

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 79-90.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022141
收稿日期:2022-03-30
修回日期:2022-06-16
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-01-29
通讯作者:
朱慧森
作者简介:E-mail: zhuhuisen@126.com基金资助:
Shi-min ZHANG( ), Jiao-yang ZHAO, Hui-sen ZHU(
), Jiao-yang ZHAO, Hui-sen ZHU( ), Kai WEI, Yong-xin WANG
), Kai WEI, Yong-xin WANG
Received:2022-03-30
Revised:2022-06-16
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-01-29
Contact:
Hui-sen ZHU
摘要:
为了探究外源硒对不同品种紫花苜蓿种子萌发阶段糖、氮物质转化,发芽指标和形态建成的影响,以甘农3号、DS310FY及中苜5号紫花苜蓿为对象,设置5个亚硒酸钠浓度(0、0.3、0.6、1.2、2.4 mg·L-1),培养10 d后测定苜蓿种子的发芽率,表型及生理指标和硒含量,并运用综合分析和相关性分析探究各生理指标与表型的关系,以筛选出最适宜的硒浓度和潜在的硒营养强化材料。结果表明:施硒处理4 d,DS310FY和甘农3号苜蓿幼苗的还原糖含量、可溶性糖含量及发芽势均在0.6 mg·L-1硒处理下显著高于对照(P<0.05);施硒处理10 d,0.3、0.6 mg·L-1硒处理下DS310FY和甘农3号苜蓿幼苗的还原糖含量、硝酸还原酶活性、发芽率及发芽指数都显著高于对照(P<0.05);而甘农3号苜蓿幼苗的胚芽长及DS310FY苜蓿幼苗的总氨基酸含量、活力指数、胚芽长、胚根长及单株鲜重,施硒后的最大值相比对照均显著提高(P<0.05);另外,0.3 mg·L-1硒处理下相比对照也显著提高了中苜5号苜蓿幼苗的蔗糖含量、发芽率及胚根直径(P<0.05)。相关性分析和各指标的变化趋势表明,苜蓿幼苗糖的积累和转化主要促进胚根的发育,而氮的积累和转化主要促进胚芽的伸长和单株鲜重的增加。因此,施硒后糖转化效率的提高主要促进苜蓿种子的萌发,而氮转化效率的提高主要促进苜蓿幼苗的形态建成。综上,以0.6 mg·L-1硒处理下DS310FY紫花苜蓿发芽阶段的物质转化和形态建成综合表现最佳,更适宜进行硒的营养强化。
张士敏, 赵娇阳, 朱慧森, 卫凯, 王永新. 硒对不同品种紫花苜蓿发芽阶段物质转化和形态建成的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 79-90.
Shi-min ZHANG, Jiao-yang ZHAO, Hui-sen ZHU, Kai WEI, Yong-xin WANG. Effects of selenium on metabolic transformation and morphogenesis in different varieties of alfalfa during the germination stage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(4): 79-90.

图1 施硒对不同品种苜蓿种子萌发的影响GN3:甘农3号M. sativa cv. Gannong No.3; ZM5: 中苜5号M. sativa Zhongmu No.5; 同一品种紫花苜蓿施硒处理,不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。The same variety of alfalfa treated with selenium, different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig. 1 Effect of selenium application on seed germination of different varieties of alfalfa
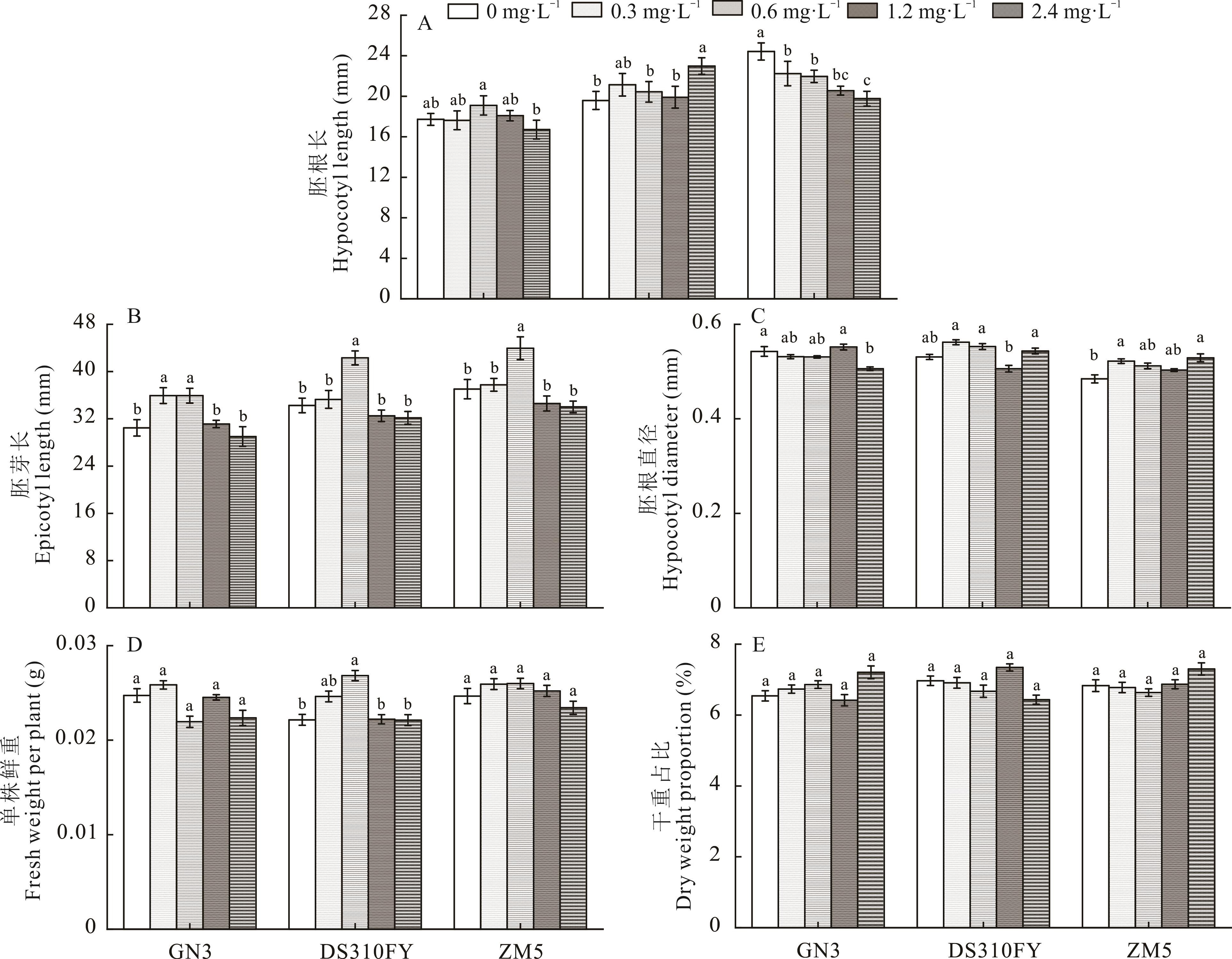
图2 施硒对不同品种苜蓿种子萌发后形态建成的影响
Fig. 2 Effect of selenium application on morphological establishment of different varieties of alfalfa seeds after germination

图3 施硒对不同品种苜蓿种子萌发后糖形态转化及氮转化的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of selenium application on sugar morphological transformation and nitrogen transformation in different varieties of alfalfa seed germination stage
处理 Treatments | 指标 Index | 甘农3号 Gannong No.3 | DS310FY | 中苜5号 Zhongmu No.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 发芽势Germination potential (%) | 90.50±0.58a | 90.25±1.71a | 82.25±2.06b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 发芽指数Germination index | 206.55±1.77a | 208.07±3.89a | 161.77±4.17b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 活力指数Vigor index | 5.34±0.30a | 5.58±0.32a | 4.20±0.20b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 硝酸还原酶Nitrate reductase (μg NO2-·g-1FW·h-1) | 42.02±2.63a | 36.64±2.01ab | 33.71±3.40b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY2 | 胚芽长Epicotyl length (mm) | 35.94±2.14b | 42.32±2.18a | 43.95±3.82a |
| GSY2, DSY4, ZMCK | 胚根长Hypocotyl length (mm) | 19.10±1.55b | 22.98±1.11a | 24.42±1.15a |
| GSY2, DSY2, ZMY4 | 还原糖Reducing sugar of 4 d (%) | 4.46±0.18b | 5.45±0.29a | 4.56±0.35b |
| GSY2, DSY1, ZMY2 | 还原糖Reducing sugar of 10 d (%) | 3.02±0.13b | 3.04±0.19b | 3.91±0.25a |
| GSY3, DSY3, ZMY4 | 蔗糖Sucrose of 10 d (%) | 4.11±0.20b | 5.46±0.16a | 5.34±0.25a |
| GSY1, DSY1, ZMY1 | 总氨基酸Total amino acid (μg·g-1) | 434.24±35.37b | 512.62±21.15a | 436.20±23.97b |
| GSY3, DSY1, ZMY1 | 可溶性糖Soluble sugar of 4 d (%) | 1.72±0.11b | 2.06±0.14a | 2.19±0.10a |
表1 施硒后不同品种苜蓿发芽指标的综合对比分析
Table 1 Comprehensive comparative analysis of germination indicators of different varieties of alfalfa after selenium application
处理 Treatments | 指标 Index | 甘农3号 Gannong No.3 | DS310FY | 中苜5号 Zhongmu No.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 发芽势Germination potential (%) | 90.50±0.58a | 90.25±1.71a | 82.25±2.06b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 发芽指数Germination index | 206.55±1.77a | 208.07±3.89a | 161.77±4.17b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 活力指数Vigor index | 5.34±0.30a | 5.58±0.32a | 4.20±0.20b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY1 | 硝酸还原酶Nitrate reductase (μg NO2-·g-1FW·h-1) | 42.02±2.63a | 36.64±2.01ab | 33.71±3.40b |
| GSY1, DSY2, ZMY2 | 胚芽长Epicotyl length (mm) | 35.94±2.14b | 42.32±2.18a | 43.95±3.82a |
| GSY2, DSY4, ZMCK | 胚根长Hypocotyl length (mm) | 19.10±1.55b | 22.98±1.11a | 24.42±1.15a |
| GSY2, DSY2, ZMY4 | 还原糖Reducing sugar of 4 d (%) | 4.46±0.18b | 5.45±0.29a | 4.56±0.35b |
| GSY2, DSY1, ZMY2 | 还原糖Reducing sugar of 10 d (%) | 3.02±0.13b | 3.04±0.19b | 3.91±0.25a |
| GSY3, DSY3, ZMY4 | 蔗糖Sucrose of 10 d (%) | 4.11±0.20b | 5.46±0.16a | 5.34±0.25a |
| GSY1, DSY1, ZMY1 | 总氨基酸Total amino acid (μg·g-1) | 434.24±35.37b | 512.62±21.15a | 436.20±23.97b |
| GSY3, DSY1, ZMY1 | 可溶性糖Soluble sugar of 4 d (%) | 1.72±0.11b | 2.06±0.14a | 2.19±0.10a |

图5 施硒后苜蓿种子萌发及生理指标间的相关性分析图中数字代表两个相交叉指标的相关性P值,无数字代表具有显著相关性(P<0.05);其中“+”代表显著正相关,“-”代表显著负相关;圆形面积越大,颜色越深,代表相关系数越高。The number in the figure represents the correlation P value of the two intersecting indicators, and no number represent significant correlation (P<0.05); “+” represents a significant positive correlation, and “-” represents a significant negative correlation; the larger the circle area, the darker the color, the higher the correlation coefficient. TAA: 总氨基酸Total amino acids; GP: 发芽势Germination potential; GR: 发芽率Germination rate; GI: 发芽指数Germination index; VI: 活力指数Vigor index; EL: 胚芽长Epicotyl length; HL: 胚根长Hypocotyl length; HD: 胚根直径Hypocotyl diameter; FW: 单株鲜重Fresh weight per plant; DW: 干重占比Dry weight proportion; RS-4: 还原糖4天Reducing sugar for 4 d; RS-10: 还原糖10天Reducing sugar for 10 d; SuC: 蔗糖Sucrose; SS: 可溶性糖Soluble sugar; NR: 硝酸还原酶Nitrate reductase; SeC: 硒含量Selenium content.
Fig. 5 Correlation analysis between alfalfa seed germination and physiological indicators after selenium application
| 1 | Malik J A, Goel S, Kaur N, et al. Selenium antagonises the toxic effects of arsenic on mungbean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) plants by restricting its uptake and enhancing the antioxidative and detoxification mechanisms. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2012, 77: 242-248. |
| 2 | Lu Y, Li X R, He M Z, et al. Seedlings growth and antioxidative enzymes activities in leaves under heavy metal stress differ between two desert plants: A perennial (Peganum harmala) and an annual (Halogeton glomeratus) grass. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2010, 32(3): 583-590. |
| 3 | Nadgórska S A, Ptasiński B, Andrzej K. Heavy metal bioaccumulation and antioxidative responses in Cardaminopsis arenosa and Plantago lanceolata leaves from metalliferous and non-metalliferous sites: A field study. Ecotoxicology, 2013, 22(9): 1422-1434. |
| 4 | Barbara H N, Slawomir D, Malgorzata W. Selenium affects physiological parameters and phytochelatins accumulation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) plants grown under cadmium exposure. Scientia Horticulturae, 2014, 172: 10-18. |
| 5 | Mora M L, Durán P, Acuňa A J, et al. Improving selenium status in plant nutrition and quality. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2015, 15(2): 486-503. |
| 6 | Dinh Q T, Cui Z, Huang J, et al. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review. Environment International, 2018, 112: 294-309. |
| 7 | Liu F, Hu H F, Liu Y, et al. Effects of basal application of selenium fertilizer on yield and antioxidation of alfalfa(Medicago sativa L.). Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2013, 21(1): 109-113. |
| 刘芳, 胡华锋, 刘巘, 等. 基施硒肥对紫花苜蓿草产量及抗氧化作用的影响. 草地学报, 2013, 21(1): 109-113. | |
| 8 | Liu H B, Bai Y G, Zhang J H, et al. Optimization of capillary arrangement for drip irrigation in alfalfa field. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2018, 34(35) : 135-142. |
| 刘洪波, 白云岗, 张江辉, 等. 紫花苜蓿田间滴灌毛管布置优化. 中国农学通报, 2018, 34(35): 135-142. | |
| 9 | Han B. Effects of selenium and cobalt fertilizer on growth and quality of alfalfa. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2016: 9. |
| 韩冰. 硒、钴肥对紫花苜蓿生长及品质的影响. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2016: 9. | |
| 10 | Han B, Chen B J, Yu H Y, et al. Effects of selenium and cobalt on aboveground biomass and quality of alfalfa grown in sandy soil. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2017, 52(4): 138-144. |
| 韩冰, 陈本建, 俞慧云, 等. 硒钴对沙质土盆栽紫花苜蓿地上生物量和品质的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2017, 52(4): 138-144. | |
| 11 | Li J L. Effects of exogenous zinc and selenium on alfalfa seedlings damaged by UV-B radiation. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2019: 40-42. |
| 李金俐. 外源锌硒对UV-B辐射损伤紫花苜蓿幼苗的影响. 晋中: 山西农业大学, 2019: 40-42. | |
| 12 | Zhang M, Tang S H, Zhang F B, et al. Effects of selenium on carbon-nitrogen metabolism and yield of rice. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016(5): 79-84. |
| 张木, 唐拴虎, 张发宝, 等. 硒对水稻碳氮代谢及产量的影响. 中国土壤与肥料, 2016(5): 79-84. | |
| 13 | Bai B, Wang Z, Gao L, et al. Effects of selenite on the growth of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L. cv. Sadie 7) and related physiological mechanisms. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2019, 41(6): 1-11. |
| 14 | Xu X Z, Zhao G Q, Du J. Effect of selenium on chilling tolerance during seed imbibition and germination of maize. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2017, 52(1): 63-67, 73. |
| 许兴泽, 赵桂琴, 杜锦. 硒对玉米种子吸胀期间生理特性和种子发芽能力的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2017, 52(1): 63-67, 73. | |
| 15 | Rao L, Luo Q X, Zhao X H. Effects of methionine-selenium on physiological index of cucumber seedling leaves under drought stress. Northern Horticulture, 2017(6): 14-18. |
| 饶玲, 罗庆熙, 赵小红. 蛋氨酸硒对干旱胁迫下黄瓜幼苗生理特性的影响. 北方园艺, 2017(6): 14-18. | |
| 16 | Zhang H. Study on processing of Se-enrichment germinating soybean and distribution of Se in its sprouts. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010: 49. |
| 张红. 大豆发芽富硒工艺及硒在豆芽中的分布研究. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010: 49. | |
| 17 | Yang Y, Wang B, Hu X F, et al. Study on organic transformation of inorganic selenium and its effects on chemical composition of sprouted brown rice. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2011, 26(9): 1-5. |
| 杨椰, 王博, 胡小芳, 等. 无机硒在糙米发芽中的有机转化及对糙米化学组分影响. 中国粮油学报, 2011, 26(9): 1-5. | |
| 18 | Shi Y H, Du T Q, Zhai H M, et al. Effects of selenium on seed germination, physiological characteristics and nutritional quality of kidney bean. Crops, 2021(3): 210-216. |
| 史雅涵, 杜天庆, 翟红梅, 等. 硒对芸豆种子萌发、生理特性及营养品质的影响. 作物杂志, 2021(3): 210-216. | |
| 19 | Li Q, Zheng B, Liu L, et al. Effects of spraying organic selenium fertilizers on selenium content and quality of apple fruits. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(9): 1316-1319. |
| 李全, 郑斌, 刘丽, 等. 喷施有机硒肥对苹果果实硒含量及品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 2016, 44(9): 1316-1319. | |
| 20 | Zhang Y Y, Jiao Z G, Ai X Z, et al. Effects of methionine-selenium added in soil on physiological characteristics and quality of muskmelon. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016, 22(2): 476-485. |
| 张杨杨, 焦自高, 艾希珍, 等. 土壤增施蛋氨酸硒对厚皮甜瓜生理特性和品质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(2): 476-485. | |
| 21 | Guo K X, Yao C X, Zhou S B, et al. Effects of selenium application on the selenium content, yield, qualities and biological characteristics of greens. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2010, 24(5): 195-198, 203. |
| 郭开秀, 姚春霞, 周守标, 等. 施用硒肥对鸡毛菜产量、品质及生理特性的影响. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(5): 195-198, 203. | |
| 22 | Hu W X, Shi Y, Cheng Y Q, et al. Effects of nano-selenium on the growth and its mineral elememt contents and quality characteristics of purple potatoes. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2020, 40(2): 296-303. |
| 胡万行, 石玉, 程玉琦, 等. 纳米硒对紫色马铃薯生长及其矿质元素含量和品质特性的影响. 西北植物学报, 2020, 40(2): 296-303. | |
| 23 | Zhou X B, Wu H Y, Wang H Y, et al. Effect of spraying selenium fertilizer on physicochemical index and quality of soybean. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2004(5): 38-42. |
| 周勋波, 吴海燕, 王海英, 等. 喷施硒肥对大豆理化指标和品质的影响. 中国粮油学报, 2004(5): 38-42. | |
| 24 | Nunes-Nesi A, Fernie A R, Stitt M. Metabolic and signaling aspects underpinning the regulation of plant carbon nitrogen interactions. Molecular Plant, 2010, 3(6): 973-996. |
| 25 | Yin G L, Wu F, Tao R, et al. Effects of rhizosphere soil extraction from alfalfa-corn and alfalfa-wheat fields on alfalfa seed germination and seedling physiology and growth. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 153-161. |
| 尹国丽, 吴芳, 陶茸, 等. 苜蓿轮作玉米\小麦土壤浸提液对苜蓿种子萌发和幼苗生理及生长的影响. 草业学报, 2018, 27(5): 153-161. | |
| 26 | He W L, Li X L, Yang L B, et al. Effects of bentonite on alfalfa seed germination and arsenic accumulation under typical organic arsenic stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2019, 27(1): 185-191. |
| 何万领, 李晓丽, 杨龙帮, 等. 膨润土对典型有机砷胁迫紫花苜蓿种子萌发与砷积累的影响. 草地学报, 2019, 27(1): 185-191. | |
| 27 | Kou J T. Physiological mechanism of 2,4-epibrassinolide-regulated salt stress tolerance in Medicago sativa. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2016: 25. |
| 寇江涛. 2,4-表油菜素内酯诱导下紫花苜蓿耐盐性生理响应研究. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2016: 25. | |
| 28 | Zuo X Q, Shi L S, Li Z, et al. Rapid determination of reducing sugars, sucrose and starch in fruits and vegetables by spectrophotometry. //The 20th National Symposium on Spectral Instruments and Analytical Monitoring. Zhenjiang: National Engineering Technology Digital Library, 2013: 169-174. |
| 左向群, 施露盛, 李征, 等. 分光光度法快速测定果蔬类还原糖, 蔗糖和淀粉. //全国第20届光谱仪器与分析监测学术研讨会. 镇江: 国家工程技术数字图书馆, 2013: 169-174. | |
| 29 | Zhang Y S, Huang X, Chen F F. Experimental course in plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2009: 113-114. |
| 张以顺, 黄霞, 陈方凤. 植物生理学实验教程. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009: 113-114. | |
| 30 | Qiao F L. Analysis and determination technique of plant physiology experiment. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2002: 120-121. |
| 乔富廉. 植物生理学实验分析测定技术. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2002: 120-121. | |
| 31 | Gao J F. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2012: 62-64. |
| 高俊凤. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版, 2012: 62-64. | |
| 32 | Zhang L, Song H, Guo Y, et al. Benefit-risk assessment of dietary selenium and its associated metals intake in China (2017-2019): Is current selenium-rich agro-food safe enough? Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 398: 123224. |
| 33 | Zhang X. Effects of different selenium fertilizer amounts and application method on selenium accumulation transportation and soil fertility in wheat. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2019: 9. |
| 张霞. 硒肥施用量及施用方式对小麦硒累积运转及土壤肥力的影响. 晋中: 山西农业大学, 2019: 9. | |
| 34 | Kaur M, Sharma S, Singh D. Influence of selenium on carbohydrate accumulation in developing wheat grains. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2018, 49(13): 1650-1659. |
| 35 | Zhao X Q, Mitani N, Yamaji N, et al. Involvement of silicon influx transporter OsNIP2; 1 in selenite uptake in rice. Plant Physiology, 2010, 153(4): 1871-1877. |
| 36 | Van Hoewyk D. A tale of two toxicities: Malformed selenoproteins and oxidative stress both contribute to selenium stress in plants. Annals of Botany, 2013, 112(6): 965-972. |
| 37 | Verspreet J, Hemdane S, Dornez E, et al. Analysis of storage and structural carbohydrates in developing wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains using quantitative analysis and microscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(38): 9251-9259. |
| 38 | Shahzadi I, Iqbal M, Rasheed R, et al. Foliar application of selenium increases fertility and grain yield in bread wheat under contrasting water availability regimes. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2017, 39(8): 1-11. |
| 39 | Túlio S L, Lessa J H D L, Souza K I D, et al. Selenium biofortification of wheat grain via foliar application and its effect on plant metabolism. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2019, 81: 10-18. |
| 40 | Msehli S E, Lambert A, Baldacci C F, et al. Crucial role of (homo) glutathione in nitrogen fixation in Medicago truncatula nodules. New Phytologist, 2011, 192(2): 496-506. |
| 41 | Lee J, Finley J W, Harnly J M. Effect of selenium fertilizer on free amino acid composition of broccoli (Brassica oleracea cv. Majestic) determined by gas chromatography with flame ionization and mass selective detection. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005, 53(23): 9105-9111. |
| 42 | Hajiboland R, Sadeghzadeh N. Effect of selenium on CO2 and NO3 - assimilation under low and adequate nitrogen supply in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Photosynthetica, 2014, 52(4): 501-510. |
| 43 | Zhu J J, Yu C M, Chen J K, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium on grass yield and nutritive value of forage ramie. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(10): 144-155. |
| 朱娟娟, 喻春明, 陈继康, 等. 外源硒对饲用苎麻草产量和营养价值的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(10): 144-155. | |
| 44 | Cheng B, Han R B, Liu J Q, et al. Study on selenium tolerance of different varieties of alfalfa seeds. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(12): 150-155. |
| 程贝, 韩如冰, 刘家齐, 等. 不同品种紫花苜蓿种子耐硒能力研究. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(12): 150-155. | |
| 45 | Hou W H, Zhao Y H, Tang X F, et al. Effects of different treatment methods on seed germination of vegetable jute. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(2): 231-236. |
| 侯文焕, 赵艳红, 唐兴富, 等. 不同处理方法对菜用黄麻种子萌发的影响. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(2): 231-236. | |
| 46 | Hu T, Li W F, Xiang C G, et al. Effect of selenium on seed germination of common vegetables and its distribution in plants. Food Science, 2015, 36(7): 45-49. |
| 胡婷, 李文芳, 向昌国, 等. 硒对常见蔬菜种子萌发的影响及在植株中的分布. 食品科学, 2015, 36(7): 45-49. | |
| 47 | Wang F G. Effects of selenium on seed germination and seedling growth of mung bean under drought stress. Yan’an: Yan’an University, 2015: 25-26. |
| 王富刚. 干旱胁迫下硒对绿豆种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响. 延安: 延安大学, 2015: 25-26. | |
| 48 | Shalaby T, Bayoumi Y, Alshaal T, et al. Selenium fortification induces growth, antioxidant activity, yield and nutritional quality of lettuce in salt-affected soil using foliar and soil applications. Plant and Soil, 2017, 421(1): 245-258. |
| 49 | Hawrylak N B. Comparative effects of selenite and selenate on growth and selenium accumulation in lettuce plants under hydroponic conditions. Plant Growth Regulation, 2013, 70(2): 149-157. |
| 50 | Jiang C, Zu C, Shen J, et al. Effects of selenium on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae,2015, 84(1): 71-77. |
| 51 | Ramos S J, Faquin V, Guilherme L R G, et al. Selenium biofortification and antioxidant activity in lettuce plants fed with selenate and selenite. Plant Soil and Environment, 2010, 56(12): 584-588. |
| 52 | Feng R, Wei C, Tu S, et al. The uptake and detoxification of antimony by plants: A review. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013, 96: 28-34. |
| 53 | Sieprawska A, Kornaś A, Filek M. Involvement of selenium in protective mechanisms of plants under environmental stress conditions-review. Acta Biologica Cracoviensia Series Botanica, 2015, 57(1): 9-20. |
| 54 | Hajiboland R, Rahmat S, Aliasgharzad N, et al. Selenium-induced enhancement in carbohydrate metabolism in nodulated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) as related to the glutathione redox state. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2015, 61(4): 676-687. |
| 55 | Yuan J H, Hu M H. Effect of EDDS treatments on FTIR-ATR, SEM-EDXS features and physiological characteristics of coleus blumei roots under Se stress. Plant Science Journal, 2014, 32(6): 620-629. |
| 袁菊红, 胡绵好. EDDS处理对硒胁迫下彩叶草根系FTIR-ATR、SEM-EDXS 特征及生理特性的影响. 植物科学学报, 2014, 32(6): 620-629. | |
| 56 | Liu X F, Li H Y, Chen L, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium on growth and physiology of ryegrass under cadmium stress. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(1): 72-79. |
| 刘霄霏, 李惠英, 陈良, 等. 外源硒对镉胁迫下黑麦草生长和生理的影响. 草地学报, 2020, 28(1): 72-79. |
| [1] | 张振粉, 黄荣, 姚博, 张旺东, 杨成德, 陈秀蓉. 欧美进口紫花苜蓿可培养种带细菌及其对动植物的致病性[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(4): 161-172. |
| [2] | 王园, 王晶, 李淑霞. 紫花苜蓿MsBBX24基因的克隆及耐盐性分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 107-117. |
| [3] | 田政, 杨正禹, 陆忠杰, 罗奔, 张茂, 董瑞. 44个紫花苜蓿品种的酸铝适应性与耐受性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 142-151. |
| [4] | 孙守江, 唐艺涵, 马馼, 李曼莉, 毛培胜. 紫花苜蓿种子吸胀期胚根线粒体AsA-GSH循环对低温胁迫的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 152-162. |
| [5] | 刘选帅, 孙延亮, 安晓霞, 马春晖, 张前兵. 施磷和接种解磷菌对紫花苜蓿光合特性及生物量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 189-199. |
| [6] | 王晓龙, 杨曌, 来永才, 李红, 钟鹏, 徐艳霞, 柴华, 李莎莎, 吴玥, 宋敏超, 周景明. 不同秋眠等级苜蓿根系性状对越冬的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(1): 144-153. |
| [7] | 孙延亮, 赵俊威, 刘选帅, 李生仪, 马春晖, 王旭哲, 张前兵. 施氮对苜蓿初花期光合日变化、叶片形态及干物质产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 63-75. |
| [8] | 王星, 黄薇, 余淑艳, 李小云, 高雪芹, 伏兵哲. 宁夏地区地下滴灌水肥耦合对紫花苜蓿种子产量及构成因素的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 76-85. |
| [9] | 郭英姿, 贾文庆, 何松林, 王政. 花叶滇苦菜浸提液对3种花卉种子萌发和幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(9): 96-106. |
| [10] | 赵建涛, 岳亚飞, 张前兵, 马春晖. 不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿品种抗寒性对新疆北疆地区覆雪厚度的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 24-34. |
| [11] | 刘彩婷, 毛丽萍, 阿依谢木, 于应文, 沈禹颖. 紫花苜蓿与垂穗披碱草混播比例对其抗寒生长生理特征的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 133-143. |
| [12] | 王雪萌, 何欣, 张涵, 宋瑞, 毛培胜, 贾善刚. 基于多光谱成像技术快速无损检测紫花苜蓿人工老化种子[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 197-208. |
| [13] | 李满有, 李东宁, 王斌, 李小云, 沈笑天, 曹立娟, 倪旺, 王腾飞, 兰剑. 不同苜蓿品种混播和播种量对牧草产量及品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(5): 61-75. |
| [14] | 孙洪仁, 王显国, 卜耀军, 乔楠, 任波. 黄土高原紫花苜蓿土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量初步研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 32-42. |
| [15] | 高丽敏, 陈春, 沈益新. 氮磷肥对季节性栽培紫花苜蓿生长及再生的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(4): 43-52. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||