

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 188-200.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2024024
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
陈悦( ), 宋品, 侯曼曼, 杨笑然, 刘丽萍, 倪迎冬(
), 宋品, 侯曼曼, 杨笑然, 刘丽萍, 倪迎冬( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-16
修回日期:2024-03-11
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通讯作者:
倪迎冬
作者简介:E-mail: niyingdong@njau.edu.cn基金资助:
Yue CHEN( ), Pin SONG, Man-man HOU, Xiao-ran YANG, Li-ping LIU, Ying-dong NI(
), Pin SONG, Man-man HOU, Xiao-ran YANG, Li-ping LIU, Ying-dong NI( )
)
Received:2024-01-16
Revised:2024-03-11
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-10-09
Contact:
Ying-dong NI
摘要:
为探讨饲喂胆汁酸对高精料日粮诱导的亚急性瘤胃酸中毒(SARA)山羊回肠黏膜结构、菌群组成和抗炎因子mRNA相对表达量的影响,本试验选取15头3月龄雄性山羊(18.19±2.83 kg),手术安置永久性瘤胃瘘管,2周恢复期后随机分为3组:对照组(CON),亚急性瘤胃酸中毒组(SARA),亚急性瘤胃酸中毒加胆汁酸组(SARA+BA),每组5只羊。CON组每天饲喂精粗比为3∶7的日粮,SARA组和SARA+BA组饲喂精粗比为7∶3的日粮, SARA+BA组每天通过瘤胃瘘管灌注饲喂3 g胆汁酸,饲喂期为6周。试验结束后采集回肠上皮组织观察形态结构、上皮内杯状细胞和潘氏细胞数量,并检测黏膜中干扰素γ(IFN-γ)及受体的mRNA相对表达量和回肠内容物中菌群组成。结果表明:与CON组相比,SARA组山羊回肠上皮刷状缘呈锯齿状不规则形态,表明有一定程度的损伤,但绒毛和隐窝处杯状细胞和潘氏细胞数量无显著差异(P>0.05),回肠黏膜中IFN-γ和受体IfnGR1 mRNA相对表达量有下降的趋势(0.05<P<0.1),回肠内容物中微生物多样性指数(Ace、Shannon)均显著降低(P<0.05),门水平上厚壁菌门的相对丰度显著增加(P<0.05),属水平有益菌Unclassified_f_Lachnospiraceae、Ruminococcus、Christensenellaceae_R-7_group相对丰度显著减少(P<0.05),但有害菌Erysipelotrichaceae_UCG-006、Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1相对丰度显著增加(P<0.05)。与SARA组相比,SARA+BA组山羊回肠上皮刷状缘光滑、结构完整,绒毛高度显著升高(P<0.05),绒毛和隐窝处杯状细胞数量无显著差异(P>0.05),但潘氏细胞显著增多(P<0.05);黏膜中IFN-γ mRNA相对表达量有上调的趋势(0.05<P<0.1),其受体IfnGR1 mRNA相对表达量显著上调(P<0.05);回肠内容物中菌群多样性指数(Ace)显著升高(P<0.05),门水平上厚壁菌门的相对丰度显著降低(P<0.05),属水平上有益菌Unclassified_f_Lachnospiraceae、Ruminococcus、Christensenellaceae_R-7_group相对丰度显著升高(P<0.05),而有害菌Erysipelotrichaceae_UCG-006、Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1相对丰度显著降低(P<0.05)。综上,饲喂胆汁酸可改善SARA山羊的回肠形态结构,缓解回肠内菌群紊乱,通过上调黏膜中抗炎因子IFN-γ和IfnGR1 mRNA相对表达量,从而缓解SARA山羊回肠黏膜的损伤。
陈悦, 宋品, 侯曼曼, 杨笑然, 刘丽萍, 倪迎冬. 饲喂胆汁酸对亚急性瘤胃酸中毒山羊回肠黏膜形态、菌群组成和IFN-γ mRNA相对表达量的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(12): 188-200.
Yue CHEN, Pin SONG, Man-man HOU, Xiao-ran YANG, Li-ping LIU, Ying-dong NI. Effects of dietary supplementation with bile acid on ileal epithelial morphology, microflora composition, and relative transcript levels of IFN-γ in the ileal mucosa of goats with subacute ruminal acidosis[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2024, 33(12): 188-200.

图1 试验流程CON: 对照组 Control group; SARA: 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒组 Subacute ruminal acidosis group; SARA+BA: 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒添加复合胆汁酸组Subacute ruminal acidosis plus complex bile acid group; 下同 The same below.
Fig.1 Test flow chart (n=5)
| 日粮组成Diet ingredient | 对照组CON (%) | 高精料组SARA (%) | 营养水平Nutrient level2) | 对照组CON | 高精料组SARA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苜蓿草 Alfalfa | 67.45 | 28.91 | 代谢能 ME (MJ·kg-1) | 1.87 | 1.90 |
| 玉米 Corn | 20.41 | 57.03 | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%) | 16.79 | 16.73 |
| 豆粕 Soybean meal | 8.50 | 10.42 | 中性洗涤纤维NDF (%) | 33.71 | 28.79 |
| 磷酸氢钙 Calcium hydrophosphate | 1.10 | 1.10 | 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF (%) | 18.22 | 14.32 |
| 石粉 Limestone | 1.20 | 1.20 | 粗灰分Ash (%) | 4.74 | 4.83 |
| 食盐 Salt | 0.40 | 0.40 | 粗脂肪 Ether extract (%) | 3.76 | 3.61 |
| 预混料 Premix1) | 0.94 | 0.94 | 淀粉Starch (%) | 24.25 | 31.21 |
| 总计 Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 钙Calcium (%) | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| 磷Phosphorus (%) | 0.42 | 0.44 |
表1 日粮配方及营养组成
Table 1 Dietary formulation and nutritional composition
| 日粮组成Diet ingredient | 对照组CON (%) | 高精料组SARA (%) | 营养水平Nutrient level2) | 对照组CON | 高精料组SARA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苜蓿草 Alfalfa | 67.45 | 28.91 | 代谢能 ME (MJ·kg-1) | 1.87 | 1.90 |
| 玉米 Corn | 20.41 | 57.03 | 粗蛋白 Crude protein (%) | 16.79 | 16.73 |
| 豆粕 Soybean meal | 8.50 | 10.42 | 中性洗涤纤维NDF (%) | 33.71 | 28.79 |
| 磷酸氢钙 Calcium hydrophosphate | 1.10 | 1.10 | 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF (%) | 18.22 | 14.32 |
| 石粉 Limestone | 1.20 | 1.20 | 粗灰分Ash (%) | 4.74 | 4.83 |
| 食盐 Salt | 0.40 | 0.40 | 粗脂肪 Ether extract (%) | 3.76 | 3.61 |
| 预混料 Premix1) | 0.94 | 0.94 | 淀粉Starch (%) | 24.25 | 31.21 |
| 总计 Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 钙Calcium (%) | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| 磷Phosphorus (%) | 0.42 | 0.44 |
| 基因Gene | 引物对序列Primer pairs sequence (5′→3′) | 产物大小Product size (bp) | 基因库编号GeneBank ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | CAGAAGTTCTTGAACGGCAGC/CTGCAGATCATCCACCGGAAT | 134 | NM_001285682.1 |
| IfnGR1 | AACACAGAAGATCCTGTTTGGA/CACCACAGACAGCAAGGATT | 147 | XM_005684807.3 |
| IfnGR2 | GGCTCGCTTATCATCAGGCT/AAGGGTCTGTCACCTGCTTG | 132 | XM_018046479.1 |
| IfnAR1 | GCGCATAAGAGCAGAAGAAGG/GGGGGACCAATCTGAGCTTC | 105 | XM_018046479.1 |
| GAPDH | GGGTCATCATCTCTGCACCT/GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA | 126 | XM_005680968.3 |
表2 PCR所用引物序列
Table 2 Primers used for PCR
| 基因Gene | 引物对序列Primer pairs sequence (5′→3′) | 产物大小Product size (bp) | 基因库编号GeneBank ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | CAGAAGTTCTTGAACGGCAGC/CTGCAGATCATCCACCGGAAT | 134 | NM_001285682.1 |
| IfnGR1 | AACACAGAAGATCCTGTTTGGA/CACCACAGACAGCAAGGATT | 147 | XM_005684807.3 |
| IfnGR2 | GGCTCGCTTATCATCAGGCT/AAGGGTCTGTCACCTGCTTG | 132 | XM_018046479.1 |
| IfnAR1 | GCGCATAAGAGCAGAAGAAGG/GGGGGACCAATCTGAGCTTC | 105 | XM_018046479.1 |
| GAPDH | GGGTCATCATCTCTGCACCT/GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA | 126 | XM_005680968.3 |

图2 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊瘤胃液pH的影响图中的显著性基于SARA组与SARA+BA组比较得出The significance in the figure is based on the comparison between the SARA group and the SARA+BA group; ***: P<0.001; *: P<0.05;#: 0.05<P<0.1;下同The same below.
Fig.2 Effect of dietary supplementation with bile acid on pH of rumen fluid of SARA goats (n=5)

图3 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊回肠黏膜形态(A)及绒毛长度、隐窝深度(B)的影响**: P<0.01; *: P<0.05; #: 0.05<P<0.1; 下同The same below.
Fig.3 Effect of dietary supplementation with bile acids on ileal mucosa morphology (A), villus height and crypt depth (B) of goats with subacute ruminal acidosis(n=5)
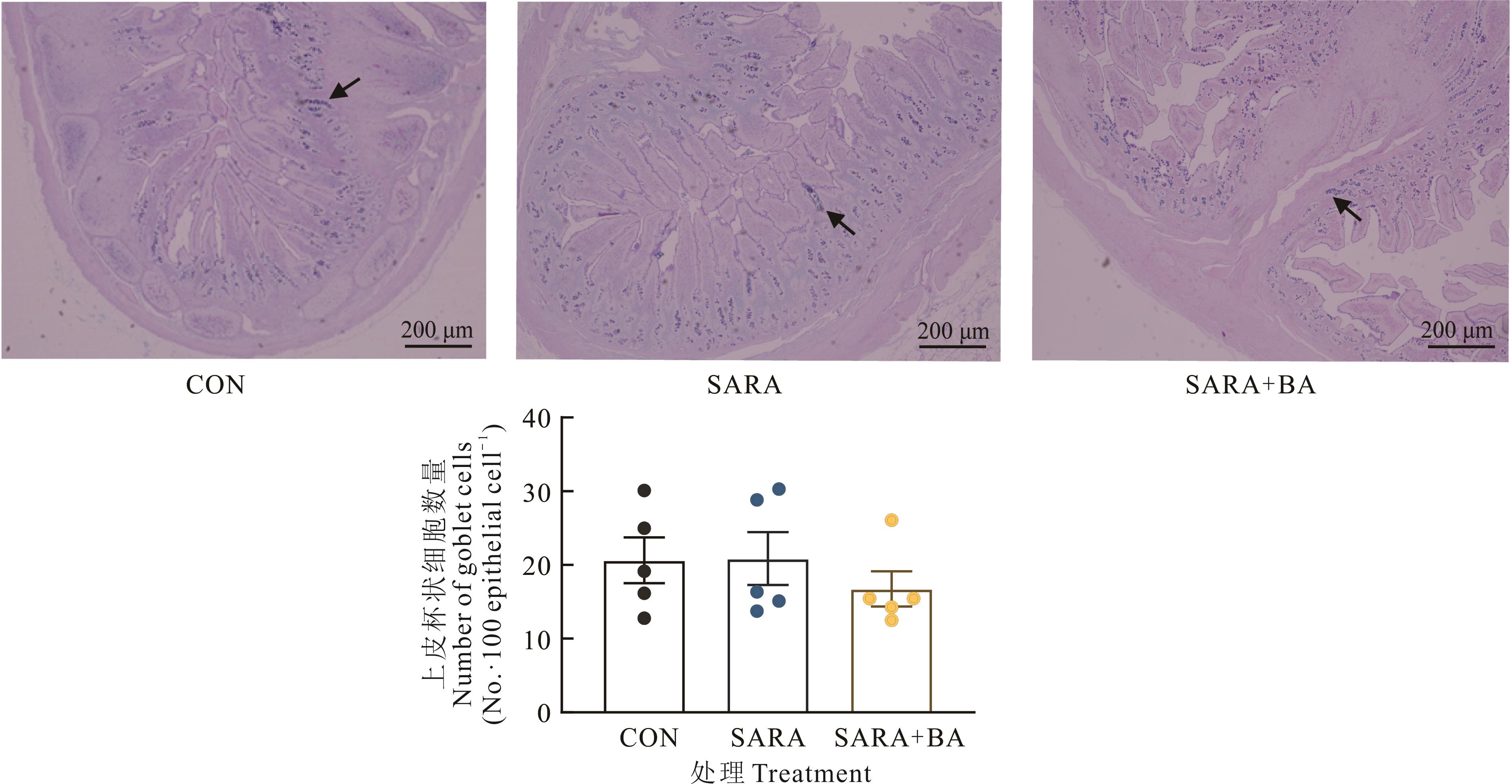
图4 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊回肠上皮杯状细胞数量的影响AB/PAS染色中杯状细胞呈蓝紫色,黑色箭头所指的为杯状细胞Goblet cells in AB/PAS staining are blue-purple, and the black arrow indicates goblet cells.
Fig.4 Effect of dietary supplementation with bile acid on the number of goblet cells in ileal mucosa of goats (n=5)
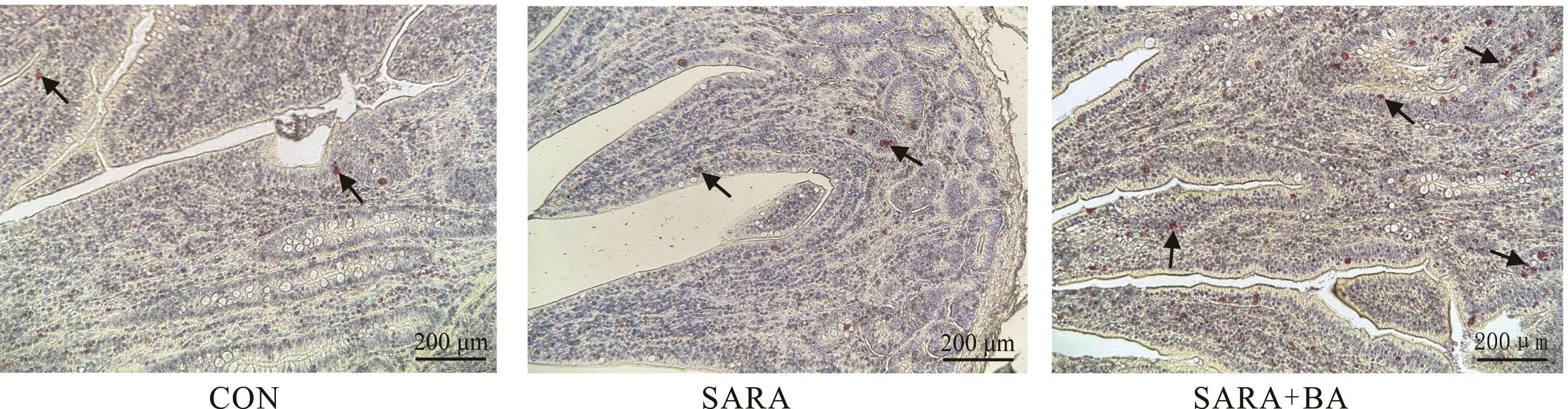
图5 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊回肠上皮潘氏细胞数量的影响荧光桃红酒石黄染色中潘氏细胞呈艳红色,黑色箭头所指的为潘氏细胞Paneth cells in fluorescent pink tartar stain are bright red, and the black arrow indicates paneth cells.
Fig. 5 Effect of dietary supplementation with bile acids on number of paneth cells in ileal mucosa of goats (n=5)
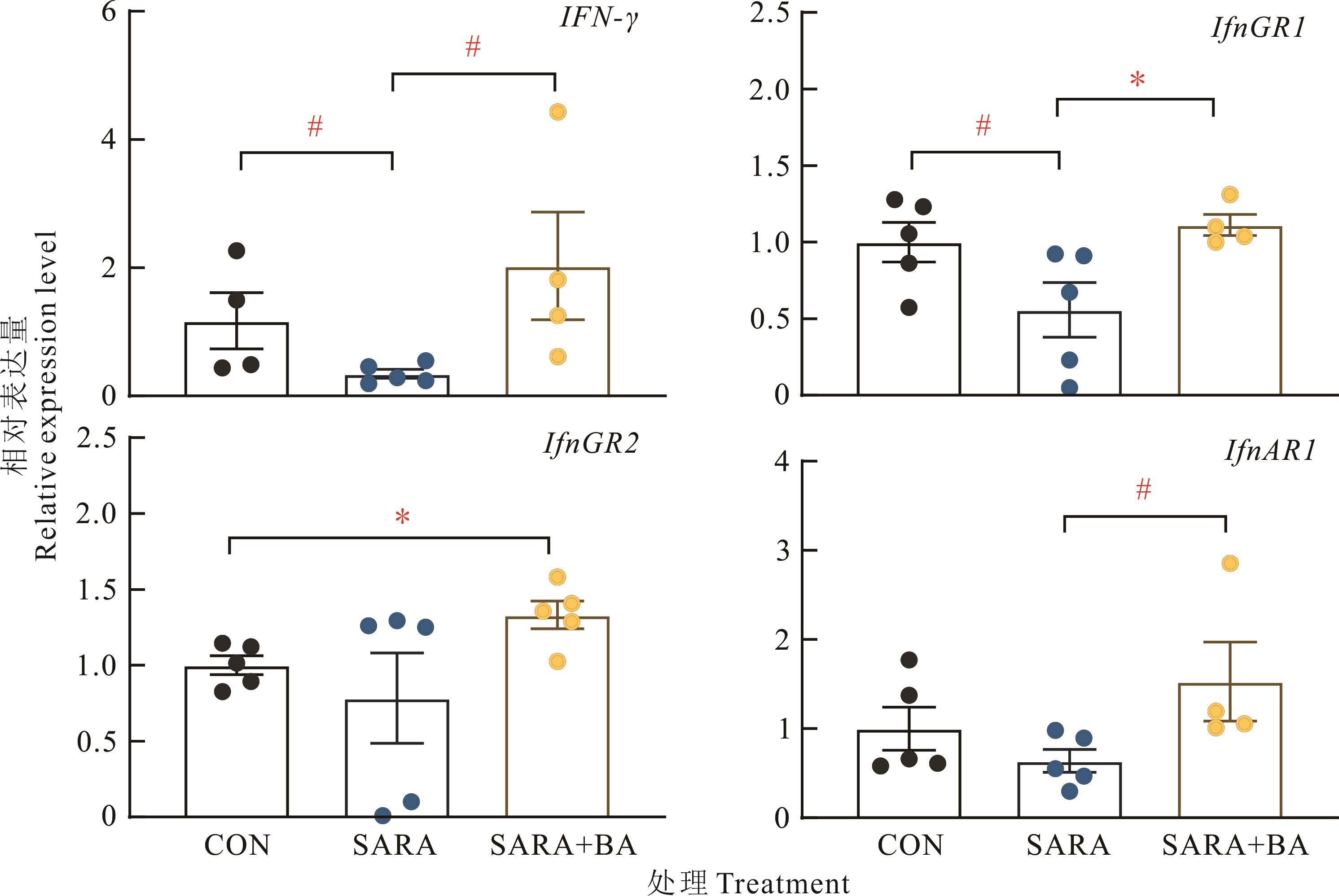
图6 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊回肠黏膜干扰素γ及其受体mRNA相对表达量的影响
Fig.6 Effects of dietary supplementation with bile acids on the relative expression levels of interferon γ and its receptor mRNA in ileal mucosa of SARA goats (n=5)
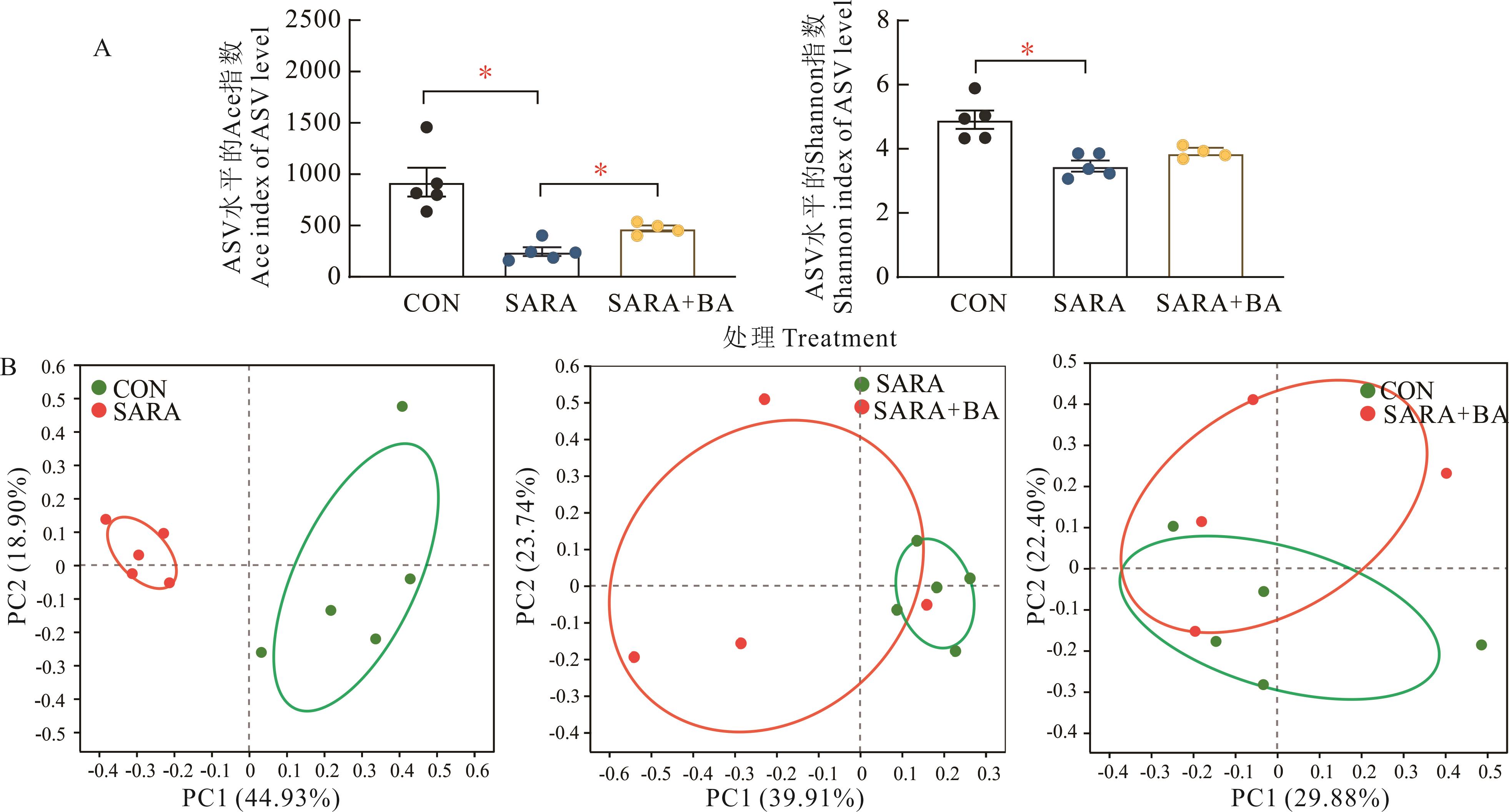
图7 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊回肠内容物中细菌α(A)和β多样性(B)的影响CON, SARA: n=5; SARA+BA: n=4.
Fig. 7 Effect of dietary supplementation with bile acids on α (A) and β diversity (B) of bacteria in the ileal digesta in goats
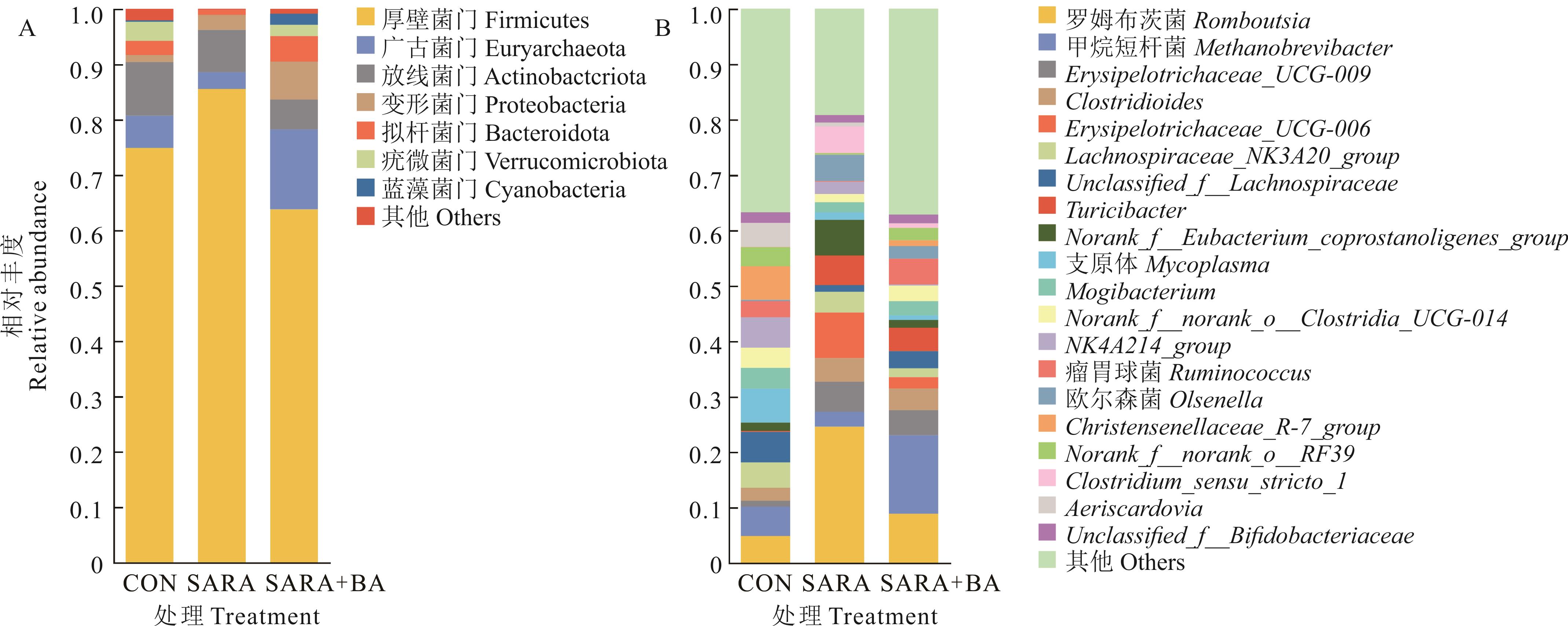
图8 饲喂胆汁酸对SARA山羊回肠细菌门水平(A)、属水平相对丰度 (B)的影响CON, SARA group: n=5; SARA+BA: n=4; 下同The same below.
Fig.8 Effect of dietary supplementation with bile acids on the relative abundance at phylum level (A) and genus level (B) of ileal bacteria in SARA goats

图9 回肠细菌门水平相对丰度差异菌门(A)及属水平相对丰度前20中的差异菌属(B)
Fig.9 Different bacteria at phylum level (A) and different bacteria (B) in the top 20 relative abundances at genu level of ileal bacteria
| 1 | Ba L J D M, Ao R G L, Wang C J, et al. Pathogenesis and research progress of subacute rumen acidosis in ruminants. Feed Research, 2023, 46(21): 145-149. |
| 巴拉吉德玛, 敖日格乐, 王纯洁, 等. 反刍动物亚急性瘤胃酸中毒的发病机理及研究进展. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(21): 145-149. | |
| 2 | Dong G, Liu S, Wu Y, et al. Diet-induced bacterial immunogens in the gastrointestinal tract of dairy cows: Impacts on immunity and metabolism. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 2011, 53(1): 48-55. |
| 3 | Acciarino A, Diwakarla S, Handreck J, et al. The role of the gastrointestinal barrier in obesity-associated systemic inflammation. Obesity Reviews, 2024, 25: e13673. |
| 4 | Elmhadi M E, Ali D K, Khogali M K, et al. Subacute ruminal acidosis in dairy herds: Microbiological and nutritional causes, consequences, and prevention strategies. Animal Nutrition, 2022, 10: 148-155. |
| 5 | Shi W R, Zhou F, Meng Q H, et al. Function and application in animal production of bile acids. Feed Research, 2023,46(15): 167-172. |
| 施文瑞, 周凡, 孟庆辉, 等. 胆汁酸的功能及其在动物生产中的应用. 饲料研究, 2023, 46(15): 167-172. | |
| 6 | He S Q, Li L X, Yao Y N, et al. Bile acid and its bidirectional interactions with gut microbiota: A review. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 2023, doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2023.2262020. |
| 7 | Hegyi P, Maléth J, Walters J R, et al. Guts and gall: Bile acids in regulation of intestinal epithelial function in health and disease. Psychological Review, 2018, 98(4): 1983-2023. |
| 8 | Cai J, Rimal B, Jiang C, et al. Bile acid metabolism and signaling, the microbiota, and metabolic disease. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108238. |
| 9 | Tao S Y. Effects of high-concentrate diet on hindgut epithelial barrier in lactating dairy goats and the mechanisms involved. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. |
| 陶诗煜. 高精料日粮对泌乳期奶山羊后段肠道上皮屏障的影响及其机制. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. | |
| 10 | Deng L Q. Make regular paraffin sections quickly. Journal of Hubei University for Nationalities (Medical Edition), 2001(4): 59. |
| 邓利群. 快速制作常规石蜡切片. 湖北民族学院学报(医学版), 2001(4): 59. | |
| 11 | Caporaso J G, Lauber C L, Walters W A, et al. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(S1): 4516-4522. |
| 12 | Plaizier J C, Danesh M M, Derakhshani H, et al. Review: Enhancing gastrointestinal health in dairy cows. Animal, 2018, 12(S2): 399-418. |
| 13 | Camilleri M, Madsen K, Spiller R, et al. Intestinal barrier function in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterology and Motility, 2012, 24(6): 503-512. |
| 14 | Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu S H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Experimental and Molecular Medicine, 2018, 50(8): 1-9. |
| 15 | Tao S Y, Duan M L, Dong H B, et al. High concentrate diet induced mucosal injuries by enhancing epithelial apoptosis and inflammatory response in the hindgut of goats. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e111596. |
| 16 | Lai Z, Lin L, Zhang J, et al. Effects of high-grain diet feeding on mucosa-associated bacterial community and gene expression of tight junction proteins and inflammatory cytokines in the small intestine of dairy cattle. Journal of Dairy Science, 2022, 105(8): 6601-6615. |
| 17 | Huai Y Y, Liang Z S, Ji S L, et al. Effects of recombinant epidermal growth factor on the proliferation of the intestinal epithelial cells in early-weaned pigs. Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 48(4): 70-75 . |
| 槐玉英, 梁梓森, 纪少丽, 等. 重组表皮生长因子对仔猪小肠上皮细胞增殖活性的影响. 畜牧与兽医, 2016, 48(4): 70-75. | |
| 18 | Guo Y S, Yan S M, Shi B L, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus fermentum supplementation on the small intestinal villus structure of broilers. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2011, 23(7): 1194-1200. |
| 郭元晟, 闫素梅, 史彬林, 等. 发酵乳酸杆菌对肉鸡小肠绒毛形态的影响. 动物营养学报, 2011, 23(7): 1194-1200. | |
| 19 | Allaire J M, Crowley S M, Law H T, et al. The intestinal epithelium: Central coordinator of mucosal immunity. Trends in Immunology, 2018, 39(9): 677-696. |
| 20 | Kim J J, Khan W I. Goblet cells and mucins: Role in innate defense in enteric infections. Pathogens, 2013, 2(1): 55-70. |
| 21 | Okumura R, Takeda K. Roles of intestinal epithelial cells in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Experimental and Molecular Medicine, 2017, 49(5): e338. |
| 22 | van der Flier L G, Clevers H. Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annual Review of Physiology, 2009, 71: 241-260. |
| 23 | Johansson M E, Hansson G C. Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2016, 16(10): 639-649. |
| 24 | Cui C, Li L, Wu L, et al. Paneth cells in farm animals: Current status and future direction. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2023, 14(1): 118. |
| 25 | Hou Q, Huang J, Ayansola H, et al. Intestinal stem cells and immune cell relationships: Potential therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 2021, doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.623691. |
| 26 | Günther C, Martini E, Wittkopf N, et al. Caspase-8 regulates tnf-α-induced epithelial necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature, 2011, 477(7364): 335-339. |
| 27 | Ergun E, Ergun L, Asti R N, et al. Light and electron microscopic morphology of paneth cells in the sheep small intestine. Revue De Medecine Veterinaire, 2003, 154(5): 351-355. |
| 28 | El Bougrini J, Pampin M, Chelbi-Alix M K. Arsenic enhances the apoptosis induced by interferon gamma: Key role of IRF-1. Cellular and Molecular Biology (Noisy-le-grand), 2006, 52(1): 9-15. |
| 29 | Gocher A M, Workman C J, Vignali D A A. Interferon-gamma: Teammate or opponent in the tumour microenvironment? Nature Reviews Immunology, 2022, 22(3): 158-172. |
| 30 | Richard N, Savoye G, Leboutte M, et al. Crohn’s disease: Why the ileum? World Journal of Gastroenterolog, 2023, 29(21): 3222-3240. |
| 31 | Thoetkiattikul H, Mhuantong W, Laothanachareon T, et al. Comparative analysis of microbial profiles in cow rumen fed with different dietary fiber by tagged 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. Current Microbiology, 2013, 67(2): 130-137. |
| 32 | Plaizier J C, Li S, Danscher A M, et al. Changes in microbiota in rumen digesta and feces due to a grain-based subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) challenge. Microbial Ecology, 2017, 74(2): 485-495. |
| 33 | Zhong X X, Huang J, Liu Z Y, et al. Effects of mannan oligosaccharides and complex probiotics on growth performance and intestinal morphology,volatile fatty acid contents and microbial structure of weaned piglets. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(7): 3099-3108. |
| 钟晓霞, 黄健, 刘志云, 等. 甘露寡糖和复合益生菌对断奶仔猪生长性能及肠道形态结构、挥发性脂肪酸含量和菌群结构的影响. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(7): 3099-3108. | |
| 34 | Crost E H, Coletto E, Bell A, et al. Ruminococcus gnavus: Friend or foe for human health. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuad014. |
| 35 | Zeng Y, Gao Y H, Peng Z L, et al. Effects of yeast culture supplementation in diets on rumen fermentation parameters and microflora of house-feeding yak. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(4): 1721-1733. |
| 曾钰, 高彦华, 彭忠利, 等. 饲粮中添加酵母培养物对舍饲牦牛瘤胃发酵参数及微生物区系的影响. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(4): 1721-1733. | |
| 36 | Guo J, Mu R, Li S, et al. Characterization of the bacterial community of rumen in dairy cows with laminitis. Genes, 2021, doi: 10.3390/genes12121996. |
| 37 | Wang K, Ren A, Zheng M, et al. Diet with a high proportion of rice alters profiles and potential function of digesta-associated microbiota in the ileum of goats. Animals, 2020, doi: 10.3390/ani10081261. |
| 38 | Chiang J Y. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Comprehensive Physiology, 2013, 3(3): 1191-1212. |
| 39 | Fogelson K A, Dorrestein P C, Zarrinpar A, et al. The gut microbial bile acid modulation and its relevance to digestive health and diseases. Gastroenterology, 2023, 164(7): 1069-1085. |
| [1] | 顾明明, 姜幸慧, 马志毅, 邱水玲, 刘浩宇, 张洺瑞, 卢佳宁, 丘宇俊, 王本治, 甘乾福. 甘薯和芋头在闽东山羊瘤胃中的降解特性及表面附着微生物群落变化[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 169-184. |
| [2] | 洪莉平, 李小冬, 于二汝, 裴成江, 尚以顺, 骆金红, 孙光, 周云昊, 李世歌, 杨航, 刘凤丹. 不同紫苏原料对贵州黑山羊血清抗氧化酶活性、瘤胃发酵参数、瘤胃微生物区系的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(9): 214-226. |
| [3] | 杨尚霖, 吴璇, 罗巧慧, 黄太华, 张正帆, 史海涛, 郭春华. 20~35 kg川中黑山羊蛋白质需要量研究[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(7): 119-129. |
| [4] | 赵洁, 陈恒光, 裴晓蒙, 于昊, 徐银莹, 茆达干. 围产期日粮添加白藜芦醇对山羊生产性能、血液指标及炎症因子基因表达的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2024, 33(4): 210-220. |
| [5] | 张涛, 牟英玉, 亓王盼, 张继友, 毛胜勇. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒耐受性不同的奶牛瘤胃上皮形态及功能差异研究[J]. 草业学报, 2023, 32(2): 131-139. |
| [6] | 穆海婷, 王英哲, 苗一凡, 郁伟杰, 徐博. 重金属铜和铅胁迫对东方山羊豆幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(11): 139-146. |
| [7] | 李俊年, 康绍华, 杨冬梅, 何纤, 李双, 陶双伦. 葛藤草粉替代苜蓿草粉对波杂山羊血清生化指标、养分表观消化率和生产性能的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 146-153. |
| [8] | 张涛, 牟英玉, 亓王盼, 郭长征, 张继友, 毛胜勇. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒耐受性不同的奶牛血浆和乳中脂肪酸及代谢物组成分析[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 101-110. |
| [9] | 孙旺斌, 付琪, 薛瑞林, 王伟萍, 张骞, 冯平. 不同枣粉添加水平对陕北白绒山羊屠宰性能和肉品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(7): 111-121. |
| [10] | 黄丽琴, 李松桥, 袁振中, 唐晶, 闫景彩, 唐启源. 全株水稻与平菇菌糠共发酵料对浏阳黑山羊屠宰性能、肉品质和器官指数的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 133-140. |
| [11] | 霍俊宏, 詹康, 黄秋生, 钟小军, 占今舜, 严学兵. 不同精粗比日粮对山羊生产性能、血清生化指标和瘤胃发酵的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 151-161. |
| [12] | 亓王盼, 牟英玉, 张涛, 张继友, 毛胜勇. 亚急性瘤胃酸中毒对泌乳奶牛血浆生化指标及代谢组的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(6): 141-150. |
| [13] | 熊忙利, 吴旭锦, 朱小甫, 张文娟. 不同苹果渣水平对关中奶山羊泌乳性能、养分表观消化率、血清生化指标及瘤胃液pH值的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(3): 81-88. |
| [14] | 王继卿, 沈继源, 刘秀, 李少斌, 罗玉柱, 赵孟丽, 郝志云, 柯娜, 宋宜泽, 乔莉蓉. 子午岭黑山羊与辽宁绒山羊产肉性能、肉品质、肌肉营养成分和脂肪酸含量比较[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(2): 166-177. |
| [15] | 吴晨, 姚志浩, 梅文晴, 冯宇妍, 陈渠, 倪迎冬. 复合维生素B对生长期山羊后段肠道菌群组成及肠黏膜的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 170-180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||