

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (3): 174-185.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2023151
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
孟超楠1( ), 赵玉洁1(
), 赵玉洁1( ), 陈佳欣1, 张旖璐1, 王彦佳1, 冯丽荣2, 孙玉刚1, 郭长虹1(
), 陈佳欣1, 张旖璐1, 王彦佳1, 冯丽荣2, 孙玉刚1, 郭长虹1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-08
修回日期:2023-06-28
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2023-12-27
通讯作者:
郭长虹
作者简介:. E-mail: kaku3008@126.com基金资助:
Chao-nan MENG1( ), Yu-jie ZHAO1(
), Yu-jie ZHAO1( ), Jia-xin CHEN1, Yi-lu ZHANG1, Yan-jia WANG1, Li-rong FENG2, Yu-gang SUN1, Chang-hong GUO1(
), Jia-xin CHEN1, Yi-lu ZHANG1, Yan-jia WANG1, Li-rong FENG2, Yu-gang SUN1, Chang-hong GUO1( )
)
Received:2023-05-08
Revised:2023-06-28
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2023-12-27
Contact:
Chang-hong GUO
摘要:
为了获得优良的固氮菌,并评价其对青贮玉米的促生效果,本研究采用稀释涂布平板法,利用阿须贝氏固体培养基从青贮玉米根际土壤中分离筛选到10株固氮菌,对其固氮能力进行分析,结果表明,菌株ZL-2和ZL-13的固氮能力较强,菌株ZL-2的固氮量为1.07 μg·mL-1,ZL-13的固氮量为0.95 μg·mL-1。通过细菌形态学、16S rDNA序列分析和生理生化特征,确定菌株ZL-2为生癌肠杆菌和ZL-13为成团泛菌。对2株固氮菌的促生特性进行分析,结果表明,2个菌株具有泌铵能力、溶磷能力、产嗜铁素能力和合成吲哚-3-乙酸(IAA)的能力。盆栽试验结果表明,接种固氮菌ZL-2和ZL-13能够显著提高青贮玉米的株高、根长、地上和地下干、鲜重(P<0.05)。田间试验结果表明,2株固氮菌单接种和双接种均能提高青贮玉米的株高、茎粗、产量、粗蛋白含量和全磷含量(P<0.05)。接种2株固氮菌的青贮玉米,其氮代谢和氨同化相关基因(ZmAMT-4、ZmAMTB、ZmGOGAT2和ZmGS1-3)的表达量显著提高(P<0.05)。因此,2株固氮菌具有较好的促生特性,在提高青贮玉米的产量和品质方面发挥了重要作用,是开发微生物菌剂的优质菌种资源。
孟超楠, 赵玉洁, 陈佳欣, 张旖璐, 王彦佳, 冯丽荣, 孙玉刚, 郭长虹. 2株青贮玉米根际固氮菌的筛选鉴定及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 174-185.
Chao-nan MENG, Yu-jie ZHAO, Jia-xin CHEN, Yi-lu ZHANG, Yan-jia WANG, Li-rong FENG, Yu-gang SUN, Chang-hong GUO. Screening and identification of two strains of nitrogen-fixing bacteria from the silage maize rhizosphere and their roles in plant growth promotion[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(3): 174-185.
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5′→3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 铵转运蛋白基因 ZmAMTB | CTACTGGGTAACTGCTGTCT | AACCCATCCACACGAGA |
| 谷氨酰胺合成酶基因 ZmGS1-3 | CTTCTGTATCCCTGAATCTACC | GTTACCGCATCATTGTCC |
| 谷氨酸合成酶基因 ZmGOGAT2 | TAGTGTTCCAACCTCTTTCC | AACACACCTTCCACGTTAG |
| 铵转运蛋白基因 ZmAMT-4 | TGACCTAATTGGTCGTGC | ATGGGGTCGCAAAGG |
| 内参基因 GADPH | TGGGCCTACTGGTCTTACTACTGA | ACATACCCACGCTTCAGATCCT |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence
基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列 Forward primer sequence (5′→3′) | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 铵转运蛋白基因 ZmAMTB | CTACTGGGTAACTGCTGTCT | AACCCATCCACACGAGA |
| 谷氨酰胺合成酶基因 ZmGS1-3 | CTTCTGTATCCCTGAATCTACC | GTTACCGCATCATTGTCC |
| 谷氨酸合成酶基因 ZmGOGAT2 | TAGTGTTCCAACCTCTTTCC | AACACACCTTCCACGTTAG |
| 铵转运蛋白基因 ZmAMT-4 | TGACCTAATTGGTCGTGC | ATGGGGTCGCAAAGG |
| 内参基因 GADPH | TGGGCCTACTGGTCTTACTACTGA | ACATACCCACGCTTCAGATCCT |
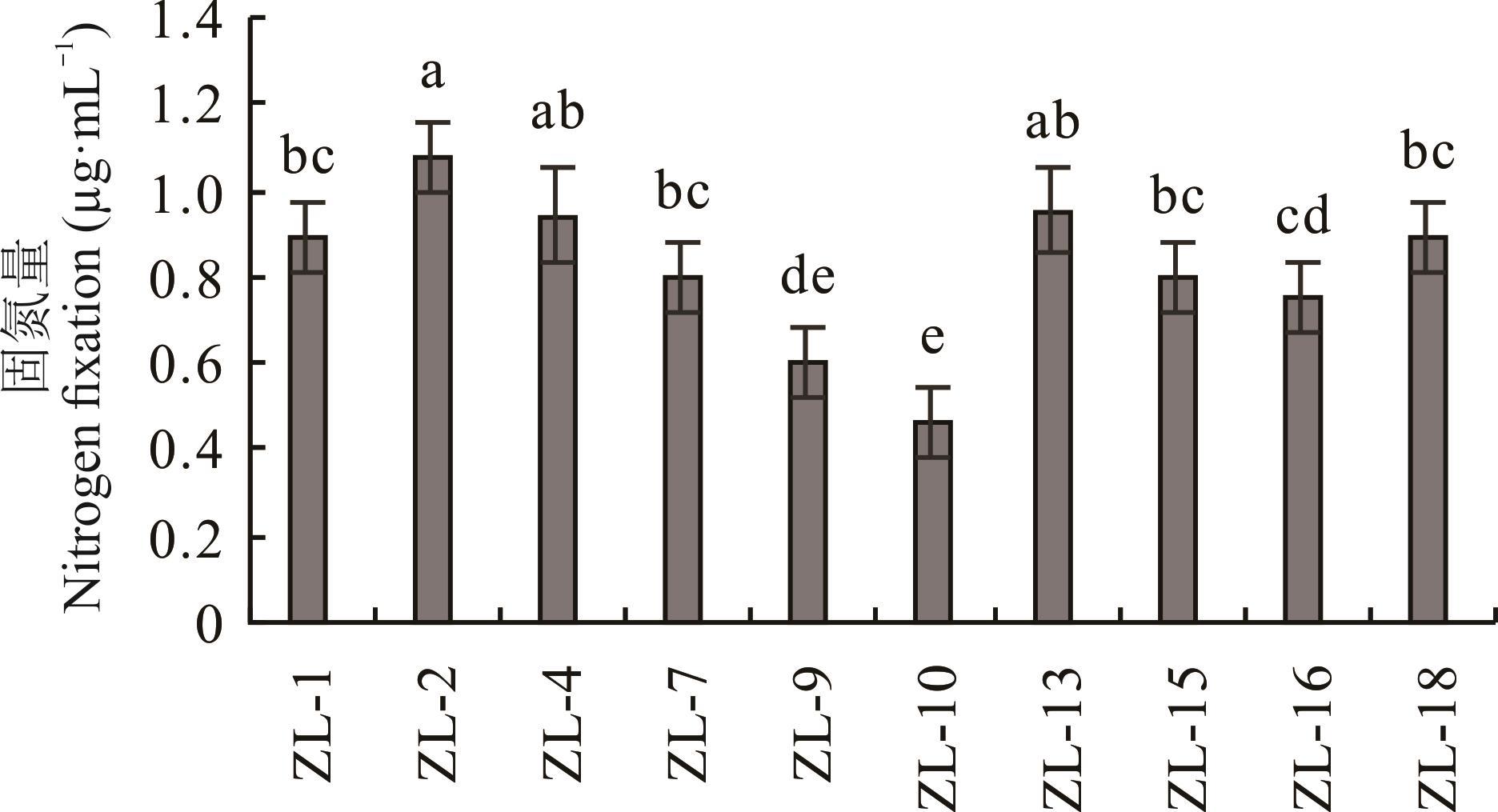
图1 菌株的固氮能力不同小写字母表示不同处理之间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Nitrogen fixation capacity of strains
指标 Index | 菌株 Strains | |
|---|---|---|
| ZL-2 | ZL-13 | |
| 甲基红 Methyl red | - | + |
| 伏普 Voges-proskaue | + | + |
| 吲哚 Indole | + | + |
| 葡萄糖 Glucose | + | - |
| 柠檬酸盐 Citrate | + | + |
| 接触酶 Catalase | + | + |
| 淀粉水解 Starch hydrolysis | + | + |
| 硫化氢 H2S | - | - |
| 明胶液化 Gelatin liquefaction | - | - |
| 脲酶 Urease | + | - |
| 革兰氏染色 Gram stain | - | - |
表2 菌株ZL-2和ZL-13生理生化特征
Table 2 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of strains ZL-2 and ZL-13
指标 Index | 菌株 Strains | |
|---|---|---|
| ZL-2 | ZL-13 | |
| 甲基红 Methyl red | - | + |
| 伏普 Voges-proskaue | + | + |
| 吲哚 Indole | + | + |
| 葡萄糖 Glucose | + | - |
| 柠檬酸盐 Citrate | + | + |
| 接触酶 Catalase | + | + |
| 淀粉水解 Starch hydrolysis | + | + |
| 硫化氢 H2S | - | - |
| 明胶液化 Gelatin liquefaction | - | - |
| 脲酶 Urease | + | - |
| 革兰氏染色 Gram stain | - | - |

图3 菌株ZL-2和ZL-13泌铵、溶磷、产嗜铁素及合成IAA能力同一色氨酸浓度下比较不同菌株合成IAA的差异性。Differences in IAA synthesis were compared among different strains at the same tryptophan concentration. *表示差异在P<0.05水平显著,**表示差异在P<0.01水平显著,***表示差异在P<0.001水平显著。* stands for significant difference at P<0.05 level, ** stands for significant difference at P<0.01, *** stands for significant difference at P<0.001.
Fig.3 Ammonium secretion, phosphorus solubilization, iron carrier and IAA production abilities of strains ZL-2 and ZL-13
处理组 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 地上鲜重 Fresh weight of shoot (g·plant-1) | 地下鲜重 Fresh weight of roots (g·plant-1) | 地上干重 Dry weight of shoot (g·plant-1) | 地下干重 Dry weight of roots (g·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 52.34±2.91c | 21.26±0.93c | 19.20±1.37b | 4.84±0.44b | 2.66±0.38b | 1.78±0.05b |
| ZL-2 | 76.50±3.64a | 29.82±0.31b | 29.78±0.20a | 7.31±0.06a | 4.12±0.02a | 2.61±0.05a |
| ZL-13 | 71.78±2.82b | 32.80±0.96a | 28.94±0.23a | 7.45±0.01a | 3.93±0.03a | 2.63±0.02a |
表3 接种菌株ZL-2和ZL-13对青贮玉米幼苗生物量的影响
Table 3 Effect of strains ZL-2 and ZL-13 inoculated on the biomass of silage maize seedlings
处理组 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 地上鲜重 Fresh weight of shoot (g·plant-1) | 地下鲜重 Fresh weight of roots (g·plant-1) | 地上干重 Dry weight of shoot (g·plant-1) | 地下干重 Dry weight of roots (g·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 52.34±2.91c | 21.26±0.93c | 19.20±1.37b | 4.84±0.44b | 2.66±0.38b | 1.78±0.05b |
| ZL-2 | 76.50±3.64a | 29.82±0.31b | 29.78±0.20a | 7.31±0.06a | 4.12±0.02a | 2.61±0.05a |
| ZL-13 | 71.78±2.82b | 32.80±0.96a | 28.94±0.23a | 7.45±0.01a | 3.93±0.03a | 2.63±0.02a |
处理组 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (m) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 鲜重 Fresh weight (kg·plant-1) | 干重 Dry weight (kg·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.77±0.03c | 34.56±0.34c | 1.77±0.15c | 1.16±0.11c |
ZL-2 ZL-13 | 3.10±0.03ab 3.07±0.04b | 39.36±0.25b 39.20±0.41b | 2.13±0.05ab 2.05±0.04b | 1.42±0.06ab 1.35±0.03b |
| ZL-2+ZL-13 | 3.15±0.09a | 40.04±0.54a | 2.19±0.02a | 1.50±0.06a |
表4 接种固氮菌对田间青贮玉米生物量的影响
Table 4 Effect of nitrogen-fixing strains inoculated on the biomass of silage maize in the field
处理组 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (m) | 茎粗 Stem diameter (mm) | 鲜重 Fresh weight (kg·plant-1) | 干重 Dry weight (kg·plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.77±0.03c | 34.56±0.34c | 1.77±0.15c | 1.16±0.11c |
ZL-2 ZL-13 | 3.10±0.03ab 3.07±0.04b | 39.36±0.25b 39.20±0.41b | 2.13±0.05ab 2.05±0.04b | 1.42±0.06ab 1.35±0.03b |
| ZL-2+ZL-13 | 3.15±0.09a | 40.04±0.54a | 2.19±0.02a | 1.50±0.06a |

图6 接种菌株ZL-2和ZL-13对青贮玉米根、茎、叶中氮代谢和氨同化基因相对表达量的影响
Fig.6 Effects of strains ZL-2 and ZL-13 inoculated on the relative expression of nitrogen metabolism and ammonia assimilation genes in roots, stems and leaves of silage maize
| 1 | Nilahyane A, Islam M A, Mesbah A O, et al. Growth, water productivity, nutritive value, and physiology responses of silage corn to water stress. Agronomy Journal, 2020, 112: 1625-1635. |
| 2 | Zhao M, Feng Y, Shi Y, et al. Yield and quality properties of silage maize and their influencing factors in China. SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences, 2022, 65(8): 1655-1666. |
| 3 | Morugán-Coronado A, Linares C, Gómez-López M D, et al. The impact of intercropping, tillage and fertilizer type on soil and crop yield in fruit orchards under Mediterranean conditions: A meta-analysis of field studies. Agricultural Systems, 2020, 178: 10. |
| 4 | Acosta-Motos J R, Penella C, José A. Towards a sustainable agriculture: strategies involving phytoprotectants against salt stress. Agronomy, 2020, 10(2): 194. |
| 5 | Dechorgnat J, Francis K L, Dhugga K S, et al. Tissue and nitrogen-linked expression profiles of ammonium and nitrate transporters in maize. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 206. |
| 6 | Carpici E B, Kuscu H, Karasu A, et al. Effect of drip irrigation levels on dry matter yield and silage quality of maize (Zea mays L.). Romanian Agricultural Research, 2017, 34: 293-299. |
| 7 | Castellano H A, Perez T V, Bedmar J E. Purple corn-associated rhizobacteria with potential for plant growth promotion. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2018, 124: 1254-1264. |
| 8 | Thanh N C, Le V B, Minh T T H. Pseudomonas PS01 isolated from maize rhizosphere alters root system architecture and promotes plant growth. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(4): 471. |
| 9 | Wang X M, Chen Z H, Li Y C, et al. Effects of different nitrogen forms and ratios on the growth of Phyllostachys edulis and Quercus glauca seedlings. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(9): 2655-2661. |
| 王兴萌, 陈志豪, 李永春, 等. 氮素形态及配比对毛竹和青冈实生苗生长特性的影响. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(9): 2655-2661. | |
| 10 | Shen R F. Contribution of ammonium preference characteristics of corn revealed by Nanjing soil to its nitrogen use efficiency. Grain Oil and Feed Technology, 2019(5): 45. |
| 沈仁芳. 南京土壤所揭示玉米铵偏好特性对其氮肥利用率的贡献. 粮油与饲料科技, 2019(5): 45. | |
| 11 | Adriana A, Fernando H S A, Heinzmann Júlia H, et al. Paenibacillus helianthi sp. nov., a nitrogen fixing species isolated from the rhizosphere of Helianthus annuus L. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2018, 111(12): 2463-2471. |
| 12 | Li Q J, Cheng J J, Sun S X, et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of associative nitrogen-fixing endophytic bacterium Kosakonia radicincitans GXGL-4A in maize. Microbiology China, 2016, 43(11): 2456-2463. |
| 李琼洁, 程杰杰, 孙帅欣, 等. 玉米联合固氮菌Kosakonia radicincitans GXGL-4A的分离鉴定与固氮特性研究. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(11): 2456-2463. | |
| 13 | Wang C, Ling J, Zhang Y Y, et al. Isolation, characterization and culture optimization of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from rhizosphere sediments of Halophila ovalis. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2018, 58(5): 817-829. |
| 王聪, 凌娟, 张燕英, 等. 海洋固氮菌和解磷菌的分离鉴定及发酵条件优化. 微生物学报, 2018, 58(5): 817-829. | |
| 14 | Jiang Y, Wu Y, Wang G W, et al. Plant growth-promoting bacterium Variovorax sp. JX14 from calcareous alluvial soil: characterization and growth promotion on peanuts. Soils, 2015, 47(4): 698-703. |
| 姜瑛, 吴越, 王国文, 等. 一株固氮解磷菌的筛选鉴定及其对花生的促生作用研究. 土壤, 2015, 47(4): 698-703. | |
| 15 | Glickmann E, Dessaux Y. A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1995, 61(2): 793-796. |
| 16 | Lin Q M, Zhao X R, Sun Y X, et al. Community characters of soil phosphobacteria in four ecosystems. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2000, 9(1): 34-37. |
| 林启美, 赵小蓉, 孙焱鑫, 等. 四种不同生态系统的土壤解磷细菌数量及种群分布. 土壤与环境, 2000, 9(1): 34-37. | |
| 17 | Wang P, Dong B, Li F D, et al. Detection and determination of the siderophores produced by wheat rhizobacteria. Microbiology China, 1994(6): 323-326. |
| 王平, 董飚, 李阜棣, 等. 小麦根圈细菌铁载体的检测. 微生物学通报, 1994(6): 323-326. | |
| 18 | Dong X Z, Cai M Y. Handbook for the identification of common bacterial systems. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. |
| 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. | |
| 19 | Zhang Y. Screening plant growth promoting rhizobacteria resources and their promotion mechanisms from rhizosphere of four forages in Ali Alpine grassland of Tibet. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2013. |
| 张英. 西藏阿里高寒草原四种牧草根际促生菌资源筛选及促生机理研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013. | |
| 20 | Li Y Z, Redmann R E, Zhu T C, et al. Nitrogen fixation in Leymus chinensis grassland in Northeast China. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2002, 10(3): 164-166. |
| 李玉中, Redmann R E, 祝廷成, 等. 羊草草原豆科牧草生物固定量研究. 草地学报, 2002, 10(3): 164-166. | |
| 21 | Buchanan R E, Gibbons N E. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Beijing: Science Press, 1984. |
| Buchanan R E, Gibbons N E. 伯杰细菌鉴定手册. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984. | |
| 22 | Kocagöz T, Yilmaz E, Ozkara S, et al. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum samples by polymerase chain reaction using a simplified procedure. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 1993, 31(6): 1435-1438. |
| 23 | Weatherburn M W. Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Analytical Chemistry, 1967, 39(8): 971-974. |
| 24 | Leveau J H J, Gerards S. Discovery of a bacterial gene cluster for catabolism of the plant hormone indole 3-acetic acid. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2008, 65(2): 238-250. |
| 25 | Zhang X S. Analysis of the factors affecting the available P content in the fermentation liquid of P bacteria determined by Mo-Sb colorimetry. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(12): 4822-4823. |
| 张祥胜. 钼锑抗比色法测定磷细菌发酵液中有效磷含量测定值的影响因素分析. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(12): 4822-4823. | |
| 26 | Xie Z L, Yang M J, Gu K D, et al. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of bacterial liquid concentration of ralstonia solanacearum. Journal of Xichang University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 36(2): 13-16. |
| 谢祯璐, 杨梦婕, 顾康蝶, 等. 分光光度计法测定不同分离源青枯雷尔氏菌菌液浓度. 西昌学院学报(自然科学版), 2022, 36(2): 13-16. | |
| 27 | Liu J J, Wei Z, Li J H. Effects of copper on leaf membrane structure and root activity of maize seedling. Botanical Studies, 2014, 55(1): 1-6. |
| 28 | Liu M Y, Lei C Y, Li J J, et al. Differential physiological and biochemical responses of cucumber to the feeding by Bemisia tabaci B and Q biotypes. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(13): 2514-2523. |
| 刘明杨, 雷彩燕, 李静静, 等. 黄瓜对B型和Q型烟粉虱取食的不同生理生化反应. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(13): 2514-2523. | |
| 29 | Bochinnock X H. Methods for biochemical analysis of plants. Jing J H, Ding Z R, translated. Beijing: Science Press, 1981. |
| Bochinnock X H. 植物生物化学分析方法. 荆家海, 丁钟荣, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981. | |
| 30 | Liu Y Q, Wang Y H, Kong W L, et al. Identification, cloning and expression patterns of the genes related to phosphate solubilization in Burkholderia multivorans WS-FJ9 under different soluble phosphate levels. AMB Express, 2020, 10(1): 1-11. |
| 31 | Lu K, Song Z G. Effects of different sprayed nanomaterials on the phosphorus content in rice seedlings. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(1): 28-36. |
| 32 | Wang J, Han J L, Yang M, et al. Study on the nitrogen uptake and metabolism in different nitrogen efficient maize varieties. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(12): 2800-2812. |
| 王健, 韩金玲, 杨敏, 等. 不同氮高效玉米品种对氮素的吸收转运和代谢研究. 核农学报, 2020, 34(12): 2800-2812. | |
| 33 | Li H M, Han G M. Analysis of the ammonium transporter gene family in maize inbred line B73. Journal of Anqing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 24(1): 73-77. |
| 李红梅, 韩国民. 玉米自交系B73铵转运蛋白基因家族分析. 安庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 24(1): 73-77. | |
| 34 | An Y, Yang X X, Zhang L, et al. Alfalfa MsCBL4 enhances calcium metabolism but not sodium transport in transgenic tobacco under salt and saline-alkali stress. Plant Cell Reports, 2020, 39(8): 997-1011. |
| 35 | Wang H, Wu Y J, An T T, et al. Lateral root elongation enhances nitrogen-use efficiency in maize genotypes at the seedling stage. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2022, 102(12): 5389-5398. |
| 36 | Wu Y G, Wang H X, Zhang Z, et al. The effect and promotion prospect of bio-organic fertilizer containing super-efficient nitrogen-fixing bacteria instead of chemical fertilizer. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 2020, 31(20): 23-24. |
| 武玉国, 王洪祥, 张振, 等. 含超高效固氮菌的生物有机肥替代化肥的效果与推广前景. 农村经济与科技, 2020, 31(20): 23-24. | |
| 37 | Zhang T, Yan L Y, He S, et al. Involvement of the ammonium transporter AmtB in nitrogenase regulation and ammonium excretion in Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501. Research in Microbiology, 2012, 163(5): 332-339. |
| 38 | Delaporte Q P, Lovaisa N C, Rapisarda V A, et al. The plant growth promoting bacteria Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus and Azospirillum brasilense contribute to the iron nutrition of strawberry plants through siderophores production. Plant Growth Regulation, 2020, 91(2): 15. |
| 39 | Islam M R, Sultana T, Joe M M, et al. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria with multiple plant growth-promoting activities enhance growth of tomato and red pepper. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2013, 53(12): 1004-1015. |
| 40 | Huang S C, Hou D, Yue H Z, et al. Effects of three growth promoting bacteria and their mixed microbial agents on growth and quality of lettuce. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(7): 1212-1221. |
| 黄书超, 侯栋, 岳宏忠, 等. 三株促生菌及其混合微生物菌剂对莴笋生长和品质的影响. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(7): 1212-1221. | |
| 41 | Lelapalli S, Baskar S, Jacob S M, et al. Characterization of phosphate solubilizing plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Lysinibacillus pakistanensis strain PCPSMR15 isolated from Oryza sativa. Current Research in Microbial Sciences, 2021, 2(2): 100080. |
| 42 | Zhao W S, Guo Q G, Yu W Q, et al. Phosphate solubilizing characteristics of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PHODB35 and its growth-promoting effect on tomato. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020, 60(7): 1370-1383. |
| 赵卫松, 郭庆港, 于稳欠, 等. 解淀粉芽胞杆菌PHODB35的溶磷特性及其对番茄的促生作用. 微生物学报, 2020, 60(7): 1370-1383. | |
| 43 | Liu Y P, Teng S S, Zhao L. Identification of a siderophore-producing bacterium Pseudomonas putida A3 and its growth-promoting effects on cucumber seedings. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011, 17(6): 1507-1514. |
| 刘艳萍, 滕松山, 赵蕾. 高产嗜铁素恶臭假单胞菌A3菌株的鉴定及其对黄瓜的促生作用. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(6): 1507-1514. | |
| 44 | Khare E, Arora N K. Effect of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in suppression of charcoal rot disease of chickpea. Current Microbiology, 2010, 61(1): 64-68. |
| 45 | Ham S H, Yoon A R, Oh H E, et al. Plant growth-promoting microorganism Pseudarthrobacter sp. NIBRBAC000502770 enhances the growth and flavonoid content of Geum aleppicum. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(6): 1241. |
| 46 | Zhang X, Tong J, Dong M, et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of nitrogen fixing endophytic bacteria and their effects on cassava production. PeerJ, 2022, 25(10): e12677. |
| 47 | Xu X P, Fu X D, Liao H. Advances in study of ammonium assimilation and its regulatory mechanism in plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 152-166. |
| 徐晓鹏, 傅向东, 廖红. 植物铵态氮同化及其调控机制的研究进展. 植物学报, 2016, 51(2): 152-166. | |
| 48 | Hou S Q, He S, Dou Y T, et al. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of ammonium transporter encoding genes amtB in associative nitrogen-fixing bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2007, 21(6): 572-576. |
| 侯胜强, 何升, 窦岳坦, 等. 固氮斯氏假单胞菌铵载体amtB基因的功能和结构分析. 核农学报, 2007, 21(6): 572-576. | |
| 49 | Li Y B, Li Y L, Zhang H W, et al. Diazotrophic Paenibacillus beijingensis BJ-18 provides nitrogen for plant and promotes plant growth, nitrogen uptake and metabolism. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10(10): 1119. |
| 50 | Brambilla S, Soto G, Odorizzi A, et al. Spontaneous mutations in the nitrate reductase gene napC drive the emergence of eco-friendly low-N2O-emitting alfalfa rhizobia in regions with different climates. Microbial Ecology, 2020, 79(4): 1044-1053. |
| [1] | 岳海旺, 魏建伟, 王广才, 刘朋程, 陈淑萍, 卜俊周. 基于环境型鉴定技术划分生态区综合评价黄淮海青贮玉米品种[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 120-138. |
| [2] | 陈嘉慧, 刘文献. 重要牧草组学数据图形可视化展示工具的构建及应用[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 57-67. |
| [3] | 蒋丛泽, 受娜, 高玮, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 陇东旱塬区不同青贮玉米品种生产性能和营养品质综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 216-228. |
| [4] | 管瑾, 郭一荻, 刘凌云, 尹淑霞, 滕珂. 结缕草叶肉细胞原生质体瞬时基因表达系统的构建[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(7): 61-71. |
| [5] | 朱丽丽, 张业猛, 李万才, 赵亚利, 李想, 陈志国. 39个我国不同生态区培育的青贮玉米品种在青海高原适应性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 68-78. |
| [6] | 刘牧野, 郭丽珠, 岳跃森, 武菊英, 范希峰, 肖国增, 滕珂. 干旱胁迫下不同性别野牛草生理及抗氧化酶基因表达差异[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 93-103. |
| [7] | 许浩宇, 赵颖, 阮倩, 朱晓林, 王宝强, 魏小红. 不同混合盐碱下藜麦幼苗的抗性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 122-130. |
| [8] | 付东青, 贾春英, 张力, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 南疆干旱灌溉区青贮玉米农艺性状和发酵品质动态分析及评价[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 111-125. |
| [9] | 李影正, 程榆林, 徐璐璐, 李万松, 严旭, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 周阳, 郑军军, 汪星宇, 张德龙, 程明军, 夏运红, 何建美, 唐祈林. 不同玉米品种(系)的全株、果穗与秸秆青贮特性比较[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 144-156. |
| [10] | 刘晓婷, 姚拓. 高寒草地耐低温植物根际促生菌的筛选鉴定及特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 178-187. |
| [11] | 曾令霜, 李培英, 孙宗玖, 孙晓梵. 两类新疆狗牙根抗旱基因型抗氧化酶保护系统及其基因表达差异分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 122-132. |
| [12] | 蒋紫薇, 刘桂宇, 安昊云, 石薇, 常生华, 张程, 贾倩民, 侯扶江. 种植密度与施氮对玉米/秣食豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. |
| [13] | 赵利清, 郝志刚, 崔笑岩, 彭向永. 赤霉素及其抑制剂调控草地早熟禾生长及赤霉素相关基因表达的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 85-91. |
| [14] | 张国香, 郭卫冷, 毕铭钰, 张力爽, 王丹, 郭长虹. 紫花苜蓿CAX基因家族鉴定及其对非生物胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 106-117. |
| [15] | 赵宁, 马晖玲, 张然, 张金青, 史毅. 丁二醇对热胁迫下匍匐翦股颖内源激素及其相关基因表达水平的调控[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(12): 118-132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||