

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 174-186.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024456
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
张然1( ), 刘琛琢1, 苑峰2, 刘亚玲2, 董笛1, 王思宁1, 邹博坤1, 李晓霞1(
), 刘琛琢1, 苑峰2, 刘亚玲2, 董笛1, 王思宁1, 邹博坤1, 李晓霞1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-19
修回日期:2025-01-09
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-07-11
通讯作者:
李晓霞
作者简介:E-mail: lixiaoxia@caf.ac.cn基金资助:
Ran ZHANG1( ), Chen-zhuo LIU1, Feng YUAN2, Ya-ling LIU2, Di DONG1, Si-ning WANG1, Bo-kun ZOU1, Xiao-xia LI1(
), Chen-zhuo LIU1, Feng YUAN2, Ya-ling LIU2, Di DONG1, Si-ning WANG1, Bo-kun ZOU1, Xiao-xia LI1( )
)
Received:2024-11-19
Revised:2025-01-09
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-07-11
Contact:
Xiao-xia LI
摘要:
长穗偃麦草因其较强的耐盐碱能力常被广泛用于建植盐碱地牧场。为探究其响应盐碱胁迫的离子平衡机制,本研究以长穗偃麦草‘Orbit’为试验材料,设置150 mmol·L-1的NaHCO3溶液人工模拟碱胁迫,测定了幼苗生长指标及矿质离子(Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Cl-、SO42-和NO3-)含量,并利用高通量Illumina Hiseq测序技术对正常处理(CK)和胁迫24 h NaHCO3处理下的叶片和根系进行了转录组学分析。结果表明:NaHCO3胁迫下,长穗偃麦草幼苗根系生物量显著增加,根冠比增大。转录组结果表明,NaHCO3处理下叶片中有1833个差异基因(different expression genes, DEGs),根系中有1536个DEGs,140个基因在叶片和根系中均差异表达。GO和KEGG富集分析发现,叶片和根系中的DEGs均显著富集在与抗氧化相关、离子结合相关、苯丙氨酸和苯丙烷类生物合成等代谢通路;离子结合通路相关DEGs包括BAK1、CIPK10、STRK1、WAK8及多条laccase基因(laccase-11和laccase-3)等,可能参与了长穗偃麦草对NaHCO3胁迫的响应过程。此外,生理试验结果进一步证明长穗偃麦草叶片和根系的离子转运与分配受到影响,表现为Na+大量积累,而对K+的吸收能力下降,K+/Na+下降,根系通过提高对其他阳离子(如Ca2+、Mg2+和Fe3+)的吸收及分配能力来保持体内营养均衡,以更好地适应盐碱环境。本研究结果可为牧草及其他作物耐盐分子育种提供优异基因资源,还可为长穗偃麦草推广及盐碱地改良利用提供理论依据。
张然, 刘琛琢, 苑峰, 刘亚玲, 董笛, 王思宁, 邹博坤, 李晓霞. 长穗偃麦草响应NaHCO3胁迫的离子平衡机制及转录组分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(10): 174-186.
Ran ZHANG, Chen-zhuo LIU, Feng YUAN, Ya-ling LIU, Di DONG, Si-ning WANG, Bo-kun ZOU, Xiao-xia LI. Ion balance mechanism and transcriptome analysis of Elytrigia elongata in response to NaHCO3 stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2025, 34(10): 174-186.
处理 Treatment | 地上部干重 Dry weight of aboveground (mg·10株-1) | 根系干重 Dry weight of root (mg·10株-1) | 根冠比 Root to shoot ratio (%) | 地上部含水量 The water content of aboveground (%) | 根系含水量 The water content of root (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.58±0.12 | 2.44±0.05 | 53.38±0.98 | 81.74±0.44 | 90.91±0.08 |
| NaHCO3 | 3.75±0.11*** | 2.94±0.05** | 78.68±2.37** | 79.98±0.36** | 86.29±0.24** |
表1 NaHCO3胁迫对长穗偃麦草生长指标的影响
Table 1 Effect of NaHCO3 stress on growth indicators of E. elongata
处理 Treatment | 地上部干重 Dry weight of aboveground (mg·10株-1) | 根系干重 Dry weight of root (mg·10株-1) | 根冠比 Root to shoot ratio (%) | 地上部含水量 The water content of aboveground (%) | 根系含水量 The water content of root (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4.58±0.12 | 2.44±0.05 | 53.38±0.98 | 81.74±0.44 | 90.91±0.08 |
| NaHCO3 | 3.75±0.11*** | 2.94±0.05** | 78.68±2.37** | 79.98±0.36** | 86.29±0.24** |
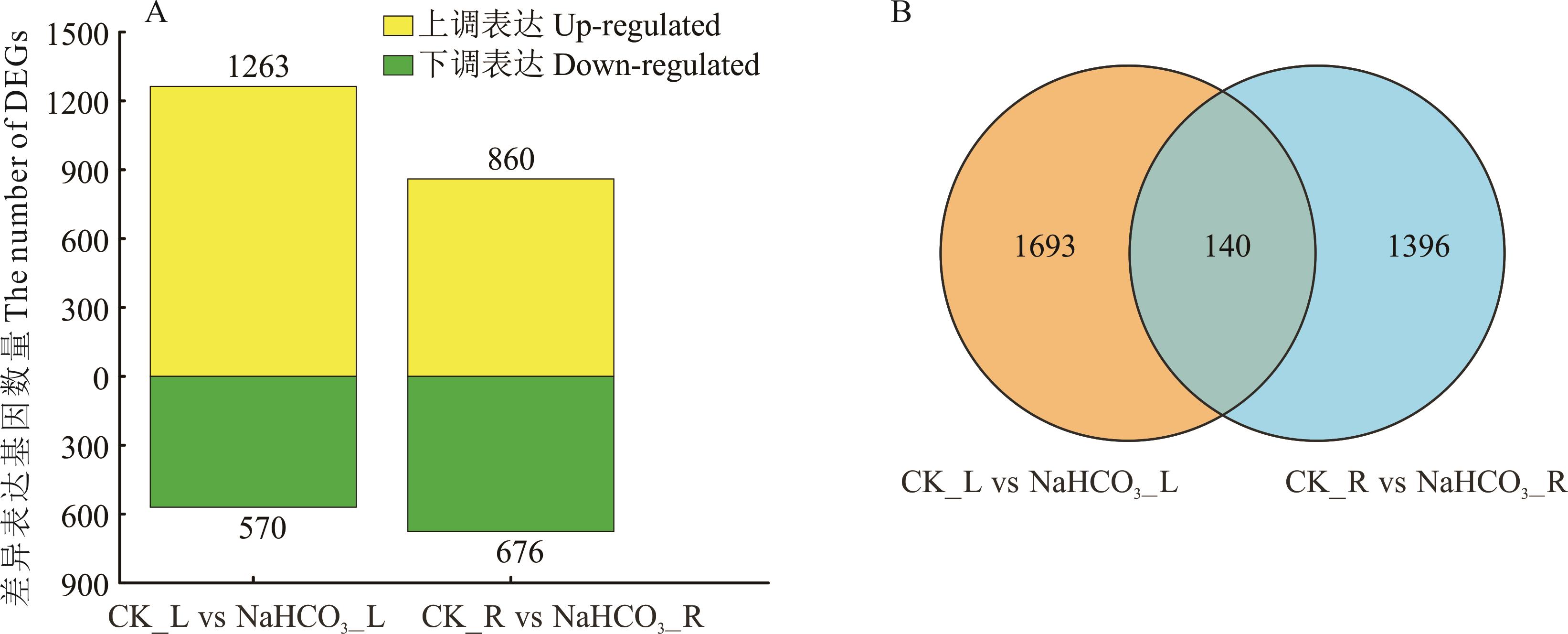
图1 差异基因表达的数目及韦恩图分析CK_L vs NaHCO3_L代表与对照相比,NaHCO3胁迫处理叶片中差异表达基因的数量;CK_R vs NaHCO3_R代表与对照相比,NaHCO3胁迫处理根系中差异表达基因的数量;下同。CK_L vs NaHCO3_L represents the number of DEGs in leaves treated with NaHCO3 stress compared to the control; CK_R vs NaHCO3_R represents the number of DEGs in roots treated with NaHCO3 stress compared to the control. The same below.
Fig.1 The number of different expression genes (DEGs) and Venn analysis

图2 NaHCO3胁迫处理下叶片和根系中差异基因KEGG富集通路分析
Fig.2 KEGG enrichment pathway of different expression genes (DEGs) in leaves and roots under NaHCO3 stress treatment
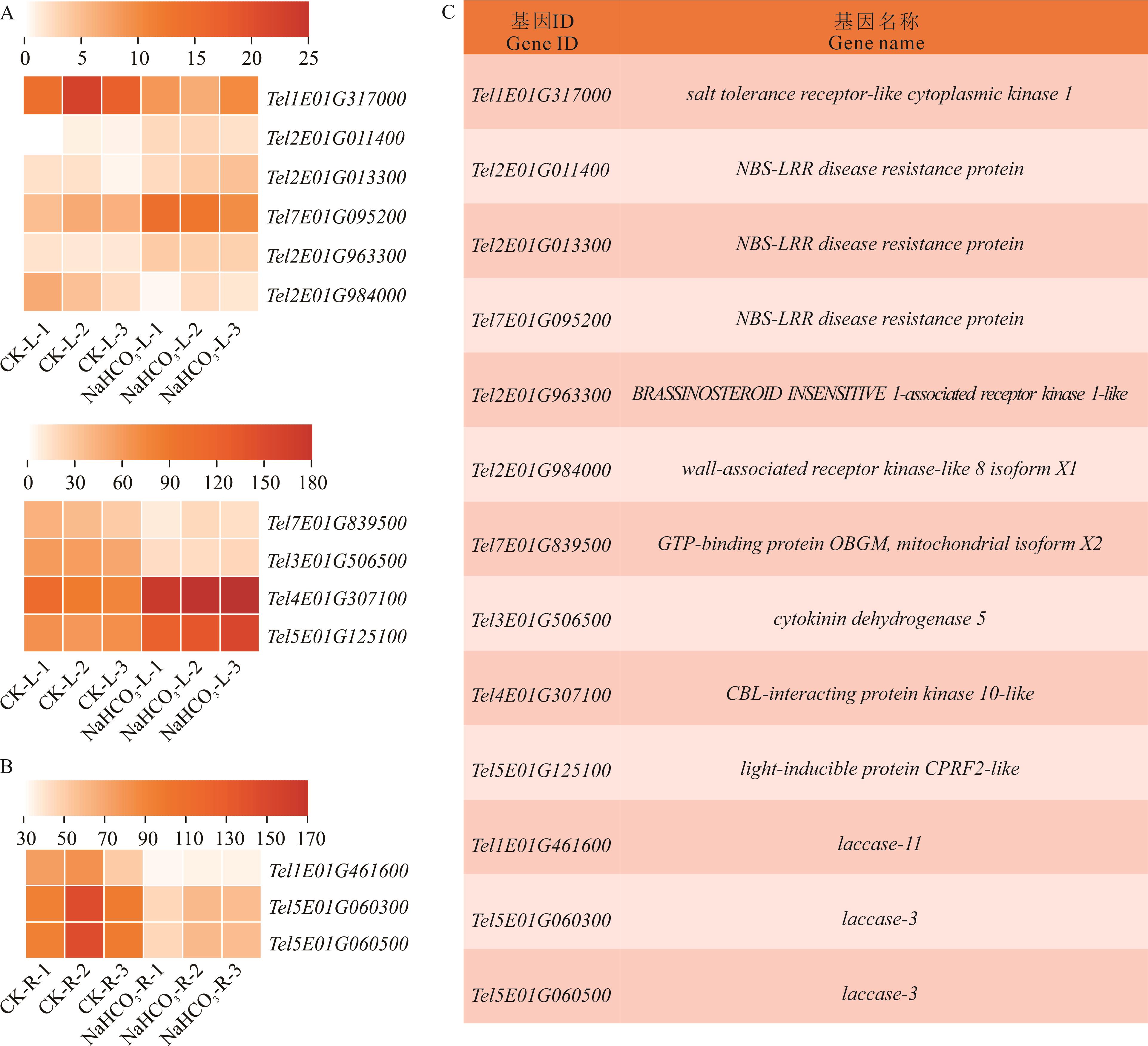
图4 NaHCO3胁迫处理下叶片和根系离子通路候选基因热图分析及基因名称CK-L-1,CK-L-2和CK-L-3代表对照处理叶片的3个生物学重复,NaHCO3-L-1,NaHCO3-L-2和NaHCO3-L-3代表NaHCO3处理叶片的3个生物学重复;CK-R-1,CK-R-2和CK-R-3代表对照处理根系的3个生物学重复,NaHCO3-R-1,NaHCO3-R-2和NaHCO3-R-3代表NaHCO3处理根系的3个生物学重复。CK-L-1, CK-L-2, and CK-L-3 represent three biological replicates of control in leaves, while NaHCO3-L-1, NaHCO3-L-2, and NaHCO3-L-3 represent three biological replicates of NaHCO3 treated in leaves; CK-R-1, CK-R-2, and CK-R-3 represent three biological replicates of control in roots, while NaHCO3-R-1, NaHCO3-R-2, and NaHCO3-R-3 represent three biological replicates of NaHCO3 treated in roots.
Fig.4 Heat map analysis of ion pathway candidate genes in leaves and roots under NaHCO3 stress treatment and gene names

图5 NaHCO3胁迫对长穗偃麦草叶片和根系Na+、K+、Ca2+、Mg2+、Fe3+和Cu2+ 含量的影响DW:干重Dry weight. *代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01,***代表P<0.001,下同。* represents P<0.05, ** represents P<0.01, *** represents P<0.001. The same below.
Fig.5 Effects of NaHCO3 stress on the contents of Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+ and Cu2+ in leaves and roots of E. elongata
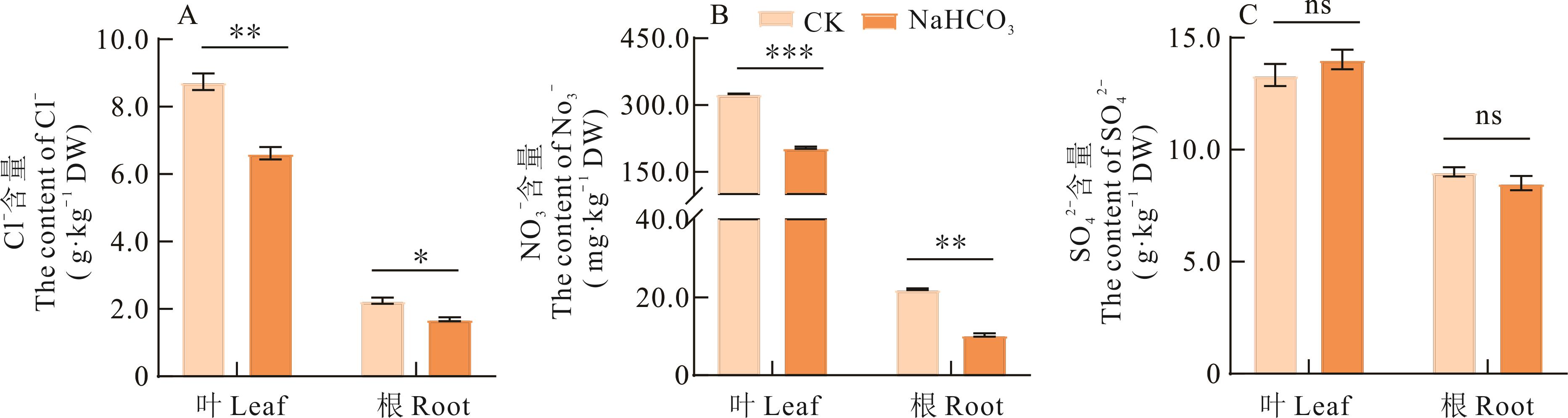
图6 NaHCO3胁迫对长穗偃麦草叶片和根系Cl-、NO3-和SO42-含量的影响ns代表P>0.05。ns represents P>0.05.
Fig.6 Effects of NaHCO3 stress on the contents of Cl-, NO3- and SO42- in leaves and roots of E. elongata
组织 Tissue | 处理 Treatment | 阳离子/Na+ Cation/Na+ | 阴离子/Cl- Anions/Cl- | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+/Na+ | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ | Fe3+/Na+ | Cu2+/Na+ | NO3-/Cl- | SO42-/Cl- | ||
叶片 Leaf | CK | 52.64±0.89 | 2.47±0.05 | 0.79±0.03 | 0.09±0.00 | 0.005±0.00 | 0.037±0.00 | 1.53±0.02 |
| NaHCO3 | 9.54±0.05*** | 0.54±0.01*** | 0.14±0.00*** | 0.03±0.00*** | 0.002±0.00*** | 0.031±0.00* | 2.12±0.12* | |
根 Root | CK | 22.52±0.37 | 1.64±0.03 | 0.38±0.01 | 0.89±0.01 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.010±0.00 | 4.02±0.21 |
| NaHCO3 | 3.87±0.03*** | 0.57±0.00*** | 0.18±0.00*** | 0.55±0.01*** | 0.002±0.00*** | 0.006±0.03** | 5.02±0.24ns | |
表2 NaHCO3胁迫处理对长穗偃麦草地上部和地下部离子分配的影响
Table 2 Effects of NaHCO3 stress on ion allocation in the upper and underground parts of E. elongata
组织 Tissue | 处理 Treatment | 阳离子/Na+ Cation/Na+ | 阴离子/Cl- Anions/Cl- | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K+/Na+ | Ca2+/Na+ | Mg2+/Na+ | Fe3+/Na+ | Cu2+/Na+ | NO3-/Cl- | SO42-/Cl- | ||
叶片 Leaf | CK | 52.64±0.89 | 2.47±0.05 | 0.79±0.03 | 0.09±0.00 | 0.005±0.00 | 0.037±0.00 | 1.53±0.02 |
| NaHCO3 | 9.54±0.05*** | 0.54±0.01*** | 0.14±0.00*** | 0.03±0.00*** | 0.002±0.00*** | 0.031±0.00* | 2.12±0.12* | |
根 Root | CK | 22.52±0.37 | 1.64±0.03 | 0.38±0.01 | 0.89±0.01 | 0.01±0.00 | 0.010±0.00 | 4.02±0.21 |
| NaHCO3 | 3.87±0.03*** | 0.57±0.00*** | 0.18±0.00*** | 0.55±0.01*** | 0.002±0.00*** | 0.006±0.03** | 5.02±0.24ns | |
| 处理Treatment | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.43±0.00 | 0.48±0.02 | 0.66±0.02 | 10.12±0.15 | 1.92±0.03 | 2.63±0.15 | 0.26±0.00 |
| NaHCO3 | 0.41±0.00** | 1.32±0.05** | 1.07±0.01*** | 19.36±0.43*** | 1.65±0.01** | 2.37±0.23ns | 0.20±0.01* |
表3 NaHCO3胁迫处理对长穗偃麦草阴阳离子运输的影响
Table 3 Effects of NaHCO3 stress on cation and anion transport in E. elongata
| 处理Treatment | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.43±0.00 | 0.48±0.02 | 0.66±0.02 | 10.12±0.15 | 1.92±0.03 | 2.63±0.15 | 0.26±0.00 |
| NaHCO3 | 0.41±0.00** | 1.32±0.05** | 1.07±0.01*** | 19.36±0.43*** | 1.65±0.01** | 2.37±0.23ns | 0.20±0.01* |
| [1] | Shabala S, Wu H, Bose J. Salt stress sensing and early signaling events in plant roots: current knowledge and hypothesis. Plant Science, 2015, 241: 109-119. |
| [2] | Tavakkoli E, Fatehi F, Coventry S, et al. Additive effects of Na+ and Cl- ions on barley growth under salinity stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(6): 2189-2203. |
| [3] | Yang Y, Guo Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytologist, 2018, 217(2): 523-539. |
| [4] | Geng G, Li R, Piergiorgio S, et al. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of sugar beet reveals different mechanisms of response to neutral salt and alkaline salt stresses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 571864. |
| [5] | Wang S F, Hu Y X, Li Z L. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and mineral ion uptake, transportation and distribution of Quercus virginiana. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(17): 4609-4616. |
| 王树凤, 胡韵雪, 李志兰. 盐胁迫对弗吉尼亚栎生长及矿质离子吸收、运输和分配的影响.生态学报, 2010, 30(17): 4609-4616. | |
| [6] | Sun J, Chen S L, Dai S X, et al. Ion flux profiles and plant ion homeostasis control under salt stress. Plant Signaling and Behavior, 2009, 4(4): 261-264. |
| [7] | Mohammad A A, Nudrat A A, Muhammad A, et al. Plant responses to environmental stresses-from gene to biotechnology. AoB Plants, 2017, 9(4).doi:10.1093/aobpla/plx025. |
| [8] | Imen T, Elena D I, Rym K, et al. Effects of NaCl or Na2SO4 salinity on plant growth, ion content and photosynthetic activity in Ocimum basilicum L. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2012, 34: 607-615. |
| [9] | Luo D, Wu Z B, Shi Y J, et al. Effects of salt stress on leaf anatomical structure and ion absorption, transportation and distribution of three Ping’ou hybrid hazelnut seedlings. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(5): 1876-1888. |
| 罗达, 吴正保, 史彦江, 等. 盐胁迫对3种平欧杂种榛幼苗叶片解剖结构及离子吸收、运输与分配的影响. 生态学报, 2022, 42(5): 1876-1888. | |
| [10] | Xu M. Effects of saline-alkali stresses on seed germination, growth and physiological traits of Elytrigia elongate L. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2020. |
| 徐曼. 盐碱胁迫对长穗偃麦草种子萌发、生长及生理特性的影响. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2020. | |
| [11] | Gengmao Z, Yu H, Xing S, et al. Salinity stress increases secondary metabolites and enzyme activity in safflower. Industrial Crops and Products, 2015, 64: 175-181. |
| [12] | Zhu J K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell, 2016, 167(2): 313-324. |
| [13] | Chakraborty K, Bishi S K, Goswami N, et al. Differential fine-regulation of enzyme driven ROS detoxification network imparts salt tolerance in contrasting peanut genotypes. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2016, 128: 79-90. |
| [14] | Zhang R, Ma X, Zhu R T, et al. Metabolic pathway and transcriptional regulation of Qinghai wild Poa pratensis in response to drought stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(6): 1508-1518. |
| 张然, 马祥, 朱瑞婷, 等. 青海野生草地早熟禾响应干旱胁迫的代谢通路及转录调控分析. 草地学报, 2020, 28(6): 1508-1518. | |
| [15] | Deng X, Xu X X, Sun Q, et al. Photosynthetic characteristics and transcriptome analysis of winter wheat seedlings under different salt concentration stress. Plant Physiology Journal, 2023, 59(9): 1819-1829. |
| 邓肖, 徐学欣, 孙芹, 等. 不同盐浓度胁迫下冬小麦幼苗光合特性及转录组分析. 植物生理学报, 2023, 59(9): 1819-1829. | |
| [16] | Li X T, Cao J, Wei X J, et al. Effeet of extended exposure to NaCl stress on the growth, ion distribution and photosynthetic characteristics of malting barley (Hordeum vulgare). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(6): 108-116. |
| 李先婷, 曹靖, 魏晓娟, 等. NaCl渐进胁迫对啤酒大麦幼苗生长、离子分配和光合特性的影响. 草业学报, 2013, 22(6): 108-116. | |
| [17] | Li J Y, Wang W Q, Yang L Q, et al. Study on the determination of chloride ions by hydrogen peroxide pretreatment and silver nitrate titration. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2024(7): 241-248. |
| 李婧怡, 王玮棋, 杨柳青, 等. 过氧化氢预处理-硝酸银滴定法测定氯离子的研究.中国土壤与肥料, 2024(7): 241-248. | |
| [18] | Ma Y F, Ma Z Q, Zhang X G. Comparison of water soluble SO4 2- chemical analysis methods in soil. Modern Chemical Research, 2017(7): 21-22. |
| 马云飞, 马琢琪, 张旭光. 土壤中水溶性SO4 2-化学分析方法对比.当代化工研究, 2017(7): 21-22. | |
| [19] | Ding J Z. An improvement of determination method of NO3 - in circulating water. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2008(3): 42, 45. |
| 丁敬增. 循环水中NO3 -测定方法的改进.山东化工, 2008(3): 42, 45. | |
| [20] | Tang X Q, Bai Y F, Liu G L, et al. Effects of NaCl stress on growth and mineral ions absorption and distribution of Platycladus orientalis seedlings. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 60-66. |
| 唐晓倩, 白应飞, 刘广亮, 等. NaCl胁迫对侧柏幼苗生长及矿质离子吸收和分配的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(9): 60-66. | |
| [21] | Wang H W, Sun S, Ge W Y, et al. Horizontal gene transfer of Fhb7 from fungus underlies Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat. Science, 2020, 368(6493): e5435. |
| [22] | Niu K J. The role of 5-aminolevulinic acid on regulation mechanism of photosynthesis in Kentucky bluegrass seedlings under drought stress. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 牛奎举. 外源5-氨基乙酰丙酸对干旱胁迫下草地早熟禾光合作用的调控机制. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2018. | |
| [23] | Huang T, Zhang J, Xu Z P, et al. Deciphering the effects of gene deletion on yeast longevity using network and machine learning approaches. Biochimie, 2012, 94(4): 1017-1025. |
| [24] | Munns R, Tester M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2008, 59: 651-681. |
| [25] | Carlos S G A, Christa T. Salt stress signals shape the plant root. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2011, 14(3): 296-302. |
| [26] | Liu X, Wang Y. Effects of salt stress on biomass and photosynthetic fluorescence characteristics of two Glycyrrhiza seedlings. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(2): 163-169. |
| 刘萱, 王芸. 盐胁迫对两种甘草幼苗生物量及光合荧光特性的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(2): 163-169. | |
| [27] | Hu G, Koh J, Yoo M J, et al. Proteomics profiling of fiber development and domestication in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Planta, 2014, 240(6): 1237-1251. |
| [28] | Luo D, Zhou Q, Wu Y. Full-length transcript sequencing and components towards salinity tolerance in the roots of cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa). BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 32. |
| [29] | Yang C, Wang L, Quan C T, et al. Relative expression profiles of genes response to salt stress and constructions of gene co-expression networks in Brassica napus L. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 237-250. |
| 杨闯, 王玲, 全成滔, 等. 甘蓝型油菜盐胁迫响应基因表达谱分析及共表达网络的构建. 作物学报, 2024, 50(1): 237-250. | |
| [30] | Sharma A, Shahzad B, Rehman A, et al. Response of phenylpropanoid pathway and the role of polyphenols in plants under abiotic stress. Molecules, 2019, 24(13): 2452. |
| [31] | Vijayata S, Ajit P S, Jyoti B. Differential expression of salt-responsive genes to salinity stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice (Oryza sativa L.) at seedling stage. Protoplasma, 2018, 255(6): 1667-1681. |
| [32] | Zhou Y B, Liu C, Tang D Y, et al. The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase STRK1 phosphorylates and activates CatC, thereby regulating H2O2 homeostasis and improving salt tolerance in rice. The Plant Cell, 2018, 30(5): 1100-1118. |
| [33] | Gou X P, Yin H J, He K, et al. Genetic evidence for an indispensable role of somatic embryogenesis receptor kinases in brassinosteroid signaling. PLoS Genetics, 2012, 8(1): e1002452. |
| [34] | Zuo C Y, Li Y W, Li Y L, et al. Relative expression patterns of laccase gene family members in upland Gossypium hirsutum L. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2023, 49(9): 2344-2361. |
| 左春阳, 李亚玮, 李焱龙, 等. 陆地棉漆酶基因家族成员表达模式分析. 作物学报, 2023, 49(9): 2344-2361. | |
| [35] | Liu Q Q. Response mechanism of lignin synthesis in rice under copper stress and the role of rice laccase in plants tolerance to heavy metal. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015. |
| 刘清泉. 铜胁迫下水稻木质素合成的响应机制及水稻漆酶在植物重金属耐性中的作用. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. | |
| [36] | Wang Q Z, Liu Q, Gao Y N, et al. Review on the mechanisms of the response to salinity-alkalinity stress in plants. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. |
| 王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 等. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 2017, 37(16): 5565-5577. | |
| [37] | Benito B, Haro B, Amtmann A, et al. The twins K+ and Na+ in plants. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2014, 171(9): 723-731. |
| [38] | Luo B Y, Chen S Y, Yang Y J, et al. Ion uptake, transportation and the expression of related genes in Chrysanthemum indicum under salt stress. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2024, 52(2): 68-74, 83. |
| 罗玢晔, 陈胜艳, 杨宇佳, 等. 盐胁迫下野菊离子的吸收转运情况及相关基因的表达. 东北林业大学学报, 2024, 52(2): 68-74, 83. | |
| [39] | Han Y, Yin S Y, Huang L. Towards plant salinity tolerance-implications from ion transporters and biochemical regulation. Plant Growth Regulation, 2015, 76: 13-23. |
| [40] | Cao X Q, Wang W C, Yin F T, et al. Effects of exogenous calcium on ion balance and photosynthetic characteristics in leaves of rapeseed seedlings under NaHCO3 stress. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2023, 42(5): 149-157. |
| 曹小强, 王卫超, 阴法庭, 等. 外源钙对NaHCO3胁迫下油菜幼苗叶片离子平衡及光合特性的影响. 华中农业大学学报, 2023, 42(5): 149-157. | |
| [41] | Bo S, Xia B, Liu M Y, et al. Screening of salt-resistant strains of Chrysanthemum indicum and preliminary study on salt-resistant mechanism. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2023, 32(1): 90-100. |
| 薄杉, 夏斌, 刘铭宇, 等. 野菊抗盐株系筛选与抗盐机理初探. 西北农业学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-100. |
| [1] | 马婷, 陈奋奇, 王勇, 哈雪, 李亚君, 马晖玲. NaCl胁迫下鹰嘴紫云英根系基因差异表达及相关通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2025, 34(4): 104-123. |
| [2] | 卜祥琪, 李姗姗, 段莹娜, 王迎春, 郑琳琳. 一氧化氮对盐碱胁迫下盐地碱蓬抗逆性及饲用品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 60-69. |
| [3] | 程鑫宇, 王继莲, 麦日艳古·亚生null, 李明源. 盐爪爪根际土壤产IAA菌株分离及促生特性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 110-121. |
| [4] | 曾兵, 尚盼盼, 沈秉娜, 王胤晨, 屈明好, 袁扬, 毕磊, 杨兴云, 李文文, 周晓丽, 郑玉倩, 郭文强, 冯彦龙, 曾兵. 淹水胁迫下鸭茅根系基因差异表达及相关通路分析[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(2): 93-111. |
| [5] | 卢晓瑜, 刘雅洁, 白彩霞, 李进华, 王子贺, 杨春雪. 虎尾草伴生和丛枝菌根真菌对碱胁迫下羊草生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 69-83. |
| [6] | 杨小涵, 伍国强, 魏明, 王北辰. HKT在植物离子稳态和响应非生物逆境胁迫中的作用[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(5): 190-202. |
| [7] | 尚盼盼, 曾兵, 屈明好, 李明阳, 杨兴云, 郑玉倩, 沈秉娜, 毕磊, 杨成, 曾兵. 红三叶响应淹水胁迫的相关通路及差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 112-128. |
| [8] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 刘秀丽, 欧晓彬, 贾海燕, 卜婷, 李娜. 盐碱胁迫下外源硫化氢对裸燕麦叶片氨基酸代谢过程的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 119-130. |
| [9] | 李瑞强, 王玉祥, 孙玉兰, 张磊, 陈爱萍. 盐胁迫对5份无芒雀麦苗期生长和生理生化的影响及综合性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 99-111. |
| [10] | 苗阳阳, 张艳蕊, 宋标, 刘旭桐, 张安琪, 吕金泽, 张浩, 张小华, 欧阳佳慧, 李旺, 曲善民. 碱蓬根际和内生细菌菌株对盐碱胁迫下苜蓿生长的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 107-117. |
| [11] | 张勇, 田小霞, 郑明利, 毛培春, 孟林. 过表达长穗偃麦草EeHKT1;4基因增强拟南芥抗旱耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 188-198. |
| [12] | 李宏伟, 郑琪, 李滨, 赵茂林, 李振声. 一种耐盐碱牧草——长穗偃麦草研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 190-199. |
| [13] | 杨志民, 邢瑞, 丁鋆嘉, 庄黎丽. 基于转录组测序的高羊茅分蘖与株高相关差异表达基因分析[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 145-163. |
| [14] | 陈雅琦, 苏楷淇, 陈泰祥, 李春杰. 混合盐碱胁迫对醉马草种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 137-157. |
| [15] | 周晶, 陈思齐, 史文娇, 阳伏林, 林辉, 林占熺. 巨菌草幼叶及根转录组功能基因测序及分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 143-155. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||