

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 64-75.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2021197
戈建珍( ), 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村(
), 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-11
修回日期:2021-08-20
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
寇建村
作者简介:E-mail: jiancun02@163.com基金资助:
Jian-zhen GE( ), Wen-hui FU, Lu ZHANG, Bao-jun LIN, Shuai ZHAO, Ma-ga-weng BAI, Jian-cun KOU(
), Wen-hui FU, Lu ZHANG, Bao-jun LIN, Shuai ZHAO, Ma-ga-weng BAI, Jian-cun KOU( )
)
Received:2021-05-11
Revised:2021-08-20
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
Jian-cun KOU
摘要:
为了解白三叶青贮后不同浓度多菌灵农药的降解情况和果园喷施多菌灵对白三叶青贮过程中细菌多样性的影响,扩大具有农药残留的果园覆盖植物利用途径,在喷施不同浓度[2.0 (RU-),2.5 (RU),3.0 g·L-1 (RU+)]的多菌灵后进行白三叶青贮,以喷水为对照,发酵60 d。采用Miseq高通量测序技术,分别在青贮开始前、青贮第3和60天取样,对白三叶中细菌群落多样性进行研究。结果表明,青贮后多菌灵降解率达到59.6%以上,喷施量越高,降解率越高;多菌灵处理显著(P<0.05)增加了白三叶青贮发酵的乳酸、乙酸、丙酸含量,乳酸在多菌灵RU-、RU、RU+浓度下分别增加了47.55%、63.24%、71.08%,乙酸分别增加了24.49%、44.90%、46.94%,丙酸分别增加了66.67%、187.50%、250.00%,有利于白三叶青贮饲料营养成分的保留;多菌灵喷施显著(P<0.05)改变了白三叶青贮菌群群落构成,增加了青贮的菌群丰度、多样性;多菌灵处理中乳球菌属、魏斯氏菌属、泛菌属、Rosenbergiella、假单胞菌属、寡养单胞菌属、肠杆菌属、芽孢杆菌属菌群丰度增加,不利于青贮发酵,但随着青贮时间的推移,寡养单胞菌属、肠杆菌属、芽孢杆菌属等菌群丰度减少。喷施多菌灵后有利于青贮发酵微生物菌群的丰度增加,对青贮发酵有害菌、多菌灵降解菌群丰度及青贮微生物多样性产生影响,青贮后多菌灵残留高于欧洲食品安全局规定的作物类动物饲料中农药最大残留量,达不到饲用标准。研究结果可为具有农药残留的白三叶青贮饲料的饲用安全性和果园覆盖植物资源的开发利用提供理论依据。
戈建珍, 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村. 多菌灵在果园白三叶青贮中的降解及其对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 64-75.
Jian-zhen GE, Wen-hui FU, Lu ZHANG, Bao-jun LIN, Shuai ZHAO, Ma-ga-weng BAI, Jian-cun KOU. Degradation of carbendazim in orchard white clover silage and its effect on the microbial fermentative community[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(7): 64-75.
| 项目Item | 空白对照 CON | RU- | RU | RU+ | 标准误SEM | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳酸Lactic acid (mg·mL-1) | 2.04±0.09c | 3.01±0.20b | 3.33±0.11a | 3.49±0.10a | 0.172 | 0.017 |
| 乙酸Acetic acid (mg·mL-1) | 0.49±0.05c | 0.61±0.04b | 0.71±0.06a | 0.72±0.04a | 0.738 | 0.030 |
| 丙酸Propionic acid (mg·mL-1) | 0.24±0.04c | 0.40±0.06b | 0.69±0.49b | 0.84±0.45a | 0.101 | 0.049 |
| pH | 4.92±0.06a | 4.65±0.04b | 4.53±0.03c | 4.62±0.04b | 0.706 | 0.044 |
| 氨态氮NH3-N (g·kg-1) | 2.86±0.13a | 2.23±0.13c | 2.60±0.23ab | 2.42±0.19bc | 0.082 | 0.031 |
| 干物质DM (g·kg-1) | 45.84±0.21a | 45.73±0.15a | 43.45±0.11c | 44.22±0.21b | 0.309 | 0.032 |
| 粗蛋白CP (g DM·kg-1) | 18.36±0.21c | 19.22±0.19a | 18.79±0.16b | 19.27±0.15a | 0.119 | 0.032 |
| 粗纤维CF (g DM·kg-1) | 17.00±0.20b | 16.97±0.15b | 17.23±0.15ab | 17.37±0.15a | 0.065 | 0.027 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维ADF (g DM·kg-1) | 24.63±0.12c | 25.07±0.12b | 26.10±0.20a | 24.77±0.21bc | 0.162 | 0.028 |
| 中性洗涤纤维NDF (g DM·kg-1) | 24.43±0.15c | 25.93±0.21a | 25.00±0.17b | 24.53±0.15c | 0.157 | 0.030 |
| 可溶性碳水化合物WSC (g DM·kg-1) | 2.48±0.09b | 3.80±0.01a | 3.83±0.02a | 3.88±0.02a | 0.178 | 0.002 |
| 粗脂肪EE (g DM·kg-1) | 3.51±0.08a | 3.56±1.00a | 3.69±0.61a | 3.46±0.18a | 0.055 | 0.067 |
表1 多菌灵对果园白三叶青贮饲料品质及营养价值的影响
Table 1 Effect of carbendazim on the quality and nutritional value of white clover silage in orchard
| 项目Item | 空白对照 CON | RU- | RU | RU+ | 标准误SEM | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳酸Lactic acid (mg·mL-1) | 2.04±0.09c | 3.01±0.20b | 3.33±0.11a | 3.49±0.10a | 0.172 | 0.017 |
| 乙酸Acetic acid (mg·mL-1) | 0.49±0.05c | 0.61±0.04b | 0.71±0.06a | 0.72±0.04a | 0.738 | 0.030 |
| 丙酸Propionic acid (mg·mL-1) | 0.24±0.04c | 0.40±0.06b | 0.69±0.49b | 0.84±0.45a | 0.101 | 0.049 |
| pH | 4.92±0.06a | 4.65±0.04b | 4.53±0.03c | 4.62±0.04b | 0.706 | 0.044 |
| 氨态氮NH3-N (g·kg-1) | 2.86±0.13a | 2.23±0.13c | 2.60±0.23ab | 2.42±0.19bc | 0.082 | 0.031 |
| 干物质DM (g·kg-1) | 45.84±0.21a | 45.73±0.15a | 43.45±0.11c | 44.22±0.21b | 0.309 | 0.032 |
| 粗蛋白CP (g DM·kg-1) | 18.36±0.21c | 19.22±0.19a | 18.79±0.16b | 19.27±0.15a | 0.119 | 0.032 |
| 粗纤维CF (g DM·kg-1) | 17.00±0.20b | 16.97±0.15b | 17.23±0.15ab | 17.37±0.15a | 0.065 | 0.027 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维ADF (g DM·kg-1) | 24.63±0.12c | 25.07±0.12b | 26.10±0.20a | 24.77±0.21bc | 0.162 | 0.028 |
| 中性洗涤纤维NDF (g DM·kg-1) | 24.43±0.15c | 25.93±0.21a | 25.00±0.17b | 24.53±0.15c | 0.157 | 0.030 |
| 可溶性碳水化合物WSC (g DM·kg-1) | 2.48±0.09b | 3.80±0.01a | 3.83±0.02a | 3.88±0.02a | 0.178 | 0.002 |
| 粗脂肪EE (g DM·kg-1) | 3.51±0.08a | 3.56±1.00a | 3.69±0.61a | 3.46±0.18a | 0.055 | 0.067 |

图1 果园生草白三叶青贮发酵过程对不同浓度多菌灵降解率的影响不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Different letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05.
Fig.1 The effect of the fermentation process of orchard grass white clover silage on the degradation rate of different concentrations of carbendazim
测序样本名称 Sequencing sample name | 原始PE reads数目 PE_reads | 去除嵌合体后有效序列数目 Nochimera | 有效序列平均长度 AvgLen (bp) | 各样品OTU总数OTUs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不喷施多菌灵(0 d,A) | 70933 | 66907 | 462 | 82 |
| 不喷施多菌灵(3 d,B) | 63698 | 54955 | 463 | 83 |
| 喷施多菌灵(3 d,C) | 59416 | 53199 | 463 | 87 |
| 喷施多菌灵(60 d,D) | 79630 | 68540 | 463 | 90 |
| 不喷施多菌灵(60 d,E) | 63874 | 58218 | 462 | 91 |
表2 优化后数据质量统计
Table 2 Data quality statistics after optimization
测序样本名称 Sequencing sample name | 原始PE reads数目 PE_reads | 去除嵌合体后有效序列数目 Nochimera | 有效序列平均长度 AvgLen (bp) | 各样品OTU总数OTUs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不喷施多菌灵(0 d,A) | 70933 | 66907 | 462 | 82 |
| 不喷施多菌灵(3 d,B) | 63698 | 54955 | 463 | 83 |
| 喷施多菌灵(3 d,C) | 59416 | 53199 | 463 | 87 |
| 喷施多菌灵(60 d,D) | 79630 | 68540 | 463 | 90 |
| 不喷施多菌灵(60 d,E) | 63874 | 58218 | 462 | 91 |
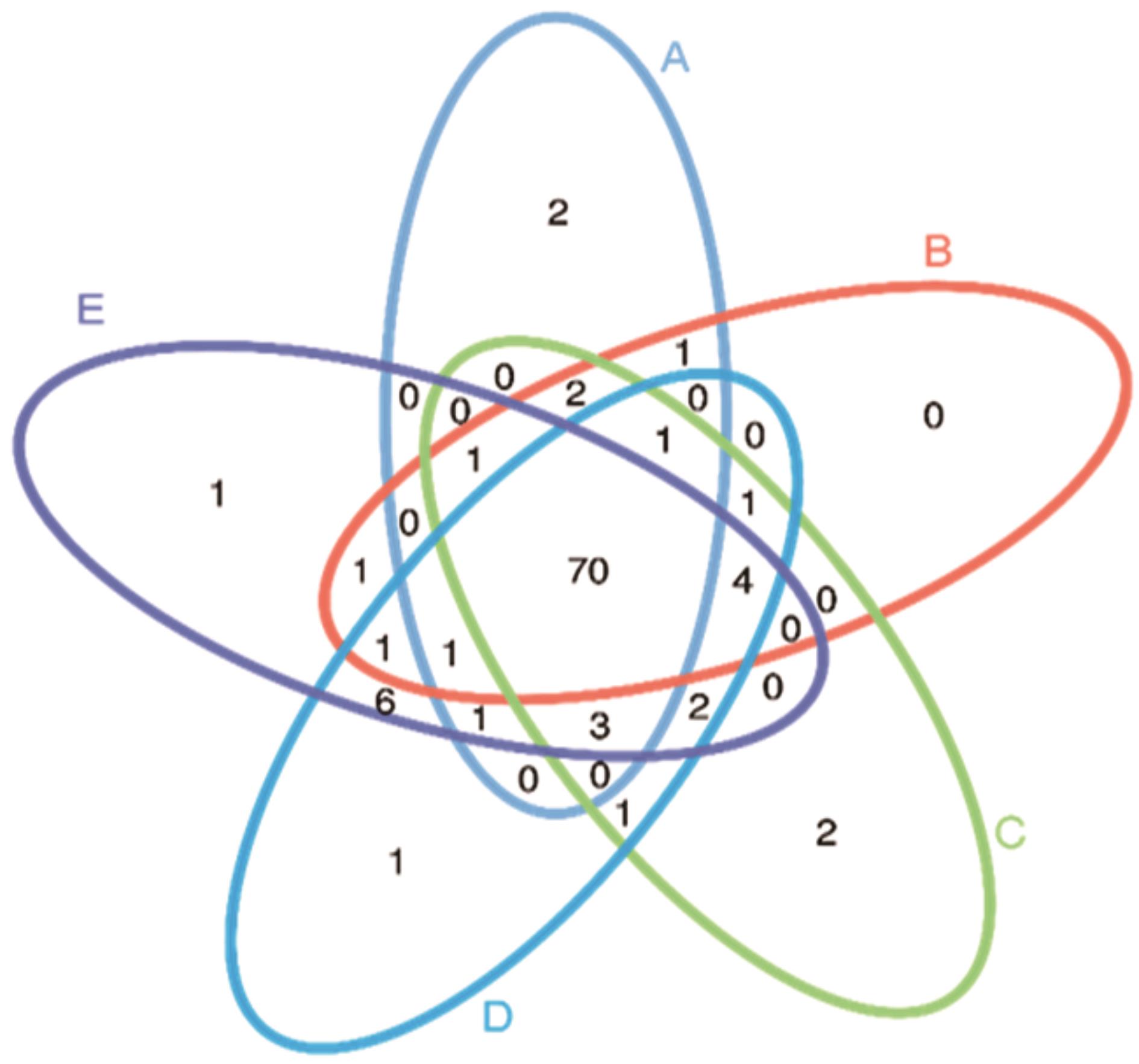
图2 OTU韦恩图韦恩图中不同颜色的圈表示不同的分组,图中的数字分别代表了每个分组特有或共有的OTU数目。A:不喷施多菌灵处理白三叶青贮第0天;B:不喷施多菌灵处理白三叶青贮第3天;C:喷施多菌灵处理青贮白三叶第3天;D:喷施多菌灵处理白三叶青贮第60天;E:不喷施多菌灵处理白三叶青贮第60天。下同。Different colored circles in the Wenn diagram represent different groups, and the numbers in the diagram represent the number of unique or common OTUs for each group. A: White clover silage treatment day 0 without carbendazim; B: White clover silage treatment day 3 without carbendazim; C: White clover silage treatment day 3 with carbendazim spray; D: The 60th day of white clover silage treatment with carbendazim; E: The 60th day of white clover silage treatment without carbendazim. The same below.
Fig.2 OTU Venn diagram
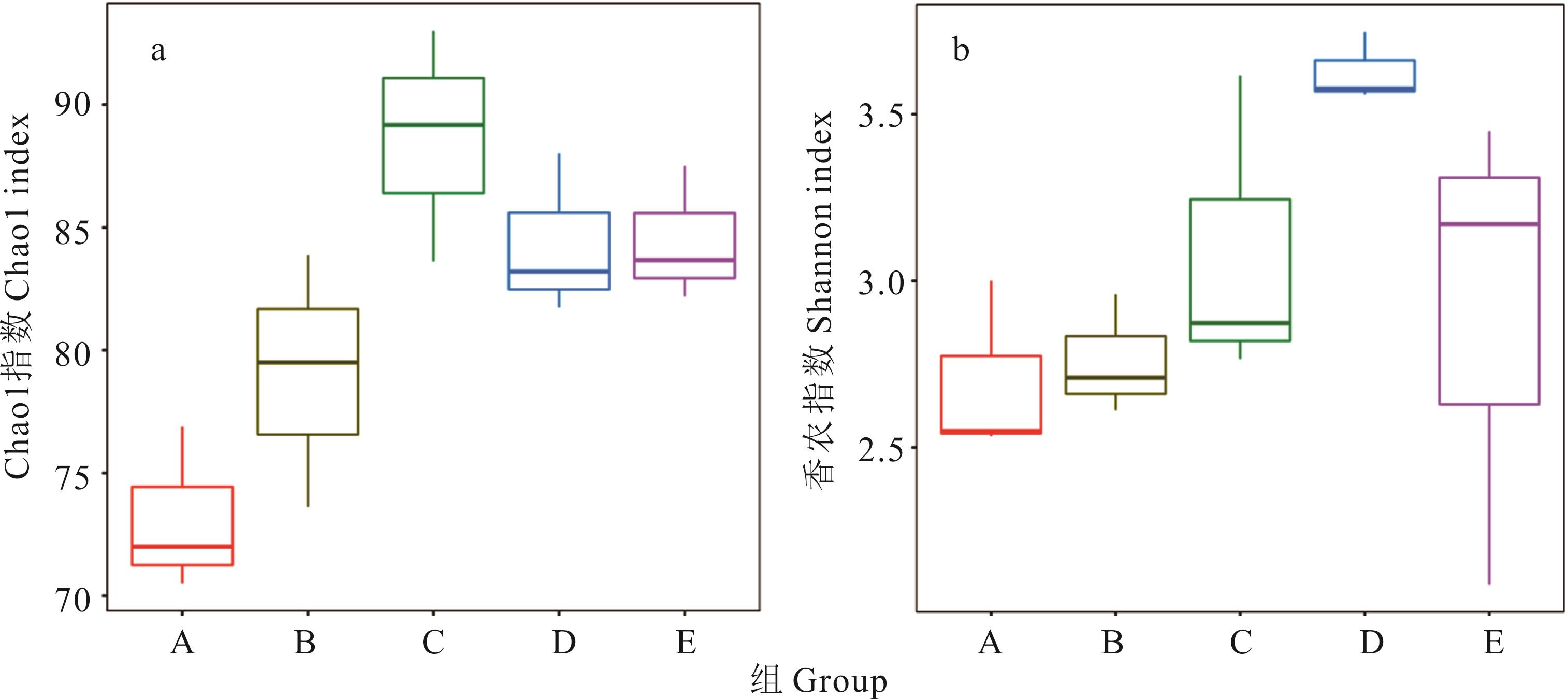
图3 DNA序列数据和微生物多样性指数分析a) Chao 1 指数,Chao 1指数越大,OTU数目越多,说明该样本物种数比较多;b)香农指数,Shannon指数越大,说明群落多样性越高。a) Chao 1 index, the greater the Chao 1 index, the greater the number of OTUs, indicating that there are more species in the sample; b) The Shannon index, the greater the Shannon index, the higher the community diversity.
Fig.3 DNA sequence data and microbial diversity index analysis
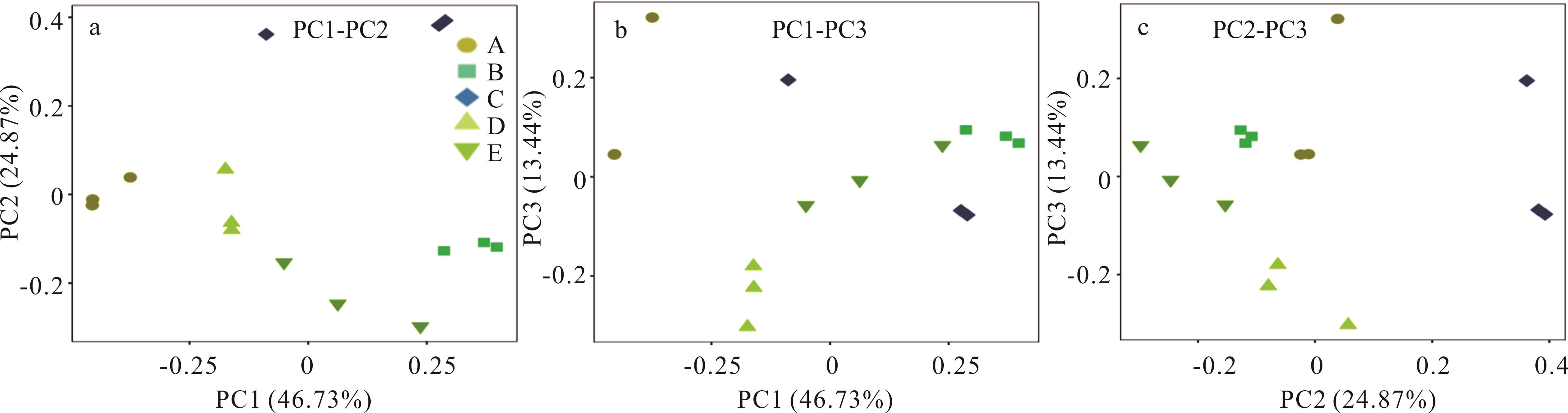
图4 基于Unifrac距离的PCoA分析同一个组的样本使用相同颜色和形状表示。x轴与y轴分别代表第一和第二主坐标。主坐标后的百分比代表此坐标对样本差异的贡献率,度量了此主坐标对原始信息量提取的多少。样本点距离的远近代表了样本中微生物群落的相似性,距离越近,相似度越高;聚集在一起的样本由相似的微生物群落构成。The samples in the same group are represented by the same color and shape. The x-axis and y-axis represent the first and second principal coordinates, respectively. The percentage after the principal coordinate represents the contribution rate of this coordinate to the sample difference, and measures how much the principal coordinate extracts the amount of original information. The distance between the sample points represents the similarity of the microbial communities in the sample. The closer the distance, the higher the similarity; The clustered samples are composed of similar microbial communities.
Fig.4 PCoA analysis based on Unifrac distance

图5 细菌群落分布使用RDP classifier贝叶斯算法对97%相似水平的OTU代表序列进行分类学分析,并在各个水平统计每个样本的群落组成,各分组在不同分类水平(门、科、属)下前30的菌群分布绘制为柱状图。Use RDP classifier Bayesian algorithm to perform taxonomic analysis on 97% similar level OTU representative sequences, and count the community composition of each sample at each level, and each group is in the top 30 under different classification levels (phyla, family, genus), the bacterial community distribution is plotted as a bar graph.
Fig.5 Bacterial community distribution
| 1 | Qin W L. Functions of growing grass in orchard in the construction of rural complex. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 23(6): 13-17. |
| 秦文利. 果园生草在田园综合体建设中的功能. 河北农业科学, 2019, 23(6): 13-17. | |
| 2 | Yang L, Mao Y F, Hu Y L, et al. Effects of orchard grass on soil fertility and apple tree nutrition. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. |
| 杨露, 毛云飞, 胡艳丽, 等. 生草改善果园土壤肥力和苹果树体营养的效果. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(2): 325-337. | |
| 3 | Li Y P, Ren Q Q, Zhang J W. Effect of growing grass on soil nutrients in orchard. Yantai Fruits, 2020, 4: 20-21. |
| 李元鹏, 任倩倩, 张京伟. 生草对果园土壤养分的影响. 烟台果树, 2020, 4: 20-21. | |
| 4 | Gou M C. Evaluation of nitrogen metabolism ability of dominant grass species in apple orchard and effect of orchard management on soil nutrients. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019. |
| 苟铭川. 自然生草苹果园优势草氮素代谢能力及刈割管理对土壤养分的影响. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. | |
| 5 | Fan X L, Wen S Y, Chen J, et al. Effect of C/N ratio on the fertility of white clover and wheat straw compost. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2018, 27(9): 1322-1327. |
| 范肖龙, 文素芸, 陈佳, 等. 碳氮比对白三叶和小麦秸秆堆肥的肥力影响. 西北农业学报, 2018, 27(9): 1322-1327. | |
| 6 | Sholberg P L, Hogue E J, Neilsen G H. Effect of orchard cover crop on incidence of low-temperature-basidiomycete rot of stored Spartan apples. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 1998, 78(1): 125-129. |
| 7 | Ripoche A, Aurélie Metay, Celette F, et al. Changing the soil surface management in vineyards: Immediate and delayed effects on the growth and yield of grapevine. Plant and Soil, 2011, 339(1/2): 259-271. |
| 8 | Huang T, Ding T, Liu D, et al. Degradation of carbendazim in soil: Effect of sewage sludge derived biochars. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(12): 3703-3710. |
| 9 | Wei Z H, Xu J, Guo M X, et al. Research progress of carbendazim in China. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(3): 125-127. |
| 魏中华, 徐娟, 郭明霞, 等. 国内多菌灵的研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(3): 125-127. | |
| 10 | Dai H L, Tian X H, Du W H, et al. Effects of silage additives on nutritional quality and silage quality of triticale and rye. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(12): 213-221. |
| 代寒凌, 田新会, 杜文华, 等. 不同添加剂处理对小黑麦和黑麦青贮营养品质和发酵品质的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(12): 213-221. | |
| 11 | Han Z Y, Wang Z Y, Liu Y N, et al. The effects of different additives on pH and crude protein content in corn straw silage. Feed Review, 2019, 7: 22-25. |
| 韩紫燕, 王忠艳, 刘亚楠, 等. 不同添加剂对玉米秸秆青贮料pH及粗蛋白质含量的影响. 饲料博览, 2019, 7: 22-25. | |
| 12 | Wan X R, Dou S Y, Li Y, et al. Effect of lactic acid bacteria preparations on microbial population counts and silage quality in maize silage during fermentation and on aerobic exposure. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. |
| 万学瑞, 豆思远, 李玉, 等. 复合乳酸菌对全株玉米青贮及有氧暴露后微生物及饲料品质的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. | |
| 13 | Huang F, Zhang L, Zhou B, et al. Research progress of silage microorganisms and their influence on the aerobic stability of silage. Acta Zoonutrimenta Sinica, 2019, 31(1): 93-100. |
| 黄峰, 张露, 周波, 等. 青贮微生物及其对青贮饲料有氧稳定性影响的研究进展. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(1): 93-100. | |
| 14 | Ruediger G A, Pardon K H, Sas A N, et al. Fate of pesticides during the winemaking process in relation to malolactic fermentation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005, 53(8): 3023-3026. |
| 15 | Regueiro J, Olalla López-Fernández, Rial-Otero R, et al. A review on the fermentation of foods and the residues of pesticides biotransformation of pesticides and effects on fermentation and food quality. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2015, 55(6): 839-863. |
| 16 | Xu D M, Zhang P, Ke W C, et al. Research progress of silage microorganisms and its effects on silage quality. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2017, 25(3): 460-465. |
| 许冬梅, 张萍, 柯文灿, 等. 青贮微生物及其对青贮饲料发酵品质影响的研究进展. 草地学报, 2017, 25(3): 460-465. | |
| 17 | Silambarasan S, Abraham J. Biodegradation of carbendazim by a potent novel Chryseobacterium sp. JAS14 and plant growth promoting Aeromonas caviae JAS15 with subsequent toxicity analysis. 3 Biotech, 2020, 10(7): 137-140. |
| 18 | Wang X G, Wang Y Q, Yan H, et al. Effects of repeated application of carbendazim on its persistence and functional diversity of soil microbial communities. Acta Pedlolgica Sinica, 2010, 47(1): 131-137. |
| 王秀国, 王一奇, 严虎, 等. 多菌灵重复施药对其持久性及土壤微生物群落功能多样性的影响. 土壤学报, 2010, 47(1): 131-137. | |
| 19 | Singh S, Singh N, Kumar V, et al. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of the fungicide carbendazim. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2016, 14(3): 317-329. |
| 20 | Abolmohammad B, Asghar B, Damalas C A, et al. Use of personal protective equipment towards pesticide exposure: Farmers’ attitudes and determinants of behavior. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639: 1156-1163. |
| 21 | Yin X, Wang Y Q, Li X Q, et al. Effects of various moisture-absorbing roughages on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of napier grass silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(7): 133-138. |
| 尹祥, 王咏琪, 李鑫琴, 等. 不同水分吸附材料对象草青贮发酵品质及好氧稳定性的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 133-138. | |
| 22 | Zhao M A, Feng Y N, Zhu Y Z, et al. Multi-residue method for determination of 238 pesticides in Chinese cabbage and cucumber by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: Comparison of different purification procedures. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2014, 62(47): 11449-11456. |
| 23 | He L W, Chen N, Lv H J, et al. Gallic acid influencing fermentation quality, nitrogen distribution and bacterial community of high-moisture mulberry leaves and stylo silage. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 295: 1-32. |
| 24 | Su R, Ni K, Wang T, et al. Effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing Lactobacillus fermentum and cellulase additives on the fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa silage. Peer Journal, 2019, 7: 7712. |
| 25 | Gharechahi J, Kharazian Z A, Sarikhan S, et al. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microbial Biotechnology, 2017, 10(6): 1663-1676. |
| 26 | He Q, Huang J W, Yang X W, et al. Effect of pesticide residues in grapes on alcoholic fermentation and elimination of chlorothalonil inhibition by chlorothalonil hydrolytic dehalogenase. Food Control, 2016, 64: 70-76. |
| 27 | Junges D, Schmidt P, Novinski C O, et al. Additive containing homo and heterolactic bacteria on the fermentation quality of maize silage. Acta Scientiarum Animal Sciences, 2013, 35(4): 371-377. |
| 28 | Li R R, Jiang D, Tian P J, et al. Effects of different varieties and cutting time on fermentation quality and protein degradation of alfalfa silage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2020, 235(3): 97-104. |
| 李荣荣, 江迪, 田朋姣, 等. 不同品种和刈割时间对苜蓿青贮发酵品质及蛋白质降解的影响. 中国草地学报, 2020, 235(3): 97-104. | |
| 29 | Yang F Y. Breeding of cellulolytic lactic acid bacteria. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2018. |
| 杨逢源. 纤维降解功能乳酸菌的选育. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2018. | |
| 30 | Fang H, Han L, Cui Y, et al. Changes in soil microbial community structure and function associated with degradation and resistance of carbendazim and chlortetracycline during repeated treatments. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 572: 1203-1212. |
| 31 | Kato S, Haruta S, Cui Z J, et al. Stable coexistence of five bacterial strains as a cellulose-degrading community. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(11): 7099-7106. |
| 32 | Wei Z H, Xu J, Guo M X, et al. Research progress of carbendazim in China. Agrochemicals Today, 2015, 11: 18-21. |
| 魏中华, 徐娟, 郭明霞, 等. 国内多菌灵的研究进展. 今日农药, 2015, 11: 18-21. | |
| 33 | Pu D, Zhang X Y, Liu G, et al. Identification and degrading bacteria GRPD-1 carbendazim degradation characteristics. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 36(2): 289-295. |
| 蒲丹, 张晓喻, 刘刚, 等. 多菌灵降解菌 GRPD-1 的鉴定及降解特性研究. 四川师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 36(2): 289-295. | |
| 34 | Xu J L, Gu X Y, Shen B, et al. Isolation and characterization of a carbendazim-degrading rhodococcus sp.djl-6. Current Microbiology, 2006, 53(1): 72-76. |
| 35 | Dord E, Tijana M, Durovic P, et al. The potency of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus plantarumto dissipate organophosphorus pesticides in wheat during fermentation. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2016, 53(12): 4205-4215. |
| 36 | Li J, Wang Y R, Nian H H, et al. The isolation, identification and degradation character of a novel carbendazim-degrading bacterium. Journal of Huaibei Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 38(3): 37-42. |
| 李杰, 王亦然, 年浩瀚, 等. 一株新的多菌灵降解菌的筛选、鉴定及其降解特性. 淮北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 38(3): 37-42. | |
| 37 | Ma Z Z, Cheng Y Y, Wang S Q, et al. Positive effects of dietary supplementation of three probiotics on milk yield, milk composition and intestinal flora in Sannan dairy goats varied in kind of probiotics. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2020, 104(3): 44-55. |
| 38 | Feld L, Hjelms M H, Nielsen M S, et al. Pesticide side effects in an agricultural soil ecosystem as measured by AMOA expression quantification and bacterial diversity changes. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0126080. |
| 39 | Zhang Q, Yu Z, Wang X, et al. Effects of chlorpyrifos and chlorantraniliprole on fermentation quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) silage inoculated with or without Lactobacillus plantarum LP. Animal Science Journal, 2017, 88(3): 456-462. |
| 40 | Xiao L, Feng Y Y, Zhao L, et al. Effect of carbendazim on bacterial genetic diversity of soil. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(9): 1640-1648. |
| 肖丽, 冯燕燕, 赵靓, 等. 多菌灵对土壤细菌遗传多样性的影响. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(9): 1640-1648. | |
| 41 | Fang H, Wang Y, Gao C, et al. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas sp. CBW capable of degrading carbendazim. Biodegradation, 2010, 21(6): 939-946. |
| [1] | 邹诗雨, 陈思葵, 唐启源, 陈东, 陈元伟, 邓攀, 黄胥莱, 李付强. 青贮剂对再生稻头季全株青贮品质和体外瘤胃发酵特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 122-132. |
| [2] | 李法喜, 王琼, 段廷玉, 聂斌, 封成智. 不同杀菌剂及其复配对箭筈豌豆炭疽病的防治研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(12): 172-183. |
| [3] | 袁洁, 马冉冉, 张文洁, 许能祥, 赵冉冉, 顾洪如, 丁成龙. 自然青贮多花黑麦草优良乳酸菌的筛选及对多花黑麦草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 132-143. |
| [4] | 程分生, 尤龙辉, 余锦林, 徐惠昌, 游惠明, 聂森, 李建民, 叶功富. 冷季型绿肥对锥栗园土壤生化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 62-75. |
| [5] | 杨凯, 史娟, 袁玉涛, 王立婷. 白三叶草叶片感染白粉病的细胞生理变化及其病原鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 92-104. |
| [6] | 侯洁茹, 段晓玥, 李州, 彭燕. 白三叶TrSAMDC1克隆及表达分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 170-178. |
| [7] | 魏勇, 王晓瑜, 李应德, 段廷玉. AM真菌在白三叶-黑麦草体系中对抗逆信号的传导作用[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 138-146. |
| [8] | 于浩然, 格根图, 王志军, 贾玉山, 连植, 贾鹏飞. 甲酸添加剂及青贮时间对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 89-95. |
| [9] | 程守丰, 梁巧兰, 魏列新, 桑旭文, 姜玉玲. 苜蓿不同品种AMV和WCMV带毒检测及生理生化特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 140-149. |
| [10] | 万学瑞, 豆思远, 李玉, 何轶群, 王川, 张小丽, 雷赵民. 复合乳酸菌对全株玉米青贮及有氧暴露后微生物及饲料品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. |
| [11] | 李影正, 严旭, 吴子周, 杨春燕, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 张萍, EBENEZERKofiSam, 周阳, 张磊, 荣廷昭, 何建美, 唐祈林. 饲草玉米不同生育期的产量、品质和青贮利用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 82-91. |
| [12] | 王建福,雷赵民,成述儒,焦婷,李洁,吴建平. 添加乳酸菌制剂和麸皮对去穗玉米秸秆青贮质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 162-169. |
| [13] | 王建福, 雷赵民, 万学瑞, 姜辉, 李洁, 吴建平. 5株乳酸菌复合物与CaCO3,酶及尿素不同组合对全株玉米青贮品质影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 90-97. |
| [14] | 王木川, 杨玉玺, 于奕东, 玉柱. 不同添加剂和青贮密度对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 156-162. |
| [15] | 邝肖,季婧,梁文学,崔国文,冀国旭,崔新,刘建,胡国富. 北方寒区紫花苜蓿/无芒雀麦混播比例和刈割时期对青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 187-198. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||