

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 134-146.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024086
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
谢金晶1( ), 朱绍玮1, 黄荣1, 杨杰1, 侯瑄1, 张振粉1,2(
), 朱绍玮1, 黄荣1, 杨杰1, 侯瑄1, 张振粉1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-19
修回日期:2024-04-22
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
张振粉
作者简介:. E-mail: zhangzf@gsau.edu.cn基金资助:
Jin-jing XIE1( ), Shao-wei ZHU1, Rong HUANG1, Jie YANG1, Xuan HOU1, Zhen-fen ZHANG1,2(
), Shao-wei ZHU1, Rong HUANG1, Jie YANG1, Xuan HOU1, Zhen-fen ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-03-19
Revised:2024-04-22
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Zhen-fen ZHANG
摘要:
为探究草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌的多样性并筛选其中促生功能优异的菌株,本研究采用稀释涂布平板法对3个品种草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌进行分离,得到30个细菌分离物。通过16S rRNA序列分析,对18株形态特征具有差异的代表性分离物进行鉴定并构建系统发育树。结果表明,分离并鉴定的种带可培养细菌有厚壁菌门、放线菌门和变形菌门,分属于6个属,分别为芽孢杆菌属、类芽孢杆菌属、假单胞菌属、短小杆菌属、寡养单胞菌属和欧文氏菌属,其中芽孢杆菌属为3个品种的共有属。对18株细菌的固氮、产吲哚-3-乙酸(indole-3-acetic acid, IAA)、溶磷、产胞外酶(蛋白酶、纤维素酶、淀粉酶)能力测定发现,菌株BM8和KTJ14同时具有上述功能中的3种。此外,采用结晶紫染色法和泳动培养基对菌株的生物被膜形成能力及泳动能力这2种促生相关的生物学特性进行测定,并讨论了生物被膜形成能力和泳动性与菌株促生功能之间的相关性,其中,KTJ16是生物被膜形成能力最强的菌株,SW5和KTJ18的泳动能力显著强于其他菌株。综合几种特性,最终筛选出具有优异促生特性的菌株为BM8、SW5、KTJ14、KTJ16和KTJ18。
谢金晶, 朱绍玮, 黄荣, 杨杰, 侯瑄, 张振粉. 草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌多样性及18个菌株促生特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 134-146.
Jin-jing XIE, Shao-wei ZHU, Rong HUANG, Jie YANG, Xuan HOU, Zhen-fen ZHANG. A study of the diversity of cultivable seed-borne bacteria in Poa pratensis and the growth-promoting characteristics of 18 bacterial strains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 134-146.
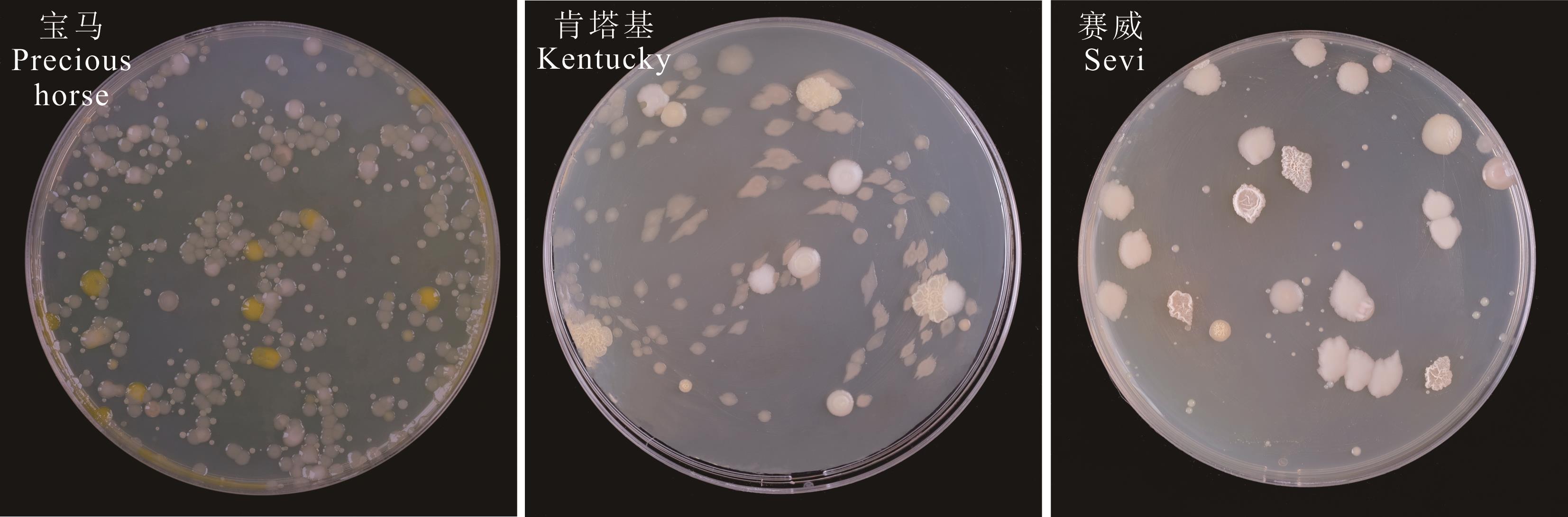
图1 草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌分离物形态特征图中均为10-2稀释梯度下的细菌分离平板。The bacterial separation plates at a 10-2 dilution gradient were all shown in the diagram.
Fig.1 Morphological characteristics of cultivable bacterium isolates in seeds of P. pratensis
菌株 Strain | 数量Number (CFU·g-1) | 属水平分类 Genus level classification | 登录号 Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| BM2 | 1.95×105a | 短小杆菌属Curtobacterium sp. | PP094560 |
| BM4 | 2.33×104def | 假单胞菌属Pseudomonas sp. | PP094561 |
| BM8 | 3.33×103f | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094562 |
| BM9 | 5.33×103ef | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094563 |
| BM10 | 2.47×104de | 短小杆菌属Curtobacterium sp. | PP094564 |
| BM12 | 1.46×105b | 假单胞菌属Pseudomonas sp. | PP094565 |
| KTJ3 | 2.27×104def | 类芽孢杆菌属Paenibacillus sp. | PP094566 |
| KTJ5 | 7.67×104c | 欧文氏菌属Erwinia sp. | PP094567 |
| KTJ9 | 1.07×104def | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094568 |
| KTJ14 | 2.13×104def | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094569 |
| KTJ16 | 8.67×103def | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094570 |
| KTJ18 | 2.67×103f | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094571 |
| SW1 | 3.47×104d | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094572 |
| SW3 | 6.67×103ef | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094574 |
| SW5 | 4.67×103ef | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094575 |
| SW9 | 3.33×103f | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094576 |
| SW10 | 1.33×104def | 寡养单胞菌属Stenotrophomonas sp. | PP094573 |
| SW11 | 5.93×104c | 类芽孢杆菌属Paenibacillus sp. | PP094577 |
表1 草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌在种子中的数量、属水平分类和登录号
Table 1 Number, genus level classification and accession number of cultivable seed-borne bacteria in P. pratensis
菌株 Strain | 数量Number (CFU·g-1) | 属水平分类 Genus level classification | 登录号 Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| BM2 | 1.95×105a | 短小杆菌属Curtobacterium sp. | PP094560 |
| BM4 | 2.33×104def | 假单胞菌属Pseudomonas sp. | PP094561 |
| BM8 | 3.33×103f | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094562 |
| BM9 | 5.33×103ef | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094563 |
| BM10 | 2.47×104de | 短小杆菌属Curtobacterium sp. | PP094564 |
| BM12 | 1.46×105b | 假单胞菌属Pseudomonas sp. | PP094565 |
| KTJ3 | 2.27×104def | 类芽孢杆菌属Paenibacillus sp. | PP094566 |
| KTJ5 | 7.67×104c | 欧文氏菌属Erwinia sp. | PP094567 |
| KTJ9 | 1.07×104def | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094568 |
| KTJ14 | 2.13×104def | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094569 |
| KTJ16 | 8.67×103def | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094570 |
| KTJ18 | 2.67×103f | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094571 |
| SW1 | 3.47×104d | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094572 |
| SW3 | 6.67×103ef | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094574 |
| SW5 | 4.67×103ef | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094575 |
| SW9 | 3.33×103f | 芽孢杆菌属Bacillus sp. | PP094576 |
| SW10 | 1.33×104def | 寡养单胞菌属Stenotrophomonas sp. | PP094573 |
| SW11 | 5.93×104c | 类芽孢杆菌属Paenibacillus sp. | PP094577 |
菌株 Strain | 固氮 NF | 产吲哚-3-乙酸 IAAP (μg·mL-1) | 溶磷 Phosphorus solubilizing (D/d ) | 产胞外酶 Producing extracellular enzymes (D/d ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机磷 Organic phosphorus | 无机磷 Inorganic phosphorus | 蛋白酶 Protease | 纤维素酶 Cellulase | 淀粉酶 Amylase | |||
| BM2 | + | - | - | - | 2.34±0.09c | - | - |
| BM4 | + | - | - | 1.20±0.024a | - | - | - |
| BM8 | + | 19.21±0.16a | - | - | 1.80±0.02de | - | - |
| BM9 | + | - | - | - | 2.41±0.09bc | 3.05±0.10cd | 2.42±0.05c |
| BM10 | + | - | - | - | 2.63±0.02ab | 3.78±0.11b | - |
| BM12 | + | - | - | 1.15±0.023a | - | - | - |
| KTJ3 | + | - | - | - | - | 3.38±0.07c | 2.93±0.07b |
| KTJ5 | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KTJ9 | + | - | - | - | 2.04±0.02d | 2.58±0.06e | 1.51±0.02d |
| KTJ14 | + | 18.42±0.12b | - | - | 1.73±0.04ef | - | - |
| KTJ16 | - | 18.46±0.23b | - | - | 1.30±0.02g | - | - |
| KTJ18 | + | - | - | - | 1.79±0.05de | 3.07±0.03cd | - |
| SW1 | - | - | - | - | 1.50±0.02fg | - | 1.37±0.02d |
| SW3 | - | - | - | - | 1.29±0.01g | 2.87±0.10de | 2.27±0.04c |
| SW5 | + | - | - | - | 2.30±0.08c | 2.96±0.07de | - |
| SW9 | + | - | - | - | 1.87±0.02de | - | - |
| SW10 | - | - | - | - | 2.75±0.13a | - | - |
| SW11 | + | - | - | - | - | 4.62±0.12a | 3.34±0.08a |
表2 草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌的固氮、产吲哚-3-乙酸、溶磷和产胞外酶能力
Table 2 The ability of nitrogen fixation (NF), indole-3-acetic acid-producing(IAAP), phosphate solubilizing and extracellular enzyme producing of cultivable seed-borne bacteria in P. pratensis
菌株 Strain | 固氮 NF | 产吲哚-3-乙酸 IAAP (μg·mL-1) | 溶磷 Phosphorus solubilizing (D/d ) | 产胞外酶 Producing extracellular enzymes (D/d ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
有机磷 Organic phosphorus | 无机磷 Inorganic phosphorus | 蛋白酶 Protease | 纤维素酶 Cellulase | 淀粉酶 Amylase | |||
| BM2 | + | - | - | - | 2.34±0.09c | - | - |
| BM4 | + | - | - | 1.20±0.024a | - | - | - |
| BM8 | + | 19.21±0.16a | - | - | 1.80±0.02de | - | - |
| BM9 | + | - | - | - | 2.41±0.09bc | 3.05±0.10cd | 2.42±0.05c |
| BM10 | + | - | - | - | 2.63±0.02ab | 3.78±0.11b | - |
| BM12 | + | - | - | 1.15±0.023a | - | - | - |
| KTJ3 | + | - | - | - | - | 3.38±0.07c | 2.93±0.07b |
| KTJ5 | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KTJ9 | + | - | - | - | 2.04±0.02d | 2.58±0.06e | 1.51±0.02d |
| KTJ14 | + | 18.42±0.12b | - | - | 1.73±0.04ef | - | - |
| KTJ16 | - | 18.46±0.23b | - | - | 1.30±0.02g | - | - |
| KTJ18 | + | - | - | - | 1.79±0.05de | 3.07±0.03cd | - |
| SW1 | - | - | - | - | 1.50±0.02fg | - | 1.37±0.02d |
| SW3 | - | - | - | - | 1.29±0.01g | 2.87±0.10de | 2.27±0.04c |
| SW5 | + | - | - | - | 2.30±0.08c | 2.96±0.07de | - |
| SW9 | + | - | - | - | 1.87±0.02de | - | - |
| SW10 | - | - | - | - | 2.75±0.13a | - | - |
| SW11 | + | - | - | - | - | 4.62±0.12a | 3.34±0.08a |
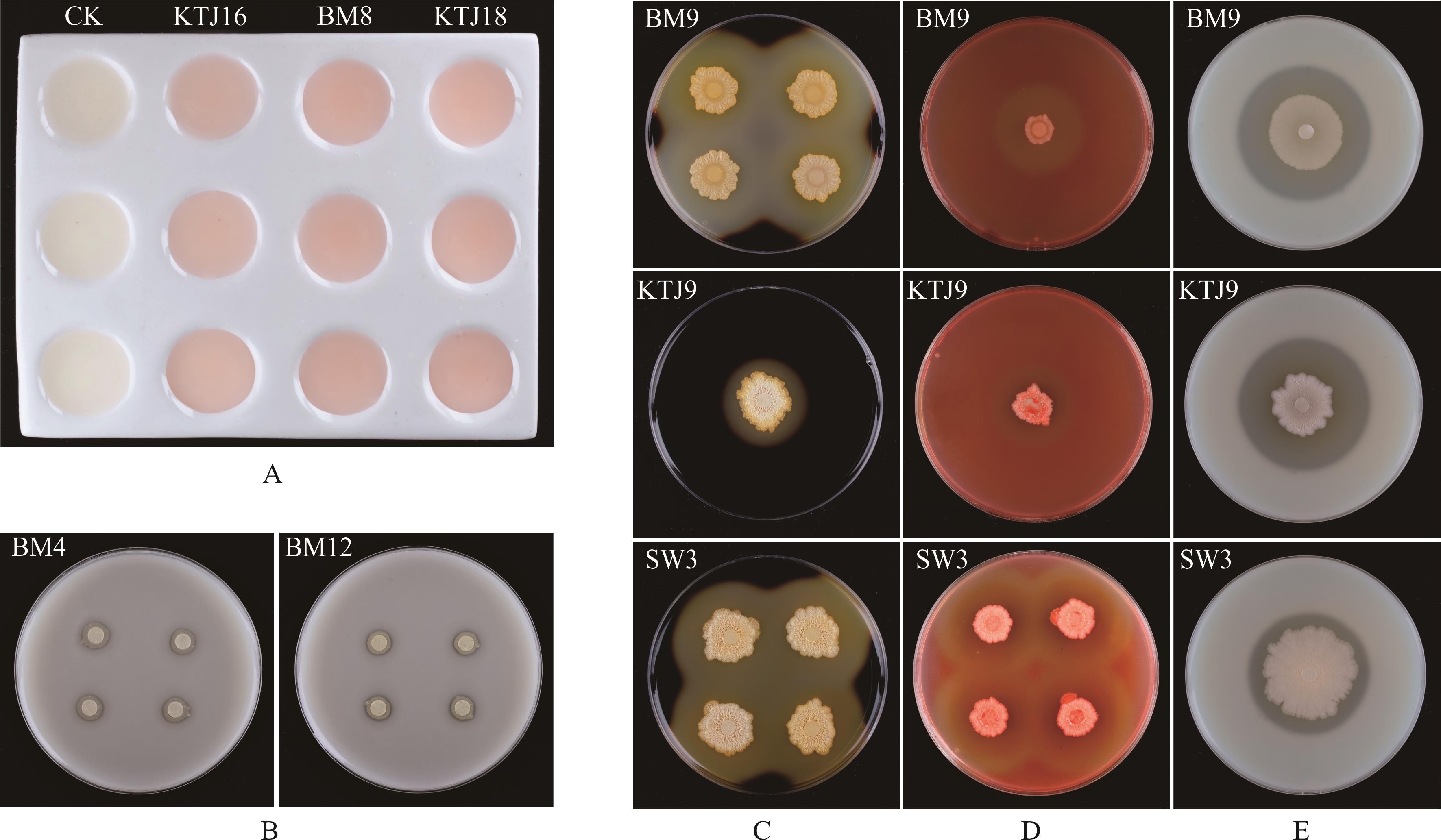
图4 草地早熟禾种带可培养细菌的产吲哚-3-乙酸、溶磷和产胞外酶能力试验A: 种带可培养细菌的吲哚-3-乙酸显色反应Indole-3-acetic acid color reaction of cultivable seed-borne bacteria; B: 种带可培养细菌在蒙金娜无机磷培养基上的生长情况Growth of culturable bacteria in Mongjna medium inorganic phosphorus medium; C, D, E: 分别为种带可培养细菌在含淀粉、羧甲基纤维素钠和脱脂牛奶的功能培养基上的生长情况The growth of cultivable seed-borne bacteria on the functional medium containing starch, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and skim milk, respectively.
Fig.4 Experiments on the indole-3-acetic acid-producing, phosphate solubilizing and extracellular enzyme producing of cultivable seed-borne bacteria in P. pratensis

图5 草地早熟禾品种可培养种带细菌在微孔板上的生物被膜产生能力(A)及其在泳动培养基上形成的浑浊区域直径(B)A图中,CK作为阴性对照。ODc和生物被膜形成能力用横线标出, 0:无生物被膜形成能力菌; 1:弱生物被膜形成能力菌; 2:中等生物被膜形成能力菌; 3:强生物被膜形成能力菌。B图中,不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。In Fig.A, CK as a negative control. ODc and biofilm formation ability were marked with a horizontal line, 0: Biofilm nonproducers; 1: Weak biofilm producers; 2: Medium biofilm producers; 3: Strong biofilm producers. In Fig. B, different letters denote significant difference (P<0.05).
Fig.5 The biofilm formation ability on microtiter plate of cultivable seed-borne bacteria in P. pratensis (A) and the diameter of turbid area formed on swimming medium (B)
| 1 | Croce P, De Luca A, Mocioni M, et al. Warm-season turfgrass species and cultivar characterizations for a Mediterranean climate. International Turfgrass Society Research Journal, 2001, 9: 855-859. |
| 2 | Zabalgogeazcoa Í, Ciudad A G, de Aldana B R V, et al. Effects of the infection by the fungal endophyte Epichloë festucae in the growth and nutrient content of Festuca rubra. European Journal of Agronomy, 2006, 24(4): 374-384. |
| 3 | Iannone L J, Pinget A D, Nagabhyru P, et al. Beneficial effects of Neotyphodium tembladerae and Neotyphodium pampeanum on a wild forage grass. Grass and Forage Science, 2012, 67(3): 382-390. |
| 4 | Truyens S, Weyens N, Cuypers A, et al. Bacterial seed endophytes: genera, vertical transmission and interaction with plants. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2015, 7(1): 40-50. |
| 5 | Brader G, Compant S, Vescio K, et al. Ecology and genomic insights into plant-pathogenic and plant-nonpathogenic endophytes. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 2017, 55: 61-83. |
| 6 | Khalaf E M, Raizada M N. Bacterial seed endophytes of domesticated cucurbits antagonize fungal and oomycete pathogens including powdery mildew. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 42. |
| 7 | Torres-Cortés G, Garcia B J, Compant S, et al. Differences in resource use lead to coexistence of seed-transmitted microbial populations. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 6648. |
| 8 | Roodi D, Millner J P, McGill C, et al. Methylobacterium, a major component of the culturable bacterial endophyte community of wild Brassica seed. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e9514. |
| 9 | Mei C, Flinn B S. The use of beneficial microbial endophytes for plant biomass and stress tolerance improvement. Recent Patents on Biotechnology, 2010, 4(1): 81-95. |
| 10 | Xu M S. Culturable bacterial community compositions from seeds of tomato and rice and function of plant growth promoting endophytic bacteria. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 许明双. 番茄和水稻种子可培养内生细菌的多样性分析及促生菌功能研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014. | |
| 11 | Shao J, Miao Y, Liu K, et al. Rhizosphere microbiome assembly involves seed-borne bacteria in compensatory phosphate solubilization. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2021, 159: 108273. |
| 12 | Srivastava S, Yadav A, Seem K, et al. Effect of high temperature on Pseudomonas putida NBRI0987 biofilm formation and expression of stress sigma factor RpoS. Current Microbiology, 2008, 56: 453-457. |
| 13 | Sun L, Cheng L, Ma Y, et al. Exopolysaccharides from Pantoea alhagi NX-11 specifically improve its root colonization and rice salt resistance. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 209: 396-404. |
| 14 | Yue Z, Shen Y, Chen Y, et al. Microbiological insights into the stress-alleviating property of an endophytic Bacillus altitudinis WR10 in wheat under low-phosphorus and high-salinity stresses. Microorganisms, 2019, 7(11): 508. |
| 15 | Li Y, Narayanan M, Shi X, et al. Biofilms formation in plant growth-promoting bacteria for alleviating agro-environmental stress. Science of the Total Environment, 2023: 167774. |
| 16 | Josenhans C, Suerbaum S. The role of motility as a virulence factor in bacteria. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 2002, 291(8): 605-614. |
| 17 | Palma V, Gutiérrez M S, Vargas O, et al. Methods to evaluate bacterial motility and its role in bacterial-host interactions. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(3): 563. |
| 18 | Ding T, Melcher U. Influences of plant species, season and location on leaf endophytic bacterial communities of non-cultivated plants. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0150895. |
| 19 | Hardoim P R, Van Overbeek L S, Berg G, et al. The hidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 2015, 79(3): 293-320. |
| 20 | Doty S L, Oakley B, Xin G, et al. Diazotrophic endophytes of native black cottonwood and willow. Symbiosis, 2009, 47: 23-33. |
| 21 | Wemheuer F, Kaiser K, Karlovsky P, et al. Bacterial endophyte communities of three agricultural important grass species differ in their response towards management regimes. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 40914. |
| 22 | Zhang Z F. Seed-borne bacteria of lucerne (Medicago sativa) and their pathogenicity. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013. |
| 张振粉. 紫花苜蓿种带细菌及其致病性. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. | |
| 23 | Xi L Q, Li D F, Wang J F, et al. Measurement of nitrogen fixation capability and excreted IAA capability of PGPB isolated from cotton rhizosphere in Salina. Arid Zone Research, 2008, 25(5): 690-694. |
| 席琳乔, 李德锋, 王静芳, 等. 棉花根际促生菌固氮和分泌生长激素能力的测定. 干旱区研究, 2008, 25(5): 690-694. | |
| 24 | Yang C D, Li Z D, Chen X R, et al. Identification, pathogen inhibiting and nitrogen fixation of endophytic bacterium Z19 of Polygonum viviparum. Microbiology China, 2014, 41(2): 267-273. |
| 杨成德, 李振东, 陈秀蓉, 等. 高寒草地珠芽蓼内生拮抗固氮菌Z19的鉴定及其固氮功能. 微生物学通报, 2014, 41(2):267-273. | |
| 25 | Verma S K, Kingsley K, Bergen M, et al. Bacterial endophytes from rice cut grass (Leersia oryzoides L.) increase growth, promote root gravitropic response, stimulate root hair formation, and protect rice seedlings from disease. Plant and Soil, 2018, 422: 223-238. |
| 26 | Dong N, Zhang D, Yu Y, et al. Exrtacellular enzyme activity and antimicrobial activity of culturable bacteria isolated from soil of Grove Mountains, East Antarctica. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2013, 53(12): 1295-1306. |
| 董宁, 张迪, 俞勇, 等. 东南极格罗夫山土壤可培养细菌的分离鉴定及其产胞外酶和抗菌活性. 微生物学报, 2013, 53(12): 1295-1306. | |
| 27 | Viksne R, Racenis K, Broks R, et al. In vitro assessment of biofilm production, antibacterial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter spp. obtained from tonsillar crypts of healthy adults. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(2): 258. |
| 28 | Qu H Y, Li X P, Meng L Y, et al. Effect of inhibitors on the motilities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2014, 33(5): 480-485. |
| 渠宏雁, 李学鹏, 孟良玉, 等. 抑制剂对副溶血性弧菌运动性的影响. 食品与生物技术学报, 2014, 33(5): 480-485. | |
| 29 | Bent E, Chanway C P. The growth-promoting effects of a bacterial endophyte on lodgepole pine are partially inhibited by the presence of other rhizobacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1998, 44(10): 980-988. |
| 30 | Zhang X H. Marine microbiology. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2007. |
| 张晓华. 海洋微生物学. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2007. | |
| 31 | Teather R M, Wood P J. Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1982, 43(4): 777-780. |
| 32 | Chang X B. Diversity of marine Actinomycetes in different environments and taxonomic analysis of 2 novel Actinomycetes. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. |
| 常显波. 不同环境海洋放线菌多样性研究及2株放线菌新菌的分类鉴定. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012. | |
| 33 | Reisner A, Krogfelt K A, Klein B M, et al. In vitro biofilm formation of commensal and pathogenic Escherichia coli strains: impact of environmental and genetic factors. Journal of Bacteriology, 2006, 188(10): 3572-3581. |
| 34 | Stepanović S, Vuković D, Hola V, et al. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. Acta Pathologica, Microbiologica, et Immunologica Scandinavica, 2007, 115(8): 891-899. |
| 35 | Barret M, Briand M, Bonneau S, et al. Emergence shapes the structure of the seed microbiota. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(4): 1257-1266. |
| 36 | Bulgarelli D, Schlaeppi K, Spaepen S, et al. Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2013, 64: 807-838. |
| 37 | Johnston-Monje D, Lundberg D S, Lazarovits G, et al. Bacterial populations in juvenile maize rhizospheres originate from both seed and soil. Plant and Soil, 2016, 405: 337-355. |
| 38 | Liu Y, Zuo S, Xu L, et al. Study on diversity of endophytic bacterial communities in seeds of hybrid maize and their parental lines. Archives of Microbiology, 2012, 194: 1001-1012. |
| 39 | Fierer N, Leff J W, Adams B J, et al. Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(52): 21390-21395. |
| 40 | Shafi S, Kamili A N, Shah M A, et al. Aquatic bacterial diversity: Magnitude, dynamics, and controlling factors. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2017, 104: 39-47. |
| 41 | Hardoim P R, Anderote F D, Reinhold-Hurek B, et al. Rice root-associated bacteria: insights into community structures across 10 cultivars: Insights into the bacterial community structure of rice cultivars. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2011, 77(1): 154-164. |
| 42 | Johnston-Monje D, Raizada M N. Conservation and diversity of seed associated endophytes in Zea across boundaries of evolution, ethnography and ecology. PLoS One, 2011, 6(6): e20396. |
| 43 | Andreote F D, Rocha U N D, Araújo W L, et al. Effect of bacterial inoculation, plant genotype and developmental stage on root-associated and endophytic bacterial communities in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2010, 97(4): 389-399. |
| 44 | Ding T, Palmer M W, Melcher U. Community terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms reveal insights into the diversity and dynamics of leaf endophytic bacteria. BMC Microbiology, 2013, 13(1): 1-11. |
| 45 | Tsotetsi T, Nepjali L, Malebe M, et al. Bacillus for plant growth promotion and stress resilience: What have we learned? Plants, 2022, 11(19): 2482. |
| 46 | Zhang Z F, Shi S L. Identification and biological attributes of seed-borne bacteria isolated from lucerne cv. Gannong No.3. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(1): 152-160. |
| 张振粉, 师尚礼. 甘农三号紫花苜蓿种带细菌的生物功能分析及鉴定. 草业学报, 2018, 27(1): 152-160. | |
| 47 | Grobeilak A, Napora A, Kacprzak M. Using plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) to improve plant growth. Ecological Engineering, 2015, 84: 22-28. |
| 48 | Zhang S, Gao P, Tong Y, et al. Overcoming nitrogen fertilizer over-use through technical and advisory approaches: A case study from Shaanxi Province, northwest China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2015, 209: 89-99. |
| 49 | Vejan P, Abduliah R, Khadiran T, et al. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agricultural sustainability-A review. Molecules, 2016, 21(5): 573. |
| 50 | Penesyan A, Paulsen I T, Kjelleberg S, et al. Three faces of biofilms: a microbial lifestyle, a nascent multicellular organism, and an incubator for diversity. NPJ Biofilms and Microbiomes, 2021, 7(1): 80. |
| 51 | Maitra D, Roy B, Chandra A, et al. Biofilm producing Bacillus vallismortis TR01K from tea rhizosphere acting as plant growth promoting agent. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 2022, 45: 102507. |
| 52 | Triveni S, Prasanna R, Shukla L, et al. Evaluating the biochemical traits of novel Trichoderma-based biofilms for use as plant growth-promoting inoculants. Annals of Microbiology, 2013, 63: 1147-1156. |
| 53 | Gutman J, Walker S L, Freger V, et al. Bacterial attachment and viscoelasticity: physicochemical and motility effects analyzed using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D). Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(1): 398-404. |
| [1] | 伍国强, 于祖隆, 魏明. PGPR调控植物响应逆境胁迫的作用机制[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(6): 203-218. |
| [2] | 段海霞, 师茜, 康生萍, 苟海青, 罗崇亮, 熊友才. 丛枝菌根真菌和根瘤菌与植物共生研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(5): 166-182. |
| [3] | 孟超楠, 赵玉洁, 陈佳欣, 张旖璐, 王彦佳, 冯丽荣, 孙玉刚, 郭长虹. 2株青贮玉米根际固氮菌的筛选鉴定及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(3): 174-185. |
| [4] | 王升升, 段珍, 周培, 张吉宇. 白花草木樨结瘤缺失型突变体的结瘤表型及生物量分析[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(10): 247-256. |
| [5] | 刘晓婷, 姚拓. 高寒草地耐低温植物根际促生菌的筛选鉴定及特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(8): 178-187. |
| [6] | 童长春, 刘晓静, 吴勇, 赵雅姣, 王静. 内源异黄酮对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮及氮效率的调控研究[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(3): 124-135. |
| [7] | 王春雯, 赵芳, 张晨, 解李娜, 马成仓. 小叶锦鸡儿灌丛对草地土壤固氮微生物群落的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(10): 28-40. |
| [8] | 魏志敏, 孙斌, 方成, 代子雯, 刘满强, 焦加国, 胡锋, 李辉信, 徐莉. 根瘤菌与固氮菌联合对毛叶苕子的促生效果[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(5): 94-102. |
| [9] | 贾雨雷, 廖真, 汪丽芳, 卜建超, 林标声, 林辉, 苏德伟, 鲁国东, 林占熺. 化肥减量配施菌草固氮菌肥对巨菌草生长、营养品质及土壤养分的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 215-223. |
| [10] | 漫静, 唐波, 邓波, 李佳欢, 何玉娟, 张佳良. 羊草根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生作用研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(1): 59-71. |
| [11] | 高丽敏, 苏晶, 田倩, 沈益新. 施氮对不同水分条件下紫花苜蓿氮素吸收及根系固氮酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 130-136. |
| [12] | 谢开云, 王玉祥, 万江春, 张树振, 隋晓青, 赵云, 张博. 混播草地中豆科/禾本科牧草氮转移机理及其影响因素[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(3): 157-170. |
| [13] | 赵雅姣, 刘晓静, 童长春, 吴勇. 紫花苜蓿/玉米间作对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(1): 95-105. |
| [14] | 高亚敏, 姚拓, 李海云, 罗慧琴, 张建贵, 杨琰珊, 刘婷. 高寒草甸嵩草、珠芽蓼根际优良植物根际促生菌的分离筛选及促生特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(11): 114-123. |
| [15] | 李海云, 姚拓, 张榕, 张洁, 李智燕, 荣良燕, 路晓雯, 杨晓蕾, 夏东慧, 罗慧琴. 红三叶根际溶磷菌的筛选与培养基优化[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(1): 170-179. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||