

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (8): 199-210.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024345
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
王红林1,2( ), 文斌3, 左艳春1,2, 张凯3, 吴子周1,2, 严旭1,2, 袁正才1,2, 邓榆川4, 肖蔹5, 陈慧5, 寇晶1,2, 傅祥超3(
), 文斌3, 左艳春1,2, 张凯3, 吴子周1,2, 严旭1,2, 袁正才1,2, 邓榆川4, 肖蔹5, 陈慧5, 寇晶1,2, 傅祥超3( ), 杜周和1,2(
), 杜周和1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-09
修回日期:2024-10-31
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-06-16
通讯作者:
傅祥超,杜周和
作者简介:E-mail: duzhouhe@126.com基金资助:
Hong-lin WANG1,2( ), Bin WEN3, Yan-chun ZUO1,2, Kai ZHANG3, Zi-zhou WU1,2, Xu YAN1,2, Zheng-cai YUAN1,2, Yu-chuan DENG4, Lian XIAO5, Hui CHEN5, Jing KOU1,2, Xiang-chao FU3(
), Bin WEN3, Yan-chun ZUO1,2, Kai ZHANG3, Zi-zhou WU1,2, Xu YAN1,2, Zheng-cai YUAN1,2, Yu-chuan DENG4, Lian XIAO5, Hui CHEN5, Jing KOU1,2, Xiang-chao FU3( ), Zhou-he DU1,2(
), Zhou-he DU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-09-09
Revised:2024-10-31
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-06-16
Contact:
Xiang-chao FU,Zhou-he DU
摘要:
为探究添加不同比例全株饲料桑对川白獭兔肠道形态、血液生化指标、肌肉中氨基酸含量及经济效益的影响,试验选用35日龄、体重相近[(1132.80±54.73) g]、健康状况良好的川白獭兔幼兔150只(公母各半),随机分为5组,每组30个重复,每个重复1只试兔。分别饲喂对应5种全价饲粮,即饲粮中分别添加0(对照)、6%、12%、18%和24%饲料桑。结果表明:添加12%组回肠及十二指肠绒毛高度最高,添加6%组回肠绒隐比显著高于对照组及添加24%组(P<0.05);添加12%组川白獭兔血液中单核细胞数目显著提高,添加18%组淋巴细胞数目显著提高(P<0.05);添加24%组总胆固醇浓度显著低于对照及添加6%组,添加24%组甘油三酯浓度显著低于对照及其他处理组(P<0.05);添加全株饲料桑对肌肉中氨基酸含量无显著影响(P>0.05),但随着添加比例的增加肌肉中肌苷酸含量显著增加(P<0.05);随着添加比例的增加饲料总成本逐渐降低,毛利润逐渐提高。综上,饲粮中添加全株饲料桑可增加川白獭兔幼兔肠道绒毛高度,降低血液中总胆固醇及甘油三酯浓度,增加肌肉中肌苷酸含量,提高经济效益。本试验条件下全株饲料桑用作川白獭兔幼兔的饲料原料时适宜添加量为24%。
王红林, 文斌, 左艳春, 张凯, 吴子周, 严旭, 袁正才, 邓榆川, 肖蔹, 陈慧, 寇晶, 傅祥超, 杜周和. 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔肠道形态、血液生化指标、肌肉中氨基酸含量及经济效益的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(8): 199-210.
Hong-lin WANG, Bin WEN, Yan-chun ZUO, Kai ZHANG, Zi-zhou WU, Xu YAN, Zheng-cai YUAN, Yu-chuan DENG, Lian XIAO, Hui CHEN, Jing KOU, Xiang-chao FU, Zhou-he DU. Effect of adding dietary whole-plant forage mulberry on the intestinal morphology, blood biochemical indicators, muscle amino acid content and economic return when raising Chuanbai rex rabbits[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(8): 199-210.
原料 Ingredients (%) | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% | 2)营养成分 2)Nutrient level | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米Corn | 18.00 | 18.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 23.00 | 消化能Digestive energy (DE, MJ·kg-1) | 9.49 | 9.45 | 9.47 | 9.49 | 9.51 |
| 麸皮Wheat bran | 13.00 | 11.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 4.00 | 粗蛋白质CP (%) | 15.95 | 15.79 | 15.80 | 15.74 | 15.96 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 17.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 15.00 | 16.00 | 淀粉Starch (%) | 14.93 | 14.63 | 15.33 | 15.26 | 16.35 |
| 苜蓿Alfalfa | 45.00 | 44.00 | 39.00 | 36.00 | 28.00 | 粗纤维CF (%) | 19.06 | 19.30 | 19.35 | 19.18 | 19.32 |
| 砻糠Rice bran | 6.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 中性洗涤纤维NDF (%) | 33.22 | 33.48 | 32.91 | 33.06 | 32.04 |
| 饲料桑Forage mulberry | 0.00 | 6.00 | 12.00 | 18.00 | 24.00 | 酸性洗涤纤维ADF (%) | 22.10 | 22.80 | 22.92 | 23.13 | 23.00 |
| 1)预混料1)Premix | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 半纤维Hemicellulose (%) | 11.12 | 10.68 | 10.00 | 9.93 | 9.04 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 粗灰分Ash (%) | 7.09 | 7.24 | 7.22 | 7.26 | 7.17 |
| 粗脂肪EE (%) | 2.34 | 2.82 | 3.28 | 3.78 | 4.23 | ||||||
| 钙Ca (%) | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.06 | ||||||
| 总磷TP (%) | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.52 | ||||||
| 赖氨酸Lys (%) | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.85 | ||||||
| 蛋氨酸+半胱氨酸Met+Cys (%) | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.64 |
表1 试验饲粮组成及营养水平(干物质基础)
Table 1 Composition and nutrient levels of basal diets (dry matter basis)
原料 Ingredients (%) | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% | 2)营养成分 2)Nutrient level | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玉米Corn | 18.00 | 18.00 | 20.00 | 20.00 | 23.00 | 消化能Digestive energy (DE, MJ·kg-1) | 9.49 | 9.45 | 9.47 | 9.49 | 9.51 |
| 麸皮Wheat bran | 13.00 | 11.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 4.00 | 粗蛋白质CP (%) | 15.95 | 15.79 | 15.80 | 15.74 | 15.96 |
| 豆粕Soybean meal | 17.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 15.00 | 16.00 | 淀粉Starch (%) | 14.93 | 14.63 | 15.33 | 15.26 | 16.35 |
| 苜蓿Alfalfa | 45.00 | 44.00 | 39.00 | 36.00 | 28.00 | 粗纤维CF (%) | 19.06 | 19.30 | 19.35 | 19.18 | 19.32 |
| 砻糠Rice bran | 6.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 中性洗涤纤维NDF (%) | 33.22 | 33.48 | 32.91 | 33.06 | 32.04 |
| 饲料桑Forage mulberry | 0.00 | 6.00 | 12.00 | 18.00 | 24.00 | 酸性洗涤纤维ADF (%) | 22.10 | 22.80 | 22.92 | 23.13 | 23.00 |
| 1)预混料1)Premix | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 半纤维Hemicellulose (%) | 11.12 | 10.68 | 10.00 | 9.93 | 9.04 |
| 合计Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 粗灰分Ash (%) | 7.09 | 7.24 | 7.22 | 7.26 | 7.17 |
| 粗脂肪EE (%) | 2.34 | 2.82 | 3.28 | 3.78 | 4.23 | ||||||
| 钙Ca (%) | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 1.05 | 1.06 | ||||||
| 总磷TP (%) | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.52 | ||||||
| 赖氨酸Lys (%) | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.85 | ||||||
| 蛋氨酸+半胱氨酸Met+Cys (%) | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.64 |
| 组织Tissue | 项目Item | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
回肠 Ileum | 绒毛高度Villus height (V) | 472.99±21.33b | 544.80±16.88a | 556.50±19.72a | 525.76±13.15a | 432.84±24.76b |
| 隐窝深度Crypt depth (C) | 98.10±3.94a | 96.59±4.04a | 100.83±4.96a | 107.47±8.07a | 107.74±6.36a | |
| V/C | 4.82±0.23bc | 5.78±0.23a | 5.73±0.37ab | 5.06±0.34abc | 4.26±0.28c | |
十二指肠 Duodenum | 绒毛高度Villus height | 1120.07±32.86ab | 1030.86±24.33b | 1206.32±29.28a | 1086.62±30.36b | 1086.58±20.64b |
| 隐窝深度Crypt depth | 95.47±8.64b | 89.34±6.02c | 100.20±5.05a | 93.14±4.62b | 106.19±6.85a | |
| V/C | 11.73±0.41a | 11.54±0.69a | 12.04±0.93a | 11.67±0.83a | 11.01±0.66a |
表2 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔回肠和十二指肠形态的影响
Table 2 Effect of whole-plant forage mulberry addition on the morphology of the ileum and duodenum in young Chuanbai rex rabbit (μm)
| 组织Tissue | 项目Item | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
回肠 Ileum | 绒毛高度Villus height (V) | 472.99±21.33b | 544.80±16.88a | 556.50±19.72a | 525.76±13.15a | 432.84±24.76b |
| 隐窝深度Crypt depth (C) | 98.10±3.94a | 96.59±4.04a | 100.83±4.96a | 107.47±8.07a | 107.74±6.36a | |
| V/C | 4.82±0.23bc | 5.78±0.23a | 5.73±0.37ab | 5.06±0.34abc | 4.26±0.28c | |
十二指肠 Duodenum | 绒毛高度Villus height | 1120.07±32.86ab | 1030.86±24.33b | 1206.32±29.28a | 1086.62±30.36b | 1086.58±20.64b |
| 隐窝深度Crypt depth | 95.47±8.64b | 89.34±6.02c | 100.20±5.05a | 93.14±4.62b | 106.19±6.85a | |
| V/C | 11.73±0.41a | 11.54±0.69a | 12.04±0.93a | 11.67±0.83a | 11.01±0.66a |
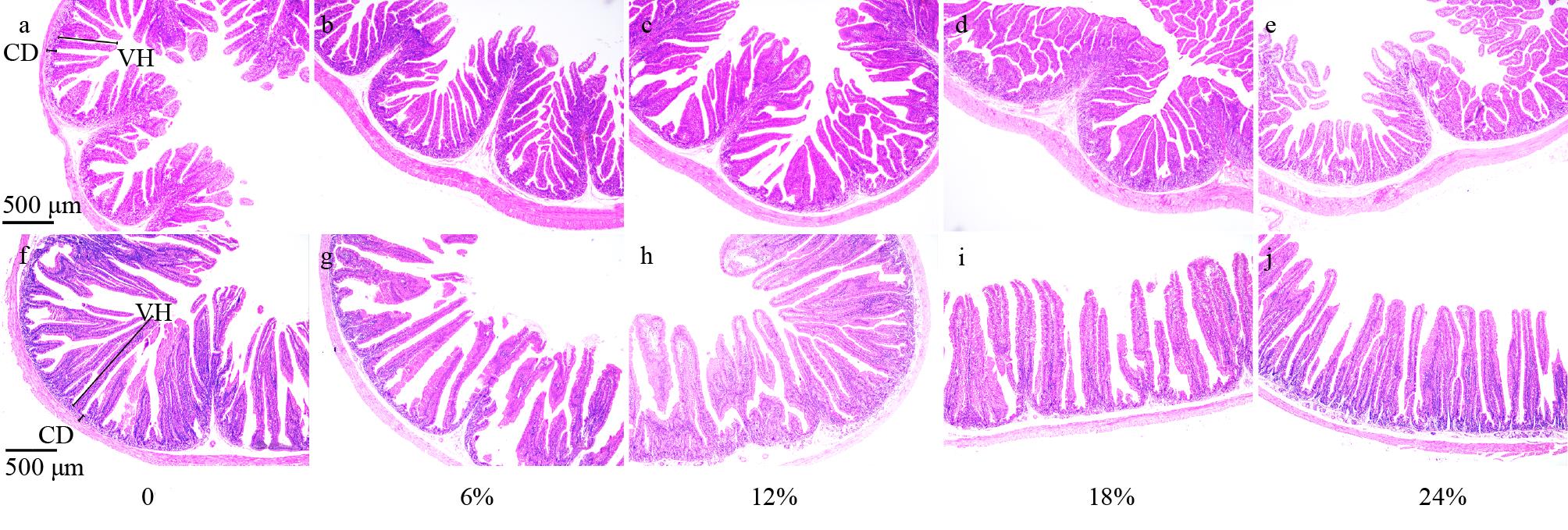
图1 添加不同比例全株饲料桑条件下川白獭兔幼兔回肠及十二指肠石蜡切片(4×10)a~e: 回肠Ileum; f~j: 十二指肠Duodenum; VH: 绒毛高度Villus height; CD: 隐窝深度Crypt depth.
Fig.1 Paraffin sections of the ileum and duodenum of young Chuanbai rex rabbit under different proportions of whole-plant forage mulberry conditions (4×10)
| 项目Items | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白细胞数目White blood cell count (×109·L-1) | 7.30±0.65b | 7.88±1.95b | 11.03±1.10a | 9.00±1.23b | 9.63±1.31b |
| 淋巴细胞数目Lymphocyte count (×109·L-1) | 0.55±0.02c | 1.73±0.06b | 1.90±0.06b | 3.08±0.08a | 1.70±0.07b |
| 淋巴细胞百分比Lymphocyte percentage (%) | 7.70±0.90c | 21.00±2.83b | 17.20±1.33b | 32.12±3.07a | 6.57±1.12c |
| 单核细胞数目Number of monocytes (×109·L-1) | 0.35±0.02d | 0.65±0.01c | 1.23±0.17a | 0.68±0.23c | 0.83±0.17b |
| 单核细胞百分比Percentage of monocytes (%) | 4.15±0.61c | 8.10±3.39b | 10.90±0.79a | 7.24±1.76b | 8.97±2.93b |
| 中性粒细胞数目Number of neutrophils (×109·L-1) | 6.35±0.45a | 5.45±0.47a | 7.87±0.01a | 5.18±0.36a | 8.03±0.84a |
| 中性粒细胞百分比Percentage of neutrophils (%) | 88.15±1.51a | 70.90±4.24a | 71.90±8.22a | 60.64±2.67a | 84.47±2.96a |
| 血红蛋白含量Hemoglobin content (g·dL-1) | 111.55±4.53a | 111.28±10.19a | 103.23±8.24a | 110.54±4.82a | 101.07±6.66a |
| 红细胞数目Red blood cell count (×1012·L-1) | 5.39±0.17a | 5.62±0.52a | 5.15±0.72a | 5.47±0.31a | 5.21±0.41a |
| 红细胞积压Erythrocytosis (%) | 42.30±1.80a | 42.50±3.68a | 38.80±4.65a | 42.14±2.07a | 39.10±2.49a |
| 平均红细胞体积Average red blood cell volume (fL) | 78.55±0.78a | 75.83±0.82a | 75.70±2.54a | 77.10±1.62a | 75.23±2.73a |
| 平均红细胞血红蛋白含量MCH (pg) | 20.65±0.20a | 19.78±0.91a | 20.20±1.42a | 20.18±0.84a | 19.40±0.99a |
| 平均红细胞血红蛋白浓度MCHC (g·dL-1) | 263.50±5.41a | 261.50±6.29a | 266.67±11.32a | 262.20±10.34a | 258.00±3.74a |
| 红细胞分布宽度标准差值RDWSD (fL) | 40.50±0.41a | 38.00±0.71ab | 37.00±1.63b | 37.40±1.74b | 38.00±1.63ab |
| 红细胞分布宽度变异系数RDWCV | 12.85±0.29a | 12.48±0.25a | 12.13±0.12a | 12.08±0.44a | 12.57±0.29a |
| 血小板数目Platelet count (×109·L-1) | 181.50±9.49a | 194.25±17.76a | 115.67±7.38a | 123.40±12.38a | 171.67±16.18a |
| 血小板压积Platelet hematocrit (%) | 0.19±0.10a | 0.18±0.17a | 0.12±0.04a | 0.12±0.05a | 0.17±0.12a |
| 平均血小板体积Average platelet volume (fL) | 10.35±0.04a | 9.80±0.63a | 10.60±0.50a | 9.94±0.45a | 9.83±0.29a |
| 血小板分布宽度Platelet distribution width (%) | 15.15±1.12a | 13.70±2.88a | 16.27±2.41a | 15.06±2.88a | 13.83±1.98a |
| 大血小板比例Large platelet ratio | 23.25±1.10a | 22.75±4.41a | 24.90±4.46a | 23.00±1.74a | 22.27±2.99a |
表3 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔血常规指标的影响
Table 3 Effects of whole-plant forage mulberry addition on blood routine parameters of young Chuanbai rex rabbits
| 项目Items | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白细胞数目White blood cell count (×109·L-1) | 7.30±0.65b | 7.88±1.95b | 11.03±1.10a | 9.00±1.23b | 9.63±1.31b |
| 淋巴细胞数目Lymphocyte count (×109·L-1) | 0.55±0.02c | 1.73±0.06b | 1.90±0.06b | 3.08±0.08a | 1.70±0.07b |
| 淋巴细胞百分比Lymphocyte percentage (%) | 7.70±0.90c | 21.00±2.83b | 17.20±1.33b | 32.12±3.07a | 6.57±1.12c |
| 单核细胞数目Number of monocytes (×109·L-1) | 0.35±0.02d | 0.65±0.01c | 1.23±0.17a | 0.68±0.23c | 0.83±0.17b |
| 单核细胞百分比Percentage of monocytes (%) | 4.15±0.61c | 8.10±3.39b | 10.90±0.79a | 7.24±1.76b | 8.97±2.93b |
| 中性粒细胞数目Number of neutrophils (×109·L-1) | 6.35±0.45a | 5.45±0.47a | 7.87±0.01a | 5.18±0.36a | 8.03±0.84a |
| 中性粒细胞百分比Percentage of neutrophils (%) | 88.15±1.51a | 70.90±4.24a | 71.90±8.22a | 60.64±2.67a | 84.47±2.96a |
| 血红蛋白含量Hemoglobin content (g·dL-1) | 111.55±4.53a | 111.28±10.19a | 103.23±8.24a | 110.54±4.82a | 101.07±6.66a |
| 红细胞数目Red blood cell count (×1012·L-1) | 5.39±0.17a | 5.62±0.52a | 5.15±0.72a | 5.47±0.31a | 5.21±0.41a |
| 红细胞积压Erythrocytosis (%) | 42.30±1.80a | 42.50±3.68a | 38.80±4.65a | 42.14±2.07a | 39.10±2.49a |
| 平均红细胞体积Average red blood cell volume (fL) | 78.55±0.78a | 75.83±0.82a | 75.70±2.54a | 77.10±1.62a | 75.23±2.73a |
| 平均红细胞血红蛋白含量MCH (pg) | 20.65±0.20a | 19.78±0.91a | 20.20±1.42a | 20.18±0.84a | 19.40±0.99a |
| 平均红细胞血红蛋白浓度MCHC (g·dL-1) | 263.50±5.41a | 261.50±6.29a | 266.67±11.32a | 262.20±10.34a | 258.00±3.74a |
| 红细胞分布宽度标准差值RDWSD (fL) | 40.50±0.41a | 38.00±0.71ab | 37.00±1.63b | 37.40±1.74b | 38.00±1.63ab |
| 红细胞分布宽度变异系数RDWCV | 12.85±0.29a | 12.48±0.25a | 12.13±0.12a | 12.08±0.44a | 12.57±0.29a |
| 血小板数目Platelet count (×109·L-1) | 181.50±9.49a | 194.25±17.76a | 115.67±7.38a | 123.40±12.38a | 171.67±16.18a |
| 血小板压积Platelet hematocrit (%) | 0.19±0.10a | 0.18±0.17a | 0.12±0.04a | 0.12±0.05a | 0.17±0.12a |
| 平均血小板体积Average platelet volume (fL) | 10.35±0.04a | 9.80±0.63a | 10.60±0.50a | 9.94±0.45a | 9.83±0.29a |
| 血小板分布宽度Platelet distribution width (%) | 15.15±1.12a | 13.70±2.88a | 16.27±2.41a | 15.06±2.88a | 13.83±1.98a |
| 大血小板比例Large platelet ratio | 23.25±1.10a | 22.75±4.41a | 24.90±4.46a | 23.00±1.74a | 22.27±2.99a |
| 项目Item | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白蛋白Albumin (g·L-1) | 23.20±0.69a | 23.27±0.62a | 22.95±0.48a | 22.29±0.55a | 23.50±0.62a |
| 球蛋白Globulin (g·L-1) | 34.80±0.85ab | 32.98±0.92b | 35.16±0.73ab | 33.73±0.82ab | 36.56±0.76a |
| 总蛋白Total protein (g·L-1) | 58.00±1.48ab | 56.25±1.88b | 58.11±1.38ab | 56.02±1.27b | 59.06±1.72a |
| 总胆固醇Total cholesterol (mmol·L-1) | 1.83±0.07a | 1.39±0.09b | 1.19±0.09bc | 0.94±0.06bc | 0.84±0.08c |
| 甘油三酯Triglyceride (mmol·L-1) | 1.09±0.06a | 1.00±0.03ab | 0.87±0.05b | 0.76±0.04b | 0.67±0.04c |
| 尿素氮Urea nitrogen (mmol·L-1) | 6.97±0.26a | 6.78±0.27a | 6.66±0.15a | 6.78±0.22a | 6.56±0.26a |
| 谷丙转氨酶Alanine aminotransferase (U·L-1) | 75.86±2.87a | 73.73±1.35a | 69.68±2.46b | 69.97±1.42b | 67.76±2.77c |
| 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase (U·L-1) | 166.35±2.05a | 162.22±3.09ab | 134.57±4.58e | 140.29±3.39d | 152.68±2.77c |
γ-谷氨酰基转移酶γ-glutamyltransferase (U·L-1) 天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶Aspartate aminotransferase (U·L-1) | 1.86±0.06b 23.61±0.71c | 2.13±0.09a 26.91±0.60b | 1.92±0.09b 26.01±0.80b | 1.77±0.13b 34.65±0.67a | 2.27±0.13a 31.30±0.48a |
表4 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔血液生化指标的影响
Table 4 Effects of whole-plant forage mulberry addition on blood biochemical parameters of young Chuanbai rex rabbits
| 项目Item | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白蛋白Albumin (g·L-1) | 23.20±0.69a | 23.27±0.62a | 22.95±0.48a | 22.29±0.55a | 23.50±0.62a |
| 球蛋白Globulin (g·L-1) | 34.80±0.85ab | 32.98±0.92b | 35.16±0.73ab | 33.73±0.82ab | 36.56±0.76a |
| 总蛋白Total protein (g·L-1) | 58.00±1.48ab | 56.25±1.88b | 58.11±1.38ab | 56.02±1.27b | 59.06±1.72a |
| 总胆固醇Total cholesterol (mmol·L-1) | 1.83±0.07a | 1.39±0.09b | 1.19±0.09bc | 0.94±0.06bc | 0.84±0.08c |
| 甘油三酯Triglyceride (mmol·L-1) | 1.09±0.06a | 1.00±0.03ab | 0.87±0.05b | 0.76±0.04b | 0.67±0.04c |
| 尿素氮Urea nitrogen (mmol·L-1) | 6.97±0.26a | 6.78±0.27a | 6.66±0.15a | 6.78±0.22a | 6.56±0.26a |
| 谷丙转氨酶Alanine aminotransferase (U·L-1) | 75.86±2.87a | 73.73±1.35a | 69.68±2.46b | 69.97±1.42b | 67.76±2.77c |
| 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase (U·L-1) | 166.35±2.05a | 162.22±3.09ab | 134.57±4.58e | 140.29±3.39d | 152.68±2.77c |
γ-谷氨酰基转移酶γ-glutamyltransferase (U·L-1) 天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶Aspartate aminotransferase (U·L-1) | 1.86±0.06b 23.61±0.71c | 2.13±0.09a 26.91±0.60b | 1.92±0.09b 26.01±0.80b | 1.77±0.13b 34.65±0.67a | 2.27±0.13a 31.30±0.48a |
| 氨基酸Amino acid | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天门冬氨酸Aspartate (g·100 g-1) | 1.86±0.02a | 1.83±0.01a | 1.88±0.02a | 1.87±0.03a | 1.86±0.02a |
| 苏氨酸Threonine (g·100 g-1) | 0.86±0.01a | 0.85±0.03a | 0.88±0.02a | 0.86±0.01a | 0.87±0.01a |
| 丝氨酸Serine (g·100 g-1) | 0.75±0.01a | 0.74±0.03a | 0.77±0.01a | 0.76±0.02a | 0.74±0.01a |
| 谷氨酸Glutamate (g·100 g-1) | 3.04±0.01a | 2.99±0.09a | 3.05±0.04a | 3.00±0.06a | 3.04±0.01a |
| 甘氨酸Glycine (g·100 g-1) | 0.91±0.02a | 0.89±0.02a | 0.94±0.03a | 0.94±0.04a | 0.90±0.03a |
| 丙氨酸Alanine (g·100 g-1) | 1.10±0.00a | 1.08±0.02a | 1.11±0.01a | 1.09±0.03a | 1.09±0.01a |
| 缬氨酸Valine (g·100 g-1) | 0.98±0.01a | 0.96±0.02a | 0.97±0.01a | 0.95±0.02a | 0.98±0.01a |
| 蛋氨酸Methionine (g·100 g-1) | 0.36±0.01a | 0.36±0.03a | 0.35±0.02a | 0.34±0.04a | 0.34±0.02a |
| 异亮氨酸Isoleucine (g·100 g-1) | 0.94±0.01a | 0.92±0.03a | 0.93±0.01a | 0.91±0.02a | 0.95±0.01a |
| 亮氨酸Leucine (g·100 g-1) | 1.57±0.01a | 1.54±0.05a | 1.57±0.01a | 1.55±0.04a | 1.57±0.01a |
| 酪氨酸Tyrosine (g·100 g-1) | 0.62±0.01a | 0.61±0.01a | 0.61±0.01a | 0.61±0.03a | 0.60±0.01a |
| 苯丙氨酸Phenylalanine (g·100 g-1) | 0.78±0.01a | 0.77±0.02a | 0.77±0.01a | 0.78±0.04a | 0.78±0.00a |
| 组氨酸Histidine (g·100 g-1) | 0.88±0.01a | 0.86±0.02a | 0.88±0.01a | 0.90±0.02a | 0.89±0.02a |
| 赖氨酸Lysine (g·100 g-1) | 1.76±0.01a | 1.73±0.05a | 1.75±0.02a | 1.72±0.04a | 1.75±0.01a |
| 精氨酸Arginine (g·100 g-1) | 1.27±0.01a | 1.23±0.03a | 1.27±0.01a | 1.25±0.04a | 1.25±0.01a |
| 脯氨酸Proline (g·100 g-1) | 0.85±0.12a | 0.77±0.05a | 0.79±0.03a | 0.81±0.02a | 0.76±0.02a |
| 氨基酸总量Total amount of amino acids (g·100 g-1) | 18.50±0.00a | 18.10±0.40a | 18.50±0.10a | 18.30±0.40a | 18.37±0.06a |
| 肌苷酸含量Inosine acid content (mg·g-1) | 1.09±0.01d | 1.15±0.06c | 1.17±0.03c | 1.22±0.04b | 1.38±0.06a |
表5 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔腿肌中氨基酸及肌苷酸含量的影响
Table 5 Effects of whole-plant forage mulberry addition on amino acids and inosine contents in young Chuanbai rex rabbits leg muscles
| 氨基酸Amino acid | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天门冬氨酸Aspartate (g·100 g-1) | 1.86±0.02a | 1.83±0.01a | 1.88±0.02a | 1.87±0.03a | 1.86±0.02a |
| 苏氨酸Threonine (g·100 g-1) | 0.86±0.01a | 0.85±0.03a | 0.88±0.02a | 0.86±0.01a | 0.87±0.01a |
| 丝氨酸Serine (g·100 g-1) | 0.75±0.01a | 0.74±0.03a | 0.77±0.01a | 0.76±0.02a | 0.74±0.01a |
| 谷氨酸Glutamate (g·100 g-1) | 3.04±0.01a | 2.99±0.09a | 3.05±0.04a | 3.00±0.06a | 3.04±0.01a |
| 甘氨酸Glycine (g·100 g-1) | 0.91±0.02a | 0.89±0.02a | 0.94±0.03a | 0.94±0.04a | 0.90±0.03a |
| 丙氨酸Alanine (g·100 g-1) | 1.10±0.00a | 1.08±0.02a | 1.11±0.01a | 1.09±0.03a | 1.09±0.01a |
| 缬氨酸Valine (g·100 g-1) | 0.98±0.01a | 0.96±0.02a | 0.97±0.01a | 0.95±0.02a | 0.98±0.01a |
| 蛋氨酸Methionine (g·100 g-1) | 0.36±0.01a | 0.36±0.03a | 0.35±0.02a | 0.34±0.04a | 0.34±0.02a |
| 异亮氨酸Isoleucine (g·100 g-1) | 0.94±0.01a | 0.92±0.03a | 0.93±0.01a | 0.91±0.02a | 0.95±0.01a |
| 亮氨酸Leucine (g·100 g-1) | 1.57±0.01a | 1.54±0.05a | 1.57±0.01a | 1.55±0.04a | 1.57±0.01a |
| 酪氨酸Tyrosine (g·100 g-1) | 0.62±0.01a | 0.61±0.01a | 0.61±0.01a | 0.61±0.03a | 0.60±0.01a |
| 苯丙氨酸Phenylalanine (g·100 g-1) | 0.78±0.01a | 0.77±0.02a | 0.77±0.01a | 0.78±0.04a | 0.78±0.00a |
| 组氨酸Histidine (g·100 g-1) | 0.88±0.01a | 0.86±0.02a | 0.88±0.01a | 0.90±0.02a | 0.89±0.02a |
| 赖氨酸Lysine (g·100 g-1) | 1.76±0.01a | 1.73±0.05a | 1.75±0.02a | 1.72±0.04a | 1.75±0.01a |
| 精氨酸Arginine (g·100 g-1) | 1.27±0.01a | 1.23±0.03a | 1.27±0.01a | 1.25±0.04a | 1.25±0.01a |
| 脯氨酸Proline (g·100 g-1) | 0.85±0.12a | 0.77±0.05a | 0.79±0.03a | 0.81±0.02a | 0.76±0.02a |
| 氨基酸总量Total amount of amino acids (g·100 g-1) | 18.50±0.00a | 18.10±0.40a | 18.50±0.10a | 18.30±0.40a | 18.37±0.06a |
| 肌苷酸含量Inosine acid content (mg·g-1) | 1.09±0.01d | 1.15±0.06c | 1.17±0.03c | 1.22±0.04b | 1.38±0.06a |
| 项目Item | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 饲料消耗量Feed consumption (kg·rabbit-1) | 4.76 | 4.48 | 4.27 | 4.40 | 4.37 |
| 饲料单价Feed unit price (CNY·kg-1) | 2.89 | 2.89 | 2.82 | 2.78 | 2.60 |
| 饲料总成本Feed total price (CNY·rabbit-1) | 13.75 | 12.91 | 12.04 | 12.23 | 11.37 |
| 其他成本Other costs (CNY·rabbit-1) | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| 平均增重Average weight gain( g·rabbit-1) | 1209.00 | 1193.00 | 1167.00 | 1183.00 | 1190.00 |
| 增重收入Weight gain income (CNY·rabbit-1) | 31.43 | 31.02 | 30.34 | 30.76 | 30.94 |
| 毛利润Gross margin (CNY·rabbit-1) | 7.68 | 8.10 | 8.31 | 8.53 | 9.57 |
表6 全株饲料桑添加量对川白獭兔幼兔经济效益的影响
Table 6 Effects of whole-plant forage mulberry addition on the economic benefits of young Chuanbai rex rabbits
| 项目Item | 对照Control | 6% | 12% | 18% | 24% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 饲料消耗量Feed consumption (kg·rabbit-1) | 4.76 | 4.48 | 4.27 | 4.40 | 4.37 |
| 饲料单价Feed unit price (CNY·kg-1) | 2.89 | 2.89 | 2.82 | 2.78 | 2.60 |
| 饲料总成本Feed total price (CNY·rabbit-1) | 13.75 | 12.91 | 12.04 | 12.23 | 11.37 |
| 其他成本Other costs (CNY·rabbit-1) | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| 平均增重Average weight gain( g·rabbit-1) | 1209.00 | 1193.00 | 1167.00 | 1183.00 | 1190.00 |
| 增重收入Weight gain income (CNY·rabbit-1) | 31.43 | 31.02 | 30.34 | 30.76 | 30.94 |
| 毛利润Gross margin (CNY·rabbit-1) | 7.68 | 8.10 | 8.31 | 8.53 | 9.57 |
| 1 | Zheng Z T. Review of domestic and international soybean markets in 2023 and outlook for 2024. Heilongjiang Grain, 2024(2): 23-26. |
| 郑祖庭. 2023年国内外大豆市场回顾及2024年展望. 黑龙江粮食, 2024(2): 23-26. | |
| 2 | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Feed ingredient directory (revised in 2018). Beijing: Issued by the 22nd Announcement of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2018. |
| 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 饲料原料目录(2018年修订). 北京: 中华人民共和国农业农村部公告第22号, 2018. | |
| 3 | Du Z H, Zuo Y C, Yan X, et al. Physiological activation and feed value of mulberry for livestock and poultry. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(10): 227-236. |
| 杜周和, 左艳春, 严旭, 等. 饲料桑生理活性物质及其饲用价值. 草业学报, 2017, 26(10): 227-236. | |
| 4 | Liu D, Ding Z Z, Hu L, et al. Effect of fermented mulberry leaves replacing basic diet on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes, nutrient apparent digestibility and meat quality of finishing pigs. Feed Research, 2023, 46(15): 17-22. |
| 刘冬, 丁兆忠, 胡蕾, 等. 发酵桑叶替代基础日粮对育肥猪生长性能、血清生化指标、养分表观消化率及肉品质的影响. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(15): 17-22. | |
| 5 | Wen P, Hu T G, Linhardt R J. Mulberry: a review of bioactive compounds and advanced processing technology. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2019, 83: 138-158. |
| 6 | Hou Q R, Tao L L, Zhao W G, et al. Production performance of rex rabbit feeding on diets containing different proportions of mulberry leaf powder. Science of Sericulture, 2016, 42(3): 500-506. |
| 侯启瑞, 陶璐璐, 赵卫国, 等. 饲粮中桑叶粉添加量对獭兔生产性能的影响. 蚕业科学, 2016, 42(3): 500-506. | |
| 7 | Wang C Z, Chen B J, Li Z H, et al. Effect of stem and leaf feed of mulberry on performance, serum biochemical indexes and meat quality of meat rabbits. Feed Research, 2021, 44(4): 51-55. |
| 王崇洲, 陈宝剑, 李正欢, 等. 饲用桑茎叶粉对肉兔生产性能、生化指标及肉品质的影响. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(4): 51-55. | |
| 8 | Guo Z Q, Mei X L, Lei M, et al. Fresh mulberry leaves-supplemented diets on performance and meat quality of rabbit. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 30(1): 215-221. |
| 郭志强, 梅秀丽, 雷岷, 等. 饲粮补充鲜桑叶对肉兔生产性能和肉品质的影响. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(1): 215-221. | |
| 9 | Huang J, Zhao N, Guo W Z, et al. Effects of fermented mulberry branch and leaf meal on production performance, egg quality and intestinal tissue morphology of laying hens. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(4): 1259-1266. |
| 黄静, 赵娜, 郭万正, 等. 发酵桑枝叶粉对蛋鸡生产性能、蛋品质、肠道组织形态的影响. 草地学报, 2024, 32(4): 1259-1266. | |
| 10 | Ye T M, Li X, Xiao J Z, et al. Effects of fermented mulberry leaf powder supplementation in diets on growth performance, serum biochemistry, and antioxidant status of growing pigs. China Sericulture, 2023, 44(1): 39-43. |
| 叶添梅, 李霞, 肖建中, 等. 生长猪饲粮中添加发酵桑叶粉对生长性能和血清生化及抗氧化性能的影响. 中国蚕业, 2023, 44(1): 39-43. | |
| 11 | Luo Y, Li H B, Xiao J Z, et al. Effects of fermented mulberry leaves on serum biochemical, antioxidant and immune indexes of Xiangxi yellow cattle×Limousin hybrid F1 fattening bulls. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(10): 4914-4921. |
| 罗阳, 李昊帮, 肖建中, 等. 发酵桑叶对湘西黄牛×利木赞杂交F1代育肥牛血清生化、抗氧化及免疫指标的影响. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(10): 4914-4921. | |
| 12 | Li F C, Xie X H, Liu L, et al. Nutrient requirements of meat rabbit: NY/T 4049-2021. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2021. |
| 李福昌, 谢晓红, 刘磊, 等. 肉兔营养需要量: NY/T 4049-2021. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. | |
| 13 | Meng F S, Zhang S, Liang M, et al. Determination of moisture in feedstuffs: GB/T 6435-2014. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2014. |
| 孟凡胜, 张苏, 梁萌, 等. 饲料中水分的测定: GB/T 6435-2014. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. | |
| 14 | Xiao Z M, Fan X, Ma D X, et al. Determination of crude protein in feed: GB/T 6432-2018. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018. |
| 肖志明, 樊霞, 马东霞, 等. 饲料中粗蛋白的测定: GB/T 6432-2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 15 | Zhang S, Li L P, Su X O, et al. Determination of crude fat in feeds: GB/T 6433-2006. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2006. |
| 张苏, 李丽蓓, 苏晓鸥, 等. 饲料中粗脂肪的测定: GB/T 6433-2006. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. | |
| 16 | Wu R X, Yang L, He Y F, et al. Determination of crude ash content in feed: GB/T 6438-2007. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2007. |
| 武润仙, 杨林, 何一帆, 等. 饲料中粗灰分的测定: GB/T 6438-2007. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. | |
| 17 | Zhang F P, Zhang Y, Zhang R, et al. Determination of neutral detergent fiber(NDF) in feeds: GB/T 20806-2022. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2022. |
| 张凤枰, 张芸, 张茹, 等. 饲料中中性洗涤纤维(NDF)的测定: GB/T 20806-2022. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. | |
| 18 | Yang F S, Song J, Zhang F P, et al. Determination of acid detergent fiber in feed: NY/T 1459-2022. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2022. |
| 杨发树, 宋军, 张凤枰, 等. 饲料中酸性洗涤纤维的测定: NY/T 1459-2022. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. | |
| 19 | Zhang W, Zhang F P, Du Y X, et al. Determination of crude fiber in feed: GB/T 6434-2022. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2022. |
| 张玮, 张凤枰, 杜亚欣, 等. 饲料中粗纤维的含量测定: GB/T 6434-2022. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. | |
| 20 | Huang T, Wang S S, Gao J F, et al. Determination of starch in feeds-polarimetry: GB/T 20194-2018. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018. |
| 黄婷, 王思思, 高俊峰, 等. 动物饲料中淀粉含量的测定-旋光法: GB/T 20194-2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. | |
| 21 | Han L J, Xiao W H, Liu X, et al. Agricultural biomass raw materials-determination of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin: NY/T 3494-2019. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2019. |
| 韩鲁佳, 肖卫华, 刘贤, 等. 农业生物质原料纤维素、半纤维素、木质素测定: NY/T 3494-2019. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019. | |
| 22 | Li Y Q, Song Y Z, Shi H T, et al. Effects of fermented astragalus on the number of epithelial goblet cells and expression of MUC2 gene in small intestinal mucosa of broilers. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2024, 45(7): 35-40. |
| 李月勤, 宋予震, 史洪涛, 等. 发酵黄芪对肉鸡小肠黏膜上皮杯状细胞数量及MUC2基因表达的影响. 家畜生态学报, 2024, 45(7): 35-40. | |
| 23 | National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. National standard for food safety determination of amino acids in food, GB 5009.124-2016. Beijing: National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration, 2016. |
| 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定, GB 5009.124-2016. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 2016. | |
| 24 | Xin G S, Bu J J, Liu H, et al. Determination of inosine and inosinic acid in muscle high performance liquid chromatography: T/NAIA 003-2020. Yinchuan: Ningxia Analytical and Testing Association of Chemistry, 2020. |
| 辛国省, 卜姣姣, 刘辉, 等. 肌肉中肌苷 肌苷酸的测定高效液相色谱法: T/NAIA 003-2020. 银川: 宁夏化学分析测试协会, 2020. | |
| 25 | Wang M, Yang C, Wang Q Y, et al. The growth performance, intestinal digestive and absorptive capabilities in piglets with different lengths of small intestines. Animal, 2020, 14(6): 1196-1203. |
| 26 | Zhou W T. The application effects of nanoselenium in hen production and the mechanism. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021. |
| 周雯婷. 纳米硒在蛋鸡生产中的应用效果及机理研究. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021. | |
| 27 | Wang Y C. Study on the feeding values of mulberry leaves power in geese diets. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 王永昌. 桑叶粉对鹅饲用价值的研究. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016. | |
| 28 | Feng X, He S J, Liu D Y. Effects of dietary adding selenium-rich yeast on weight, blood routine, serum biochemical indexes and antioxidant function of Wandong cattle in summer. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2022, 34(8): 5116-5125. |
| 冯星, 贺绍君, 刘德义. 夏季饲粮中添加富硒酵母对皖东黄牛体重、血常规、血清生化指标和抗氧化功能的影响. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(8): 5116-5125. | |
| 29 | Yin F Q, Wu Z M, Wang Z J, et al. Effects of different concentrate to forage ratio on growth performance, blood biochemistry and rumen microbial diversity of Leizhou goats. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2018, 38(1): 80-86. |
| 尹福泉, 吴征敏, 王志敬, 等. 不同精粗比饲粮对雷州山羊生长性能、血液生化指标和瘤胃微生物多样性的影响. 广东海洋大学学报, 2018, 38(1): 80-86. | |
| 30 | Zhang P, Yang J, Gao X, et al. Research progress on the anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of flavonoids. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 50(2): 134-137. |
| 张鹏, 杨杰, 高翔, 等. 黄酮类化合物抗炎作用及其作用机制研究进展. 畜牧与兽医, 2018, 50(2): 134-137. | |
| 31 | Raycoquard I, Cropet C, Van G M, et al. Lymphopenia as a prognostic factor for overall survival in advanced carcinomas, sarcomas and lymphomas. Cancer Research, 2009, 69(13): 5383-5391. |
| 32 | Yang X L, Ding C G, Li J X, et al. Effects of N-carbamylglutamic on growth performance, blood routine indexes and plasma antioxidant and immune indexes of female Hu sheep at different physiological stages. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2024, 36(7): 4473-4485. |
| 杨兴林, 丁常根, 李金昕, 等. N-氨甲酰谷氨酸对不同生理阶段湖羊母羊生长性能、血常规指标及血浆抗氧化、免疫指标的影响. 动物营养学报, 2024, 36(7): 4473-4485. | |
| 33 | Zhang H, Zhao F F, Nie H T, et al. Dietary N-carbamylglutamate and rumen-protected L-arginine supplementation during intrauterine growth restriction in undernourished ewes improve fetal thymus development and immune function. Reproduction, Fertility, and Development, 2018, 30(11): 1522-1531. |
| 34 | Wang D Y, Bian H, Zhu Y Z, et al. Effects of mulberry leaf powder on cholesterol content and fatty acid composition of egg yolk. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2011, 23(8): 139-143. |
| 王道营, 卞欢, 诸永志, 等. 桑叶粉对鸡蛋蛋黄胆固醇含量和脂肪酸组成的影响. 江西农业学报, 2011, 23(8): 139-143. | |
| 35 | Li Y G, Zhong S, Lv Z Q, et al. Inhibitory kinetics of α-sucrase by 1-deoxynojirimycin from mulberry leaves. Science of Sericulture, 2010, 36(6): 885-888. |
| 李有贵, 钟石, 吕志强, 等. 桑叶1-脱氧野尻霉素(DNJ)对α-蔗糖酶的抑制动力学研究. 蚕业科学, 2010, 36(6): 885-888. | |
| 36 | Fan Q W, Guo W Z, Zhao N, et al. Effects of different proportions of basal diet replaced by fermented feed mulberry on growth performance, nutrient apparent digestibility, blood physiological and biochemical indexes and serum antioxidant indexes of beef cattle. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(11): 7235-7246. |
| 樊启文, 郭万正, 赵娜, 等. 不同比例发酵饲料桑替代基础饲粮对肉牛生长性能、养分表观消化率、血液生理生化指标、血清抗氧化指标的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(11): 7235-7246. | |
| 37 | Wang L L, Chen X Y, Qin R Y, et al. Effects of fermented sawdust mushroom bran on growth performance, serum biochemical indexes, rumen fermentation parameters and nutrient apparent digestibility of sheep. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(8): 5271-5283. |
| 王乐乐, 陈翔宇, 秦荣艳, 等. 发酵木屑菌糠对绵羊生长性能、血清生化指标、瘤胃发酵参数及营养物质表观消化率的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(8): 5271-5283. | |
| 38 | Tang A J. Effects of corn silage supplemented with Eucommia ulmoides leaves on growth performance, blood indexes and meat quality of sheep. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2020. |
| 唐艾嘉. 添加杜仲叶的玉米青贮对绵羊生长性能、血液指标和肉品质的影响. 开封: 河南大学, 2020. | |
| 39 | Lan C Y, Dong G Z, Huang X Z, et al. Effect of ground mulberry leaf on growth, slaughter performance and meat quality of broilers. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2012, 48(13): 27-31. |
| 兰翠英, 董国忠, 黄先智, 等. 桑叶粉对肉鸡生长性能和屠宰性能及肉质的影响. 中国畜牧杂志, 2012, 48(13): 27-31. | |
| 40 | Li W L. Effects of mulberry leaves on performance, serum biochemical parameters, immune function, antioxidation and meat quality in meat sheep. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2012. |
| 李伟玲. 桑叶对肉羊生产性能、血液生化指标、免疫抗氧化功能和肉品质的影响. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2012. | |
| 41 | Fu X C, Wang L H, Liu H Z, et al. Study on the optimal addition level of kiwifruit branch powder in the diet of young rex rabbits. Heilongjiang Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 645(9): 124-135. |
| 傅祥超, 王丽焕, 刘汉中, 等. 仔獭兔饲料中猕猴桃枝条粉适宜添加量的研究. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2022, 645(9): 124-135. | |
| 42 | Wang H L, Zuo Y C, Zhou X K, et al. Influence of high planting density herbal cultivating on yield and quality of whole-plant mulberry (Morus alba). Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(5): 952-962. |
| 王红林, 左艳春, 周晓康, 等. 高密度草本化栽培对饲料桑全株产量及品质的影响. 草业科学, 2020, 37(5): 952-962. | |
| 43 | Wang Y, Zhang Y, Han J J, et al. Effects of replacing whole corn silage with Morus alba silage on growth performance and nutrient digestion and metabolism of fattening Hu sheep. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2023, 35(6): 3822-3831. |
| 王瑶, 张雨, 韩佳佳, 等. 蛋白桑青贮替代全株玉米青贮对育肥湖羊生长性能和营养物质消化代谢的影响. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(6): 3822-3831. |
| [1] | 刘启林, 王小军, 王金兰, 刘文辉, 马巧玲, 李建辉, 张生原, 曹文侠, 李文. 氮磷配施对高寒区老芒麦饲草产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(6): 193-202. |
| [2] | 占今舜, 江浩筠, 王海波, 贾浩滨, 潘月, 钟小军, 霍俊宏. 羔羊断奶前后血清生化指标、抗氧化和免疫性能的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(5): 202-211. |
| [3] | 王腾飞, 马霞, 刘金龙, 王斌, 张译尹, 李佳旺, 马江萍, 王小兵, 兰剑. 引黄灌区复种饲用燕麦种植模式产量、品质及经济效益分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 27-37. |
| [4] | 张峰硕, 季秋蓉, 何婷莉, 苏曲杨昂毛, 王志有, 侯生珍, 桂林生. 低蛋白日粮中不同比例氨基酸对藏羊背腰最长肌肉品质、氨基酸和脂肪酸组成以及维生素和矿物质含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 198-208. |
| [5] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 欧晓彬, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. 盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢对裸燕麦叶片氨基酸代谢过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 119-130. |
| [6] | 张耀, 黄小云, 陈鑫珠, 黄勤楼, 黄秀声, 韩海东. 海鲜菇菌糠发酵饲料对山羊屠宰性能及肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 195-205. |
| [7] | 索效军, 张年, 杨前平, 陶虎, 熊琪, 李晓锋, 张凤, 陈明新. 日粮添加花生秧和苜蓿草粉对波麻杂交羊增重性能、内脏器官发育及血液指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 146-154. |
| [8] | 张生伟, 王小平, 张展海, 马友记, 滚双宝, 杨巧丽, 高小莉, 张保军. 青贮杂交构树对杜湖杂交肉羊生长性能、血清生化指标和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 89-99. |
| [9] | 吴勇, 刘晓静, 蔺芳, 童长春. 河西荒漠灌区紫花苜蓿施肥效应及其基于数据包络分析法的经济效益研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 94-105. |
| [10] | 李秀璋, 宋辉, 张宗豪, 徐海峰, 刘欣, 李玉玲, 李春杰. 甘肃内生真菌基因组密码子使用的偏好性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 67-77. |
| [11] | 占今舜, 霍俊宏, 胡耀, 钟小军, 武艳平. 不同精粗比全混合日粮对努比亚山羊肉品质、血清指标和器官发育的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(10): 139-148. |
| [12] | 田春丽, 李斌, 刘芳, 赵颖, 刘世亮, 介晓磊, 胡华锋. 硒、锌元素配施对紫花苜蓿产量、植株体内硒锌积累和氨基酸含量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 142-153. |
| [13] | 孙雪丽, 李秋凤, 刘英财, 曹玉凤, 王增林, 李艺, 赵洋洋, 葛瀚聪, 刘桃桃, 赵立新. 全株青贮玉米对西门塔尔杂交牛生产性能、表观消化率及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 201-209. |
| [14] | 许承琪, 徐海鹏, 金少红, 舒朝成, 郭正刚. 藏南农牧交错带农牧互作模式下土地利用效益耦合度分析[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 194-203. |
| [15] | 李江文, 李治国, 蒋立宏, 靳宇曦, 王舒新, 韩梦琪, 于丰源, 韩国栋. 呼伦贝尔短尾羊产前补饲精喂对家畜个体特征及生产效益的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(7): 90-97. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||