

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 159-170.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024016
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
黄佩珊( ), 臧美琪, 张炜灵, 陈俊戬, 刘立轩, 张庆(
), 臧美琪, 张炜灵, 陈俊戬, 刘立轩, 张庆( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-11
修回日期:2024-02-29
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-07-15
通讯作者:
张庆
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: zqing1988@126.com基金资助:
Pei-shan HUANG( ), Mei-qi ZANG, Wei-ling ZHANG, Jun-jian CHEN, Li-xuan LIU, Qing ZHANG(
), Mei-qi ZANG, Wei-ling ZHANG, Jun-jian CHEN, Li-xuan LIU, Qing ZHANG( )
)
Received:2024-01-11
Revised:2024-02-29
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-07-15
Contact:
Qing ZHANG
摘要:
为探究黄梁木叶多酚(NCLP)超声辅助提取最佳工艺条件,并研究其对柱花草青贮品质的影响。采用响应面分析法中Box-Behnken Design试验优化NCLP提取工艺条件,同时柱花草青贮试验设3个处理:无添加(对照,CK)、添加1% NCLP(NCLP1)和2% NCLP(NCLP2)。青贮30 d后,测定以上3个处理柱花草的营养成分和发酵品质。结果表明,黄梁木叶多酚的最佳提取工艺为:甲醇浓度71%、液料比30 mL·g-1、提取时间37 min、超声功率250 W。在该提取条件下获得的黄梁木叶多酚为136.82 mg GAE·g-1 DM。在柱花草青贮中添加NCLP可极显著降低pH值、氨态氮含量和干物质损失率(P<0.01),极显著增加乳酸菌数量、乳酸和乙酸含量(P<0.01)。此外,添加2% NCLP还能显著增加真蛋白的含量(P<0.05),显著降低中性洗涤纤维和酸性洗涤纤维的含量(P<0.05)。综上,本研究获得了NCLP的最佳提取工艺,发现NCLP能改善柱花草的青贮品质,以2%NCLP改善效果更好。
黄佩珊, 臧美琪, 张炜灵, 陈俊戬, 刘立轩, 张庆. 黄梁木叶多酚提取工艺优化及其对柱花草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 159-170.
Pei-shan HUANG, Mei-qi ZANG, Wei-ling ZHANG, Jun-jian CHEN, Li-xuan LIU, Qing ZHANG. Optimization of extraction process of Neolamarckia cadamba leaf polyphenols and its effect on Stylosanthes guianensis silage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(10): 159-170.
| 因素Factors | 水平Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| A甲醇浓度Methanol concentration (%) | 60 | 70 | 80 |
| B液料比Liquid-solid ratio (mL·g-1) | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| C提取时间Extraction time (min) | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| D超声功率Ultrasonic power (W) | 200 | 250 | 300 |
表1 响应面分析因素与水平
Table 1 The levels of factors employed of Box-Behnken design
| 因素Factors | 水平Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| A甲醇浓度Methanol concentration (%) | 60 | 70 | 80 |
| B液料比Liquid-solid ratio (mL·g-1) | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| C提取时间Extraction time (min) | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| D超声功率Ultrasonic power (W) | 200 | 250 | 300 |
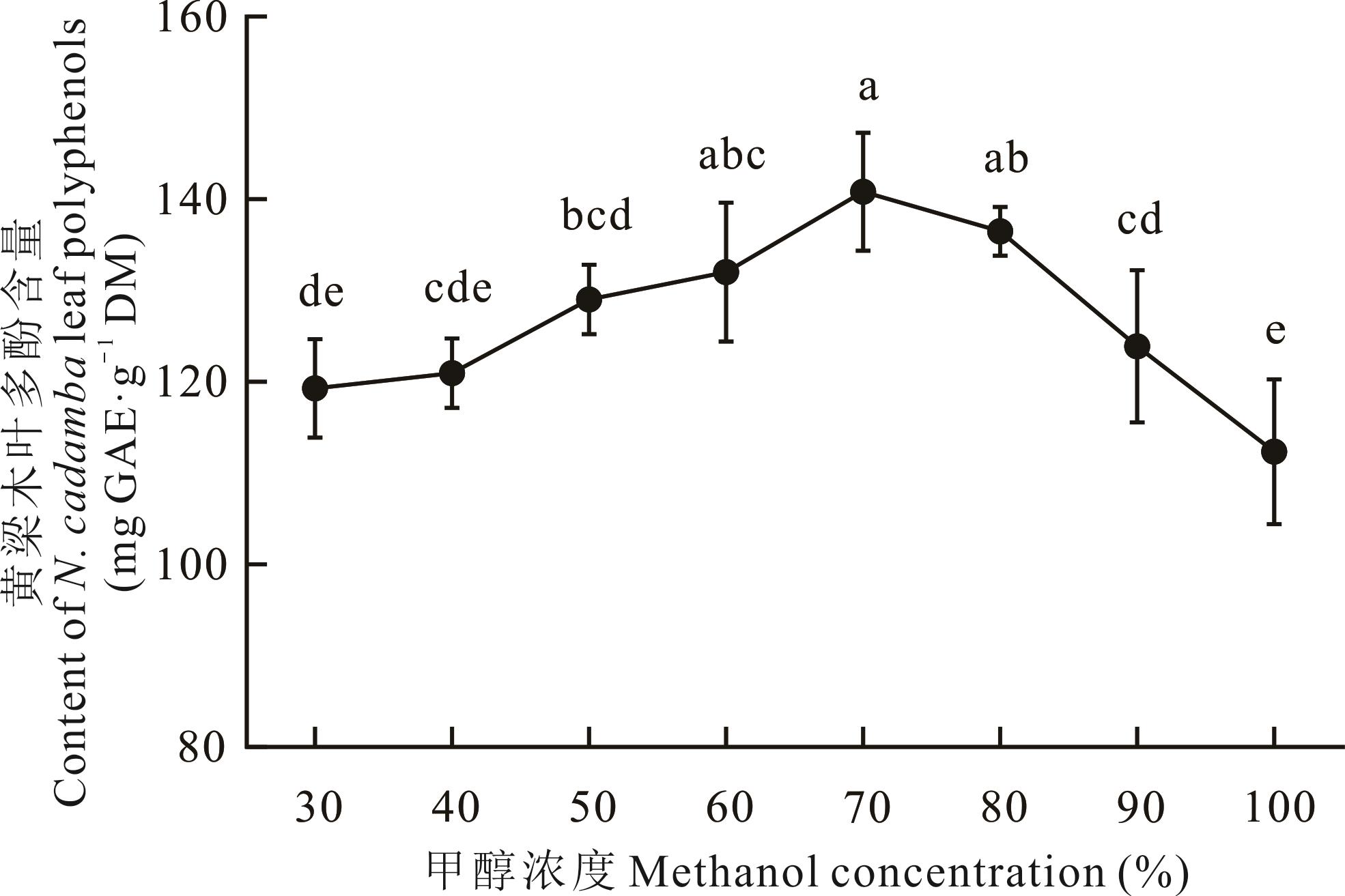
图1 甲醇浓度对黄梁木叶多酚提取效果的影响小写字母表示差异性显著,P<0.05。下同。The different small letters mean the significant differences (P<0.05). The same below.
Fig.1 Effect of methanol concentration on N. cadamba leaf polyphenols extraction
编号 No. | 影响因素Factors | NCLP含量Content of NCLP (mg GAE·g-1 DM) | 编号 No. | 影响因素Factors | NCLP含量Content of NCLP (mg GAE·g-1 DM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 106.06 | 13 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 105.95 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 99.85 | 14 | 0 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 106.29 |
| 3 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 113.42 | 15 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 124.40 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 122.90 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 135.05 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 110.83 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 134.92 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 138.67 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 103.99 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 104.45 | 19 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 120.23 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 137.90 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 117.21 |
| 9 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 101.87 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 135.89 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 109.62 | 22 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 104.34 |
| 11 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 114.63 | 23 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 95.43 |
| 12 | -1 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 101.66 | 24 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 106.76 |
表2 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 2 Experimental design and results of the Box-Behnken trials
编号 No. | 影响因素Factors | NCLP含量Content of NCLP (mg GAE·g-1 DM) | 编号 No. | 影响因素Factors | NCLP含量Content of NCLP (mg GAE·g-1 DM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | ||||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 106.06 | 13 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 105.95 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 99.85 | 14 | 0 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 106.29 |
| 3 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 113.42 | 15 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 124.40 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 122.90 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 135.05 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 110.83 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 134.92 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 138.67 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 103.99 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 104.45 | 19 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 120.23 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 137.90 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 117.21 |
| 9 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 101.87 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 135.89 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 109.62 | 22 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 104.34 |
| 11 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 114.63 | 23 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 95.43 |
| 12 | -1 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 101.66 | 24 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 106.76 |
| 来源Source | 平方和Sum of squares | 自由度Degree of freedom | 均方Mean square | F值F-value | P值P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 45.63 | 1 | 45.63 | 3.67 | 0.0761 |
| B | 17.98 | 1 | 17.98 | 1.45 | 0.2491 |
| C | 121.41 | 1 | 121.41 | 9.76 | 0.0075 |
| D | 56.77 | 1 | 56.77 | 4.57 | 0.0508 |
| AB | 37.52 | 1 | 37.52 | 3.02 | 0.1043 |
| AC | 75.00 | 1 | 75.00 | 6.03 | 0.0277 |
| AD | 24.85 | 1 | 24.85 | 2.00 | 0.1793 |
| BC | 363.86 | 1 | 363.86 | 29.26 | <0.0001 |
| BD | 78.94 | 1 | 78.94 | 6.35 | 0.0245 |
| CD | 5.02 | 1 | 5.02 | 0.40 | 0.5355 |
| A2 | 1775.52 | 1 | 1775.52 | 142.79 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 2165.36 | 1 | 2165.36 | 174.14 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 295.84 | 1 | 295.84 | 23.79 | 0.0002 |
| D2 | 1460.37 | 1 | 1460.37 | 117.45 | <0.0001 |
| 模型Model | 4763.16 | 14 | 340.23 | 27.36 | <0.0001 |
| 残差Residual | 174.08 | 14 | 12.43 | ||
| 失拟项Lack of fit | 162.44 | 10 | 16.24 | 5.58 | 0.0560 |
| 纯误差Pure error | 11.64 | 4 | 2.91 |
表3 响应面试验的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the quadratic model of NCLP
| 来源Source | 平方和Sum of squares | 自由度Degree of freedom | 均方Mean square | F值F-value | P值P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 45.63 | 1 | 45.63 | 3.67 | 0.0761 |
| B | 17.98 | 1 | 17.98 | 1.45 | 0.2491 |
| C | 121.41 | 1 | 121.41 | 9.76 | 0.0075 |
| D | 56.77 | 1 | 56.77 | 4.57 | 0.0508 |
| AB | 37.52 | 1 | 37.52 | 3.02 | 0.1043 |
| AC | 75.00 | 1 | 75.00 | 6.03 | 0.0277 |
| AD | 24.85 | 1 | 24.85 | 2.00 | 0.1793 |
| BC | 363.86 | 1 | 363.86 | 29.26 | <0.0001 |
| BD | 78.94 | 1 | 78.94 | 6.35 | 0.0245 |
| CD | 5.02 | 1 | 5.02 | 0.40 | 0.5355 |
| A2 | 1775.52 | 1 | 1775.52 | 142.79 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 2165.36 | 1 | 2165.36 | 174.14 | <0.0001 |
| C2 | 295.84 | 1 | 295.84 | 23.79 | 0.0002 |
| D2 | 1460.37 | 1 | 1460.37 | 117.45 | <0.0001 |
| 模型Model | 4763.16 | 14 | 340.23 | 27.36 | <0.0001 |
| 残差Residual | 174.08 | 14 | 12.43 | ||
| 失拟项Lack of fit | 162.44 | 10 | 16.24 | 5.58 | 0.0560 |
| 纯误差Pure error | 11.64 | 4 | 2.91 |
项目 Item | 柱花草 S. guianensis |
|---|---|
| 干物质Dry matter (% FM) | 32.23±0.30 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (% DM) | 10.74±0.45 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (% DM) | 62.38±0.17 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (% DM) | 47.01±1.12 |
| 可溶性碳水化合物Water-soluble carbohydrates (% DM) | 1.79±0.06 |
| 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 4.52±0.26 |
| 大肠杆菌Coliform (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 4.80±0.10 |
| 酵母菌Yeasts (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 3.32±0.11 |
| 霉菌Molds (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 2.98±0.05 |
表4 青贮原料的特性
Table 4 The characteristics of silage materials
项目 Item | 柱花草 S. guianensis |
|---|---|
| 干物质Dry matter (% FM) | 32.23±0.30 |
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (% DM) | 10.74±0.45 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (% DM) | 62.38±0.17 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (% DM) | 47.01±1.12 |
| 可溶性碳水化合物Water-soluble carbohydrates (% DM) | 1.79±0.06 |
| 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 4.52±0.26 |
| 大肠杆菌Coliform (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 4.80±0.10 |
| 酵母菌Yeasts (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 3.32±0.11 |
| 霉菌Molds (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 2.98±0.05 |
项目 Items | 处理Treatments | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NCLP1 | NCLP2 | |||
| 干物质Dry matter (% FM) | 32.32 | 32.77 | 33.11 | 0.19 | 0.26 |
| 干物质损失率Dry matter loss rate (%) | 1.97a | 1.73b | 1.65c | 0.05 | <0.01 |
| pH | 5.09a | 4.71b | 4.58c | 0.08 | <0.01 |
| 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 8.25b | 8.57a | 8.59a | 0.07 | <0.01 |
| 大肠杆菌Coliform (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 2.10 | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - |
| 霉菌Molds (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - |
| 酵母菌Yeasts (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - |
| 乳酸Lactic acid (% DM) | 1.21b | 2.20a | 2.23a | 0.17 | <0.01 |
| 乙酸Acetic acid (% DM) | 1.67c | 3.01b | 4.06a | 0.35 | <0.01 |
| 丙酸Propionic acid (% DM) | ND | ND | ND | - | - |
| 丁酸Butyric acid (% DM) | ND | ND | ND | - | - |
表5 黄梁木叶多酚提取物对柱花草青贮发酵品质和微生物数量的影响
Table 5 The effect of N. cadamba leaves’ polyphenolson the fermentation quality and microbial population of S. guianensis silage
项目 Items | 处理Treatments | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NCLP1 | NCLP2 | |||
| 干物质Dry matter (% FM) | 32.32 | 32.77 | 33.11 | 0.19 | 0.26 |
| 干物质损失率Dry matter loss rate (%) | 1.97a | 1.73b | 1.65c | 0.05 | <0.01 |
| pH | 5.09a | 4.71b | 4.58c | 0.08 | <0.01 |
| 乳酸菌Lactic acid bacteria (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 8.25b | 8.57a | 8.59a | 0.07 | <0.01 |
| 大肠杆菌Coliform (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | 2.10 | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - |
| 霉菌Molds (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - |
| 酵母菌Yeasts (lg cfu·g-1 FM) | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | - | - |
| 乳酸Lactic acid (% DM) | 1.21b | 2.20a | 2.23a | 0.17 | <0.01 |
| 乙酸Acetic acid (% DM) | 1.67c | 3.01b | 4.06a | 0.35 | <0.01 |
| 丙酸Propionic acid (% DM) | ND | ND | ND | - | - |
| 丁酸Butyric acid (% DM) | ND | ND | ND | - | - |
项目 Items | 处理Treatments | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NCLP1 | NCLP2 | |||
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (% DM) | 9.92 | 9.92 | 9.70 | 0.12 | 0.72 |
| 真蛋白True protein (% DM) | 6.46b | 6.80ab | 7.29a | 0.14 | 0.02 |
| 非蛋白氮Non-protein nitrogen (% DM) | 3.47 | 3.13 | 2.41 | 0.22 | 0.14 |
| 氨态氮NH3-N (% TN) | 8.27a | 4.52b | 4.12b | 0.70 | <0.01 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (% DM) | 63.64a | 62.00ab | 59.98b | 0.66 | 0.04 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (% DM) | 49.05a | 47.22ab | 46.51b | 0.47 | 0.04 |
表6 黄梁木叶多酚提取物对柱花草青贮蛋白组分和纤维含量的影响
Table 6 The effect of N. cadamba leaves’ polyphenols on the protein fraction and fiber content of S. guianensis silage
项目 Items | 处理Treatments | 标准误 SEM | P值 P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | NCLP1 | NCLP2 | |||
| 粗蛋白Crude protein (% DM) | 9.92 | 9.92 | 9.70 | 0.12 | 0.72 |
| 真蛋白True protein (% DM) | 6.46b | 6.80ab | 7.29a | 0.14 | 0.02 |
| 非蛋白氮Non-protein nitrogen (% DM) | 3.47 | 3.13 | 2.41 | 0.22 | 0.14 |
| 氨态氮NH3-N (% TN) | 8.27a | 4.52b | 4.12b | 0.70 | <0.01 |
| 中性洗涤纤维Neutral detergent fiber (% DM) | 63.64a | 62.00ab | 59.98b | 0.66 | 0.04 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维Acid detergent fiber (% DM) | 49.05a | 47.22ab | 46.51b | 0.47 | 0.04 |
| 1 | Zhao X, Ouyang K, Gan S, et al. Biochemical and molecular changes associated with heteroxylan biosynthesis in Neolamarckia cadamba (Rubiaceae) during xylogenesis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2014, 5(11): 602-616. |
| 2 | Pandey A, Negi P S. Phytochemical composition, in vitro antioxidant activity and antibacterial mechanisms of Neolamarckia cadamba fruits extracts. Natural Product Research, 2018, 32(10): 1189-1192. |
| 3 | Wang Y, Wang X K, Zhou W, et al. Effects of moisture content and additive on silage quality of Neolamarckia cadamba leaves. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2018, 39(4): 80-86. |
| 王益, 王学凯, 周玮, 等. 含水量及添加剂对黄梁木叶青贮品质的影响. 华南农业大学学报, 2018, 39(4): 80-86. | |
| 4 | Chandel M, Sharma U, Kumar N, et al. Antioxidant activity and identification of bioactive compounds from leaves of Anthocephalus cadamba by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 2012, 5(12): 977-985. |
| 5 | Khandelwal V, Bhatia A K, Goel A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant efficacy of aqueous extract of Anthocephalus cadamba leaves. Journal of Pure & Applied Microbiology, 2016, 10(1): 209-216. |
| 6 | Zhou W, Wei W Q, Li M, et al. Review on green extraction technology of plant polyphenols. Farm Products Processing, 2023(7): 74-77. |
| 周婉, 魏婉倩, 李猛, 等. 植物多酚绿色提取技术研究进展. 农产品加工, 2023(7): 74-77. | |
| 7 | Tian F L, Huang W J, Wang Z, et al. Research progress on the extraction of plant polyphenols. Food & Machinery, 2020, 36(9): 211-216. |
| 田富林, 黄文晶, 王展, 等. 植物多酚提取研究进展. 食品与机械, 2020, 36(9): 211-216. | |
| 8 | Dai Y L, Shen W Z, Liao S T, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of mulberry polyphenols using response surface methodology. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2016, 37(8): 1588-1594. |
| 代燕丽, 沈维治, 廖森泰, 等. 响应面法优化超声波辅助提取桑叶多酚工艺. 热带作物学报, 2016, 37(8): 1588-1594. | |
| 9 | Ning Z X, Zhu L B, Zhu D, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of blackcurrant polyphenols by response surface methodology and its antioxidant activity. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(22): 221-228. |
| 宁志雪, 朱立斌, 朱丹, 等. 响应面法优化超声波辅助提取黑加仑多酚工艺及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(22): 221-228. | |
| 10 | Liu G D, Bai C J, He H X, et al. The selection and utilization of Stylosanthes guianensis cv. Reyan No.5. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2001, 9(1): 1-7. |
| 刘国道, 白昌军, 何华玄, 等. 热研5号柱花草选育研究. 草地学报, 2001, 9(1): 1-7. | |
| 11 | Denek N, Can A, Avci M, et al. The effect of molasses-based pre-fermented juice on the fermentation quality of first-cut lucerne silage. Grass and Forage Science, 2011, 66(2): 243-250. |
| 12 | Julkunen-Tiitto R. Phenolic constituents in the leaves of northern willows: methods for the analysis of certain phenolics. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1985, 33(2): 213-217. |
| 13 | Broderick G A, Kang J H. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. Journal of Dairy Science, 1980, 63(1): 64-75. |
| 14 | Wang Y, Wang C, Zhou W, et al. Effects of wilting and Lactobacillus plantarum addition on the fermentation quality and microbial community of Moringa oleifera leaf silage. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9(8): 1817-1825. |
| 15 | Wang C, Wang Y, Zhou W, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum (LP) and moisture on feed quality and tannin content of Moringa oleifera leaf silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(6): 109-118. |
| 王成, 王益, 周玮, 等. 植物乳杆菌和含水量对辣木叶青贮品质和单宁含量的影响. 草业学报, 2019, 28(6): 109-118. | |
| 16 | Ma S M, Jiao T, Shi S L, et al. Effects of mixed lactic acid bacteria preparation on silage quality of different green corns. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2022, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| 马淑敏, 焦婷, 师尚礼, 等. 混合型乳酸菌制剂对不同品种青饲玉米青贮品质的影响. 草地学报, 2022, 30(6): 1558-1568. | |
| 17 | Li L, Zhao X F, Zhao G. Effects of ensilaging on the protein components in ensilaged forage. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2010, 32(6): 110-112. |
| 李玲, 赵秀芬, 赵钢. 青贮处理对饲料蛋白质组分的影响. 中国草地学报, 2010, 32(6): 110-112. | |
| 18 | Licitra G, Hernandez T M, Van Soest P J. Standardization of procedures for nitrogen fractionation of ruminant feeds. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 1996, 57(4): 347-358. |
| 19 | Mcdonald P, Henderson A R. Determination of water-soluble carbohydrates in grass. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1964, 15(6): 395-398. |
| 20 | Van Soest P J, Robertson J B, Lewis B A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science, 1991, 74(10): 3583-3597. |
| 21 | Chen J F, Lin X, Chen Z W. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of cucumber polyphenol by response surface methodology and its tyrosinaseinhibitory activities. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2021, 34(12): 16-22. |
| 陈建福, 林洵, 陈仲巍. 响应面法优化超声辅助提取黄瓜多酚工艺及其对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用. 中国瓜菜, 2021, 34(12): 16-22. | |
| 22 | Xu J, Tang R, Ji S C, et al. Research of the extraction processing of tea polyphenols. Food Research and Development, 2016, 37(5): 86-90, 91. |
| 徐婕, 汤韧, 吉树臣, 等. 酶法辅助提取茶多酚的工艺研究. 食品研究与开发, 2016, 37(5): 86-90, 91. | |
| 23 | Vilkhu K, Mawson R, Simons L, et al. Applications and opportunities for ultrasound assisted extraction in the food industry — A review. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2008, 9(2): 161-169. |
| 24 | Xing M, Fei P, Shi E C, et al. Optimization of extraction and antioxidant activity of polyphenols from Eucommia ulmoides male flower by response surface methodology. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(7): 201-207, 214. |
| 邢敏, 费鹏, 史恩聪, 等. 响应面法优化杜仲雄花多酚提取工艺及其抗氧化活性. 食品科技, 2021, 46(7): 201-207, 214. | |
| 25 | Liu Q, Zhang J, Shi S, et al. The effects of wilting and storage temperatures on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of stylo silage. Animal Science Journal, 2011, 82(4): 549-553. |
| 26 | Dong C, Liu P, Wang X, et al. Effects of phenyllactic acid on fermentation parameters, nitrogen fractions and bacterial community of high-moisture stylo silage. Fermentation, 2023, 9(6): 572-587. |
| 27 | Li X Q, Fan Y, Tian J, et al. Research progress on silage in southern China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2022, 44(6): 106-114. |
| 李鑫琴, 樊杨, 田静, 等. 中国南方青贮饲料研究进展. 中国草地学报, 2022, 44(6): 106-114. | |
| 28 | Wang C, He L, Xing Y, et al. Effects of mixing Neolamarckia cadamba leaves on fermentation quality, microbial community of high moisture alfalfa and stylo silage. Microbial Biotechnology, 2019, 12(5): 869-878. |
| 29 | Gao H J, Liu Z D, Sun R. Effects of additives, water content and storage time on alfalfa silage. China Feed, 2020(13): 35-39. |
| 高海娟, 刘泽东, 孙蕊. 添加剂、含水量及贮藏时间对苜蓿青贮的影响. 中国饲料, 2020(13): 35-39. | |
| 30 | Guyader J, Baron V, Beauchemin K. Corn forage yield and quality for silage in short growing season areas of the Canadian prairies. Agronomy, 2018, 8(9): 164. |
| 31 | Kung L, Stough E C, Mcdonell E E, et al. The effect of wide swathing on wilting times and nutritive value of alfalfa haylage. Journal of Dairy Science, 2010, 93(4): 1770-1773. |
| 32 | Cai Y, Benno Y, Ogawa M, et al. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(8): 2982-2987. |
| 33 | Borreani G, Tabacco E, Schmidt R J, et al. Silage review: Factors affecting dry matter and quality losses in silages. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(5): 3952-3979. |
| 34 | Zheng M Y, Wu S, Guo X, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus and cellulase on the silage quality of Amomum villosum leaves. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(5): 1113-1117. |
| 郑明扬, 吴硕, 郭香, 等. 添加乳酸菌和纤维素酶对砂仁叶青贮品质的影响. 草地学报, 2021, 29(5): 1113-1117. | |
| 35 | Zhang Y L. Factors influencing the quality of silage. China Dairy, 2002(5): 14-16. |
| 张英来. 影响青贮饲料质量的因素. 中国乳业, 2002(5): 14-16. | |
| 36 | Guo X S, Ding W R, Yu Z. The evaluation system of fermentation quality of ensiled forage and its improvement. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2008, 30(4): 100-106. |
| 郭旭生, 丁武蓉, 玉柱. 青贮饲料发酵品质评定体系及其新进展. 中国草地学报, 2008, 30(4): 100-106. | |
| 37 | Ji H Q, Meng L N, Yu M, et al. Quality evaluation of silages. Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2021(6): 92-96. |
| 冀红芹, 孟令楠, 于明, 等. 青贮饲料的质量评价. 现代畜牧兽医, 2021(6): 92-96. | |
| 38 | Tian J, Cao C X, Huang L Y, et al. Screening low-nutrient-tolerant lactic acid bacteria and their effects on the fermentation quality of silages from poor materials. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2023, 32(9): 222-230. |
| 田静, 曹彩霞, 黄莉莹, 等. 耐低营养乳酸菌筛选及对难青贮牧草发酵品质的影响. 草业学报, 2023, 32(9): 222-230. | |
| 39 | He L, Lv H, Xing Y, et al. The nutrients in Moringa oleifera leaf contribute to the improvement of stylo and alfalfa silage: Fermentation, nutrition and bacterial community. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 301(4): 122733. |
| 40 | Guo X, Chen D K, Chen N, et al. Effect of moisture content and additives on the fermentation quality of Neolamarckia cadamba leaf silage. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2021, 30(8): 199-205. |
| 郭香, 陈德奎, 陈娜, 等. 含水量和添加剂对黄梁木叶青贮发酵品质的影响. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 199-205. | |
| 41 | Ohshima M, Mcdonald P. A review of the changes in nitrogenous compounds of herbage during ensilage. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1978, 29(6): 497-505. |
| 42 | Li X, Tian J, Zhang Q, et al. Effects of mixing red clover with alfalfa at different ratios on dynamics of proteolysis and protease activities during ensiling. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(10): 8954-8964. |
| 43 | Li Z X, Dong C X, Liu P, et al. Synergy of Moringa oleifera leaves and Neolamarckia cadamba leaves on silage fermentation and proteolysis activity. Feed Industry, 2023, 44(18): 9-16. |
| 李紫欣, 董晨曦, 刘萍, 等. 辣木叶与黄梁木叶混贮的组合效应: 发酵参数和蛋白质水解. 饲料工业, 2023, 44(18): 9-16. | |
| 44 | Huang X D, Liang J B, Tan H Y, et al. Molecular weight and protein binding affinity of Leucaena condensed tannins and their effects on in vitro fermentation parameters. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2010, 159(3): 81-87. |
| 45 | Wang L, Gao R, Zhuo X L, et al. Membership function analysis for concentrate-to-forage ratio and ensiling time in total mixed ration fermentation. Pratacultural Science, 2023, 40(10): 2711-2720. |
| 王磊, 高润, 卓兴良, 等. 发酵全混合日粮精粗比及贮藏时间的隶属函数分析. 草业科学, 2023, 40(10): 2711-2720. |
| [1] | 戈建珍, 傅文慧, 张露, 蔺宝珺, 赵帅, 白玛噶翁, 寇建村. 多菌灵在果园白三叶青贮中的降解及其对微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(7): 64-75. |
| [2] | 邹诗雨, 陈思葵, 唐启源, 陈东, 陈元伟, 邓攀, 黄胥莱, 李付强. 青贮剂对再生稻头季全株青贮品质和体外瘤胃发酵特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 122-132. |
| [3] | 袁洁, 马冉冉, 张文洁, 许能祥, 赵冉冉, 顾洪如, 丁成龙. 自然青贮多花黑麦草优良乳酸菌的筛选及对多花黑麦草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 132-143. |
| [4] | 于浩然, 格根图, 王志军, 贾玉山, 连植, 贾鹏飞. 甲酸添加剂及青贮时间对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 89-95. |
| [5] | 万学瑞, 豆思远, 李玉, 何轶群, 王川, 张小丽, 雷赵民. 复合乳酸菌对全株玉米青贮及有氧暴露后微生物及饲料品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 83-90. |
| [6] | 李影正, 严旭, 吴子周, 杨春燕, 李晓锋, 何如钰, 张萍, EBENEZERKofiSam, 周阳, 张磊, 荣廷昭, 何建美, 唐祈林. 饲草玉米不同生育期的产量、品质和青贮利用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(7): 82-91. |
| [7] | 王建福,雷赵民,成述儒,焦婷,李洁,吴建平. 添加乳酸菌制剂和麸皮对去穗玉米秸秆青贮质量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(4): 162-169. |
| [8] | 王建福, 雷赵民, 万学瑞, 姜辉, 李洁, 吴建平. 5株乳酸菌复合物与CaCO3,酶及尿素不同组合对全株玉米青贮品质影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(3): 90-97. |
| [9] | 王木川, 杨玉玺, 于奕东, 玉柱. 不同添加剂和青贮密度对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(2): 156-162. |
| [10] | 邝肖,季婧,梁文学,崔国文,冀国旭,崔新,刘建,胡国富. 北方寒区紫花苜蓿/无芒雀麦混播比例和刈割时期对青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(12): 187-198. |
| [11] | 陶莲, 冯文晓, 王玉荣, 刁其玉. 微生态制剂对玉米秸秆青贮发酵品质、营养成分及瘤胃降解率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(9): 152-160. |
| [12] | 陶雅, 李峰, 高凤芹, 徐春城, 孙启忠. 籽粒苋与青贮玉米混贮品质及微生物特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(12): 119-129. |
| [13] | 李真真,白春生,余奕东,玉柱. 刈割期及添加剂对苜蓿青贮品质及CNCPS蛋白组分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 167-172. |
| [14] | 刘辉, 卜登攀, 吕中旺, 李发弟, 刘士杰, 张开展, 王加启. 凋萎和不同添加剂对紫花苜蓿青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(5): 126-133. |
| [15] | 张晓庆, 金艳梅, 李发弟, 王育青, 李鹏. 麻叶荨麻与玉米粉混贮对青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(1): 190-195. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||