

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 149-160.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024008
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
吕帅磊1( ), 常单娜1(
), 常单娜1( ), 周国朋1, 刘蕊2, 赵鑫1, 刘佳3, 徐昌旭3, 曹卫东1(
), 周国朋1, 刘蕊2, 赵鑫1, 刘佳3, 徐昌旭3, 曹卫东1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-04
修回日期:2024-04-29
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-09-09
通讯作者:
曹卫东
作者简介:E-mail: caoweidong@caas.cn基金资助:
Shuai-lei LYU1( ), Dan-na CHANG1(
), Dan-na CHANG1( ), Guo-peng ZHOU1, Rui LIU2, Xin ZHAO1, Jia LIU3, Chang-xu XU3, Wei-dong CAO1(
), Guo-peng ZHOU1, Rui LIU2, Xin ZHAO1, Jia LIU3, Chang-xu XU3, Wei-dong CAO1( )
)
Received:2024-01-04
Revised:2024-04-29
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-09-09
Contact:
Wei-dong CAO
摘要:
绿肥-水稻轮作是我国南方稻田常见的生产模式,研究绿肥活化磷矿粉的效果及对后茬水稻产量、磷素吸收的影响,可为江西红壤利用磷矿粉替代部分磷肥提供理论支撑。在江西南昌开展盆栽试验,设置绿肥种类和磷矿粉用量双因素,绿肥种类为紫云英(MV)、油菜(RA)、黑麦草(RY)及冬闲(WF)对照;磷矿粉用量为0(P0)、0.74(P1)和1.48 g·kg-1(P2),共12个处理。测定绿肥盛花期干物重、磷素吸收量、土壤磷库和磷酸酶活性,早稻、晚稻产量及磷素吸收量。结果显示,MVP2、RAP2和RYP2处理的地上部干物重分别为18.31、18.07和25.33 g·pot-1,较P0处理分别增加42.0%、42.7%和38.6%;磷素吸收量分别为49.10、60.83和36.13 mg·pot-1,较P0处理分别提高40.5%、86.7%和45.5%。与P0处理相比,施用磷矿粉增加了不同处理土壤总磷、微生物量磷含量和稳定性磷库占比,增幅分别为13.4%~34.2%、23.0%~93.2%和4.0%~10.6%。与WF处理相比,绿肥处理活性磷库占比提高0.4%~1.0%,中等活性磷库占比降低0.6%~2.9%。各处理早稻和晚稻籽粒产量分别为26.33~45.87 g·pot-1和39.17~49.04 g·pot-1。与P0处理相比,MVP1和MVP2处理晚稻籽粒产量分别增加8.5%和11.8%,早稻籽粒磷素吸收量分别提高34.4%和23.3%,MVP1处理晚稻籽粒磷素吸收量提高30.3%;RAP1处理晚稻籽粒产量增加9.1%;RYP1处理早稻籽粒磷素吸收量提高20.0%。与WF处理相比,MVP1、RAP1和RYP1处理早稻季磷矿粉利用率分别提高了2.2%、1.5%和2.3%,MVP2处理提高了1.9%,MVP1处理晚稻季磷矿粉利用率提高了2.6%。综上,施用磷矿粉提高了绿肥生物量及磷素吸收量,紫云英和油菜活化磷矿粉效果优于黑麦草,紫云英处理后茬水稻的产量及磷素吸收量、磷矿粉利用率高于油菜和黑麦草处理。
吕帅磊, 常单娜, 周国朋, 刘蕊, 赵鑫, 刘佳, 徐昌旭, 曹卫东. 江西红壤绿肥季施用磷矿粉的磷素效应[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(11): 149-160.
Shuai-lei LYU, Dan-na CHANG, Guo-peng ZHOU, Rui LIU, Xin ZHAO, Jia LIU, Chang-xu XU, Wei-dong CAO. The phosphorus effect of applying phosphate rock powder during the green manure season in red soil of Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(11): 149-160.
处理 Treatment | 干物重 Dry weight (g·pot-1) | 有机碳 Organic carbon (g·pot-1) | 总氮 Total nitrogen (mg·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MVP0 | 12.90 | 4.85 | 397.14 |
| MVP1 | 13.97 | 5.11 | 401.63 |
| MVP2 | 18.31 | 7.36 | 488.85 |
| RAP0 | 12.67 | 5.73 | 193.90 |
| RAP1 | 16.52 | 6.31 | 219.94 |
| RAP2 | 18.07 | 7.84 | 224.59 |
| RYP0 | 18.28 | 8.75 | 83.54 |
| RYP1 | 23.68 | 11.66 | 144.64 |
| RYP2 | 25.33 | 12.43 | 160.93 |
表1 不同处理绿肥翻压干物重、有机碳及总氮累积量
Table 1 Dry weight, organic carbon, and total nitrogen accumulation of green manure under different treatments
处理 Treatment | 干物重 Dry weight (g·pot-1) | 有机碳 Organic carbon (g·pot-1) | 总氮 Total nitrogen (mg·pot-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MVP0 | 12.90 | 4.85 | 397.14 |
| MVP1 | 13.97 | 5.11 | 401.63 |
| MVP2 | 18.31 | 7.36 | 488.85 |
| RAP0 | 12.67 | 5.73 | 193.90 |
| RAP1 | 16.52 | 6.31 | 219.94 |
| RAP2 | 18.07 | 7.84 | 224.59 |
| RYP0 | 18.28 | 8.75 | 83.54 |
| RYP1 | 23.68 | 11.66 | 144.64 |
| RYP2 | 25.33 | 12.43 | 160.93 |
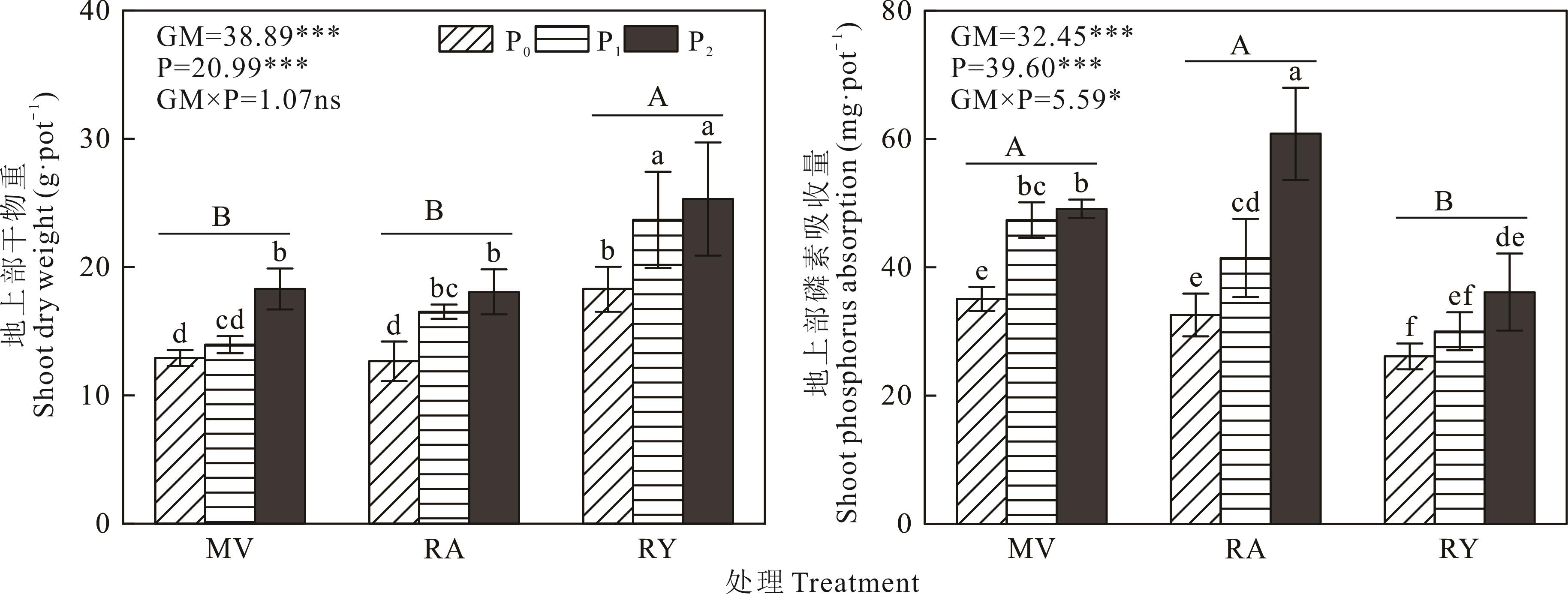
图1 施用磷矿粉对绿肥地上部干物重及磷素吸收的影响GM、P分别表示绿肥种类和磷矿粉施用量;MV、RA、RY分别表示紫云英、油菜和黑麦草处理;P0、P1、P2分别表示磷矿粉施用量依次为0、0.74和1.48 g·kg-1;柱上不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(n=4,P<0.05),不同大写字母表示绿肥处理组平均值间差异显著(n=12,P<0.05);*代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01,***代表P<0.001,ns代表无显著差异;下同。GM and P represent green manure type and rock phosphate application amount, respectively. MV, RA and RY refer to the treatments with Chinese milk vetch, rape and ryegrass, respectively. P0, P1 and P2 represent the dosages of rock phosphate as 0, 0.74 and 1.48 g·kg-1, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (n=4, P<0.05), and different uppercase letters indicate significant differences among the average values of the green manure treatment groups (n=12, P<0.05); * represent P<0.05, ** represent P<0.01, *** represent P<0.001, ns represent no significant difference; the same below.
Fig.1 Effect of applying phosphate rock powder on shoot dry weight and phosphorus absorption of green manure
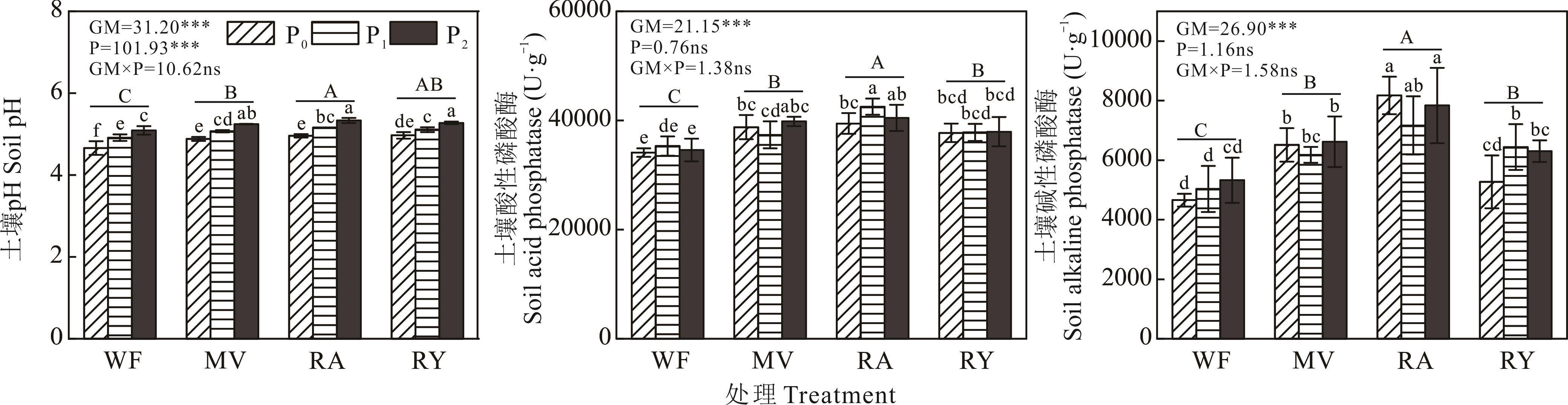
图2 施用磷矿粉对不同绿肥处理土壤pH和磷酸酶活性的影响WF: 冬闲处理Winter fallow treatments. 下同The same below.
Fig.2 Effect of applying phosphate rock powder on soil pH and phosphatase activity in different green manure treatments

图3 施用磷矿粉对不同绿肥处理土壤总磷、有效磷、微生物生物量磷含量的影响
Fig.3 Effect of applying phosphate rock powder on soil total phosphorus, available phosphorus and microbial biomass phosphorus content in different green manure treatments
处理 Treatment | 活性磷库 Labile P | 中等活性磷库 Moderately labile P | 稳定性磷库 Stable P |
|---|---|---|---|
| WFP0 | 63.65±3.01a | 162.50±1.58a | 305.83±8.04c |
| WFP1 | 65.37±1.06a | 161.14±0.94a | 404.08±3.08b |
| WFP2 | 63.48±0.76a | 162.83±1.06a | 483.06±13.77a |
| 平均值Average | 64.17±1.02A | 162.15±0.68A | 397.66±22.40A |
| MVP0 | 67.95±1.72a | 151.61±0.43a | 303.64±6.31b |
| MVP1 | 63.14±1.63ab | 155.93±2.53a | 417.55±13.77a |
| MVP2 | 59.89±2.52b | 141.92±2.08b | 437.02±7.89a |
| 平均值Average | 63.66±1.44A | 149.82±2.03B | 86.07±18.47A |
| RAP0 | 66.56±1.72a | 152.25±1.81ab | 306.48±7.19c |
| RAP1 | 68.56±2.40a | 154.93±1.39a | 384.84±6.65b |
| RAP2 | 65.94±1.87a | 148.66±2.80b | 449.60±18.87a |
| 平均值Average | 67.02±1.11A | 151.95±1.34B | 380.30±18.77A |
| RYP0 | 60.83±1.90b | 144.28±2.30c | 316.95±7.05c |
| RYP1 | 66.31±1.22a | 150.60±1.24b | 397.63±16.57b |
| RYP2 | 65.14±1.54ab | 156.35±1.90a | 476.24±2.11a |
| 平均值Average | 64.1±1.09A | 150.41±1.78B | 396.97±20.36A |
| GM | 2.02ns | 30.99*** | 1.94ns |
| P | 1.41ns | 3.97* | 214.09*** |
| GM×P | 2.15ns | 8.83*** | 2.15ns |
表2 施用磷矿粉对不同绿肥处理土壤磷库含量的影响
Table 2 Effect of applying phosphate rock powder on phosphorus storage in different green manure treatments (mg·kg-1)
处理 Treatment | 活性磷库 Labile P | 中等活性磷库 Moderately labile P | 稳定性磷库 Stable P |
|---|---|---|---|
| WFP0 | 63.65±3.01a | 162.50±1.58a | 305.83±8.04c |
| WFP1 | 65.37±1.06a | 161.14±0.94a | 404.08±3.08b |
| WFP2 | 63.48±0.76a | 162.83±1.06a | 483.06±13.77a |
| 平均值Average | 64.17±1.02A | 162.15±0.68A | 397.66±22.40A |
| MVP0 | 67.95±1.72a | 151.61±0.43a | 303.64±6.31b |
| MVP1 | 63.14±1.63ab | 155.93±2.53a | 417.55±13.77a |
| MVP2 | 59.89±2.52b | 141.92±2.08b | 437.02±7.89a |
| 平均值Average | 63.66±1.44A | 149.82±2.03B | 86.07±18.47A |
| RAP0 | 66.56±1.72a | 152.25±1.81ab | 306.48±7.19c |
| RAP1 | 68.56±2.40a | 154.93±1.39a | 384.84±6.65b |
| RAP2 | 65.94±1.87a | 148.66±2.80b | 449.60±18.87a |
| 平均值Average | 67.02±1.11A | 151.95±1.34B | 380.30±18.77A |
| RYP0 | 60.83±1.90b | 144.28±2.30c | 316.95±7.05c |
| RYP1 | 66.31±1.22a | 150.60±1.24b | 397.63±16.57b |
| RYP2 | 65.14±1.54ab | 156.35±1.90a | 476.24±2.11a |
| 平均值Average | 64.1±1.09A | 150.41±1.78B | 396.97±20.36A |
| GM | 2.02ns | 30.99*** | 1.94ns |
| P | 1.41ns | 3.97* | 214.09*** |
| GM×P | 2.15ns | 8.83*** | 2.15ns |
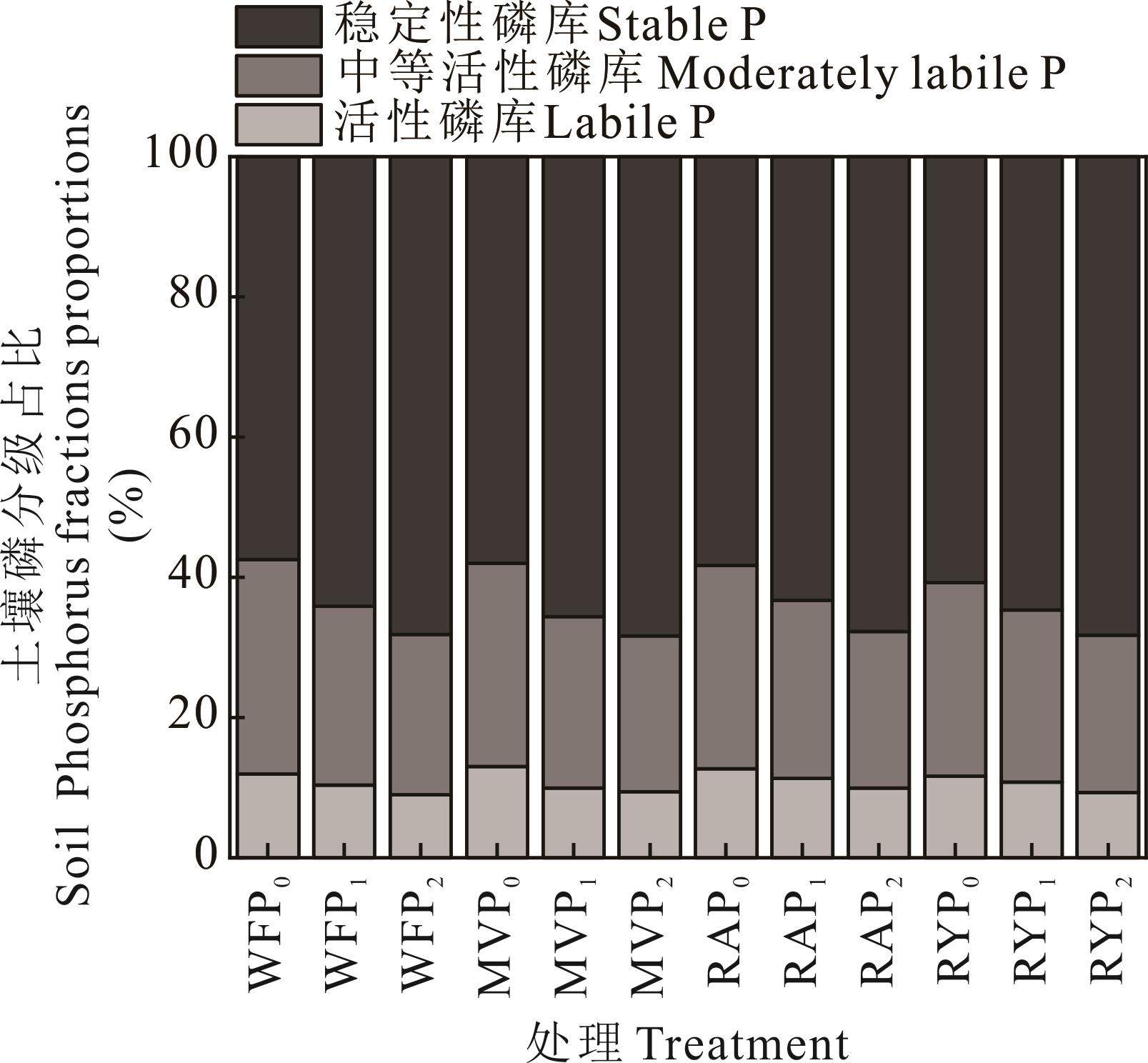
图4 施用磷矿粉对不同绿肥处理土壤磷分级占比的影响
Fig.4 Effect of applying phosphate rock powder on proportion of soil phosphorus fractions in different green manure treatments
| 处理 | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 籽粒产量Grain yield | 秸秆产量Straw yield | 籽粒产量Grain yield | 秸秆产量Straw yield |
| WFP0 | 26.33±1.02e | 34.70±1.89a | 39.17±0.76a | 33.64±1.49a |
| WFP1 | 30.33±2.31de | 32.51±2.86ab | 39.75±0.60a | 36.16±1.39a |
| WFP2 | 28.91±3.70de | 31.51±1.50abc | 41.29±1.17a | 38.57±2.45a |
| 平均值Average | 28.52±1.37C | 32.90±1.19A | 40.07±0.53C | 36.12±1.14A |
| MVP0 | 41.25±1.37ab | 29.79±0.92bc | 43.88±0.29b | 39.34±0.92a |
| MVP1 | 41.95±0.94a | 30.38±0.48abc | 47.60±0.67a | 37.34±2.12a |
| MVP2 | 45.87±0.65a | 32.72±2.46ab | 49.04±1.27a | 39.30±1.29a |
| 平均值Average | 43.02±0.81A | 30.97±0.89A | 46.84±0.79A | 38.66±0.85A |
| RAP0 | 29.15±1.73de | 30.72±1.02abc | 42.75±1.16b | 37.27±1.58a |
| RAP1 | 33.29±1.54cd | 32.31±1.90ab | 46.63±1.56a | 38.95±2.51a |
| RAP2 | 30.47±2.25cde | 27.12±0.66c | 41.53±1.22b | 37.27±1.61a |
| 平均值Average | 30.97±1.10BC | 30.04±0.94A | 43.64±0.95B | 37.87±1.04A |
| RYP0 | 32.57±2.44cd | 29.19±1.88bc | 41.58±0.39a | 40.37±2.56a |
| RYP1 | 35.96±2.18bc | 31.30±1.49abc | 40.82±0.23a | 36.14±1.84a |
| RYP2 | 33.41±2.10cd | 32.64±0.59ab | 40.46±0.61a | 39.50±1.34a |
| 平均值Average | 33.98±1.25B | 31.04±0.86A | 40.95±0.27C | 38.67±1.17A |
| GM | 32.27*** | 1.60ns | 32.51*** | 1.28ns |
| P | 2.73ns | 0.17ns | 4.17* | 0.75ns |
| GM×P | 0.69ns | 1.82ns | 4.66** | 1.01ns |
表3 不同处理后茬水稻籽粒及秸秆产量
Table 3 Grain and yield of subsequent rice in different treatments (g·pot -1)
| 处理 | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 籽粒产量Grain yield | 秸秆产量Straw yield | 籽粒产量Grain yield | 秸秆产量Straw yield |
| WFP0 | 26.33±1.02e | 34.70±1.89a | 39.17±0.76a | 33.64±1.49a |
| WFP1 | 30.33±2.31de | 32.51±2.86ab | 39.75±0.60a | 36.16±1.39a |
| WFP2 | 28.91±3.70de | 31.51±1.50abc | 41.29±1.17a | 38.57±2.45a |
| 平均值Average | 28.52±1.37C | 32.90±1.19A | 40.07±0.53C | 36.12±1.14A |
| MVP0 | 41.25±1.37ab | 29.79±0.92bc | 43.88±0.29b | 39.34±0.92a |
| MVP1 | 41.95±0.94a | 30.38±0.48abc | 47.60±0.67a | 37.34±2.12a |
| MVP2 | 45.87±0.65a | 32.72±2.46ab | 49.04±1.27a | 39.30±1.29a |
| 平均值Average | 43.02±0.81A | 30.97±0.89A | 46.84±0.79A | 38.66±0.85A |
| RAP0 | 29.15±1.73de | 30.72±1.02abc | 42.75±1.16b | 37.27±1.58a |
| RAP1 | 33.29±1.54cd | 32.31±1.90ab | 46.63±1.56a | 38.95±2.51a |
| RAP2 | 30.47±2.25cde | 27.12±0.66c | 41.53±1.22b | 37.27±1.61a |
| 平均值Average | 30.97±1.10BC | 30.04±0.94A | 43.64±0.95B | 37.87±1.04A |
| RYP0 | 32.57±2.44cd | 29.19±1.88bc | 41.58±0.39a | 40.37±2.56a |
| RYP1 | 35.96±2.18bc | 31.30±1.49abc | 40.82±0.23a | 36.14±1.84a |
| RYP2 | 33.41±2.10cd | 32.64±0.59ab | 40.46±0.61a | 39.50±1.34a |
| 平均值Average | 33.98±1.25B | 31.04±0.86A | 40.95±0.27C | 38.67±1.17A |
| GM | 32.27*** | 1.60ns | 32.51*** | 1.28ns |
| P | 2.73ns | 0.17ns | 4.17* | 0.75ns |
| GM×P | 0.69ns | 1.82ns | 4.66** | 1.01ns |
处理 Treatment | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
籽粒磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption in rice | 秸秆磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption of straw | 籽粒磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption in rice | 秸秆磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption of straw | |
| WFP0 | 78.67±4.97g | 75.95±3.59a | 112.04±11.03bcd | 25.29±1.35cd |
| WFP1 | 94.30±3.02ef | 62.29±4.39bc | 120.7±10.57bc | 28.93±2.71bc |
| WFP2 | 94.39±7.36ef | 54.58±4.91bcde | 106.34±8.90cd | 37.09±2.70a |
| 平均值Average | 89.12±3.60C | 64.27±3.50A | 113.03±5.62BC | 30.44±1.92AB |
| MVP0 | 106.87±5.33cde | 46.80±3.29def | 117.02±5.99bc | 22.69±2.06d |
| MVP1 | 143.57±6.93a | 36.66±4.84f | 152.43±11.81a | 27.37±2.15bcd |
| MVP2 | 131.81±4.97ab | 65.82±5.66ab | 129.24±2.94bc | 28.90±1.44bc |
| 平均值Average | 127.42±5.52A | 49.76±4.40B | 132.95±6.02A | 26.32±1.27C |
| RAP0 | 91.73±2.87fg | 43.17±2.46ef | 92.07±2.38d | 26.55±0.22bcd |
| RAP1 | 96.43±5.03def | 56.58±4.90bcd | 105.06±10.54cd | 30.35±2.14bc |
| RAP2 | 101.71±4.48def | 46.63±1.86def | 112.96±9.57bcd | 26.52±0.50bcd |
| 平均值Average | 96.62±2.53C | 48.79±2.45B | 103.36±5.07C | 27.78±0.85BC |
| RYP0 | 98.64±3.51def | 42.44±3.13ef | 113.11±3.45bcd | 29.59±0.48bc |
| RYP1 | 118.42±2.72bc | 50.32±6.47cde | 113.40±4.50bcd | 30.71±1.82b |
| RYP2 | 110.27±5.96cd | 50.29±6.10cde | 130.84±8.93ab | 37.03±1.82a |
| 平均值Average | 109.11±3.32B | 47.68±3.05B | 119.09±4.06B | 32.43±1.26A |
| GM | 33.84*** | 8.96*** | 6.42*** | 6.82*** |
| P | 16.77*** | 0.45ns | 3.30* | 12.39*** |
| GM×P | 1.89ns | 6.47*** | 1.78ns | 2.81* |
表4 不同处理后茬水稻地上部磷吸收量
Table 4 Shoot phosphorus absorption of subsequent rice in different treatments (mg·pot -1)
处理 Treatment | 早稻Early rice | 晚稻Late rice | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
籽粒磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption in rice | 秸秆磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption of straw | 籽粒磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption in rice | 秸秆磷素吸收量 Phosphorus absorption of straw | |
| WFP0 | 78.67±4.97g | 75.95±3.59a | 112.04±11.03bcd | 25.29±1.35cd |
| WFP1 | 94.30±3.02ef | 62.29±4.39bc | 120.7±10.57bc | 28.93±2.71bc |
| WFP2 | 94.39±7.36ef | 54.58±4.91bcde | 106.34±8.90cd | 37.09±2.70a |
| 平均值Average | 89.12±3.60C | 64.27±3.50A | 113.03±5.62BC | 30.44±1.92AB |
| MVP0 | 106.87±5.33cde | 46.80±3.29def | 117.02±5.99bc | 22.69±2.06d |
| MVP1 | 143.57±6.93a | 36.66±4.84f | 152.43±11.81a | 27.37±2.15bcd |
| MVP2 | 131.81±4.97ab | 65.82±5.66ab | 129.24±2.94bc | 28.90±1.44bc |
| 平均值Average | 127.42±5.52A | 49.76±4.40B | 132.95±6.02A | 26.32±1.27C |
| RAP0 | 91.73±2.87fg | 43.17±2.46ef | 92.07±2.38d | 26.55±0.22bcd |
| RAP1 | 96.43±5.03def | 56.58±4.90bcd | 105.06±10.54cd | 30.35±2.14bc |
| RAP2 | 101.71±4.48def | 46.63±1.86def | 112.96±9.57bcd | 26.52±0.50bcd |
| 平均值Average | 96.62±2.53C | 48.79±2.45B | 103.36±5.07C | 27.78±0.85BC |
| RYP0 | 98.64±3.51def | 42.44±3.13ef | 113.11±3.45bcd | 29.59±0.48bc |
| RYP1 | 118.42±2.72bc | 50.32±6.47cde | 113.40±4.50bcd | 30.71±1.82b |
| RYP2 | 110.27±5.96cd | 50.29±6.10cde | 130.84±8.93ab | 37.03±1.82a |
| 平均值Average | 109.11±3.32B | 47.68±3.05B | 119.09±4.06B | 32.43±1.26A |
| GM | 33.84*** | 8.96*** | 6.42*** | 6.82*** |
| P | 16.77*** | 0.45ns | 3.30* | 12.39*** |
| GM×P | 1.89ns | 6.47*** | 1.78ns | 2.81* |
| 1 | Chang D N, Chen Z Y, Han M, et al. Differences in phosphorus acquisition characteristics and rhizosphere properties among different hairy vetch genotypes. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(4): 122-134. |
| 常单娜, 陈子英, 韩梅, 等. 毛叶苕子磷获取特征及根际特性的基因型差异. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 122-134. | |
| 2 | Wang Y K, Cai Z J, Feng G. Effects of different phosphorus application techniques on phosphorus availability in a rape system in a red soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(1): 235-246. |
| 王一锟, 蔡泽江, 冯固. 不同磷肥调控措施下红壤磷素有效性和利用率的变化. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(1): 235-246. | |
| 3 | Du J X, Liu K L, Huang J, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of soil available phosphorus and its response to phosphorus balance in paddy soil in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(2): 476-486. |
| 都江雪, 柳开楼, 黄晶, 等. 稻田土壤有效磷时空演变特征及其对磷平衡的响应. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(2): 476-486. | |
| 4 | Zhang H P, Liu Q, Peng J W, et al. Prospects of medium-low grade rock phosphate application in agricultural production. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2012, 43(4): 477-480. |
| 张海鹏, 刘强, 彭建伟, 等. 中低品位磷矿在农业生产上的应用展望. 南方农业学报, 2012, 43(4): 477-480. | |
| 5 | Zhao X, Cai M D, Dong Q Q, et al. Advances of mechanisms and technology pathway of efficient utilization of medium-low grade phosphate rock resources. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2018, 24(4): 1121-1130. |
| 赵鑫, 蔡慢弟, 董倩倩, 等. 中低品位磷矿资源高效利用机制与途径研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(4): 1121-1130. | |
| 6 | Shao X Q, Yao H L, Cui S H, et al. Activated low-grade phosphate rocks for simultaneously reducing the phosphorus loss and cadmium uptake by rice in paddy soil. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 780: 146550. |
| 7 | Thien S J, Myers R. Determination of bioavailable phosphorus in soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1992, 26(3): 331-336. |
| 8 | Chen Y Y, Mathiyazhagan N, Shi X J, et al. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Their agroecological function and optimistic application for enhancing agro-productivity. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 901: 166468. |
| 9 | Chen Y P, Rekha P D, Arun A B, et al. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Applied Soil Ecology, 2006, 34(1): 33-41. |
| 10 | Li C J. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2008. |
| 李春俭. 高级植物营养学. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2008. | |
| 11 | Neumann G, Martinoia E. Cluster roots-An underground adaptation for survival in extreme environments. Trends in Plant Science, 2002, 7(4): 162-167. |
| 12 | Cao W D, Bao X G, Xu C X, et al. Reviews and prospects on science and technology of green manure in China. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. |
| 曹卫东, 包兴国, 徐昌旭, 等. 中国绿肥科研60年回顾与未来展望. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(6): 1450-1461. | |
| 13 | Gao S J, Zhou G P, Chang D N, et al. Southern China can produce more high-quality rice with less N by green manuring. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 196: 107025. |
| 14 | Cao W D, Huang H X. Ideas on restoration and development of green manures in China. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2009(4): 1-3. |
| 曹卫东, 黄鸿翔. 关于我国恢复和发展绿肥若干问题的思考. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009(4): 1-3. | |
| 15 | Lyu Y, Tang H L, Li H G, et al. Major crop species show differential balance between root morphological and physiological responses to variable phosphorus supply. Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1939. |
| 16 | Lan Z M, Lin X J, Zhang W G, et al. Effect of P deficiency on the emergence of Astragalus L. root exudates and mobilization of sparingly soluble phosphorus. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2012, 45(8): 1521-1531. |
| 兰忠明, 林新坚, 张伟光, 等. 缺磷对紫云英根系分泌物产生及难溶性磷活化的影响. 中国农业科学, 2012, 45(8): 1521-1531. | |
| 17 | Wang L S, Liu D. Functions and regulation of phosphate starvation-induced secreted acid phosphatases in higher plants. Plant Science, 2018, 271: 108-116. |
| 18 | Jiang B F. A study on rock phosphate of China for agriculture use. Scientia Agriculture Sinica, 1988(4): 62-67. |
| 蒋柏藩. 中国磷矿农业利用的研究. 中国农业科学, 1988(4): 62-67. | |
| 19 | Xie W J. Studies on rape’s activation and utilization of different forms inorganic phosphorus of acid soil and it’s physiological change. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2005. |
| 谢文娟. 油菜对酸性土壤不同形态无机磷的活化利用及其生理变化研究. 南宁: 广西大学, 2005. | |
| 20 | Gu C M, Li Y, Li Y S, et al.Effects of organic acid composition in the decomposed liquid of green manure crops on the activation level of AlPO4 and FePO4·2H2O. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(9): 1627-1635. |
| 顾炽明, 李越, 李银水, 等. 绿肥腐解液中有机酸组成对铝磷和铁磷活化能力的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(9): 1627-1635. | |
| 21 | Mckenney D J, Wang S W, Drury C F, et al. Dentrification and mineralization in soil amended with legume, grass, and corn residues. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1993, 57(4): 1013-1020. |
| 22 | Eichler-Loebermann B, Schiemenz K, Makadi M, et al. Nutrient cycling by using residues of bio-energy production-Effects of biomass ashes on plant and soil parameters. Cereal Research Communications, 2008, 36(7): 1259-1262. |
| 23 | Bao S D. Soil agrochemical analysis (The Third Edition). Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000: 263-270. |
| 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版). 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 263-270. | |
| 24 | Liu B, Wang S, Wang J, et al. The great potential for phytoremediation of abandoned tailings pond using ectomycorrhizal Pinus sylvestris. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 719: 137475. |
| 25 | Tiessen H, Moir J O. Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1993: 75-86. |
| 26 | Ren Y. Effect of phosphate rock on growth and nutrient uptake of green manure crops and following rice. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022. |
| 任洋. 磷矿粉对绿肥及后茬水稻生长和养分吸收的影响. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. | |
| 27 | Jiao B. Chinese green manure. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1986. |
| 焦彬. 中国绿肥. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1986. | |
| 28 | Wang Z R, Zang H L. The fertilizer efficiency of phosphate rock powder fertilizer on several acidic soils in Jiangsu Province. Soils, 1974(4): 29-32. |
| 王振荣, 臧惠林. 磷矿粉肥在江苏几种酸性土壤上的肥效. 土壤, 1974(4): 29-32. | |
| 29 | Wu A J. Mechanisms of root responses to low phosphorus stress in different crop species/genotypes with contrasting root systems. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. |
| 吴爱姣. 不同根系类型作物/品种的根系对低磷胁迫的响应机制. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2021. | |
| 30 | Wang W H, Zhou X B, Zhou Y X, et al. The mechanism of rhizosphere phosphorus activation of two rape genotypes (Brassica napus L.) with different P efficiencies. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2011, 17(6): 1379-1387. |
| 王文华, 周鑫斌, 周永祥, 等. 不同磷效率油菜根际土壤磷活化机理研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(6): 1379-1387. | |
| 31 | Zhang H, Gao Y J, An R. Testing method of rape root exudates by GC-MS analysis. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(3): 290-295. |
| 张红, 高亚军, 安蓉. 油菜根系分泌物的GC-MS检测方法研究. 农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(3): 290-295. | |
| 32 | Ye G K, E S Z, Chen Z Y, et al. The forms and classification methods of phosphorus in soil: Research progress. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(1): 96-102. |
| 冶赓康, 俄胜哲, 陈政宇, 等. 土壤中磷的存在形态及分级方法研究进展. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(1): 96-102. | |
| 33 | Peng Y, Duan Y S, Huo W G, et al. Soil microbial biomass phosphorus can serve as an index to reflect soil phosphorus fertility. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2021, 57: 657-669. |
| 34 | Yang L, Zhou X, Liao Y L, et al. Co-incorporation of rice straw and green manure benefits rice yield and nutrient uptake. Crop Science, 2019, 59: 749-759. |
| 35 | Gao J S, Cao W D, Dong C H, et al. Effect of long-term rice-green manure rotation on rice yield. China Journal of Rice Science, 2010, 24(6): 672-676. |
| 高菊生, 曹卫东, 董春华, 等. 长期稻-稻-绿肥轮作对水稻产量的影响. 中国水稻科学, 2010, 24(6): 672-676. | |
| 36 | Li Y Z, Han T F, Liu K L, et al. Response of soil enzyme activity and rice yield to winter green manure incorporation in red paddy soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(7): 1313-1322. |
| 李亚贞, 韩天富, 柳开楼, 等. 红壤稻田土壤酶活性及水稻产量对翻压冬季绿肥的响应.植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(7): 1313-1322. | |
| 37 | Zhou G P, Gao S J, Lu Y H, et al.Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil and Tillage Research, 2020, 197: 104499. |
| 38 | Zhang L, Xu C X, Liu J, et al. Effects of green manure on yield and nitrogen utilization of double rice under reduced 20% chemical fertilizer input in Jiangxi Province. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(5): 845-856. |
| 张磊, 徐昌旭, 刘佳, 等. 减施20%化肥下绿肥翻压量对江西双季稻产量及氮素利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(5): 845-856. | |
| 39 | Zhou C H, Zhao Z K, Pan X H, et al. Integration of growing milk vetch in winter and reducing nitrogen fertilizer application can improve rice yield in double-rice cropping system. Rice Science, 2016, 23(3): 132-143. |
| [1] | 王峥, 常伟, 李俊诚, 苏连泰, 高鲤, 周鹏, 安渊. 紫花苜蓿还田对饲料玉米产量和氮素吸收转运的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(8): 63-73. |
| [2] | 赵文军, 刘蕊, 王正旭, 冯瑜, 薛开政, 刘魁, 徐梓荷, 曹卫东, 付利波, 尹梅, 陈华. 烤烟-绿肥轮作对云南烟田土壤质量与微生物养分限制的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(10): 147-158. |
| [3] | 张学良, 张宇亭, 刘瑞, 谢军, 张建伟, 徐文静, 石孝均. 绿肥不同还田方式对土壤温室气体排放的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 25-33. |
| [4] | 古丽君, 段廷玉. 光叶紫花苕研究状况的文献分析——基于CNKI数据库的文献计量[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 221-228. |
| [5] | 陈晓芬, 张路平, 秦文婧, 陈静蕊, 徐样庚, 刘明, 李忠佩, 徐昌旭, 刘佳. 红壤旱地上4种冬绿肥适宜播种量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 137-146. |
| [6] | 吕汉强, 于爱忠, 王玉珑, 苏向向, 吕奕彤, 柴强. 干旱绿洲灌区玉米氮素吸收利用对绿肥还田利用方式的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 93-103. |
| [7] | 杨叶华, 张松, 王帅, 刘正兰, 方林发, 张学良, 刘瑞, 张建伟, 张宇亭, 石孝均. 中国不同区域常见绿肥产量和养分含量特征及替代氮肥潜力评估[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 39-55. |
| [8] | 肖博文, 冯伟, 段廷玉. 二月兰种带真菌致病性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 121-130. |
| [9] | 王登科, 于翔宇, 张学风, 黄蕾, 李晓婷, 贺治斌, 康林, 王党军, 姚露花, 郭彦军. 酸、铝和盐胁迫对夏季豆科绿肥作物种子萌发及根瘤菌抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10): 35-44. |
| [10] | 万水霞, 唐杉, 蒋光月, 李帆, 郭熙盛, 王允青, 曹卫东. 紫云英与化肥配施对土壤微生物特征和作物产量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(6): 109-117. |
| [11] | 杜青峰, 王党军, 于翔宇, 姚露花, 和玉吉, 王瑞, 马生兰, 郭彦军. 玉米间作夏季绿肥对当季植物养分吸收和土壤养分有效性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 225-233. |
| [12] | 陈国军, 闫慧峰, 吴凯, 杨举田, 田雷, 谭效磊, 宗浩, 陈秀斋, 张永春, 孙延国, 刘海伟, 石屹. 不同收获期的籽粒苋绿肥还田对土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3): 215-224. |
| [13] | 周玲红, 魏甲彬, 唐先亮, 成小琳, 肖志祥, 徐华勤, 唐剑武. 冬季种养结合对稻田土壤微生物量及有效碳氮库的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(11): 103-114. |
| [14] | 孙艳茹,石屹,陈国军,闫慧峰. PEG模拟干旱胁迫下8种绿肥作物萌发特性与抗旱性评价[J]. 草业学报, 2015, 24(3): 89-98. |
| [15] | 李正,刘国顺,敬海霞,叶协锋,解昌盛,向永光,张文平,杨超,王永,习相银. 绿肥与化肥配施对植烟土壤微生物量及供氮能力的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2011, 20(6): 126-134. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||