

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 44-53.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022038
杜鹏冲1( ), 潘昱臻1, 侯双利2, 王智慧1, 王洪义1(
), 潘昱臻1, 侯双利2, 王智慧1, 王洪义1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-18
修回日期:2022-03-03
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-12-01
通讯作者:
王洪义
作者简介:E-mail: why021@163.com基金资助:
Peng-chong DU1( ), Yu-zhen PAN1, Shuang-li HOU2, Zhi-hui WANG1, Hong-yi WANG1(
), Yu-zhen PAN1, Shuang-li HOU2, Zhi-hui WANG1, Hong-yi WANG1( )
)
Received:2022-01-18
Revised:2022-03-03
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2022-12-01
Contact:
Hong-yi WANG
摘要:
凋落物分解是草地生态系统能量流动和物质循环的重要过程,其分解与初始化学组成(内因)和土壤环境(外因)等因素有关。氮(N)、磷(P)作为植物生长所必需的大量元素,影响生命活动的很多过程,是凋落物分解中内因和外因的重要调控因素。以呼伦贝尔草甸草原中羊草、糙隐子草和披针叶黄华3种植物为研究对象,采用网袋分解法,研究氮磷养分添加在内因和外因方面对凋落物分解的影响。结果表明:1)凋落物分解过程受物种内在因素和土壤环境等外在因素的共同影响,在提高凋落物分解速率上,养分添加在外因方面作用大于内因方面;2)外因方面,氮磷养分添加显著促进3种凋落物分解;内因方面,对糙隐子草和披针叶黄华有促进作用,而对羊草则表现为抑制作用;3)凋落物分解过程中N、P元素的释放与凋落物初始N、P含量和土壤中N、P含量呈正相关关系。研究结果揭示了土壤氮磷养分差异是影响凋落物分解和养分释放的主导因素,今后研究应更多关注外在因素变化对凋落物分解过程的影响。
杜鹏冲, 潘昱臻, 侯双利, 王智慧, 王洪义. 氮磷添加对呼伦贝尔草地凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 44-53.
Peng-chong DU, Yu-zhen PAN, Shuang-li HOU, Zhi-hui WANG, Hong-yi WANG. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on litter decomposition in Hulunber steppe[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(2): 44-53.
凋落物种类 Litter species | 养分添加 Nutrient addition | 碳 Carbon (g·kg-1) | 氮 Nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 磷 Phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
羊草 L. chinensis | CK | 305.0±4.5a | 10.7±0.1b | 1.08±0.11c | 28.5±4.5ab |
| N | 296.0±8.5a | 14.5±2.2a | 0.98±0.08c | 20.8±8.5c | |
| P | 278.6±9.1b | 9.4±0.3c | 3.18±0.04b | 29.6±9.1a | |
| NP | 264.6±0.3c | 13.8±0.1a | 3.90±0.26a | 22.4±0.2bc | |
糙隐子草 C. squarrosa | CK | 221.5±4.4a | 10.1±0.5bc | 1.54±0.04c | 21.9±0.6a |
| N | 199.1±8.9b | 11.4±1.0ab | 0.76±0.10d | 17.5±0.6b | |
| P | 199.1±10.9b | 9.1±0.9c | 3.70±0.28a | 22.1±1.1a | |
| NP | 190.0±14.8b | 12.2±0.2a | 2.80±0.03b | 20.9±1.4a | |
披针叶黄华 T. lanceolata | CK | 252.5±4.2a | 18.0±0.1b | 1.26±0.03b | 14.0±1.3ab |
| N | 259.3±8.1a | 21.1±0.1a | 1.18±0.09b | 12.3±0.3b | |
| P | 223.7±0.1b | 15.4±1.2c | 1.27±0.02b | 14.6±0.1a | |
| NP | 208.1±2.0c | 15.9±0.9c | 1.64±0.01a | 13.1±0.6b |
表1 各凋落物初始化学元素组成
Table 1 The initial chemical elements of each litter
凋落物种类 Litter species | 养分添加 Nutrient addition | 碳 Carbon (g·kg-1) | 氮 Nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 磷 Phosphorus (g·kg-1) | 碳氮比 C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
羊草 L. chinensis | CK | 305.0±4.5a | 10.7±0.1b | 1.08±0.11c | 28.5±4.5ab |
| N | 296.0±8.5a | 14.5±2.2a | 0.98±0.08c | 20.8±8.5c | |
| P | 278.6±9.1b | 9.4±0.3c | 3.18±0.04b | 29.6±9.1a | |
| NP | 264.6±0.3c | 13.8±0.1a | 3.90±0.26a | 22.4±0.2bc | |
糙隐子草 C. squarrosa | CK | 221.5±4.4a | 10.1±0.5bc | 1.54±0.04c | 21.9±0.6a |
| N | 199.1±8.9b | 11.4±1.0ab | 0.76±0.10d | 17.5±0.6b | |
| P | 199.1±10.9b | 9.1±0.9c | 3.70±0.28a | 22.1±1.1a | |
| NP | 190.0±14.8b | 12.2±0.2a | 2.80±0.03b | 20.9±1.4a | |
披针叶黄华 T. lanceolata | CK | 252.5±4.2a | 18.0±0.1b | 1.26±0.03b | 14.0±1.3ab |
| N | 259.3±8.1a | 21.1±0.1a | 1.18±0.09b | 12.3±0.3b | |
| P | 223.7±0.1b | 15.4±1.2c | 1.27±0.02b | 14.6±0.1a | |
| NP | 208.1±2.0c | 15.9±0.9c | 1.64±0.01a | 13.1±0.6b |
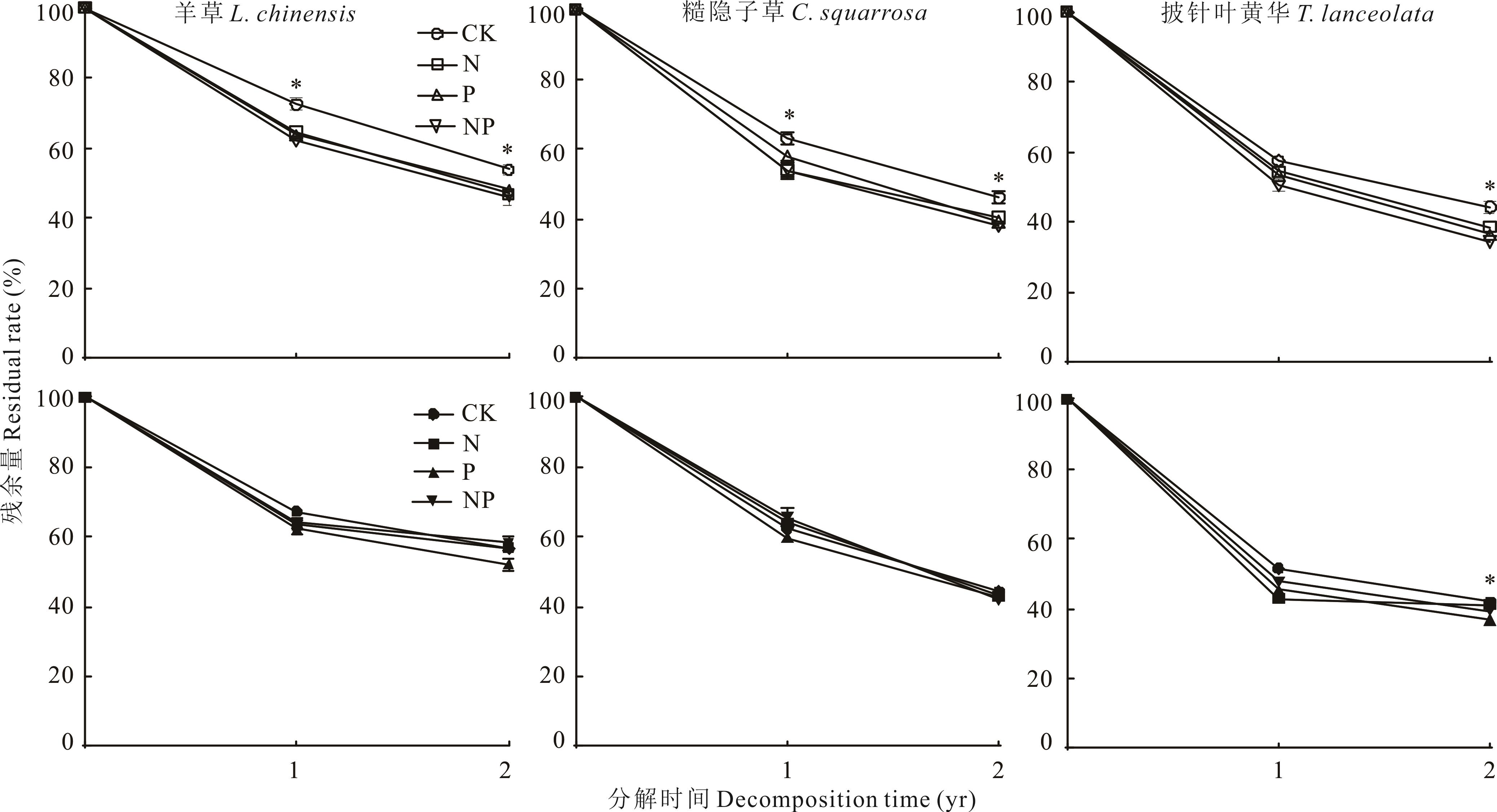
图1 养分添加下3种植物凋落物残余量变化表示样方内分解, 表示样方外分解。*表示不同处理间差异达到显著水平(P<0.05),下同。 indicates inside quadrat treatments, indicates outside quadrat treatments. * means the significant variation among different treatments (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Changes of litter residual rate of three plants under nutrient addition
凋落物种类 Litter species | 分解位点 Decomposition site | 养分添加 Nutrient addition | 回归方程 Equation | 分解系数 Decomposition coefficient | 半分解时间 Half-decaying time (yr) | 分解95%时间 95% decaying time (yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
羊草 L. chinensis | 样方内 Inside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.303t | 0.303 | 2.28 | 9.87 |
| N | y=e-0.356t | 0.356 | 1.94 | 8.40 | ||
| P | y=e-0.362t | 0.362 | 1.91 | 8.25 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.403t | 0.403 | 1.71 | 7.41 | ||
样方外 Outside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.300t | 0.300 | 2.34 | 10.10 | |
| N | y=e-0.288t | 0.288 | 2.40 | 11.31 | ||
| P | y=e-0.321t | 0.321 | 2.16 | 9.33 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.273t | 0.273 | 2.53 | 10.94 | ||
糙隐子草 C. squarrosa | 样方内 Inside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.412t | 0.412 | 1.68 | 7.26 |
| N | y=e-0.454t | 0.454 | 1.52 | 6.59 | ||
| P | y=e-0.469t | 0.469 | 1.47 | 6.38 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.487t | 0.487 | 1.42 | 6.14 | ||
样方外 Outside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.405t | 0.405 | 1.71 | 7.38 | |
| N | y=e-0.421t | 0.421 | 1.65 | 7.12 | ||
| P | y=e-0.423t | 0.423 | 1.63 | 7.08 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.432t | 0.432 | 1.60 | 6.92 | ||
披针叶黄华 T. lanceolata | 样方内 Inside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.427t | 0.427 | 1.62 | 7.01 |
| N | y=e-0.476t | 0.476 | 1.45 | 6.29 | ||
| P | y=e-0.504t | 0.504 | 1.37 | 5.94 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.533t | 0.533 | 1.30 | 5.61 | ||
样方外 Outside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.433t | 0.433 | 1.60 | 6.91 | |
| N | y=e-0.444t | 0.444 | 1.56 | 6.74 | ||
| P | y=e-0.499t | 0.499 | 1.38 | 6.01 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.464t | 0.464 | 1.49 | 6.45 |
表2 3种植物凋落物残留率随时间的指数方程
Table 2 Exponential equation of litter residual rate of three plants with time
凋落物种类 Litter species | 分解位点 Decomposition site | 养分添加 Nutrient addition | 回归方程 Equation | 分解系数 Decomposition coefficient | 半分解时间 Half-decaying time (yr) | 分解95%时间 95% decaying time (yr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
羊草 L. chinensis | 样方内 Inside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.303t | 0.303 | 2.28 | 9.87 |
| N | y=e-0.356t | 0.356 | 1.94 | 8.40 | ||
| P | y=e-0.362t | 0.362 | 1.91 | 8.25 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.403t | 0.403 | 1.71 | 7.41 | ||
样方外 Outside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.300t | 0.300 | 2.34 | 10.10 | |
| N | y=e-0.288t | 0.288 | 2.40 | 11.31 | ||
| P | y=e-0.321t | 0.321 | 2.16 | 9.33 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.273t | 0.273 | 2.53 | 10.94 | ||
糙隐子草 C. squarrosa | 样方内 Inside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.412t | 0.412 | 1.68 | 7.26 |
| N | y=e-0.454t | 0.454 | 1.52 | 6.59 | ||
| P | y=e-0.469t | 0.469 | 1.47 | 6.38 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.487t | 0.487 | 1.42 | 6.14 | ||
样方外 Outside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.405t | 0.405 | 1.71 | 7.38 | |
| N | y=e-0.421t | 0.421 | 1.65 | 7.12 | ||
| P | y=e-0.423t | 0.423 | 1.63 | 7.08 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.432t | 0.432 | 1.60 | 6.92 | ||
披针叶黄华 T. lanceolata | 样方内 Inside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.427t | 0.427 | 1.62 | 7.01 |
| N | y=e-0.476t | 0.476 | 1.45 | 6.29 | ||
| P | y=e-0.504t | 0.504 | 1.37 | 5.94 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.533t | 0.533 | 1.30 | 5.61 | ||
样方外 Outside quadrat | CK | y=e-0.433t | 0.433 | 1.60 | 6.91 | |
| N | y=e-0.444t | 0.444 | 1.56 | 6.74 | ||
| P | y=e-0.499t | 0.499 | 1.38 | 6.01 | ||
| NP | y=e-0.464t | 0.464 | 1.49 | 6.45 |
| 1 | Carrera A L, Bertiller M B.Combined effects of leaf litter and soil microsite on decomposition process in arid rangelands. Journal of Environmental Management, 2013, 114(15): 505-511. |
| 2 | Li H, Chen W M, Chen X, et al. Poisonous weed species and their harmfulness in the grassland of Yili regions, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China. Pratacultural Science, 2010, 27(11): 171-173. |
| 李宏, 陈卫民, 陈翔, 等. 新疆伊犁草原毒害草种类及其发生与危害. 草业科学, 2010, 27(11): 171-173. | |
| 3 | Garibald L A, Semmartin M, Chaneton E J. Grazing-induced changes in plant composition affect litter quality and nutrient cycling in flooding Pampa grasslands. Oecologia, 2017, 151(4): 650-662. |
| 4 | Wang Z H, Wang Z R, Li T P, et al. N and P fertilization enhanced carbon decomposition function by shifting microbes towards an r-selected community in meadow grassland soils. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 132: 108306. |
| 5 | Chen J, Li Y, Huang J H. Decomposition of mixed litter of four dominant species in an Inner Mongolia steppe. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2011, 35(1): 9-16. |
| 陈瑾, 李扬, 黄建辉. 内蒙古典型草原4种优势植物凋落物的混合分解研究. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(1): 9-16. | |
| 6 | Yang L L, Gong J R, Liu M, et al. Advances in the effect of nitrogen deposition on grassland litter decomposition. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(8): 894-913. |
| 杨丽丽, 龚吉蕊, 刘敏, 等. 氮沉降对草地凋落物分解的影响研究进展. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(8): 894-913. | |
| 7 | Zhao H M, Huang G, Ma J, et al. Study on dynamic status of litter decomposition and nutrients of typical desert plants. Arid Zone Research, 2012, 29(4): 628-634. |
| 赵红梅, 黄刚, 马健, 等. 典型荒漠植物凋落物分解及养分动态研究. 干旱区研究, 2012, 29(4): 628-634. | |
| 8 | Hou S L, Hättenschwiler S, Yang J J, et al. Increasing rates of long-term nitrogen deposition consistently increased litter decomposition in a semi-arid grassland. New Phytologist, 2021, 229: 296-307. |
| 9 | Wang M M, Hou F J. Influence of main factors on grass litter decomposition. Pratacultural Science, 2012, 29(10): 1631-1637. |
| 王苗苗, 侯扶江. 草地凋落物分解的主要影响因素. 草业科学, 2012, 29(10): 1631-1637. | |
| 10 | Zhang Y H, Feng J C, Isbell F, et al. Productivity depends more on the rate than the frequency of N addition in a temperate grassland. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 12558. |
| 11 | Peñuelas J, Poulter B, Sardans J, et al. Human-induced nitrogen-phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 2934. |
| 12 | Zhan S X, Wang Y, Zhu Z C, et al. Nitrogen enrichment alters plant N∶P stoichiometry and intensifies phosphorus limitation in a steppe ecosystem. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, 134: 21-32. |
| 13 | Berg B, Staaf H. Decompostion rate and chemical changes in decomposing needle litter of Scotspine Ⅱ. Influence of chemical composition. Ecological Bulletins-NFR, 1980, 32: 373-390. |
| 14 | Keeler B L, Hobbie S E, Kellogg L E. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: Implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems, 2009, 12(1): 1-15. |
| 15 | Galloway J N, Townsend A R, Erisman J W, et al. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions and potential solutions. Science, 2008, 320(5): 889-892. |
| 16 | Hou S L, Lv X T. Mixing effects of litter decomposition at plant organ and species levels in a temperate grassland. Plant Soil, 2021, 459: 387-396. |
| 17 | Dukes J S, Field C B. Diverse mechanisms for CO2 effects on grassland litter decomposition. Global Change Biology, 2000, 6(6): 145-154. |
| 18 | Michs P, Aber J D, Boone R D, et al. Short-term soil respiration and nitrogen immobilization response to nitrogen applications in contron and nitrogen-enriched temperate forests. Forest Ecology & Management, 2004, 196(1): 57-70. |
| 19 | Wang H Y, Chang J F, Wang Z W. Responses of community species diversity and productivity to nitrogen and phosphorus addition during restoration of degraded grassland. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(13): 2604-2613. |
| 王洪义, 常继方, 王正文. 退化草地恢复过程中群落物种多样性及生产力对氮磷养分的响应. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(13): 2604-2613. | |
| 20 | Bao S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2013. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013. | |
| 21 | Wood T G. Field investigations on the decomposition of leaves of Eucalyptus delegatensis in relation to environmental factors. Pedobiology, 1991, 14: 343-371. |
| 22 | Li W Y, Qiu X, Bai L, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on litter decomposition on the Stipa baicalensis steppe. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(8): 43-53. |
| 李文亚, 邱璇, 白龙, 等. 氮、磷添加对贝加尔针茅草原凋落物分解的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 43-53. | |
| 23 | Gong X J. The response of litter decomposition to carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus additions for four typical tree species in mid-subtropical zone. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2011. |
| 弓晓静. 中亚热带四种树种凋落叶分解对碳氮磷调控的响应. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2011. | |
| 24 | He Y T, Qi Y C, Dong Y S, et al. Advances in the influence of external nitrogen input on soil microbiological characteristics of grassland Ecosystem. Advances in Earth Science, 2010, 25(8): 877-885. |
| 何亚婷, 齐玉春, 董云社, 等. 外源氮输入对草地土壤微生物特性影响的研究进展. 地球科学进展, 2010, 25(8): 877-885. | |
| 25 | Olander L P, Vitousek P M. Regulation of soil phosphatase and chitinase activity by N and P availability. Biogeochemistry, 2000, 49(2): 175-191. |
| 26 | Berg B, McClaugherty C. Plant litter: Decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration. Berlin: Springer, 2003. |
| 27 | Song X Z, Jiang H, Ma Y D. Litter decomposition across climate zone in Eastern China: The integrated influence of climate and litter quality. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2009, 29(10): 5219-5226. |
| 宋新章, 江洪, 马元丹. 中国东部气候带凋落物分解特征-气候和基质质量的综合影响. 生态学报, 2009, 29(10): 5219-5226. | |
| 28 | Wen H Y, Fu H, Guo D. Influence of nitrogen addition on Stipa bungeana and Heteropappus altaicus litter decomposition and nutrient release in a steppe located on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 2014-2022. |
| 文海燕, 傅华, 郭丁. 黄土高原典型草原优势植物凋落物分解及养分释放对氮添加的响应. 生态学报, 2017, 37(6): 2014-2022. | |
| 29 | Sarah E, Hobbie, Laura G. Litter decomposition in moist acidic and non-acidic tundra with different glacial histories. Oecologia, 2004, 140(1): 113-124. |
| 30 | Liu H L, Li X L, Liang Y M. Effects of raising soil fertilities by planting different forage sepcies on newly-built terrence land on China loess hilly regions. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 1998, 18(2): 287-291. |
| 刘洪岭, 李香兰, 梁一民. 禾本科及豆科牧草对黄土丘陵区台田土壤培肥效果的比较研究. 西北植物学报, 1998, 18(2): 287-291. | |
| 31 | Harpole W S, Tilman D. Grassland species loss resulting from reduce niche dimension. Nature, 2007, 446: 791-793. |
| 32 | Hobbie S E. Interactions between litter lignin and soil nitrogen availability during leaf litter decomposition in a Hawaiian montane forest. Ecosystems, 2000, 3: 484-494. |
| 33 | Ye R H, Shan Y M, Zhang P J, et al. Effects of nitrogen and water addition on litter decomposition in desert grassland under different grazing intensities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 31(11): 3631-3638. |
| 晔薷罕, 单玉梅, 张璞进, 等. 荒漠草原不同放牧强度背景下添加氮水对凋落物分解的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 31(11): 3631-3638. | |
| 34 | Wang H Y, Wang Z W, Ding R, et al. The impacts of nitrogen deposition on community N∶P stoichiometry do not depend on phosphorus availability in a temperate meadow steppe. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 82-89. |
| 35 | Berg B. Litter decomposition and organic matter turnover in northern forest soils. Forest Ecology and Management, 2000, 133: 13-22. |
| 36 | Kondo R, Iimori T, Imamura H, et al. Polymerization of DHP and depolymerization of DHP-glucoside by lignin oxidizing enzymes. Biotechnology, 1990, 13: 181-188. |
| 37 | Zhao Y T, Li X F, Han S J, et al. Soil enzyme activities under two forest types as affected by different levels of nitrogen deposition. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(12): 2769-2773. |
| 赵玉涛, 李雪峰, 韩士杰, 等. 不同氮沉降水平下两种林型的主要土壤酶活性. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(12): 2769-2773. | |
| 38 | Ge X M, Wu L, Tang L Z. Review on research progress of relationships between enzyme and litter decomposition. World Forestry Research, 2013, 26(1): 43-47. |
| 葛晓敏, 吴麟, 唐罗忠. 森林凋落物分解与酶的相互关系的研究进展. 世界林业研究, 2013, 26(1): 43-47. | |
| 39 | Cornwell W K, Cornelissen J H C, Amatangelo K, et al. Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(10): 1065-1071. |
| 40 | Chen Y, Wang F M, Mo Q F, et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on woody debris decomposition in a secondary tropical forest of South China. Chinese Journal Applied Environmental Biology, 2015, 21(4): 747-753. |
| 陈瑶, 王法明, 莫其锋, 等. 氮磷添加对华南热带森林尾叶桉木质残体分解和养分动态的影响. 应用与环境生物学报, 2015, 21(4): 747-753. | |
| 41 | Liao L P, Gao H, Wang S L, et al. The effect of nitrogen addition on soil nutrient leaching and the decomposition of Chinese fir leaf litter. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2000, 24(1): 34-39. |
| 廖利平, 高洪, 汪思龙, 等. 外加氮源对杉木叶凋落物分解及土壤养分淋失的影响. 植物生态学报, 2000, 24(1): 34-39. | |
| 42 | Berg B, Matzer E. Effect to N deposition on decomposition of plant litter and soil organic matter in forest ecosystems. Enviornmental Reviews, 1997, 5(1): 1-25. |
| 43 | Yang J S, Liu J S, Yu J B, et al. Decomposition and nutrient dynamics of marsh litter in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(5): 1207-1212. |
| 杨继松, 刘景双, 于君宝, 等. 三江平原沼泽湿地枯落物分解及营养动态. 生态学报, 2006, 26(5): 1207-1212. |
| [1] | 李鑫, 魏雪, 王长庭, 任晓, 吴鹏飞. 外源性养分添加对高寒草甸土壤节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 155-164. |
| [2] | 汪梦寒, 董利利, 李富翠, 韩烈保, 王祥. 不同有机/无机氮添加对草原土壤氮素分配和转化特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 36-46. |
| [3] | 唐立涛, 毛睿, 王长庭, 李洁, 胡雷, 字洪标. 氮磷添加对高寒草甸植物群落根系特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 105-116. |
| [4] | 宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 王宏生, 鲍根生. 内生真菌对高寒草地紫花针茅凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 150-158. |
| [5] | 彭艳, 孙晶远, 马素洁, 王向涛, 孙磊, 魏学红. 氮磷添加对藏北人工牧草生产性能和品质的评价[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 52-64. |
| [6] | 张静静, 刘尊驰, 鄢创, 王云霞, 刘凯, 时新荣, 袁志友. 土壤pH值变化对3种草原类型土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 69-81. |
| [7] | 聂莹莹, 陈金强, 辛晓平, 徐丽君, 杨桂霞, 王旭. 呼伦贝尔草甸草原区主要植物种群生态位特征与物种多样性对封育年限响应[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 15-25. |
| [8] | 郭剑波, 赵国强, 贾书刚, 董俊夫, 陈龙, 王淑平. 施肥对高寒草原草地质量指数及土壤性质影响的综合评价[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 85-93. |
| [9] | 岳可欣, 龚吉蕊, 于上媛, 宝音陶格涛, 杨波, 王彪, 朱趁趁, 张子荷, 矢佳昱. 氮添加下典型草原凋落物质量和土壤酶活性对凋落物分解速率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 71-82. |
| [10] | 聂莹莹, 徐丽君, 辛晓平, 陈宝瑞, 张保辉. 围栏封育对温性草甸草原植物群落构成及生态位特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 11-22. |
| [11] | 刘晶, 谢婉余, 张巧明, 徐少君. 黄土丘陵区不同植物凋落叶片的分解及养分释放特性[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(9): 25-33. |
| [12] | 李文亚, 邱璇, 白龙, 杨殿林. 氮、磷添加对贝加尔针茅草原凋落物分解的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(8): 43-53. |
| [13] | 那亚, 孙启忠, 王红梅. 呼伦贝尔草甸草原牧草青贮饲料脂肪酸成分研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(2): 215-223. |
| [14] | 李小龙, 曹文侠, 李文, 张晓燕, 徐长林, 韦应莉, 师尚礼. 划破草皮对不同地形高寒草甸草原土壤特征及地下生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 26-33. |
| [15] | 胡飞龙, 闫妍, 卢晓强, 吴军, 丁晖, 刘志民. 内蒙古草甸草原生物量碳分配格局[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(4): 36-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||