

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 79-92.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2022421
张东( ), 侯晨, 马文明(
), 侯晨, 马文明( ), 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷
), 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷
收稿日期:2022-10-27
修回日期:2022-12-19
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-07-12
通讯作者:
马文明
作者简介:E-mail: Mawmtf@swun.edu.cn基金资助:
Dong ZHANG( ), Chen HOU, Wen-ming MA(
), Chen HOU, Wen-ming MA( ), Chang-ting WANG, Zhuo-ma DENGZENG, Ting ZHANG
), Chang-ting WANG, Zhuo-ma DENGZENG, Ting ZHANG
Received:2022-10-27
Revised:2022-12-19
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-07-12
Contact:
Wen-ming MA
摘要:
灌丛化是影响草地土壤物质循环的重要生态过程。为探究草地灌丛化梯度变化对土壤酶活性的影响,本研究以青藏高原东缘3种典型灌丛高山绣线菊、小叶锦鸡儿、金露梅和未灌丛化草地为研究对象,分析不同灌丛化梯度下(未灌丛化、轻度灌丛化和重度灌丛化),0~10 cm、10~20 cm、20~40 cm、40~60 cm和60~80 cm土壤理化性质及蔗糖酶(sucrase)、脲酶(urease)、多酚氧化酶(polyphenol oxidase)、葡萄糖苷酶(glucosidase)、蛋白酶(protease)和纤维素酶(cellulase)活性。结果表明:灌丛化草地土壤0~20 cm土层中,pH和土壤有机碳(SOC)含量显著高于未灌丛化草地,土壤含水率(SWC)和全氮(TN)显著低于未灌丛化草地(P<0.05);蛋白酶、葡萄糖苷酶、纤维素酶、脲酶和蔗糖酶活性显著低于未灌丛化草地(P<0.05),多酚氧化酶活性在灌丛化与未灌丛化草地间无显著性差异,且不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性随土层加深而降低;土壤酶活性在不同灌丛化梯度下和不同土壤深度发生变异的主要解释因子为SWC,分别可解释各土层土壤酶活性变异的41.2%、50.5%、37.1%、41.5%和26.0%;结构方程模型(SEM)表明,不同灌丛化梯度主要影响SOC、pH和SOC∶TN,对SWC和TN无显著影响,且不同灌丛化梯度可通过影响pH和SOC含量间接影响蔗糖酶、脲酶、葡萄糖苷酶、蛋白酶、多酚氧化酶和纤维素酶活性,灌丛化梯度不直接显著影响SWC(P>0.05),但SWC仍是影响6种酶活性的主要因子,其可直接正向影响该6种酶活性,也可通过负向影响土壤pH或正向影响SOC进一步影响TN,从而影响酶活性。因此,研究区草地灌木侵入导致土壤酶活性降低利于土壤有机碳固存。
张东, 侯晨, 马文明, 王长庭, 邓增卓玛, 张婷. 高寒草地不同灌丛化梯度下土壤酶活性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 79-92.
Dong ZHANG, Chen HOU, Wen-ming MA, Chang-ting WANG, Zhuo-ma DENGZENG, Ting ZHANG. Study on soil enzyme activities under shrub encroachment gradients in alpine grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 79-92.
样地类型 Plot type | 灌丛化梯度Shrub encroachment gradients | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 物种数 Species number | 灌丛盖度 Shrub coverage (%) | 重要值 Important value | 主要草本植物 Dominant herb species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | 轻度Lightly | 3484 | 11 | 34 | 49.3 | 剪股颖A. clavata, 薹草Carex, 垂穗披碱草E. nutans, 一把伞南星Arisaema erubescens, 发草D. cespitosa, 花锚Halenia corniculata, 矮生嵩草Kobresia humilis, 棘豆Oxytropis yunnanensis, 冷蒿Artemisia frigida, 草玉梅Anemone rivularis, 条叶银莲花Anemone coelestina var. linearis, 鹅绒委陵菜Potentilla anserina |
| 重度Heavily | 15 | 81 | 50.1 | |||
| SA | 轻度Lightly | 3484 | 12 | 26 | 26.6 | |
| 重度Heavily | 14 | 68 | 51.0 | |||
| CM | 轻度Lightly | 3484 | 10 | 30 | 20.1 | |
| 重度Heavily | 15 | 72 | 38.6 | |||
| GS | 未灌丛化No shrubs | 3484 | 13 | NA | NA |
表1 研究区基本概况
Table 1 General information on the study area
样地类型 Plot type | 灌丛化梯度Shrub encroachment gradients | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 物种数 Species number | 灌丛盖度 Shrub coverage (%) | 重要值 Important value | 主要草本植物 Dominant herb species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF | 轻度Lightly | 3484 | 11 | 34 | 49.3 | 剪股颖A. clavata, 薹草Carex, 垂穗披碱草E. nutans, 一把伞南星Arisaema erubescens, 发草D. cespitosa, 花锚Halenia corniculata, 矮生嵩草Kobresia humilis, 棘豆Oxytropis yunnanensis, 冷蒿Artemisia frigida, 草玉梅Anemone rivularis, 条叶银莲花Anemone coelestina var. linearis, 鹅绒委陵菜Potentilla anserina |
| 重度Heavily | 15 | 81 | 50.1 | |||
| SA | 轻度Lightly | 3484 | 12 | 26 | 26.6 | |
| 重度Heavily | 14 | 68 | 51.0 | |||
| CM | 轻度Lightly | 3484 | 10 | 30 | 20.1 | |
| 重度Heavily | 15 | 72 | 38.6 | |||
| GS | 未灌丛化No shrubs | 3484 | 13 | NA | NA |
理化指标 Physicochemical index | 土层 Soil depth (cm) | 未灌丛化草地 No shrubs grassland | 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 小叶锦鸡儿 C. microphylla | 金露梅 P. fruticosa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Lightly | 重度Heavily | 轻度Lightly | 重度Heavily | 轻度Lightly | 重度Heavily | |||
| pH (1∶5) | 0~10 | 5.30±0.09d | 5.90±0.14b | 6.19±0.02a | 5.77±0.09bc | 5.51±0.36cd | 5.84±0.02b | 5.68±0.08bc |
| 10~20 | 5.38±0.15b | 5.92±0.14a | 6.04±0.12a | 5.71±0.31ab | 5.69±0.33ab | 5.72±0.25ab | 5.97±0.40a | |
| 20~40 | 5.47±0.09c | 6.18±0.08ab | 6.03±0.05ab | 6.14±0.14ab | 5.91±0.43b | 6.23±0.13ab | 6.38±0.27a | |
| 40~60 | 5.64±0.33c | 6.47±0.06ab | 6.21±0.05ab | 6.38±0.07ab | 5.93±0.63bc | 6.44±0.22ab | 6.59±0.19a | |
| 60~80 | 5.84±0.34c | 6.74±0.10a | 6.44±0.11ab | 6.40±0.10ab | 6.25±0.23b | 6.64±0.10a | 6.68±0.25a | |
土壤含水率 Soil water content (%) | 0~10 | 1.82±0.27a | 0.74±0.12b | 0.42±0.01c | 0.43±0.38c | 0.49±0.10c | 0.42±0.07c | 0.54±0.08bc |
| 10~20 | 1.47±0.12a | 0.58±0.03b | 0.43±0.02c | 0.29±0.22d | 0.33±0.04cd | 0.31±0.04d | 0.41±0.09cd | |
| 20~40 | 1.14±0.15a | 0.47±0.06b | 0.49±0.01b | 0.22±0.04c | 0.22±0.05c | 0.25±0.03c | 0.28±0.06c | |
| 40~60 | 0.33±0.12ab | 0.30±0.10b | 0.43±0.03a | 0.16±0.02c | 0.18±0.01c | 0.17±0.01c | 0.23±0.05bc | |
| 60~80 | 0.28±0.09ab | 0.23±0.02bc | 0.31±0.03a | 0.18±0.02cd | 0.19±0.01cd | 0.13±0.04d | 0.17±0.04cd | |
土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 0~10 | 32.45±27.87c | 115.64±12.35b | 82.81±19.62bc | 106.04±23.76b | 58.06±16.66bc | 212.00±59.18a | 198.37±66.25a |
| 10~20 | 31.14±19.55b | 94.24±6.40a | 95.14±25.87a | 88.04±14.29a | 99.22±39.43a | 115.18±34.80a | 89.10±5.58a | |
| 20~40 | 28.02±26.87a | 83.22±61.05a | 56.80±33.97a | 41.93±10.89a | 65.52±73.59a | 66.91±15.77a | 82.77±38.64a | |
| 40~60 | 43.20±27.56a | 54.58±39.16a | 76.65±36.26a | 31.60±25.09a | 38.58±46.82a | 55.19±43.61a | 55.27±39.78a | |
| 60~80 | 42.10±19.77ab | 10.32±8.38b | 28.92±18.64ab | 6.66±1.46b | 24.69±19.75ab | 68.68±48.82a | 36.96±28.75ab | |
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 0~10 | 14.13±1.21a | 4.84±0.29c | 4.86±1.00c | 4.95±0.39c | 4.69±0.52c | 8.21±0.87b | 7.12±0.23b |
| 10~20 | 10.28±1.27a | 3.79±0.43c | 5.11±0.64bc | 3.98±0.70c | 3.79±0.85c | 5.55±0.20b | 5.10±0.44bc | |
| 20~40 | 5.04±1.96a | 2.66±0.90ab | 5.09±2.36a | 2.91±0.67ab | 2.23±0.08b | 3.71±0.24ab | 3.56±0.41ab | |
| 40~60 | 1.50±0.60cd | 0.81±0.42d | 2.72±0.48a | 1.39±0.30cd | 1.15±0.20cd | 1.87±0.12bc | 2.33±0.55ab | |
| 60~80 | 0.52±0.09bc | 0.35±0.01c | 1.51±0.45a | 0.84±0.13bc | 0.99±0.30ab | 0.99±0.23ab | 1.52±0.58a | |
表 2 不同灌丛化梯度对土壤理化性质的影响
Table 2 Effect of different shrub encroachment gradients gradients on soil physicochemical properties
理化指标 Physicochemical index | 土层 Soil depth (cm) | 未灌丛化草地 No shrubs grassland | 高山绣线菊 S. alpina | 小叶锦鸡儿 C. microphylla | 金露梅 P. fruticosa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度Lightly | 重度Heavily | 轻度Lightly | 重度Heavily | 轻度Lightly | 重度Heavily | |||
| pH (1∶5) | 0~10 | 5.30±0.09d | 5.90±0.14b | 6.19±0.02a | 5.77±0.09bc | 5.51±0.36cd | 5.84±0.02b | 5.68±0.08bc |
| 10~20 | 5.38±0.15b | 5.92±0.14a | 6.04±0.12a | 5.71±0.31ab | 5.69±0.33ab | 5.72±0.25ab | 5.97±0.40a | |
| 20~40 | 5.47±0.09c | 6.18±0.08ab | 6.03±0.05ab | 6.14±0.14ab | 5.91±0.43b | 6.23±0.13ab | 6.38±0.27a | |
| 40~60 | 5.64±0.33c | 6.47±0.06ab | 6.21±0.05ab | 6.38±0.07ab | 5.93±0.63bc | 6.44±0.22ab | 6.59±0.19a | |
| 60~80 | 5.84±0.34c | 6.74±0.10a | 6.44±0.11ab | 6.40±0.10ab | 6.25±0.23b | 6.64±0.10a | 6.68±0.25a | |
土壤含水率 Soil water content (%) | 0~10 | 1.82±0.27a | 0.74±0.12b | 0.42±0.01c | 0.43±0.38c | 0.49±0.10c | 0.42±0.07c | 0.54±0.08bc |
| 10~20 | 1.47±0.12a | 0.58±0.03b | 0.43±0.02c | 0.29±0.22d | 0.33±0.04cd | 0.31±0.04d | 0.41±0.09cd | |
| 20~40 | 1.14±0.15a | 0.47±0.06b | 0.49±0.01b | 0.22±0.04c | 0.22±0.05c | 0.25±0.03c | 0.28±0.06c | |
| 40~60 | 0.33±0.12ab | 0.30±0.10b | 0.43±0.03a | 0.16±0.02c | 0.18±0.01c | 0.17±0.01c | 0.23±0.05bc | |
| 60~80 | 0.28±0.09ab | 0.23±0.02bc | 0.31±0.03a | 0.18±0.02cd | 0.19±0.01cd | 0.13±0.04d | 0.17±0.04cd | |
土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon (g·kg-1) | 0~10 | 32.45±27.87c | 115.64±12.35b | 82.81±19.62bc | 106.04±23.76b | 58.06±16.66bc | 212.00±59.18a | 198.37±66.25a |
| 10~20 | 31.14±19.55b | 94.24±6.40a | 95.14±25.87a | 88.04±14.29a | 99.22±39.43a | 115.18±34.80a | 89.10±5.58a | |
| 20~40 | 28.02±26.87a | 83.22±61.05a | 56.80±33.97a | 41.93±10.89a | 65.52±73.59a | 66.91±15.77a | 82.77±38.64a | |
| 40~60 | 43.20±27.56a | 54.58±39.16a | 76.65±36.26a | 31.60±25.09a | 38.58±46.82a | 55.19±43.61a | 55.27±39.78a | |
| 60~80 | 42.10±19.77ab | 10.32±8.38b | 28.92±18.64ab | 6.66±1.46b | 24.69±19.75ab | 68.68±48.82a | 36.96±28.75ab | |
全氮 Total nitrogen (g·kg-1) | 0~10 | 14.13±1.21a | 4.84±0.29c | 4.86±1.00c | 4.95±0.39c | 4.69±0.52c | 8.21±0.87b | 7.12±0.23b |
| 10~20 | 10.28±1.27a | 3.79±0.43c | 5.11±0.64bc | 3.98±0.70c | 3.79±0.85c | 5.55±0.20b | 5.10±0.44bc | |
| 20~40 | 5.04±1.96a | 2.66±0.90ab | 5.09±2.36a | 2.91±0.67ab | 2.23±0.08b | 3.71±0.24ab | 3.56±0.41ab | |
| 40~60 | 1.50±0.60cd | 0.81±0.42d | 2.72±0.48a | 1.39±0.30cd | 1.15±0.20cd | 1.87±0.12bc | 2.33±0.55ab | |
| 60~80 | 0.52±0.09bc | 0.35±0.01c | 1.51±0.45a | 0.84±0.13bc | 0.99±0.30ab | 0.99±0.23ab | 1.52±0.58a | |
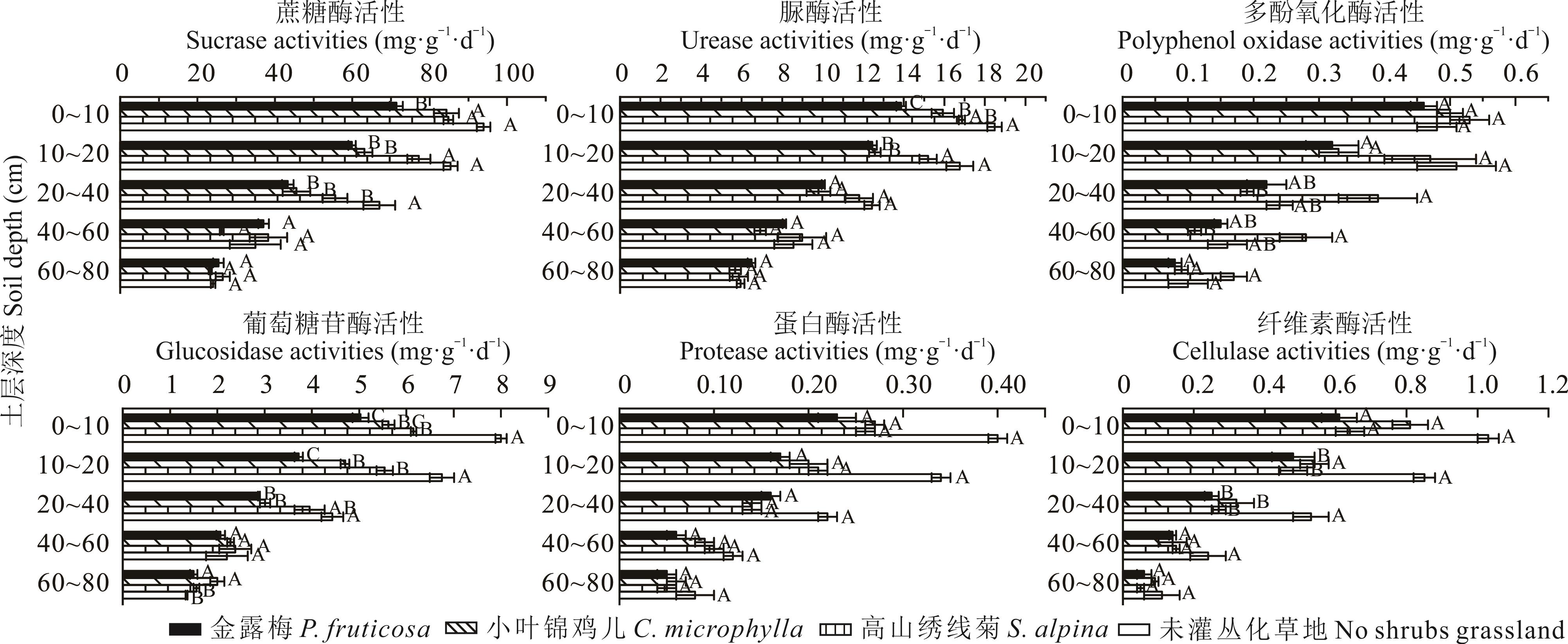
图1 轻度灌丛化各样地的土壤酶活性不同大写字母代表不同样地相同土层间差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。Different capital letters represent the significant differences among different site of the same soil layers (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Soil enzyme activity of sample plots under lightly shrub covered

图3 不同灌丛化梯度下的土壤酶活性a: 高山绣线菊S. alpina; b: 小叶锦鸡儿C. microphylla; c: 金露梅P. fruticose.不同大写字母表示同一样地相同土层不同灌丛化梯度间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different capital letters represent the significant differences in the same soil layer and sample plot among different shrub encroachment gradients (P<0.05).
Fig.3 Soil enzyme activity under different shrub encroachment gradients

图4 不同灌丛化梯度草地0~80 cm土壤理化性质与酶活性RDA分析a: 0~10 cm; b: 10~20 cm; c: 20~40 cm; d: 40~60 cm; e: 60~80 cm. RDA: 冗余分析Redundancy analysis; SOC∶TN: 土壤有机碳∶全氮Soil organic carbon∶total nitrogen; SWC: 土壤含水率Soil water content; SUC: 土壤蔗糖酶活性Soil sucrase activity; URE: 土壤脲酶活性Soil urease activity; POX: 土壤多酚氧化酶活性Soil polyphenol oxidase activity; GLU: 土壤葡萄糖苷酶活性Soil glucosidase activity; PRO: 土壤蛋白酶活性Soil protease activity; CEL: 土壤纤维素酶活性Soil cellulase activity.
Fig.4 RDA analysis of soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities of grassland with different shrub encroachment gradients in 0-80 cm
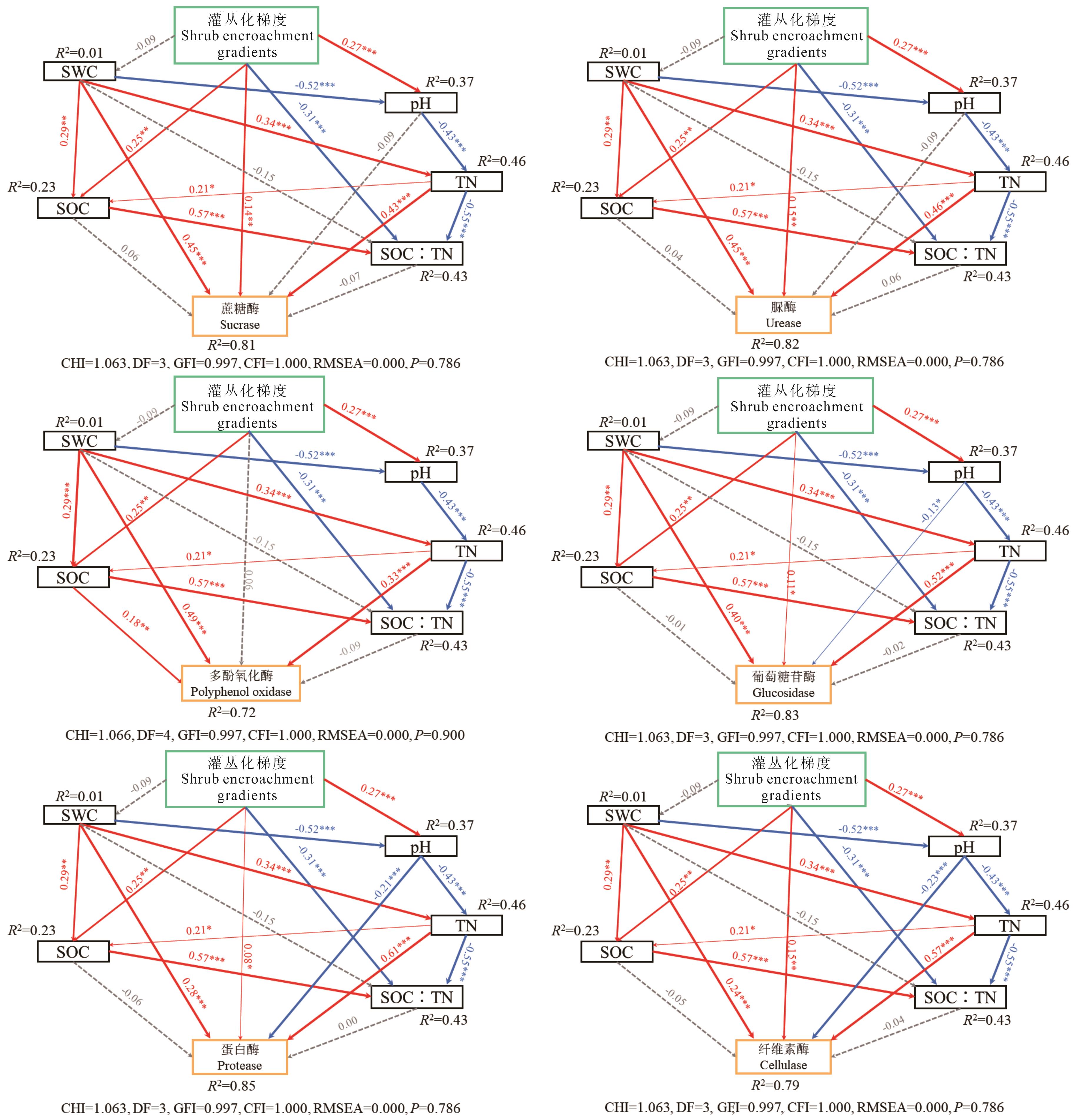
图5 不同灌丛化梯度下各土壤性质与土壤酶结构方程模型分析CHI: 卡方值Chi-Square; DF: 自由度Degrees of freedom; GFI: 适配度指数Goodness-of-fit; CFI: 相对拟合指标Comparative fit index; RMSEA: 近似误差均方根Root mean square error of approximation. P>0.05、GFI>0.90、CFI>0.95和RMSEA<0.05表示模型具有较好的拟合度;红色箭头表示有显著正向影响,蓝色箭头表示有显著负向影响,箭头线粗细表示模型中路径系数的大小,灰色虚线表示无显著影响。P>0.05, GFI>0.90, CFI>0.95 and RMSEA<0.05 indicate that the model has a good fit; red arrows indicate a significant positive effect, blue arrows indicate a significant negative effect, the thickness of the arrow line indicates the magnitude of the path coefficient in the model, grey dashed lines indicate no significant effect. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001.
Fig.5 Structural equation model of soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities of grassland with shrub encroachment gradients
| 1 | Pan R R, Li X Y, Hu G R, et al. Characteristis of soil organic carbon distribution and its controlling factors on hillslope in seasonal frozen area of Qinghai Lake Basin. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(18): 6374-6384. |
| 潘蕊蕊, 李小雁, 胡广荣, 等. 青海湖流域季节性冻土区坡面土壤有机碳分布特征及其影响因素. 生态学报, 2020, 40(18): 6374-6384. | |
| 2 | Brandt J S, Haynes M A, Kuemmerl T, et al. Regime shift on the roof of the world: Alpine meadows converting to shrublands in the southern Himalayas. Biological Conservation, 2013, 158(2): 116-127. |
| 3 | Van A O W. Causes and consequences of woody plant encroachment into western North American grasslands. Journal of Environment Management, 2009, 90(10): 2931-2942. |
| 4 | Zhang Z C, Liu Y F, Zeng C, et al. Shrub encroachment impaired the structure and functioning of alpine meadow communities on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Degradation and Development, 2022, 33: 2454-2463. |
| 5 | Liu C W, Ma W M, Zhou Q P, et al. Study on the geochemical cycles of carbon and nitrogen in shrub encroachment soils. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(4): 645-657. |
| 刘超文, 马文明, 周青平, 等. 草地灌丛化土壤碳氮地球化学循环. 草业科学, 2020, 37(4): 645-657. | |
| 6 | Li H, Shen H, Chen L, et al. Effects of shrub encroachment on soil organic carbon in global grasslands. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 28974. |
| 7 | Xiong X G, Han X G. Spatial heterogeneity in soil carbon and nitrogen resources, caused by Caragana microphylla in the thicketization of semiarid grassland, Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(7): 1678-1683. |
| 熊小刚, 韩兴国. 内蒙古半干旱草原灌丛化过程中小叶锦鸡儿引起的土壤碳、氮资源空间异质性分布. 生态学报, 2005, 25(7): 1678-1683. | |
| 8 | He J L. Effects of Potentilla fruticosa on vegetation characteristics and soil properties in alpine meadow of Tibetan Plateau. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017. |
| 何俊龄. 金露梅对青藏高原高寒草甸植被特征和土壤性质的影响. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017. | |
| 9 | Turnbull L, Wainwright J, Brazier R E, et al. Biotic and abiotic changes in ecosystem structure over a shrub-encroachment gradient in the southwestern USA. Ecosystems, 2010, 13(8): 1239-1255. |
| 10 | Liu X L, Hu J, Zhou Q P, et al. Effects of typical shrub-encroached grassland on vegetation characteristics and soil nutrients in the Zoige Plateau. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(4): 901-908. |
| 刘小龙, 胡健, 周青平, 等. 若尔盖高原典型草地灌丛化对植被特征和土壤养分的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(4): 901-908. | |
| 11 | Du H P, Zhan Z Y, Li X G. Differences in biological stability of soil organic carbon pools between shrub and Polygonum viviparum grassland at alpine site. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2007, 42(3): 91-96. |
| 杜慧平, 展争艳, 李小刚. 高寒灌丛与珠芽蓼草地土壤有机碳的稳定性. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2007, 42(3): 91-96. | |
| 12 | Hughes R F, Archer S R, Asner G P, et al. Changes in aboveground primary production and carbon and nitrogen pools accompanying woody plant encroachment in a temperate savanna. Global Change Biology, 2006, 12(9): 1733-1747. |
| 13 | Ding W, Wang Y B, Xiang G H, et al. Effects of Caragana microphylla encroachment on community structure and ecosystem function of a typical steppe. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2020, 44(1): 33-43. |
| 丁威, 王玉冰, 向官海, 等. 小叶锦鸡儿灌丛化对典型草原群落结构与生态系统功能的影响. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(1): 33-43. | |
| 14 | Wang Z W, Wan S Z, Jiang H M, et al. Soil enzyme activities and their influencing factors among different alpine grasslands on the Qingzang Plateau. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2021, 45(5): 528-538. |
| 汪子微, 万松泽, 蒋洪毛, 等. 青藏高原不同高寒草地类型土壤酶活性及其影响因子. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(5): 528-538. | |
| 15 | Shi H L, Liu M P, Pang W H, et al. Determination and analysis of soil enzyme activities in different alpine grasslands. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 56(15): 2835-2839. |
| 史惠兰, 刘梦萍, 庞文豪, 等. 不同类型高寒草地土壤酶活性测定与分析. 湖北农业科学, 2017, 56(15): 2835-2839. | |
| 16 | Howard K S C, Eldridge D J, SoliveresS. Positive effects of shrubs on plant species diversity do not change along a gradient in grazing pressure in an arid shrubland. Basic and Applied Ecology, 2012, 13(2): 159-168. |
| 17 | Suo N J, Tan Y R, Zhu W X, et al. Soil enzyme activity of different grassland types on the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2012, 21(4): 10-15. |
| 索南吉, 谈嫣蓉, 朱炜歆, 等. 青藏高原东缘不同草地类型土壤酶活性研究. 草业学报, 2012, 21(4): 10-15. | |
| 18 | Wu X D, Zhang X J, Xie Y Z, et al. Vertical distribution characters of soil organic carbon and soil enzyme activity in alfalfa field with different growing years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2013, 22(1): 245-251. |
| 吴旭东, 张晓娟, 谢应忠, 等. 不同种植年限紫花苜蓿人工草地土壤有机碳及土壤酶活性垂直分布特征. 草业学报, 2013, 22(1): 245-251. | |
| 19 | Tai J C, Yang H S, Zhang Q G, et al. Soil enzyme activity and distribution in alfalfa field with different growing years. Pratacultural Science, 2008, 25(4): 76-78. |
| 邰继承, 杨恒山, 张庆国, 等. 不同生长年限紫花苜蓿人工草地土壤酶活性及分布. 草业科学, 2008, 25(4): 76-78. | |
| 20 | Liao C, Clark P E, Degloria S D. Bush encroachment dynamics and rangeland management implications in southern Ethiopia. Ecology and Evolution, 2018, 8(23): 11694-11703. |
| 21 | Lu R K. Soil agrochemical analysis methods. Beijing: Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2000. |
| 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法. 北京: 农业科技出版社, 2000. | |
| 22 | Guan S Y. Soil enzyme and its research methods. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1986. |
| 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法. 北京: 农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 23 | Chen H. Effects of shrub-encroached grassland on the stability of soil aggregates and their cements in alpine grassland. Chengdu: Southwest Minzu University, 2021. |
| 陈红. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其胶结物质的影响. 成都: 西南民族大学, 2021. | |
| 24 | Liu J X. Correlative research on the activity of enzyme and soil nutrient in the different types of farmland. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2004(4): 523-525. |
| 刘建新. 不同农田土壤酶活性与土壤养分相关关系研究. 土壤通报, 2004(4): 523-525. | |
| 25 | Liao J D, Boutton T W. Soil microbial biomass response to woody plant invasion of grassland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2008, 40(5): 1207-1216. |
| 26 | She Y D, Yang X Y, Ma L, et al. Study on the characteristics and interrelationship of plant community and soil in degraded alpine meadow. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(S1): 62-71. |
| 佘延娣, 杨晓渊, 马丽, 等. 退化高寒草甸植物群落和土壤特征及其相互关系研究. 草地学报, 2021, 29(S1): 62-71. | |
| 27 | Lett M S, Knapp A K. Woody plant encroachment and removal in mesic grassland: production and composition responses of herbaceous vegetation. American Midland and Naturalist, 2015, 153(2): 217-231. |
| 28 | Li W, Cheng Y X, Sun Y, et al. Effects of different straw returning amount on aquaculture water, soil nutrients, and enzyme activity in rice-crayfish fields during spring. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2023, 46(1): 83-91. |
| 李威, 成永旭, 孙颖, 等. 不同秸秆还田量对春季稻虾田水质、土壤养分及酶活性的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 2023, 46(1): 83-91. | |
| 29 | Wei Y L, Cao W X, Li J H, et al. Phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) analysis of soil microbial community structure with different intensities of grazing and fencing in alpine shrubland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4897-4908. |
| 韦应莉, 曹文侠, 李建宏, 等. 不同放牧与围封高寒灌丛草地土壤微生物群落结构PLFA分析. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4897-4908. | |
| 30 | Li S Y, Sun J, Wang Y, et al. Characteristics of soil enzyme activities in different degraded gradient grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science, 2020, 37(12): 2389-2402. |
| 李邵宇, 孙建, 王毅, 等. 青藏高原不同退化梯度草地土壤酶活性特征. 草业科学, 2020, 37(12): 2389-2402. | |
| 31 | Hao J C, Wu Y Y, Lian B, et al. Properties of polyphenol oxidase in soil and its significance. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2006, 37(3): 470-474. |
| 郝建朝, 吴沿友, 连宾, 等. 土壤多酚氧化酶性质研究及意义. 土壤通报, 2006, 37(3): 470-474. | |
| 32 | Wang H, Yang Y, Xi D, et al. Impacts of labile organic carbon input on the priming effect of three forest soils in Wuyi Mountain. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(24): 9184-9194. |
| 王浩, 杨钰, 习丹, 等. 易分解有机碳输入量对武夷山不同林型土壤激发效应的影响. 生态学报, 2020, 40(24): 9184-9194. | |
| 33 | Liu S, Sheng K Y, Liu X S, et al. Contents of soil organic carbon and nitrogen forms in rhizosphere soil of Cunninghamia lanceolata and the rhizosphere effect. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(7): 1957-1964. |
| 刘顺, 盛可银, 刘喜帅, 等. 陈山红心杉根际土壤有机碳、氮含量及根际效应. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(7): 1957-1964. | |
| 34 | Ha W X, Zhou J X, Pang D B, et al. Soil organic carbon fraction and enzyme activities under different restoration methods in karst area. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2019, 41(2): 1-11. |
| 哈文秀, 周金星, 庞丹波, 等. 岩溶区不同恢复方式下土壤有机碳组分及酶活性研究. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(2): 1-11. | |
| 35 | Ma W W, Wang L X, Li N, et al. Dynamic effects of nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities in soils with different moisture content. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(19): 7218-7228. |
| 马伟伟, 王丽霞, 李娜, 等. 不同水氮水平对川西亚高山林地土壤酶活性的影响. 生态学报, 2019, 39(19): 7218-7228. | |
| 36 | Xia G D, Zhu S X, Li W J, et al. Effects of land use types on soil nutrients, enzyme activities and stoichiometric characteristics in karst coal mining areas. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2022, 12(6): 67-76. |
| 夏国栋, 朱四喜, 李武江, 等. 喀斯特煤矿区土地利用类型对土壤养分、酶活性及化学计量特征的影响. 中国无机分析化学, 2022, 12(6): 67-76. | |
| 37 | Li Y S, Wang G X, Ding Y J, et al. Spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture in alpine meadow area of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Advances in Water Science, 2008(1): 61-67. |
| 李元寿, 王根绪, 丁永建, 等. 青藏高原高寒草甸区土壤水分的空间异质性. 水科学进展, 2008(1): 61-67. | |
| 38 | Wang Y, Liu B Y, Liu M, et al. Synergistic and inhibitory effects of soil enzymes along desertified gradients of the Zoige alpine meadow. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(4): 939-951. |
| 王毅, 刘碧颖, 刘苗, 等. 若尔盖地区沙化草地土壤酶协同和抑制效应. 草业科学, 2019, 36(4): 939-951. | |
| 39 | Qin J H, Zhang Y, Zhao Y C, et al. Soil physicochemical properties and variations of nutrients and enzyme activity in the degrading grasslands in the upper reaches of the Heihe River, Qilian Mountains. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2014, 36(2): 335-346. |
| 秦嘉海, 张勇, 赵芸晨, 等. 祁连山黑河上游不同退化草地土壤理化性质及养分和酶活性的变化规律. 冰川冻土, 2014, 36(2): 335-346. | |
| 40 | Bai X, Dippold M A, An S, et al. Extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry: The effect of soil microbial element limitation during leaf litter decomposition. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 121: 107200. |
| 41 | Zhang Q, Yin B F, Li J W, et al. Effects of moss mortality on soil enzyme activities in a temperate desert. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2022, 46(3): 350-361. |
| 张庆, 尹本丰, 李继文, 等. 荒漠藓类植物死亡对表层土壤酶活性的影响. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(3): 350-361. | |
| 42 | Mikutta R, Kleber M, Torn M S, et al. Stabilization of soil organic matter: Association with minerals or chemical recalcitrance. Biogeochemistry, 2006, 77(1): 25-56. |
| [1] | 凤紫棋, 孙文义, 穆兴民, 高鹏, 赵广举, 陈帅. 南方山区杉木人工林林下草本植物多样性的影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 17-26. |
| [2] | 宋达成, 吴昊, 王理德, 王飞, 张裕凯, 赵学成. 双龙沟废弃矿区不同造林年限人工沙棘林土壤重金属分布特征及其对酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(8): 61-70. |
| [3] | 马嵩科, 霍克, 张冬霞, 张静, 张俊豪, 柴雪茹, 王贺正. 玉米秸秆还田配施氮肥对豫西旱地小麦土壤酶活性和氮肥利用效率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(6): 120-133. |
| [4] | 王志婷, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 李东方, 刘小勇. 半干旱草甸草地不同处理下植被特征与土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(3): 41-55. |
| [5] | 王春雯, 赵芳, 张晨, 解李娜, 马成仓. 小叶锦鸡儿灌丛对草地土壤固氮微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 28-40. |
| [6] | 马文明, 刘超文, 周青平, 邓增卓玛, 唐思洪, 迪力亚尔·莫合塔尔null, 侯晨. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体生态化学计量学及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 57-68. |
| [7] | 程分生, 尤龙辉, 余锦林, 徐惠昌, 游惠明, 聂森, 李建民, 叶功富. 冷季型绿肥对锥栗园土壤生化性质及微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 62-75. |
| [8] | 周诗晶, 罗佳宁, 刘仲淼, 董超, 秦燕, 吴淑娟, 甘红军, 谢菲, 庄光辉, 伏兵哲, 牛得草. 箭筈豌豆种植密度对土壤微生物养分代谢的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 63-72. |
| [9] | 陈红, 马文明, 周青平, 杨智, 刘超文, 刘金秋, 杜中曼. 高寒草地灌丛化对土壤团聚体稳定性及其铁铝氧化物分异的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(9): 73-84. |
| [10] | 宗文贞, 郭家昊, 贾云龙, 郑永兴, 杨旭, 胡芳弟, 王静. 单宁在植物-土壤氮循环中作用的研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(7): 174-183. |
| [11] | 董雪, 郝玉光, 辛智鸣, 段瑞兵, 黄雅茹, 李新乐, 马媛, 刘芳. 浑善达克沙地3种灌木土壤分形特征与养分关系[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 172-181. |
| [12] | 冯军, 石超, 门胜男, Hafiz Athar Hussain, 柯剑鸿, Linna Cholidah, 陈锦芬, 郭欣, 武海燕, 冉泰霖, 向信华, 王龙昌. 不同降雨下旱地油菜节水节肥技术对土壤养分及酶活性的调控效应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4): 51-62. |
| [13] | 张建军, 党翼, 赵刚, 王磊, 樊廷录, 李尚中, 雷康宁. 留膜留茬免耕栽培对旱作玉米田土壤养分、微生物数量及酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 123-133. |
| [14] | 李争艳, 徐智明, 师尚礼, 贺春贵. 江淮地区不同轮茬作物对苜蓿产量及根际土壤质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 28-39. |
| [15] | 李国旗, 赵盼盼, 邵文山, 靳长青. 围封条件下荒漠草原两种植物群落土壤理化性状与酶活性的研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 49-59. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||