Mechanism of molybdenum nitrogenase. Chemical Reviews, 1996, 96(7): 2983-3011. |
| 4 | Seefeldt L C, Hoffman B M, Dean D R. Mechanism of Mo-dependent nitrogenase. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2009, 78(1): 701-722. |
| 5 | Zhang Q L, Lin M, Ping S Z. Biological nitrogen fixation and its application in sustainable agriculture. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2008(2): 1-4. |
| 张秋磊, 林敏, 平淑珍. 生物固氮及在可持续农业中的应用. 生物技术通报, 2008(2): 1-4. | |
| 6 | Li Q, Liu H W, Wang W L. Colonization of Azorhizobium caulinodans in wheat and nutrient-related miRNA expression. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(4): 930-937. |
| 李强, 刘华伟, 王渭玲. 田菁茎瘤固氮根瘤菌在小麦体内的定殖及营养元素相关miRNA的表达. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(4): 930-937. | |
| 7 | Li J F, Zhang S Q, Shi S L, et al. Position and quantity of endogensis rhizobia in alfalfa plant. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2009, 17(6): 1200-1205. |
| 李剑峰, 张淑卿, 师尚礼, 等. 苜蓿内生根瘤菌分布部位与数量变化动态. 中国生态农业学报, 2009, 17(6): 1200-1205. | |
| 8 | Qi J. Screening of alfalfa seeds and its growth-promoting ability. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2006. |
| 祁娟. 苜蓿种子内生根瘤菌筛选及其促生能力研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2006. | |
| 9 | Zhang Y T, Shi S L, Miao Y Y, et al. Effects of KH2PO4 on rhizobia migration and colonization in alfalfa seedlings. Grassland and Turf, 2018, 38(3): 40-49. |
| 张运婷, 师尚礼, 苗阳阳, 等. 磷酸二氢钾对苜蓿幼苗体内根瘤菌运移及定殖的影响. 草原与草坪, 2018, 38(3): 40-49. | |
| 10 | Miao Y Y. Effects of exogenous materials on the migration and colonization of rhizobia in alfalfa plants. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2017. |
| 苗阳阳. 外源物质对苜蓿内生根瘤菌运移定殖的影响研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2017. | |
| 11 | Liu X J. Development and self-regulation of root nodules in legume plants. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(34): 13110-13114. |
| 刘旭娇. 豆科植物根瘤的发育及其自我调整. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(34): 13110-13114. | |
| 12 | Zeng B Q, Qian B. Evaluation and application of auxin and cytokinin in promoting rooting of pines. Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 1990(3): 58-62. |
| 曾斌琦, 钱波. 生长素和细胞分裂素促进松类生根效果的评价及应用. 福建林业科技, 1990(3): 58-62. | |
| 13 | Ke M Y. Mechanism of auxin transport in salicylic acid-induced immune response and soybean nodule development. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2022. |
| 柯美玉. 生长素运输在水杨酸诱导的免疫反应和大豆根瘤发育中的作用机制研究. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2022. | |
| 14 | Zhang S Q. Migration of rhizobia inside alfalfa plants and influencing factors. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 张淑卿. 根瘤菌在苜蓿植株体内的运移及影响因素. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2012. | |
| 15 | Yang Q L. Application technology of plant growth regulator in vegetable production. Agricultural Science and Technology and Information, 2012(23): 21-22. |
| 杨庆礼. 植物生长调节剂在蔬菜生产上的应用技术. 农业科技与信息, 2012(23): 21-22. | |
| 16 | Liu Y. Transcriptional analysis of differentially expressed genes involved in selective nodulation in Bradyrhizobium diazoeficiens at the presence of soybean root exudate. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. |
| 刘尧. 大豆根系分泌物诱导后Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens选择性结瘤相关基因表达差异分析. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018. | |
| 17 | Liu W, Zhao Z F, Feng Y J, et al. Regulation of plant hormones on the formation and development of legumes root nodules. Soybean Science, 2013, 32(2): 262-266. |
| 刘薇, 赵振芳, 冯永君, 等. 植物激素在豆科植物根瘤形成和发育过程中的调控作用. 大豆科学, 2013, 32(2): 262-266. | |
| 18 | Yi C X, Hu J Q, Zhou B Y. Effects of brassinosteroid and gibberellin on chilling resistance and floral formation of Litchi chinensis. South China Fruit Tree, 2024, 53(2): 68-74, 82. |
| 易晨歆, 胡嘉琪, 周碧燕. 油菜素内酯和赤霉素处理对荔枝抗寒性及成花的影响. 中国南方果树, 2024, 53(2): 68-74, 82. | |
| 19 | McGuiness P N, Reid J B, Foo E. The role of gibberellins and brassinosteroids in nodulation and arbuscular mycorrhizal associations. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 269. |
| 20 | Liu C, Shi S L, Kang W J, et al. Effects of storage methods on the transmissibility of endophytic rhizobia from alfalfa seeds. Grassland and Turf, 2022, 42(2): 18-27. |
| 刘畅, 师尚礼, 康文娟, 等. 贮藏方法对紫花苜蓿种子内生根瘤菌传代能力的影响. 草原与草坪, 2022, 42(2): 18-27. | |
| 21 | Huo P H. Antimicrobial-resistant rhizobia screening and effect verification of undesired microbe control in the prepared rhizobia inoculant. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 霍平慧. 耐抑菌剂根瘤菌筛选及耐药菌株制备菌剂抑杂菌效果研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2014. | |
| 22 | Ji Y L. Study on growth-promoting effect of Robinia pseudoacacia rhizobia on Platycodon gradiflorus. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2014, 26(5): 72-75. |
| 冀玉良. 刺槐根瘤菌对桔梗的促生作用研究. 江西农业学报, 2014, 26(5): 72-75. | |
| 23 | Song J Q, Wang Y X, Zhang B. Effects of endogenous hormone change and exogenous auxin on the germination process of alfalfa seed. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(3): 691-696. |
| 宋佳琦, 王玉祥, 张博. 内源激素变化及外源生长素对紫花苜蓿种子萌发过程的影响. 草地学报, 2018, 26(3): 691-696. | |
| 24 | Anuradha S, Seeta Ram Rao S. Effect of brassinosteroids on salinity stress induced inhibition of seed germination and seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Growth Regulation, 2001, 33(2): 151-153. |
| 25 | Kang W J. Biotype classification of Medicago sativa rhizobia and its transcriptome analysis. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 康文娟. 紫花苜蓿根瘤菌生物型划分及其转录组学分析. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2019. | |
| 26 | Li J F, Shi S L, Zhang S Q. Effects of the pH value of an acid environment on early growth and physiology of Medicago sativa W525. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(2): 47-54. |
| 李剑峰, 师尚礼, 张淑卿. 环境酸度对紫花苜蓿早期生长和生理的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(2): 47-54. | |
| 27 | Elsayed A. Induction of rhizobium inoculants harboring salicylic acid gene. Australian Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, 2015. DOI:10.13140/RG.2.1.1869.0724.2015. |
| 28 | Wang S Q, Han X Z, Qiao Y F, et al. Effects of low molecular organic acids on nitrogen accumulation, nodulation, and nitrogen fixation of soybean (Glycine max L.) under phosphorus deficiency stress. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(5): 1079-1084. |
| 王树起, 韩晓增, 乔云发, 等. 缺磷条件下低分子量有机酸对大豆氮积累和结瘤固氮的影响. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(5): 1079-1084. | |
| 29 | Zuo Y M, Liu Y X, Zhang F S. Effects of improvement of iron nutrition by mixed cropping with maize on nodule microstructure and leghaemoglobin content of peanut. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2003(1): 33-38. |
| 左元梅, 刘永秀, 张福锁. 与玉米混作改善花生铁营养对其根瘤形态结构及豆血红蛋白含量的影响. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2003(1): 33-38. | |
| 30 | Che B, Jin C, Zhang S, et al. Expression and identification of replication and transcription-competent ebola virus-like particles. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2017, 33(3): 325-330. |
| 车彬, 金聪, 张硕, 等. 复制型埃博拉病毒样颗粒的表达和鉴定. 病毒学报, 2017, 33(3): 325-330. | |
| 31 | Zhu H R, Liu S, Yu Y P, et al. Research progress on detection methods of plant growth regulators. Fertilizer and Health, 2021, 48(6): 15-18, 53. |
| 朱海荣, 刘爽, 于燕萍, 等. 植物生长调节剂检测方法研究进展. 肥料与健康, 2021, 48(6): 15-18, 53. | |
| 32 | Eva Benková, Michniewicz M, Sauer M, et al. Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell, 2003, 115(5): 591-602. |
| 33 | Pii Y, Crimi M, Cremonese G, et al. Auxin and nitric oxide control indeterminate nodule formation. BMC Plant Biology, 2007, 7(1): 21. |
| 34 | Ferguson B J, Mathesius U. Phytohormone regulation of legume-rhizobia interactions. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 2014, 40(7): 770-790. |
| 35 | Teale W D, Paponov I A, Palme K. Auxin in action: signalling, transport and the control of plant growth and development. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2006, 7(11): 847-859. |
| 36 | Lin J, Roswanjaya Y, Kohlen W, et al. Nitrate restricts nodule organogenesis through inhibition of cytokinin biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 6544. |
| 37 | Nandwal A S, Bharti S. Effect of kinetin and indole acetic acid on growth, yield and nitrogen fixing efficiency of nodules in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 1982, 25(4): 358-363. |
| 38 | Mens C, Li D, Haaima L E, et al. Local and systemic effect of cytokinins on soybean nodulation and regulation of their isopentenyl transferase (IPT) biosynthesis genes following rhizobia inoculation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1105. |
| 39 | Liu D L, Gu W Y, Qin Y L, et al. Effects of exogenous CTK on the growth and character of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Pratacultural Science, 2005, 22(10): 36-40. |
| 刘大林, 谷文英, 秦玉玲, 等. 外源细胞分裂素对紫花苜蓿生长及品质的影响. 草业科学, 2005, 22(10): 36-40. | |
| 40 | Shang X Y, Zhou L F, Shi X Y, et al. Self-activation detection and expression analysis of cytokinin response regulator ARR9 of Medicago truncatula. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2021, 43(12): 1-10. |
| 尚骁尧, 周玲芳, 石欣玥, 等. 蒺藜苜蓿细胞分裂素响应调节因子ARR9自激活检测及表达分析. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(12): 1-10. | |
| 41 | Wang W J, Ma D M, Zhao L J, et al. Effects of 2,4-table brassinolide on enzyme activity and root ion distribution and absorption in alfalfa seedlings. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(6): 1363-1368. |
| 王文静, 麻冬梅, 赵丽娟, 等. 2, 4-表油菜素内酯对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿生理指标及根系离子积累的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(6): 1363-1368. |
| [1] | 郭璟, 王越, 祁存英, 李静. 内生真菌浸种对燕麦生长和根部内生真菌群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(1): 151-160. |
| [2] | 伍国强, 于祖隆, 魏明. PGPR调控植物响应逆境胁迫的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 203-218. |
| [3] | 邹晓璐, 张文静, 吕红, 秦楠, 赵晓军, 殷辉, 任璐. 醉鱼草内生细菌 ZJ1的生物学特性及防病促生效果[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 106-114. |
| [4] | 程鑫宇, 王继莲, 麦日艳古·亚生null, 李明源. 盐爪爪根际土壤产IAA菌株分离及促生特性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 110-121. |
| [5] | 孟超楠, 赵玉洁, 陈佳欣, 张旖璐, 王彦佳, 冯丽荣, 孙玉刚, 郭长虹. 2株青贮玉米根际固氮菌的筛选鉴定及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 174-185. |
| [6] | 亓琳, 包云, 杨莹博, 王晓凌, 赵威. 硝态氮诱导细胞分裂素强化燕麦锶富集机制的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 74-82. |
| [7] | 朱城强, 温绍福, 江润海, 张梅, 蔡治宏, 何玥琛, 陈鑫, 侯秀丽. 铅胁迫下吲哚乙酸对狗牙根铅累积及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 96-107. |
| [8] | 崔婷, 王勇, 马晖玲. 外源IAA作用下草地早熟禾中调控Cd长距离运输的关键基因表达及其代谢通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 146-156. |
| [9] | 刘晓婷, 姚拓. 高寒草地耐低温植物根际促生菌的筛选鉴定及特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 178-187. |
| [10] | 陈意超, 孙晓莹, 解智杰, 周攀, 张露, 高雪莉, 李东, 刘晓风. 根际促生菌的筛选及其在尾矿改良中的应用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 50-63. |
| [11] | 张晴, 邢静, 姚佳明, 殷庭超, 黄心如, 何悦, 张敬, 徐彬. 多年生黑麦草细胞分裂素信号通路B类ARR转录因子LpARR10的耐镉功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 135-143. |
| [12] | 吴慧丽, 田薇, 纪燕玲, 娄来清, 蔡庆生. 促进镉吸收积累的植物根际促生菌的筛选及其对一年生黑麦草的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 53-61. |
| [13] | 张宁, 曹允馨, 徐伟, 常智慧. 干旱胁迫下污泥对草地早熟禾生长及激素代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 167-176. |
| [14] | 漫静, 唐波, 邓波, 李佳欢, 何玉娟, 张佳良. 羊草根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 59-71. |
| [15] | 周瀚洋, 孙鹏越, 尉欣荣, 周雨, 张智伟, 高金柱, 赵东豪, 罗艺岚, 呼天明, 付娟娟. 琥珀酸黄杆菌缓解遮阴对多年生黑麦草胁迫的效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 137-143. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||