

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 80-90.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022279
李彤瑶1,2( ), 周青平1,2, 陈有军1,2, 詹圆1,2, 汪辉1,2(
), 周青平1,2, 陈有军1,2, 詹圆1,2, 汪辉1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-28
修回日期:2022-08-31
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2022-12-30
通讯作者:
汪辉
作者简介:E-mail: zzbjwh@163.com基金资助:
Tong-yao LI1,2( ), Qing-ping ZHOU1,2, You-jun CHEN1,2, Yuan ZHAN1,2, Hui WANG1,2(
), Qing-ping ZHOU1,2, You-jun CHEN1,2, Yuan ZHAN1,2, Hui WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-06-28
Revised:2022-08-31
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2022-12-30
Contact:
Hui WANG
摘要:
氮素是禾本科植物生长和发育所必需的大量元素之一,但过量施用氮肥不仅造成环境污染,而且增加生产成本、降低收益。基于青藏高原地区披碱草属牧草种子需求量大、产量较低的现状,本研究以同德短芒披碱草、青牧1号老芒麦2个披碱草属牧草品种为试验材料,设置0、45、90、135、180和225 kg N·hm-2等6个氮肥施用水平,研究分析了施氮量对披碱草属牧草种子生产和氮肥利用效率的影响,以期为披碱草属牧草种子生产提供理论依据。结果表明,施氮可促进披碱草属牧草生长,能够显著提高其株高、分蘖数等牧草营养生产性状,同时可提高种子产量及单位面积生殖枝数、每穗小穗数、每穗种子数和种子千粒重等产量组分;且随着施氮量的增加,各生长性能指标呈现先增加后降低或趋于稳定的变化趋势。随着施氮量的增加,除青牧1号老芒麦氮肥利用效率先增加后降低外,2个品种氮肥农学利用率和偏生产力逐渐降低。本研究中,同德短芒披碱草和青牧1号老芒麦的种子产量分别为712~1661 kg·hm-2和701~1626 kg·hm-2。从节约成本角度考虑,在川西北高寒地区开展披碱草属牧草种子生产适宜施氮量为135~180 kg·hm-2。相关分析和通径分析的结果表明,种子产量组分中,单位面积生殖枝数和每穗种子数对种子产量的直接贡献较大。
李彤瑶, 周青平, 陈有军, 詹圆, 汪辉. 氮肥用量对披碱草属牧草种子产量和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 80-90.
Tong-yao LI, Qing-ping ZHOU, You-jun CHEN, Yuan ZHAN, Hui WANG. Effects of nitrogen application rate on seed yield and nitrogen use efficiency of Elymus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(3): 80-90.
取样时间 Sampling time | 施氮水平 Nitrogen application | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height (cm) | 分蘖数 Tillers (No.·m-2) | 营养枝占比 Proportion of vegetative tillers (%) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 分蘖数 Tillers (No.·m-2) | 营养枝占比 Proportion of vegetative tillers (%) | ||
| S1 | N0 | 50.30a | 805b | 41b | 50.23a | 812a | 62ab |
| N1 | 51.77a | 1279ab | 55ab | 51.00a | 985a | 74a | |
| N2 | 51.87a | 1193ab | 62ab | 54.40a | 1187a | 63ab | |
| N3 | 61.37a | 1211ab | 53ab | 47.70a | 1069a | 58ab | |
| N4 | 53.87a | 1824a | 69a | 47.70a | 1032a | 63ab | |
| N5 | 58.23a | 1795a | 66a | 53.33a | 1020a | 45b | |
| S2 | N0 | 65.57ab | 1227b | 43a | 62.27b | 997c | 48a |
| N1 | 81.10a | 1569ab | 52a | 76.23ab | 1204bc | 63a | |
| N2 | 71.17ab | 1761ab | 59a | 75.37ab | 1685abc | 61a | |
| N3 | 74.93ab | 1659ab | 58a | 78.90a | 2336a | 65a | |
| N4 | 74.10ab | 1956a | 55a | 87.43a | 2170ab | 61a | |
| N5 | 60.47b | 1973a | 62a | 81.20a | 2040ab | 49a | |
| S3 | N0 | 85.27b | 1031c | 28c | 86.17c | 921b | 45a |
| N1 | 104.03a | 1727b | 53b | 92.57bc | 1377ab | 58a | |
| N2 | 103.53a | 2323a | 64ab | 103.27ab | 1957ab | 62a | |
| N3 | 103.93a | 2471a | 68a | 104.80ab | 2209ab | 66a | |
| N4 | 104.50a | 2043ab | 58ab | 112.13a | 2101ab | 58a | |
| N5 | 112.77a | 2259a | 52b | 109.43a | 2352a | 52a | |
| S4 | N0 | 88.43b | 933b | 32b | 90.50c | 925b | 40b |
| N1 | 103.43a | 1807a | 50a | 100.43bc | 1816a | 65a | |
| N2 | 106.00a | 1864a | 60a | 110.30ab | 1719a | 61a | |
| N3 | 112.03a | 2031a | 54a | 110.87ab | 1861a | 59ab | |
| N4 | 113.53a | 1993a | 48ab | 119.87a | 2043a | 55ab | |
| N5 | 112.77a | 1704a | 50a | 117.87a | 1912a | 51ab | |
表1 施氮对2个品种株高和分蘖数的影响
Table 1 Effects of nitrogen application on the plant height and the tiller number per square meter of two cultivars
取样时间 Sampling time | 施氮水平 Nitrogen application | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
株高 Plant height (cm) | 分蘖数 Tillers (No.·m-2) | 营养枝占比 Proportion of vegetative tillers (%) | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 分蘖数 Tillers (No.·m-2) | 营养枝占比 Proportion of vegetative tillers (%) | ||
| S1 | N0 | 50.30a | 805b | 41b | 50.23a | 812a | 62ab |
| N1 | 51.77a | 1279ab | 55ab | 51.00a | 985a | 74a | |
| N2 | 51.87a | 1193ab | 62ab | 54.40a | 1187a | 63ab | |
| N3 | 61.37a | 1211ab | 53ab | 47.70a | 1069a | 58ab | |
| N4 | 53.87a | 1824a | 69a | 47.70a | 1032a | 63ab | |
| N5 | 58.23a | 1795a | 66a | 53.33a | 1020a | 45b | |
| S2 | N0 | 65.57ab | 1227b | 43a | 62.27b | 997c | 48a |
| N1 | 81.10a | 1569ab | 52a | 76.23ab | 1204bc | 63a | |
| N2 | 71.17ab | 1761ab | 59a | 75.37ab | 1685abc | 61a | |
| N3 | 74.93ab | 1659ab | 58a | 78.90a | 2336a | 65a | |
| N4 | 74.10ab | 1956a | 55a | 87.43a | 2170ab | 61a | |
| N5 | 60.47b | 1973a | 62a | 81.20a | 2040ab | 49a | |
| S3 | N0 | 85.27b | 1031c | 28c | 86.17c | 921b | 45a |
| N1 | 104.03a | 1727b | 53b | 92.57bc | 1377ab | 58a | |
| N2 | 103.53a | 2323a | 64ab | 103.27ab | 1957ab | 62a | |
| N3 | 103.93a | 2471a | 68a | 104.80ab | 2209ab | 66a | |
| N4 | 104.50a | 2043ab | 58ab | 112.13a | 2101ab | 58a | |
| N5 | 112.77a | 2259a | 52b | 109.43a | 2352a | 52a | |
| S4 | N0 | 88.43b | 933b | 32b | 90.50c | 925b | 40b |
| N1 | 103.43a | 1807a | 50a | 100.43bc | 1816a | 65a | |
| N2 | 106.00a | 1864a | 60a | 110.30ab | 1719a | 61a | |
| N3 | 112.03a | 2031a | 54a | 110.87ab | 1861a | 59ab | |
| N4 | 113.53a | 1993a | 48ab | 119.87a | 2043a | 55ab | |
| N5 | 112.77a | 1704a | 50a | 117.87a | 1912a | 51ab | |
品种 Cultivars | 施氮水平 Nitrogen application | 穗长 Ear length (cm) | 每穗小穗数 Spikelets per ear (No.) | 每穗种子数 Seeds per ear (No.) | 每小穗种子数 Seeds per spikelet (No.) | 千粒重 1000-seed weight (g) | 种子产量 Seed yield (kg·hm-2) | 收获指数 Harvest index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
同德短芒披碱草 E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | N0 | 12.85a | 28.22b | 80.07b | 2.87a | 0.4708b | 712c | 0.1800ab |
| N1 | 14.51a | 30.74ab | 88.66ab | 3.02a | 0.5497a | 1211ab | 0.2408a | |
| N2 | 14.17a | 31.27ab | 96.65ab | 3.22a | 0.5053ab | 1198ab | 0.2067ab | |
| N3 | 14.72a | 31.18ab | 94.85ab | 3.02a | 0.5740a | 1179bc | 0.1700b | |
| N4 | 15.10a | 35.35a | 103.40a | 3.00a | 0.5704a | 1623ab | 0.2000ab | |
| N5 | 14.53a | 32.29ab | 95.20ab | 2.96a | 0.5499a | 1661a | 0.1833ab | |
青牧1号老芒麦 E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | N0 | 15.22b | 33.69b | 101.78c | 3.11a | 0.4217b | 717b | 0.2200ab |
| N1 | 16.50ab | 41.58a | 120.00ab | 3.11a | 0.5284a | 701b | 0.1600c | |
| N2 | 18.92a | 39.71ab | 124.24ab | 3.45a | 0.4273b | 1168ab | 0.2067abc | |
| N3 | 16.66ab | 39.05ab | 131.87a | 3.47a | 0.4509ab | 1607a | 0.2400a | |
| N4 | 17.27ab | 38.33ab | 127.93ab | 3.33a | 0.4576ab | 1626a | 0.1900bc | |
| N5 | 16.62ab | 29.29b | 113.82bc | 3.02a | 0.3961b | 1575a | 0.1967abc |
表2 施氮对2个披碱草属牧草品种种子产量和产量组分的影响
Table 2 Effects of nitrogen application on seed yield and yield components of two Elymus cultivars
品种 Cultivars | 施氮水平 Nitrogen application | 穗长 Ear length (cm) | 每穗小穗数 Spikelets per ear (No.) | 每穗种子数 Seeds per ear (No.) | 每小穗种子数 Seeds per spikelet (No.) | 千粒重 1000-seed weight (g) | 种子产量 Seed yield (kg·hm-2) | 收获指数 Harvest index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
同德短芒披碱草 E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | N0 | 12.85a | 28.22b | 80.07b | 2.87a | 0.4708b | 712c | 0.1800ab |
| N1 | 14.51a | 30.74ab | 88.66ab | 3.02a | 0.5497a | 1211ab | 0.2408a | |
| N2 | 14.17a | 31.27ab | 96.65ab | 3.22a | 0.5053ab | 1198ab | 0.2067ab | |
| N3 | 14.72a | 31.18ab | 94.85ab | 3.02a | 0.5740a | 1179bc | 0.1700b | |
| N4 | 15.10a | 35.35a | 103.40a | 3.00a | 0.5704a | 1623ab | 0.2000ab | |
| N5 | 14.53a | 32.29ab | 95.20ab | 2.96a | 0.5499a | 1661a | 0.1833ab | |
青牧1号老芒麦 E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | N0 | 15.22b | 33.69b | 101.78c | 3.11a | 0.4217b | 717b | 0.2200ab |
| N1 | 16.50ab | 41.58a | 120.00ab | 3.11a | 0.5284a | 701b | 0.1600c | |
| N2 | 18.92a | 39.71ab | 124.24ab | 3.45a | 0.4273b | 1168ab | 0.2067abc | |
| N3 | 16.66ab | 39.05ab | 131.87a | 3.47a | 0.4509ab | 1607a | 0.2400a | |
| N4 | 17.27ab | 38.33ab | 127.93ab | 3.33a | 0.4576ab | 1626a | 0.1900bc | |
| N5 | 16.62ab | 29.29b | 113.82bc | 3.02a | 0.3961b | 1575a | 0.1967abc |
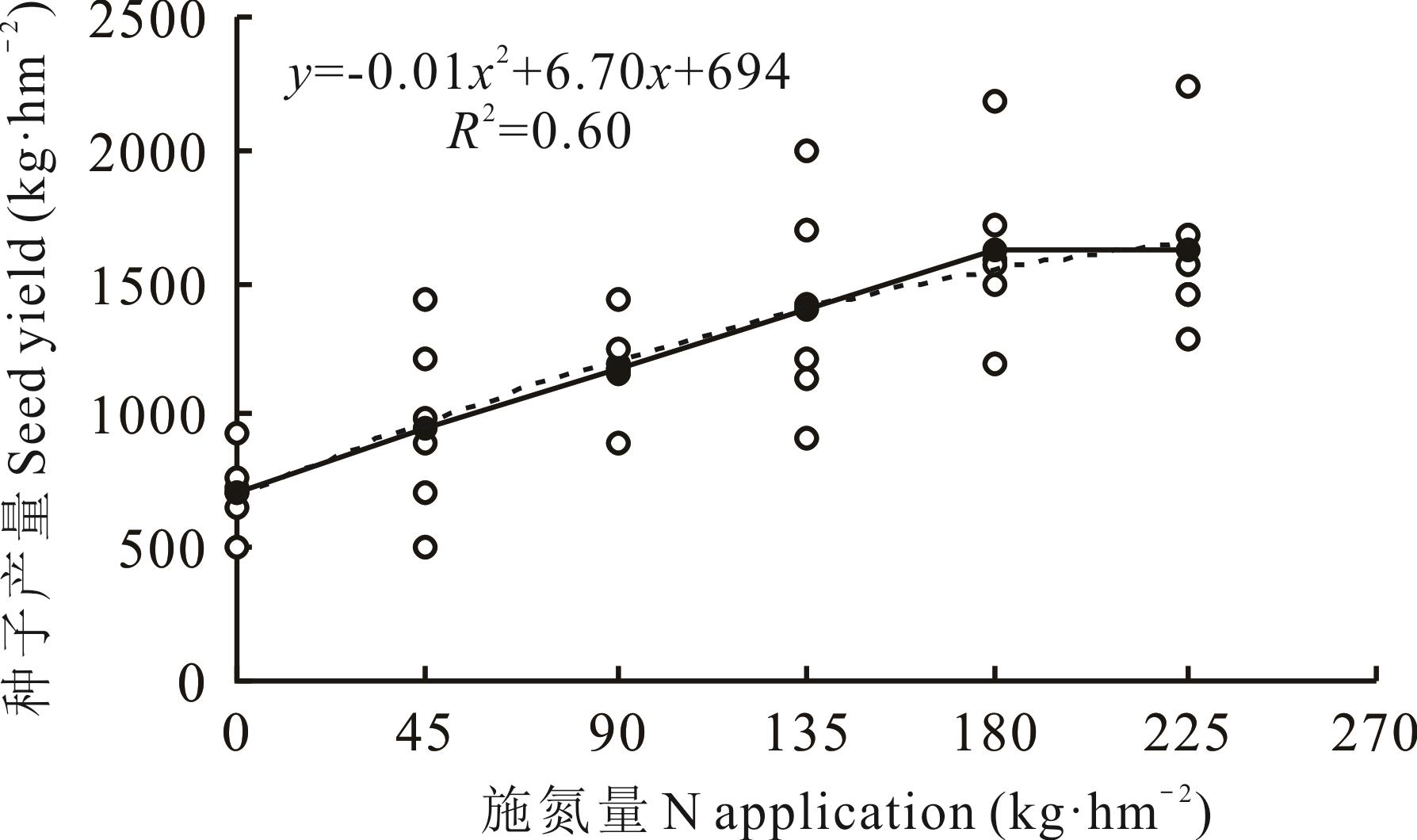
图2 种子产量与施氮量的回归关系虚线为种子产量与施氮量间的回归曲线,实线为种子产量均值的连线。Dotted line shows the regression curve between seed yield and N application amount. Full line connects the average seed yield at each N application.
Fig.2 Regression relation between seed yield and nitrogen application
系数 Coefficient | 品种 Cultivars | 单位面积生殖枝数 Fertile tillers per square meter | 穗长 Ear length | 每小穗种子数Seeds per spikelet | 每穗小穗数 Spikelets per ear | 每穗种子数Seeds per ear | 千粒重 1000-seed weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数Correlation coefficient | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 0.59* | 0.52* | 0.19 | 0.63** | 0.64** | 0.34 |
| 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | 0.53* | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 0.58* | -0.20 | |
| 通径系数Pathway coefficient | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 0.42* | -0.16 | -0.11 | 0.01 | 0.67* | -0.05 |
| 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | 0.42* | -0.02 | -0.09 | -0.04 | 0.66* | -0.31 |
表3 种子产量组分与种子产量间的相关系数和通径系数
Table 3 Correlation coefficients and pathway coefficient between seed yield components and seed yield
系数 Coefficient | 品种 Cultivars | 单位面积生殖枝数 Fertile tillers per square meter | 穗长 Ear length | 每小穗种子数Seeds per spikelet | 每穗小穗数 Spikelets per ear | 每穗种子数Seeds per ear | 千粒重 1000-seed weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数Correlation coefficient | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 0.59* | 0.52* | 0.19 | 0.63** | 0.64** | 0.34 |
| 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | 0.53* | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 0.58* | -0.20 | |
| 通径系数Pathway coefficient | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 0.42* | -0.16 | -0.11 | 0.01 | 0.67* | -0.05 |
| 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | 0.42* | -0.02 | -0.09 | -0.04 | 0.66* | -0.31 |
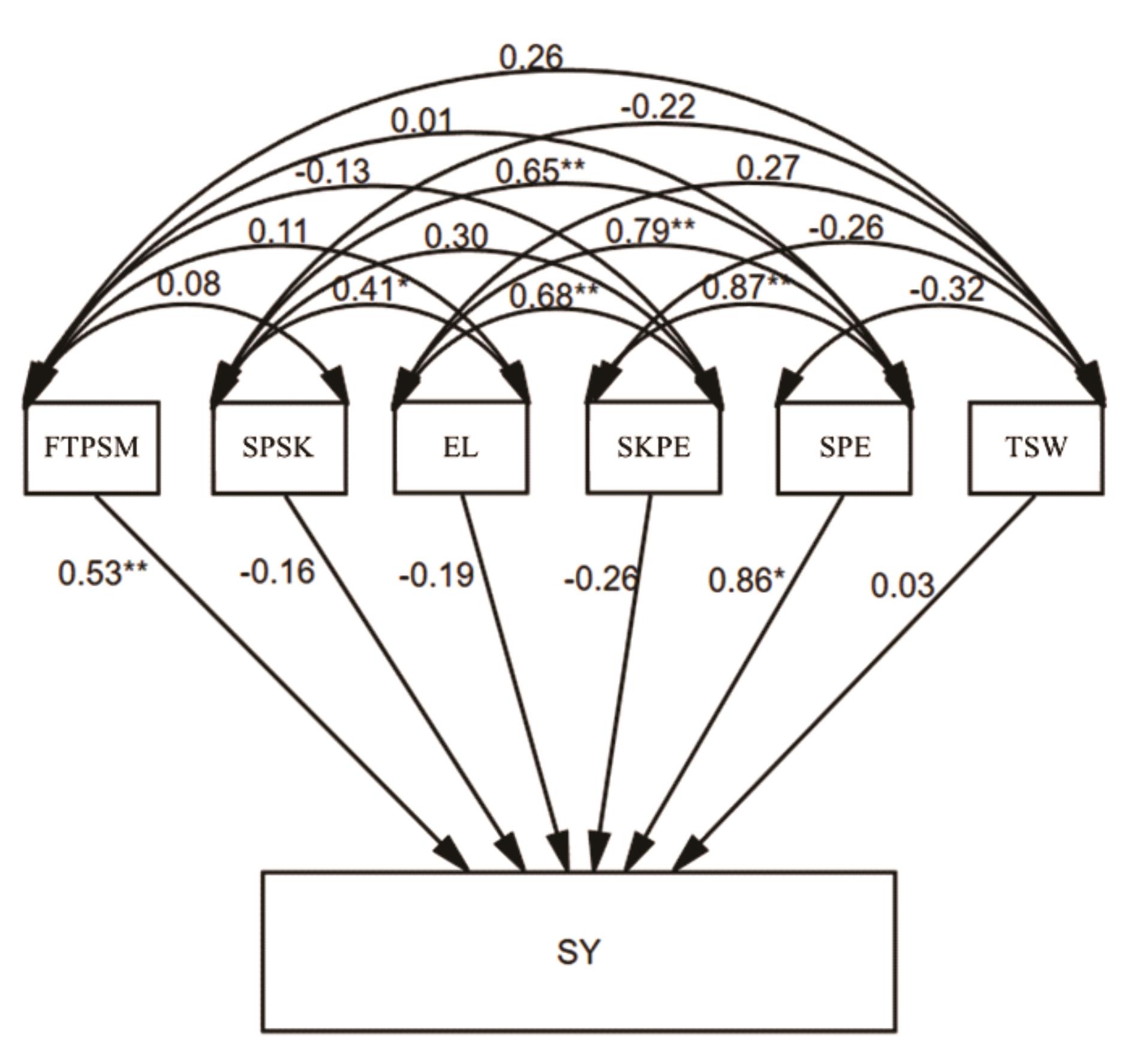
图3 种子产量组分与种子产量的结构方程模型双箭头表示产量组分间相关系数,单箭头表示产量组分对种子产量的直接通径系数。FTPSM: 单位面积生殖枝数;SPSK: 每小穗种子数;EL: 穗长;SKPE:每穗小穗数;SPE: 每穗种子数;TSW: 千粒重;SY: 种子产量。*: P<0.05;**: P<0.01. Double sided arrow shows the correlation coefficient among seed yield components and single sided arrow shows the direct pathway coefficient of seed yield components to seed yield. FTPSM: Fertile tillers per square meter; SPSK: Seeds per spikelet; EL: Ear length; SKPE: Spikelets per ear; SPE: Seeds per ear; TSW: 1000-seed weight; SY: Seed yield.
Fig.3 Structural model of seed yield and yield components
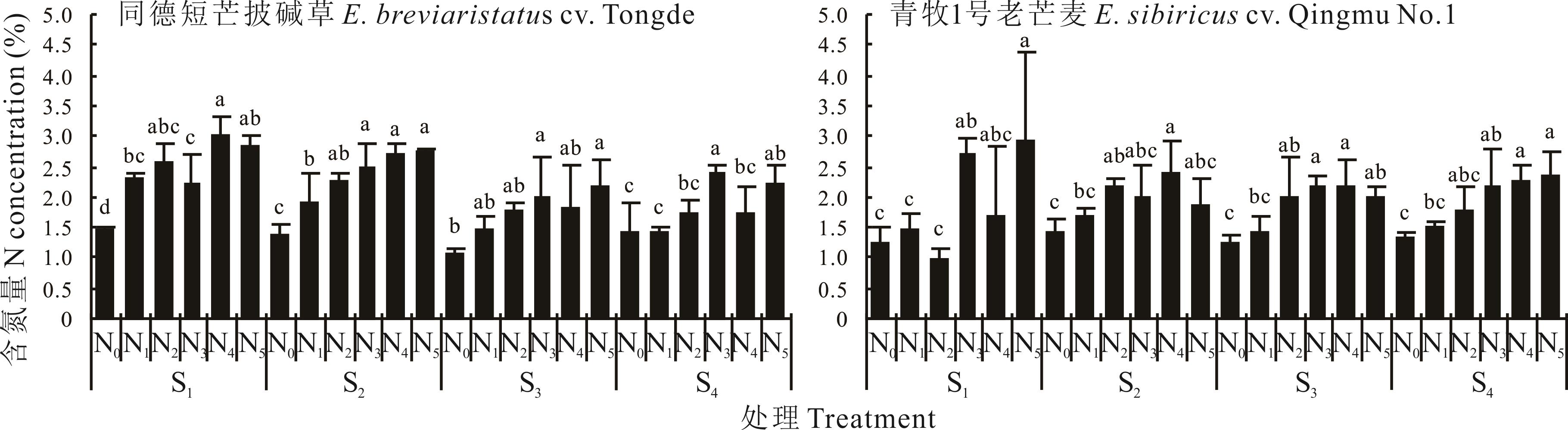
图4 施氮对2个品种全氮含量的影响同一时期不同字母表示在P<0.05水平下差异显著。下同。Different letters in the same period indicate significant differences at the level of P<0.05. The same below.
Fig.4 Effect of nitrogen application on total nitrogen content of two cultivars
施氮水平 Nitrogen application | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
氮肥农学利用率 Nitrogen agronomic utilization efficiency | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial productivity | 氮肥农学利用率 Nitrogen agronomic utilization efficiency | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial productivity | |
| N1 | 11.08a | 26.90a | -0.36b | 15.58a |
| N2 | 5.33b | 13.31b | 5.01a | 12.98ab |
| N3 | 3.46b | 8.73bc | 6.60a | 11.91abc |
| N4 | 5.06b | 9.02bc | 5.05a | 9.03bc |
| N5 | 4.22b | 7.38c | 3.81ab | 7.00c |
表4 施氮对2个品种氮肥农学利用率和偏生产力的影响
Table 4 Effect of nitrogen on agronomic utilization efficiency and partial productivity of two cultivars (kg·kg-1)
施氮水平 Nitrogen application | 同德短芒披碱草E. breviaristatus cv. Tongde | 青牧1号老芒麦E. sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
氮肥农学利用率 Nitrogen agronomic utilization efficiency | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial productivity | 氮肥农学利用率 Nitrogen agronomic utilization efficiency | 氮肥偏生产力 Nitrogen partial productivity | |
| N1 | 11.08a | 26.90a | -0.36b | 15.58a |
| N2 | 5.33b | 13.31b | 5.01a | 12.98ab |
| N3 | 3.46b | 8.73bc | 6.60a | 11.91abc |
| N4 | 5.06b | 9.02bc | 5.05a | 9.03bc |
| N5 | 4.22b | 7.38c | 3.81ab | 7.00c |
| 1 | Chen M J, Jia S X. Chinese forage plants. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2002: 48. |
| 陈默君, 贾慎修. 中国饲用植物. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002: 48. | |
| 2 | Guo Y P, Guo B Z. Studies on relationships among the genera and phylogenesis of the tribe Triticeae. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 1991, 11(2): 159-169. |
| 郭延平, 郭本兆. 小麦族植物的属间亲缘和系统发育的探讨. 西北植物学报, 1991, 11(2): 159-169. | |
| 3 | Gao Z H, Lei Y X, Zhou Q P. Research progress of molecular systematics of Elymus and its related genera. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(2): 107-115. |
| 高子涵, 雷映霞, 周青平. 广义披碱草属及其近缘属植物的分子系统学研究现状. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(2): 107-115. | |
| 4 | Wang M Y, Mao P S. Research advancement on seed production technology of forage grasses in China. Seed, 2012, 31(9): 55-60. |
| 王明亚, 毛培胜. 中国禾本科牧草种子生产技术研究进展. 种子, 2012, 31(9): 55-60. | |
| 5 | Luo K, Zhang J Y, Wang Y R. Effect of planting density and phosphorus fertiliser on seed yield of Melilotus officinalis. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(7): 112-119. |
| 骆凯, 张吉宇, 王彦荣. 种植密度和施磷肥对黄花草木樨种子产量的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(7): 112-119. | |
| 6 | Chen L L, Ren W, Mao P S, et al. Effects of nitrogen application on seed yield and nitrogen accumulation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(6): 98-104. |
| 陈玲玲, 任伟, 毛培胜, 等. 氮素对紫花苜蓿种子产量与氮累积动态变化的影响. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 98-104. | |
| 7 | Wang H, Zhang W X, Zheng H M, et al.Effect of phosphorus application and pod position on the germination characteristics of alfalfa seed. Seed, 2016, 35(3): 29-32, 36. |
| 汪辉, 张文旭, 郑慧敏, 等. 施磷处理和结荚位置对紫花苜蓿种子发芽特性的影响. 种子, 2016, 35(3): 29-32, 36. | |
| 8 | Sun J H, Wang Y R, Guo Y X. Variation in seed yield components among varieties of Poa pratensis. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2002, 13(8): 948-952. |
| 孙建华, 王彦荣, 郭玉霞. 草地早熟禾种子产量构成因素的品种差异. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(8): 948-952. | |
| 9 | Liu K Q, Liu W H, Wei X X, et al. Effect of different sowing rates and row spacings on seed yield of Avena sativa cv. Qingyan No.1. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(2): 82-91. |
| 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 魏小星, 等. 不同播量和行距对‘青燕1号’燕麦种子产量的影响. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 82-91. | |
| 10 | Tao Q B, Bai M J, Han Y H, et al. Optimizing between-row and within-row spacing for Artemisia sphaerocephala (Asteraceae) seed production. Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 139: 111490. |
| 11 | Fu B Z, Zhou Y F, Li X, et al. Effect of water and fertilizer coupling on Leymus chinensis in the Ningxia irrigation area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2020, 29(5): 98-108. |
| 伏兵哲, 周燕飞, 李雪, 等. 宁夏引黄灌区羊草水肥耦合效应研究. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 98-108. | |
| 12 | Zhang X, Nie G, Huang L K, et al. Effect of plant growth regulators on seed yield of Dactylis glomerata. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(6): 93-100. |
| 张旭, 聂刚, 黄琳凯, 等. 植物生长调节剂对鸭茅种子产量的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 93-100. | |
| 13 | Nie X M, Zhao G Q, Chai J K, et al. Occurrence of barley yellow dwarf virus at different growth stages of oat and its effect on seed yield. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(3): 136-141. |
| 聂秀美, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽, 等. 红叶病在燕麦不同生育时期的发生情况及对种子产量的影响. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(3): 136-141. | |
| 14 | Song X D, Zhao G Q, Chai J K. Effects of different herbicides on weed control, grain yield and hull rate in naked oats. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(1): 171-178. |
| 宋旭东, 赵桂琴, 柴继宽. 不同类型除草剂的田间防效及其对裸燕麦带壳率和产量的影响. 草业学报, 2016, 25(1): 171-178. | |
| 15 | Jan W E, Mark A S, James G, et al. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(10): 636-639. |
| 16 | Yi X Y, Yuan M, Yin C B. The chemicals input status and transformation path of the planting industry in China. Strategic Study of CAE, 2017, 19(4): 124-129. |
| 易小燕, 袁梦, 尹昌斌. 我国种植业化学品投入状况与转变路径研究. 中国工程科学, 2017, 19(4): 124-129. | |
| 17 | Yu F, Shi W M. Nitrogen use efficiencies of major grain crops in China in recent 10 years. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6): 1311-1324. |
| 于飞, 施卫明. 近10年中国大陆主要粮食作物氮肥利用率分析. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6): 1311-1324. | |
| 18 | The Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. The action plan for zero growth in fertilizer use by 2020. Qinghai Agro-Technology Extension, 2015(2): 3-5, 11. |
| 中华人民共和国农业部. 到2020年化肥使用量零增长行动方案. 青海农技推广, 2015(2): 3-5, 11. | |
| 19 | Song J H, Hu T M, Wang Q Z, et al. Correlation analysis of nitrogen application rate and Tibetan wild Elymus nutans seed yield and its yield factors. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(5): 22-26. |
| 宋江湖, 呼天明, 王佺珍, 等. 施N量与西藏野生垂穗披碱草种子产量及产量因子的相关性分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 36(5): 22-26. | |
| 20 | Mao P S, Han J G, Wang P R, et al. Effects of fertilizer application on seed yield of smooth bromegrass and siberian wildrye. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2000, 8(4): 273-278. |
| 毛培胜, 韩建国, 王培戎, 等. 施肥对无芒雀麦和老芒麦种子产量的影响. 草地学报, 2000, 8(4): 273-278. | |
| 21 | Li W Q, Xu B M, Feng Y J, et al. The effect of nitrogen on ryegrass growth and its internal components. Grassland of China, 2003, 25(1): 28-31. |
| 李文庆, 徐保民, 冯永军, 等. 氮肥对黑麦草生长及其内部组分的影响. 中国草地, 2003, 25(1): 28-31. | |
| 22 | Qiao A H. Study on seed production techniques of Elymus nutans in east Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005. |
| 乔安海. 青藏高原东部地区垂穗披碱草种子生产技术研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. | |
| 23 | Luo J, Zhang S Z, Tang F, et al. Effect of nitrogen application on seed yield of Elymus sibiricus under different densities. Grass-feeding Livestock, 2020(3): 28-34. |
| 罗金, 张树振, 唐凤, 等. 不同密度条件下施氮对老芒麦种子产量的影响. 草食家畜, 2020(3): 28-34. | |
| 24 | Wang M Y. Roles of nitrogen application on seed yield and yield components in Siberian wildrye. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 王明亚. 施氮对老芒麦种子产量及产量因子的作用. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. | |
| 25 | Gao P, Li C, Chen B J, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on seed yield, seed constitutive factors and seed vigor of Elymus sibiricus L. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 42(2): 126-131. |
| 高朋, 李聪, 陈本建, 等. 施氮对老芒麦种子产量及其构成因子和种子活力的影响. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 2010, 42(2): 126-131. | |
| 26 | Jiang S Q, Li D R, Han J G, et al. The effects of split-nitrogen application in spring on seed yield and nitrogen use efficiency in Russian wildrye. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2008, 16(5): 512-517. |
| 江生泉, 李德荣, 韩建国, 等. 春季分施氮肥对新麦草种子产量及氮肥利用率的影响. 草地学报, 2008, 16(5): 512-517. | |
| 27 | Ma C H, Han J G, Zhang L, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on seed quality and yield components of tall fescue in Xinjiang. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2003, 12(6): 74-78. |
| 马春晖, 韩建国, 张玲, 等. 施氮肥对高羊茅种子质量和产量组成的影响. 草业学报, 2003, 12(6): 74-78. | |
| 28 | Feng S Z, Liu N, Huang X X, et al. Effects of nitrogen rate on grain yield, dry matter accumulation and LAI of dryland spring maize. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 54(9): 2065-2069. |
| 冯尚宗, 刘宁, 黄孝新, 等. 施氮量对旱地春玉米产量、干物质积累及叶面积指数的影响. 湖北农业科学, 2015, 54(9): 2065-2069. | |
| 29 | Zhang J H, Li Q F, Li X L. Studies on the seed yield components of Elymus sibiricus without irrigation. Grassland of China, 2000(6): 35-38. |
| 张锦华, 李青丰, 李显利. 旱作老芒麦种子产量构成因子的研究. 中国草地, 2000(6): 35-38. | |
| 30 | Zhang X F, Li J H, Tian F P, et al. Influence of different nitrogen fertilization on orchardgrass yield in the Lhasa area of Tibet. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2011, 20(7): 192-195. |
| 张小甫, 李锦华, 田福平, 等. 西藏拉萨地区不同施氮量对鸭茅产量的影响. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(7): 192-195. | |
| 31 | Fang L N, Han J G, Wang P, et al. Seed yield response of smooth brome to nitrogen, plant growth regulator and environmental influences. Grassland of China, 2001, 23(4): 32-37. |
| 房丽宁, 韩建国, 王培, 等. 氮肥、植物生长调节剂和环境因素对无芒雀麦种子生产的影响. 中国草地, 2001, 23(4): 32-37. | |
| 32 | Chen Z H. Study on seed production techniques of tall fescue in Beijing. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2002. |
| 陈志宏. 北京地区高羊茅等牧草种子生产技术的研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2002. | |
| 33 | Gislum R, Deleuran L C, Kristensen K, et al. Optimum distribution between autumn-applied and spring-applied nitrogen in seed production of tall fescue. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2012, 35(9): 1394-1410. |
| 34 | Oral E. Effect of nitrogen fertilization levels on grain yield and yield components in triticale based on AMMI and GGE biplot analysis. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2018, 16(4): 4865-4878. |
| 35 | Liang X Y, Zhang X Q, Zhang J H. Effect of different nitrogen application on the production performance of orchardgrass.Grassland and Turf, 2004(2): 8-12. |
| 梁小玉, 张新全, 张锦华. 不同施氮量和时间对鸭茅生产利用的影响. 草原与草坪, 2004(2): 8-12. | |
| 36 | Watson C E, Watson V H. Nitrogen and date of defoliation effects on seed yield and seed quality of tall fescuel. Agronomy Journal, 1982, 74(5): 891-893. |
| 37 | Wang M Y, Hou L Y, Zhang Q, et al. Influence of row spacing and P and N applications on seed yield components and seed yield of siberian wildrye (Elymus sibiricus L.). Crop Science, 2017, 57(4): 2205-2212. |
| 38 | Seker H, Serin Y. Explanation of the relationships between seed yield and some morphological traits insmoothbromegrass (Bromus inermis Leyss.) by path analysis. European Journal of Agronomy, 2004, 21(1): 1-6. |
| 39 | Zhang T, Wang X, Han J, et al. Effects of between-row and within-row spacing on alfalfaseed yields. Crop Science, 2008, 48(2): 794-803. |
| 40 | Zhang J M, Wang S M. Effects of row width and fertilization on seed production of “Lanyin 3”turf-typezoysiagrass. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 1997, 6(3): 47-51. |
| 张巨明, 王锁民. 行距及施肥量对兰引3号结缕草种子产量的影响. 草业学报, 1997, 6(3): 47-51. | |
| 41 | Chen Z H, Han J G, Chen H M, et al.Effect of fertilization-N on tall fescue seed yield and yield components of seed crop. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2005, 13(3): 215-218. |
| 陈志宏, 韩建国, 陈会敏, 等. 施氮对高羊茅种子产量组分和产量的影响. 草地学报, 2005, 13(3): 215-218. | |
| 42 | Hebblethwaite P D, Ivins J D. Nitrogen studies in Lolium perenne grown for seed I. Level of application. Journal of the British Grassland Society, 1977, 32(4): 195-204. |
| 43 | Young W C, Chilcote D O, Youngberg H W. Spring-applied nitrogen and productivity of cool-season grass seed crops. Agronomy Journal, 1999, 91(2): 339-343. |
| 44 | Hu Y J, Zhu D W, Xing Z P, et al. Modifying nitrogen fertilization ratio to increase the yield and nitrogen uptake of super Japonica rice. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21(1): 12-22. |
| 胡雅杰, 朱大伟, 邢志鹏, 等. 改进施氮运筹对水稻产量和氮素吸收利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21(1): 12-22. | |
| 45 | Xu R L, Dai Q G, Wang X Q, et al. Study on the effect of nitrogen fertilizer application rate, application period and transportation on nitrogen utilization in rice. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2005(2): 19-22. |
| 许仁良, 戴其根, 王秀芹, 等. 氮肥施用量、施用时期及运筹对水稻氮素利用率影响研究. 江苏农业科学, 2005(2): 19-22. | |
| 46 | Moose S, Below F E. Biotechnology approaches to improving maize nitrogen use efficiency. Berlin: Springer, 2009. |
| 47 | Ju X T, Liu X J, Zou G Y, et al. Evaluation of nitrogen loss way in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2002, 35(12): 1493-1499. |
| 巨晓棠, 刘学军, 邹国元, 等. 冬小麦/夏玉米轮作体系中氮素的损失途径分析. 中国农业科学, 2002, 35(12): 1493-1499. | |
| 48 | Wang M Y, He M R, Li Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rate on yield and nitrogen uptake and utilization of different wheat varieties. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(4): 241-248. |
| 王茂莹, 贺明荣, 李玉, 等. 施氮量对不同小麦品种产量及氮素吸收利用的影响. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(4): 241-248. | |
| 49 | Cao Y J, Han S, Sha S, et al. Effects of nitrogen rate and planting density on the yield formation and the nitrogen fertilizer utilization in summer maize in Dongting Lake area. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 45(2):131-137. |
| 曹亚娟, 韩霜, 沙莎, 等. 施氮量和种植密度对洞庭湖区夏玉米产量及氮素利用的影响. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 45(2): 131-137. | |
| 50 | Li Y S, Lu J W, Liao X, et al. Effect of nitrogen application rate on yield and nitrogen fertilization efficiency in rapeseed. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2011, 33(4): 379-383. |
| 李银水, 鲁剑巍, 廖星, 等. 氮肥用量对油菜产量及氮素利用效率的影响. 中国油料作物学报, 2011, 33(4): 379-383. | |
| 51 | Li X F, Cheng J Q, Liang J, et al. Effects of total straw returning and nitrogen application on grain yield and nitrogen absorption and utilization of machine transplanted Japonica rice. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 912-924. |
| 李晓峰, 程金秋, 梁健, 等. 秸秆全量还田与氮肥运筹对机插粳稻产量及氮素吸收利用的影响. 作物学报, 2017, 43(6): 912-924. | |
| 52 | Liang Q D. Effects of nitrogen application rate and planting density on growth, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of rice. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020. |
| 梁青铎. 施氮量和机插密度对水稻生长、产量和氮肥利用效率的影响. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. | |
| 53 | Liu L J. Fertilizer-N use efficiency and its regulation approaches in rice. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2005. |
| 刘立军. 水稻氮肥利用效率及其调控途径. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2005. | |
| 54 | Ma J J. Comparative study on growth characteristics and nitrogen utilization among ten varieties of Italian ryegrass under Cu2+ treatment. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2011. |
| 马晶晶. Cu2+处理下10个多花黑麦草品种生长特性和氮素利用的比较研究. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2011. | |
| 55 | Wang Z, Zhang W, Beebout S S, et al. Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crops Research, 2016, 193: 54-69. |
| [1] | 钱文武, 郭鹏, 朱慧森, 张士敏, 李德颖. 草地早熟禾叶片表皮特征、解剖结构及光合特性对不同施氮量的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 131-143. |
| [2] | 高玮, 受娜, 蒋丛泽, 马仁诗, 沈禹颖, 杨宪龙. 施氮量对饲用高粱干物质积累、分配及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 26-35. |
| [3] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [4] | 周大梁, 石薇, 蒋紫薇, 魏正业, 梁欢欢, 贾倩民. 沟垄集雨下密度和施氮对黄土高原青贮玉米叶片酶活性及水氮利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 126-143. |
| [5] | 蒋紫薇, 刘桂宇, 安昊云, 石薇, 常生华, 张程, 贾倩民, 侯扶江. 种植密度与施氮对玉米/秣食豆间作系统饲草产量、品质和氮肥利用的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 157-171. |
| [6] | 潘静, 张俊超, 陈有军, 周青平. 基于SCoT标记的披碱草属种质遗传多样性分析及指纹图谱构建[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 48-60. |
| [7] | 王玉霞, 柴锦隆, 周洋洋, 徐长林, 王琳, 鱼小军. 种植方式对陇中干旱区扁蓿豆种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 60-72. |
| [8] | 王红林, 左艳春, 严旭, 周晓康, 寇晶, 杨希智, 郭俊英, 蒲军, 张浩仁, 杜周和. 刈割高度与施氮量对饲料桑全株产量及营养品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 203-211. |
| [9] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 贾瑜琀. 不同施氮水平对柳枝稷光合特性及抗旱性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 107-115. |
| [10] | 伏兵哲, 周燕飞, 李雪, 倪彪, 高雪芹. 宁夏引黄灌区羊草水肥耦合效应研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 98-108. |
| [11] | 康彩睿, 谢军红, 李玲玲, 王嘉男, 郭喜军, 彭正凯, 王进斌, Setor kwami Fudjoe, 王林林. 种植密度与施氮量对陇中旱农区玉米产量及光合特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 141-149. |
| [12] | 高丽敏, 田倩, 苏晶, 沈益新. 施氮水平对甜高粱干物质产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 192-198. |
| [13] | 张梦, 李本银, 刘春增, 吕玉虎, 张成兰, 陈雪青, 曹卫东. 紫云英荚果分层成熟特性及其种子产量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 64-72. |
| [14] | 刘凯强, 刘文辉, 魏小星, 贾志锋, 石正海. 不同播量和行距对‘青燕1号’燕麦种子产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 82-91. |
| [15] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 常雯雯. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||