

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 25-33.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020431
张学良1( ), 张宇亭1, 刘瑞1, 谢军1, 张建伟1, 徐文静1, 石孝均1,2(
), 张宇亭1, 刘瑞1, 谢军1, 张建伟1, 徐文静1, 石孝均1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-27
修回日期:2020-11-30
出版日期:2021-05-20
发布日期:2021-04-16
通讯作者:
石孝均
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: shixj@swu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xue-liang ZHANG1( ), Yu-ting ZHANG1, Rui LIU1, Jun XIE1, Jian-wei ZHANG1, Wen-jing XU1, Xiao-jun SHI1,2(
), Yu-ting ZHANG1, Rui LIU1, Jun XIE1, Jian-wei ZHANG1, Wen-jing XU1, Xiao-jun SHI1,2( )
)
Received:2020-09-27
Revised:2020-11-30
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-04-16
Contact:
Xiao-jun SHI
摘要:
为探究不同绿肥在翻压和覆盖两种还田方式下引起的温室气体排放及对土壤微生物量碳氮的影响。采用室内培养试验,设置光叶苕子翻压(VB)、光叶苕子覆盖(VS)、黑麦草翻压(RB)、黑麦草覆盖(RS)和无绿肥(CK) 5个处理,测定土壤CO2、N2O、CH4浓度和微生物量碳(MBC)和微生物量氮(MBN)含量,分析了土壤温室气体的排放速率、累积排放量以及综合增温潜势。结果表明,绿肥还田显著提高了土壤CO2、N2O的排放,不同还田方式(翻压与覆盖还田)及不同绿肥品种对CO2、N2O排放的影响存在显著差异。覆盖还田较翻压还田显著降低了CO2、N2O排放。培养期内绿肥覆盖处理CO2的排放速率和累积排放量比翻压处理降低17.07%~18.55%和8.15%~9.79%;N2O的排放速率和累积排放量降低22.91%~38.35%和17.97%~34.39%。在相同还田方式下,不同绿肥品种显著影响了CO2、N2O排放,豆科绿肥还田引起的CO2、N2O累积排放量比禾本科绿肥高8.87%~10.85%和21.90%~52.42%。各处理土壤温室气体的排放与土壤微生物量碳、微生物量氮(MBC、MBN)含量呈显著正相关,绿肥翻压还田显著提升了MBC、MBN含量,比覆盖还田高21.42%~40.52%和28.22%~34.23%。综上,绿肥覆盖还田比翻压还田更能有效减少土壤温室气体的排放,且有利于保护生态环境和节约人工成本,但是对作物生长及产量的影响有待田间试验验证。
张学良, 张宇亭, 刘瑞, 谢军, 张建伟, 徐文静, 石孝均. 绿肥不同还田方式对土壤温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 25-33.
Xue-liang ZHANG, Yu-ting ZHANG, Rui LIU, Jun XIE, Jian-wei ZHANG, Wen-jing XU, Xiao-jun SHI. Effects of green manure return regimes on soil greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(5): 25-33.
| 绿肥Green manure | 碳Carbon (%DM) | 氮Nitrogen (%DM) | 磷Phosphorus (%DM) | 钾Potassium (%DM) | 碳氮比C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多年生黑麦草L. perennel | 47.19±1.75 | 2.03±0.26 | 0.53±0.03 | 4.26±0.19 | 23.24±2.57 |
| 光叶苕子V. villosa | 43.46±1.09 | 3.91±0.13 | 0.50±0.04 | 5.12±0.17 | 11.11±0.36 |
表1 供试绿肥养分含量
Table 1 The content of green manure
| 绿肥Green manure | 碳Carbon (%DM) | 氮Nitrogen (%DM) | 磷Phosphorus (%DM) | 钾Potassium (%DM) | 碳氮比C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多年生黑麦草L. perennel | 47.19±1.75 | 2.03±0.26 | 0.53±0.03 | 4.26±0.19 | 23.24±2.57 |
| 光叶苕子V. villosa | 43.46±1.09 | 3.91±0.13 | 0.50±0.04 | 5.12±0.17 | 11.11±0.36 |
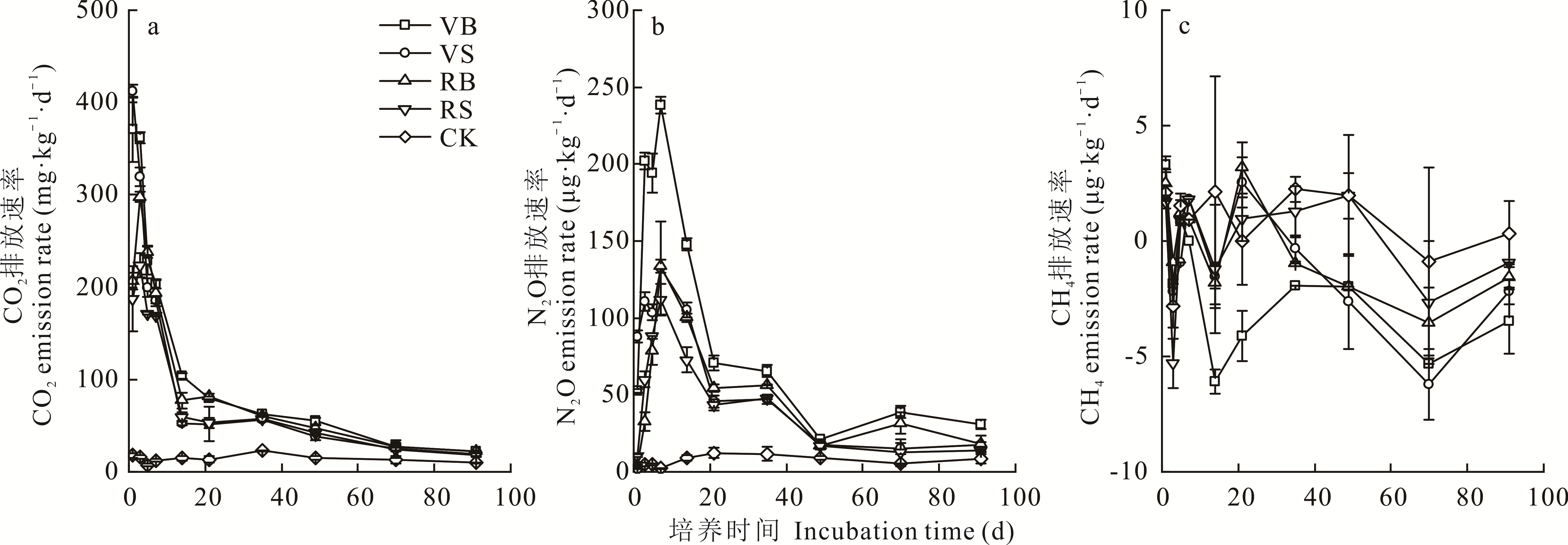
图1 绿肥不同还田方式对土壤温室气体排放速率的影响VB:光叶苕子翻压Vetch bury; VS:光叶苕子覆盖Vetch surface; RB:黑麦草翻压 Ryegrass bury; RS:黑麦草覆盖 Ryegrass surface; CK:对照Control.下同 The same below.
Fig.1 Effect of different returning methods of green manure on soil greenhouse gas release rate
项目 Item | 增温潜势Warming potential | 综合增温潜势 Comprehensive GWP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | N2O | ||
| VB | 6.19a | -0.0089a | 1.55a | 7.73a |
| VS | 5.04c | -0.0061b | 0.96b | 5.99c |
| RB | 5.58b | -0.0039b | 1.02b | 6.60b |
| RS | 4.63d | -0.0010c | 0.78c | 5.42d |
| CK | 1.34e | 0.0018d | 0.21d | 1.55e |
表2 不同处理土壤温室气体的增温潜势
Table 2 Global warming potential (GWP) of greenhouse gases in different treatments (g CO2·kg-1)
项目 Item | 增温潜势Warming potential | 综合增温潜势 Comprehensive GWP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | N2O | ||
| VB | 6.19a | -0.0089a | 1.55a | 7.73a |
| VS | 5.04c | -0.0061b | 0.96b | 5.99c |
| RB | 5.58b | -0.0039b | 1.02b | 6.60b |
| RS | 4.63d | -0.0010c | 0.78c | 5.42d |
| CK | 1.34e | 0.0018d | 0.21d | 1.55e |
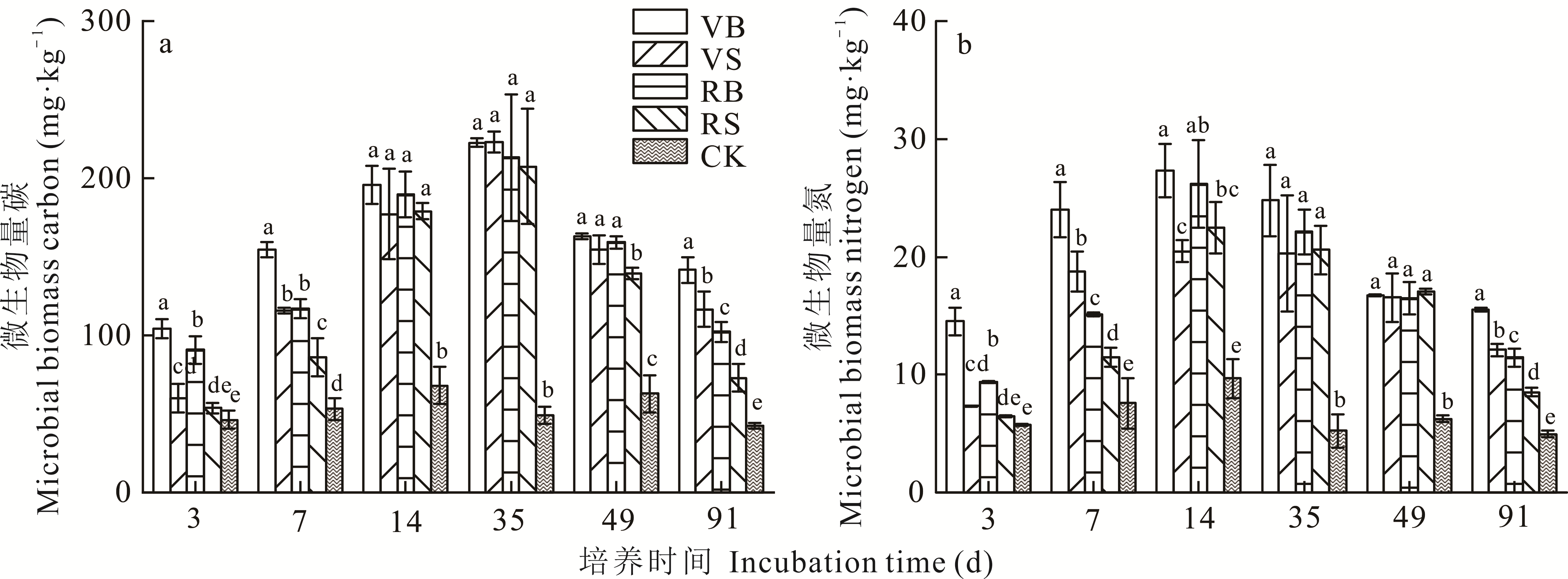
图3 绿肥不同还田方式对土壤微生物量碳氮的影响不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different small letters indicate significant difference among the treatments (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Effect of different returning methods of green manure on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen
| 项目Item | N2O | CH4 | 增温潜势GWP | 微生物量碳MBC | 微生物量氮MBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 0.930** | -0.824** | 0.997** | 0.878** | 0.915** |
| N2O | -0.895** | 0.955** | 0.943** | 0.976** | |
| CH4 | -0.848** | -0.926** | -0.947** | ||
| 增温潜势GWP | 0.901** | 0.938** | |||
| 微生物量碳MBC | 0.977** |
表3 温室气体累计排放量与微生物生物量碳、氮的相关性分析
Table 3 The correlation analysis of greenhouse gases cumulative emission, microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen
| 项目Item | N2O | CH4 | 增温潜势GWP | 微生物量碳MBC | 微生物量氮MBN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | 0.930** | -0.824** | 0.997** | 0.878** | 0.915** |
| N2O | -0.895** | 0.955** | 0.943** | 0.976** | |
| CH4 | -0.848** | -0.926** | -0.947** | ||
| 增温潜势GWP | 0.901** | 0.938** | |||
| 微生物量碳MBC | 0.977** |
| 1 | Han J L, Hao S, Liu Z J, et al. Characteristics of CO2 and N2O emissions under two land use types in the Loess Plateau of China. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(11): 5164-5172. |
| 韩佳乐, 郝珊, 刘振杰, 等. 黄土高原地区两种土地利用方式CO2和N2O排放特征. 环境科学, 2019, 40(11): 5164-5172. | |
| 2 | Kuppusamy S, Thavamani P, Megharaj M, et al. Agronomic and remedial benefits and risks of applying biochar to soil: Current knowledge and future research directions. Environment International, 2016, 87: 1-12. |
| 3 | Gao H J, Zhang W J, Peng C, et al. Emission characteristics of greenhouse gas from maize field of black soil region under long-term fertilization. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2017, 34(5): 422-430. |
| 高洪军, 张卫建, 彭畅, 等.长期施肥下黑土玉米田土壤温室气体的排放特征. 农业资源与环境学报, 2017, 34(5): 422-430. | |
| 4 | Matz B, Davidson O, Bosch P, et al. Climate change 2007: Mitigation of climate change: Working in group Ⅲ contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC. Computational Geometry, 2007(2): 1-21. |
| 5 | Sanz C A, García M S, Quemada M, et al. Do cover crops enhance N2O, CO2 or CH4 emissions from soil in Mediteerranean arable systems? Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 466/467: 164-174. |
| 6 | Singly R J, Ghosh B N, Sharma N K, et al. Effect of seven years of nutrient supplementation through organic and inorganic sources on productivity, soil and water conservation, and soil fertility changes of maize-wheat rotation in North-western Indian Himalayas. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2017, 249: 177-186. |
| 7 | Chang D N, Liu C Z, Li B Y, et al. Effects of incorporating Chinese milk vetch on reductive material characteristics and greenhouse gas emissions in paddy soil. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(12): 133-144. |
| 常单娜, 刘春增, 李本银, 等. 翻压紫云英对稻田土壤还原物质变化特征及温室气体排放的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): | |
| 133-144. | |
| 8 | Mancinelli R, Marinari S, Felice V D, et al. Soil property, CO2 emission and aridity index as agroecological indicators to assess the mineralization of cover crop green manure in a Mediterranean environment. Ecological Indicators, 2013, 34: 31-40. |
| 9 | Pachauri R, Reisinger A. Climate change 2014: Synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Journal of Romance Studies, 2014, 4(2): 85-88. |
| 10 | Jenkinson D S, Brookes P C, Powrson D S. Measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2004, 36: 5-7. |
| 11 | Ye J, Wang Y X, Wang F, et al. Simulation study on organic carbon mineralization in soil of tea plantations with application of green legume fertilizer. Acta Tea Sinica, 2016, 57(3): 133-137. |
| 叶菁, 王义祥, 王峰, 等. 豆科绿肥对茶园土壤有机碳矿化的模拟研究. 茶叶学报, 2016, 57(3): 133-137. | |
| 12 | Zhao X, Wang J, Wang S, et al. Successive straw biochar application as a strategy to sequester carbon and improve fertility: A pot experiment with two rice/wheat rotations in paddy soil. Plant and Soil, 2014, 378(1/2): 279-294. |
| 13 | Zhu B, Yi L X, Hu Y G, et al. Effects of ryegrass incorporation on CH4 and N2O emission from double rice paddy soil. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultutal Engineering , 2011, 27(12): 241-245. |
| 朱波, 易丽霞, 胡跃高, 等. 黑麦草鲜草翻压还田对双季稻CH4与 N2O 排放的影响. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(12): 241-245. | |
| 14 | Li Y C, Hou C C, Li Y, et al. Effects of no-till and straw mulch on greenhouse gas emission from farmland: A review. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(6): 1076-1083. |
| 李英臣, 侯翠翠, 李勇, 等. 免耕和秸秆覆盖对农田土壤温室气体排放的影响. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(6): 1076-1083. | |
| 15 | Al-kaisi M M, Yin X. Tillage and crop residue effects on soil carbon and carbon dioxide emission in corn-soybean rotation . Journal of Environmental Quality, 2005, 34: 437-445. |
| 16 | Huang T, Huang G B, Yu A Z, et al. Effects of different tillage measures on the CO2 emission flux from winter wheat field. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2009, 44(6): 28-32. |
| 黄涛, 黄高宝, 于爱忠, 等.不同耕作措施对冬小麦田CO2排放通量的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2009, 44(6): 28-32. | |
| 17 | Cheng C, Zeng Y J, Yang X X, et al. Effect of different tillage methods on net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in double rice cropping systems. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(6): 1887-1895. |
| 成臣, 曾勇军, 杨秀霞, 等. 不同耕作方式对稻田净增温潜势和温室气体强度的影响. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(6): 1887-1895. | |
| 18 | Bender M, Conrad R. Kinetics of methane oxidation in oxic soils . Chemosphere, 1993, 26(1/4): 687-696. |
| 19 | Chen W, Lu W F, Duan B W, et al. Effect of rice straw manure on methane emission in late-rice paddy fields. Acta Pedologica Sinica , 2002, 39(2): 170-176. |
| 陈苇, 卢婉芳, 段彬伍, 等. 稻草还田对晚稻稻田甲烷排放的影响. 土壤学报, 2002, 39(2): 170-176. | |
| 20 | Jiang C S, Wang Y S, Zheng X H, et al. Advances in the research on methane emission from paddy fields and its affecting factors. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004, 35(5): 663-669. |
| 江长胜, 王跃思, 郑循华, 等.稻田甲烷排放影响及研究进展. 土壤通报, 2004, 35(5): 663-669. | |
| 21 | Wan Y F, Li Y E, Gao Q Z, et al. Field managements affect yield, soil carbon, and greenhouse gases emission of winter wheat in North China Plain. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(12): 2495-2500. |
| 万运帆, 李玉娥, 高清竹, 等.田间管理对华北平原冬小麦产量土壤碳及温室气体排放的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(12): 2495-2500. | |
| 22 | Wang X Y, Zhang R Z, Cai L Q, et al. Emission characteristics of CH4 and N2O fluxes from dryland field under different nitrogen treatments. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35(11): 3655-3661. |
| 王旭燕, 张仁陟, 蔡立群, 等. 不同施氮处理下旱作农田土壤CH4、N2O气体排放特征研究. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(11): 3655-3661. | |
| 23 | Sant A S A C, Martins M R, Goulart J M, et al. Biological nitrogen fixation and soil N2O emissions from legumne residues in an Acrisol in Se Brazil. Geoderma Regional, 2018, 15: e00196. |
| 24 | Fungo B, Lehmann J, Kalbitz K, et al. Ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions from a field ultisol amended with tithonia green manure, urea, and biochar. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2019, 55(2): 135-148. |
| 25 | Sharifi M, Lynch D H, Hammermeister A, et al. Effect of green manure and suppl emental fertility amendments on selected soil quality parameters in an organic potato rotationin Eastern Canada. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2014, 100(2): 135-146. |
| 26 | Petersen S O, Mutegi J K, Hansen E M, et al. Tillage effects on N2O emissions as influenced bya winter cover crop. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2011, 43(7): 1509-1517. |
| 27 | Mancinelli R, Marinari S, Felice V D, et al. Soil property, CO2 emission and aridity index as agroecological indicators to assess the mineralization of cover crop green manure in a Mediterranean environment. Ecological Indicators, 2013, 34: 31-40. |
| 28 | Cao W D, Huang H X. Ideas on restoration and development of green manures in China. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2009(4): 1-3. |
| 曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(4): 1-3. | |
| 29 | Kliiber H D, Conrad R. Effects of nitrate, nitrite, NO and N2O on methanogenesis and other redox processes in anoxic rice field soil. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 1998, 25(3): 301-318. |
| 30 | Qin X B, Li Y E, Shi S W, et al. Multivariate regression analysis of greenhouse gas emissions associated with activities and populations of soil microbes in a double-rice paddy soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(6): 1811-1819. |
| 秦晓波, 李玉娥, 石生伟, 等. 稻田温室气体排放与土壤微生物菌群的多元回归分析. 生态学报, 2012, 32(6): 1811-1819. | |
| 31 | Le M J, Roger P. Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: A review. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2001, 37(1): 25-50. |
| [1] | 吕汉强, 于爱忠, 王玉珑, 苏向向, 吕奕彤, 柴强. 干旱绿洲灌区玉米氮素吸收利用对绿肥还田利用方式的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 93-103. |
| [2] | 杨叶华, 张松, 王帅, 刘正兰, 方林发, 张学良, 刘瑞, 张建伟, 张宇亭, 石孝均. 中国不同区域常见绿肥产量和养分含量特征及替代氮肥潜力评估[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. |
| [3] | 肖博文, 冯伟, 段廷玉. 二月兰种带真菌致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 121-130. |
| [4] | 邓长芳, 罗珠珠, 李玲玲, 牛伊宁, 蔡立群, 张仁陟, 谢军红. 黄土高原雨养农业区不同种植模式土壤温室气体排放特征[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 1-13. |
| [5] | 戈小荣, 王俊, 张祺, 付鑫, 李志鹏. 不同降水格局下填闲种植对旱作冬小麦农田夏闲期土壤温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 27-38. |
| [6] | 常单娜, 刘春增, 李本银, 吕玉虎, 潘兹亮, 高嵩涓, 曹卫东. 翻压紫云英对稻田土壤还原物质变化特征及温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 133-144. |
| [7] | 王登科, 于翔宇, 张学风, 黄蕾, 李晓婷, 贺治斌, 康林, 王党军, 姚露花, 郭彦军. 酸、铝和盐胁迫对夏季豆科绿肥作物种子萌发及根瘤菌抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 35-44. |
| [8] | 王冬雪, 高永恒, 安小娟, 王瑞, 谢青琰. 青藏高原高寒湿地温室气体释放对水位变化的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 27-35. |
| [9] | 杜青峰, 王党军, 于翔宇, 姚露花, 和玉吉, 王瑞, 马生兰, 郭彦军. 玉米间作夏季绿肥对当季植物养分吸收和土壤养分有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 225-233. |
| [10] | 陈国军, 闫慧峰, 吴凯, 杨举田, 田雷, 谭效磊, 宗浩, 陈秀斋, 张永春, 孙延国, 刘海伟, 石屹. 不同收获期的籽粒苋绿肥还田对土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 215-224. |
| [11] | 周玲红, 魏甲彬, 唐先亮, 成小琳, 肖志祥, 徐华勤, 唐剑武. 冬季种养结合对稻田土壤微生物量及有效碳氮库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 103-114. |
| [12] | 孙艳茹,石屹,陈国军,闫慧峰. PEG模拟干旱胁迫下8种绿肥作物萌发特性与抗旱性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 89-98. |
| [13] | 马钢,王平,王冬雪,徐世权. 高寒灌丛土壤温室气体释放对添加不同形态氮素的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 20-29. |
| [14] | 李正,刘国顺,敬海霞,叶协锋,解昌盛,向永光,张文平,杨超,王永,习相银. 绿肥与化肥配施对植烟土壤微生物量及供氮能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6): 126-134. |
| [15] | 李正,刘国顺,敬海霞,解昌盛,向永光,杨超,郑文冉,叶协锋. 翻压绿肥对植烟土壤微生物量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(3): 225-232. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||